本文将介绍带有MysqlMaster/Slave的Datamapper的详细情况,特别是关于mysqldaul的相关信息。我们将通过案例分析、数据研究等多种方式,帮助您更全面地了解这个主题,同时也将涉
本文将介绍带有Mysql Master / Slave的Datamapper的详细情况,特别是关于mysql daul的相关信息。我们将通过案例分析、数据研究等多种方式,帮助您更全面地了解这个主题,同时也将涉及一些关于A2-04-10.MySQL DATA TYPES-Mastering MySQL TIME Data Type、docker mysql master slave、master and slave have equal MySQL server ids、master and slave have equal MySQL server UUIDs 解决方法的知识。
本文目录一览:- 带有Mysql Master / Slave的Datamapper(mysql daul)
- A2-04-10.MySQL DATA TYPES-Mastering MySQL TIME Data Type
- docker mysql master slave
- master and slave have equal MySQL server ids
- master and slave have equal MySQL server UUIDs 解决方法

带有Mysql Master / Slave的Datamapper(mysql daul)
我似乎无法找到有关如何使用datamapper与mysql主/从设置进行通信的任何信息.我正在使用dm-MysqL-adapter运行rails3
解决方法:
您可以使用DataMapper的Multiple Data Store功能:
DataMapper.setup(:default, 'MysqL://master-host/mydb')
DataMapper.setup(:slave, 'MysqL://slave-host/mydb')
现在,无论何时您想从奴隶中读取,请使用:
DataMapper.repository(:slave) do
Person.first
end
不幸的是,它看起来不像你可以做透明的read-from-slave写入到master:
[…] This will use your connection to the :external data-store and the
first Person it finds. Later, when you call .save on that person,
it’ll get saved back to the :external data-store; An object is aware
of what context it came from and should be saved back to.
因此,如果您尝试保存从从站检索到的人员,则会在修改后尝试将其存储回从属数据库.

A2-04-10.MySQL DATA TYPES-Mastering MySQL TIME Data Type
转载自:http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-time/
Mastering MySQL TIME Data Type
Summary: in this tutorial, we will introduce you to the MySQL TIME data type and show you useful temporal functions to manipulate time data effectively.
Introduction to MySQL TIME data type
MySQL uses the ''HH:MM:SS'' format for querying and displaying a time value that represents a time of day, which is within 24 hours. To represent a time interval between two events, MySQL uses the ''HHH:MM:SS'' format, which is larger than 24 hours.
To define a TIME column, you use the following syntax:
|
1
|
column_name
TIME;
|
For example, the following snippet defines a column named start_at with TIME data type.
|
1
|
start_at
TIME;
|
A TIME value ranges from -838:59:59 to 838:59:59. In addition, a TIME value can have fractional seconds part that is up to microseconds precision (6 digits). To define a column whose data type is TIMEwith a fractional second precision part, you use the following syntax:
|
1
|
column_name
TIME(N);
|
N is an integer that represents the fractional part, which is up to 6 digits.
The following snippet defines a column with TIME data type including 3 digits of fractional seconds.
|
1
|
begin_at
TIME(3);
|
A TIME value takes 3 bytes for storage. In case a TIME value includes fractional second precision, it will take additional bytes based on the number of digits of the fractional second precision. The following table illustrates the storage required for fractional second precision.
| Fractional Second Precision | Storage (BYTES) |
| 0 | 0 |
| 1, 2 | 1 |
| 3, 4 | 2 |
| 5, 6 | 3 |
For example, TIME and TIME(0) takes 3 bytes. TIME(1) and TIME(2) takes 4 bytes (3 + 1); TIME(3) and TIME(6) take 5 and 6 bytes.
MySQL TIME data type example
Let’s take a look at an example of using the TIME data type for columns in a table.
First, create a new table named tests that consists of four columns: id, name, start_at, and end_at. The data types of the start_at and end_at columns are TIME.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
CREATE TABLE tests (
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
start_at TIME,
end_at TIME
);
|
Second, insert a row into the tests table.
|
1
2
|
INSERT INTO tests(name,start_at,end_at)
VALUES(''Test 1'', ''08:00:00'',''10:00:00'');
|
Third, query data from the tests table.
|
1
2
3
4
|
SELECT
name, start_at, end_at
FROM
tests;
|
![]()
Notice that we use ''HH:MM:SS'' as the literal time value in the INSERT statement. Let’s examine all the valid time literals that MySQL can recognize.
MySQL TIME literals
MySQL recognizes various time formats besides the ''HH:MM:SS'' format that we mentioned earlier.
MySQL allows you to use the ''HHMMSS'' format without delimiter ( : ) to represent time value. For example, ''08:30:00'' and ''10:15:00'' can be rewritten as ''083000'' and ''101500''.
|
1
2
|
INSERT INTO tests(name,start_at,end_at)
VALUES(''Test 2'',''083000'',''101500'');
|
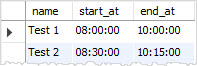
However, 108000 is not a valid time value because 80 does not represent the correct minute. In this case, MySQL will raise an error if you try to insert an invalid time value into a table.
|
1
2
|
INSERT INTO tests(name,start_at,end_at)
VALUES(''Test invalid'',''083000'',''108000'');
|
MySQL issued the following error message after executing the above statement.
|
1
|
Error
Code: 1292. Incorrect time value: ''108000'' for column ''end_at'' at row 1
|
In addition to the string format, MySQL accepts the HHMMSS as a number that represents a time value. You can also use SS, MMSS. For example, instead of using ''082000'', you can use 082000 as follows:
|
1
2
|
INSERT INTO tests(name,start_at,end_at)
VALUES(''Test 3'',082000,102000);
|
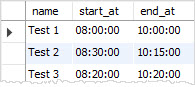
For the time interval, you can use the ''D HH:MM:SS'' format where D represents days with a range from 0 to 34. A more flexible syntax is ''HH:MM'', ''D HH:MM'', ''D HH'', or ''SS''.
If you use the delimiter:, you can use 1 digit to represent hours, minutes, or seconds. For example, 9:5:0 can be used instead of ''09:05:00''.
|
1
2
|
INSERT INTO tests(name,start_at,end_at)
VALUES(''Test 4'',''9:5:0'',100500);
|
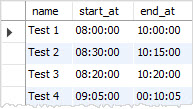
Useful MySQL TIME functions
MySQL provides several useful temporal functions for manipulating TIME data.
Getting to know the current time
To get the current time of the database server, you use the CURRENT_TIME function. The CURRENT_TIMEfunction returns the current time value as a string ( ''HH:MM:SS'') or a numeric value ( HHMMSS) depending on the context where the function is used.
The following statements illustrate the CURRENT_TIME function in both string and numeric contexts:
|
1
2
3
|
SELECT
CURRENT_TIME() AS string_now,
CURRENT_TIME() + 0 AS numeric_now;
|
![]()
Adding and Subtracting time from a TIME value
To add a TIME value to another TIME value, you use the ADDTIME function. To subtract a TIME value from another TIME value, you use the SUBTIME function.
The following statement adds and subtracts 2 hours 30 minutes to and from the current time.
|
1
2
3
4
|
SELECT
CURRENT_TIME(),
ADDTIME(CURRENT_TIME(), 023000),
SUBTIME(CURRENT_TIME(), 023000);
|
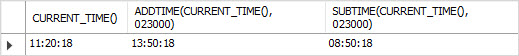
In addition, you can use the TIMEDIFF() function to get a difference between two TIME values.
|
1
2
3
4
|
SELECT
TIMEDIFF(end_at, start_at)
FROM
tests;
|
Formatting MySQL TIME values
Although MySQL uses ''HH:MM:SS'' when retrieving and displaying the a TIME value, you can display the TIME value in your preferred way using the TIME_FORMAT function.
The TIME_FORMAT function is like the DATE_FORMAT function except that the TIME_FORMAT function is used to format a TIME value only.
See the following example.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
SELECT
name,
TIME_FORMAT(start_at, ''%h:%i %p'') start_at,
TIME_FORMAT(end_at, ''%h:%i %p'') end_at
FROM
tests;
|
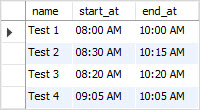
In the time format string above:
-
%hmeans two-digit hours from 0 to 12. -
%imeans two-digit minutes from 0 to 60. -
%pmeans AM or PM.
Extracting hour, minute, and second from a TIME value
To extract the hour, minute, and second from a TIME value, you use HOUR, MINUTE, and SECONDfunctions as follows:
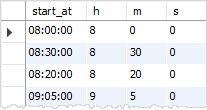
Getting UTC time value
To get the UTC time, you use UTC_TIME function as follows:
|
1
2
3
|
SELECT
CURRENT_TIME(),
UTC_TIME();
|
![]()
In this tutorial, we have been covered a lot about MySQL TIME data type and some commonly used temporal functions for manipulating TIME values.

docker mysql master slave
#!/bin/bash
master_port=3306
master_name=mysql_master
slave_port=3307
slave_name=mysql_slave
passwd=123456
# -------------------------------
docker run \
--name ${master_name} \
-h ${master_name} \
-p ${master_port}:3306 \
-v /data/${master_name}/conf:/etc/mysql/conf.d \
-v /data/${master_name}/data:/var/lib/mysql \
-v /data/${master_name}/logs:/var/log/mysql \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=${passwd} \
-d mysql:5.6
docker run \
--name ${slave_name} \
-h ${slave_name} \
-p ${slave_port}:3306 \
-v /data/${slave_name}/conf:/etc/mysql/conf.d \
-v /data/${slave_name}/data:/var/lib/mysql \
-v /data/${slave_name}/logs:/var/log/mysql \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=${passwd} \
--link ${master_name}:mysql_master \
-d mysql:5.6
cat > /data/${master_name}/conf/my.cnf << EOF
[mysqld]
server_id=1
log-bin=mysql-bin
binlog-ignore-db=information_schema
binlog-ignore-db=performance_schema
max_connections=2000
slow-query-log=1
slow-query-log-file=/var/log/mysql/mysql-slow.log
long_query_time=3
log-queries-not-using-indexes
wait_timeout=600
interactive_timeout=600
EOF
cat > /data/${slave_name}/conf/my.cnf << EOF
[mysqld]
server_id=2
log-bin=mysql-bin
binlog-ignore-db=information_schema
binlog-ignore-db=performance_schema
log-slave-updates
slave-skip-errors=all
slave-net-timeout=60
max_connections=2000
slow-query-log=1
slow-query-log-file=/var/log/mysql/mysql-slow.log
long_query_time=3
log-queries-not-using-indexes
wait_timeout=600
interactive_timeout=600
EOF
docker restart ${master_name}
docker restart ${slave_name}
sleep 3s
docker exec -it ${master_name} echo "Asia/shanghai" > /etc/timezone
docker exec -it ${master_name} cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
docker exec -it ${master_name} date
docker exec -it ${slave_name} echo "Asia/shanghai" > /etc/timezone
docker exec -it ${slave_name} cp /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime
docker exec -it ${slave_name} date
docker exec -it ${master_name} mysql -uroot -p${passwd} -e "
grant replication slave on *.* to ''repl''@''172.17.0.%'' identified by ''Repl1580'';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO ''root''@''172.17.0.%'' IDENTIFIED BY ''${passwd}'' with grant option;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
delete from mysql.user where host = ''%'';
select host, user, password from mysql.user;
"
docker exec -it ${slave_name} mysql -uroot -p${passwd} -e "
stop slave;
change master to master_host=''mysql_master'',master_port=3306,master_user=''repl'',master_password=''Repl1580'';
start slave;
show slave status \G;
"

master and slave have equal MySQL server ids
蚊子今天下午搭了一主三从的
蚊子今天下午搭了一主三从的mysql复制,结果所有服务器都配置好后,,发现从上报如下的错误
复制代码 代码如下:
Last_IO_Error: Fatal error: The slave I/O thread stops because master and slave have equal MySQL server ids; these ids must be different for replication to work (or the --replicate-same-server-id option must be used on slave but this does not always make sense; please check the manual before using it).
意思就是从上的server_id和主的一样的,经查看发现从上的/etc/my.cnf中的server_id=1这行我没有注释掉(在下面复制部分我设置了server_id),于是马上把这行注释掉了,然后重启mysql,发现还是报同样的错误。
使用如下命令查看了一下server_id
复制代码 代码如下:
mysql> show variables like ''server_id'';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| server_id | 1 |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
发现,mysql并没有从my.cnf文件中更新server_id,既然这样就只能手动修改了
复制代码 代码如下:
mysql> set global server_id=2; #此处的数值和my.cnf里设置的一样就行
mysql> slave start;
如此执行后,slave恢复了正常。
不过稍后蚊子使用/etc/init.d/mysqld restart重启了mysql服务,然后查看slave状态,发现又出现了上面的错误,然后查看server_id发现这个数值又恢复到了1。
之后蚊子又重新查看了一下/etc/my.cnf的内容,确认应该不是这个文件的问题,于是去google查了一下,看到mysql在启动的时候会查找/etc/my.cnf、DATADIR/my.cnf,USER_HOME/my.cnf。
于是我执行了
复制代码 代码如下:
find / -name "my.cnf"
居然在/usr/local/mysql这个目录下发现了my.cnf文件,于是蚊子将这个文件删除了,然后再重启mysql服务,发现一切恢复了正常。如果有人也出现类似的问题,不妨试试这个办法吧。

master and slave have equal MySQL server UUIDs 解决方法
使用rsync配置了大量
使用rsync配置了大量mysql,省去了大量编译和配置的时间,随逐个修改master和slave服务器的my.cnf,后,发现数据不能同步
使用rsync配置了大量mysql,省去了大量编译和配置的时间,随逐个修改master和slave服务器的my.cnf,后,发现数据不能同步,
在slave服务器show slave status:
Fatal error: The slave I/O thread stops because master and slave have equal MySQL server UUIDs; these UUIDs must be different for replication to work.
首先检查:
mysql> show variables like ‘server_id'';
+—————+——-+
| Variable_name | Value |
+—————+——-+
| server_id | 3 |
+—————+——-+
主从并不一样,排除该问题。
继续排查,找到原因在于,拷贝整个data目录,把auto.cnf文件也拷贝过来了,里面记录了数据库的uuid,,每个库的uuid应该是不一样的。
[auto]
server-uuid=6dcee5be-8cdb-11e2-9408-90e2ba2e2ea6
解决办法,按照这个16进制格式,随便改下,重启mysql即可。
关于带有Mysql Master / Slave的Datamapper和mysql daul的介绍已经告一段落,感谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于A2-04-10.MySQL DATA TYPES-Mastering MySQL TIME Data Type、docker mysql master slave、master and slave have equal MySQL server ids、master and slave have equal MySQL server UUIDs 解决方法的相关信息,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:





