对于Sigmoid和tanh激活函数中有多少计算操作?感兴趣的读者,本文将会是一篇不错的选择,我们将详细介绍tanh激活函数和sigmoid关系,并为您提供关于AI神经网络激活函数sigmoid及ma
对于Sigmoid 和 tanh 激活函数中有多少计算操作?感兴趣的读者,本文将会是一篇不错的选择,我们将详细介绍tanh激活函数和sigmoid关系,并为您提供关于AI神经网络激活函数sigmoid及matlab的sigmf、ANN 神经网络 ——Sigmoid 激活函数编程练习 (Python 实现)、LSTM输入门中tanh激活函数的使用、python实现并绘制 sigmoid函数,tanh函数,ReLU函数,PReLU函数的有用信息。
本文目录一览:- Sigmoid 和 tanh 激活函数中有多少计算操作?(tanh激活函数和sigmoid关系)
- AI神经网络激活函数sigmoid及matlab的sigmf
- ANN 神经网络 ——Sigmoid 激活函数编程练习 (Python 实现)
- LSTM输入门中tanh激活函数的使用
- python实现并绘制 sigmoid函数,tanh函数,ReLU函数,PReLU函数

Sigmoid 和 tanh 激活函数中有多少计算操作?(tanh激活函数和sigmoid关系)
如何解决Sigmoid 和 tanh 激活函数中有多少计算操作??
我正在为 LSTM 模块创建一个计算图。
例如,在大小为 A=nxl 和 B=lxm 的两个矩形矩阵相乘的情况下,我们可以得到操作总数为 Operations(AxB) = n*l*m + n*(l-1)*m 其中 n*l*m 是乘法次数,n*(l-1)*m 是加法次数。
如何根据输入大小计算 Sigmoid 和 tanh 激活函数中的运算次数(加/减、乘/除等)?
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)

AI神经网络激活函数sigmoid及matlab的sigmf
神经网络中引入激活函数sigmoid作用是逻辑回归(logistic regression),引入非线性化。数学中的标准sigmoid输出范围是(0,1)。sigmoid的数学定义:
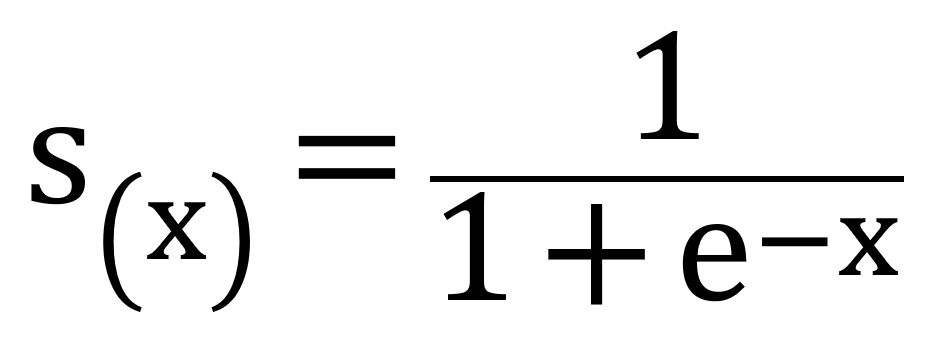
在matlab中,对于sigmoid的定义实现是sigmf,但是sigmf包含多个参数:
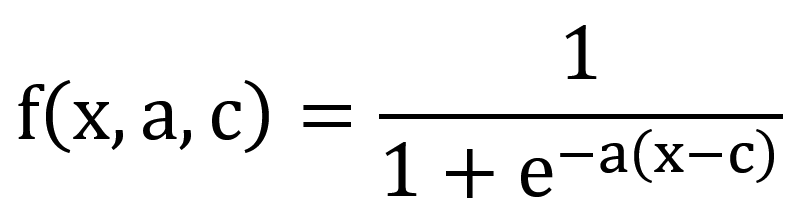
用MATLAB跑出不同的sigmoid函数曲线:
x1=-10:0.1:10;
y1=sigmf(x1,[1 2]);
plot(x1,y1,''g'');
hold on;
y2=sigmf(x1,[1 0])+0.2;
plot(x1,y2,''b'');
hold on;
y3 =1./(1+exp(-x1));
plot(x1,y3,''r'');
hold on;
legend(''sigmf(x1,[1 2])'',''sigmf(x1,[1 0])+0.2'',''标准sigmoid函数'');
grid on;曲线如图所示:
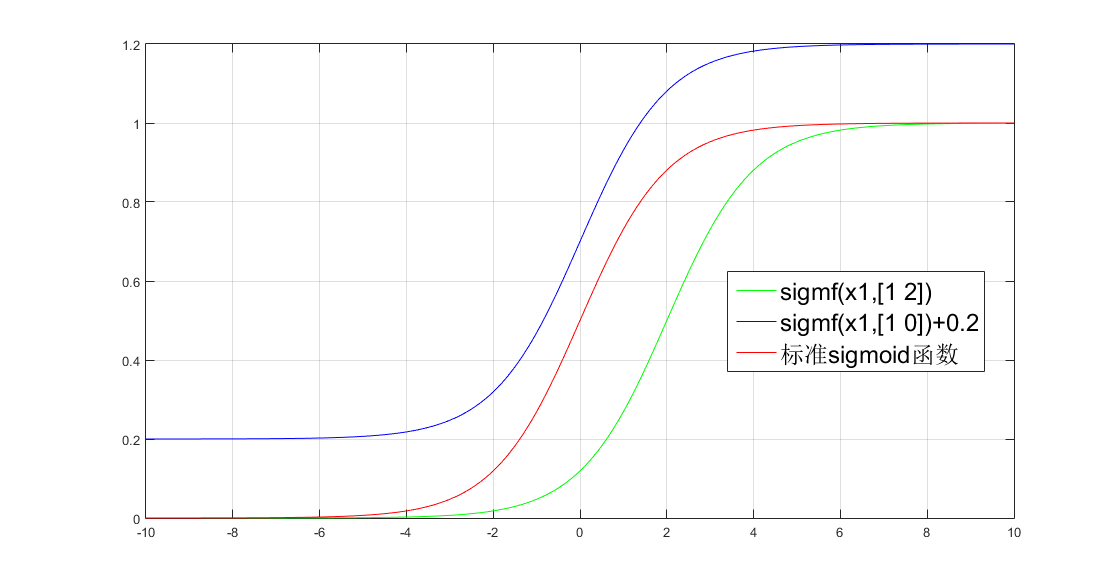
红色的y3曲线,是逻辑回归sigmoid函数的数学标准定义。把matlab中的sigmf参数a=1,c=0,那么sigmf就变成标准sigmoid数学定义实现。蓝色的y2曲线是标准sigmoid函数的y值再加0.2,其中a=1 ,c=0。

ANN 神经网络 ——Sigmoid 激活函数编程练习 (Python 实现)

# ----------
#
# There are two functions to finish:
# First, in activate(), write the sigmoid activation function.
# Second, in update(), write the gradient descent update rule. Updates should be
# performed online, revising the weights after each data point.
#
# ----------
import numpy as np
class Sigmoid:
"""
This class models an artificial neuron with sigmoid activation function.
"""
def __init__(self, weights = np.array([1])):
"""
Initialize weights based on input arguments. Note that no type-checking
is being performed here for simplicity of code.
"""
self.weights = weights
# NOTE: You do not need to worry about these two attribues for this
# programming quiz, but these will be useful for if you want to create
# a network out of these sigmoid units!
self.last_input = 0 # strength of last input
self.delta = 0 # error signal
def activate(self, values):
"""
Takes in @param values, a list of numbers equal to length of weights.
@return the output of a sigmoid unit with given inputs based on unit
weights.
"""
# YOUR CODE HERE
# First calculate the strength of the input signal.
strength = np.dot(values, self.weights)
self.last_input = strength
# TODO: Modify strength using the sigmoid activation function and
# return as output signal.
# HINT: You may want to create a helper function to compute the
# logistic function since you will need it for the update function.
result = self.logistic(strength)
return result
def logistic(self,strength):
return 1/(1+np.exp(-strength))
def update(self, values, train, eta=.1):
"""
Takes in a 2D array @param values consisting of a LIST of inputs and a
1D array @param train, consisting of a corresponding list of expected
outputs. Updates internal weights according to gradient descent using
these values and an optional learning rate, @param eta.
"""
# TODO: for each data point...
for X, y_true in zip(values, train):
# obtain the output signal for that point
y_pred = self.activate(X)
# YOUR CODE HERE
# TODO: compute derivative of logistic function at input strength
# Recall: d/dx logistic(x) = logistic(x)*(1-logistic(x))
dx = self.logistic(self.last_input)*(1 - self.logistic(self.last_input) )
print ("dx{}:".format(dx))
print (''\n'')
# TODO: update self.weights based on learning rate, signal accuracy,
# function slope (derivative) and input value
delta_w = eta * (y_true - y_pred) * dx * X
print ("delta_w:{} weight before {}".format(delta_w, self.weights))
self.weights += delta_w
print ("delta_w:{} weight after {}".format(delta_w, self.weights))
print (''\n'')
def test():
"""
A few tests to make sure that the perceptron class performs as expected.
Nothing should show up in the output if all the assertions pass.
"""
def sum_almost_equal(array1, array2, tol = 1e-5):
return sum(abs(array1 - array2)) < tol
u1 = Sigmoid(weights=[3,-2,1])
assert abs(u1.activate(np.array([1,2,3])) - 0.880797) < 1e-5
u1.update(np.array([[1,2,3]]),np.array([0]))
assert sum_almost_equal(u1.weights, np.array([2.990752, -2.018496, 0.972257]))
u2 = Sigmoid(weights=[0,3,-1])
u2.update(np.array([[-3,-1,2],[2,1,2]]),np.array([1,0]))
assert sum_almost_equal(u2.weights, np.array([-0.030739, 2.984961, -1.027437]))
if __name__ == "__main__":
test()
OUTPUT
Running test()...
dx0.104993585404:
delta_w:[-0.0092478 -0.01849561 -0.02774341] weight before [3, -2, 1]
delta_w:[-0.0092478 -0.01849561 -0.02774341] weight after [ 2.9907522 -2.01849561 0.97225659]
dx0.00664805667079:
delta_w:[-0.00198107 -0.00066036 0.00132071] weight before [0, 3, -1]
delta_w:[-0.00198107 -0.00066036 0.00132071] weight after [ -1.98106867e-03 2.99933964e+00 -9.98679288e-01]
dx0.196791859198:
delta_w:[-0.02875794 -0.01437897 -0.02875794] weight before [ -1.98106867e-03 2.99933964e+00 -9.98679288e-01]
delta_w:[-0.02875794 -0.01437897 -0.02875794] weight after [-0.03073901 2.98496067 -1.02743723]
All done!

LSTM输入门中tanh激活函数的使用
如何解决LSTM输入门中tanh激活函数的使用?
在学习 LSTM 时,我了解了在输入门中使用 2 个不同的激活函数 - sigmoid 和 tanh。我使用了 sigmoid 但没有使用 tanh。在这篇 stackoverflow 文章中,about use of tanh 说我们希望它的二阶导数在变为零之前保持很长时间,我不明白他为什么要谈论二阶导数。此外,他有点说 tanh 消除了消失梯度(在第二段中),但在我阅读的所有文章中,他们都说 Leaky ReLU 有助于消除它。因此我想了解 LSTM 中的 tanh。这不是重复的问题,我只是想了解之前回答的问题。谢谢!?
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)

python实现并绘制 sigmoid函数,tanh函数,ReLU函数,PReLU函数
<a href="http://www.jqhtml.com/18054.html" target="_blank">Python绘制正余弦函数图像</a>
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import mpl_toolkits.axisartist as axisartist
def sigmoid(x):
return 1. / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def tanh(x):
return (np.exp(x) - np.exp(-x)) / (np.exp(x) + np.exp(-x))
def relu(x):
return np.where(x<0,0,x)
def prelu(x):
return np.where(x<0,0.5*x,x)
def plot_sigmoid():
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
y = sigmoid(x)
fig = plt.figure()
# ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax = axisartist.Subplot(fig,111)
ax.spines[''top''].set_color(''none'')
ax.spines[''right''].set_color(''none'')
# ax.spines[''bottom''].set_color(''none'')
# ax.spines[''left''].set_color(''none'')
ax.axis[''bottom''].set_axisline_style("-|>",size=1.5)
ax.spines[''left''].set_position((''data'', 0))
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.xlim([-10.05, 10.05])
plt.ylim([-0.02, 1.02])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("sigmoid.png")
plt.show()
def plot_tanh():
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
y = tanh(x)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.spines[''top''].set_color(''none'')
ax.spines[''right''].set_color(''none'')
# ax.spines[''bottom''].set_color(''none'')
# ax.spines[''left''].set_color(''none'')
ax.spines[''left''].set_position((''data'', 0))
ax.spines[''bottom''].set_position((''data'', 0))
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.xlim([-10.05, 10.05])
plt.ylim([-1.02, 1.02])
ax.set_yticks([-1.0, -0.5, 0.5, 1.0])
ax.set_xticks([-10, -5, 5, 10])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("tanh.png")
plt.show()
def plot_relu():
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
y = relu(x)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.spines[''top''].set_color(''none'')
ax.spines[''right''].set_color(''none'')
# ax.spines[''bottom''].set_color(''none'')
# ax.spines[''left''].set_color(''none'')
ax.spines[''left''].set_position((''data'', 0))
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.xlim([-10.05, 10.05])
plt.ylim([0, 10.02])
ax.set_yticks([2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("relu.png")
plt.show()
def plot_prelu():
x = np.arange(-10, 10, 0.1)
y = prelu(x)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax.spines[''top''].set_color(''none'')
ax.spines[''right''].set_color(''none'')
# ax.spines[''bottom''].set_color(''none'')
# ax.spines[''left''].set_color(''none'')
ax.spines[''left''].set_position((''data'', 0))
ax.spines[''bottom''].set_position((''data'', 0))
ax.plot(x, y)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("prelu.png")
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
plot_sigmoid()
plot_tanh()
plot_relu()
plot_prelu()
今天关于Sigmoid 和 tanh 激活函数中有多少计算操作?和tanh激活函数和sigmoid关系的介绍到此结束,谢谢您的阅读,有关AI神经网络激活函数sigmoid及matlab的sigmf、ANN 神经网络 ——Sigmoid 激活函数编程练习 (Python 实现)、LSTM输入门中tanh激活函数的使用、python实现并绘制 sigmoid函数,tanh函数,ReLU函数,PReLU函数等更多相关知识的信息可以在本站进行查询。
本文标签:





