总结
以上是小编为你收集整理的使用jsoncpp解析JSON数据全部内容。
如果觉得小编网站内容还不错,欢迎将小编网站推荐给好友。

Android-Gson解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组)
上一篇博客,Android-解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组),介绍了使用 org.json.JSONArray;/org.json.JSONObject; 来解析JSON数据;
Google Android 还提供来另外一种方式来解析JSON数据,那就是Gson;
Gson是非常方便的JSON解析/封装/处理等等,强大的工具类:
特点:Gson可以把JSON对象数据->转换映射为Bean对象
Gson可以把JSON数组数据->转换映射为集合
Gson可以把Bean对象->转换为JSON对象数据
Gson可以把集合->转换为JSON数组数据
...........
首先要在app/build.gradle配置文件中,导入,Gson支持包
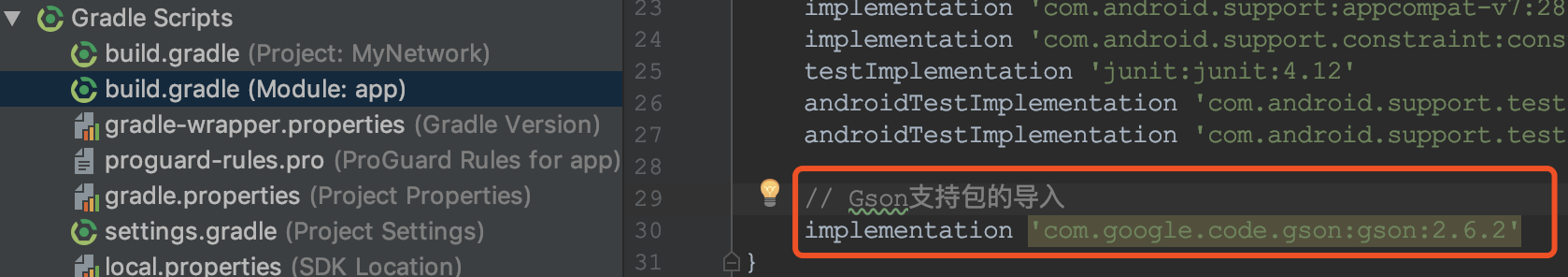
// Gson支持包的导入
implementation ''com.google.code.gson:gson:2.6.2''
需要解析的JSON数据:
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSON1
{
"name":"李四",
"age":99,
"hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
}
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSONArray1
[
{
"name":"君君",
"age":89,
"sex":"男"
},
{
"name":"小君",
"age":99,
"sex":"女"
},
{
"name":"大君",
"age":88,
"sex":"男"
}
]
定义一个Bean
定义的name/age/hobby 必须要和JSON数据里面的一模一样
package liudeli.mynetwork01.entity;
/**
* 定义一个Bean
* 定义的name/age/hobby 必须要和JSON数据里面的一模一样
* {
* "name":"李四",
* "age":99,
* "hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
* }
*/
public class Student2 {
private String name;
private int age;
private String hobby;
public Student2(String name, int age, String hobby) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name=''" + name + ''\'''' +
", age=" + age +
", hobby=''" + hobby + ''\'''' +
''}'';
}
}
定义的name/age/sex 必须要和JSON数据里面的一模一样
package liudeli.mynetwork01.entity;
/**
* 定义一个Bean
* 定义的name/age/sex 必须要和JSON数据里面的一模一样
*
* [
* {
* "name":"君君",
* "age":89,
* "sex":"男"
* },
* {
* "name":"小君",
* "age":99,
* "sex":"女"
* },
* {
* "name":"大君",
* "age":88,
* "sex":"男"
* }
* ]
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String sex;
public Student(String name, int age, String sex) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name=''" + name + ''\'''' +
", age=" + age +
", sex=''" + sex + ''\'''' +
''}'';
}
}
GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity.java
package liudeli.mynetwork01;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import com.google.gson.reflect.TypeToken;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import liudeli.mynetwork01.entity.Student;
import liudeli.mynetwork01.entity.Student2;
public class GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity extends Activity {
private final String TAG = GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity.class.getSimpleName();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_gson_analyze);
}
/**
* Gson解析JSON对象
* {
* "name":"李四",
* "age":99,
* "hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
* }
*/
public void gonsAnalyzeJSONObject(View view) {
String jsonData = readFile("pottingJSON1");
// Log.d(TAG, "jsonData:" + jsonData);
Gson gson = new Gson();
Student2 student2 = gson.fromJson(jsonData, Student2.class);
Log.d(TAG, "gonsAnalyzeJSONObject 解析后的结果:" + student2.toString());
}
/**
* Gson解析JSON数组
* [
* {
* "name":"君君",
* "age":89,
* "sex":"男"
* },
* {
* "name":"小君",
* "age":99,
* "sex":"女"
* },
* {
* "name":"大君",
* "age":88,
* "sex":"男"
* }
* ]
* @param view
*/
public void gonsAnalyzeJSONArray(View view) {
String jsonData = readFile("pottingJSONArray1");
// Log.d(TAG, "jsonData:" + jsonData);
Gson gson = new Gson();
/**
* TypeToken<List<需要映射的Bean对象>>(){}.getType()
*/
List<Student> list = gson.fromJson(jsonData, new TypeToken<List<Student>>(){}.getType()); // 参数二:需要指定类型,类型来决定解析的集合
for (Student student: list) {
Log.d(TAG, "gonsAnalyzeJSONArray 解析后的结果:" + student.toString());
}
}
/**
* 读取文件里面的字符串
* @param fileName
* @return
*/
private String readFile(String fileName) {
String result = null;
try {
InputStream inputStream = openFileInput(fileName);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] bytes = new byte[inputStream.available()];
inputStream.read(bytes);
baos.write(bytes, 0,bytes.length);
result = new String(baos.toByteArray());
baos.close();
inputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
}
activity_gson_analyze.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Gson解析JSON对象"
android:onClick="gonsAnalyzeJSONObject"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Gson解析JSON数组"
android:onClick="gonsAnalyzeJSONArray"
/>
</LinearLayout>
日志的打印:
使用Gson解析,JSON对象数据:
12-23 23:00:52.108 9729-9729/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity: gonsAnalyzeJSONObject 解析后的结果:Student{name=''李四'', age=99, hobby=''爱好是练习截拳道''}
使用Gson解析,JSON数组数据:
12-23 23:00:53.199 9729-9729/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity: gonsAnalyzeJSONArray 解析后的结果:Student{name=''君君'', age=89, sex=''男''}
12-23 23:00:53.199 9729-9729/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity: gonsAnalyzeJSONArray 解析后的结果:Student{name=''小君'', age=99, sex=''女''}
12-23 23:00:53.199 9729-9729/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/GsonAnalyzeJSONActivity: gonsAnalyzeJSONArray 解析后的结果:Student{name=''大君'', age=88, sex=''男''}

Android-解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组)
在上一篇博客中,Android-封装JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组),讲解到Android真实开发中更多的是去解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组)
封装JSON的数据是在服务器端进行封装了,Android更多的工作是解析(JSON对象/JSON数组),所以Android开发JSON数据的解析非常重要
JSON数据,是存储在文件里面:
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSON1
{
"name":"李四",
"age":99,
"hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
}
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSON2
{
"student":{
"name":"李四",
"age":99,
"hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
}
}
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSON3
{
"student":{
"name":"李四",
"age":99,
"hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道",
"dog":{
"name":"阿黄",
"age":77,
"sex":"母"
}
}
}
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSONArray1
[
{
"name":"君君",
"age":89,
"sex":"男"
},
{
"name":"小君",
"age":99,
"sex":"女"
},
{
"name":"大君",
"age":88,
"sex":"男"
}
]
/data/data/liudeli.mynetwork01/files/pottingJSONArray2
{
"person":[
{
"name":"君君",
"age":89,
"sex":"男"
},
{
"name":"小君",
"age":99,
"sex":"女"
},
{
"name":"大君",
"age":88,
"sex":"男"
}
]
}
为什么要使用jsonObject.optString, 不使用jsonObject.getString
因为jsonObject.optString获取null不会报错
看着JSON数据,一步一步的解析就好了,当明白JSON数据格式后,解析是非常容易的:
AnalyzeJSONActivity.java
package liudeli.mynetwork01;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.text.TextUtils;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import java.io.InputStream;
public class AnalyzeJSONActivity extends Activity {
private final String TAG = AnalyzeJSONActivity.class.getSimpleName();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_analyze_json);
}
/**
* 解析JSON对象
* {
* "name":"李四",
* "age":99,
* "hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
* }
* @param view
*/
public void analyzeJSON1(View view) {
String result = readFile("pottingJSON1");
// Log.d(TAG, "result:" + result);
try{
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(result);
/**
* 为什么要使用jsonObject.optString, 不使用jsonObject.getString
* 因为jsonObject.optString获取null不会报错
*/
String name = jsonObject.optString("name", null);
int age = jsonObject.optInt("age", 0);
String hobby = jsonObject.optString("hobby", null);
// 日志打印结果:
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSON1解析的结果:name:" + name + " age:" + age + " hobby:" + hobby);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 解析JSON对象-带Key
* {
* "student":{
* "name":"李四",
* "age":99,
* "hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道"
* }
* }
* @param view
*/
public void analyzeJSON2(View view) {
String result = readFile("pottingJSON2");
// Log.d(TAG, "result:" + result);
try{
// 整个最大的JSON对象
JSONObject jsonObjectALL = new JSONObject(result);
/**
* 为什么要使用jsonObject.optString, 不使用jsonObject.getString
* 因为jsonObject.optString获取null不会报错
*/
String student = jsonObjectALL.optString("student", null);
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(student)) {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(student);
String name = jsonObject.optString("name", null);
int age = jsonObject.optInt("age", 0);
String hobby = jsonObject.optString("hobby", null);
// 日志打印结果:
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSON2解析的结果:name:" + name + " age:" + age + " hobby:" + hobby);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 解析JSON对象-嵌套对象
* {
* "student":{
* "name":"李四",
* "age":99,
* "hobby":"爱好是练习截拳道",
* "dog":{
* "name":"阿黄",
* "age":77,
* "sex":"母"
* }
* }
* }
* @param view
*/
public void analyzeJSON3(View view) {
String result = readFile("pottingJSON3");
// Log.d(TAG, "result:" + result);
try{
// 整个最大的JSON对象
JSONObject jsonObjectALL = new JSONObject(result);
/**
* 为什么要使用jsonObject.optString, 不使用jsonObject.getString
* 因为jsonObject.optString获取null不会报错
*/
String student = jsonObjectALL.optString("student", null);
if (!TextUtils.isEmpty(student)) {
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject(student);
String name = jsonObject.optString("name", null);
int age = jsonObject.optInt("age", 0);
String hobby = jsonObject.optString("hobby", null);
// 以下是dog JSON 对象相关的解析
String dogStr = jsonObject.optString("dog", null);
// 定义dog的JSON对象
JSONObject dogJSONObject = new JSONObject(dogStr);
String dogName = dogJSONObject.optString("name", null);
int dogAge = dogJSONObject.optInt("age", 0);
String dogSex = dogJSONObject.optString("sex", null);
// 日志打印结果:
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSON3解析的结果:name:" + name + " age:" + age + " hobby:" + hobby + "\n"
+ "dogName:" + dogName + " dogAge:" + dogAge + " dogSex:" + dogSex);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 解析JSON数组
* [
* {
* "name":"君君",
* "age":89,
* "sex":"男"
* },
* {
* "name":"小君",
* "age":99,
* "sex":"女"
* },
* {
* "name":"大君",
* "age":88,
* "sex":"男"
* }
* ]
* @param view
*/
public void analyzeJSONArray1(View view) {
String result = readFile("pottingJSONArray1");
// Log.d(TAG, "result:" + result);
try{
// 整个最大的JSON数组
JSONArray jsonArray = new JSONArray(result);
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSONArray1 jsonArray:" + jsonArray);
// [{"name":"君君","age":89,"sex":"男"},{"name":"小君","age":99,"sex":"女"},{"name":"大君","age":88,"sex":"男"}]
for (int i = 0; i < jsonArray.length(); i++) {
// JSON数组里面的具体-JSON对象
JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);
String name = jsonObject.optString("name", null);
int age = jsonObject.optInt("age", 0);
String sex = jsonObject.optString("sex", null);
// 日志打印结果:
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSONArray1 解析的结果:name" + name + " age:" + age + " sex:" + sex);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 解析JSON数组-带Key
* {
* "person":[
* {
* "name":"君君",
* "age":89,
* "sex":"男"
* },
* {
* "name":"小君",
* "age":99,
* "sex":"女"
* },
* {
* "name":"大君",
* "age":88,
* "sex":"男"
* }
* ]
* }
* @param view
*/
public void analyzeJSONArray2(View view) {
String result = readFile("pottingJSONArray2");
// Log.d(TAG, "result:" + result);
try{
/**
* JSON数组在牛逼,一旦有了 key person 这样的标记,就必须先是个 JSON对象
* 最外层的JSON对象,最大的哪个 { ... }
*/
JSONObject jsonObjectALL = new JSONObject(result);
// 通过标识(person),获取JSON数组
JSONArray jsonArray = jsonObjectALL.getJSONArray("person");
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSONArray1 jsonArray:" + jsonArray);
// [{"name":"君君","age":89,"sex":"男"},{"name":"小君","age":99,"sex":"女"},{"name":"大君","age":88,"sex":"男"}]
for (int i = 0; i < jsonArray.length(); i++) {
// JSON数组里面的具体-JSON对象
JSONObject jsonObject = jsonArray.getJSONObject(i);
String name = jsonObject.optString("name", null);
int age = jsonObject.optInt("age", 0);
String sex = jsonObject.optString("sex", null);
// 日志打印结果:
Log.d(TAG, "analyzeJSONArray2 解析的结果:name" + name + " age:" + age + " sex:" + sex);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 读取文件里面的字符串
* @param fileName
* @return
*/
private String readFile(String fileName) {
String result = null;
try {
InputStream inputStream = openFileInput(fileName);
byte[] bytes = new byte[inputStream.available()];
inputStream.read(bytes);
result = new String(bytes);
inputStream.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return result;
}
/**
* 定义一个Bean
*/
/*class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private String hobby;
public Student(String name, int age, String hobby) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name=''" + name + ''\'''' +
", age=" + age +
", hobby=''" + hobby + ''\'''' +
''}'';
}
}*/
}
activity_analyze_json.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="解析JSON对象"
android:onClick="analyzeJSON1"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="解析JSON对象-带Key"
android:onClick="analyzeJSON2"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="解析JSON对象-嵌套对象"
android:onClick="analyzeJSON3"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="解析JSON数组"
android:onClick="analyzeJSONArray1"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="解析JSON数组-带Key"
android:onClick="analyzeJSONArray2"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
所有解析JSON的Log打印:
analyzeJSON1
12-23 21:46:44.127 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSON1解析的结果:name:李四 age:99 hobby:爱好是练习截拳道
analyzeJSON2
12-23 21:46:59.161 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSON2解析的结果:name:李四 age:99 hobby:爱好是练习截拳道
analyzeJSON3
12-23 21:47:12.240 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSON3解析的结果:name:李四 age:99 hobby:爱好是练习截拳道
dogName:阿黄 dogAge:77 dogSex:母
analyzeJSONArray1
12-23 21:47:35.108 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSONArray1 解析的结果:name君君 age:89 sex:男
12-23 21:47:35.108 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSONArray1 解析的结果:name小君 age:99 sex:女
12-23 21:47:35.108 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSONArray1 解析的结果:name大君 age:88 sex:男
analyzeJSONArray2
12-23 21:47:55.457 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSONArray2 解析的结果:name君君 age:89 sex:男
12-23 21:47:55.457 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSONArray2 解析的结果:name小君 age:99 sex:女
12-23 21:47:55.457 8204-8204/liudeli.mynetwork01 D/AnalyzeJSONActivity: analyzeJSONArray2 解析的结果:name大君 age:88 sex:男

C#中使用JsonConvert解析JSON
using Newtonsoft.Json
首先添加Newtonsoft.Json的引用
1.JSON序列化
string JsonStr= JsonConvert.SerializeObject(Entity);
public class RecordResult
{
[JsonProperty("status")]
public int Status { get; set; }
[JsonProperty("error")]
public int Error { get; set; }
}
RecordResult result = new RecordResult();
result.Status = 1;
result.Error = "Error message";
string jsonStr = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(result);
2.JSON反序列化
Class model = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<Class>(jsonstr);
var result = (RecordResult)JsonConvert.DeserializeObject(jsonstring, typeof(RecordResult))
//或者
var result = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<RecordResult>(jsonstring)

C#使用LitJson解析Json数据
//接受MQ服务器返回的值
private void jieshou(string zhiling, string can1, string can2, string can3, string can4, string can5)
{
Console.Write("============================================="+"指令:" + zhiling + " can1=" + can1 + " can2=" + can2 + " can3=" + can3 + " can4=" + can4 + " can5=" + can5 + "\n");
if(can1=="0"&&can3==null){
Console.Write("对比分数不合格或服务器上没有这个人的人员信息");
}
else if (!can1.Equals("0")) {
Console.Write("服务没连接上!!!!");
}
else if (can1.Equals("0") && can3 != "" && can3 != null)
{
can3 = "cardId=" + can3;
//将can3的参数发送给服务器
byte[] ByteData = System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetBytes(can3);
//将数据发送给服务器,并返回json数据
string jieshou = PostData(path, ByteData);
Console.WriteLine("+++++++++++++++" + jieshou);
//使用LitJson的JsonData方法进行解析
JsonData deJson = JsonMapper.ToObject(jieshou);
//遍历返回的json数据
foreach (JsonData item in deJson)
{
//创建对象
User user = new User();
//名字
user.name = item["name"].ToString();
//Console.WriteLine(user.name = item["name"].ToString());
//身份证号码
user.cardId = item["cardId"].ToString();
//Console.WriteLine(user.name = item["cardId"].ToString());
//部门简称
user.DepartName = item["bumen"].ToString();
this.label2.Text = user.name + " " + user.DepartName;
//Console.WriteLine(user.name = item["bumen"].ToString());
}
}
}
//网络请求部分
public static string PostData(string url, byte[] postData)
{
HttpWebRequest myRequest = (HttpWebRequest)WebRequest.Create(url);
myRequest.Method = "POST";
myRequest.ContentType = "application/x-www-form-urlencoded";
myRequest.ContentLength = postData.Length;
Stream newStream = myRequest.GetRequestStream();
// Send the data.
newStream.Write(postData, 0, postData.Length);
newStream.Close();
// Get response
HttpWebResponse myResponse = (HttpWebResponse)myRequest.GetResponse();
StreamReader reader = new StreamReader(myResponse.GetResponseStream(), Encoding.UTF8);
return reader.ReadToEnd();
}
关于使用jsoncpp解析JSON数据和jsoncpp解析json文件的问题我们已经讲解完毕,感谢您的阅读,如果还想了解更多关于Android-Gson解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组)、Android-解析JSON数据(JSON对象/JSON数组)、C#中使用JsonConvert解析JSON、C#使用LitJson解析Json数据等相关内容,可以在本站寻找。











