如果您想了解反射-->解析JSON数据和反射java的知识,那么本篇文章将是您的不二之选。我们将深入剖析反射-->解析JSON数据的各个方面,并为您解答反射java的疑在这篇文章中,我们将为您介绍反射
如果您想了解反射--> 解析JSON数据和反射java的知识,那么本篇文章将是您的不二之选。我们将深入剖析反射--> 解析JSON数据的各个方面,并为您解答反射java的疑在这篇文章中,我们将为您介绍反射--> 解析JSON数据的相关知识,同时也会详细的解释反射java的运用方法,并给出实际的案例分析,希望能帮助到您!
本文目录一览:- 反射--> 解析JSON数据(反射java)
- Android-Gson解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组)
- Android-解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组)
- C#使用LitJson解析Json数据
- C#解析json数据

反射--> 解析JSON数据(反射java)
方法一
Persons.json文件
[
{
"name": "Chris",
"age": 18,
"city": "Shanghai",
"job": "iOS"
},
{
"name": "Ada",
"age": 16,
"city": "Beijing",
"job": "student"
},
{
"name": "Rita",
"age": 17,
"city": "Xiamen",
"job": "HR"
}
]Model.h类
1 #import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
2
3 @interface PersonModel : NSObject
4
5 @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
6 @property (nonatomic, assign) NSInteger age;
7 @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *city;
8 @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *job;
9 @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *sex;
10
11 - (instancetype)initWithNSDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dict;
12
13 @end
Model.m类
1 #import "PersonModel.h"
2 #import <objc/runtime.h>
3
4 @implementation PersonModel
5
6 - (instancetype)initWithNSDictionary:(NSDictionary *)dict {
7 self = [super init];
8 if (self) {
9 [self prepareModel:dict];
10 }
11 return self;
12 }
13
14 - (void)prepareModel:(NSDictionary *)dict {
15 NSMutableArray *keys = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
16
17 u_int count = 0;
18 objc_property_t *properties = class_copyPropertyList([self class], &count);
19 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
20 objc_property_t property = properties[i];
21 const char *propertyCString = property_getName(property);
22 NSString *propertyName = [NSString stringWithCString:propertyCString encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
23 [keys addObject:propertyName];
24 }
25 free(properties);
26
27 for (NSString *key in keys) {
28 if ([dict valueForKey:key]) {
29 [self setValue:[dict valueForKey:key] forKey:key];
30 }
31 }
32 }
33
34 @end
调用
1 NSString *file = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"Persons" ofType:@"json"];
2 NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:file];
3 NSMutableArray *array = [NSJSONSerialization JSONObjectWithData:data options:NSJSONReadingMutableContainers error:nil];
4
5 for (NSDictionary *model in array) {
6 PersonModel *person = [[PersonModel alloc] initWithNSDictionary:model];
7 NSLog(@"%@, %ld, %@, %@", person.name, (long)person.age, person.city, person.job);
8 }
打印结果:

方法二
数据模型的父类是:JSONModel
JSONModel的子类是:JSONPerson, JSONStudent, JSONTeacther等;
JSONStudent.h中
1 @import JSONModel;
2
3 @interface JSONStudent : JSONModel
4
5 @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString * id;
6 @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString * name;
7 @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString * nickName;
8 @property (nonatomic, copy) NSString * phoneNumber;
9
10 @end
注意:这是用OC来写的!
获取属性
1 func getAllProperties<T: JSONModel>(anyClass: T) -> [String] {
2 var properties = [String]()
3 let count = UnsafeMutablePointer<UInt32>.allocate(capacity: 0)
4 let buff = class_copyPropertyList(object_getClass(anyClass), count)
5 let countInt = Int(count[0])
6
7 for i in 0..<countInt {
8 let temp = buff![i]
9 let tempPro = property_getName(temp)
10 let proper = String(utf8String: tempPro!)
11 properties.append(proper!)
12 }
13 return properties
14
15 }
注意:获取属性使用Swift写的,单纯用Swift和OC要简单!
使用
1 func returnListStudent(students: [JSONStudent]) {
2 for item in students {
3 let studentProperties = self.getAllProperties(anyClass: item)
4 for i in 0..< studentProperties.count{
5 print("值是:\(item.value(forKey: studentProperties[I]))" + "属性是:\(studentProperties[i])"self.dataError)
6 }
7 }
8 }
方法三
User.swift
1 import UIKit
2
3 class User: NSObject {
4 var name:String = "" //姓名
5 var nickname:String? //昵称
6 var age:Int? //年龄
7 var emails:[String]? //邮件地址
8 }
Mirror
属性
// 实例化
let user = User()
let mirror: Mirror = Mirror(reflecting:user)
// subjectType:对象类型
print(mirror.subjectType) // 打印出:User
// children:反射对象的属性集合
// displayStyle:反射对象展示类型
// advance 的使用
let children = mirror.children
let p0 = advance(children.startIndex, 0, children.endIndex) // name 的位置
let p0Mirror = Mirror(reflecting: children[p0].value) // name 的反射
print(p0Mirror.subjectType) //Optional<String> 这个就是name 的类型
调用:
1 @objc func testOne() {
2 // 得到应用名称
3 let nameSpace = Bundle.main.object(forInfoDictionaryKey: "CFBundleName") as! String
4 let clsName = "User"
5 // 使用NSClassFromString通过类名得到实例(得到类的完整路径, 注意分隔符是小数点;并判断数据类型是否符合预期。 备注: as?后面的格式是类名.Type, cls可能是nil)
6 guard let cls = NSClassFromString(nameSpace + "." + clsName) as? NSObject.Type else { return } //得到类完整路径
7 print("------_>\(cls)")
8 let user = cls.init()
9 print("------111111_>\(user)")
10
11 // 使用Mirror得到属性值
12 let mirror = Mirror(reflecting: user)
13 for case let(key?, value) in mirror.children {
14 print("key:\(key), value: \(value)") //打印成员属性
15 }
16 print(mirror.subjectType) //反射对象的数据类型</span>
17
18 }
打印:


Android-Gson解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组)
上一篇博客,Android-解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组),介绍了使用 org.json.JSONArray;/org.json.JSONObject; 来解析JSON数据;
Google Android 还提供来另外一种方式来解析JSON数据,那就是Gson;
Gson是非常方便的JSON解析/封装/处理等等,强大的工具类:
特点:Gson可以把JSON对象数据->转换映射为Bean对象
Gson可以把JSON数组数据->转换映射为集合
Gson可以把Bean对象->转换为JSON对象数据
Gson可以把集合->转换为JSON数组数据
...........
首先要在app/build.gradle配置文件中,导入,Gson支持包
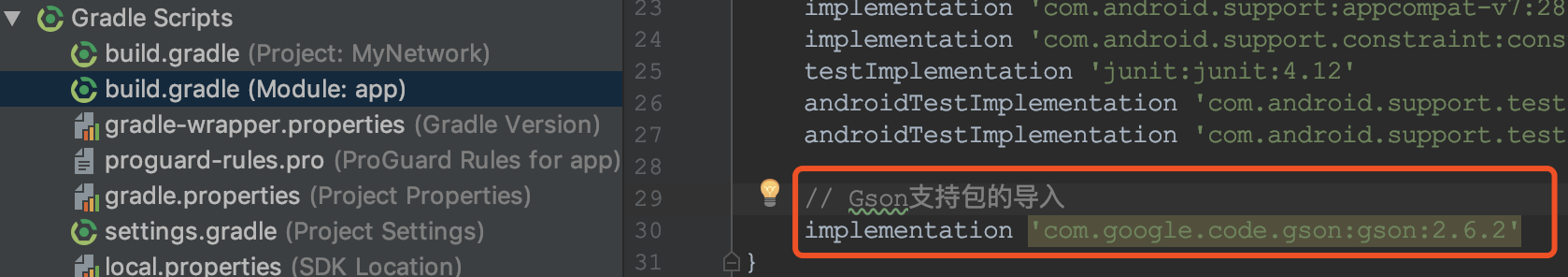
// Gson支持包的导入
implementation ''com.google.code.gson:gson:2.6.2''
需要解析的JSON数据:
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSON1
{
"name":"李四",
"age":99,
"hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
}/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSONArray1
[
{
"name":"君君",
"age":89,
"sex":"男"
},
{
"name":"小君",
"age":99,
"sex":"女"
},
{
"name":"大君",
"age":88,
"sex":"男"
}
]
定义一个Bean
定义的name/age/hobby 必须要和JSON数据里面的一模一样
package liudeli.mynetwork01.entity;
/**
* 定义一个Bean
* 定义的name/age/hobby 必须要和JSON数据里面的一模一样
* {
* "name":"李四",
* "age":99,
* "hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
* }
*/
public class Student2 {
private String name;
private int age;
private String hobby;
public Student2(String name, int age, String hobby) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name=''" + name + ''\'''' +
", age=" + age +
", hobby=''" + hobby + ''\'''' +
''}'';
}
}
定义的name/age/sex 必须要和JSON数据里面的一模一样
package liudeli.mynetwork01.entity;
/**
* 定义一个Bean
* 定义的name/age/sex 必须要和JSON数据里面的一模一样
*
* [
* {
* "name":"君君",
* "age":89,
* "sex":"男"
* },
* {
* "name":"小君",
* "age":99,
* "sex":"女"
* },
* {
* "name":"大君",
* "age":88,
* "sex":"男"
* }
* ]
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public Student(String name, int age, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name=''" + name + ''\'''' +
", age=" + age +
", sex=''" + sex + ''\'''' +
''}'';
}
}
GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity.java
package liudeli.mynetwork01;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import liudeli.mynetwork01.entity.Student;
import liudeli.mynetwork01.entity.Student2;
public class GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity extends Activity {
private final String TAG = GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity.class.getSimpleName();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_gson_analyze);
}
/**
* Gson解析JSON对象
* {
* "name":"李四",
* "age":99,
* "hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
* }
*/
public void gonsAnalyzeJSONObject(View view) {
String jsonData = readFile("pottingJSON1");
// Log.d(TAG, "jsonData:" + jsonData);
Gson gson = new Gson();
Student2 student2 = gson.fromJson(jsonData, Student2.class);
Log.d(TAG, "gonsAnalyzeJSONObject 解析后的结果:" + student2.toString());
}
/**
* Gson解析JSON数组
* [
* {
* "name":"君君",
* "age":89,
* "sex":"男"
* },
* {
* "name":"小君",
* "age":99,
* "sex":"女"
* },
* {
* "name":"大君",
* "age":88,
* "sex":"男"
* }
* ]
* @param view
*/
public void gonsAnalyzeJSONArray(View view) {
String jsonData = readFile("pottingJSONArray1");
// Log.d(TAG, "jsonData:" + jsonData);
Gson gson = new Gson();
/**
* TypeToken<List<需要映射的Bean对象>>(){}.getType()
*/
List<Student> list = gson.fromJson(jsonData, new TypeToken<List<Student>>(){}.getType()); // 参数二:需要指定类型,类型来决定解析的集合
for (Student student: list) {
Log.d(TAG, "gonsAnalyzeJSONArray 解析后的结果:" + student.toString());
}
}
/**
* 读取文件里面的字符串
* @param fileName
* @return
*/
private String readFile(String fileName) {
String result = null;
try {
InputStream inputStream = openFileInput(fileName);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[inputStream.available()];
inputStream.read(bytes);
baos.write(bytes, 0,bytes.length);
result = new String(baos.toByteArray());
baos.close();
inputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
activity_gson_analyze.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Gson解析JSON对象"
android:onClick="gonsAnalyzeJSONObject"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Gson解析JSON数组"
android:onClick="gonsAnalyzeJSONArray"
/>
</LinearLayout>
日志的打印:
使用Gson解析,JSON对象数据:
12-23 23:00:52.108 9729-9729/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity: gonsAnalyzeJSONObject 解析后的结果:Student{name=''李四'', age=99, hobby=''爱好是练习截拳道''}
使用Gson解析,JSON数组数据:
12-23 23:00:53.199 9729-9729/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity: gonsAnalyzeJSONArray 解析后的结果:Student{name=''君君'', age=89, sex=''男''}
12-23 23:00:53.199 9729-9729/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity: gonsAnalyzeJSONArray 解析后的结果:Student{name=''小君'', age=99, sex=''女''}
12-23 23:00:53.199 9729-9729/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity: gonsAnalyzeJSONArray 解析后的结果:Student{name=''大君'', age=88, sex=''男''}

Android-解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组)
在上一篇博客中,Android-封装JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组),讲解到Android真实开发中更多的是去解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组)
封装JSON的数据是在服务器端进行封装了,Android更多的工作是解析(JSON对象/JSON数组),所以Android开发JSON数据的解析非常重要
JSON数据,是存储在文件里面:
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSON1
{
"name":"李四",
"age":99,
"hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
}
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSON2
{
"student":{
"name":"李四",
"age":99,
"hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
}
}
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSON3
{
"student":{
"name":"李四",
"age":99,
"hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道",
"dog":{
"name":"阿黄",
"age":77,
"sex":"母"
}
}
}
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSONArray1
[
{
"name":"君君",
"age":89,
"sex":"男"
},
{
"name":"小君",
"age":99,
"sex":"女"
},
{
"name":"大君",
"age":88,
"sex":"男"
}
]
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSONArray2
{
"person":[
{
"name":"君君",
"age":89,
"sex":"男"
},
{
"name":"小君",
"age":99,
"sex":"女"
},
{
"name":"大君",
"age":88,
"sex":"男"
}
]
}
为什么要使用jsonObject.optString, 不使用jsonObject.getString
因为jsonObject.optString获取null不会报错
看着JSON数据,一步一步的解析就好了,当明白JSON数据格式后,解析是非常容易的:
AnalyzeJSONActivity.java
package liudeli.mynetwork01;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class AnalyzeJSONActivity extends Activity {
private final String TAG = AnalyzeJSONActivity.class.getSimpleName();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_analyze_json);
}
/**
* 解析JSON对象
* {
* "name":"李四",
* "age":99,
* "hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
* }
* @param view
*/
public void analyzeJSON1(View view) {
String result = readFile("pottingJSON1");
// Log.d(TAG, "result:" + result);
try{
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(result);
/**
* 为什么要使用jsonObject.optString, 不使用jsonObject.getString
* 因为jsonObject.optString获取null不会报错
*/
String name = jsonObject.optString("name", null);
int age = jsonObject.optInt("age", 0);
String hobby = jsonObject.optString("hobby", null);
// 日志打印结果:
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSON1解析的结果:name:" + name + " age:" + age + " hobby:" + hobby);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 解析JSON对象-带Key
* {
* "student":{
* "name":"李四",
* "age":99,
* "hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
* }
* }
* @param view
*/
public void analyzeJSON2(View view) {
String result = readFile("pottingJSON2");
// Log.d(TAG, "result:" + result);
try{
// 整个最大的JSON对象
JSONObject jsonObjectALL = new JSONObject(result);
/**
* 为什么要使用jsonObject.optString, 不使用jsonObject.getString
* 因为jsonObject.optString获取null不会报错
*/
String student = jsonObjectALL.optString("student", null);
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(student)) {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(student);
String name = jsonObject.optString("name", null);
int age = jsonObject.optInt("age", 0);
String hobby = jsonObject.optString("hobby", null);
// 日志打印结果:
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSON2解析的结果:name:" + name + " age:" + age + " hobby:" + hobby);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 解析JSON对象-嵌套对象
* {
* "student":{
* "name":"李四",
* "age":99,
* "hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道",
* "dog":{
* "name":"阿黄",
* "age":77,
* "sex":"母"
* }
* }
* }
* @param view
*/
public void analyzeJSON3(View view) {
String result = readFile("pottingJSON3");
// Log.d(TAG, "result:" + result);
try{
// 整个最大的JSON对象
JSONObject jsonObjectALL = new JSONObject(result);
/**
* 为什么要使用jsonObject.optString, 不使用jsonObject.getString
* 因为jsonObject.optString获取null不会报错
*/
String student = jsonObjectALL.optString("student", null);
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(student)) {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(student);
String name = jsonObject.optString("name", null);
int age = jsonObject.optInt("age", 0);
String hobby = jsonObject.optString("hobby", null);
// 以下是dog JSON 对象相关的解析
String dogStr = jsonObject.optString("dog", null);
// 定义dog的JSON对象
JSONObject dogJSONObject = new JSONObject(dogStr);
String dogName = dogJSONObject.optString("name", null);
int dogAge = dogJSONObject.optInt("age", 0);
String dogSex = dogJSONObject.optString("sex", null);
// 日志打印结果:
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSON3解析的结果:name:" + name + " age:" + age + " hobby:" + hobby + "\n"
+ "dogName:" + dogName + " dogAge:" + dogAge + " dogSex:" + dogSex);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 解析JSON数组
* [
* {
* "name":"君君",
* "age":89,
* "sex":"男"
* },
* {
* "name":"小君",
* "age":99,
* "sex":"女"
* },
* {
* "name":"大君",
* "age":88,
* "sex":"男"
* }
* ]
* @param view
*/
public void analyzeJSONArray1(View view) {
String result = readFile("pottingJSONArray1");
// Log.d(TAG, "result:" + result);
try{
// 整个最大的JSON数组
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray(result);
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSONArray1 jsonArray:" + jsonArray);
// [{"name":"君君","age":89,"sex":"男"},{"name":"小君","age":99,"sex":"女"},{"name":"大君","age":88,"sex":"男"}]
for (int i = 0; i < jsonArray.length(); i++) {
// JSON数组里面的具体-JSON对象
JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);
String name = jsonObject.optString("name", null);
int age = jsonObject.optInt("age", 0);
String sex = jsonObject.optString("sex", null);
// 日志打印结果:
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSONArray1 解析的结果:name" + name + " age:" + age + " sex:" + sex);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 解析JSON数组-带Key
* {
* "person":[
* {
* "name":"君君",
* "age":89,
* "sex":"男"
* },
* {
* "name":"小君",
* "age":99,
* "sex":"女"
* },
* {
* "name":"大君",
* "age":88,
* "sex":"男"
* }
* ]
* }
* @param view
*/
public void analyzeJSONArray2(View view) {
String result = readFile("pottingJSONArray2");
// Log.d(TAG, "result:" + result);
try{
/**
* JSON数组在牛逼,一旦有了 key person 这样的标记,就必须先是个 JSON对象
* 最外层的JSON对象,最大的哪个 { ... }
*/
JSONObject jsonObjectALL = new JSONObject(result);
// 通过标识(person),获取JSON数组
JSONArray jsonArray = jsonObjectALL.getJSONArray("person");
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSONArray1 jsonArray:" + jsonArray);
// [{"name":"君君","age":89,"sex":"男"},{"name":"小君","age":99,"sex":"女"},{"name":"大君","age":88,"sex":"男"}]
for (int i = 0; i < jsonArray.length(); i++) {
// JSON数组里面的具体-JSON对象
JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);
String name = jsonObject.optString("name", null);
int age = jsonObject.optInt("age", 0);
String sex = jsonObject.optString("sex", null);
// 日志打印结果:
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSONArray2 解析的结果:name" + name + " age:" + age + " sex:" + sex);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 读取文件里面的字符串
* @param fileName
* @return
*/
private String readFile(String fileName) {
String result = null;
try {
InputStream inputStream = openFileInput(fileName);
byte[] bytes = new byte[inputStream.available()];
inputStream.read(bytes);
result = new String(bytes);
inputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 定义一个Bean
*/
/*class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String hobby;
public Student(String name, int age, String hobby) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name=''" + name + ''\'''' +
", age=" + age +
", hobby=''" + hobby + ''\'''' +
''}'';
}
}*/
}
activity_analyze_json.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="解析JSON对象"
android:onClick="analyzeJSON1"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="解析JSON对象-带Key"
android:onClick="analyzeJSON2"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="解析JSON对象-嵌套对象"
android:onClick="analyzeJSON3"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="解析JSON数组"
android:onClick="analyzeJSONArray1"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="解析JSON数组-带Key"
android:onClick="analyzeJSONArray2"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
所有解析JSON的Log打印:
analyzeJSON1
12-23 21:46:44.127 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSON1解析的结果:name:李四 age:99 hobby:爱好是练习截拳道
analyzeJSON2
12-23 21:46:59.161 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSON2解析的结果:name:李四 age:99 hobby:爱好是练习截拳道
analyzeJSON3
12-23 21:47:12.240 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSON3解析的结果:name:李四 age:99 hobby:爱好是练习截拳道
dogName:阿黄 dogAge:77 dogSex:母
analyzeJSONArray1
12-23 21:47:35.108 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSONArray1 解析的结果:name君君 age:89 sex:男
12-23 21:47:35.108 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSONArray1 解析的结果:name小君 age:99 sex:女
12-23 21:47:35.108 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSONArray1 解析的结果:name大君 age:88 sex:男
analyzeJSONArray2
12-23 21:47:55.457 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSONArray2 解析的结果:name君君 age:89 sex:男
12-23 21:47:55.457 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSONArray2 解析的结果:name小君 age:99 sex:女
12-23 21:47:55.457 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSONArray2 解析的结果:name大君 age:88 sex:男

C#使用LitJson解析Json数据
//接受MQ服务器返回的值
private void jieshou(string zhiling, string can1, string can2, string can3, string can4, string can5)
{
Console.Write("============================================="+"指令:" + zhiling + " can1=" + can1 + " can2=" + can2 + " can3=" + can3 + " can4=" + can4 + " can5=" + can5 + "\n");
if(can1=="0"&&can3==null){
Console.Write("对比分数不合格或服务器上没有这个人的人员信息");
}
else if (!can1.Equals("0")) {
Console.Write("服务没连接上!!!!");
}
else if (can1.Equals("0") && can3 != "" && can3 != null)
{
can3 = "cardId=" + can3;
//将can3的参数发送给服务器
byte[] ByteData = System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetBytes(can3);
//将数据发送给服务器,并返回json数据
string jieshou = PostData(path, ByteData);
Console.WriteLine("+++++++++++++++" + jieshou);
//使用LitJson的JsonData方法进行解析
JsonData deJson = JsonMapper.ToObject(jieshou);
//遍历返回的json数据
foreach (JsonData item in deJson)
{
//创建对象
User user = new User();
//名字
user.name = item["name"].ToString();
//Console.WriteLine(user.name = item["name"].ToString());
//身份证号码
user.cardId = item["cardId"].ToString();
//Console.WriteLine(user.name = item["cardId"].ToString());
//部门简称
user.DepartName = item["bumen"].ToString();
this.label2.Text = user.name + " " + user.DepartName;
//Console.WriteLine(user.name = item["bumen"].ToString());
}
}
}
//网络请求部分
public static string PostData(string url, byte[] postData)
{
HttpWebRequest myRequest = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(url);
myRequest.Method = "POST";
myRequest.ContentType = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded";
myRequest.ContentLength = postData.Length;
Stream newStream = myRequest.GetRequestStream();
// Send the data.
newStream.Write(postData, 0, postData.Length);
newStream.Close();
// Get response
HttpWebResponse myResponse = (HttpWebResponse)myRequest.GetResponse();
StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(myResponse.GetResponseStream(), Encoding.UTF8);
return reader.ReadToEnd();
}

C#解析json数据
借用的是七牛的C# sdk ,参考见文章最后。你也可以参考 Json.net开源库。感谢oschina网友的热心回复。using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.IO;
using QBox;
using LitJson;
using QBox.Auth;
namespace json_parse
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string confjson = "";
StreamReader sr = new StreamReader("./conf.json");
while (!sr.EndOfStream)
{
string str = sr.ReadLine();
confjson += str;
}
sr.Close();
Console.WriteLine(confjson);
Console.WriteLine();
LitJson.JsonData data = LitJson.JsonMapper.ToObject(confjson);//解析json
if (data.IsObject)
{
Console.WriteLine(data["is_public"]);
Console.WriteLine(data["key_prefix"]);
Console.WriteLine(data["debug_level"]);
}
LitJson.JsonData data1 = new LitJson.JsonData ();//产生json
data1["id"] = 10;
data1["name"] = "testname";
data1["point"] = new JsonData();
data1["point"]["x"] = 15;
data1["point"]["y"] = 20;
data1["score"] = new JsonData();
data1["score"].Add(90);
data1["score"].Add(100);
string jsondata1 = data1.ToJson();
Console.WriteLine(jsondata1);
Console.Read();
}
}
}{ "is_public": 1,
"key_prefix": "2013-8-14-",
"debug_level": 1
}今天的关于反射--> 解析JSON数据和反射java的分享已经结束,谢谢您的关注,如果想了解更多关于Android-Gson解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组)、Android-解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组)、C#使用LitJson解析Json数据、C#解析json数据的相关知识,请在本站进行查询。
本文标签:





