在本文中,我们将为您详细介绍java.beans.beancontext.BeanContext的实例源码的相关知识,并且为您解答关于beanjava的疑问,此外,我们还会提供一些关于Applicat
在本文中,我们将为您详细介绍java.beans.beancontext.BeanContext的实例源码的相关知识,并且为您解答关于bean java的疑问,此外,我们还会提供一些关于ApplicationContext注入Bean(多线程中注入Bean)、bean实例化的三种方式 bean标签常用属性 单例模式和多例模式的对象 BeanFactory和ApplicationContext:、FLEX通过ANE调用安卓 ExtensionContext.createExtensionContext 返回null、java – Spring 3 applicationContext-security-JDBC.xml有bean:bean不是bean?的有用信息。
本文目录一览:- java.beans.beancontext.BeanContext的实例源码(bean java)
- ApplicationContext注入Bean(多线程中注入Bean)
- bean实例化的三种方式 bean标签常用属性 单例模式和多例模式的对象 BeanFactory和ApplicationContext:
- FLEX通过ANE调用安卓 ExtensionContext.createExtensionContext 返回null
- java – Spring 3 applicationContext-security-JDBC.xml有bean:bean不是bean?

java.beans.beancontext.BeanContext的实例源码(bean java)
private static Children getChildren(DataObject dobj,boolean noBeanInfo) {
if (noBeanInfo) {
return Children.LEAF;
}
InstanceCookie inst = (InstanceCookie)dobj.getCookie(InstanceCookie.class);
if (inst == null) return Children.LEAF;
try {
Class clazz = inst.instanceClass();
if (BeanContext.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ||
BeanContextProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return new InstanceChildren ();
} else {
return Children.LEAF;
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
return Children.LEAF;
}
}
private void init() {
try {
InstanceCookie ic = (InstanceCookie) dobj.getCookie(InstanceCookie.class);
if (ic == null) {
bean = null;
return;
}
Class clazz = ic.instanceClass();
if (BeanContext.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
bean = ic.instanceCreate();
} else if (BeanContextProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
bean = ((BeanContextProxy) ic.instanceCreate()).getBeanContextProxy();
} else {
bean = null;
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
bean = null;
Exceptions.printstacktrace(ex);
}
if (bean != null) {
// attaches a listener to the bean
((BeanContext) bean).addBeanContextMembershipListener (contextL);
}
updateKeys();
}
/** Create nodes for a given key.
* @param key the key
* @return child nodes for this key or null if there should be no
* nodes for this key
*/
protected Node[] createNodes(Object key) {
Object ctx = bean;
if (bean == null) return new Node[0];
try {
if (key instanceof BeanContextSupport) {
BeanContextSupport bcs = (BeanContextSupport)key;
if (((BeanContext) ctx).contains (bcs.getBeanContextPeer())) {
// sometimes a BeanContextSupport occures in the list of
// beans children even there is its peer. we think that
// it is desirable to hide the context if the peer is
// also present
return new Node[0];
}
}
return new Node[] { new BeanContextNode (key,task) };
} catch (IntrospectionException ex) {
// ignore the exception
return new Node[0];
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static Object internalInstantiate(ClassLoader cls,String beanName,BeanContext context,Object initializer) throws IOException,ClassNotFoundException {
// First try to load it from a serialization file.
Object result = null;
// If it didn't work,try to instantiate it from the given classloader
ClassLoader classLoader = cls == null ? ClassLoader
.getSystemClassLoader() : cls;
try {
result = Class.forName(beanName,true,classLoader).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(e.getClass() + ": " //$NON-NLS-1$
+ e.getMessage());
}
if (result != null) {
if (null != context) {
context.add(result);
}
}
return result;
}
private void assertEqualsSerially(BeanContextServiceAvailableEvent orig,BeanContextServiceAvailableEvent ser) {
assertNull(ser.getSource());
// check propagatedFrom
if (orig.getPropagatedFrom() instanceof Serializable) {
BeanContext origFrom = orig.getPropagatedFrom();
BeanContext serFrom = ser.getPropagatedFrom();
assertEquals(origFrom.getClass(),serFrom.getClass());
if (origFrom instanceof MockBeanContextDelegateS) {
assertEquals(((MockBeanContextDelegateS) origFrom).id,((MockBeanContextDelegateS) serFrom).id);
}
}
// check serviceClass
assertEquals(orig.getServiceClass(),ser.getServiceClass());
}
private void assertEqualsSerially(BeanContextMembershipEvent orig,BeanContextMembershipEvent ser) {
assertNull(ser.getSource());
// check propagatedFrom
if (orig.getPropagatedFrom() instanceof Serializable) {
BeanContext origFrom = orig.getPropagatedFrom();
BeanContext serFrom = ser.getPropagatedFrom();
assertEquals(origFrom.getClass(),((MockBeanContextDelegateS) serFrom).id);
}
}
// check children
Collection origChildren = (Collection) Utils.getField(orig,"children");
Collection serChildren = (Collection) Utils.getField(ser,"children");
assertEquals(origChildren,serChildren);
}
private static Children getChildren(DataObject dobj,boolean noBeanInfo) {
if (noBeanInfo) {
return Children.LEAF;
}
InstanceCookie inst = (InstanceCookie)dobj.getCookie(InstanceCookie.class);
if (inst == null) return Children.LEAF;
try {
Class clazz = inst.instanceClass();
if (BeanContext.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz) ||
BeanContextProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(clazz)) {
return new InstanceChildren ((InstanceDataObject) dobj);
} else {
return Children.LEAF;
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
return Children.LEAF;
}
}
private static Children getChildren(Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof BeanContext) {
return new BeanChildren((BeanContext) bean);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanContextProxy) {
BeanContextChild bch = ((BeanContextProxy) bean).getBeanContextProxy();
if (bch instanceof BeanContext) {
return new BeanChildren((BeanContext) bch);
}
}
return Children.LEAF;
}
protected void removeNotify () {
if (contextL != null && bean != null)
((BeanContext) bean).removeBeanContextMembershipListener (contextL);
contextL = null;
setKeys(Collections.emptySet());
}
private void updateKeys() {
if (bean == null) {
setKeys(Collections.emptySet());
} else {
setKeys(((BeanContext) bean).toArray());
}
}
private static Children getChildren (Object bean,SerialDatanode task) {
if (bean instanceof BeanContext)
return new BeanChildren ((BeanContext)bean,new beanfactoryImpl(task));
if (bean instanceof BeanContextProxy) {
java.beans.beancontext.BeanContextChild bch = ((BeanContextProxy)bean).getBeanContextProxy();
if (bch instanceof BeanContext)
return new BeanChildren ((BeanContext)bch,new beanfactoryImpl(task));
}
return Children.LEAF;
}
/**
* Contruct a BeanContextMembershipEvent
*
* @param bc The BeanContext source
* @param changes The Children affected
* @throws NullPointerException if <CODE>changes</CODE> is <CODE>null</CODE>
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public BeanContextMembershipEvent(BeanContext bc,Collection changes) {
super(bc);
if (changes == null) throw new NullPointerException(
"BeanContextMembershipEvent constructor: changes is null.");
children = changes;
}
/**
* Contruct a BeanContextMembershipEvent
*
* @param bc The BeanContext source
* @param changes The Children affected
* @throws NullPointerException if <CODE>changes</CODE> is <CODE>null</CODE>
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public BeanContextMembershipEvent(BeanContext bc,Collection changes) {
super(bc);
if (changes == null) throw new NullPointerException(
"BeanContextMembershipEvent constructor: changes is null.");
children = changes;
}
private static BeanContext fill(BeanContext context) {
context.add(new JLabel("label"));
context.add(new JButton("button"));
JButton button = new JButton();
button.setText("another button");
context.add(button);
return context;
}
/**
* Contruct a BeanContextMembershipEvent
*
* @param bc The BeanContext source
* @param changes The Children affected
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code changes} is {@code null}
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public BeanContextMembershipEvent(BeanContext bc,Collection changes) {
super(bc);
if (changes == null) throw new NullPointerException(
"BeanContextMembershipEvent constructor: changes is null.");
children = changes;
}
private static BeanContext fill(BeanContext context) {
context.add(new JLabel("label"));
context.add(new JButton("button"));
JButton button = new JButton();
button.setText("another button");
context.add(button);
return context;
}
/**
* Contruct a BeanContextMembershipEvent
*
* @param bc The BeanContext source
* @param changes The Children affected
* @throws NullPointerException if {@code changes} is {@code null}
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public BeanContextMembershipEvent(BeanContext bc,Collection changes) {
super(bc);
if (changes == null) throw new NullPointerException(
"BeanContextMembershipEvent constructor: changes is null.");
children = changes;
}
private static BeanContext fill(BeanContext context) {
context.add(new JLabel("label"));
context.add(new JButton("button"));
JButton button = new JButton();
button.setText("another button");
context.add(button);
return context;
}
/**
* Contruct a BeanContextMembershipEvent
*
* @param bc The BeanContext source
* @param changes The Children affected
* @throws NullPointerException if <CODE>changes</CODE> is <CODE>null</CODE>
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public BeanContextMembershipEvent(BeanContext bc,Collection changes) {
super(bc);
if (changes == null) throw new NullPointerException(
"BeanContextMembershipEvent constructor: changes is null.");
children = changes;
}
/**
* Contruct a BeanContextMembershipEvent
*
* @param bc The BeanContext source
* @param changes The Children affected
* @throws NullPointerException if <CODE>changes</CODE> is <CODE>null</CODE>
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public BeanContextMembershipEvent(BeanContext bc,Collection changes) {
super(bc);
if (changes == null) throw new NullPointerException(
"BeanContextMembershipEvent constructor: changes is null.");
children = changes;
}
private static BeanContext fill(BeanContext context) {
context.add(new JLabel("label"));
context.add(new JButton("button"));
JButton button = new JButton();
button.setText("another button");
context.add(button);
return context;
}
/**
* Contruct a BeanContextMembershipEvent
*
* @param bc The BeanContext source
* @param changes The Children affected
* @throws NullPointerException if <CODE>changes</CODE> is <CODE>null</CODE>
*/
@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes")
public BeanContextMembershipEvent(BeanContext bc,Collection changes) {
super(bc);
if (changes == null) throw new NullPointerException(
"BeanContextMembershipEvent constructor: changes is null.");
children = changes;
}
private static BeanContext fill(BeanContext context) {
context.add(new JLabel("label"));
context.add(new JButton("button"));
JButton button = new JButton();
button.setText("another button");
context.add(button);
return context;
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
@Override
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment();
if (!GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()) {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
@Override
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
super.setBeanContext(bc);
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
@Override
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) throws PropertyVetoException {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
if (!GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()) {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
@Override
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
if (!GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()) {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
@Override
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
if (!GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()) {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
@Override
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment();
if (!GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()) {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment ge =
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment();
if (!ge.isHeadless()) {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
super.setBeanContext(bc);
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) throws PropertyVetoException {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment ge =
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment();
if (!ge.isHeadless()) {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment ge =
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment();
if (!ge.isHeadless()){
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment ge =
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment();
if (!ge.isHeadless()) {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment ge =
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment();
if (!ge.isHeadless()){
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
@Override
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
java.awt.GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment();
if (!GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()) {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
@Override
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
super.setBeanContext(bc);
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
@Override
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) throws PropertyVetoException {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
if (!GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()) {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
@Override
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
if (!GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()) {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}
/**
* Set a bean context for this bean
*
* @param bc a <code>BeanContext</code> value
*/
@Override
public void setBeanContext(BeanContext bc) {
m_beanContext = bc;
m_design = m_beanContext.isDesignTime();
if (m_design) {
appearanceDesign();
} else {
if (!GraphicsEnvironment.isHeadless()) {
appearanceFinal();
}
}
}

ApplicationContext注入Bean(多线程中注入Bean)
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、线程中注入Service层或Dao层
- 总结
前言
通常我们用一下几种方式注入 :
1、
@Autowired是通过 byType 的方式去注入的, 使用该注解,要求接口只能有一个实现类。
2、@Resource可以通过 byName 和 byType的方式注入, 默认先按 byName的方式进行匹配,如果匹配不到,再按 byType的方式进行匹配。
3、@Qualifier注解可以按名称注入, 但是注意是 类名。
一、线程中注入Service层或Dao层
有些情况我们需要在工具类或在new一个线程之后,线程中注入Service层或Dao层,
这时候用以上方法是注入不进去
用以下方法即可注入:
package com.java.base.config;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
/***
*
* <p>Title: MyApplicationContext</p>
* <p>Description: ApplicationContextAware 通过它spring容器会自动把上下文环境对象调用ApplicationContextAware接口中的setApplicationContext方法。
* 通过这个上下文环境对象得到spring容器中的Bean
* 在我们写的工具类获取线程中不能直接通过Spring注入,这个时候就需要通过ApplicationContext获取Bean
* </p>
* @author shy
*/
@Service
public class MyApplicationContext implements ApplicationContextAware {
private static ApplicationContext context;
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
context = applicationContext;
}
public static <T> T getBean(final Class<T> requiredType) {
return context.getBean(requiredType);
}
public static <T> T getBean(final String beanName) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
final T bean = (T) context.getBean(beanName);
return bean;
}
public static <T> Map<String, T> getBeans(final Class<T> requiredType) {
return context.getBeansOfType(requiredType);
}
public static Map<String, Object> getBeansWithAnnotation(final Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType) {
return context.getBeansWithAnnotation(annotationType);
}
}
private XXXrService xxxService = MyApplicationContext.getBean(XXXService.class);
总结
如果此篇文章有帮助到您, 希望打大佬们能
关注、点赞、收藏、评论支持一波,非常感谢大家!
如果有不对的地方请指正!!!
参考1

bean实例化的三种方式 bean标签常用属性 单例模式和多例模式的对象 BeanFactory和ApplicationContext:
bean实例化的三种方式 bean标签常用属性 单例模式和多例模式的对象 beanfactory和ApplicationContext:
- 学习网站/博客:
- 1.bean实例化的三种方式:
- 页面结构整体布局:
- 运行结果如下:
- 代码如下:
- pom.xml:
- Student:
- MyStaticFactory :
- MyInstanceFactory :
- Test:
- spring-1.xml:
- 2.bean标签常用属性:
- 代码整体布局:
- 运行结果:
- 添加/修改的代码如下:
- spring-2.xml:(添加)
- Student:(修改)
- (test)Test2:
- 3.单例模式和多例模式的对象:
- 运行结果:
- God:
- Test:
- (singleton)God:(添加)
- (singleton)Test:(添加)
- 4.BeanFactory和ApplicationContext:
学习网站/博客:
spring https://spring.io/
The loC Container https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.html#beans
Spring官方文档(中文版!!!) https://blog.csdn.net/li1376417539/article/details/104951358/
1.bean实例化的三种方式:



页面结构整体布局:
运行结果如下:
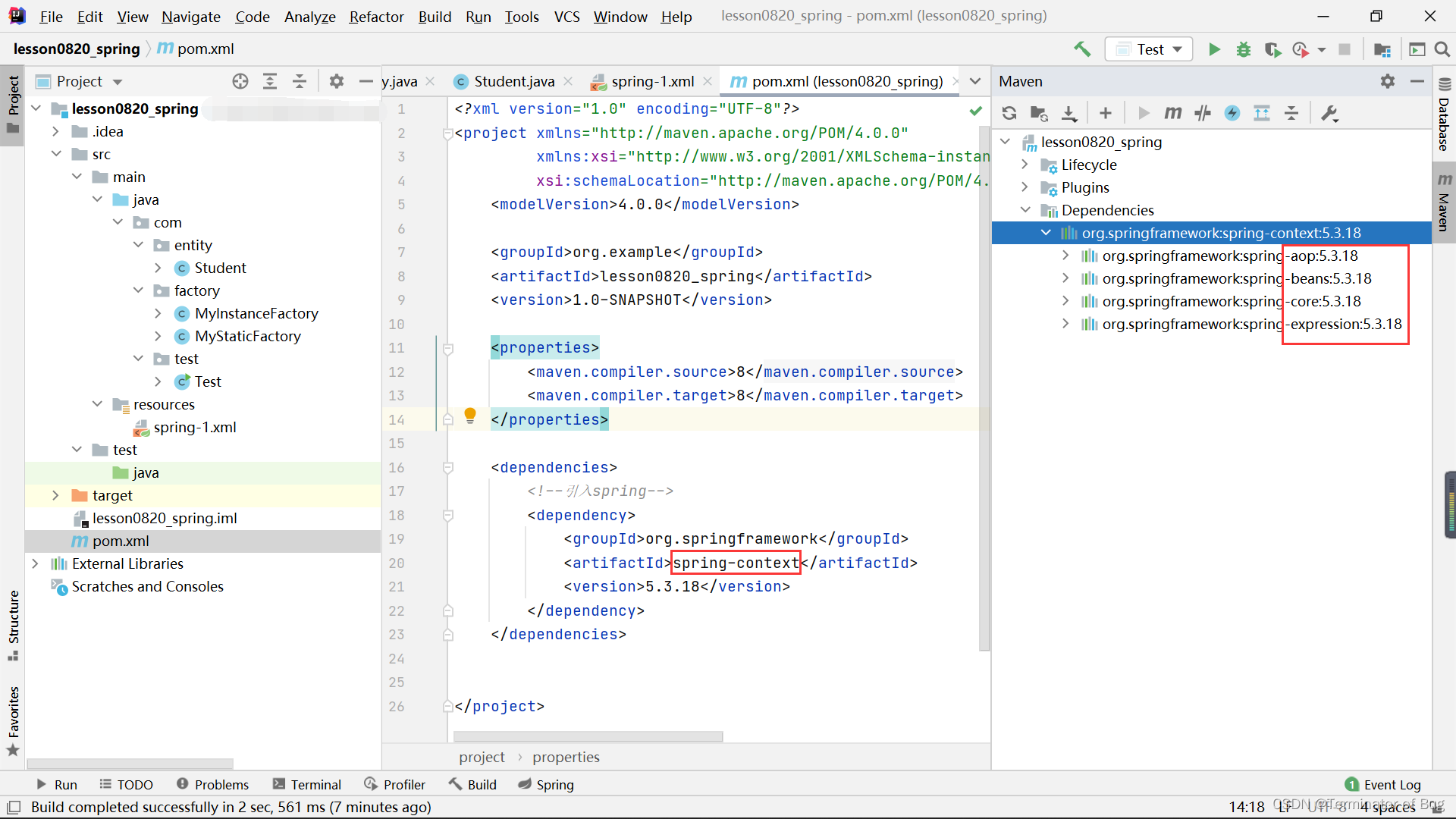
代码如下:
pom.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>lesson0820_spring</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!--引入spring-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.18</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
Student:
package com.entity;
public class Student {
public Student(){
System.out.println("这是Student的构造方法...");
}
public void introduce(){
System.out.println("我是一个学生");
}
}
MyStaticFactory :
package com.factory;
import com.entity.Student;
/**
* 静态工厂
*/
public class MyStaticFactory {
/**
* 静态返回学生实例
* @return
*/
public static Student createInstance(){
System.out.println("调用静态工厂.....MyStaticFactory...createInstance");
return new Student();
}
}
MyInstanceFactory :
package com.factory;
import com.entity.Student;
/**
* 实例工厂
*/
public class MyInstanceFactory {
/**
* 定义创建对象的实例方法
* @return
*/
public Student createInstance(){
return new Student();
}
}
Test:
package com.test;
import com.entity.Student;
import com.factory.MyInstanceFactory;
import com.factory.MyStaticFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClasspathXmlApplicationContext;
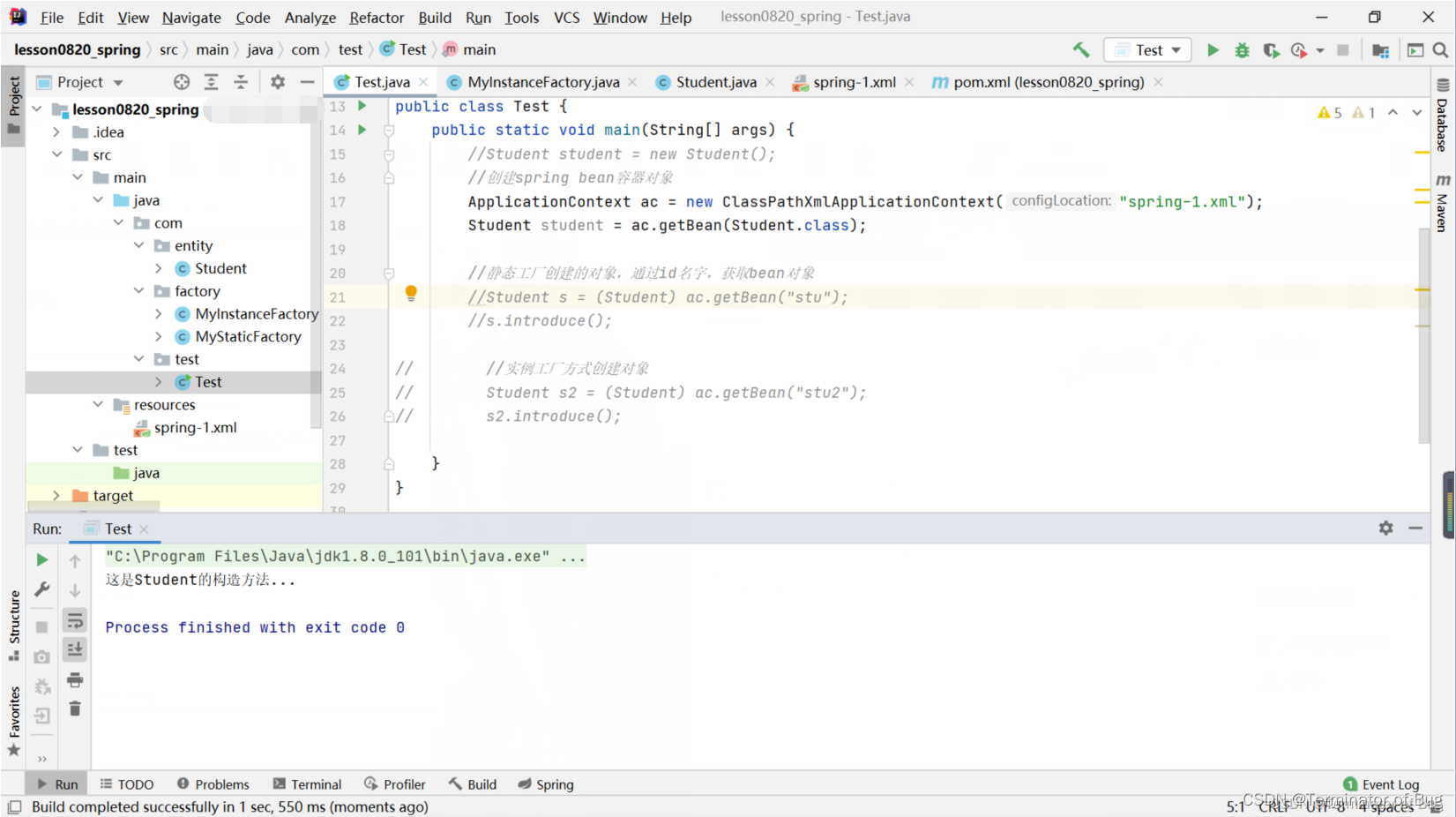
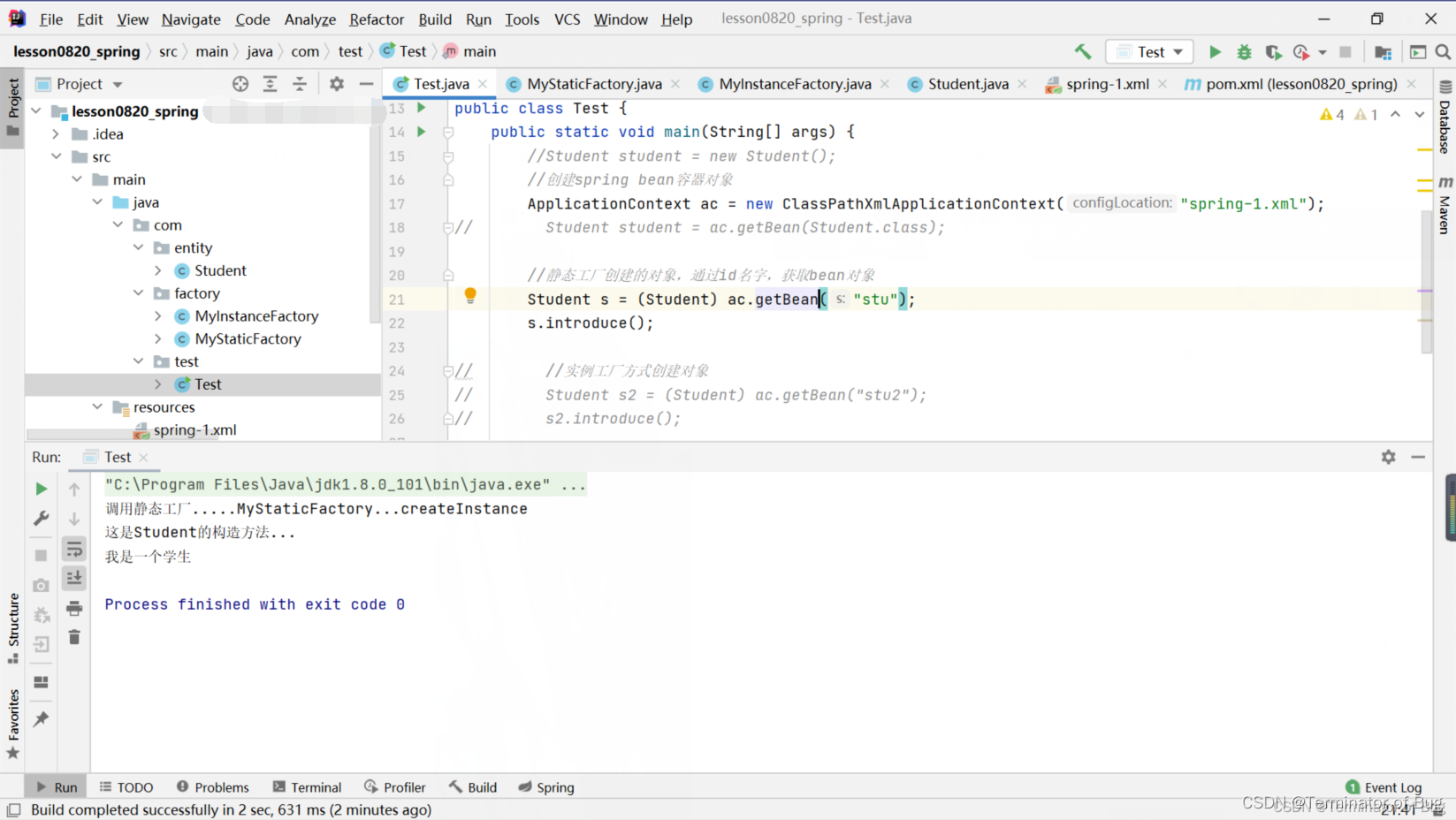
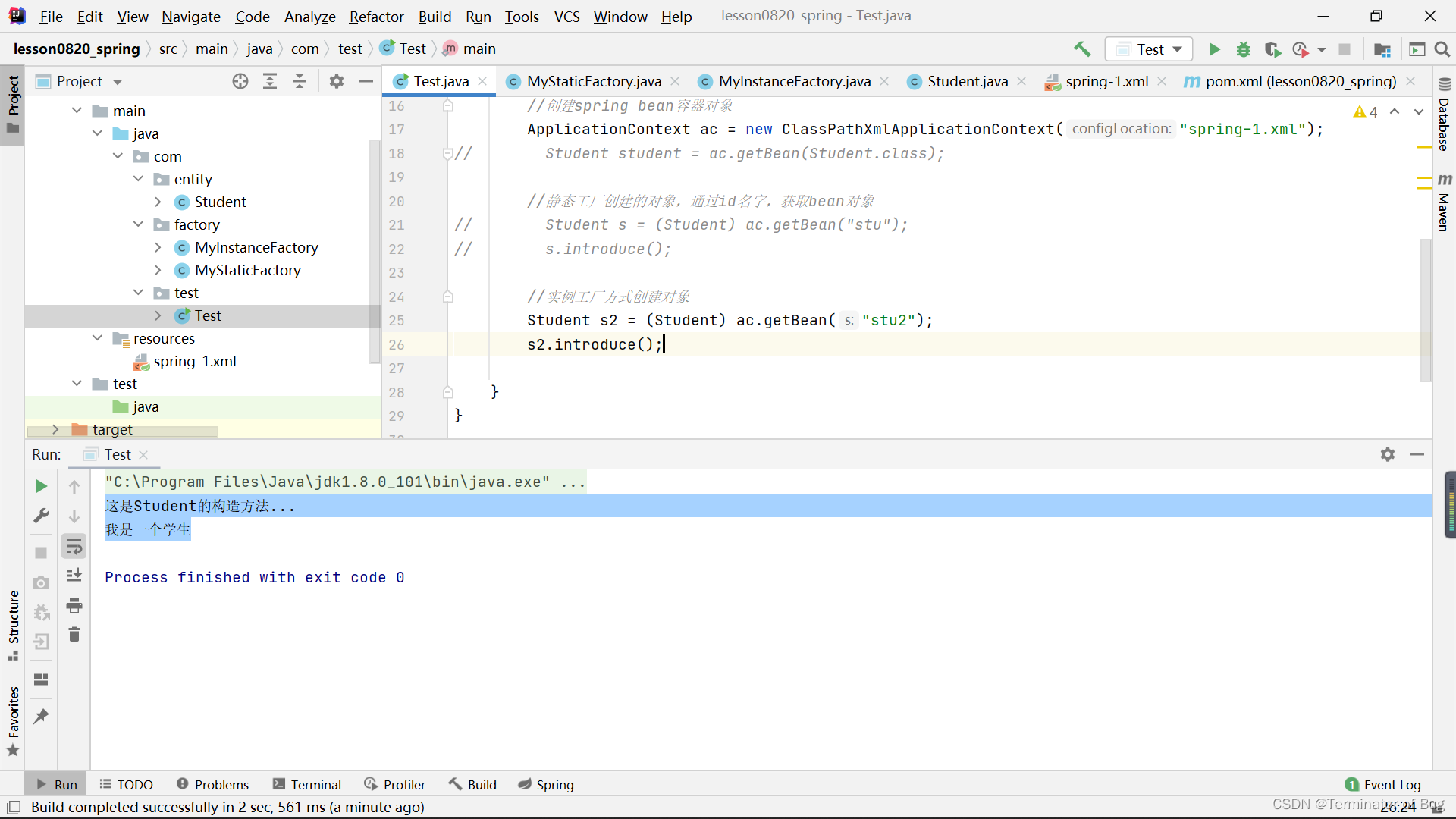
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Student student = new Student();
//创建spring bean容器对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClasspathXmlApplicationContext("spring-1.xml");
// Student student = ac.getBean(Student.class);
//静态工厂创建的对象,通过id名字,获取bean对象
// Student s = (Student) ac.getBean("stu");
// s.introduce();
//实例工厂方式创建对象
Student s2 = (Student) ac.getBean("stu2");
s2.introduce();
}
}
spring-1.xml:
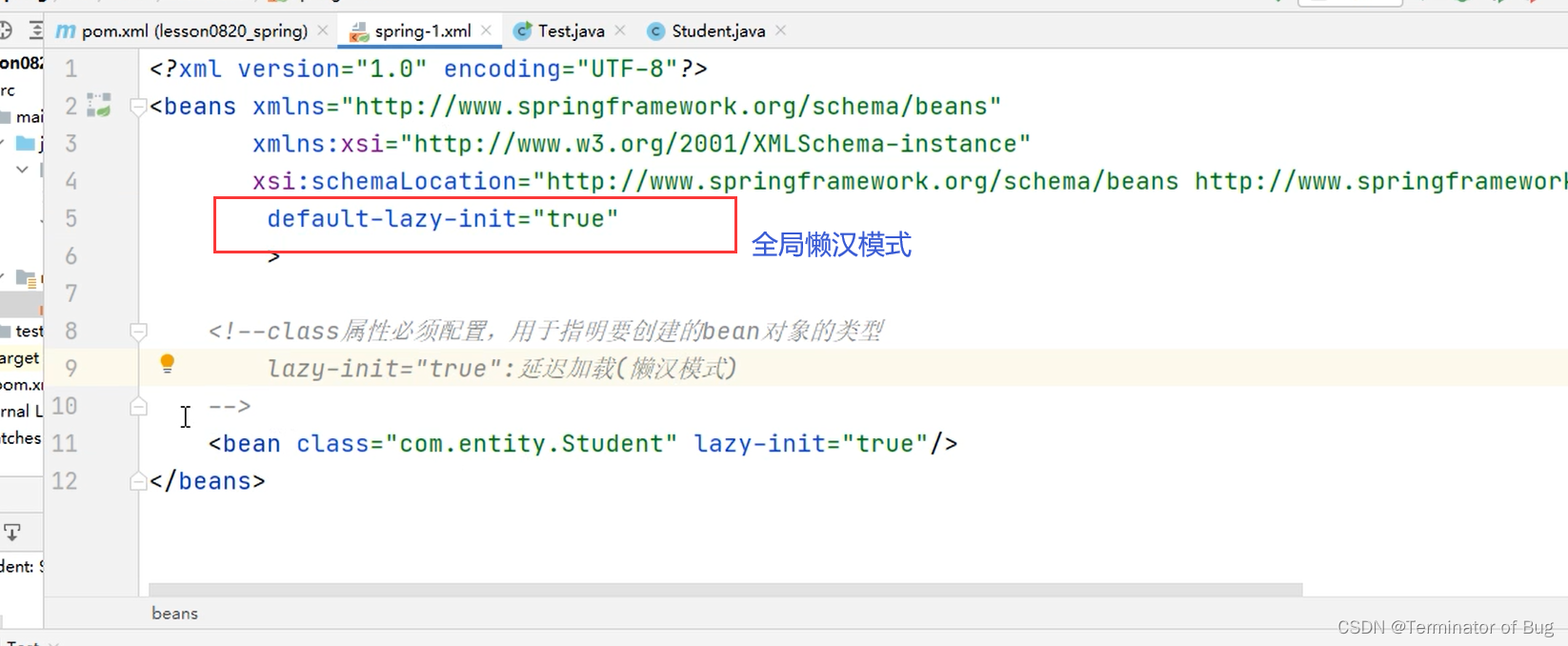
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
default-lazy-init="true"
>
<!--class属性必须配置,用于指明要创建的bean对象的类型
lazy-init="true":延迟加载(懒汉模式)
1.bean的方式定义对象
-->
<!-- <beanlazy-init="true"/>-->
<!--2.静态工厂方式创建学生对象-->
<bean id="stu"factory-method="createInstance"/>
<!--3.实例工厂创建对象-->
<bean id="fac"/>
<bean id="stu2" factory-bean="fac" factory-method="createInstance"/>
</beans>
2.bean标签常用属性:

代码整体布局:
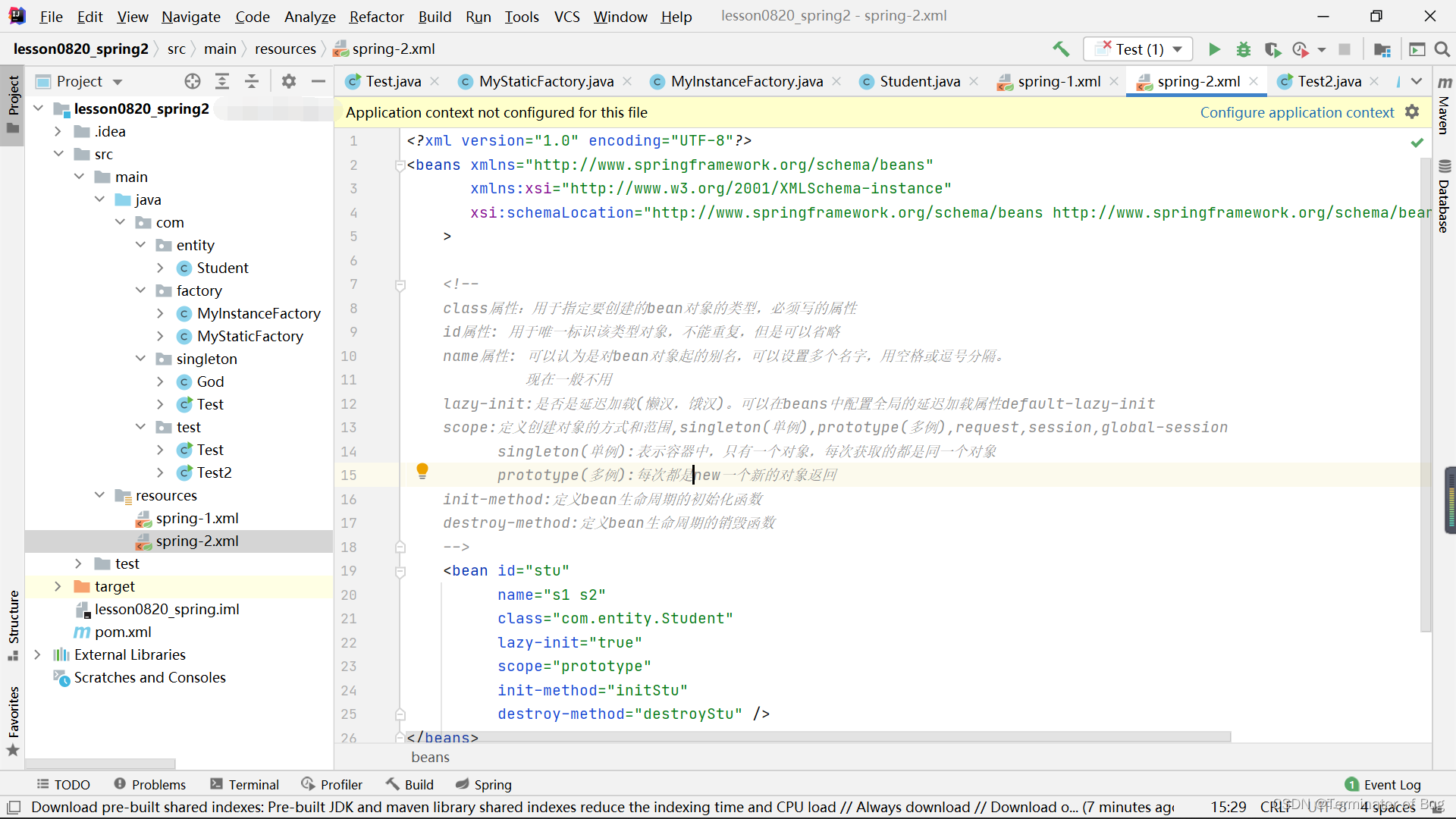
运行结果:
添加/修改的代码如下:
spring-2.xml:(添加)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"
>
<!--
class属性:用于指定要创建的bean对象的类型,必须写的属性
id属性: 用于唯一标识该类型对象,不能重复,但是可以省略
name属性: 可以认为是对bean对象起的别名,可以设置多个名字,用空格或逗号分隔。
现在一般不用
lazy-init:是否是延迟加载(懒汉,饿汉)。可以在beans中配置全局的延迟加载属性default-lazy-init
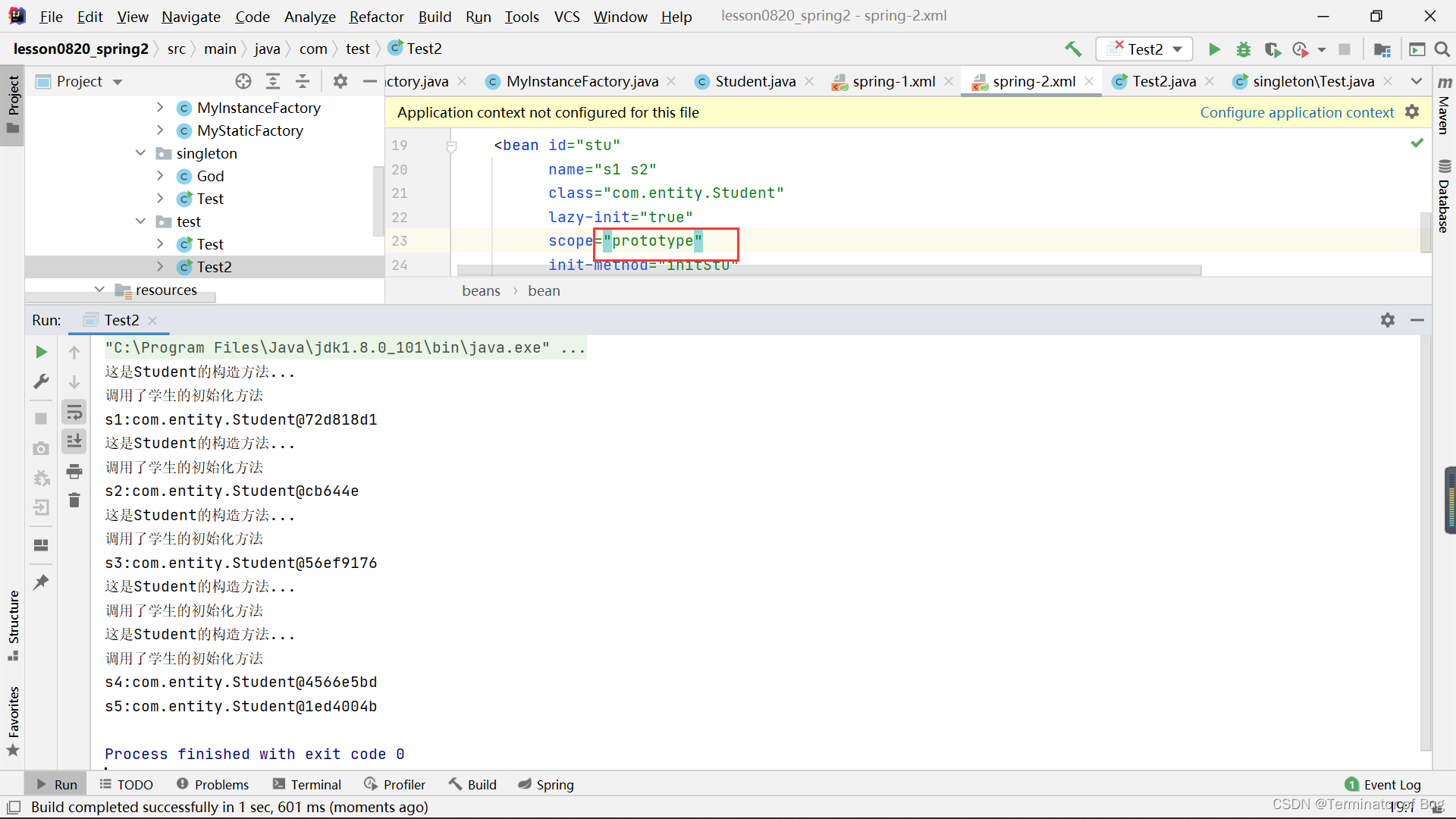
scope:定义创建对象的方式和范围,singleton(单例),prototype(多例),request,session,global-session
singleton(单例):表示容器中,只有一个对象,每次获取的都是同一个对象
prototype(多例):每次都是new一个新的对象返回
init-method:定义bean生命周期的初始化函数
destroy-method:定义bean生命周期的销毁函数
-->
<bean id="stu"
name="s1 s2"lazy-init="true"
scope="prototype"
init-method="initStu"
destroy-method="destroyStu" />
</beans>
Student:(修改)
package com.entity;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
public class Student {
public Student(){
System.out.println("这是Student的构造方法...");
}
//自我介绍
public void introduce(){
System.out.println("我是一个学生");
}
//学生初始化
public void initStu(){
System.out.println("调用了学生的初始化方法");
}
//学生销毁
public void destroyStu(){
System.out.println("调用了学生的销毁方法");
}
}
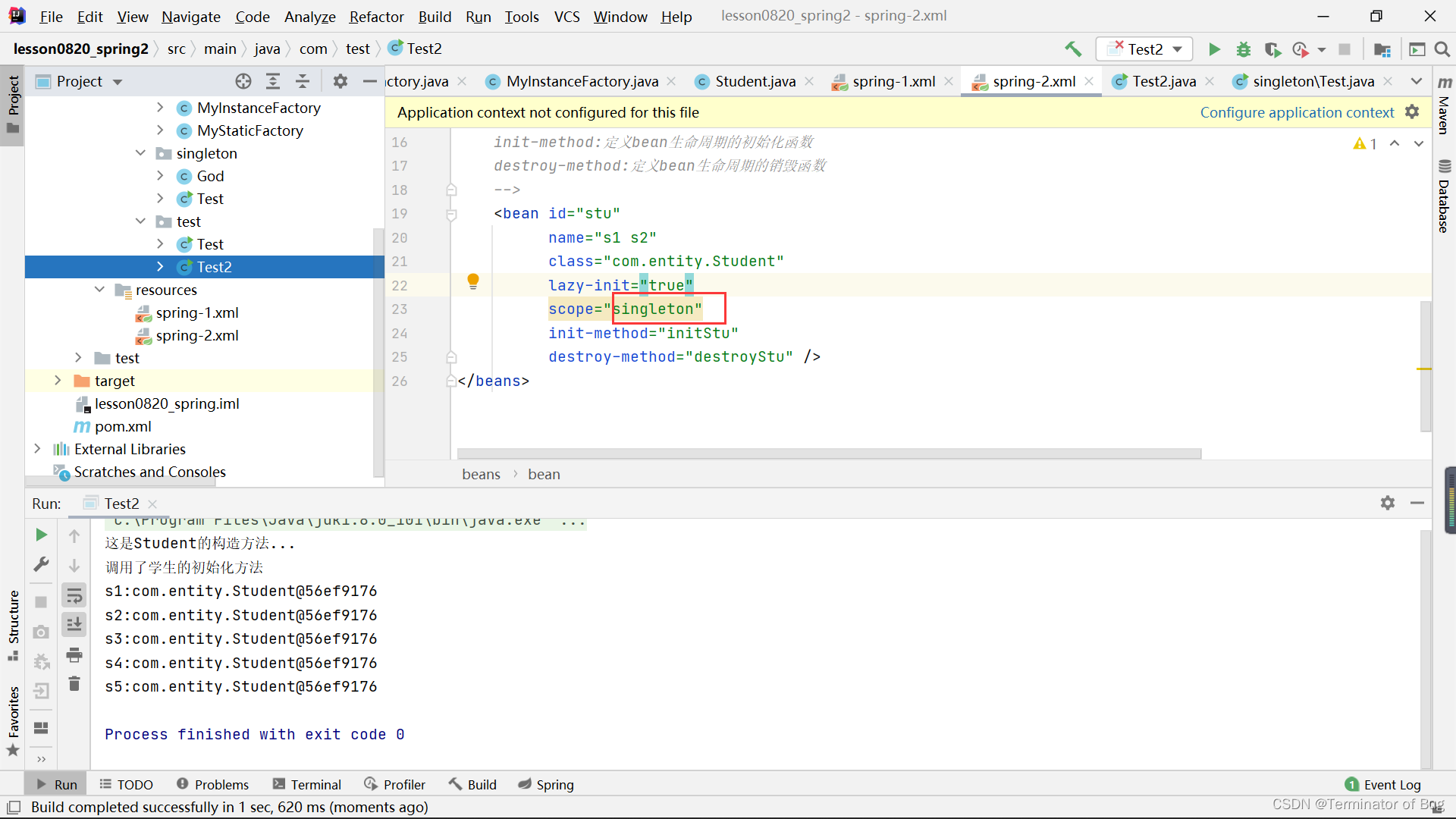
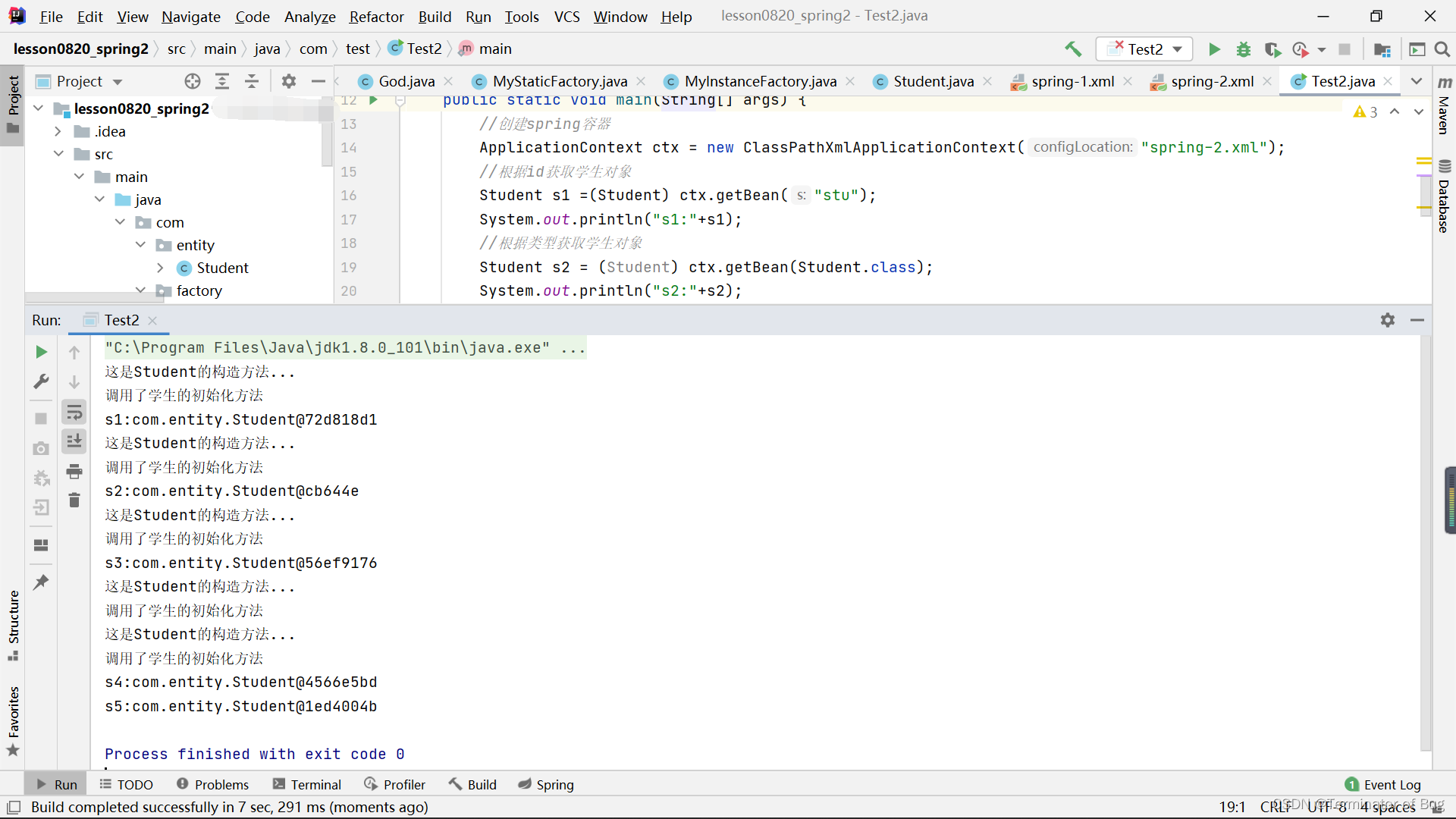
(test)Test2:
package com.test;
import com.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClasspathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建spring容器
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClasspathXmlApplicationContext("spring-2.xml");
//根据id获取学生对象
Student s1 =(Student) ctx.getBean("stu");
System.out.println("s1:"+s1);
//根据类型获取学生对象
Student s2 = (Student) ctx.getBean(Student.class);
System.out.println("s2:"+s2);
//根据id和类型获取学生对象
Student s3 = ctx.getBean("stu",Student.class);
System.out.println("s3:"+s3);
//根据name属性获取学生对象
Student s4 = (Student) ctx.getBean("s1");
Student s5 = (Student) ctx.getBean("s2");
System.out.println("s4:"+s4);
System.out.println("s5:"+s5);
}
}
3.单例模式和多例模式的对象:

运行结果:
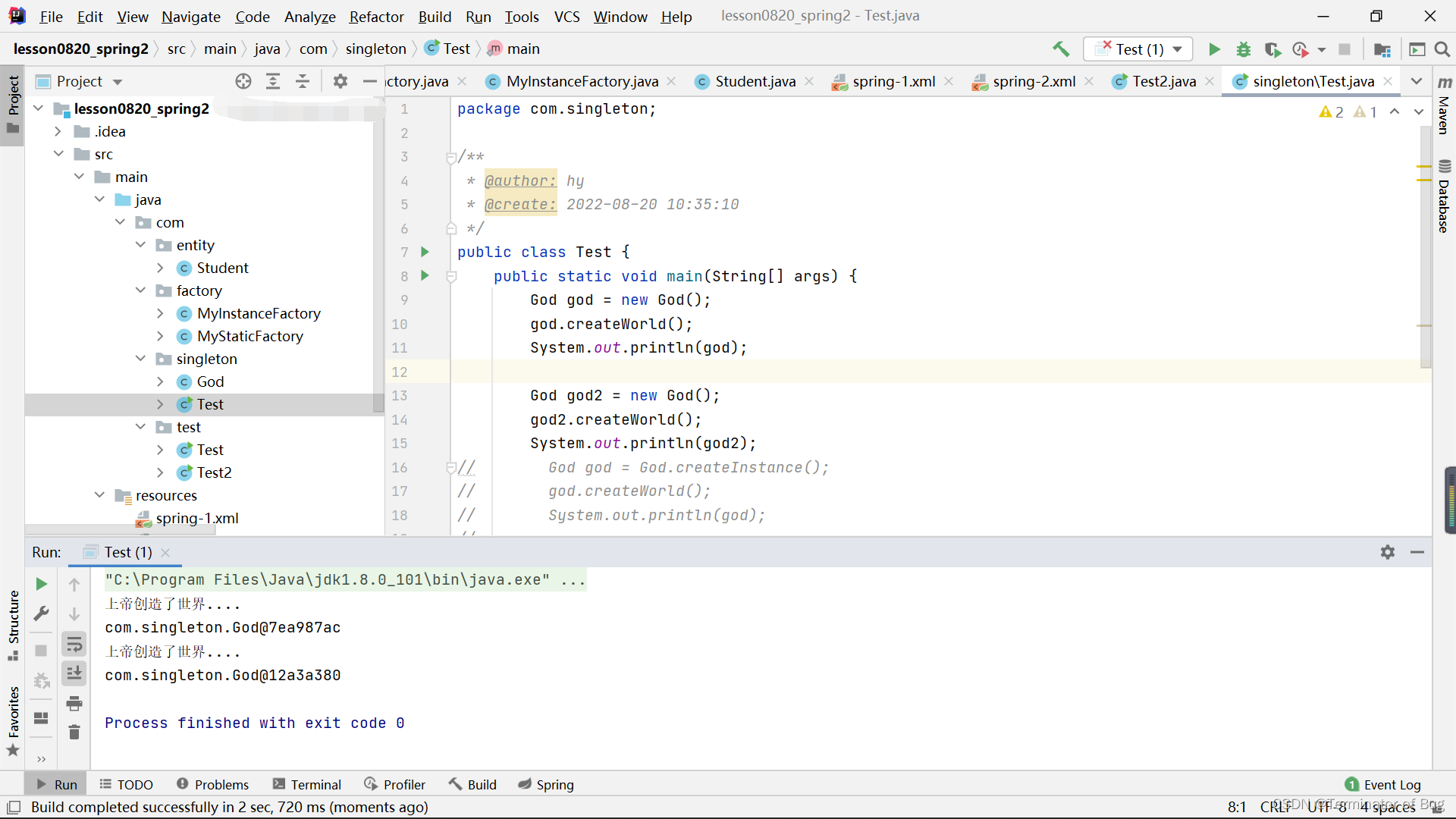
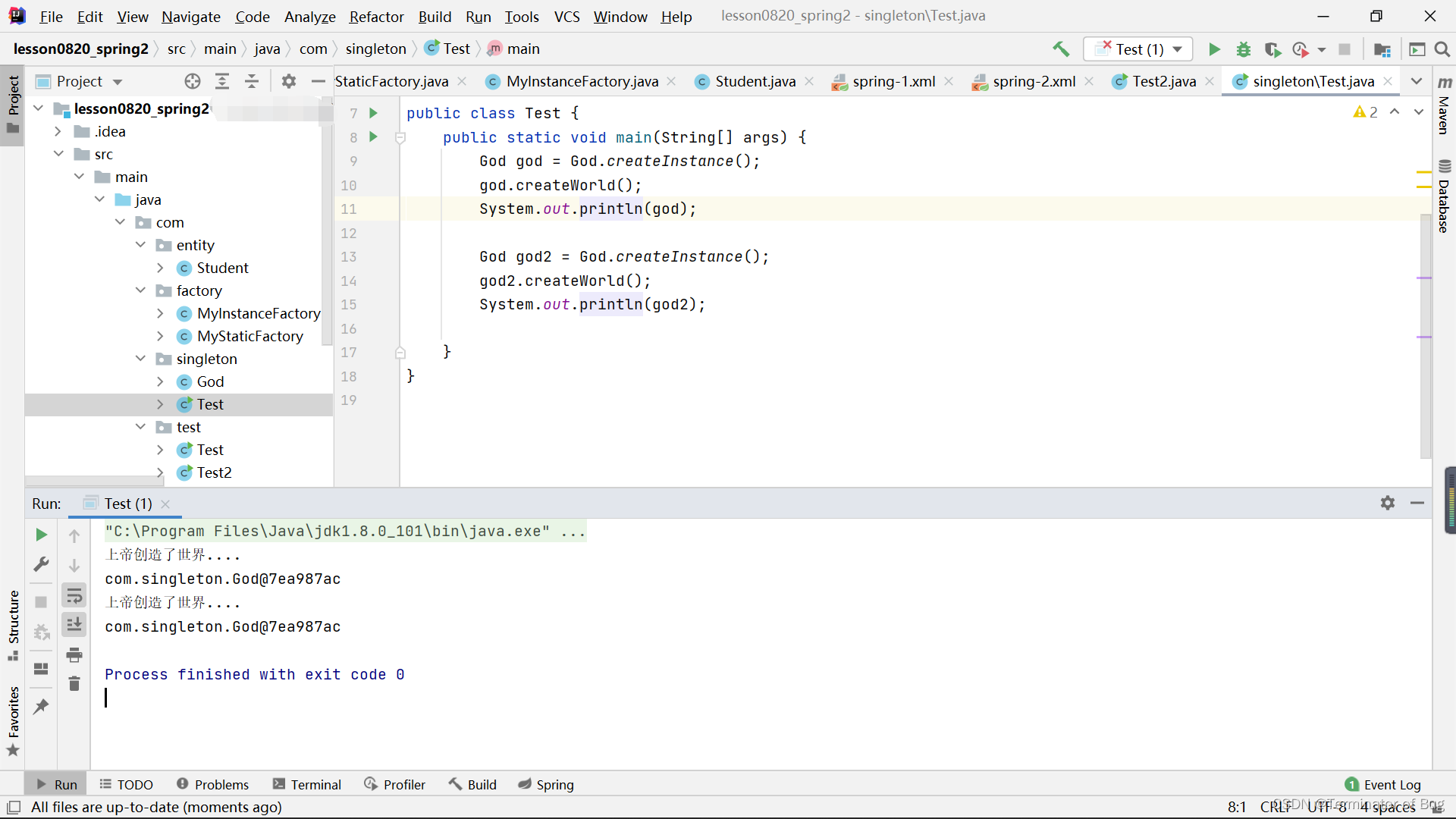
God:
package com.singleton;
public class God {
public void createWorld(){
System.out.println("上帝创造了世界....");
}
}
Test:
package com.singleton;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god = new God();
god.createWorld();
System.out.println(god);
God god2 = new God();
god2.createWorld();
System.out.println(god2);
}
}
(singleton)God:(添加)
package com.singleton;
public class God {
//3.定义静态私有对象
private static God god;
//1.构造私有化
private God(){
}
//2.定义静态工厂获取实例的方法,用于获取对象
public static God createInstance(){
if (god==null){
god = new God();
}
return god;
}
public void createWorld(){
System.out.println("上帝创造了世界....");
}
}
(singleton)Test:(添加)
package com.singleton;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god = God.createInstance();
god.createWorld();
System.out.println(god);
God god2 = God.createInstance();
god2.createWorld();
System.out.println(god2);
}
}
4.beanfactory和ApplicationContext:
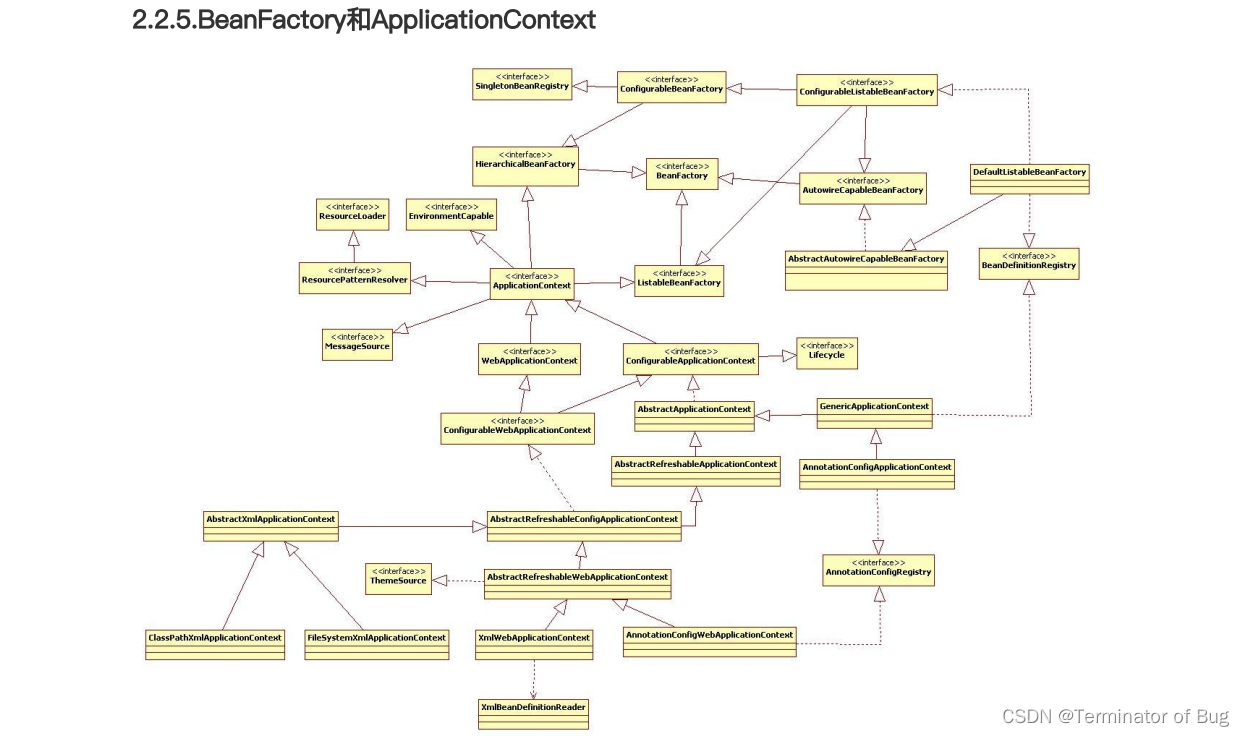
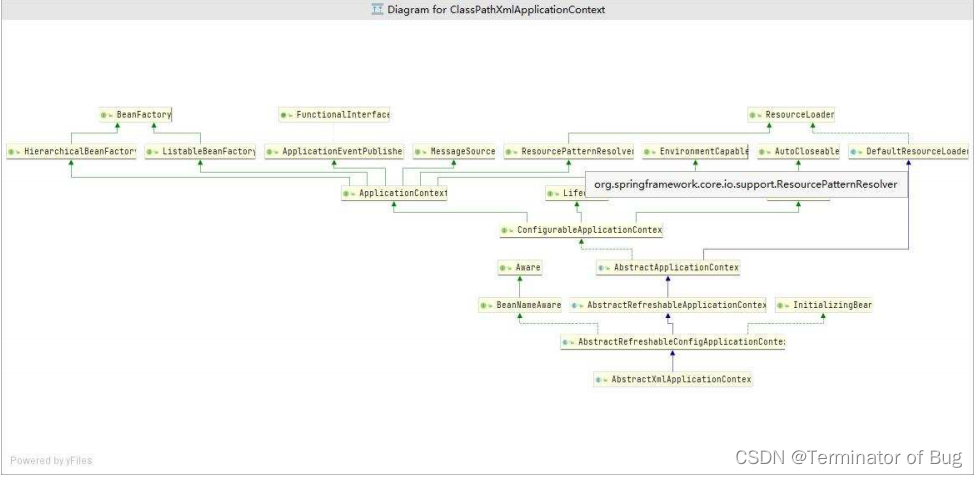
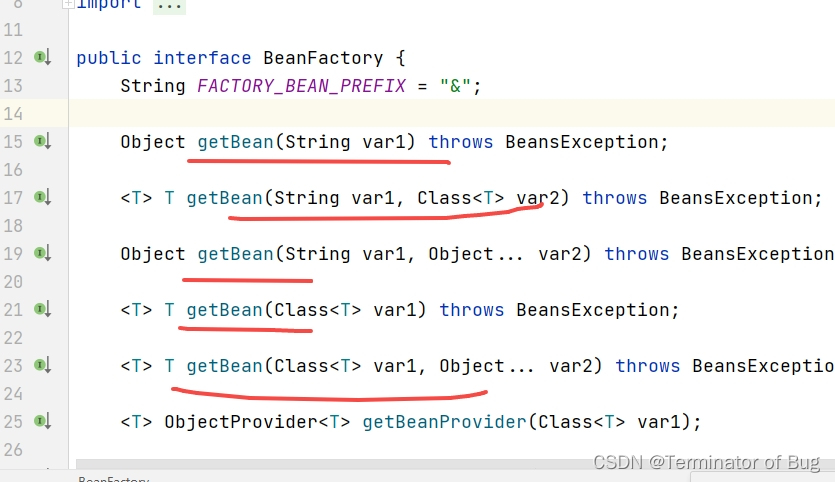
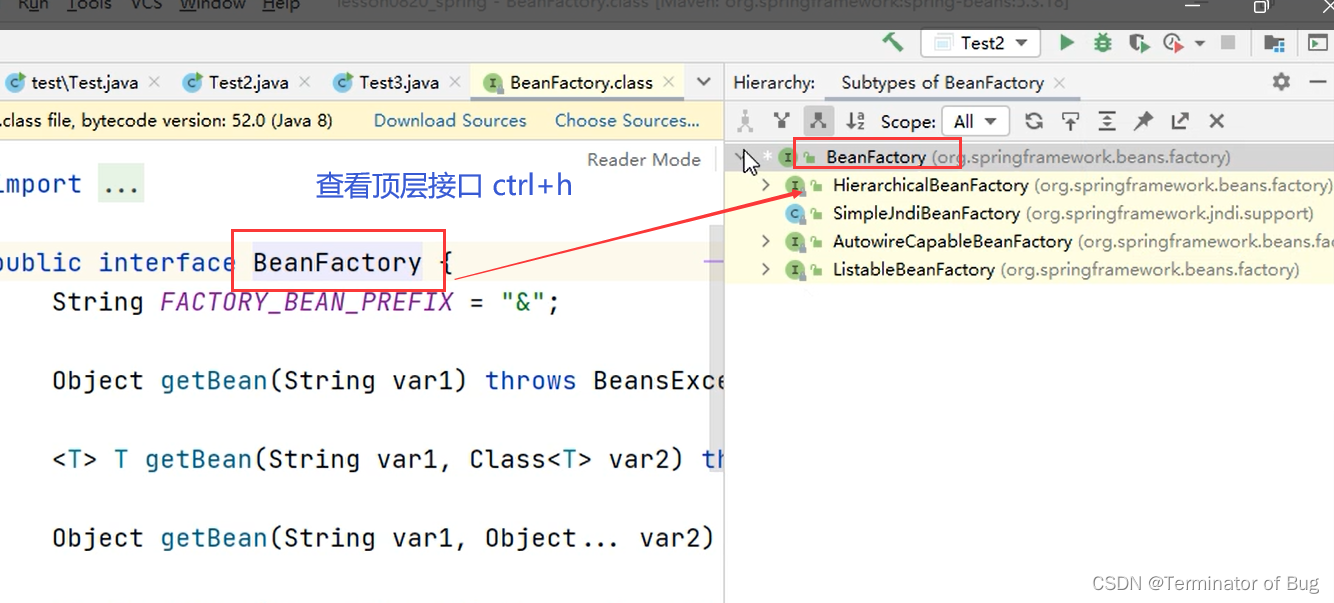
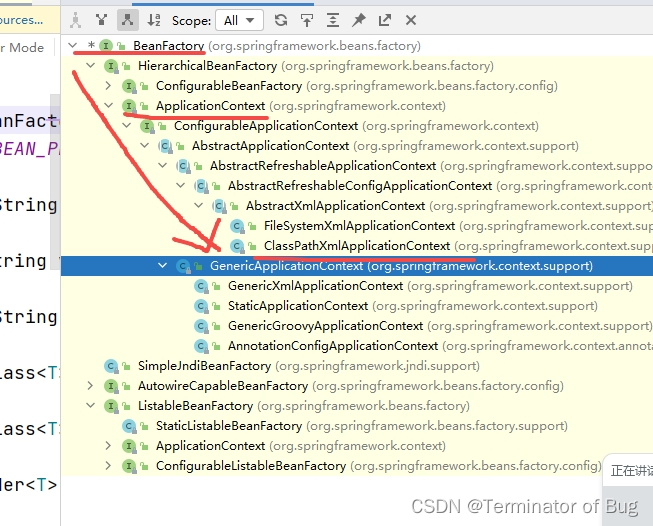
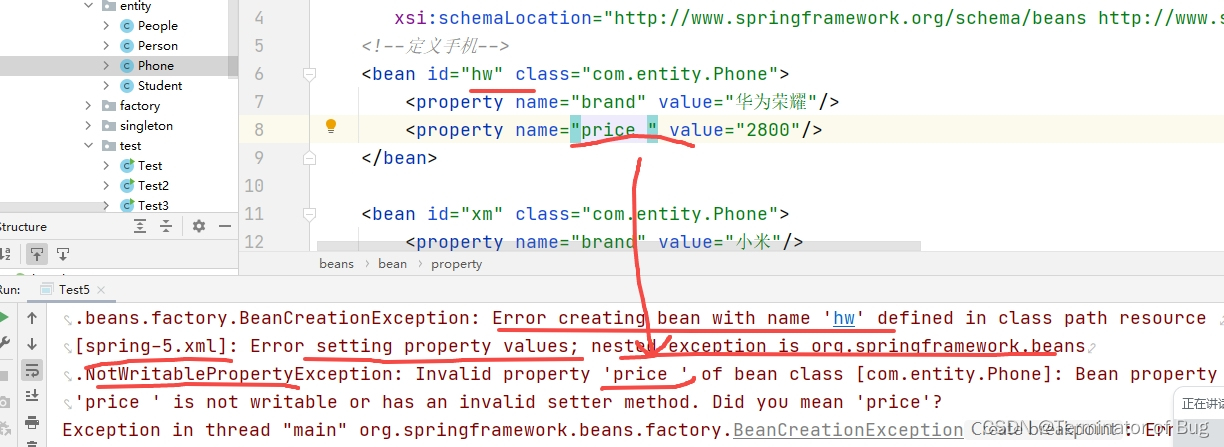
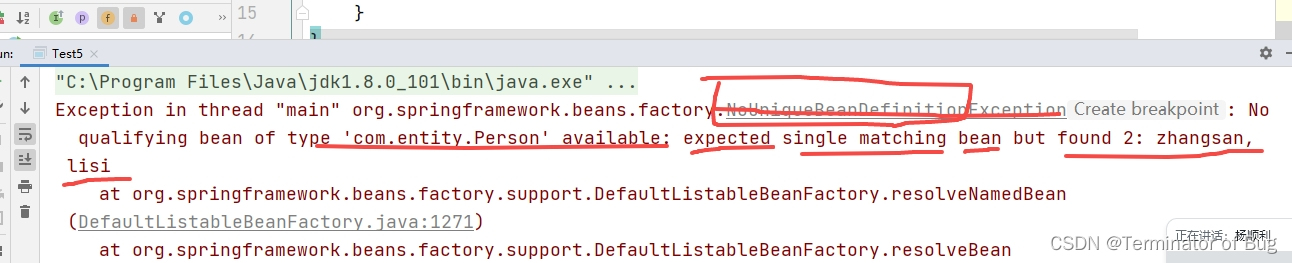
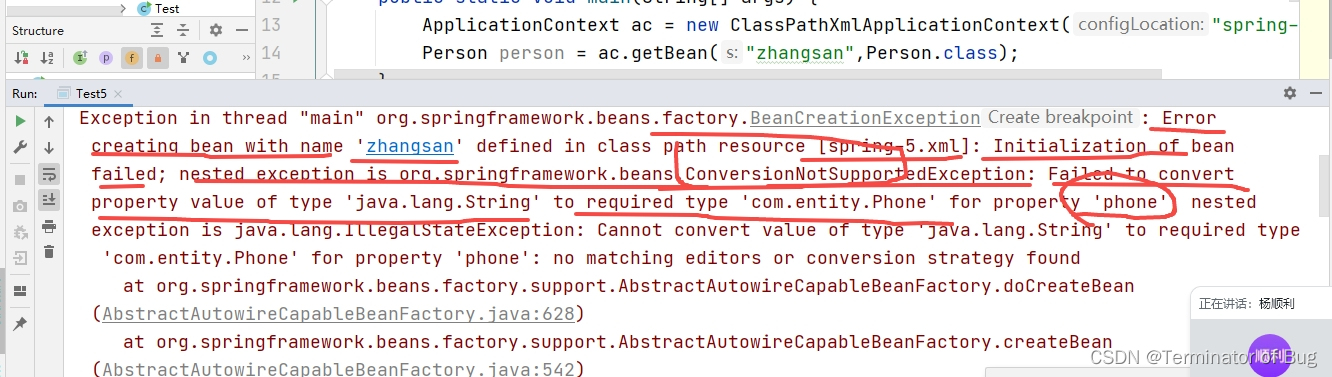
// A code block
var foo = 'bar';
// A code block
var foo = 'bar';
// A code block
var foo = 'bar';
// A code block
var foo = 'bar';
// A code block
var foo = 'bar';
// A code block
var foo = 'bar';
// A code block
var foo = 'bar';
// A code block
var foo = 'bar';
// A code block
var foo = 'bar';

FLEX通过ANE调用安卓 ExtensionContext.createExtensionContext 返回null
总结
以上是小编为你收集整理的FLEX通过ANE调用安卓 ExtensionContext.createExtensionContext 返回null全部内容。
如果觉得小编网站内容还不错,欢迎将小编网站推荐给好友。

java – Spring 3 applicationContext-security-JDBC.xml有bean:bean不是bean?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans:beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:jdbc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/jdbc/spring-jdbc-3.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-3.0.xsd">
<http auto-config="true" use-expressions="true">
<intercept-url pattern="/friends/**" access="hasRole('ROLE_USER')" />
<form-login login-page="/login.html"
default-target-url="/index.html" always-use-default-target="true"
authentication-failure-url="/login.html?authFailed=true" />
</http>
<authentication-manager alias="authenticationManager">
<authentication-provider>
<jdbc-user-service data-source-ref="dataSource" />
</authentication-provider>
</authentication-manager>
<beans:bean id="propertyConfigurer"https://www.jb51.cc/tag/fig/" target="_blank">fig.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<beans:property name="location" value="classpath:jdbc.properties" />
</beans:bean>
<beans:bean id="dataSource">
<beans:property name="driverClassName" value="${database.driver}" />
<beans:property name="url" value="${database.url}" />
<beans:property name="username" value="${database.user}" />
<beans:property name="password" value="${database.password}" />
<beans:property name="initialSize" value="5" />
<beans:property name="maxActive" value="10" />
</beans:bean>
</beans:beans>
解决方法
如果您的配置文件集中在其中一个扩展名称空间上 – 再次,让我们使用安全性作为示例 – 如果您将默认名称空间声明为扩展名称空间而不是标准bean名称空间,它可以清理该文件.那是什么
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
确实 – 它使安全性成为默认命名空间,这意味着您不必使用sec:或security:作为前缀.
但是当您将安全性设置为默认值时,则在使用beans命名空间元素时必须明确.因此bean:前缀.
解.如果您更喜欢bean作为默认值,只需将默认命名空间更改为beans:
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
替代方案.或者,如果你想输入更短的东西,你可以这样做
xmlns:b="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
代替
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
这将允许你做的事情
<b:bean id="beanId"/>
我们今天的关于java.beans.beancontext.BeanContext的实例源码和bean java的分享已经告一段落,感谢您的关注,如果您想了解更多关于ApplicationContext注入Bean(多线程中注入Bean)、bean实例化的三种方式 bean标签常用属性 单例模式和多例模式的对象 BeanFactory和ApplicationContext:、FLEX通过ANE调用安卓 ExtensionContext.createExtensionContext 返回null、java – Spring 3 applicationContext-security-JDBC.xml有bean:bean不是bean?的相关信息,请在本站查询。
本文标签:





