对于想了解jsonlib中jsonConfig的配置的读者,本文将是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将详细介绍jsonconfig设置,并且为您提供关于angular–如何创建配置文件(tsconfig.js
对于想了解jsonlib中jsonConfig的配置的读者,本文将是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将详细介绍jsonconfig设置,并且为您提供关于angular – 如何创建配置文件(tsconfig.json,typings.json,package.json)?、angular项目中ts的配置编译tsconfig.json、C#轻量级配置文件组件EasyJsonConfig、com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField的实例源码的有价值信息。
本文目录一览:- jsonlib中jsonConfig的配置(jsonconfig设置)
- angular – 如何创建配置文件(tsconfig.json,typings.json,package.json)?
- angular项目中ts的配置编译tsconfig.json
- C#轻量级配置文件组件EasyJsonConfig
- com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField的实例源码

jsonlib中jsonConfig的配置(jsonconfig设置)
json-lib的普及率应该还是比较广的,不过在Spring中倒是倾向于jackson,无奈新项目做到一般才知道jackson,所以还是依旧使用了json-lib~
改变某种类型默认值的序列化值
在序列化的时候,比较常见的问题是数据库为null的int型字段,被序列化后就赋值成0了,这在有些时候不是我们想看到的结果,那怎么办呢?
json-lib提供了JsonConfig对象供我们来自定义一些序列化时的操作:
jsonConfig.registerDefaultValueProcessor(Integer.class,new DefaultValueProcessor() {
@Override
public Object getDefaultValue(Class type) {
return null;
}
});
也就是说,对于需要 序列化的对象的Integer的字段来说,只要值为null(也就是Integer的默认值),那么在序列化成json的时候,该key的value则也会为null
我们可以通过以下代码测试一下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
JsonConfig jsonConfig = new JsonConfig();
jsonConfig.registerDefaultValueProcessor(Integer.class,new DefaultValueProcessor() {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public Object getDefaultValue(Class type) {
return "";
}
});
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setName("zhu");
employee.setRole(1);
System.out.println(JSONObject.fromObject(employee));
System.out.println(JSONObject.fromObject(employee,jsonConfig));
}
输出为:
{"depno":"","empno":"","groupno":0,"name":"zhu","online":0,"phone":"","role":1}
{"depno":"","groupno":null,"online":null,"role":1}
改变某种类型的序列化策略
就拿Date类型来说吧,如果说按照默认的序列化策略,看看会是什么结果:
{"birthday":{"date":24,"day":3,"hours":11,"minutes":33,"month":11,"seconds":4,"time":1419391984356,"timezoneOffset":-480,"year":114}}
我想大多数情况下你应该不会是想要这种结果吧?格式化成“yyyy-MM-dd”这种格式也许是最常见的
那么我们可以通过为Date类型的字段配置一个我们自己的Processor:
首先,我们需要实现JsonValueProcessor接口,这个接口有两个方法需要实现:
<pre name="code">public Object processObjectValue(String paramString,Object paramObject,JsonConfig paramJsonConfig); public Object processArrayValue(Object paramObject,JsonConfig paramJsonConfig);
当对象的某个属性是该类型时,那么调用processObjectValue(...)方法来序列化该属性
而当对象的某个属性是该类型的数组或List时,那么调用processArrayValue(...)方法来序列化该属性
知道了这个,下面我们就来实现序列化中Date类型的格式化吧,这里对于Date的数组类型就不处理了,直接返回null:
public static void main(String[] args) {
JsonConfig jsonConfig = new JsonConfig();
jsonConfig.registerjsonValueProcessor(Date.class,new JsonValueProcessor() {
/**
* paramString -> 参数名 paramObject -> 参数值
*/
@Override
public Object processObjectValue(String paramString,JsonConfig paramJsonConfig) {
if (paramObject == null) {
return null;
}
String ret = null;
try {
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat(
"yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
ret = format.format((Date) paramObject);
} catch (Exception e) {
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat(
"yyyy-MM-dd");
ret = format.format((Date) paramObject);
}
return ret;
}
@Override
public Object processArrayValue(Object paramObject,JsonConfig paramJsonConfig) {
return null;
}
});
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setName("zhu");
employee.setRole(1);
employee.setBirthday(new Date());
System.out.println("no jsonConfig:" + JSONObject.fromObject(employee));
System.out.println("with jsonConfig:" + JSONObject.fromObject(employee,jsonConfig));
}
输出结果是:
no jsonConfig:{"birthday":{"date":24,"hours":13,"minutes":46,"seconds":31,"time":1419399991491,"year":114},"depno":"","role":1}
with jsonConfig:{"birthday":"2014-12-24 13:46:31","role":1}过滤需要序列化的属性
public static void main(String[] args) {
JsonConfig jsonConfig = new JsonConfig();
jsonConfig.setJsonPropertyFilter(new PropertyFilter() {
@Override
public boolean apply(Object source,String name,Object value) {
return value == null;
}
});
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setName("zhu");
employee.setRole(1);
System.out.println("no jsonConfig:" + JSONObject.fromObject(employee));
System.out.println("with jsonConfig:" + JSONObject.fromObject(employee,jsonConfig));
}
输出结果是:
no jsonConfig:{"birthday":null,"role":1}
with jsonConfig:{"name":"zhu","role":1}第二种过滤方式,直接根据属性的名称:
public static void main(String[] args) {
JsonConfig jsonConfig = new JsonConfig();
jsonConfig.setExcludes(new String[] { "depno","empno","groupno","online" });
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setName("zhu");
employee.setRole(1);
System.out.println("no jsonConfig:" + JSONObject.fromObject(employee));
System.out.println("with jsonConfig:"
+ JSONObject.fromObject(employee,jsonConfig));
}
可以看到,这里通过jsonConfig.setExcludes(new String[]{"double","boolean"});将double和boolean这两个属性
输出结果:
no jsonConfig:{"birthday":null,"role":1}
with jsonConfig:{"birthday":null,"role":1}

angular – 如何创建配置文件(tsconfig.json,typings.json,package.json)?
但我想更多地了解这些文件.
我们如何手动创建它?
从哪里可以了解更多关于这些文件的信息?
包括有关项目使用的包和库的信息,
还可以包含npm脚本,它有助于运行应用程序的任务,如运行测试,构建js等等……
npm init来初始化新的package.json文件
文档:
npm docs
tsconfig.json
提供有关将过程打字稿编译为javascript的信息.在哪个版本应该编译ts,js文件应该包括源映射,以及此文件中通常描述的此类信息.
tsc –init到init新的tsconfig.json文件
docs:tsconfig docs
typings.json
包括对外部库的定义类型文件的引用,它可以帮助您的应用程序更智能感知.如果要为应用程序编写类型,则需要了解所使用的其他库的类型.
typings init初始化新的typings.json文件(应全局或本地安装)
更多信息:
typings package(帮助生成typings.json文件并保存依赖项)
types defenitions(库类型定义数据库)
full tsconfig scheme
希望它能帮到你!

angular项目中ts的配置编译tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
/* 基本选项 */
"target": "es5", // 指定 ECMAScript 目标版本: ''ES3'' (default), ''ES5'', ''ES2015'', ''ES2016'', ''ES2017'', or ''ESNEXT''
"module": "commonjs", // 指定使用模块: ''commonjs'', ''amd'', ''system'', ''umd'' or ''es2015''
"lib": [], // 指定要包含在编译中的库文件
"allowJs": true, // 允许编译 javascript 文件
"checkJs": true, // 报告 javascript 文件中的错误
"jsx": "preserve", // 指定 jsx 代码的生成: ''preserve'', ''react-native'', or ''react''
"declaration": true, // 生成相应的 ''.d.ts'' 文件
"sourceMap": true, // 生成相应的 ''.map'' 文件
"outFile": "./", // 将输出文件合并为一个文件
"outDir": "./", // 指定输出目录
"rootDir": "./", // 用来控制输出目录结构 --outDir.
"removeComments": true, // 删除编译后的所有的注释
"noEmit": true, // 不生成输出文件
"importHelpers": true, // 从 tslib 导入辅助工具函数
"isolatedModules": true, // 将每个文件做为单独的模块 (与 ''ts.transpileModule'' 类似).
/* 严格的类型检查选项 */
"strict": true, // 启用所有严格类型检查选项
"noImplicitAny": true, // 在表达式和声明上有隐含的 any类型时报错
"strictNullChecks": true, // 启用严格的 null 检查
"noImplicitThis": true, // 当 this 表达式值为 any 类型的时候,生成一个错误
"alwaysStrict": true, // 以严格模式检查每个模块,并在每个文件里加入 ''use strict''
/* 额外的检查 */
"noUnusedLocals": true, // 有未使用的变量时,抛出错误
"noUnusedParameters": true, // 有未使用的参数时,抛出错误
"noImplicitReturns": true, // 并不是所有函数里的代码都有返回值时,抛出错误
"noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": true, // 报告 switch 语句的 fallthrough 错误。(即,不允许 switch 的 case 语句贯穿)
/* 模块解析选项 */
"moduleResolution": "node", // 选择模块解析策略: ''node'' (Node.js) or ''classic'' (TypeScript pre-1.6)
"baseUrl": "./", // 用于解析非相对模块名称的基目录
"paths": {}, // 模块名到基于 baseUrl 的路径映射的列表
"rootDirs": [], // 根文件夹列表,其组合内容表示项目运行时的结构内容
"typeRoots": [], // 包含类型声明的文件列表
"types": [], // 需要包含的类型声明文件名列表
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true, // 允许从没有设置默认导出的模块中默认导入。
/* Source Map Options */
"sourceRoot": "./", // 指定调试器应该找到 TypeScript 文件而不是源文件的位置
"mapRoot": "./", // 指定调试器应该找到映射文件而不是生成文件的位置
"inlineSourceMap": true, // 生成单个 soucemaps 文件,而不是将 sourcemaps 生成不同的文件
"inlineSources": true, // 将代码与 sourcemaps 生成到一个文件中,要求同时设置了 --inlineSourceMap 或 --sourceMap 属性
/* 其他选项 */
"experimentalDecorators": true, // 启用装饰器
"emitDecoratorMetadata": true // 为装饰器提供元数据的支持
}
}

C#轻量级配置文件组件EasyJsonConfig
一、课程介绍
一、本次分享课程《C#轻量级配置文件EasyJsonConfig》适合人群如下:
1、有一定的NET开发基础。
2、喜欢阿笨的干货分享课程的童鞋们。
二、今天我们要如何优雅解决的项目中经常遇到配置文件config读写的痛点问题
1)、你是否在为找到一款轻量级配置文件组件四处寻找而感到烦恼?
2)、你是否在还在使用app.config、web.config这么原始的配置文件方式而感到烦恼?
3)、你是否在寻找一款可以支持自定义文件存储目录以及支持自定义配置文件项的组件而感到烦恼?
4)、你是否在寻找一款可以支持“热修改”( 而无要需重启应用程序读取配置文件)的配置文件组件而感到烦恼?(强烈推荐)
如果您大家有遇到这类配置文件读写烦恼的话,那么可以学习一下阿笨给大家分享的轻量级配置文件组件EasyJsonConfig。
废话不多说,直接上干货,我们不生产干货,我们只是干货的搬运工。
二、涉及覆盖的知识点
1、C# 自定义配置文件存储目录和自定义配置文件项(完全兼容Web项目和WinForm项目) (阿笨家的干货,开箱即用!)
2、C# 如何实现监听配置文件变更同时支持“热修改”读取(无需重启应用程序)。(强烈推荐)
3、C# 对象的深拷贝(Deep Copy)实战运用。
4、C# EasyJsonConfig实现自定义按照功能模块分类读写配置文件。(强烈推荐)
5、C# EasyJsonConfig实现全局读写配置文件appsettings.json。(强烈推荐)
6、如何优雅的一行代码搞定配置文件读取和写入漂亮的JSON格式配置文件。(强烈推荐)
7、C# 微软单元测试UnitTest项目应用程序运用。
三、源码在线解读和演示
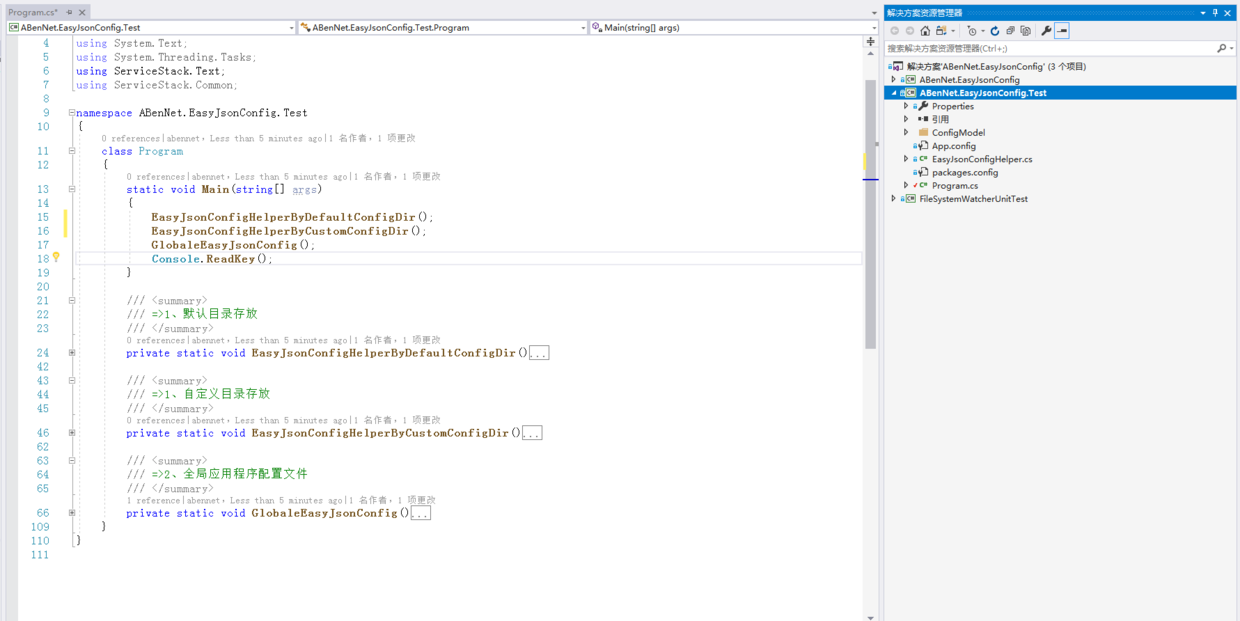
四、总结
一千个读者就有一千个哈姆雷特!仁者见仁智者见智。希望大家学习完阿笨分享的《C#轻量级配置文件组件EasyJsonConfig》课程后有所收获,做到学以致用,阿笨分享的”轮子“肯定不是最好的,也不可能满足适应所有的项目,大家可以根据自己的实际项目需求场景不断的升级和完善。
最后还是送大家一句话:师父领进门修行在个人,希望大家在学习的道路上一直坚持下。

com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField的实例源码
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public boolean isSymmetric(){
if (getRowCount() != getColumnCount()) return false;
for (Map.Entry<Integer,Vec> rowEntry : rows.entrySet())
{
int row = rowEntry.getKey();
Vec rowVec = rowEntry.getValue();
for (Integer col : rowVec.getData().keySet())
{
if (row == col.intValue()) continue;
if(Doubleutils.equals(rowVec.get(col),this.get(col,row))){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public FieldDeserializer createFieldDeserializer(ParserConfig mapping,//
JavaBeanInfo beanInfo,//
FieldInfo fieldInfo) {
Class<?> clazz = beanInfo.clazz;
Class<?> fieldClass = fieldInfo.fieldClass;
Class<?> deserializeUsing = null;
JSONField annotation = fieldInfo.getAnnotation();
if (annotation != null) {
deserializeUsing = annotation.deserializeUsing();
if (deserializeUsing == Void.class) {
deserializeUsing = null;
}
}
if (deserializeUsing == null && (fieldClass == List.class || fieldClass == ArrayList.class)) {
return new ArrayListTypeFieldDeserializer(mapping,clazz,fieldInfo);
}
return new DefaultFieldDeserializer(mapping,fieldInfo);
}
public static JSONField getSupperMethodAnnotation(Class<?> clazz,Method method) {
for (Class<?> interfaceClass : clazz.getInterfaces()) {
for (Method interfaceMethod : interfaceClass.getmethods()) {
if (interfaceMethod.getName().equals(method.getName()) && interfaceMethod.getParameterTypes().length == method.getParameterTypes().length) {
boolean match = true;
for (int i = 0; i < interfaceMethod.getParameterTypes().length; i++) {
if (!interfaceMethod.getParameterTypes()[i].equals(method.getParameterTypes()[i])) {
match = false;
break;
}
}
if (match) {
JSONField annotation = (JSONField) interfaceMethod.getAnnotation(JSONField.class);
if (annotation != null) {
return annotation;
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
public FieldDeserializer createFieldDeserializer(ParserConfig mapping,fieldInfo);
}
return new DefaultFieldDeserializerBug569(mapping,fieldInfo);
}
public FieldSerializer(FieldInfo fieldInfo){
super();
this.fieldInfo = fieldInfo;
fieldInfo.setAccessible(true);
this.double_quoted_fieldPrefix = '"' + fieldInfo.getName() + "\":";
this.single_quoted_fieldPrefix = '\'' + fieldInfo.getName() + "\':";
this.un_quoted_fieldPrefix = fieldInfo.getName() + ":";
JSONField annotation = fieldInfo.getAnnotation(JSONField.class);
if (annotation != null) {
for (SerializerFeature feature : annotation.serialzefeatures()) {
if (feature == SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue) {
writeNull = true;
}
}
}
}
public JSONField getAnnotation() {
if (this.fieldAnnotation != null) {
return this.fieldAnnotation;
}
return this.methodAnnotation;
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
protected String getPrimaryKey() {
if (primaryKey != null) {
return primaryKey;
}
String[] primaryKeys = getPrimaryKeys();
if (null != primaryKeys && primaryKeys.length == 1) {
primaryKey = primaryKeys[0];
}
JbootAssert.assertTrue(primaryKey != null,String.format("get PrimaryKey is error in[%s]",getClass()));
return primaryKey;
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public RemotingCommandType getType() {
if (this.isResponseType()) {
return RemotingCommandType.RESPONSE_COMMAND;
}
return RemotingCommandType.REQUEST_COMMAND;
}
private void _enum(Class<?> cls,MethodVisitor mw,FieldInfo property,Context context) {
boolean writeEnumUsingToString = false;
JSONField annotation = (JSONField) property.getAnnotation(JSONField.class);
if (annotation != null) {
for (SerializerFeature feature : annotation.serialzefeatures()) {
if (feature == SerializerFeature.WriteEnumUsingToString) {
writeEnumUsingToString = true;
}
}
}
Label _not_null = new Label();
Label _end_if = new Label();
Label _end = new Label();
_nameApply(mw,property,context,_end);
_get(mw,property);
mw.visitTypeInsn(192,"java/lang/Enum");
mw.visitvarInsn(58,context.var("enum"));
_filters(mw,_end);
mw.visitvarInsn(25,context.var("enum"));
mw.visitJumpInsn(199,_not_null);
_if_write_null(mw,context);
mw.visitJumpInsn(167,_end_if);
mw.visitLabel(_not_null);
mw.visitvarInsn(25,context.var("out"));
mw.visitvarInsn(21,context.var("seperator"));
mw.visitvarInsn(25,context.fieldName());
mw.visitvarInsn(25,context.var("enum"));
if (writeEnumUsingToString) {
mw.visitMethodInsn(182,"java/lang/Object","toString","()Ljava/lang/String;");
mw.visitMethodInsn(182,"com/alibaba/fastjson/serializer/SerializeWriter","writeFieldValue","(CLjava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)V");
} else {
mw.visitMethodInsn(182,"(CLjava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/Enum;)V");
}
_seperator(mw,context);
mw.visitLabel(_end_if);
mw.visitLabel(_end);
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public TransactionType getTransactionType() {
return transactionType;
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public boolean isrefundSuccess(int num) {
return String.valueOf(num).equals(successNum);
}
@JSONField(name="id")
public VOBuilder kkId(int id) {
vo.id = id;
return this;
}
@JSONField(name = "next_openid")
public void setNextOpenid(String nextOpenid) {
this.nextOpenid = nextOpenid;
}
@JSONField(deserialize = true)
public void setA3(String a3) {
this.a3 = a3;
}
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public boolean isOnewayRPC() {
int bits = 1 << RPC_ONEWAY;
return (this.flag & bits) == bits;
}
@JSONField(name="DESC")
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
@JSONField(name = "sub_button")
public void setSubButton(List<MenuButton> subButton) {
this.subButton = subButton;
}
@JSONField(name = "kf_nick")
public void setKfNick(String kfNick) {
this.kfNick = kfNick;
}
@JSONField(name="CName")
public String getCompanyName() {
return companyName;
}
@JSONField(name="CName")
public void setCompanyName(String companyName) {
this.companyName = companyName;
}
@JSONField(name = "sub_button")
public List<MenuButton> getSubButton() {
return subButton;
}
@JSONField(deserialize = false)
public void setA2(String a2) {
this.a2 = a2;
}
@JSONField(name="KV")
public void setKeepgoingValidate(boolean keepgoingValidate) {
this.keepgoingValidate = keepgoingValidate;
}
@JSONField(name = "mid")
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
@JSONField(name="CR")
public void setCheckCircularReference(boolean checkCircularReference) {
this.checkCircularReference = checkCircularReference;
}
@JSONField(serialize = true,deserialize = false)
public void setSpec(Spec spec) {
this.spec = spec;
}
@JSONField(label = "secret")
public String getpassword() {
return password;
}
/**
* 用户所在的分组ID
*/
@JSONField(name = "groupid")
public int getGroupId() {
return groupId;
}
/** @return the TSUID */
@JSONField(name = "tsuid")
public final String getTSUID() {
return tsuid;
}
@JSONField(serialzefeatures=SerializerFeature.disableCircularReferenceDetect)
public Object getB() {
return b;
}
@JSONField(name = "status")
public void setStatus(Integer status) {
this.status = status;
}
private void _enum(Class<?> clazz,Context context) {
boolean writeEnumUsingToString = false;
JSONField annotation = property.getAnnotation(JSONField.class);
if (annotation != null) {
for (SerializerFeature feature : annotation.serialzefeatures()) {
if (feature == SerializerFeature.WriteEnumUsingToString) {
writeEnumUsingToString = true;
}
}
}
Label _not_null = new Label();
Label _end_if = new Label();
Label _end = new Label();
_nameApply(mw,property);
mw.visitTypeInsn(CHECKCAST,"java/lang/Enum"); // cast
mw.visitvarInsn(ASTORE,context.var("enum"));
_filters(mw,_end);
mw.visitvarInsn(ALOAD,context.var("enum"));
mw.visitJumpInsn(IFNONNULL,context);
mw.visitJumpInsn(GOTO,_end_if);
mw.visitLabel(_not_null);
mw.visitvarInsn(ALOAD,context.var("out"));
mw.visitvarInsn(ILOAD,context.var("seperator"));
mw.visitvarInsn(ALOAD,context.fieldName());
mw.visitvarInsn(ALOAD,context.var("enum"));
if (writeEnumUsingToString) {
mw.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL,"()Ljava/lang/String;");
mw.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL,"(CLjava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/String;)V");
} else {
mw.visitMethodInsn(INVOKEVIRTUAL,"(CLjava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/Enum;)V");
}
_seperator(mw,context);
mw.visitLabel(_end_if);
mw.visitLabel(_end);
}
/** @param tsuid the TSUID to set */
@JSONField(name = "tsuid")
public final void setTSUID(String tsuid) {
this.tsuid = tsuid;
}
@Override
@JSONField(serialize = false)
public String getX() {
return x;
}
@JSONCreator
public HostPoint(@JSONField(name = "address") HostAddress addr) {
this.address = addr;
}
@JSONCreator
public Fingerprint(@JSONField(name = "source") String fingerprint) {
this.source = fingerprint;
}
/**
* 用户关注时间,为时间戳。
* 如果用户曾多次关注,则取最后关注时间
*/
@JSONField(name = "subscribe_time")
public String getSubscribeTime() {
return subscribeTime;
}
@JSONField(name = "groupid")
public void setGroupId(int groupId) {
this.groupId = groupId;
}
@JSONField(name = "_id")
public void set_id(Long _id) {
this._id = _id;
}
@JSONField void setBig(boolean value);
今天关于jsonlib中jsonConfig的配置和jsonconfig设置的介绍到此结束,谢谢您的阅读,有关angular – 如何创建配置文件(tsconfig.json,typings.json,package.json)?、angular项目中ts的配置编译tsconfig.json、C#轻量级配置文件组件EasyJsonConfig、com.alibaba.fastjson.annotation.JSONField的实例源码等更多相关知识的信息可以在本站进行查询。
本文标签:





