针对sshtunnelPython的SSH通讯隧道和ssh隧道详细使用教程这两个问题,本篇文章进行了详细的解答,同时本文还将给你拓展bash脚本ssh到一个盒子,让我到一个pythonshell、go
针对sshtunnel Python 的 SSH 通讯隧道和ssh隧道详细使用教程这两个问题,本篇文章进行了详细的解答,同时本文还将给你拓展bash脚本ssh到一个盒子,让我到一个python shell、go的ssh tunnel、HeidiSQL不通过SSH Tunnel隧道访问服务器数据库、HTTPTunnel 1.4.0 发布,HTTP 隧道通讯库等相关知识,希望可以帮助到你。
本文目录一览:- sshtunnel Python 的 SSH 通讯隧道(ssh隧道详细使用教程)
- bash脚本ssh到一个盒子,让我到一个python shell
- go的ssh tunnel
- HeidiSQL不通过SSH Tunnel隧道访问服务器数据库
- HTTPTunnel 1.4.0 发布,HTTP 隧道通讯库

sshtunnel Python 的 SSH 通讯隧道(ssh隧道详细使用教程)
sshtunnel 介绍
sshtunnel 是 Python 开发的一个服务,用来与远程服务器建立 SSH 通讯隧道。
示例代码:
from sshtunnel import SSHTunnelForwarder
server = SSHTunnelForwarder(
''pahaz.urfuclub.ru'',
ssh_username="pahaz",
ssh_password="secret",
remote_bind_address=(''127.0.0.1'', 8080)
)
server.start()
print(server.local_bind_port) # show assigned local port
# work with `SECRET SERVICE` through `server.local_bind_port`.
server.stop()
sshtunnel 官网
https://github.com/pahaz/sshtunnel

bash脚本ssh到一个盒子,让我到一个python shell
我想写一个脚本,让我直接到另一个盒子上的python shell,这样我就不必先运行ssh再运行python。
当我做“ssh主机名python”它只是挂起 – 这是事实,python是互动的。 “ssh主机名猫x”工作正常。
有没有一些SSH的选项,将使这项工作?
我如何削减开始和结束使用Bash节?
Linux根据目录中的另一个文件重命名文件?
简单的shell linux C实现,用freopenredirect标准输出
在bash中快速引用标准输出(即前一个命令的输出)?
如何压缩多个文件夹,每个文件夹到自己的压缩文件?
为什么sorting – 像这样sorting>
使用jq从json输出中获取键值
shell脚本中的“&&”variables和外部variables之间的区别
从java调用一个简单的shell脚本不起作用
如何过滤掉文件中的所有唯一行?
ssh -t user@host python
-t标志强制ssh为连接分配一个伪终端。 通常情况下,如果在ssh命令行上给出了一个命令,这将导致python以非交互模式运行。
其实想通了,我需要做的ssh -t主机名python
你需要-t选项来强制分配一个伪tty
ssh -t host python

go的ssh tunnel
该链接为讲解
https://elliotchance.medium.com/how-to-create-an-ssh-tunnel-in-go-b63722d682aa
package main
import (
"fmt"
"golang.org/x/crypto/ssh"
"io"
"io/IoUtil"
"log"
"net"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
type Endpoint struct {
Host string
Port int
User string
}
func NewEndpoint(s string) *Endpoint {
endpoint := &Endpoint{
Host: s,
}
if parts := strings.Split(endpoint.Host, "@"); len(parts) > 1 {
endpoint.User = parts[0]
endpoint.Host = parts[1]
}
if parts := strings.Split(endpoint.Host, ":"); len(parts) > 1 {
endpoint.Host = parts[0]
endpoint.Port, _ = strconv.Atoi(parts[1])
}
return endpoint
}
func (endpoint *Endpoint) String() string {
return fmt.Sprintf("%s:%d", endpoint.Host, endpoint.Port)
}
type SSHTunnel struct {
Local *Endpoint
Server *Endpoint
Remote *Endpoint
Config *ssh.ClientConfig
Log *log.Logger
}
func (tunnel *SSHTunnel) logf(fmt string, args ...interface{}) {
if tunnel.Log != nil {
tunnel.Log.Printf(fmt, args...)
}
}
func (tunnel *SSHTunnel) Start() error {
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", tunnel.Local.String())
if err != nil {
return err
}
defer listener.Close()
tunnel.Local.Port = listener.Addr().(*net.TCPAddr).Port
for {
conn, err := listener.Accept()
if err != nil {
return err
}
tunnel.logf("accepted connection")
go tunnel.forward(conn)
}
}
func (tunnel *SSHTunnel) forward(localConn net.Conn) {
serverConn, err := ssh.Dial("tcp", tunnel.Server.String(), tunnel.Config)
if err != nil {
tunnel.logf("server dial error: %s", err)
return
}
tunnel.logf("connected to %s (1 of 2)\n", tunnel.Server.String())
remoteConn, err := serverConn.Dial("tcp", tunnel.Remote.String())
if err != nil {
tunnel.logf("remote dial error: %s", err)
return
}
tunnel.logf("connected to %s (2 of 2)\n", tunnel.Remote.String())
copyConn := func(writer, reader net.Conn) {
_, err := io.copy(writer, reader)
if err != nil {
tunnel.logf("io.copy error: %s", err)
}
}
go copyConn(localConn, remoteConn)
go copyConn(remoteConn, localConn)
}
func PrivateKeyFile(file string) ssh.AuthMethod {
buffer, err := IoUtil.ReadFile(file)
if err != nil {
return nil
}
key, err := ssh.ParsePrivateKey(buffer)
if err != nil {
return nil
}
return ssh.PublicKeys(key)
}
func NewSSHTunnel(tunnel string, auth ssh.AuthMethod, destination string) *SSHTunnel {
// A random port will be chosen for us.
localEndpoint := NewEndpoint("localhost:0")
server := NewEndpoint(tunnel)
if server.Port == 0 {
server.Port = 22
}
sshTunnel := &SSHTunnel{
Config: &ssh.ClientConfig{
User: server.User,
Auth: []ssh.AuthMethod{auth},
HostKeyCallback: func(hostname string, remote net.Addr, key ssh.PublicKey) error {
// Always accept key.
return nil
},
},
Local: localEndpoint,
Server: server,
Remote: NewEndpoint(destination),
}
return sshTunnel
}
应用实例:
func main() {
// Setup the tunnel, but do not yet start it yet.
tunnel := NewSSHTunnel(
// User and host of tunnel server, it will default to port 22
// if not specified.
"ec2-user@jumpBox.us-east-1.mydomain.com",
// Pick ONE of the following authentication methods:
PrivateKeyFile("path/to/private/key.pem"), // 1. private key
ssh.Password("password"), // 2. password
// The destination host and port of the actual server.
"dqrsdfdssdfx.us-east-1.redshift.amazonaws.com:5439",
)
// You can provide a logger for debugging, or remove this line to
// make it silent.
tunnel.Log = log.New(os.Stdout, "", log.Ldate | log.Lmicroseconds)
// Start the server in the background. You will need to wait a
// small amount of time for it to bind to the localhost port
// before you can start sending connections.
go tunnel.Start()
time.Sleep(100 * time.Millisecond)
// NewSSHTunnel will bind to a random port so that you can have
// multiple SSH tunnels available. The port is available through:
// tunnel.Local.Port
// You can use any normal Go code to connect to the destination
// server through localhost. You may need to use 127.0.0.1 for
// some libraries.
//
// Here is an example of connecting to a Postgresql server:
conn := fmt.Sprintf("host=127.0.0.1 port=%d username=foo", tunnel.Local.Port)
db, err := sql.Open("postgres", conn)
// ...
}
更方便的包:
https://github.com/elliotchance/sshtunnel

HeidiSQL不通过SSH Tunnel隧道访问服务器数据库
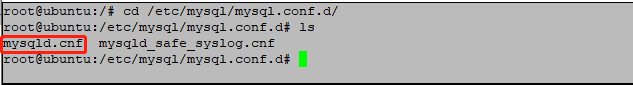
1)先进入服务器里面,使用命令进入到数据库目录mysql.conf.d这个目录下面找一个文件。
输入命令:cd /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d
![]()
2)进入当前目录后使用ls命令查看一下mysql.cnf是否在当前目录下面
输入命令:ls
3)文件存在后,使用命令打开文件,准备修改里面的配置。
输入命令:vi mysql.cnf
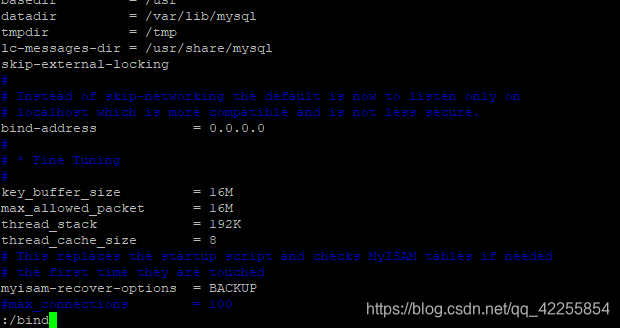
4)打开文件后,在命令模式下敲斜杆( / ),这时在状态栏(也就是屏幕左下脚)就出现了 “/” 然后输入bind敲回车就可以了。如果你要继续查找此关键字,敲字符 n 就可以继续查找了。
a.按住键盘上的“ESC”进入切换命令模式
b.按住键盘“shift”和“:”进入命令模式
5)修改bind-address = 0.0.0.0 (一般初始值是=127.0.0.1)
a.按住键盘上的“ESC”进入切换命令模式
b.按住键盘“i”进入文本编辑模式,修改值
c.按住键盘上的“ESC”进入切换命令模式,按住键盘“shift”和“:”进入命令模式
d.左下角输入“wq!”保存文本
e.reboot重启一下服务器
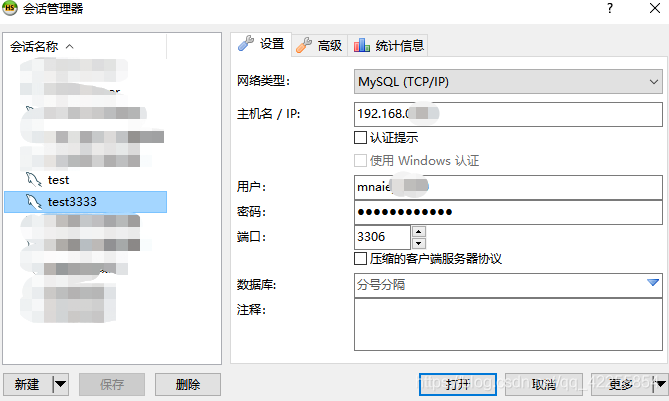
6) 大功告成,登录HeidiSQL,输入对应的数据库登录名、密码,进入该服务器数据库


HTTPTunnel 1.4.0 发布,HTTP 隧道通讯库
HTTPTunnel 1.4.0 发布,该版本增加对 IPv6 下的 TCP/UDP 隧道的支持,显著改进隧道到流媒体网站和其他高带宽应用的吞吐量,修复了一些 bug 和小调整。
HTTPTunnel 是一个 C++ 开发用于在两台机器之间进行 HTTP 隧道通讯的类库。HTTP隧道是一种在HTTP协议层上进行Socket通讯的机制。
关于sshtunnel Python 的 SSH 通讯隧道和ssh隧道详细使用教程的介绍已经告一段落,感谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于bash脚本ssh到一个盒子,让我到一个python shell、go的ssh tunnel、HeidiSQL不通过SSH Tunnel隧道访问服务器数据库、HTTPTunnel 1.4.0 发布,HTTP 隧道通讯库的相关信息,请在本站寻找。
本文标签: