对于一文读懂SuperEdge分布式健康检查(云端)感兴趣的读者,本文将提供您所需要的所有信息,并且为您提供关于18.从零开始编写一个类nginx工具,主动式健康检查源码实现、Checkup——分布式
对于一文读懂 SuperEdge 分布式健康检查(云端)感兴趣的读者,本文将提供您所需要的所有信息,并且为您提供关于18. 从零开始编写一个类 nginx 工具,主动式健康检查源码实现、Checkup —— 分布式无锁站点健康检查工具、docker 健康检查中的多个健康检查卷发、nginx容器配置健康检查接口,消灭云厂商lb频繁健康检查日志的宝贵知识。
本文目录一览:- 一文读懂 SuperEdge 分布式健康检查(云端)
- 18. 从零开始编写一个类 nginx 工具,主动式健康检查源码实现
- Checkup —— 分布式无锁站点健康检查工具
- docker 健康检查中的多个健康检查卷发
- nginx容器配置健康检查接口,消灭云厂商lb频繁健康检查日志

一文读懂 SuperEdge 分布式健康检查(云端)
杜杨浩,腾讯云高级工程师,热衷于开源、容器和Kubernetes。目前主要从事镜像仓库、Kubernetes集群高可用&备份还原,以及边缘计算相关研发工作。
前言
SuperEdge分布式健康检查功能由边端的edge-health-daemon以及云端的edge-health-admission组成:
- edge-health-daemon:对同区域边缘节点执行分布式健康检查,并向apiserver发送健康状态投票结果(给node打annotation)
- edge-health-admission:不断根据node edge-health annotation调整kube-controller-manager设置的node taint(去掉NoExecute taint)以及endpoints(将失联节点上的pods从endpoint subsets notReadyAddresses移到addresses中),从而实现云端和边端共同决定节点状态
整体架构如下所示:
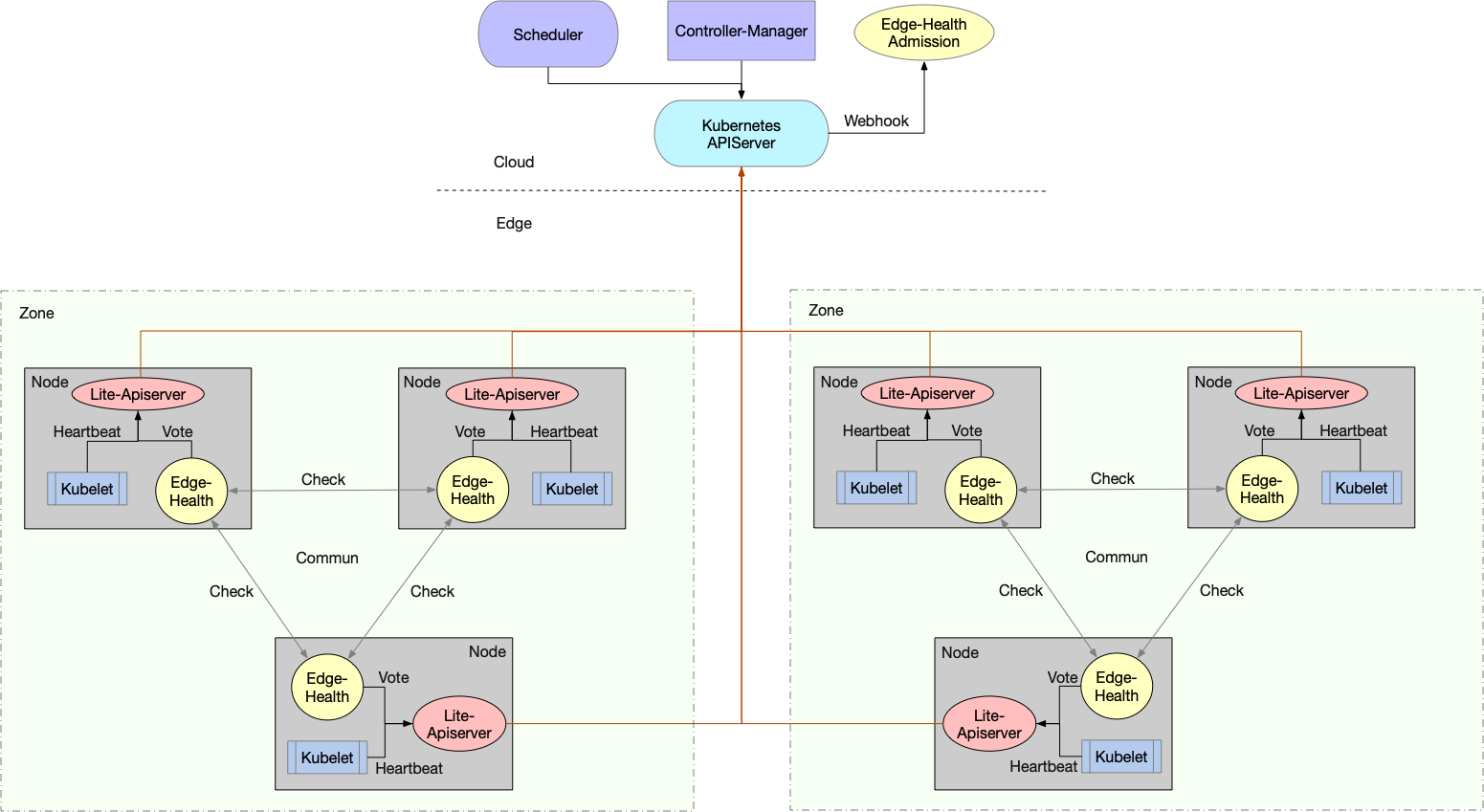
之所以创建edge-health-admission云端组件,是因为当云边断连时,kube-controller-manager会执行如下操作:
- 失联的节点被置为ConditionUnknown状态,并被添加NoSchedule和NoExecute的taints
- 失联的节点上的pod从Service的Endpoint列表中移除
当edge-health-daemon在边端根据健康检查判断节点状态正常时,会更新node:去掉NoExecute taint。但是在node成功更新之后又会被kube-controller-manager给刷回去(再次添加NoExecute taint),因此必须添加Kubernetes mutating admission webhook也即edge-health-admission,将kube-controller-manager对node api resource的更改做调整,最终实现分布式健康检查效果
在深入源码之前先介绍一下Kubernetes Admission Controllers
An admission controller is a piece of code that intercepts requests to the Kubernetes API server prior to persistence of the object, but after the request is authenticated and authorized. The controllers consist of the list below, are compiled into the kube-apiserver binary, and may only be configured by the cluster administrator. In that list, there are two special controllers: MutatingAdmissionWebhook and ValidatingAdmissionWebhook. These execute the mutating and validating (respectively) admission control webhooks which are configured in the API.
Kubernetes Admission Controllers是kube-apiserver处理api请求的某个环节,用于在api请求认证&鉴权之后,对象持久化之前进行调用,对请求进行校验或者修改(or both)
Kubernetes Admission Controllers包括多种admission,大多数都内嵌在kube-apiserver代码中了。其中MutatingAdmissionWebhook以及ValidatingAdmissionWebhook controller比较特殊,它们分别会调用外部构造的mutating admission control webhooks以及validating admission control webhooks
Admission webhooks are HTTP callbacks that receive admission requests and do something with them. You can define two types of admission webhooks, validating admission webhook and mutating admission webhook. Mutating admission webhooks are invoked first, and can modify objects sent to the API server to enforce custom defaults. After all object modifications are complete, and after the incoming object is validated by the API server, validating admission webhooks are invoked and can reject requests to enforce custom policies.
Admission Webhooks是一个HTTP回调服务,接受AdmissionReview请求并进行处理,按照处理方式的不同,可以将Admission Webhooks分类如下:
- validating admission webhook:通过ValidatingWebhookConfiguration配置,会对api请求进行准入校验,但是不能修改请求对象
- mutating admission webhook:通过MutatingWebhookConfiguration配置,会对api请求进行准入校验以及修改请求对象
两种类型的webhooks都需要定义如下Matching requests字段:
- admissionReviewVersions:定义了apiserver所支持的AdmissionReview api resoure的版本列表(API servers send the first AdmissionReview version in the admissionReviewVersions list they support)
- name:webhook名称(如果一个WebhookConfiguration中定义了多个webhooks,需要保证名称的唯一性)
- clientConfig:定义了webhook server的访问地址(url or service)以及CA bundle(optionally include a custom CA bundle to use to verify the TLS connection)
- namespaceSelector:限定了匹配请求资源的命名空间labelSelector
- objectSelector:限定了匹配请求资源本身的labelSelector
- rules:限定了匹配请求的operations,apiGroups,apiVersions,resources以及resource scope,如下:
- operations:规定了请求操作列表(Can be "CREATE", "UPDATE", "DELETE", "CONNECT", or "*" to match all.)
- apiGroups:规定了请求资源的API groups列表("" is the core API group. "*" matches all API groups.)
- apiVersions:规定了请求资源的API versions列表("*" matches all API versions.)
- resources:规定了请求资源类型(node, deployment and etc)
- scope:规定了请求资源的范围(Cluster,Namespaced or *)
- timeoutSeconds:规定了webhook回应的超时时间,如果超时了,根据failurePolicy进行处理
- failurePolicy:规定了apiserver对admission webhook请求失败的处理策略:
- Ignore:means that an error calling the webhook is ignored and the API request is allowed to continue.
- Fail:means that an error calling the webhook causes the admission to fail and the API request to be rejected.
- matchPolicy:规定了rules如何匹配到来的api请求,如下:
- Exact:完全匹配rules列表限制
- Equivalent:如果修改请求资源(apiserver可以实现对象在不同版本的转化)可以转化为能够配置rules列表限制,则认为该请求匹配,可以发送给admission webhook
- reinvocationPolicy:In v1.15+, to allow mutating admission plugins to observe changes made by other plugins, built-in mutating admission plugins are re-run if a mutating webhook modifies an object, and mutating webhooks can specify a reinvocationPolicy to control whether they are reinvoked as well.
- Never: the webhook must not be called more than once in a single admission evaluation
- IfNeeded: the webhook may be called again as part of the admission evaluation if the object being admitted is modified by other admission plugins after the initial webhook call.
- Side effects:某些webhooks除了修改AdmissionReview的内容外,还会连带修改其它的资源("side effects")。而sideEffects指示了Webhooks是否具有"side effects",取值如下:
- None: calling the webhook will have no side effects.
- NoneOnDryRun: calling the webhook will possibly have side effects, but if a request with dryRun: true is sent to the webhook, the webhook will suppress the side effects (the webhook is dryRun-aware).
这里给出edge-health-admission对应的MutatingWebhookConfiguration作为参考示例:
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: MutatingWebhookConfiguration
metadata:
name: edge-health-admission
webhooks:
- admissionReviewVersions:
- v1
clientConfig:
caBundle: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCk1JSUNwRENDQVl3Q0NRQ2RaL0w2akZSSkdqQU5CZ2txaGtpRzl3MEJBUXNGQURBVU1SSXdFQVlEVlFRRERBbFgKYVhObE1tTWdRMEV3SGhjTk1qQXdOekU0TURRek9ERTNXaGNOTkRjeE1qQTBNRFF6T0RFM1dqQVVNUkl3RUFZRApWUVFEREFsWGFYTmxNbU1nUTBFd2dnRWlNQTBHQ1NxR1NJYjNEUUVCQVFVQUE0SUJEd0F3Z2dFS0FvSUJBUUNSCnhHT2hrODlvVkRHZklyVDBrYVkwajdJQVJGZ2NlVVFmVldSZVhVcjh5eEVOQkF6ZnJNVVZyOWlCNmEwR2VFL3cKZzdVdW8vQWtwUEgrbzNQNjFxdWYrTkg1UDBEWHBUd1pmWU56VWtyaUVja3FOSkYzL2liV0o1WGpFZUZSZWpidgpST1V1VEZabmNWOVRaeTJISVF2UzhTRzRBTWJHVmptQXlDMStLODBKdDI3QUl4YmdndmVVTW8xWFNHYnRxOXlJCmM3Zk1QTXJMSHhaOUl5aTZla3BwMnJrNVdpeU5YbXZhSVA4SmZMaEdnTU56YlJaS1RtL0ZKdDdyV0dhQ1orNXgKV0kxRGJYQ2MyWWhmbThqU1BqZ3NNQTlaNURONDU5ellJSkVhSTFHeFI3MlhaUVFMTm8zdE5jd3IzVlQxVlpiTgo1cmhHQlVaTFlrMERtd25vWTBCekFnTUJBQUV3RFFZSktvWklodmNOQVFFTEJRQURnZ0VCQUhuUDJibnJBcWlWCjYzWkpMVzM0UWFDMnRreVFScTNVSUtWR3RVZHFobWRVQ0I1SXRoSUlleUdVRVdqVExpc3BDQzVZRHh4YVdrQjUKTUxTYTlUY0s3SkNOdkdJQUdQSDlILzRaeXRIRW10aFhiR1hJQ3FEVUVmSUVwVy9ObUgvcnBPQUxhYlRvSUVzeQpVNWZPUy9PVVZUM3ZoSldlRjdPblpIOWpnYk1SZG9zVElhaHdQdTEzZEtZMi8zcEtxRW1Cd1JkbXBvTExGbW9MCmVTUFQ4SjREZExGRkh2QWJKalFVbjhKQTZjOHUrMzZJZDIrWE1sTGRZYTdnTnhvZTExQTl6eFJQczRXdlpiMnQKUXZpbHZTbkFWb0ZUSVozSlpjRXVWQXllNFNRY1dKc3FLMlM0UER1VkNFdlg0SmRCRlA2NFhvU08zM3pXaWhtLworMXg3OXZHMUpFcz0KLS0tLS1FTkQgQ0VSVElGSUNBVEUtLS0tLQo=
service:
namespace: kube-system
name: edge-health-admission
path: /node-taint
failurePolicy: Ignore
matchPolicy: Exact
name: node-taint.k8s.io
namespaceSelector: {}
objectSelector: {}
reinvocationPolicy: Never
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ''*''
apiVersions:
- ''*''
operations:
- UPDATE
resources:
- nodes
scope: ''*''
sideEffects: None
timeoutSeconds: 5
- admissionReviewVersions:
- v1
clientConfig:
caBundle: LS0tLS1CRUdJTiBDRVJUSUZJQ0FURS0tLS0tCk1JSUNwRENDQVl3Q0NRQ2RaL0w2akZSSkdqQU5CZ2txaGtpRzl3MEJBUXNGQURBVU1SSXdFQVlEVlFRRERBbFgKYVhObE1tTWdRMEV3SGhjTk1qQXdOekU0TURRek9ERTNXaGNOTkRjeE1qQTBNRFF6T0RFM1dqQVVNUkl3RUFZRApWUVFEREFsWGFYTmxNbU1nUTBFd2dnRWlNQTBHQ1NxR1NJYjNEUUVCQVFVQUE0SUJEd0F3Z2dFS0FvSUJBUUNSCnhHT2hrODlvVkRHZklyVDBrYVkwajdJQVJGZ2NlVVFmVldSZVhVcjh5eEVOQkF6ZnJNVVZyOWlCNmEwR2VFL3cKZzdVdW8vQWtwUEgrbzNQNjFxdWYrTkg1UDBEWHBUd1pmWU56VWtyaUVja3FOSkYzL2liV0o1WGpFZUZSZWpidgpST1V1VEZabmNWOVRaeTJISVF2UzhTRzRBTWJHVmptQXlDMStLODBKdDI3QUl4YmdndmVVTW8xWFNHYnRxOXlJCmM3Zk1QTXJMSHhaOUl5aTZla3BwMnJrNVdpeU5YbXZhSVA4SmZMaEdnTU56YlJaS1RtL0ZKdDdyV0dhQ1orNXgKV0kxRGJYQ2MyWWhmbThqU1BqZ3NNQTlaNURONDU5ellJSkVhSTFHeFI3MlhaUVFMTm8zdE5jd3IzVlQxVlpiTgo1cmhHQlVaTFlrMERtd25vWTBCekFnTUJBQUV3RFFZSktvWklodmNOQVFFTEJRQURnZ0VCQUhuUDJibnJBcWlWCjYzWkpMVzM0UWFDMnRreVFScTNVSUtWR3RVZHFobWRVQ0I1SXRoSUlleUdVRVdqVExpc3BDQzVZRHh4YVdrQjUKTUxTYTlUY0s3SkNOdkdJQUdQSDlILzRaeXRIRW10aFhiR1hJQ3FEVUVmSUVwVy9ObUgvcnBPQUxhYlRvSUVzeQpVNWZPUy9PVVZUM3ZoSldlRjdPblpIOWpnYk1SZG9zVElhaHdQdTEzZEtZMi8zcEtxRW1Cd1JkbXBvTExGbW9MCmVTUFQ4SjREZExGRkh2QWJKalFVbjhKQTZjOHUrMzZJZDIrWE1sTGRZYTdnTnhvZTExQTl6eFJQczRXdlpiMnQKUXZpbHZTbkFWb0ZUSVozSlpjRXVWQXllNFNRY1dKc3FLMlM0UER1VkNFdlg0SmRCRlA2NFhvU08zM3pXaWhtLworMXg3OXZHMUpFcz0KLS0tLS1FTkQgQ0VSVElGSUNBVEUtLS0tLQo=
service:
namespace: kube-system
name: edge-health-admission
path: /endpoint
failurePolicy: Ignore
matchPolicy: Exact
name: endpoint.k8s.io
namespaceSelector: {}
objectSelector: {}
reinvocationPolicy: Never
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ''*''
apiVersions:
- ''*''
operations:
- UPDATE
resources:
- endpoints
scope: ''*''
sideEffects: None
timeoutSeconds: 5
kube-apiserver会发送AdmissionReview(apiGroup: admission.k8s.io,apiVersion:v1 or v1beta1)给Webhooks,并封装成JSON格式,示例如下:
# This example shows the data contained in an AdmissionReview object for a request to update the scale subresource of an apps/v1 Deployment
{
"apiVersion": "admission.k8s.io/v1",
"kind": "AdmissionReview",
"request": {
# Random uid uniquely identifying this admission call
"uid": "705ab4f5-6393-11e8-b7cc-42010a800002",
# Fully-qualified group/version/kind of the incoming object
"kind": {"group":"autoscaling","version":"v1","kind":"Scale"},
# Fully-qualified group/version/kind of the resource being modified
"resource": {"group":"apps","version":"v1","resource":"deployments"},
# subresource, if the request is to a subresource
"subResource": "scale",
# Fully-qualified group/version/kind of the incoming object in the original request to the API server.
# This only differs from `kind` if the webhook specified `matchPolicy: Equivalent` and the
# original request to the API server was converted to a version the webhook registered for.
"requestKind": {"group":"autoscaling","version":"v1","kind":"Scale"},
# Fully-qualified group/version/kind of the resource being modified in the original request to the API server.
# This only differs from `resource` if the webhook specified `matchPolicy: Equivalent` and the
# original request to the API server was converted to a version the webhook registered for.
"requestResource": {"group":"apps","version":"v1","resource":"deployments"},
# subresource, if the request is to a subresource
# This only differs from `subResource` if the webhook specified `matchPolicy: Equivalent` and the
# original request to the API server was converted to a version the webhook registered for.
"requestSubResource": "scale",
# Name of the resource being modified
"name": "my-deployment",
# Namespace of the resource being modified, if the resource is namespaced (or is a Namespace object)
"namespace": "my-namespace",
# operation can be CREATE, UPDATE, DELETE, or CONNECT
"operation": "UPDATE",
"userInfo": {
# Username of the authenticated user making the request to the API server
"username": "admin",
# UID of the authenticated user making the request to the API server
"uid": "014fbff9a07c",
# Group memberships of the authenticated user making the request to the API server
"groups": ["system:authenticated","my-admin-group"],
# Arbitrary extra info associated with the user making the request to the API server.
# This is populated by the API server authentication layer and should be included
# if any SubjectAccessReview checks are performed by the webhook.
"extra": {
"some-key":["some-value1", "some-value2"]
}
},
# object is the new object being admitted.
# It is null for DELETE operations.
"object": {"apiVersion":"autoscaling/v1","kind":"Scale",...},
# oldObject is the existing object.
# It is null for CREATE and CONNECT operations.
"oldObject": {"apiVersion":"autoscaling/v1","kind":"Scale",...},
# options contains the options for the operation being admitted, like meta.k8s.io/v1 CreateOptions, UpdateOptions, or DeleteOptions.
# It is null for CONNECT operations.
"options": {"apiVersion":"meta.k8s.io/v1","kind":"UpdateOptions",...},
# dryRun indicates the API request is running in dry run mode and will not be persisted.
# Webhooks with side effects should avoid actuating those side effects when dryRun is true.
# See http://k8s.io/docs/reference/using-api/api-concepts/#make-a-dry-run-request for more details.
"dryRun": false
}
}
而Webhooks需要向kube-apiserver回应具有相同版本的AdmissionReview,并封装成JSON格式,包含如下关键字段:
- uid:拷贝发送给webhooks的AdmissionReview request.uid字段
- allowed:true表示准许;false表示不准许
- status:当不准许请求时,可以通过status给出相关原因(http code and message)
- patch:base64编码,包含mutating admission webhook对请求对象的一系列JSON patch操作
- patchType:目前只支持JSONPatch类型
示例如下:
# a webhook response to add that label would be:
{
"apiVersion": "admission.k8s.io/v1",
"kind": "AdmissionReview",
"response": {
"uid": "<value from request.uid>",
"allowed": true,
"patchType": "JSONPatch",
"patch": "W3sib3AiOiAiYWRkIiwgInBhdGgiOiAiL3NwZWMvcmVwbGljYXMiLCAidmFsdWUiOiAzfV0="
}
}
edge-health-admission实际上就是一个mutating admission webhook,选择性地对endpoints以及node UPDATE请求进行修改,下面将详细分析其原理
edge-health-admission源码分析
edge-health-admission完全参考官方示例编写,如下是监听入口:
func (eha *EdgeHealthAdmission) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
if !cache.WaitForNamedCacheSync("edge-health-admission", stopCh, eha.cfg.NodeInformer.Informer().HasSynced) {
return
}
http.HandleFunc("/node-taint", eha.serveNodeTaint)
http.HandleFunc("/endpoint", eha.serveEndpoint)
server := &http.Server{
Addr: eha.cfg.Addr,
}
go func() {
if err := server.ListenAndServeTLS(eha.cfg.CertFile, eha.cfg.KeyFile); err != http.ErrServerClosed {
klog.Fatalf("ListenAndServeTLS err %+v", err)
}
}()
for {
select {
case <-stopCh:
ctx, cancel := context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), 2*time.Second)
defer cancel()
if err := server.Shutdown(ctx); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Server: program exit, server exit error %+v", err)
}
return
default:
}
}
}
这里会注册两种路由处理函数:
- node-taint:对应处理函数serveNodeTaint,负责对node UPDATE请求进行更改
- endpoint:对应处理函数serveEndpoint,负责对endpoints UPDATE请求进行更改
而这两个函数都会调用serve函数,如下:
// serve handles the http portion of a request prior to handing to an admit function
func serve(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request, admit admitFunc) {
var body []byte
if r.Body != nil {
if data, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body); err == nil {
body = data
}
}
// verify the content type is accurate
contentType := r.Header.Get("Content-Type")
if contentType != "application/json" {
klog.Errorf("contentType=%s, expect application/json", contentType)
return
}
klog.V(4).Info(fmt.Sprintf("handling request: %s", body))
// The AdmissionReview that was sent to the webhook
requestedAdmissionReview := admissionv1.AdmissionReview{}
// The AdmissionReview that will be returned
responseAdmissionReview := admissionv1.AdmissionReview{}
deserializer := codecs.UniversalDeserializer()
if _, _, err := deserializer.Decode(body, nil, &requestedAdmissionReview); err != nil {
klog.Error(err)
responseAdmissionReview.Response = toAdmissionResponse(err)
} else {
// pass to admitFunc
responseAdmissionReview.Response = admit(requestedAdmissionReview)
}
// Return the same UID
responseAdmissionReview.Response.UID = requestedAdmissionReview.Request.UID
klog.V(4).Info(fmt.Sprintf("sending response: %+v", responseAdmissionReview.Response))
respBytes, err := json.Marshal(responseAdmissionReview)
if err != nil {
klog.Error(err)
}
if _, err := w.Write(respBytes); err != nil {
klog.Error(err)
}
}
serve逻辑如下所示:
- 解析request.Body为AdmissionReview对象,并赋值给requestedAdmissionReview
- 对AdmissionReview对象执行admit函数,并赋值给回responseAdmissionReview
- 设置responseAdmissionReview.Response.UID为请求的AdmissionReview.Request.UID
其中serveNodeTaint以及serveEndpoint对应的admit函数分别为:mutateNodeTaint以及mutateEndpoint,下面依次分析:
1、mutateNodeTaint
mutateNodeTaint会对node UPDATE请求按照分布式健康检查结果进行修改:
func (eha *EdgeHealthAdmission) mutateNodeTaint(ar admissionv1.AdmissionReview) *admissionv1.AdmissionResponse {
klog.V(4).Info("mutating node taint")
nodeResource := metav1.GroupVersionResource{Group: "", Version: "v1", Resource: "nodes"}
if ar.Request.Resource != nodeResource {
klog.Errorf("expect resource to be %s", nodeResource)
return nil
}
var node corev1.Node
deserializer := codecs.UniversalDeserializer()
if _, _, err := deserializer.Decode(ar.Request.Object.Raw, nil, &node); err != nil {
klog.Error(err)
return toAdmissionResponse(err)
}
reviewResponse := admissionv1.AdmissionResponse{}
reviewResponse.Allowed = true
if index, condition := util.GetNodeCondition(&node.Status, v1.NodeReady); index != -1 && condition.Status == v1.ConditionUnknown {
if node.Annotations != nil {
var patches []*patch
if healthy, existed := node.Annotations[common.NodeHealthAnnotation]; existed && healthy == common.NodeHealthAnnotationPros {
if index, existed := util.TaintExistsPosition(node.Spec.Taints, common.UnreachableNoExecuteTaint); existed {
patches = append(patches, &patch{
OP: "remove",
Path: fmt.Sprintf("/spec/taints/%d", index),
})
klog.V(4).Infof("UnreachableNoExecuteTaint: remove %d taints %s", index, node.Spec.Taints[index])
}
}
if len(patches) > 0 {
patchBytes, _ := json.Marshal(patches)
reviewResponse.Patch = patchBytes
pt := admissionv1.PatchTypeJSONPatch
reviewResponse.PatchType = &pt
}
}
}
return &reviewResponse
}
主体逻辑如下:
- 检查AdmissionReview.Request.Resource是否为node资源的group/version/kind
- 将AdmissionReview.Request.Object.Raw转化为node对象
- 设置AdmissionReview.Response.Allowed为true,表示无论如何都准许该请求
- 执行协助边端健康检查核心逻辑:在节点处于ConditionUnknown状态且分布式健康检查结果为正常的情况下,若节点存在NoExecute(node.kubernetes.io/unreachable) taint,则将其移除
总的来说,mutateNodeTaint的作用就是:不断修正被kube-controller-manager更新的节点状态,去掉NoExecute(node.kubernetes.io/unreachable) taint,让节点不会被驱逐
2、mutateEndpoint
mutateEndpoint会对endpoints UPDATE请求按照分布式健康检查结果进行修改:
func (eha *EdgeHealthAdmission) mutateEndpoint(ar admissionv1.AdmissionReview) *admissionv1.AdmissionResponse {
klog.V(4).Info("mutating endpoint")
endpointResource := metav1.GroupVersionResource{Group: "", Version: "v1", Resource: "endpoints"}
if ar.Request.Resource != endpointResource {
klog.Errorf("expect resource to be %s", endpointResource)
return nil
}
var endpoint corev1.Endpoints
deserializer := codecs.UniversalDeserializer()
if _, _, err := deserializer.Decode(ar.Request.Object.Raw, nil, &endpoint); err != nil {
klog.Error(err)
return toAdmissionResponse(err)
}
reviewResponse := admissionv1.AdmissionResponse{}
reviewResponse.Allowed = true
for epSubsetIndex, epSubset := range endpoint.Subsets {
for notReadyAddrIndex, EndpointAddress := range epSubset.NotReadyAddresses {
if node, err := eha.nodeLister.Get(*EndpointAddress.NodeName); err == nil {
if index, condition := util.GetNodeCondition(&node.Status, v1.NodeReady); index != -1 && condition.Status == v1.ConditionUnknown {
if node.Annotations != nil {
var patches []*patch
if healthy, existed := node.Annotations[common.NodeHealthAnnotation]; existed && healthy == common.NodeHealthAnnotationPros {
// TODO: handle readiness probes failure
// Remove address on node from endpoint notReadyAddresses
patches = append(patches, &patch{
OP: "remove",
Path: fmt.Sprintf("/subsets/%d/notReadyAddresses/%d", epSubsetIndex, notReadyAddrIndex),
})
// Add address on node to endpoint readyAddresses
TargetRef := map[string]interface{}{}
TargetRef["kind"] = EndpointAddress.TargetRef.Kind
TargetRef["namespace"] = EndpointAddress.TargetRef.Namespace
TargetRef["name"] = EndpointAddress.TargetRef.Name
TargetRef["uid"] = EndpointAddress.TargetRef.UID
TargetRef["apiVersion"] = EndpointAddress.TargetRef.APIVersion
TargetRef["resourceVersion"] = EndpointAddress.TargetRef.ResourceVersion
TargetRef["fieldPath"] = EndpointAddress.TargetRef.FieldPath
patches = append(patches, &patch{
OP: "add",
Path: fmt.Sprintf("/subsets/%d/addresses/0", epSubsetIndex),
Value: map[string]interface{}{
"ip": EndpointAddress.IP,
"hostname": EndpointAddress.Hostname,
"nodeName": EndpointAddress.NodeName,
"targetRef": TargetRef,
},
})
if len(patches) != 0 {
patchBytes, _ := json.Marshal(patches)
reviewResponse.Patch = patchBytes
pt := admissionv1.PatchTypeJSONPatch
reviewResponse.PatchType = &pt
}
}
}
}
} else {
klog.Errorf("Get pod''s node err %+v", err)
}
}
}
return &reviewResponse
}
主体逻辑如下:
- 检查AdmissionReview.Request.Resource是否为endpoints资源的group/version/kind
- 将AdmissionReview.Request.Object.Raw转化为endpoints对象
- 设置AdmissionReview.Response.Allowed为true,表示无论如何都准许该请求
- 遍历endpoints.Subset.NotReadyAddresses,如果EndpointAddress所在节点处于ConditionUnknown状态且分布式健康检查结果为正常,则将该EndpointAddress从endpoints.Subset.NotReadyAddresses移到endpoints.Subset.Addresses
总的来说,mutateEndpoint的作用就是:不断修正被kube-controller-manager更新的endpoints状态,将分布式健康检查正常节点上的负载从endpoints.Subset.NotReadyAddresses移到endpoints.Subset.Addresses中,让服务依旧可用
总结
- SuperEdge分布式健康检查功能由边端的edge-health-daemon以及云端的edge-health-admission组成:
- edge-health-daemon:对同区域边缘节点执行分布式健康检查,并向apiserver发送健康状态投票结果(给node打annotation)
- edge-health-admission:不断根据node edge-health annotation调整kube-controller-manager设置的node taint(去掉NoExecute taint)以及endpoints(将失联节点上的pods从endpoint subsets notReadyAddresses移到addresses中),从而实现云端和边端共同决定节点状态
- 之所以创建edge-health-admission云端组件,是因为当云边断连时,kube-controller-manager会将失联的节点置为ConditionUnknown状态,并添加NoSchedule和NoExecute的taints;同时失联的节点上的pod从Service的Endpoint列表中移除。当edge-health-daemon在边端根据健康检查判断节点状态正常时,会更新node:去掉NoExecute taint。但是在node成功更新之后又会被kube-controller-manager给刷回去(再次添加NoExecute taint),因此必须添加Kubernetes mutating admission webhook也即edge-health-admission,将kube-controller-manager对node api resource的更改做调整,最终实现分布式健康检查效果
- Kubernetes Admission Controllers是kube-apiserver处理api请求的某个环节,用于在api请求认证&鉴权之后,对象持久化之前进行调用,对请求进行校验或者修改(or both);包括多种admission,大多数都内嵌在kube-apiserver代码中了。其中MutatingAdmissionWebhook以及ValidatingAdmissionWebhook controller比较特殊,它们分别会调用外部构造的mutating admission control webhooks以及validating admission control webhooks
- Admission Webhooks是一个HTTP回调服务,接受AdmissionReview请求并进行处理,按照处理方式的不同,可以将Admission Webhooks分类如下:
- validating admission webhook:通过ValidatingWebhookConfiguration配置,会对api请求进行准入校验,但是不能修改请求对象
- mutating admission webhook:通过MutatingWebhookConfiguration配置,会对api请求进行准入校验以及修改请求对象
- kube-apiserver会发送AdmissionReview(apiGroup:
admission.k8s.io,apiVersion:v1 or v1beta1)给Webhooks,并封装成JSON格式;而Webhooks需要向kube-apiserver回应具有相同版本的AdmissionReview,并封装成JSON格式,包含如下关键字段:- uid:拷贝发送给webhooks的AdmissionReview request.uid字段
- allowed:true表示准许;false表示不准许
- status:当不准许请求时,可以通过status给出相关原因(http code and message)
- patch:base64编码,包含mutating admission webhook对请求对象的一系列JSON patch操作
- patchType:目前只支持JSONPatch类型
- edge-health-admission实际上就是一个mutating admission webhook,选择性地对endpoints以及node UPDATE请求进行修改,包含如下处理逻辑:
- mutateNodeTaint:不断修正被kube-controller-manager更新的节点状态,去掉NoExecute(node.kubernetes.io/unreachable) taint,让节点不会被驱逐
- mutateEndpoint:不断修正被kube-controller-manager更新的endpoints状态,将分布式健康检查正常节点上的负载从endpoints.Subset.NotReadyAddresses移到endpoints.Subset.Addresses中,让服务依旧可用
【腾讯云原生】云说新品、云研新术、云游新活、云赏资讯,扫码关注同名公众号,及时获取更多干货!!

18. 从零开始编写一个类 nginx 工具,主动式健康检查源码实现

wmproxy
wmproxy 将用 Rust 实现 http/https 代理,socks5 代理,反向代理,静态文件服务器,后续将实现 websocket 代理,内外网穿透等,会将实现过程分享出来,感兴趣的可以一起造个轮子法
项目地址
gite: https://gitee.com/tickbh/wmproxy
github: https://github.com/tickbh/wmproxy
为什么我们需要主动
主动可以让我们掌握好系统的稳定性,假设我们有一条连接不可达,连接超时的判定是 5 秒,需要检测失败 3 次才认定为失败,那么此时从我们开始检测,到判定失败需要耗时 15 秒。
如果此时我们是个高并发的系统,每秒的 QPS 是 1000,我们有三个地址判定,那么此时我们有 1/3 的失败概率。那么在 15 秒内,我们会收到 15000 个请求,会造成 5000 个请求失败,如果是重要的数据,我们会丢失很多重要数据。
如果此时客户端拥有重试机制,那么客户端在失败的时候会发起重试,而且系统可能会反复的分配到那台不可达的系统,将会造成短时间内请求数激增,可能引发系统的雪崩。
所以此时我们主动知道目标端的系统稳定性极其重要。
网络访问示意图
以下是没有主动健康检查
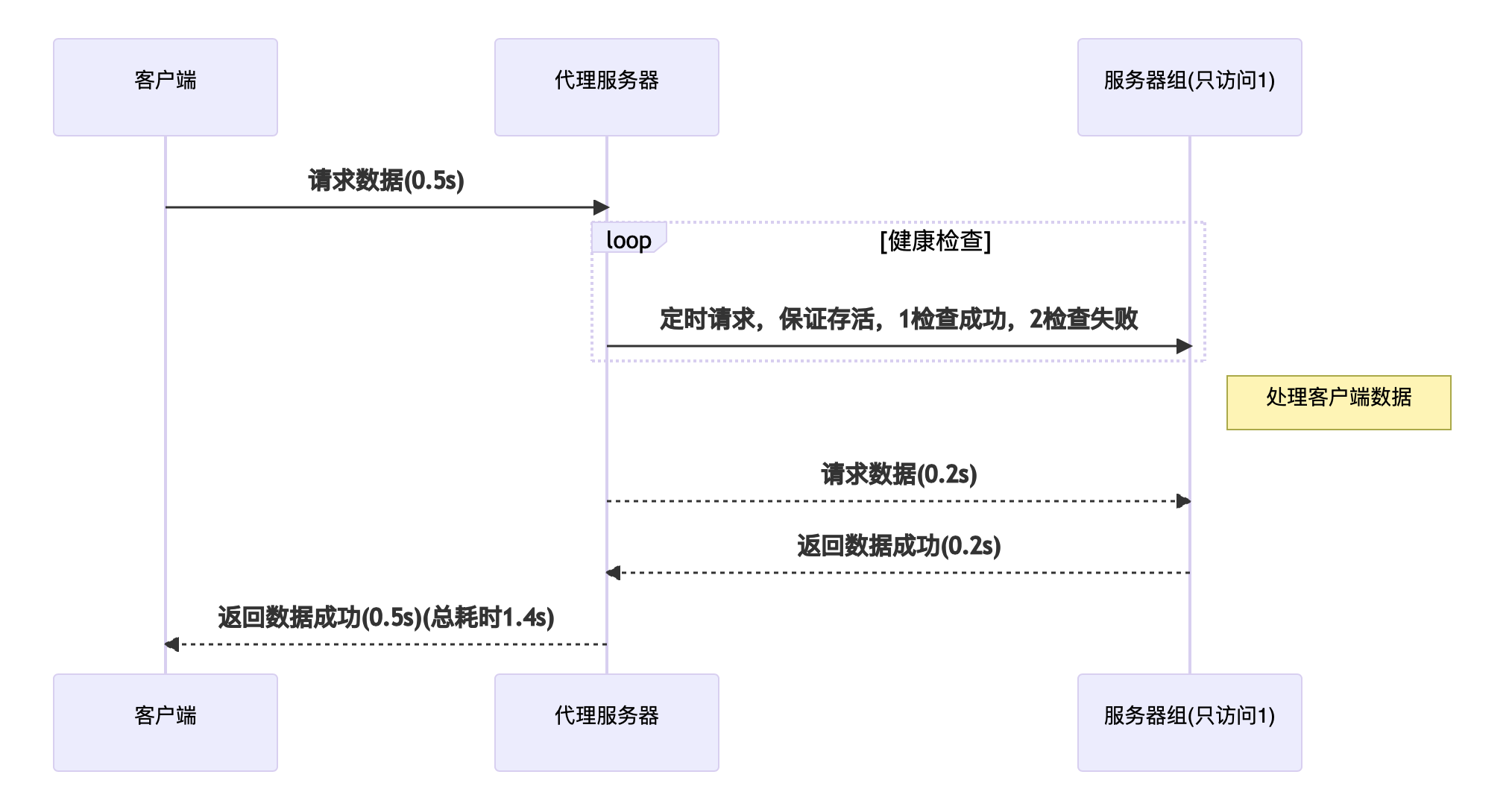
如果出错的时候,一个请求的平均时长可能会达到 (1.4s + 5s) / 2 = (3.2s),比正常访问多了 (3.2 - 1.4) = 1.8s,节点的宕机会对系统的稳定性产生较大的影响
以下是主动健康检查,它保证了访问后端服务器组均是正常的状态
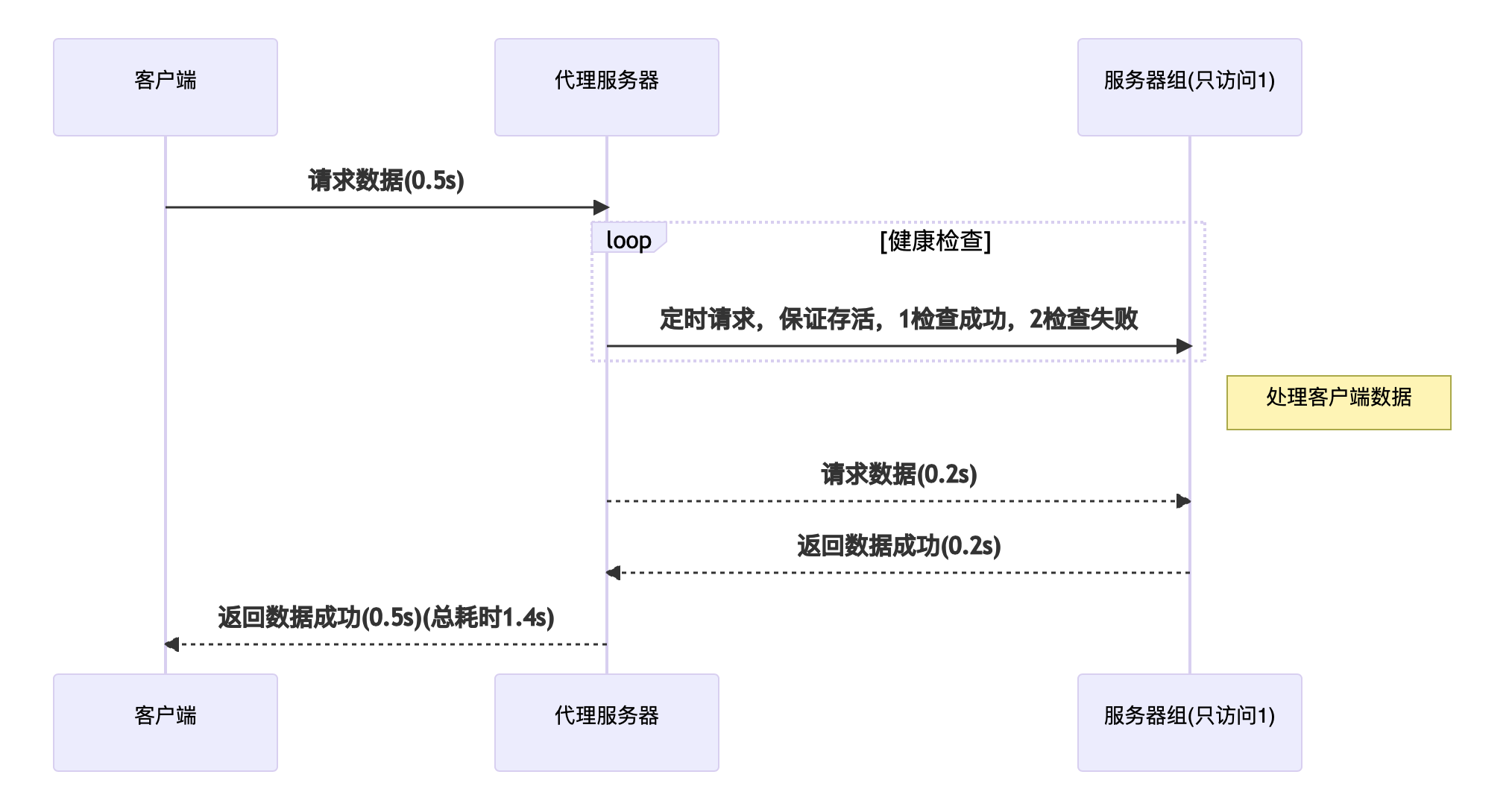
服务器2 出错的时候,主动检查已经检查出服务器2 不可用,负载均衡的时候选择已经把服务器2 摘除,所以系统的平均耗时 1.4s,系统依然保持稳定
健康检查的种类
在目前的系统中有以下两分类:
- HTTP 请求特定的方法及路径,判断返回是否得到预期的 status 或者 body
- TCP 仅只能测试连通性,如果能连接表示正常,会出现能连接但无服务的情况
健康检查的准备
我们需要从配置中读出所有的需要健康检查的类型,即需要去重,把同一个指向的地址过滤掉 配置有可能被重新加载,所以我们需要预留发送配置的方式(或者后续类似 nginx 用新开进程的方式则不需要),此处做一个预留。
-
如何去重 像这种简单级别的去重通常用
HashSet复杂度为O(1)或者用简单的Vec复杂度为O(n),以SocketAddr的为键值,判断是否有重复的数据。 -
如何保证不影响主线程 把健康请求的方法移到异步函数,用
tokio::spawn中处理,在健康检查的情况下保证不影响其它数据处理 -
如果同时处理多个地址的健康检查 每一次健康检查都会在一个异步函数中执行,在我们调用完请求后,我们会对当前该异步进行
tokio::time::sleep以让出当前 CPU。 -
如何按指定间隔时间请求 因为每一次健康请求都是在异步函数中,我们不确认之前的异步是否完成,所以我们在每次请求前都记录
last_request,我们在请求前调用HealthCheck::check_can_request判断当前是否可以发送请求来保证间隔时间内不多次请求造成服务器的压力。 -
超时连接判定处理 利用
tokio::time::timeout和future做组合,等超时的时候直接按错误处理
部分实现源码
主要源码定义在 check/active.rs 中,主要的定义两个类
/// 单项健康检查
#[derive(Debug, Clone)]
pub struct OneHealth {
/// 主动检查地址
pub addr: SocketAddr,
/// 主动检查方法, 有http/https/tcp等
pub method: String,
/// 每次检查间隔
pub interval: Duration,
/// 最后一次记录时间
pub last_record: Instant,
}
/// 主动式健康检查
pub struct ActiveHealth {
/// 所有的健康列表
pub healths: Vec<OneHealth>,
/// 接收健康列表,当配置变更时重新载入
pub receiver: Receiver<Vec<OneHealth>>,
}
我们在配置的时候获取所有需要主动检查的数据
/// 获取所有待健康检查的列表
pub fn get_health_check(&self) -> Vec<OneHealth> {
let mut result = vec![];
let mut already: HashSet<SocketAddr> = HashSet::new();
if let Some(proxy) = &self.proxy {
// ...
}
if let Some(http) = &self.http {
// ...
}
result
}
主要的检查源码,所有的最终信息都落在 HealthCheck 中的静态变量里:
pub async fn do_check(&self) -> ProxyResult<()> {
// 防止短时间内健康检查的连接过多, 做一定的超时处理, 或者等上一条消息处理完毕
if !HealthCheck::check_can_request(&self.addr, self.interval) {
return Ok(())
}
if self.method.eq_ignore_ascii_case("http") {
match tokio::time::timeout(self.interval + Duration::from_secs(1), self.connect_http()).await {
Ok(r) => match r {
Ok(r) => {
if r.status().is_server_error() {
log::trace!("主动健康检查:HTTP:{}, 返回失败:{}", self.addr, r.status());
HealthCheck::add_fall_down(self.addr);
} else {
HealthCheck::add_rise_up(self.addr);
}
}
Err(e) => {
log::trace!("主动健康检查:HTTP:{}, 发生错误:{:?}", self.addr, e);
HealthCheck::add_fall_down(self.addr);
}
},
Err(e) => {
log::trace!("主动健康检查:HTTP:{}, 发生超时:{:?}", self.addr, e);
HealthCheck::add_fall_down(self.addr);
},
}
} else {
match tokio::time::timeout(Duration::from_secs(3), self.connect_http()).await {
Ok(r) => {
match r {
Ok(_) => {
HealthCheck::add_rise_up(self.addr);
}
Err(e) => {
log::trace!("主动健康检查:TCP:{}, 发生错误:{:?}", self.addr, e);
HealthCheck::add_fall_down(self.addr);
}
}
}
Err(e) => {
log::trace!("主动健康检查:TCP:{}, 发生超时:{:?}", self.addr, e);
HealthCheck::add_fall_down(self.addr);
}
}
}
Ok(())
}
结语
主动检查可以及时的更早的发现系统中不稳定的因素,是系统稳定性的基石,也可以通过更早的发现因素来通知运维介入,我们的目的是使系统更稳定,更健壮,处理延时更少。
点击 <font color=green>[关注]</font>,<font color=green>[在看]</font>,<font color=green>[点赞]</font> 是对作者最大的支持

Checkup —— 分布式无锁站点健康检查工具
Checkup 是一个用于分布式无锁站点健康检查的工具

docker 健康检查中的多个健康检查卷发
如何解决docker 健康检查中的多个健康检查卷发?
为了确保容器的健康检查,我需要执行多个 URL。
curl -f http://example.com 和 curl -f http://example2.com
是否可以执行多个 curl 检查 docker 健康检查?
解决方法
虽然我无法测试,但我认为你可以使用以下
<如果你想先手动检查这个命令(没有退出部分),你可以通过
检查最后一个错误代码<=和
length - 1
nginx容器配置健康检查接口,消灭云厂商lb频繁健康检查日志
背景
云厂商LB将流量负载到后端Nginx后通常会有频繁的健康检查机制,默认检查/目录,当我们把Nginx部署到容器内,默认会将/var/log/Nginx/*.log的标准日志输出,而LB的健康检查次数太多,干扰看容器日志并且增加很多无效日志。
配置
在server中增加location:healthcheck配置,并修改LB的健康检查地址为/healthcheck,将这类日志都输出到一个独立的日志中即可,标准输出的内容终于干净了。
location ~ ^/healthcheck {
default_type text/html;
return 200 'ok!';
access_log /var/log/Nginx/health_access.log main;
}
关于一文读懂 SuperEdge 分布式健康检查(云端)的介绍现已完结,谢谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于18. 从零开始编写一个类 nginx 工具,主动式健康检查源码实现、Checkup —— 分布式无锁站点健康检查工具、docker 健康检查中的多个健康检查卷发、nginx容器配置健康检查接口,消灭云厂商lb频繁健康检查日志的相关知识,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:






