以上就是给各位分享centos7mini版配置apache站点-非迷你版本类似,其中也会对完美运行进行解释,同时本文还将给你拓展01.vm虚拟机、centos7mini安装、jdk安装、4.1.1Ce
以上就是给各位分享centos7mini 版配置 apache 站点 - 非迷你版本类似,其中也会对完美运行进行解释,同时本文还将给你拓展01.vm 虚拟机、centos7mini 安装、jdk 安装、4.1.1 Centos7---4.2.1 Apache、apache 多端口配置多站点(centos7)、Apache 系列:Centos7.2 下安装与配置 apache等相关知识,如果能碰巧解决你现在面临的问题,别忘了关注本站,现在开始吧!
本文目录一览:- centos7mini 版配置 apache 站点 - 非迷你版本类似(完美运行)(centos7 apache常规配置)
- 01.vm 虚拟机、centos7mini 安装、jdk 安装
- 4.1.1 Centos7---4.2.1 Apache
- apache 多端口配置多站点(centos7)
- Apache 系列:Centos7.2 下安装与配置 apache

centos7mini 版配置 apache 站点 - 非迷你版本类似(完美运行)(centos7 apache常规配置)
Mac 下基于 PD 进行 centos7 安装环境
1.centos7 迷你版本(用于服务器)参考这篇 centos7 安装 lamp 进行安装(非迷你版本配置类似)
2. 配置 /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf 进行虚拟主机配置
#
# This is the main Apache HTTP server configuration file. It contains the
# configuration directives that give the server its instructions.
# See <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/> for detailed information.
# In particular, see
# <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/directives.html>
# for a discussion of each configuration directive.
#
# Do NOT simply read the instructions in here without understanding
# what they do. They''re here only as hints or reminders. If you are unsure
# consult the online docs. You have been warned.
#
# Configuration and logfile names: If the filenames you specify for many
# of the server''s control files begin with "/" (or "drive:/" for Win32), the
# server will use that explicit path. If the filenames do *not* begin
# with "/", the value of ServerRoot is prepended -- so ''log/access_log''
# with ServerRoot set to ''/www'' will be interpreted by the
# server as ''/www/log/access_log'', where as ''/log/access_log'' will be
# interpreted as ''/log/access_log''.
#
# ServerRoot: The top of the directory tree under which the server''s
# configuration, error, and log files are kept.
#
# Do not add a slash at the end of the directory path. If you point
# ServerRoot at a non-local disk, be sure to specify a local disk on the
# Mutex directive, if file-based mutexes are used. If you wish to share the
# same ServerRoot for multiple httpd daemons, you will need to change at
# least PidFile.
#
ServerRoot "/etc/httpd"
#
# Listen: Allows you to bind Apache to specific IP addresses and/or
# ports, instead of the default. See also the <VirtualHost>
# directive.
#
# Change this to Listen on specific IP addresses as shown below to
# prevent Apache from glomming onto all bound IP addresses.
#
#Listen 12.34.56.78:80
Listen 80
#
# Dynamic Shared Object (DSO) Support
#
# To be able to use the functionality of a module which was built as a DSO you
# have to place corresponding `LoadModule'' lines at this location so the
# directives contained in it are actually available _before_ they are used.
# Statically compiled modules (those listed by `httpd -l'') do not need
# to be loaded here.
#
# Example:
# LoadModule foo_module modules/mod_foo.so
#
Include conf.modules.d/*.conf
#
# If you wish httpd to run as a different user or group, you must run
# httpd as root initially and it will switch.
#
# User/Group: The name (or #number) of the user/group to run httpd as.
# It is usually good practice to create a dedicated user and group for
# running httpd, as with most system services.
#
User apache
Group apache
# ''Main'' server configuration
#
# The directives in this section set up the values used by the ''main''
# server, which responds to any requests that aren''t handled by a
# <VirtualHost> definition. These values also provide defaults for
# any <VirtualHost> containers you may define later in the file.
#
# All of these directives may appear inside <VirtualHost> containers,
# in which case these default settings will be overridden for the
# virtual host being defined.
#
#
# ServerAdmin: Your address, where problems with the server should be
# e-mailed. This address appears on some server-generated pages, such
# as error documents. e.g. admin@your-domain.com
#
ServerAdmin root@localhost
#
# ServerName gives the name and port that the server uses to identify itself.
# This can often be determined automatically, but we recommend you specify
# it explicitly to prevent problems during startup.
#
# If your host doesn''t have a registered DNS name, enter its IP address here.
#
#ServerName www.example.com:80
ServerName www.ceshi.cn:80
#
# Deny access to the entirety of your server''s filesystem. You must
# explicitly permit access to web content directories in other
# <Directory> blocks below.
#
<Directory />
AllowOverride none
Require all denied
</Directory>
#
# Note that from this point forward you must specifically allow
# particular features to be enabled - so if something''s not working as
# you might expect, make sure that you have specifically enabled it
# below.
#
#
# DocumentRoot: The directory out of which you will serve your
# documents. By default, all requests are taken from this directory, but
# symbolic links and aliases may be used to point to other locations.
#
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"
#
# Relax access to content within /var/www.
#
<Directory "/var/www">
AllowOverride None
# Allow open access:
Require all granted
</Directory>
# Further relax access to the default document root:
<Directory "/var/www/html">
#
# Possible values for the Options directive are "None", "All",
# or any combination of:
# Indexes Includes FollowSymLinks SymLinksifOwnerMatch ExecCGI MultiViews
#
# Note that "MultiViews" must be named *explicitly* --- "Options All"
# doesn''t give it to you.
#
# The Options directive is both complicated and important. Please see
# http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/core.html#options
# for more information.
#
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
#
# AllowOverride controls what directives may be placed in .htaccess files.
# It can be "All", "None", or any combination of the keywords:
# Options FileInfo AuthConfig Limit
#
AllowOverride All
#
# Controls who can get stuff from this server.
#
#Require all granted
Order allow,deny
Allow from all
</Directory>
#
# DirectoryIndex: sets the file that Apache will serve if a directory
# is requested.
#
<IfModule dir_module>
DirectoryIndex index.html
</IfModule>
#
# The following lines prevent .htaccess and .htpasswd files from being
# viewed by Web clients.
#
<Files ".ht*">
Require all denied
</Files>
#
# ErrorLog: The location of the error log file.
# If you do not specify an ErrorLog directive within a <VirtualHost>
# container, error messages relating to that virtual host will be
# logged here. If you *do* define an error logfile for a <VirtualHost>
# container, that host''s errors will be logged there and not here.
#
ErrorLog "logs/error_log"
#
# LogLevel: Control the number of messages logged to the error_log.
# Possible values include: debug, info, notice, warn, error, crit,
# alert, emerg.
#
LogLevel warn
<IfModule log_config_module>
#
# The following directives define some format nicknames for use with
# a CustomLog directive (see below).
#
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" common
<IfModule logio_module>
# You need to enable mod_logio.c to use %I and %O
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\" %I %O" combinedio
</IfModule>
#
# The location and format of the access logfile (Common Logfile Format).
# If you do not define any access logfiles within a <VirtualHost>
# container, they will be logged here. Contrariwise, if you *do*
# define per-<VirtualHost> access logfiles, transactions will be
# logged therein and *not* in this file.
#
#CustomLog "logs/access_log" common
#
# If you prefer a logfile with access, agent, and referer information
# (Combined Logfile Format) you can use the following directive.
#
CustomLog "logs/access_log" combined
</IfModule>
<IfModule alias_module>
#
# Redirect: Allows you to tell clients about documents that used to
# exist in your server''s namespace, but do not anymore. The client
# will make a new request for the document at its new location.
# Example:
# Redirect permanent /foo http://www.example.com/bar
#
# Alias: Maps web paths into filesystem paths and is used to
# access content that does not live under the DocumentRoot.
# Example:
# Alias /webpath /full/filesystem/path
#
# If you include a trailing / on /webpath then the server will
# require it to be present in the URL. You will also likely
# need to provide a <Directory> section to allow access to
# the filesystem path.
#
# ScriptAlias: This controls which directories contain server scripts.
# ScriptAliases are essentially the same as Aliases, except that
# documents in the target directory are treated as applications and
# run by the server when requested rather than as documents sent to the
# client. The same rules about trailing "/" apply to ScriptAlias
# directives as to Alias.
#
ScriptAlias /cgi-bin/ "/var/www/cgi-bin/"
</IfModule>
#
# "/var/www/cgi-bin" should be changed to whatever your ScriptAliased
# CGI directory exists, if you have that configured.
#
<Directory "/var/www/cgi-bin">
AllowOverride None
Options None
Require all granted
</Directory>
<IfModule mime_module>
#
# TypesConfig points to the file containing the list of mappings from
# filename extension to MIME-type.
#
TypesConfig /etc/mime.types
#
# AddType allows you to add to or override the MIME configuration
# file specified in TypesConfig for specific file types.
#
#AddType application/x-gzip .tgz
#
# AddEncoding allows you to have certain browsers uncompress
# information on the fly. Note: Not all browsers support this.
#
#AddEncoding x-compress .Z
#AddEncoding x-gzip .gz .tgz
#
# If the AddEncoding directives above are commented-out, then you
# probably should define those extensions to indicate media types:
#
AddType application/x-compress .Z
AddType application/x-gzip .gz .tgz
#
# AddHandler allows you to map certain file extensions to "handlers":
# actions unrelated to filetype. These can be either built into the server
# or added with the Action directive (see below)
#
# To use CGI scripts outside of ScriptAliased directories:
# (You will also need to add "ExecCGI" to the "Options" directive.)
#
#AddHandler cgi-script .cgi
# For type maps (negotiated resources):
#AddHandler type-map var
#
# Filters allow you to process content before it is sent to the client.
#
# To parse .shtml files for server-side includes (SSI):
# (You will also need to add "Includes" to the "Options" directive.)
#
AddType text/html .shtml
AddOutputFilter INCLUDES .shtml
</IfModule>
#
# Specify a default charset for all content served; this enables
# interpretation of all content as UTF-8 by default. To use the
# default browser choice (ISO-8859-1), or to allow the META tags
# in HTML content to override this choice, comment out this
# directive:
#
AddDefaultCharset UTF-8
<IfModule mime_magic_module>
#
# The mod_mime_magic module allows the server to use various hints from the
# contents of the file itself to determine its type. The MIMEMagicFile
# directive tells the module where the hint definitions are located.
#
MIMEMagicFile conf/magic
</IfModule>
#
# Customizable error responses come in three flavors:
# 1) plain text 2) local redirects 3) external redirects
#
# Some examples:
#ErrorDocument 500 "The server made a boo boo."
#ErrorDocument 404 /missing.html
#ErrorDocument 404 "/cgi-bin/missing_handler.pl"
#ErrorDocument 402 http://www.example.com/subscription_info.html
#
#
# EnableMMAP and EnableSendfile: On systems that support it,
# memory-mapping or the sendfile syscall may be used to deliver
# files. This usually improves server performance, but must
# be turned off when serving from networked-mounted
# filesystems or if support for these functions is otherwise
# broken on your system.
# Defaults if commented: EnableMMAP On, EnableSendfile Off
#
#EnableMMAP off
EnableSendfile on
# Supplemental configuration
#
# Load config files in the "/etc/httpd/conf.d" directory, if any.
#以下增加虚拟主机配置,可以配置多站点
NameVirtualHost *:80
# VirtualHost example:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@www.ceshi.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/yiiblog/frontend/web
ServerName www.ceshi.cn
ErrorLog logs/www.ceshi.cn-error_log
CustomLog logs/www.ceshi.cn-access_log common
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@www.ceshi.cn
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/yiiblog/backend/web
ServerName admin.ceshi.cn
ErrorLog logs/admin.ceshi.cn-error_log
CustomLog logs/admin.ceshi.cn-access_log common
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@www.yiishop.cn
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/yiishop/web
ServerName www.yiishop.cn
ErrorLog logs/www.yiishop.cn-error_log
CustomLog logs/www.yiishop.cn-access_log common
</VirtualHost>
IncludeOptional conf.d/*.conf
注意:
1. 在安装的时候,出现文件的权限问题,需要 chmod -R 775 /文件地址 或者直接 775 换成 777
2. 同时出现 yii 高级版本的时候 assets 不能写,需要关闭 SELinux
3.apache 配置时可能还需要把项目目录文件权限给 apache:apache 否则可能会报错,我的项目在 advanced/
原因:apache 没有权限:Invalid Configuration – yii\base\InvalidConfigException
The directory is not writable by the Web process: /var/www/html/advanced/frontend/web/assets
[root@bogon html]# chown -R root:root advanced/
[root@bogon html]# ls -l
总用量 28352
drwxrwxrwx. 9 root root 4096 1 月 9 01:04 advanced
改成
[root@bogon html]# chown -R apache:apache advanced/
[root@bogon html]# ls -l
总用量 28352
drwxrwxrwx. 9 apache apache 4096 1 月 9 01:04 advanced
4. 如果还是显示上面的权限错误就需要关闭 SELinux, 参考下面,最好是修改 /etc/selinux/config 文件,否则重启后又是开启了 SELinux,导致无法访问
注意:目前出现的权限主要是 SELinux 开启导致的,默认是开启的,所以需要关闭,至于文件是不是 chown -R root:root advanced/ 并没有关系,因为我已经给了文件所有人的权限,下面两者都可以访问,毕竟都是 777 的权限了,可以根据需要关闭某些权限的,比如开启 775 即可
drwxrwxrwx. 9 root root 4096 1 月 9 01:04 advanced
drwxrwxrwx. 9 apache apache 4096 1 月 9 01:04 advanced
查看 SELinux 状态:
1、/usr/sbin/sestatus -v ## 如果 SELinux status 参数为 enabled 即为开启状态
SELinux status: enabled
2、getenforce ## 也可以用这个命令检查
关闭 SELinux:
1、临时关闭(不用重启机器):
setenforce 0 ## 设置 SELinux 成为 permissive 模式
##setenforce 1 设置 SELinux 成为 enforcing 模式
2、修改配置文件需要重启机器:
修改 /etc/selinux/config 文件
将 SELINUX=enforcing 改为 SELINUX=disabled
重启机器即可
其他事项配置的时候出现再总结,目前完美解决,使用 centos7 配置 lamp,至此花了好几天晚上研究的终于 lanp 完成,有问题留言,互相学习,下次再出一个 lnmp
提醒:本次使用的是 mariadb,同等于 myql
更新于 2018 年 1 月 9 日,后续有问题可以留言,我会继续更新
G
M
T
| Detect languageAfrikaansAlbanianArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSerbianSesothoSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSundaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshYiddishYorubaZulu |
|
AfrikaansAlbanianArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSerbianSesothoSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSundaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshYiddishYorubaZulu |
|
|
|
|
|
Text-to-speech function is limited to 200 characters
|
|
Options : History : Feedback : Donate | Close |
| Detect languageAfrikaansAlbanianArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSerbianSesothoSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSundaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshYiddishYorubaZulu |
|
AfrikaansAlbanianArabicArmenianAzerbaijaniBasqueBelarusianBengaliBosnianBulgarianCatalanCebuanoChichewaChinese (Simplified)Chinese (Traditional)CroatianCzechDanishDutchEnglishEsperantoEstonianFilipinoFinnishFrenchGalicianGeorgianGermanGreekGujaratiHaitian CreoleHausaHebrewHindiHmongHungarianIcelandicIgboIndonesianIrishItalianJapaneseJavaneseKannadaKazakhKhmerKoreanLaoLatinLatvianLithuanianMacedonianMalagasyMalayMalayalamMalteseMaoriMarathiMongolianMyanmar (Burmese)NepaliNorwegianPersianPolishPortuguesePunjabiRomanianRussianSerbianSesothoSinhalaSlovakSlovenianSomaliSpanishSundaneseSwahiliSwedishTajikTamilTeluguThaiTurkishUkrainianUrduUzbekVietnameseWelshYiddishYorubaZulu |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Options : History : Feedback : Donate | Close |

01.vm 虚拟机、centos7mini 安装、jdk 安装
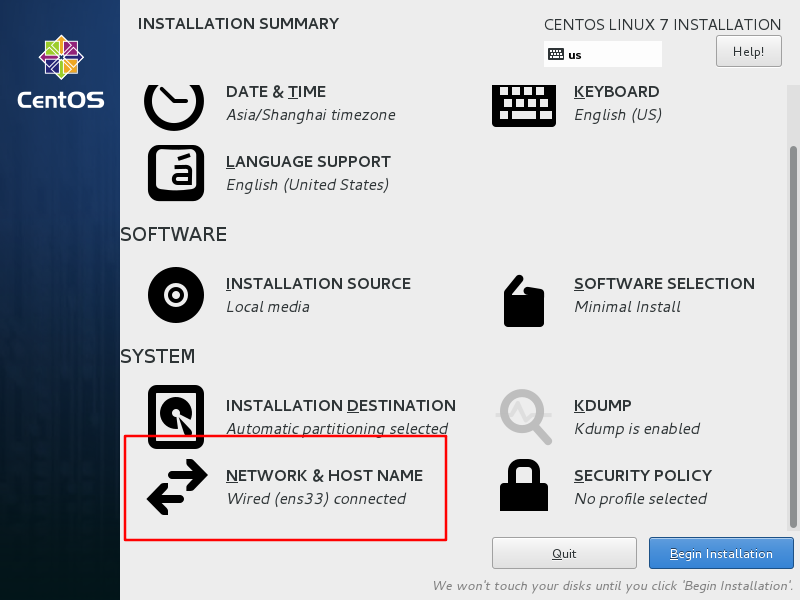
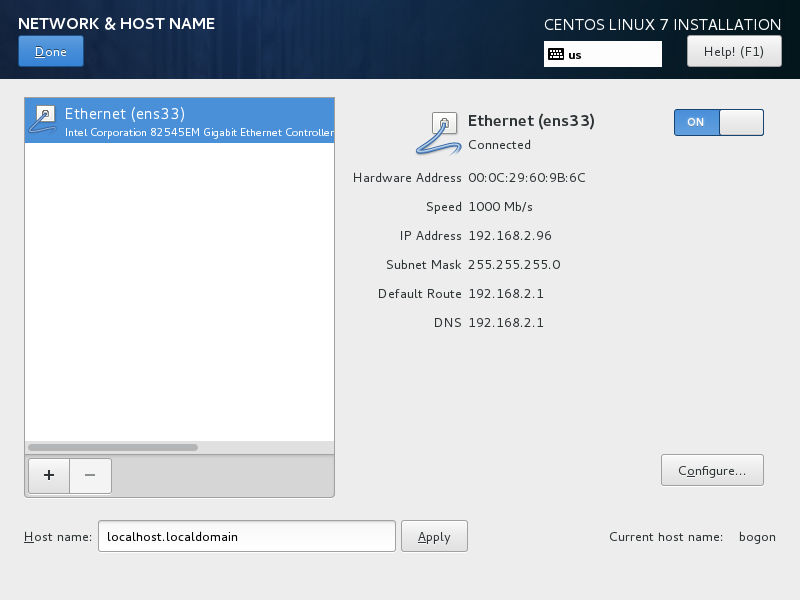
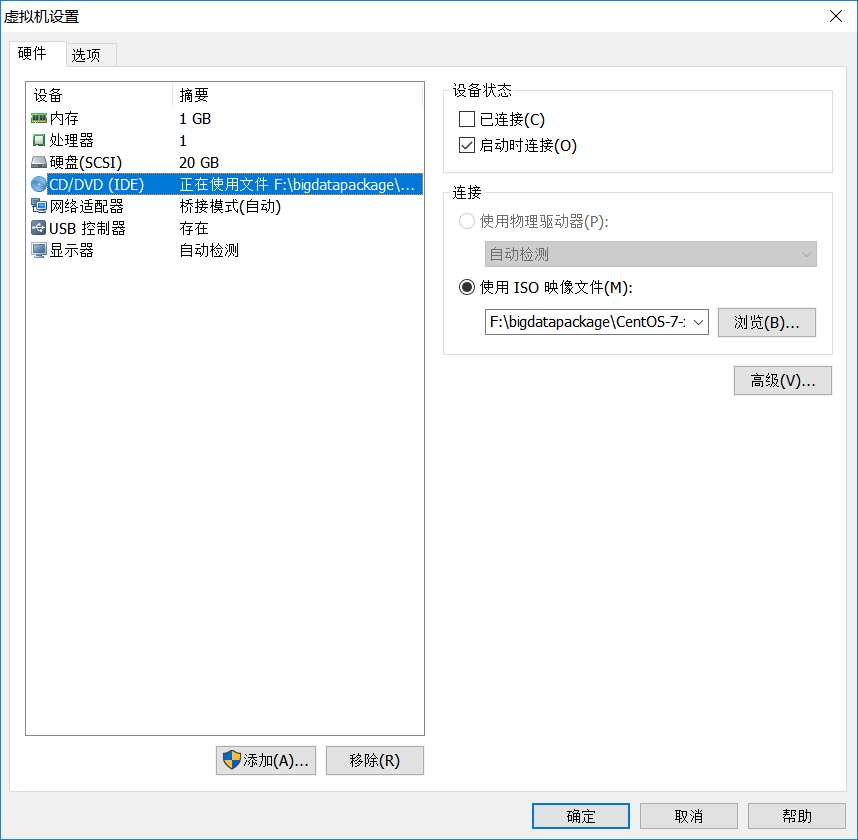
-c 创建.tar 格式的文件
-x 解开.tar 格式的文件
-f 使用归档文件
-v 显示详细信息
-t 查看包内文件
-j 使用 baip2 程序
-z 使用 gzip 程序
-p 打包时保留文件及目录的权限
-P 打包时保留文件及目录的绝对路径
-C 释放的目的地
指定目录 -C 解压到 user 下
例子 tar -zxvf aaa.gz -C /var/local/user

4.1.1 Centos7---4.2.1 Apache
4.1.1 Centos7
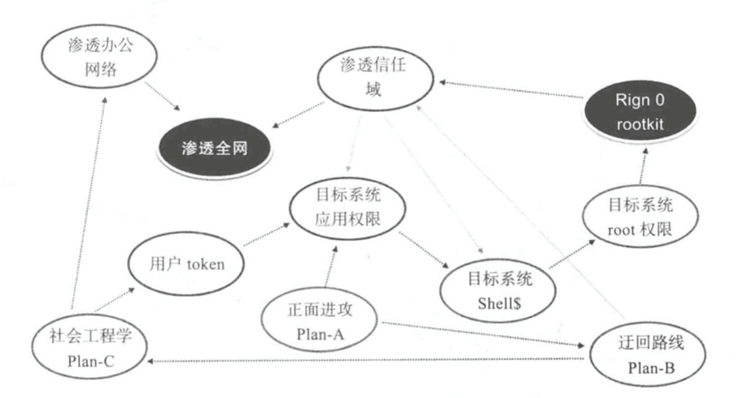
安全加固-Centos7
攻击者视角
SSH密码
yum -y install expect
mkpasswd
服务器上所有账号的密码都要采用毫无关联的强密码,密码为不少于16位的大小写字母数字特殊符号的组合。
修改SSH配置文件
改默认端口 禁止root帐号登录 指定允许登录帐号
启用强制密码长度策略
/etc/login.defs
PASS_MIN_LEN 13
检查是否存在除root之外UID为0的用户
awk -F: ''($3 == 0) { print $1 }'' /etc/passwd
检测登陆系统是否需要密码
awk -F: ''($2 == ""){print $1}'' /etc/passwd
帐户口令复杂度及定期更换
禁用NAT
echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
Bash日志
设置环境变量为只读:
readonly HISTFILE
readonly HISTFILESIZE
readonly HISTSIZE
readonly HISTCMD
readonly HISTCONTROL
readonly HISTIGNORE
为history文件添加时间
export HISTTIMEFORMAT=‘%F %T’
设置history文件只能追加:
chatter +a ~/.bash_history
4.2.1 Apache
安全加固-Apache
服务器Banner信息隐藏
/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
ServerTokens Prod
ServerSignature Off
PHP配置
/etc/php.ini
expose_php = off
防止列目录泄露敏感信息
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks改为 Options FollowSymLinks
指定目录禁止php解析
<Directory "/var/www/html/uploads">
php_flag engine off
</Directory>
限制管理员后台特定IP访问
<Directory "/var/www/html/admin">
Order Deny,Allow
Deny from all
Allow from 192.168.1.111
</Directory>
关闭对.htaccess的支持
AllowOverride None

apache 多端口配置多站点(centos7)
<table><tr>
<td><pre>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
总结
以上是小编为你收集整理的apache 多端口配置多站点(centos7)全部内容。
如果觉得小编网站内容还不错,欢迎将小编网站推荐给好友。

Apache 系列:Centos7.2 下安装与配置 apache
Centos7.2 下安装与配置 apache (一)
配置机:腾讯云服务器,centos7.2
一、安装 Apache 服务(Apache 软件安装包叫 httpd)
yum install httpd -y
二、开启 Apache 服务
systemctl start httpd
三、设置开机自启 Apache 服务
systemctl enable httpd
四、cd var/www/html(apache 网页的存放路径,默认下面是没有网页的)
五、vi index.html

六、访问网页 (访问服务器的话,访问公有 ip)
相关配置
配置目录及相关配置文件:
服务目录 /etc/httpd
主配置文件 /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
网站数据目录 /var/www/html
访问日志 /var/log/httpd/access_log
错误日志 /var/log/httpd/error_log
【httpd安装后各文件的内容及存放位置】
服务脚本:/etc/rc.d/init.d/httpd
运行目录:/etc/httpd
配置文件:/etc/httpd/conf/
主配置文件:httpd.conf
扩展配置文件:/etc/httpd/conf.d/*.conf
socket:
http: 80/tcp,
https: 443/tcp
网页文件目录(DocumentRoot):
静态页面:/var/www/html
动态页面(CGI): /var/www/cgi-bin/
默认主页面:index.html index.php
常见主配置文件(/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf)配置参数:
ServerRoot 服务目录
ServerAdmin 管理员邮箱
User 运行服务的用户
Group 运行服务的用户组
ServerName 网站服务器的域名
DocumentRoot 网站数据目录
Listen 监听的IP地址与端口号
DirectoryIndex 默认的索引页页面
ErrorLog 错误日志文件
CustomLog 访问日志文件
Timeout 网页超时时间,默认为300秒.
Include 需要加载的其他文件
今天关于centos7mini 版配置 apache 站点 - 非迷你版本类似和完美运行的讲解已经结束,谢谢您的阅读,如果想了解更多关于01.vm 虚拟机、centos7mini 安装、jdk 安装、4.1.1 Centos7---4.2.1 Apache、apache 多端口配置多站点(centos7)、Apache 系列:Centos7.2 下安装与配置 apache的相关知识,请在本站搜索。
本文标签:





