本文将介绍c–为双向链表实现begin()和end()的详细情况,特别是关于双向链表c++实现的相关信息。我们将通过案例分析、数据研究等多种方式,帮助您更全面地了解这个主题,同时也将涉及一些关于Alg
本文将介绍c – 为双向链表实现begin()和end()的详细情况,特别是关于双向链表c++实现的相关信息。我们将通过案例分析、数据研究等多种方式,帮助您更全面地了解这个主题,同时也将涉及一些关于Algs4-1.3.33一个双向队列Deque-双向链表实现、c – 如何将二叉搜索树转换为双向链表?、C语言双向链表实现根据使用频率安排元素位置的功能实例代码、golang LRU实现(使用双向链表实现)的知识。
本文目录一览:- c – 为双向链表实现begin()和end()(双向链表c++实现)
- Algs4-1.3.33一个双向队列Deque-双向链表实现
- c – 如何将二叉搜索树转换为双向链表?
- C语言双向链表实现根据使用频率安排元素位置的功能实例代码
- golang LRU实现(使用双向链表实现)

c – 为双向链表实现begin()和end()(双向链表c++实现)
根据我的理解,begin()应该指向第一个节点,而end()应该指向一个元素超过最后一个元素.我需要确保当我调用end()时我可以减少回到有效的最后一个元素.我还需要确保我可以做正常的遍历,比如……
while (beg != end ) { do something; beg++; }
本质上,我的链表只使用包含数据元素的节点,指向前一节点的指针和指向下一个节点的指针.
当我第一次尝试实现我的end()时,我的最后一个节点的下一个指针是nullptr.它可以单独工作,但不会像stl一样工作.
关于如何以与标准库相同的方式实现begin()和end()的任何建议?
解决方法
草图:
class List
{
private:
struct Node {
Node* prevIoUs;
Node* next;
Node() : prevIoUs(this),next(this) {}
};
struct Datanode : Node {
int data;
};
public:
class iterator
{
friend class List;
private:
iterator(Node* node) : m_node(node) {}
public:
iterator() : m_node(0) {}
iterator& operator ++() {
m_node = m_node->next;
return *this;
}
int& operator * () {
// Note: Dereferncing the end (sentinal node) is undefined behavior.
return reinterpret_cast<Datanode*>(m_node)->data;
}
// More iterator functions.
private:
Node* m_node;
};
public:
List() : m_sentinal(new Node) {}
iterator begin() { return iterator(m_sentinal->next); }
iterator end() { return iterator(m_sentinal); }
iterator insert(iterator position,int data) {
Datanode* data_node = new Datanode; // pass data
Node* current = position.m_node;
data_node->next = current;
data_node->prevIoUs = current->prevIoUs;
current->prevIoUs->next = data_node;
current->prevIoUs = data_node;
return iterator(current);
}
void append(int data) {
insert(end(),data);
}
private:
Node* m_sentinal;
};

Algs4-1.3.33一个双向队列Deque-双向链表实现
表1.3.9泛型双向队列的API
public class Deque<Item> implements Iterable<Item>
Deque()//创建空双向队列
boolean isEmpty()//双向队列是否为空
int size()//双向队列中的元素数量
void pushLeft(Item item)//向左端添加一个新元素
void pushRight(Item item)//向右端添加一个新元素
Item popLeft() 从左端删除一个元素
Item popRight()从右端删除一个元素
编写一个使用双向链表实现这份API的Deque类。
答:
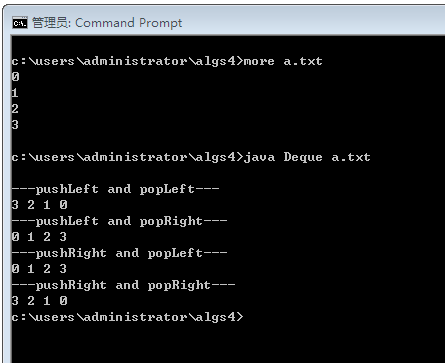
import java.util.Iterator;
public class Deque<Item> implements Iterable<Item>
{
private class Node
{
Item item;
Node prev;
Node next;
}
private int N;
private Node left;
private Node right;
public Deque()
{
left=null;
right=null;
N=0;
}
public boolean isEmpty()
{return N==0;}
public int size()
{return N;}
public void pushLeft(Item item)
{
Node oldLeft=left;
left=new Node();
left.item=item;
left.prev=null;
left.next=oldLeft;
if(isEmpty())
right=left;
else
oldLeft.prev=left;
N++;
}
public void pushRight(Item item)
{
Node oldRight=right;
right=new Node();
right.item=item;
right.prev=oldRight;
right.next=null;
if(isEmpty())
left=right;
else
oldRight.next=right;
N++;
}
public Item popLeft()
{
Item item;
if(size()==0)
{
item=null;
}
else if(size()==1)
{
item=left.item;
left=null;
right=null;
N--;
}
else
{
Node oldLeft=left;
left=left.next;
left.prev=null;
oldLeft.next=null;
item=oldLeft.item;
N--;
}
return item;
}
public Item popRight()
{
Item item;
if(size()==0)
{
item=null;
}
else if(size()==1)
{
item=right.item;
left=null;
right=null;
N--;
}
else
{
Node oldRight=right;
right=right.prev;
oldRight.prev=null;
right.next=null;
item=oldRight.item;
N--;
}
return item;
}
public Iterator<Item> iterator() {return new ListIterator();}
private class ListIterator implements Iterator<Item>
{
private Node current=left;
public boolean hasNext(){return current!=null;}
public void remove(){}
public Item next()
{
Item item=current.item;
current=current.next;
return item;
}//end next
}//end class ListIterator
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Deque<String> q=new Deque<String>();
In in1=new In(args[0]);
In in2=new In(args[0]);
In in3=new In(args[0]);
In in4=new In(args[0]);
//pushLeft and popLeft
StdOut.printf("\n---pushLeft and popLeft---\n");
while(!in1.isEmpty())
{
String item=in1.readString();
q.pushLeft(item);
}
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
StdOut.print(q.popLeft()+" ");
}
//pushLeft and popRight
StdOut.printf("\n---pushLeft and popRight---\n");
while(!in2.isEmpty())
{
String item=in2.readString();
q.pushLeft(item);
}
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
StdOut.print(q.popRight()+" ");
}
//pushRight and popLeft
StdOut.printf("\n---pushRight and popLeft---\n");
while(!in3.isEmpty())
{
String item=in3.readString();
q.pushRight(item);
}
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
StdOut.print(q.popLeft()+" ");
}
//pushRight and popRight
StdOut.printf("\n---pushRight and popRight---\n");
while(!in4.isEmpty())
{
String item=in4.readString();
q.pushRight(item);
}
while(!q.isEmpty())
{
StdOut.print(q.popRight()+" ");
}
}
}

c – 如何将二叉搜索树转换为双向链表?
鉴于树:
1
|
+-------+---------+
| |
2 3
| |
+----+---+ +----+---+
| | | |
4 5 6 7
| | | |
+--+--+ +--+--+ +--+--+ +--+--+
| | | | | | | |
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
节点结构:
struct node
{
char * data;
node * left;
node * right;
};
创建列表(之字形顺序):
1 <-> 3 <-> 2 <-> 4 <-> 5 <-> 6 <-> 7 <-> 15 <-> ... <-> 8
有人可以帮帮我吗.
解决方法
在实现算法之后,创建链表应该是明智的(因为它只是将每个访问过的元素附加到列表中)

C语言双向链表实现根据使用频率安排元素位置的功能实例代码
C语言双向链表应用
前言:
平时使用音乐播放器时,播放列表中的歌曲可以很方便地进行增添,删除,去重等操作。但其本质都可以抽象成一个双向链表。为了更方便用户的使用,我认为还可以增加一个将最常播放的音乐放在播放列表的头部的功能,那么如何实现呢?
请看代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#define OK 1
#define ERROR 0
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
typedef int status;
typedef int elemtype;
typedef struct node{
elemtype data;
int freq;
struct node * next;
struct node * prior;
}node;
typedef struct node* dlinklist;
status visit(elemtype c){
printf("%d ",c);
}
/*双向链表初始化*/
status initdlinklist(dlinklist * head,dlinklist * tail){
(*head)=(dlinklist)malloc(sizeof(node));
(*tail)=(dlinklist)malloc(sizeof(node));
if(!(*head)||!(*tail))
return ERROR;
/*这一步很关键*/
(*head)->prior=NULL;
(*tail)->next=NULL;
(*head)->freq=0;
(*tail)->freq=0;
/*链表为空时让头指向尾*/
(*head)->next=(*tail);
(*tail)->prior=(*head);
}
/*判定是否为空*/
status emptylinklist(dlinklist head,dlinklist tail){
if(head->next==tail)
return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
/*尾插法创建链表*/
status createdlinklist(dlinklist head,dlinklist tail,elemtype data){
dlinklist pmove=head,qmove=tail,pinsert;
pinsert=(dlinklist)malloc(sizeof(node));
if(!pinsert)
return ERROR;
else{
pinsert->data=data;
pinsert->prior=pmove;
pinsert->next=pmove->next;
pmove->next->prior=pinsert;
pmove->next=pinsert;
}
}
/*正序打印链表*/
status traverselist(dlinklist head,dlinklist tail){
dlinklist pmove=head->next;
while(pmove!=tail){
visit(pmove->data);
pmove=pmove->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
status traverselist2(dlinklist head,dlinklist tail){
dlinklist pmove=head->next;
while(pmove!=tail){
visit(pmove->freq);
pmove=pmove->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
/*在链表头插入元素*/
status inserthead(dlinklist head,elemtype data){
dlinklist pinsert;
pinsert=(dlinklist)malloc(sizeof(node));
pinsert->data=data;
pinsert->next=NULL;
pinsert->prior=NULL;
tail->prior->next=pinsert;
pinsert->prior=tail->prior;
pinsert->next=tail;
tail->prior=pinsert;
return OK;
}
/*按使用频次排序*/
status locateorder(dlinklist head,elemtype data){
dlinklist pmove=head->next,qmove;
while(pmove!=tail&&pmove->data!=data)
pmove=pmove->next;
if(pmove==tail){
printf("未找到\n");
return ERROR;
}
else{
pmove->freq++;
qmove=pmove->prior;
while(qmove!=head&&qmove->freq<pmove->freq)//向前寻找比pmove->freq大的qmove->freq
qmove=qmove->prior;
if(qmove->next!=pmove){//如果找到的qmove和pmove不是直接的前驱后继关系
pmove->next->prior=pmove->prior;
pmove->prior->next=pmove->next;//将pmove取下
pmove->prior=qmove;
pmove->next=qmove->next;
qmove->next->prior=pmove;
qmove->next=pmove;//插到qmove之后
}
}
}
int main(void){
dlinklist head,tail,pmove=head;
int i=0;
initdlinklist(&head,&tail);
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
inserthead(head,i);
printf("未经过排序的链表为\n");
traverselist(head,tail);
printf("在按使用频率排序后的链表为:\n");
locateorder(head,5);
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
locateorder(head,6);
}
traverselist(head,tail);
printf("各元素使用频率为\n");
traverselist2(head,tail);
}
要实现这一功能,最重要的函数是locateorder(),其实现思路是:如果某个元素的使用频率不为0,则定义一个向链表头移动的游标,寻找一个比该元素使用频率高的元素,将该元素插到找到的元素之后即可。
感谢阅读,希望能帮助到大家,谢谢大家对本站的支持!

golang LRU实现(使用双向链表实现)
LRU(Least recently used,最近最少使用)算法根据数据的历史访问记录来进行淘汰数据,其核心思想是“如果数据最近被访问过,那么将来被访问的几率也更高”。
lru.go
type Key interface{}
type entry struct {
key Key
value interface{}
}
type Cache Struct {
MaxEntries int
Onevicted func(key Key,value interface{})
ll *list.List
cache map[interface{}]*list.Element
}
定义了Key,entry,Cache类型,
Key:interface{}类型,在Go中interface{}可以指向任意对象,也就任意对象都是先这个接口,你可以把它看成Java/C#中的Object,C/C++中的void*。
Cache:MaxEntires表示Cache中最大可以有的KV数,Onevicted是一个回调函数,在触发淘汰时调用,ll是一个链表,cache是一个map,key为interface{}, value为list.Element其指向的类型是entry类型。
通过数据结构我们可以猜到LRU的实现,Get一次放到list头,每次Add的时候判断是否满,满则淘汰掉list尾的数据
// 创建一个Cache
func New(maxEntries int) *Cache {
return &Cache{
MaxEntries: maxEntries,ll: list.New(),cache: make(map[interface{}]*list.Element),}
}
// 向Cache中插入一个KV,如果缓存已满,则删除最久为使用的对象。
func (c *Cache) Add(key Key,value interface{}) {
if c.cache == nil {
c.cache = make(map[interface{}]*list.Element)
c.ll = list.New()
}
if ee,ok := c.cache[key]; ok {
c.ll.MovetoFront(ee)
ee.Value.(*entry).value = value
return
}
ele := c.ll.PushFront(&entry{key,value})
c.cache[key] = ele
if c.MaxEntries != 0 && c.ll.Len() > c.MaxEntries {
c.RemoveOldest()
}
}
// 从Cache中获取一个key对应的value,并把key移动到列表的开头。表示最近使用过。
func (c *Cache) Get(key Key) (value interface{},ok bool) {
if c.cache == nil {
return
}
if ele,hit := c.cache[key]; hit {
c.ll.MovetoFront(ele)
return ele.Value.(*entry).value,true
}
return
}
// 从Cache中删除一个key
func (c *Cache) Remove(key Key) {
if c.cache == nil {
return
}
if ele,hit := c.cache[key]; hit {
c.removeElement(ele)
}
}
// 从Cache中删除最久未被访问的数据
func (c *Cache) RemoveOldest() {
if c.cache == nil {
return
}
ele := c.ll.Back()
if ele != nil {
c.removeElement(ele)
}
}
// 获取当前Cache中的元素个数
func (c *Cache) Len() int {
if c.cache == nil {
return 0
}
return c.ll.Len()
}
//删除缓存中的元素,私有方法
func (c *Cache) removeElement(e *list.Element) {
c.ll.Remove(e)
kv := e.Value.(*entry)
delete(c.cache,kv.key)
if c.Onevicted != nil {
c.Onevicted(kv.key,kv.value)
}
}
这里我们看到了Go中如何实现一个类的成员方法,在func之后加类,在Go中接口的实现并不是和Java中那样子,而是只要某个类只要实现了某个接口的所有方法,即可认为该类实现了该接口。
类似的比如说在java中有2个接口名字不同,即使方法相同也是不一样的,而Go里面认为这是一样的。
另外Go中开头字母大写的变量名,类名,方法名表示对外可知,小写开头的表示对外不暴露。
另外类实这种代码ele.Value.(*entry).value,其中(*entry)表示将Value转成*entry类型访问。今天关于c – 为双向链表实现begin()和end()和双向链表c++实现的介绍到此结束,谢谢您的阅读,有关Algs4-1.3.33一个双向队列Deque-双向链表实现、c – 如何将二叉搜索树转换为双向链表?、C语言双向链表实现根据使用频率安排元素位置的功能实例代码、golang LRU实现(使用双向链表实现)等更多相关知识的信息可以在本站进行查询。
本文标签:





