本文的目的是介绍iPhoneBackupinformation/note的详细情况,我们将通过专业的研究、有关数据的分析等多种方式,同时也不会遗漏关于"Format"didnotcompletenor
本文的目的是介绍iPhone Backup information/note的详细情况,我们将通过专业的研究、有关数据的分析等多种方式,同时也不会遗漏关于"Format" did not complete normally. Please see the log for more information. 解决、"libtinfo.so.6: no version information" 使用 conda/miniconda 运行 Python 脚本、<知识库的构建> 1–1 信息提取:动机 Information Extraction:Motivation、Backtrack 命令解析(information gathering)的知识。
本文目录一览:- iPhone Backup information/note
- "Format" did not complete normally. Please see the log for more information. 解决
- "libtinfo.so.6: no version information" 使用 conda/miniconda 运行 Python 脚本
- <知识库的构建> 1–1 信息提取:动机 Information Extraction:Motivation
- Backtrack 命令解析(information gathering)

iPhone Backup information/note
Folder location
~/Library/Application Support/MobileSync/BackupFile- Info.plist
Each device's Info.plist file is created by iTunes. It stores your iTunes preferences for that unit along with basic device information.
- Manifest.plist
The Manifest.plist file is created by the iPhone backup utility on your computer. It uses this manifest to check files for corruption and (inadvertently,I'm sure) prevent any data changes on the Mac side from being sent back to the iPhone.
- .mdbackup files
the mdbackup files are created by the iPhone backup utility. If you delete any of these files,they're re-created the next time you sync and back up.
- /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/mobiledevice.framework/ Resources/AppleMobileDeviceHelper.app/Contents/Resources/AppleMobileBackup
command for manually force a sync or a backup; ambackup is a symbolic link for the command
./ambackup --backup --target targetid
The device immediately backs up to disk. This goes surprisingly fast,even when you've deleted or moved the backup folder. So don't expect it to take a long time.
In order to restore a device,you run the AppleMobileBackup program using the restore switch,like this:
./ambackup --restore --target targetid
This throws your iPhone into restore mode and returns any uncorrupted files from the backup folder to your device. This takes quite a bit longer than the backup,so prepare to wait a few minutes for it to complete.
If you want to restore your phone from a folder that is different from the target ID normally used,supply a source folder name as follows:
./ambackup --restore --target targetid --source sourcefoldername
Read mdbackup files in Cocoa
mdbackup files are property lists and are created in a compressed binary format. These files are just as readable from your Foundation Cocoa programs as any other property list. The key to recovering data lies in de-serializing the data stored in that property list dictionary.
Read mdbackup property lists into your program just as you would read any other plist
[NSDictionary dictionaryWithContentsOfFile:mdbackupath];
This call creates a new NSDictionary object and initializes with the contents of the property list (or in this case mdbackup) file.
Once loaded,you may access the file data from the dictionary. Request the object associated with the @"Data" key
NSData *data = [mdbackupDict objectForKey:@"Data"];
Store that data out to disk
[data writetoFile:outfile atomically:YES];
The name of the file is stored in the @"Path" key. Use this value to restore the data to a file with the same name.
Create subset backup files
You can easily strip a manifest of its extraneous applications and files and re-embed that stripped manifest into the Manifest.plist file and restore just that subset. Here are the steps:
- Create a new working directory in ~/Library/Application Support/MobileSync/Backups.
- copy the Manifest.plist file and the mdbackups you want to restore into the working directory.
- Read in the @"Data" item from Manifest.plist and deserialize it to a dictionary. Remove all the items in the @"Applications" subdictionary and everything but the specific mdbackup files you want to use from the @"Files" subdictionary.
- Reserialize the updated dictionary,add it back into the Manifest @"Data" and sign the reserialzed data with SHA1.
- Perform a restore using --source as the working directory. Only the selected files will transfer to the iPhone.
Sample Code:
// Read in the file to embed
NSMutableString *embedFile = [NSMutableString stringWithCString:argv[1] encoding:1];
if (![[NSFileManager defaultManager] fileExistsAtPath:embedFile])
{
fprintf(stderr,"File %s does not exist\n",argv[1]);
exit(-1);
}
NSData *pdata = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:embedFile];
// Read in the mdbackup file
NSMutableString *mfile = [NSMutableString stringWithCString:argv[2] encoding:1];
if (![[NSFileManager defaultManager] fileExistsAtPath:mfile])
{
fprintf(stderr,argv[2]);
exit(-1);
}
NSMutableDictionary *plist = [NSMutableDictionary dictionaryWithContentsOfFile:mfile];
// Add the embedded file
[plist setobject:pdata forKey:@"Data"];
// Serialize the output
Nsstring *errorString;
// nspropertyListXMLFormat_v1_0
NSData *outData = [nspropertyListSerialization dataFromPropertyList:plist format:nspropertyListBinaryFormat_v1_0 errorDescription:&errorString];
[outData writetoFile:[@"out-" stringByAppendingString:mfile] atomically:NO];
Tools
Erica Sadun's utility to examine and extract backup files
a command-line Mac-based application that scans through backup folders and extracts files. For example,to recover all the png images from your backups,you Could issue mdhelper -C png. Run the utility without arguments to see the built-in options.
What mdhelper does is this. It locates all backup folders. It reads in the Info.plist and Manifest.plist files and it lets you extract manifests and files based on a variety of search options. It stores extracted data on your desktop in a recovered iPhone files folder.
iPhone/iPod Touch Backup Extractor
This application converts the iPhone / iPod Touch backups that are created by iTunes into readily usable Mac OS X files. It is designed to run on Mac OS X Leopard only. The current version works with iTunes 8.2 and iPhone OS 3.0 or lower.
"Format" did not complete normally. Please see the log for more information. 解决
在 使用 MyEclipse 编写 web.xml 时使用 Ctrl+Shift+F 无法格式排版代码,出现 "Format" did not complete normally. Please see the log for more information.Overlapping text edits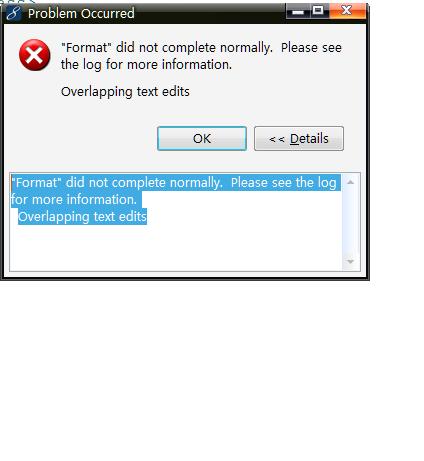 ,
,
主要可能原因是 <web-app></web-app> 中多了些空格所致,试着将其删掉之后问题完美解决

"libtinfo.so.6: no version information" 使用 conda/miniconda 运行 Python 脚本
如何解决"libtinfo.so.6: no version information" 使用 conda/miniconda 运行 Python 脚本?
我是 Anaconda 和 Miniconda 套件的第一次用户,我在使用它运行代码时遇到了问题。每次我尝试在 Anaconda 或 miniconda 中运行 python 脚本时,都会出现这个问题:
/miniconda3/lib/libtinfo.so.6:没有可用的版本信息(/bin/bash 需要) /anaconda3/lib/libtinfo.so.6:没有可用的版本信息(/bin/bash 需要)
我查看了所有帮助文档和我的目录,该文件在那里并且是 libtinfo.so.6.2 和 libtinfo.so.6 的符号
如有任何建议,我们将不胜感激。
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)

<知识库的构建> 1–1 信息提取:动机 Information Extraction:Motivation
引自 Fabian Suchanek的讲义
IE (Information extraction) : 从数字化文本中导出事实的,结构化的文本的过程
关键字:Digital text documents,deriving,factual,structured
信息提取会遇到这样几个困难:
- 二义性 ambiguity,即同一名字对应多个不同的entity
- 句子检测:即不知道从哪到哪是我们需要的句子成分
- 动词词组 verbal phrases:例如work as,be famous as 等等,he works as singer, he is famous as a singer, etc, 动词有很多种,变化很多,所以很难给实体加标签
- 解析句子:句子成分复杂,难
- 表格解读 table interpretation : 例如,不知道把提头当做hasXX 还是把表格内行的题目当做hasXX
- 解析文字:格式变化过多,例如:日期就有很多种写法,所以难
- 断句 segmentation:句子成分复杂,难
- HTML没写好:annotation没做好,难以获取到信息
做信息提取的原因:
- 未提取的信息:有重复,无清晰结构
- 提取后的信息:重复少,有结构性,useful
信息提取的应用:
- 电邮:把相关日期从邮件中提取出来添加至calendar,etc
- 智能助理 intelligent assistant:提取出用户的信息,进行自动提醒
- 售后服务:提取出用户需要进行维护的部分,及预约的维修日期
- 网购:从用户下单的行为中提取出相关信息,名字,购买物品,价格
- etc
知识图 Knowledge graph:是根据
- 不同结构的信息来源
- 和在web上进行信息提取所得到 (Knowledge Vault)
关于知识图的应用:问题回答功能 例如siri
- 回答的答案可以是很有结构的信息
- 有结构的信息是从数字化的结构的文本中上进行提取得到的
知识库举例:
- YAGO:从维基百科或者其他地方提取信息,建立了很大的知识图
- DEANNA
- IBM WATSON:问题回答系统
计算机很聪明吗,它是如何获取信息的呢
- 可以回答问题,但是从数据库中找到的答案
- 可以看懂自然语言并回答问题,但是是解析+数据库找答案
- 在回答问题方面可以打败人类,但也没好很多
- 可以开汽车,开飞机,etc,但这只是computation所带来的结果

Backtrack 命令解析(information gathering)
1、 Dnstracer:information gathering/networkanalysis/dns analysis 用来探测解析目标域名的dnsserver。 dnstracer www.google.com
2、 Dig即domain information groper;用户探测域名解析的详细信息。
3、 Host:解析域名的详细IP地址
4、 Sqlmap: information gathering/database analysis/mysql analysis/ 是扫描服务器是否存在sql注入漏洞,注入一般步骤
Get方法:sqlmap –uhttp://hostname.com?id=1 --dbs
Post方法:
sqlmap –u http://hostname.com --data “username=name&password=pass” --dbs
如果返回结果,说明存在sql注入漏洞,应该可以看到数据库名了。
探查表名:Sqlmap –uhttp://hostname.com?id=1 –D basename –tables
探查列名:sqlmap –uhttp://hostname.com?id=1 –D basename –T tablename –columns
查看数据:
sqlmap –uhttp://hostname.com?id=1 –D basename –T tablename –Ccolumnsname –dump
5、 Dbpwaduit:information gathering/databaseanalysis用来探测数据库用户名和密码,支持mysql、mssql、DB2。需要指定字典文件。
6、 Dirb:是information gathering/webapplication analysis /web crawlers/下的服务器目录、文件探测命令
dirb http://hostname.com 其中-X 命令可以在每条字典数据后加后缀,如:
dirbhttp://hostname.com –X .html
7、 Webshag-gui:information gathering/webapplication analysis /web crawlers/ 是服务器探测工具,可以探测服务器的基本信息,可以探测服务器目录文件。
8、 xprobe2: /information gathering/network analysis/os fingerprinting/ 用来探测目标住的操作系统类型。xprobe2 192.168.1.100, 但是好像数据库很久没有更新了,结果不是很准确。
9. autoscan: /information gathering/network analysis/network scanners/ 它是个用于查找在线主机的图形化网络扫描工具。用来确定目标机器上开放的端口和操作系统,也可以连接到代理服务器进行扫描。
10. netifera: /information gathering/network analysis/network scanners/ 用来扫描网络中主机TCP UDP DNS的信息,图形化界面。
11. Nmap : /information gathering/network analysis/network scanners/ 是个一综合的 功能全面的端口扫描工具。端口扫描,主机发现,服务版本识别,操作系统识别,网络路由跟踪,nmap脚本引擎(检查网络服务中的漏洞,枚举目标系统资源)。默认命令 nmap 192.168.1.100, nmap 192.168.1.0/24 。
TCP扫描选项: -sT(连续扫描,进行三次握手,慢,会被目标主机记录), -sS(半开连接,nmap发送syn包后,等待,如果有返回syn/ack包,则端口开放;RST包,则端口关闭;没有包则说明端口被过滤)。
UDP扫描选项 : -sU .
nmap默认扫描1000个常用端口, -p:扫描1-1024个, -p-:扫描1-65535个。
nmap -sN -p 22, 25, 80, 3306 192.168.1.100 用TCP(null)的方式扫描22,25,80,3306端口。
nmap -sC 192.168.1.100 使用默认分类脚本探测目标主机。
zenmap是nmap的图形化工具,路径和nmap相同。
12. unicornscan:/information gathering/network analysis/network scanners/ 是一个信息收集和对应关系分析引擎工具,它对给予TCP/IP的设备进行扫描。
13. amap: /information gathering/network analysis/service fingerprinting/ 是一个服务枚举工具,可以识别目标系统指定端口上运行的服务及其版本。版本信息很重要,方便查找相应版本上的漏洞。amap -bq 192.168.1.100 3306 80 探测目标主机3306,80端口上运行的服务及其版本。-bq 控制获取欢迎信息时,不报告端口关闭或者不可识别。
14. httprint: /information gathering/network analysis/service fingerprinting/是一个用于检测HTTP服务器软件和版本的应用程序。
./httprint -h 192.168.1.100 -s signatures.txt,探测主机上运行的web服务器,-h -s设置主机IP地址签名文件。
15. httpsqash: /information gathering/network analysis/service fingerprinting/ 扫描http服务器。
./httpsqash -r www.hostname.com
本文是由youthflies发表在易踪网(yeetrack.com)上的原创文章,原文地址:http://www.yeetrack.com/?p=8
Backtrack 命令解析(information gathering)
Backtrack命令解析(Vulnerability assessment)
我们今天的关于iPhone Backup information/note的分享就到这里,谢谢您的阅读,如果想了解更多关于"Format" did not complete normally. Please see the log for more information. 解决、"libtinfo.so.6: no version information" 使用 conda/miniconda 运行 Python 脚本、<知识库的构建> 1–1 信息提取:动机 Information Extraction:Motivation、Backtrack 命令解析(information gathering)的相关信息,可以在本站进行搜索。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

