在本文中,我们将给您介绍关于计算范德蒙德矩阵的有效方法的详细内容,并且为您解答计算范德蒙德矩阵的有效方法是什么的相关问题,此外,我们还将为您提供关于1960范德蒙矩阵(数学贪心)、51nod范德蒙矩阵
在本文中,我们将给您介绍关于计算范德蒙德矩阵的有效方法的详细内容,并且为您解答计算范德蒙德矩阵的有效方法是什么的相关问题,此外,我们还将为您提供关于1960 范德蒙矩阵(数学贪心)、51nod 范德蒙矩阵、awk – 计算符合某些条件的数量的有效方法、C – 初始化结构的有效方法的知识。
本文目录一览:
计算范德蒙德矩阵的有效方法(计算范德蒙德矩阵的有效方法是什么)
我正在计算Vandermondematrix一个相当大的一维数组。做到这一点的自然而干净的方法是使用np.vander()。但是,我发现这是大约。比基于列表理解的方法
慢2.5倍 。
In [43]: x = np.arange(5000)
In [44]: N = 4
In [45]: %timeit np.vander(x,N,increasing=True)
155 µs ± 205 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs,10000 loops each)
# one of the listed approaches from the documentation
In [46]: %timeit np.flip(np.column_stack([x**(N-1-i) for i in range(N)]),axis=1)
65.3 µs ± 235 ns per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs,10000 loops each)
In [47]: np.all(np.vander(x,increasing=True) == np.flip(np.column_stack([x**(N-1-i) for i in range(N)]),axis=1))
Out[47]: True
我试图了解瓶颈在哪里以及为什么本机实现的速度要慢np.vander()约
2.5倍 。
效率对我的实施至关重要。因此,也欢迎更快的选择!

1960 范德蒙矩阵(数学贪心)
1960 范德蒙矩阵

 然后推广一下就是每一个G列向量乘以每一个V行向量的和,然后直接贪心就行了。
然后推广一下就是每一个G列向量乘以每一个V行向量的和,然后直接贪心就行了。
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const ll mod = 1e9 + 7;
const int maxn = 100010;
ll num[maxn];
ll inv(ll t, ll p = mod)
{//求t关于p的逆元,注意:t要小于p,最好传参前先把t%p一下
return t == 1 ? 1 : (p - p / t) * inv(p % t, p) % p;
}
ll pow(ll x, ll n)
{
ll ans = 1;
for (; n;n>>=1, x=x*x%mod)
if (n & 1)ans = ans*x%mod;
return ans;
}
int main()
{
ll n, m;
scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &m);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
scanf("%lld", &num[i]);
sort(num + 1, num + m+1);
ll ans = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; ++i)
{
ll a0 = ((i - 1)*n + 1)%mod, an = i*n%mod;
ll A = (a0 + an) % mod*n%mod*inv(2)%mod, X;
num[i] %= mod;
if (num[i] == 0)X = 1;
else if (num[i] == 1)X = n;
else {
X = (pow(num[i], n) - 1) % mod*inv(num[i] - 1) % mod;
}
ans = (ans + X*A%mod) % mod;
}
printf("%lld\n", ans);
}

51nod 范德蒙矩阵
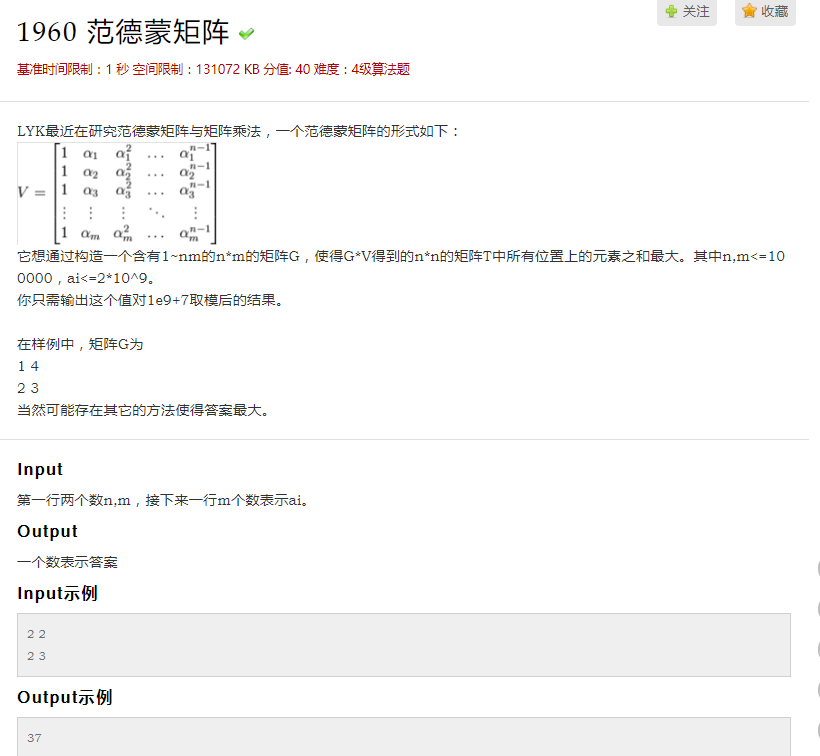
思路: 根据矩阵乘法的定义,G中的第i行第j列的元素 ai,j ,对答案的贡献为 ai,j∗ T中第j行的所有元素之和。
因此我们可以将T中根据每行的和进行排序。第i行的和可以通过公式 (ai^n−1)/(ai−1)直接得出。
注意考虑 ai=1,ai=0 以及 ai>MOD 的特殊情况即可。还有就是对于除法取模需要用到逆元(费马小定理)
一开始没注意除法取模 狂WA 12遍也是心累。。。。。
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<algorithm>
3 #include<cstring>
4 #include<cmath>
5
6 using namespace std;
7 typedef long long LL;
8 const LL mod = 1e9 + 7;
9 const int maxn = 1e5 + 10;
10 LL b[maxn], ans, a[maxn];
11 LL n, m;
12 LL Pow(LL a, LL b)//快速幂
13 {
14 LL ans = 1;
15 while (b) {
16 if (b & 1) {
17 ans *= a;ans %= mod;
18 }
19 a *= a;a %= mod;
20 b >>= 1;
21 }
22 return ans;
23 }
24 int main()
25 {
26 ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
27 while (cin >> n >> m) {
28 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
29 cin >> a[i];
30 }
31 sort(a + 1, a + m + 1);
32 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
33 a[i] = (a[i] % mod + mod) % mod;
34 if (a[i] == 0)b[i] = 1;
35 else if (a[i] == 1)b[i] = n;
36 else { //费马小定理对除法取模
37 b[i] = (Pow(a[i], n) - 1 + mod) % mod;
38 b[i] = b[i] * Pow(a[i] - 1, mod - 2) % mod;
39 }
40 }
41 //以下是求解
42 ans = 0;
43 LL num = (n*(n + 1) / 2) % mod;
44 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
45 ans = (ans + (num*b[i]) % mod) % mod;
46 num = (num + n * n) % mod;
47 }
48 cout << ans << endl;
49 }
50 return 0;
51 }

awk – 计算符合某些条件的数量的有效方法
我想出了这个命令:
awk '$4>$1 {print}' sampleFile | wc -l
有没有更好的方法来找到数字而不是使用wc -l
解决方法
awk '$4 > $1 { count++ } END { print count }' file.txt

C – 初始化结构的有效方法
struct {
int iMyInt;
char cMyChar;
double dCoordinates[128];
} s_t;
我的方法是这样做:
s_t myStruct = { 0 };
我的同事改为建议这种做法:
s_t myStruct = { };
他指出我的方法在两部分操作中初始化单个元素,然后初始化其余元素,而他的方法在一个部分操作中初始化整个结构,这个操作更快,更有效.
这是真的,如果是这样的话,所有编译器优化级别的情况总是如此(即:编译器是否会解决这个问题并为我优化它)?
谢谢.
解决方法
struct s_t {
int iMyInt;
char cMyChar;
double dCoordinates[128];
};
这就是说:在你的具体情况下,两种方法是相同的,一切都是零.对于使用任何上述成员和/或数组元素的通用测试代码,在-O3和偶数-O0处没有区别(在-O0,它甚至在两种情况下都调用整个结构上的memset).
s_t obj = {0};
movq %rcx,%rdi
movl %eax,%esi
callq memset
s_t obj = {};
movq %rcx,%esi
callq memset
今天关于计算范德蒙德矩阵的有效方法和计算范德蒙德矩阵的有效方法是什么的讲解已经结束,谢谢您的阅读,如果想了解更多关于1960 范德蒙矩阵(数学贪心)、51nod 范德蒙矩阵、awk – 计算符合某些条件的数量的有效方法、C – 初始化结构的有效方法的相关知识,请在本站搜索。
本文标签:





