想了解cocos2dx安卓makefileAndroid.mk,动态引用cpp地址的新动态吗?本文将为您提供详细的信息,我们还将为您解答关于cocos动态加载的相关问题,此外,我们还将为您介绍关于关于
想了解cocos2dx 安卓makefile Android.mk,动态引用cpp地址的新动态吗?本文将为您提供详细的信息,我们还将为您解答关于cocos动态加载的相关问题,此外,我们还将为您介绍关于
- cocos2dx 安卓makefile Android.mk,动态引用cpp地址(cocos动态加载)
关于cocos2dx接Android sdk的一些坑 - Android Cocos2dx-js 游戏 APP 逆向
- Android cocos2dx游戏开发——示例程序HelloCpp源码分析
- android-ndk – 从java(android)调用C(cocos2dx)方法进行我的应用内结算

cocos2dx 安卓makefile Android.mk,动态引用cpp地址(cocos动态加载)
原因:
每次加一个cpp,都要改写Android.mk 一次,修改了引用脚本,就不用每次都该了。
修改LOCAL_SRC_FILES 的赋值
转自
http://suool.net/
原来的。
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir)
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE := cocos2dcpp_shared
LOCAL_MODULE_FILENAME := libcocos2dcpp
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := hellocpp/main.cpp \
../../Classes/AppDelegate.cpp \
../../Classes/HelloWorldScene.cpp
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES := $(LOCAL_PATH)/../../Classes
# _COCOS_HEADER_ANDROID_BEGIN
# _COCOS_HEADER_ANDROID_END
LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES := cocos2dx_static
# _COCOS_LIB_ANDROID_BEGIN
# _COCOS_LIB_ANDROID_END
include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY)
$(call import-module,./prebuilt-mk)
# _COCOS_LIB_IMPORT_ANDROID_BEGIN
# _COCOS_LIB_IMPORT_ANDROID_END
修改后的:
LOCAL_PATH := $(call my-dir) include $(CLEAR_VARS) LOCAL_MODULE := cocos2dcpp_shared LOCAL_MODULE_FILENAME := libcocos2dcpp # 遍历目录及子目录的函数 define walk $(wildcard $(1)) $(foreach e,$(wildcard $(1)/*),$(call walk,$(e))) endef # 遍历Classes目录 ALLFILES = $(call walk,$(LOCAL_PATH)/../../Classes) FILE_LIST := hellocpp/main.cpp # 从所有文件中提取出所有.cpp文件 FILE_LIST += $(filter %.cpp,$(ALLFILES)) LOCAL_SRC_FILES := $(FILE_LIST:$(LOCAL_PATH)/%=%) LOCAL_C_INCLUDES := $(LOCAL_PATH)/../../Classes # _COCOS_HEADER_ANDROID_BEGIN # _COCOS_HEADER_ANDROID_END LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES := cocos2dx_static # _COCOS_LIB_ANDROID_BEGIN # _COCOS_LIB_ANDROID_END include $(BUILD_SHARED_LIBRARY) $(call import-module,./prebuilt-mk) # _COCOS_LIB_IMPORT_ANDROID_BEGIN # _COCOS_LIB_IMPORT_ANDROID_END

关于cocos2dx接Android sdk的一些坑
简单说说UI线程 :在Android中,有个非常重要的家伙非常霸道,那就是UI线程。这霸道之一:不能被阻塞。 之二:系统对每一个组件的调用都从UI线程分发出去。
简单说说openGL线程:但凡cocos2dx 启动的绘制线程都是openGL线程。就这么多
任何SDK界面的调用,必须从UI线程中调用,所以需要放到主线程中。如果我们直接从GL线程中调用,轻则调用不了,重者程序蹦死。
解决办法:
得到主线程的handler,这里简单说一种,就是在onCreate中new一个静态handler。
或者new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()),且叫mainHandler吧,
启动一个线程,
- ThreadsendThread=newThread(newRunnable(){
- publicvoidrun(){
- mainHandler.post(sendRun);
- }
- });

Android Cocos2dx-js 游戏 APP 逆向

1 Cocos2dx-js 资源文件
Cocos2dx-js 开发的游戏应用,其游戏核心内容被打包到了 Android 应用的 Assets 目录中。其中包含了经过加密的 jsc 文件,正因为经过加密处理,无法获取游戏核心逻辑。通常需要对 jsc 文件进行解密处理。Assets 目录结构如下图所示。
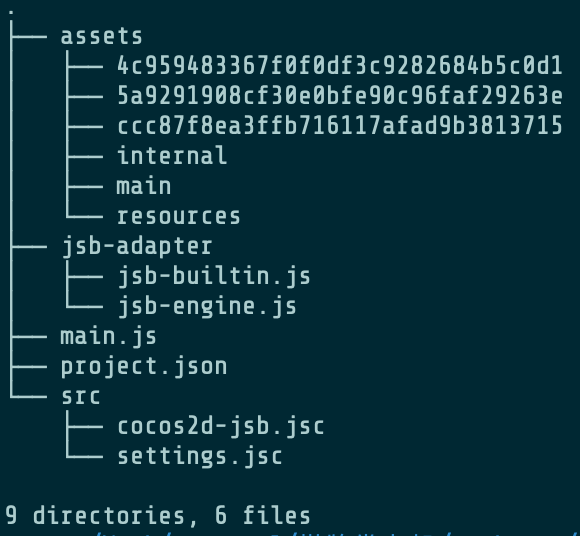
2 获取 key
2.1 静态获取
静态方式直接使用 ida 打开 so 文件,以 jsb 和 encrypt 为关键字,可以定位到部分加密函数,其中 xxtea 系列函数尤为可以。尤其是 jsb_set_xxtea_key。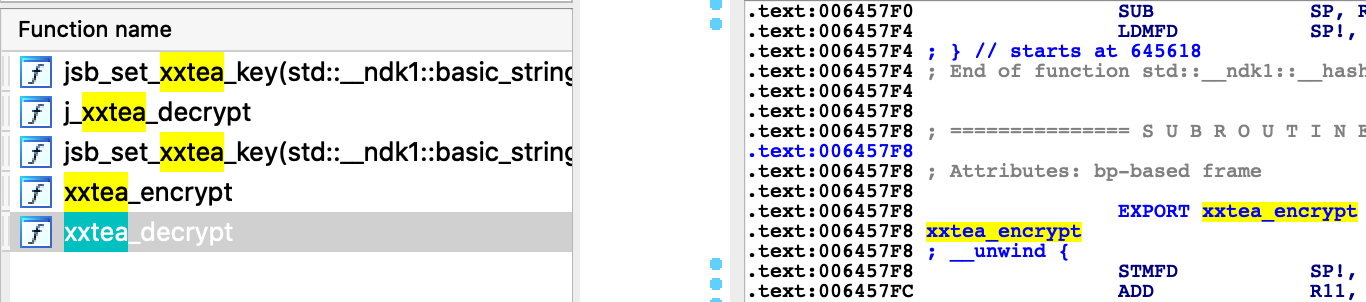 函数 jsb_set_xxtea_key 看起来像是设置 key 的地方,F5 伪代码看下,传入了一个字符串化的指针参数,大概率可能是 Key。回溯调用该函数的地方,看下传入的参数值。最终在 applicationDidFinishLaunching 函数中找到了指针指向的字符串。
函数 jsb_set_xxtea_key 看起来像是设置 key 的地方,F5 伪代码看下,传入了一个字符串化的指针参数,大概率可能是 Key。回溯调用该函数的地方,看下传入的参数值。最终在 applicationDidFinishLaunching 函数中找到了指针指向的字符串。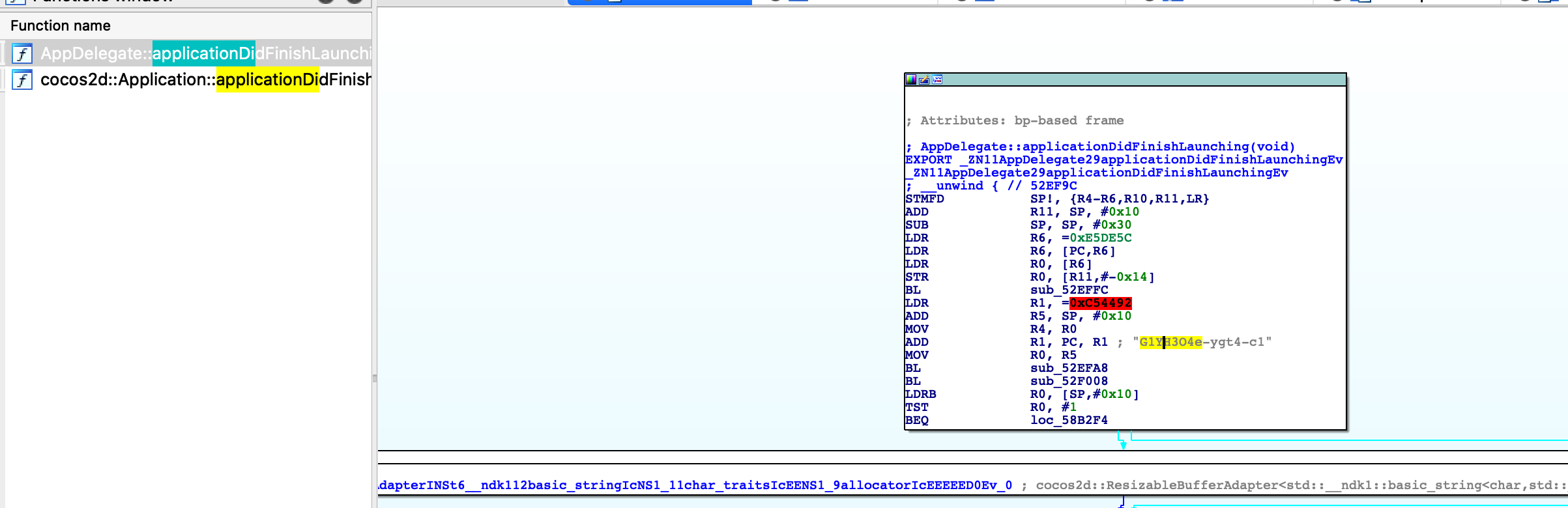
2.2 动态获取
根据上述静态获取方式的方法,同样可以使用 hook 的方式来取得 jsc 的加密 key。只需 hook jsb_set_xxtea_key 或者解密函数,然后获取该函数的参数即可。根据 so 和导出函数名可以快速写出 hook 脚本。
function hookJava() { Java.perform(function() { var Cocos2dxActivity = Java.use("org.cocos2dx.lib.Cocos2dxActivity") Cocos2dxActivity.onLoadNativeLibraries.implementation = function() { this.onLoadNativeLibraries() hookNative() } }) } function hookNative() { Interceptor.attach(Module.findExportByName("libcocos2djs.so", "xxtea_decrypt"), { // 打印入参 onEnter: function (args) { console.log("cocos key is : ", Memory.readUtf8String(args[2])); }, // 打印返回值 onLeave: function (returnValue) { } }) } hookJava()
3 解密 jsc 文件
此处解密需要用到 jsc 解密工具,直接填入解密 key,拖入加密的 jsc 文件即可完成解密工作,之后就可以明文的方式浏览游戏逻辑。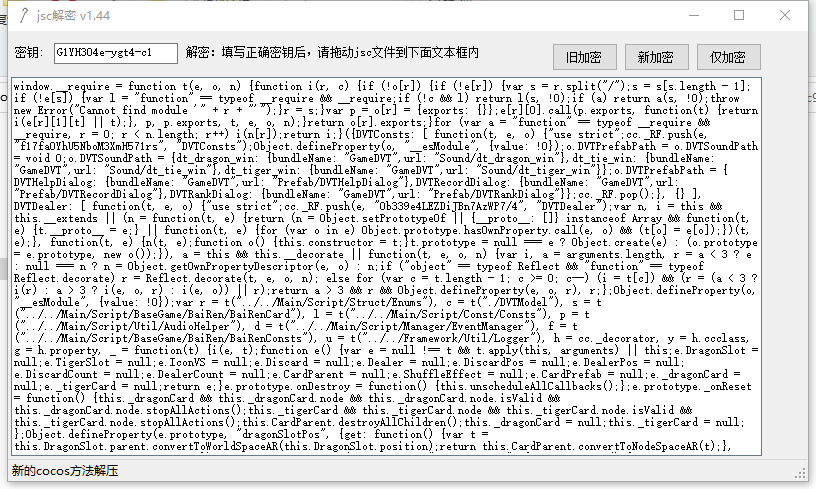

Android cocos2dx游戏开发——示例程序HelloCpp源码分析
本文通过分析cocos2dx提供的示例程序HelloCpp来分析cocos2dx的启动过程。
我们从HelloCpp.java开始:
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
package org.cocos2dx.hellocpp;
import org.cocos2dx.lib.Cocos2dxActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class HelloCpp extends Cocos2dxActivity{
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
}
static {
System.loadLibrary("hellocpp");
}
}
HelloCpp是一个Activity,首先会执行静态代码块,加载libhellocpp.so库,然后就是执行onCreate方法,这里调用了父类的onCreate方法。我们看看Cocos2dxActivity的onCreate方法,该类在cocos2dx的库工程libcocos2dx中:
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
@Override
protected void onCreate(final Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
sContext = this;
this.mHandler = new Cocos2dxHandler(this);
this.init();
Cocos2dxHelper.init(this, this);
}
这里主要是执行初始化过程,Cocos2dxHandler主要处理显示Dialog的消息,Cocos2dxHelper是个辅助类,我们主要看init()方法:
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
public void init() {
// FrameLayout
ViewGroup.LayoutParams framelayout_params =
new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT);
FrameLayout framelayout = new FrameLayout(this);
framelayout.setLayoutParams(framelayout_params);
// Cocos2dxEditText layout
ViewGroup.LayoutParams edittext_layout_params =
new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL_PARENT,
ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
Cocos2dxEditText edittext = new Cocos2dxEditText(this);
edittext.setLayoutParams(edittext_layout_params);
// ...add to FrameLayout
framelayout.addView(edittext);
// Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView
this.mGLSurfaceView = this.onCreateView();
// ...add to FrameLayout
framelayout.addView(this.mGLSurfaceView);
// Switch to supported OpenGL (ARGB888) mode on emulator
if (isAndroidEmulator())
this.mGLSurfaceView.setEGLConfigChooser(8 , 8, 8, 8, 16, 0);
this.mGLSurfaceView.setCocos2dxRenderer(new Cocos2dxRenderer());
this.mGLSurfaceView.setCocos2dxEditText(edittext);
// Set framelayout as the content view
setContentView(framelayout);
}
这里就是为Activity绑定View Hierarchy,大家做Android开发的对着一定很熟悉。View Hierarchy的根View是个FrameLayout,FrameLayout又包含一个EditText和一个GLSurfaceView,这个GLSurfaceView就是cocos引擎用来绘制游戏画面的关键View,我们来详细分析一下它。首先看一下Cocos2dxActivity的onCreateView方法:
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
public Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView onCreateView() {
return new Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView(this);
}
该方法就是新建一个Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView,Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView又继承于GLSurfaceView。我们都知道GLSurfaceView的核心就是Renderer,初始化时会调用Renderer的onSurfaceCreated方法,每一帧的绘制是通过调用Renderer的onDrawFrame方法。Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView的Renderer是一个Cocos2dxRenderer对象,我们先来看Cocos2dxRenderer对象的onSurfaceCreated方法:
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(final GL10 pGL10, final EGLConfig pEGLConfig) {
Cocos2dxRenderer.nativeInit(this.mScreenWidth, this.mScreenHeight);
this.mLastTickInNanoSeconds = System.nanoTime();
}
这里调用了一个本地方法nativeInit(final int pWidth, final int pHeight),本地方法的实现在jni/hellocpp/main.cpp中实现的:
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
void Java_org_cocos2dx_lib_Cocos2dxRenderer_nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jobject thiz, jint w, jint h)
{
if (!CCDirector::sharedDirector()->getOpenGLView())
{
CCEGLView *view = CCEGLView::sharedOpenGLView();
view->setFrameSize(w, h);
AppDelegate *pAppDelegate = new AppDelegate();
CCApplication::sharedApplication()->run();
}
else
{
......
}
}
CCDirector是游戏的导演类,一个游戏只有一个导演类用来控制和管理场景。CCDirector::sharedDirector()是个静态方法,用来获取导演类的单例对象:
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
CCDirector* CCDirector::sharedDirector(void)
{
if (!s_SharedDirector)
{
s_SharedDirector = new CCDisplayLinkDirector();
s_SharedDirector->init();
}
return s_SharedDirector;
}
CCCCDisplayLinkDirector是CCDirector的子类。我们再回到nativeinit方法中,获取到导演类的单例对象后又调用了它的getOpenGLView()方法:
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
inline CCEGLView* getOpenGLView(void) { return m_pobOpenGLView; }
该方法返回用于游戏绘制的CCEGLView,在Android平台下,这个CCEGLView其实没有什么作用,因为游戏都是绘制在Cocos2dxGLSurfaceView上的。由于我们是初始化过程,所以此时m_pobOpenGLView为null,所以if (!CCDirector::sharedDirector()->getOpenGLView())条件成立,执行以下的代码:
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
CCEGLView *view = CCEGLView::sharedOpenGLView();
view->setFrameSize(w, h);
AppDelegate *pAppDelegate = new AppDelegate();
CCApplication::sharedApplication()->run();
同样,我们先获取一个CCEGLView的单例对象,接下来又新建了一个AppDelegate对象,大家可能在工程中找不到AppDelegate类。我们打开工程目录的上一级目录:
我们的Android工程是在proj.android文件夹中,而AppDelegate类就在Classes文件夹中。因为cocos2dx是跨平台的,而AppDelegate在各个平台之间是通用的不需要修改的,所以就放在一个公用的目录下。
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
#ifndef _APP_DELEGATE_H_
#define _APP_DELEGATE_H_
#include "cocos2d.h"
/**
@brief The cocos2d Application.
The reason for implement as private inheritance is to hide some interface call by CCDirector.
*/
class AppDelegate : private cocos2d::CCApplication
{
public:
AppDelegate();
virtual ~AppDelegate();
/**
@brief Implement CCDirector and CCScene init code here.
@return true Initialize success, app continue.
@return false Initialize failed, app terminate.
*/
virtual bool applicationDidFinishLaunching();
/**
@brief The function be called when the application enter background
@param the pointer of the application
*/
virtual void applicationDidEnterBackground();
/**
@brief The function be called when the application enter foreground
@param the pointer of the application
*/
virtual void applicationWillEnterForeground();
};
#endif // _APP_DELEGATE_H_
AppDelegate是继承CCApplication类的,我们看一下CCApplication的构造方法:
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
// sharedApplication pointer
CCApplication * CCApplication::sm_pSharedApplication = 0;
CCApplication::CCApplication()
{
CCAssert(! sm_pSharedApplication, "");
sm_pSharedApplication = this;
}
我们看到在新建CCApplication对象时,会把该对象赋给一个全局变量sm_pSharedApplication。所以我们在new AppDelegate()的时候,就把它象赋给全局变量sm_pSharedApplication。我们再看下CCApplication的CCApplication::sharedApplication方法:
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
CCApplication* CCApplication::sharedApplication()
{
CCAssert(sm_pSharedApplication, "");
return sm_pSharedApplication;
}
此时,sm_pSharedApplication指向的是一个AppDelegate对象。所以我们执行CCApplication::sharedApplication()->run()时其实执行的是AppDelegate对象的run方法。现在我们应该明白这个类为什么叫AppDelegate了,因为CCApplication的工作实际都委托给了AppDelegate类了。看一下AppDelegate的方法:
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
int CCApplication::run()
{
// Initialize instance and cocos2d.
if (! applicationDidFinishLaunching())
{
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
[java] view plaincopy![]()
![]()
bool AppDelegate::applicationDidFinishLaunching() {
// initialize director
CCDirector* pDirector = CCDirector::sharedDirector();
CCEGLView* pEGLView = CCEGLView::sharedOpenGLView();
pDirector->setOpenGLView(pEGLView);
CCSize frameSize = pEGLView->getFrameSize();
// Set the design resolution
#if (CC_TARGET_PLATFORM == CC_PLATFORM_WINRT) || (CC_TARGET_PLATFORM == CC_PLATFORM_WP8)
pEGLView->setDesignResolutionSize(designResolutionSize.width, designResolutionSize.height, kResolutionShowAll);
#else
pEGLView->setDesignResolutionSize(designResolutionSize.width, designResolutionSize.height, kResolutionNoBorder);
#endif
vector<string> searchPath;
// In this demo, we select resource according to the frame''s height.
// If the resource size is different from design resolution size, you need to set contentScaleFactor.
// We use the ratio of resource''s height to the height of design resolution,
// this can make sure that the resource''s height could fit for the height of design resolution.
// if the frame''s height is larger than the height of medium resource size, select large resource.
if (frameSize.height > mediumResource.size.height)
{
searchPath.push_back(largeResource.directory);
pDirector->setContentScaleFactor(MIN(largeResource.size.height/designResolutionSize.height, largeResource.size.width/designResolutionSize.width));
}
// if the frame''s height is larger than the height of small resource size, select medium resource.
else if (frameSize.height > smallResource.size.height)
{
searchPath.push_back(mediumResource.directory);
pDirector->setContentScaleFactor(MIN(mediumResource.size.height/designResolutionSize.height, mediumResource.size.width/designResolutionSize.width));
}
// if the frame''s height is smaller than the height of medium resource size, select small resource.
else
{
searchPath.push_back(smallResource.directory);
pDirector->setContentScaleFactor(MIN(smallResource.size.height/designResolutionSize.height, smallResource.size.width/designResolutionSize.width));
}
// set searching path
CCFileUtils::sharedFileUtils()->setSearchPaths(searchPath);
// turn on display FPS
pDirector->setDisplayStats(true);
// set FPS. the default value is 1.0/60 if you don''t call this
pDirector->setAnimationInterval(1.0 / 60);
// create a scene. it''s an autorelease object
CCScene *pScene = HelloWorld::scene();
// run
pDirector->runWithScene(pScene);
return true;
}

android-ndk – 从java(android)调用C(cocos2dx)方法进行我的应用内结算
这是我通过jni调用我的java函数的方式.
JniMethodInfo t;
JniHelper::getStaticmethodInfo(t,"com/test/project/Project","BuyProduct","(Ljava/lang/String;)V");
char buffer[20];
sprintf(buffer,"product1");
jstring StringArg1 = t.env->NewStringUTF(buffer);
t.env->CallStaticVoidMethod(t.classID,t.methodID,StringArg1);
应用内结算工作正常,但现在我必须给我的c类打电话,告知产品购买是否成功.
我只能通过提到指定的返回类型返回调用方法的结果,但是应用程序内进程是一个异步进程 – 经过大量的方法调用,我的控件不会返回到同一个方法.所以返回一个值是行不通的.
那么有没有其他方法将值(在我的情况下是应用程序内购买的结果)从java函数传递给我的c类???
解决方法
基本上cocos2dxHelper.java中有一个方法只有定义而不是实现,通常它看起来像
public static native blahblah();
并且在cpp文件中有一个相应的函数被调用
Java_org_cocos2dx_cocos2dxHelper_blahblah()
如果你用runOnUIThread()调用Java代码中的blahblah(),那就是c函数
Java_org_cocos2dx_cocos2dxHelper_blahblah()
将被召唤.
顺便说一句,c代码需要在extern C {}中
关于cocos2dx 安卓makefile Android.mk,动态引用cpp地址和cocos动态加载的问题就给大家分享到这里,感谢你花时间阅读本站内容,更多关于
本文标签:





