想了解使用ReactNative和django-modeltranslation更改语言的新动态吗?本文将为您提供详细的信息,我们还将为您解答关于reactnative多语言切换的相关问题,此外,我们
想了解使用 React Native 和 django-modeltranslation 更改语言的新动态吗?本文将为您提供详细的信息,我们还将为您解答关于react native 多语言切换的相关问题,此外,我们还将为您介绍关于ACL2019: 《GraphRel: Modeling Text as Relational Graphs for Joint Entity and Relation Extraction》源码解析、Android ReactNative java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError:可以找到要加载的DSO:libreactnativejni.so、ArangoDB - a native multi-model database、Connecting Language and Knowledge Bases with Embedding Models for Relation Extraction的新知识。
本文目录一览:- 使用 React Native 和 django-modeltranslation 更改语言(react native 多语言切换)
- ACL2019: 《GraphRel: Modeling Text as Relational Graphs for Joint Entity and Relation Extraction》源码解析
- Android ReactNative java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError:可以找到要加载的DSO:libreactnativejni.so
- ArangoDB - a native multi-model database
- Connecting Language and Knowledge Bases with Embedding Models for Relation Extraction

使用 React Native 和 django-modeltranslation 更改语言(react native 多语言切换)
如果你想让你的应用程序完全多语言,你需要做两件事。
- 适用于您的应用的翻译系统
- API 的翻译系统。
首先,使用预先构建的上下文 api 或创建自己的上下文 api 以支持更改应用程序内的语言。像这样:https://medium.com/@ally_20818/multi-language-text-with-react-native-react-context-b76d5677346d
当用户更改语言时,将语言名称或密钥存储在 async-storage 或其他一些数据库中。
根据所选语言更改 react-native 端的文本。
在进行 api 调用时,也要发送所选语言。在 api 端获取所选语言并根据语言返回相应的文本。
更新:
由于您没有在 react-native 端存储任何文本,您只需要添加一个选择器(react-native-picker/picker 是一个本地选择器)并存储所选的语言键(en、de、uk 等) case) 在像 react-native-async-storage 这样的数据库中。当您使用 react-native 发出 api 请求时,请包含一个额外的标头或发布数据,其中包含选定的语言键。您可以在 django 后端获取并使用该密钥。

ACL2019: 《GraphRel: Modeling Text as Relational Graphs for Joint Entity and Relation Extraction》源码解析
论文地址:《GraphRel: Modeling Text as Relational Graphs for Joint Entity and Relation Extraction》
GitHub 地址:GraphRel
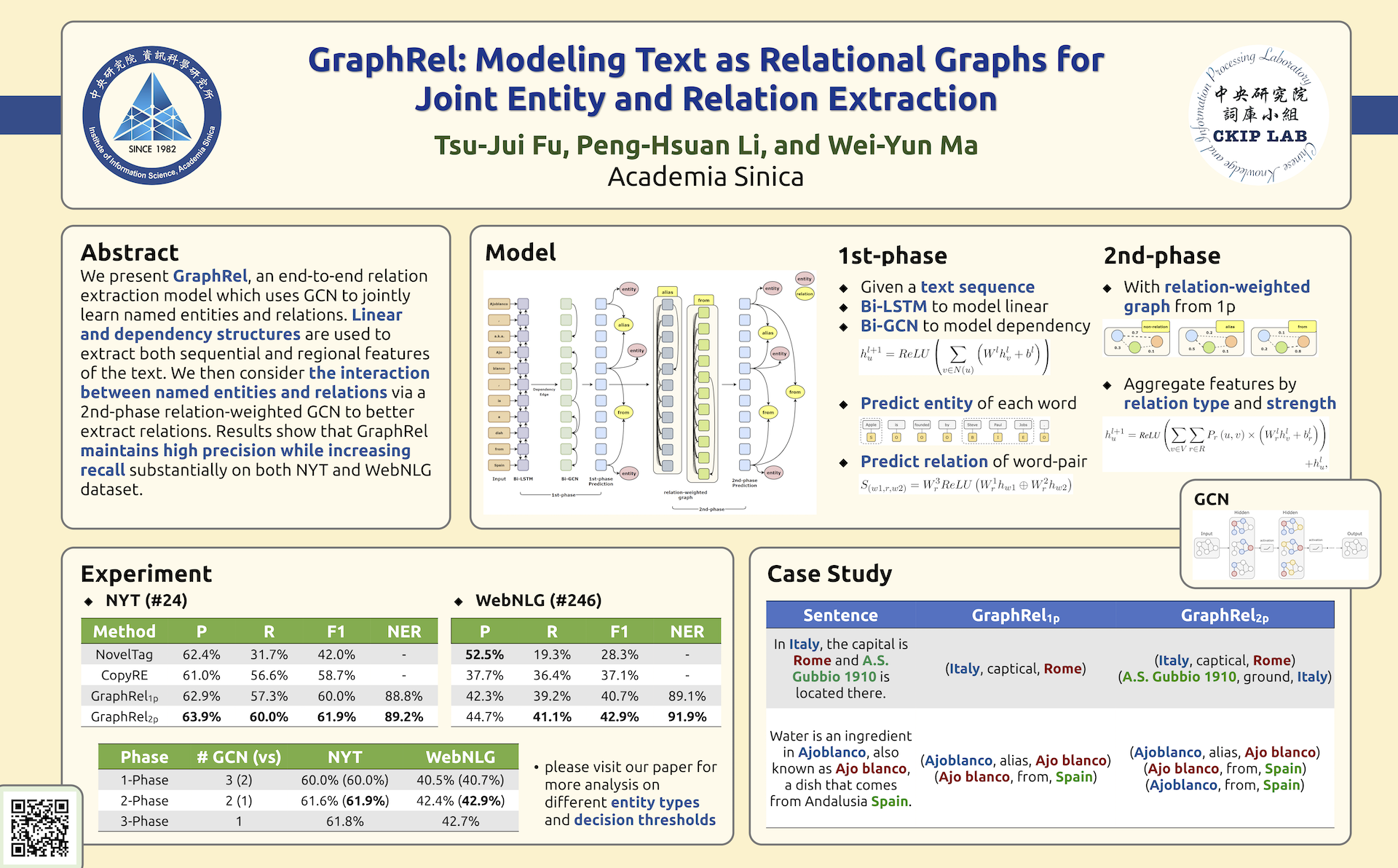
提出一种端到端关系抽取模型 GraphRel,该模型利用图卷积网络(GCNs)来联合学习命名实体和实体间关系。与以往的 baseline 相比,我们通过关系加权 GCN 来考虑命名实体和关系之间的交互,以更好地提取关系。线性结构和依存句法结构用来提取文本的序列特征和区域特征,而完整的词图则进一步用于提取文本所有词对之间的潜在特征。利用基于图的方法,对重叠关系的预测比以前的顺序方法有了实质性的改进。我们在两个公开数据集上评估 GraphRel: NYT 和 WebNLG。结果表明,GraphRel 在保持较高的查准率(Precision)的同时,显著提高了查全率(Recall)。此外,GraphRel 的性能比之前的研究分别提高了 3.2% 和 5.8%(F1 分数),为关系抽取提供了一个新的技术水平。
下图为本文模型结构:

在第一阶段,我们采用 BiRNN 和 GCN 两种方法来提取顺序依存词和区域依存词的特征。给定单词特征,我们预测每个单词的关系和所有单词的实体。然后,在第二阶段,基于预测的第一阶段的关系,我们为每一个关系建立完整的关系图,在每一个图上整合实体与实体之间的每一个关系。
下图为 Poster:
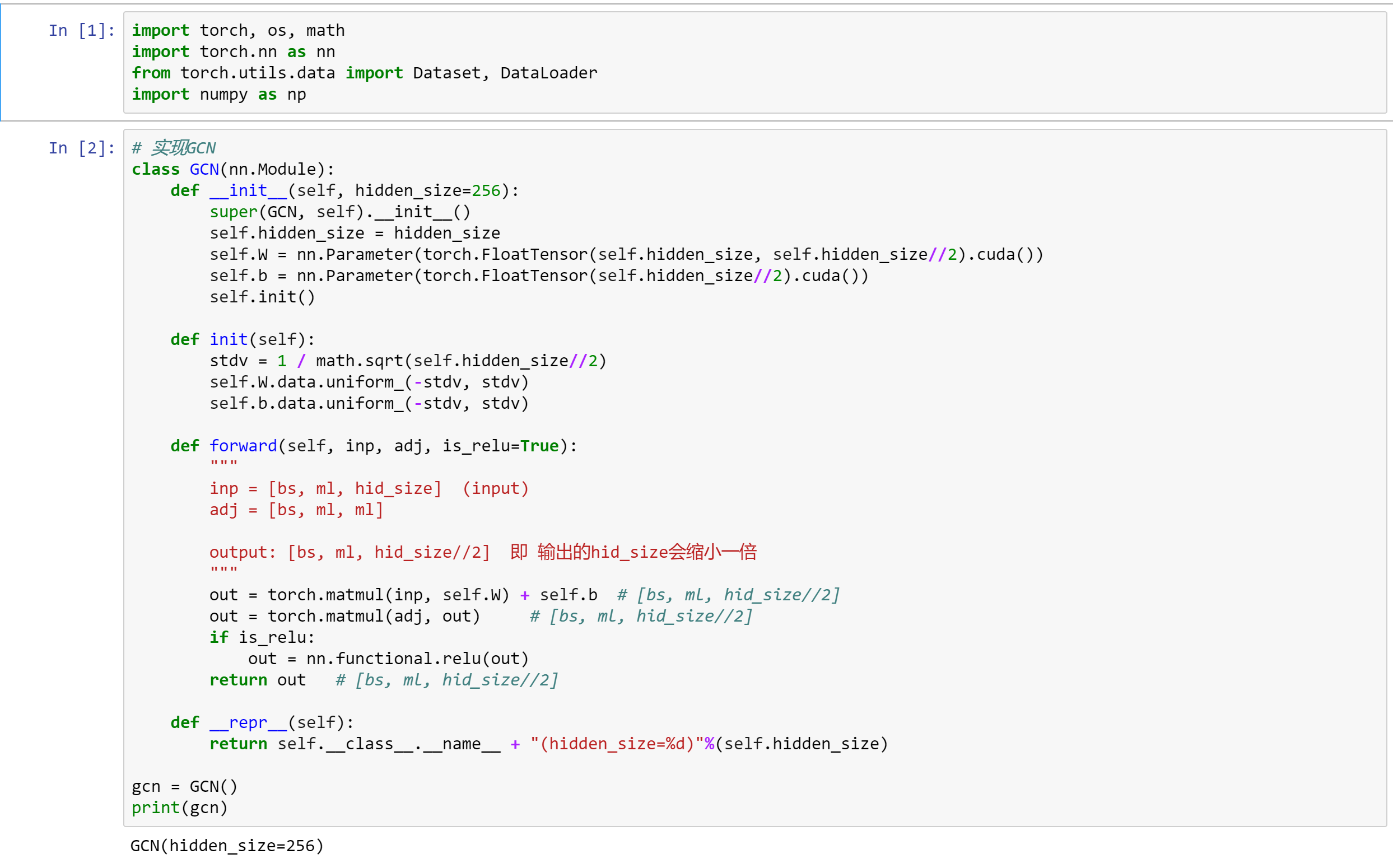
以下为源码解析:




以上。总结一下:本文 idea 比较新颖,值得细读,是一篇真正的 ACL 顶会文章~

Android ReactNative java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError:可以找到要加载的DSO:libreactnativejni.so
我一直在尝试将ReactNative添加到我现有的android应用程序中.我遵循了this链接中的说明.我可以添加它,但是一旦打开react native活动,应用程序就会崩溃.我已经开始使用服务器
adb reverse tcp:8081 tcp:8081
并开始使用本机
react-native start
我得到一个对话框,提示js文件正在加载.但是最后以崩溃告终.以下是在logcat中打印的错误:
java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError: Couldn't find DSO to load: libreactnativejni.so
at com.facebook.soloader.soLoader.loadLibraryBySoName(SoLoader.java:213)
at com.facebook.soloader.soLoader.loadLibrary(SoLoader.java:178)
at com.facebook.react.bridge.JSCJavaScriptExecutor.<clinit>(JSCJavaScriptExecutor.java:19)
at com.facebook.react.ReactInstanceManager.onjsBundleLoadedFromServer(ReactInstanceManager.java:413)
at com.facebook.react.ReactInstanceManager.createReactContextInBackground(ReactInstanceManager.java:236)
我完全迷路了,因为我无法找出导致此问题的原因.
提前致谢.
解决方法:
这是由以下问题引起的(开放2年)https://github.com/facebook/react-native/issues/2814
从问题:
React Native on Android doesn’t provide a 64-bit version of the
libreactnativejni.sonative library, which can cause compatibility issues on 64-bit devices. I ran into this while attempting to integrate React Native with a large existing application I’m developing.
来自Facebook的反应:
“Thanks for reporting! Yes we don’t provide 64-bit version of the native code and the system should always fall back to 32-bit.“
And:
“Most Android projects use a number of 3rd-party libraries, and any that include native 64-bit code will cause React Native to fail.“
以下SO回答Use 32-bit jni libraries on 64-bit android解释了回退到32位库以及您无法混合使用的事实.因此,如果找到64位,则所有都应为64位
我建议阅读Github问题#2814.建议了多个修复程序,但是哪种方法有效取决于您的情况.
发行人还写了一个博客:Mixing 32- and 64-bit Dependencies in Android
希望这可以帮助!

ArangoDB - a native multi-model database
Unlike many NoSQL databases, ArangoDB is a native multi-model database. You can store your data as key/value pairs, graphs or documents and access any or all of your data using a single declarative query language. You can combine different models in one query. And, due to its native multi-model approach, you can build high performance applications and scale horizontally with all three data models.
Native vs. Layered
Many vendors call themselves “multi-model,” but there is an important difference between adding a graph layer to say a key/value or document store and ArangoDB’s native multi-mode approach.
With ArangoDB, using the same core and the same query language for all data models, users can combine different models and features in a single query. ArangoDB doesn’t “switch” between models behind the scenes and it doesn’t shovel data from A to B in order to execute queries. This gives ArangoDB stronger performance advantages when compared to the “layered” approaches.
For more information on performance, see High Performance with ArangoDB.
Database models
Document model
Each document in ArangoDB can store as many attributes as you like. (The default maximum size is 32MB, but you can configure it for larger documents.) ArangoDB provides a wide feature-set for querying and operating on documents, including horizontally scaled JOIN’s, secondary indexes, and ACID transactions.
Key/Value model
Every document has a unique key and stores data as values on attributes. When you store one value to the document, ArangoDB can serve as a modern and highly scalable key/value store. You might find this useful when storing shopping cart entries in an e-commerce platform or managing sensoric data for IoT applications.
Graph model
ArangoDB provides a mature graph store with a full feature-set, including pattern matching, shortest path, and complete traversals, and it can perform graph queries very fast compared to many leading graph solutions.
When building a graph, ArangoDB creates special documents to represent vertices and edges. These documents contain _to and _from attributes used in connecting documents. Using an edge index, ArangoDB can process graph queries with high performance.
Each edge and vertex can contain complex data in the form of nested properties, and all graph functions are deeply integrated into the ArangoDB Query Language, (AQL). These allow ArangoDB to compete with other graph solutions on performance. With ArangoDB you can also distribute your graph to a cluster.
When to use ArangoDB
Native multi-model databases shine particularly in three situations:
Staying flexible in developing new ideas
In situations when developing a new product or service, you might not know all your requirements for at the outset. Changes in your product or the need for new features can lead to changes in your data model.With a multi-model database, you are able to easily react to those changes. You can apply your knowledge of one technology to several use cases and requirements.No need to learn a new technology or build a new tech-stack.
Developing software as a team
ArangoDB enables teams to cooperate across use cases. For instance, one team starts work on an application that requires a Document database. In the course of development, members of this team learns tips and tricks about the usage of ArangoDB. Another team begins work on a Graph database.Both teams can exchange their experience with ArangoDB and optimize their usage. This shortens the learning curve, deepens teamwork and reduces the time to get your solutions live.
Combining different data models in one query
No need to build two or three tech-stacks to support your application. These create risky connections between different single-model databases. Instead, ArangoDB is designed it easier to develop modular applications.
Advantages of ArangoDB
Consolidation
As a native multi-model database, ArangoDB minimizes the components that you need to maintain, reducing the complexity of the technology stack for your application or usage. This means a lower total cost of ownership, increasing flexibility and consolidating your overall technical needs.
Simplified Performance Scaling
Applications grow and mature over time. With ArangoDB, you can easily react to growing performance and storage needs by independently scaling with different data models. ArangoDB scales both vertically and horizontally, and if your performance needs decrease, you can just as easily scale down your back-end system to save on hardware and operational requirements.
Reduced Operational Complexity
In the concept of Polyglot Persistence, the goal is to use the best tools for whatever jobs you may have. When working with single-model databases, this can lead to various operational challenges. Certain tasks require a document database, while others require a graph database. Integrating them is a complex task in itself, but creating a large cohesive system with data consistency and fault tolerance between separate, unrelated database systems may prove impossible.
Polyglot Persistence is about choosing the right data model for the right job. A native multi-model database allows you to have polyglot data without the complexity, but with data consistency on a fault tolerant system. With ArangoDB, you can use the right data model for the right job.
Strong Data Consistency
When using multiple single-model databases, data consistency becomes an issue. These databases aren’t meant to talk to each other, which means you need to implement some form of transaction functionality to keep your data consistent between different models.
With ArangoDB, a single back-end manages your different data models with support for ACID transactions. ArangoDB provides strong consistency on a single instance and atomic operations when operating in cluster mode.
Fault Tolerance
Building fault tolerant systems with many unrelated components is a challenging task in itself. When working with clusters, this grows even more difficult. Deploying and maintaining such systems requires deep expertise of several different technologies and technology stacks. Moreover, bringing together multiple subsystems that were designed to run independently imposes significant engineering and operational costs.
The solution to these challenges is a multi-model database and a consolidated technology stack. By design, ArangoDB enables modern, modular architectures with different data models running and works for cluster usage as well.
Lower Total Cost of Ownership
Each database technology you use needs ongoing maintenance, patches, bug fixes and other modifications delivered by the vendor. Each new update has to be tested by a specialized team member and tested for their overall fit into the current system. Using a multi-model database significantly reduces these maintenance costs as it allows you to reduce the number of database technologies you need for your application.
Transactions
It is a real challenge to provide transactional guarantees across multiple machines and few NoSQL database provide these guarantees. As a native multi-model database, ArangoDB requires transactions to ensure data consistency. ArangoDB provides strong consistency on single instances and atomic single document operations when running in cluster mode.

Connecting Language and Knowledge Bases with Embedding Models for Relation Extraction
摘要:这篇文章提出了一种新的从无结构文本中进行关系抽取的方式,这种方式从文本和现存知识中抽取关系。
信息抽取目标在于从无结构文本中生成结构化数据来补全知识库。
这篇文章主要关注基于弱监督从知识库(KB knowledge base)中进行关系抽取(RE relation extraction)
关系(RE)抽取是信息抽取(IE information extraction)的子任务,考虑所有的实体通过不同的方式已经被检测出来,比如命名实体识别。关系抽取是在给定一对提取的实体(h,t)作为上下文的情况下,将文本序列中陈述为真的关系对应到知识库中的关系。该任务是弱监督的,因为文本中检测到的每一个实体对(h,t),所有提及的关系都将被标记为知识库中连接h和t的关系,无论是否实际表达是或否。
我们的方法更容易整合到现存的系统中,因为KB数据是通过额外的评分项目来使用的,评分是预先单独训练的,不共享嵌入式表示。此外,我们实验部分展示了我们系统可以处理大量关系。
3 基于嵌入式的框架(Embedding-based Framework)
我们学习两个模型:
1、将文本中提及的关系对应知识库中关系
2、知识库中实体和关系的嵌入式表示向量
上两种模型使得我们可以同时使用文本语料库和知识库信息进行关系抽取
每一个子模型的目标都是学习知识库中实体或关系,或者文本中的单词或特征的嵌入式表示向量
嵌入式到底是什么
3.1 连接文本和关系
Sm2r(m,r)函数:基于嵌入式,对文本中提到的关系m和知识库中关系r的相似性进行评分。
首先将单词和特征投影到嵌入空间,计算这个投影和关系嵌入之间的相似性(文中的点积)

f(m)将文本中存在的单词或特征的向量简单的累加,再与r相乘
关系抽取的性能指标有时使用针对同一实体对的所有提及聚合的精确召回曲线(precision recall curves)来测量。在这种情况下,需要校准不同提及的预测分数,以便最有信息的分数越高。
我们今天的关于使用 React Native 和 django-modeltranslation 更改语言和react native 多语言切换的分享已经告一段落,感谢您的关注,如果您想了解更多关于ACL2019: 《GraphRel: Modeling Text as Relational Graphs for Joint Entity and Relation Extraction》源码解析、Android ReactNative java.lang.UnsatisfiedLinkError:可以找到要加载的DSO:libreactnativejni.so、ArangoDB - a native multi-model database、Connecting Language and Knowledge Bases with Embedding Models for Relation Extraction的相关信息,请在本站查询。
本文标签:





