本文将带您了解关于用不同维度的子数组展平numpy数组的新内容,同时我们还将为您解释sumproduct数组维度不一样的相关知识,另外,我们还将为您提供关于2022-01-13:K个不同整数的子数组。
本文将带您了解关于用不同维度的子数组展平numpy数组的新内容,同时我们还将为您解释sumproduct数组维度不一样的相关知识,另外,我们还将为您提供关于2022-01-13:K 个不同整数的子数组。 给定一个正整数数组 A,如果 A 的某个子数组中不同整数的个数恰好为 K,则称 A 的这个连续、不一定不同的子数组为好子数组。 (例如,[1,2,3,1、python numpy将数组拆分为不相等的子数组、python – 从N维Numpy数组中仅获取非零子数组、python – 在具有不同多重性但相同维度的数组上同时使用numpy repeat的实用信息。
本文目录一览:- 用不同维度的子数组展平numpy数组(sumproduct数组维度不一样)
- 2022-01-13:K 个不同整数的子数组。 给定一个正整数数组 A,如果 A 的某个子数组中不同整数的个数恰好为 K,则称 A 的这个连续、不一定不同的子数组为好子数组。 (例如,[1,2,3,1
- python numpy将数组拆分为不相等的子数组
- python – 从N维Numpy数组中仅获取非零子数组
- python – 在具有不同多重性但相同维度的数组上同时使用numpy repeat

用不同维度的子数组展平numpy数组(sumproduct数组维度不一样)
这似乎很简单,但是我还没有找到如何使用来做的事情numpy。考虑示例数组:
import numpy as npaa = np.array([np.array([13.16]), np.array([1.58 , 1.2]), np.array([13.1]), np.array([1. , 2.6])], dtype=object)我需要一种通用的方法,使用将该数组展平为单个N元素数组N=every float in all the sub-arrays。在这种情况下,它将是:
aa = np.array([13.16, 1.58 , 1.2, 13.1, 1. , 2.6])我试过了np.ndarray.flatten()(尝试了所有的“ order”选项),但是我得到了相同的不变aa数组。
为什么np.ndarray.flatten()不工作,我该怎么做?
解决方案应该尽可能通用,因为aa我在这里使用的示例数组实际上将在我的真实代码中填充不同长度的子数组。
答案1
小编典典您可以使用numpy.hstack
>>> np.hstack(aa)array([13.16, 1.58, 1.2 , 13.1 , 1. , 2.6 ])
2022-01-13:K 个不同整数的子数组。 给定一个正整数数组 A,如果 A 的某个子数组中不同整数的个数恰好为 K,则称 A 的这个连续、不一定不同的子数组为好子数组。 (例如,[1,2,3,1
2022-01-13:K 个不同整数的子数组。
给定一个正整数数组 A,如果 A 的某个子数组中不同整数的个数恰好为 K,则称 A 的这个连续、不一定不同的子数组为好子数组。
(例如,[1,2,3,1,2] 中有 3 个不同的整数:1,2,以及 3。)
返回 A 中好子数组的数目。
来自力扣992。
答案2022-01-13:
两个窗口的滑动窗口。k-1窗口,k窗口。
时间复杂度:O(N)。
空间复杂度:O(N)。
代码用golang编写。代码如下:
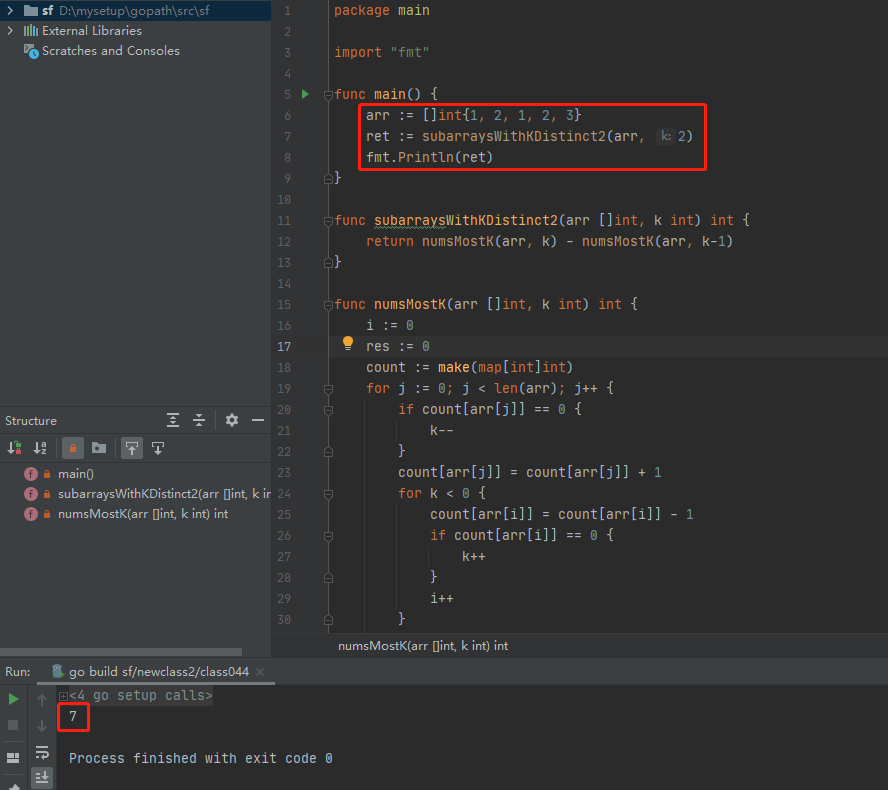
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
arr := []int{
1, 2, 1, 2, 3}
ret := subarraysWithKDistinct2(arr, 2)
fmt.Println(ret)
}
func subarraysWithKDistinct2(arr []int, k int) int {
return numsMostK(arr, k) - numsMostK(arr, k-1)
}
func numsMostK(arr []int, k int) int {
i := 0
res := 0
count := make(map[int]int)
for j := 0; j < len(arr); j++ {
if count[arr[j]] == 0 {
k--
}
count[arr[j]] = count[arr[j]] + 1
for k < 0 {
count[arr[i]] = count[arr[i]] - 1
if count[arr[i]] == 0 {
k++
}
i++
}
res += j - i + 1
}
return res
}执行结果如下:
左神java代码

python numpy将数组拆分为不相等的子数组
我试图将数组拆分为n个部分。有时这些部分的大小相同,有时它们的大小不同。
我正在尝试使用:
split = np.split(list, size)当大小均分为列表时,此方法工作正常,否则失败。有没有一种方法可以用额外的“很少”元素来“填充”最终的数组?
答案1
小编典典def split_padded(a,n): padding = (-len(a))%n return np.split(np.concatenate((a,np.zeros(padding))),n)
python – 从N维Numpy数组中仅获取非零子数组
基本上’arr’有1756020个小阵列形状(28,4).在1756020阵列中,967210是“全零”,788810具有所有非零值.我想删除所有967210’全零’小数组.我使用条件arr [i] == 0.any()编写了一个if else循环,但这需要花费很多时间.有没有更好的方法呢?
解决方法
numpy.any.
# set up 4d array of ones A = np.ones((5,3,4)) # make second of shape (3,4) = 0 A[1] = 0 # or A[1,...] = 0; or A[1,:,:] = 0 # find out which are non-zero res = np.any(A,axis=(1,2,3)) print(res) [True False True True True]
此功能在numpy v0.17向上提供.根据docs:
axis : None or int or tuple of ints,optional
If this is a tuple of ints,a reduction is performed on multiple axes,instead of a single axis or all the axes as before.

python – 在具有不同多重性但相同维度的数组上同时使用numpy repeat
npts = 4 tmp_reds = np.array([''red'',''red'',''red'']) tmp_blues = np.array([''blue'',''blue'',''blue''])
我使用np.repeat创建多重性:
red_occupations = [1,1,2] blue_occupations = [0,2,1] x = np.repeat(tmp_reds,red_occupations) y = np.repeat(tmp_blues,blue_occupations) print(x) [''red'' ''red'' ''red'' ''red''] print(y) [''blue'' ''blue'' ''blue'']
我想要的是以下x和y的组合:
desired_array = np.array([''red'',''blue''])
因此,desired_array以下列方式定义:
(1)应用red_occupations的第一个元素的多重性
(2)应用blue_occupations的第一个元素的多重性
(3)应用red_occupations的第二个元素的多重性
(4)应用blue_occupations的第二个元素的多重性
…
(2 * npts-1)应用red_occupations的npts元素的多重性
(2 * npts)应用blue_occupations的npts元素的多重性
所以这似乎是np.repeat正常使用的直接概括.通常,np.repeat完全如上所述,但只有一个数组.有没有人知道一些聪明的方法来使用多维数组,然后使用np.repeat可以实现扁平化或其他类似技巧?
我总是可以创建desired_array而不使用numpy,使用简单的zipped for循环和连续列表追加.但是,实际问题有npts~1e7,速度很关键.
解决方法
# Two 1D color arrays tmp1 = np.array([''red'',''green'']) tmp2 = np.array([''white'',''black'',''blue'']) # Multiplicity arrays color1_occupations = [1,2] color2_occupations = [0,1] # Stack those two color arrays and two multiplicity arrays separately tmp12 = np.column_stack((tmp1,tmp2)) color_occupations = np.column_stack((color1_occupations,color2_occupations)) # Use np.repeat to get stacked multiplicities for stacked color arrays out = np.repeat(tmp12,color_occupations.ravel())
给我们 –
In [180]: out Out[180]: array([''red'',''green'',''blue''],dtype=''|S5'')
关于用不同维度的子数组展平numpy数组和sumproduct数组维度不一样的问题我们已经讲解完毕,感谢您的阅读,如果还想了解更多关于2022-01-13:K 个不同整数的子数组。 给定一个正整数数组 A,如果 A 的某个子数组中不同整数的个数恰好为 K,则称 A 的这个连续、不一定不同的子数组为好子数组。 (例如,[1,2,3,1、python numpy将数组拆分为不相等的子数组、python – 从N维Numpy数组中仅获取非零子数组、python – 在具有不同多重性但相同维度的数组上同时使用numpy repeat等相关内容,可以在本站寻找。
本文标签:





