如果您想了解若依mybatis配置和若依mybatisplus的知识,那么本篇文章将是您的不二之选。我们将深入剖析若依mybatis配置的各个方面,并为您解答若依mybatisplus的疑在这篇文章中
如果您想了解若依 mybatis配置和若依 mybatisplus的知识,那么本篇文章将是您的不二之选。我们将深入剖析若依 mybatis配置的各个方面,并为您解答若依 mybatisplus的疑在这篇文章中,我们将为您介绍若依 mybatis配置的相关知识,同时也会详细的解释若依 mybatisplus的运用方法,并给出实际的案例分析,希望能帮助到您!
本文目录一览:- 若依 mybatis配置(若依 mybatisplus)
- ibatis配置类似mybatis的plugins来配置拦截器的问题
- MyBatis 学习 之 一、MyBatis 简介与配置 MyBatis+Spring+MySql
- mybatis(二) - mybatis配置文件详解
- MyBatis—02—代替Dao层的mapper映射文件;MyBatis配置文件详解

若依 mybatis配置(若依 mybatisplus)
package com.um.core.config;
import org.apache.ibatis.io.VFS;
import org.apache.ibatis.session.sqlSessionFactory;
import org.mybatis.spring.sqlSessionfactorybean;
import org.mybatis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootVFS;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.io.DefaultResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePatternResolver;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.CachingMetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReader;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Mybatis支持*匹配扫描包
*
* @author um
*/
//@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig
{
@Autowired
private Environment env;
static final String DEFAULT_RESOURCE_PATTERN = "**/*.class";
public static String setTypeAliasesPackage(String typeAliasesPackage)
{
ResourcePatternResolver resolver = (ResourcePatternResolver) new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
MetadataReaderFactory MetadataReaderFactory = new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(resolver);
List<String> allResult = new ArrayList<String>();
try
{
for (String aliasesPackage : typeAliasesPackage.split(","))
{
List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>();
aliasesPackage = ResourcePatternResolver.CLAsspATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX
+ ClassUtils.convertClassNametoResourcePath(aliasesPackage.trim()) + "/" + DEFAULT_RESOURCE_PATTERN;
Resource[] resources = resolver.getResources(aliasesPackage);
if (resources != null && resources.length > 0)
{
MetadataReader MetadataReader = null;
for (Resource resource : resources)
{
if (resource.isReadable())
{
MetadataReader = MetadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(resource);
try
{
result.add(Class.forName(MetadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName()).getPackage().getName());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException e)
{
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
}
if (result.size() > 0)
{
HashSet<String> hashResult = new HashSet<String>(result);
allResult.addAll(hashResult);
}
}
if (allResult.size() > 0)
{
typeAliasesPackage = String.join(",", (String[]) allResult.toArray(new String[0]));
}
else
{
throw new RuntimeException("mybatis typeAliasesPackage 路径扫描错误,参数typeAliasesPackage:" + typeAliasesPackage + "未找到任何包");
}
}
catch (IOException e)
{
e.printstacktrace();
}
return typeAliasesPackage;
}
@Bean
public sqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception
{
String typeAliasesPackage = env.getProperty("mybatis.typeAliasesPackage");
String mapperLocations = env.getProperty("mybatis.mapperLocations");
String configLocation = env.getProperty("mybatis.configLocation");
typeAliasesPackage = setTypeAliasesPackage(typeAliasesPackage);
VFS.addImplClass(SpringBootVFS.class);
final sqlSessionfactorybean sessionFactory = new sqlSessionfactorybean();
sessionFactory.setDataSource(dataSource);
sessionFactory.setTypeAliasesPackage(typeAliasesPackage);
sessionFactory.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources(mapperLocations));
sessionFactory.setConfigLocation(new DefaultResourceLoader().getResource(configLocation));
return sessionFactory.getobject();
}
}
package com.um.core.config;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.annotation.DbType;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.handlers.MetaObjectHandler;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.injector.AbstractMethod;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.injector.DefaultsqlInjector;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.core.injector.IsqlInjector;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.MybatisPlusInterceptor;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.inner.OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.plugins.inner.PaginationInnerInterceptor;
import com.um.core.security.CreateAndUpdateMetaObjectHandler;
import com.um.framework.mybatisplus.methods.InsertAll;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.EnableTransactionManagement;
import java.util.List;
/**
* mybatis-plus配置类
*
* @author Lion Li
*/
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)
@Configuration
// 指定要扫描的Mapper类的包的路径
@MapperScan("${mybatis-plus.mapperPackage}")
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
// 分页插件
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(paginationInnerInterceptor());
// 乐观锁插件
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(optimisticLockerInnerInterceptor());
// 阻断插件
// interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(blockAttackInnerInterceptor());
return interceptor;
}
/**
* 分页插件,自动识别数据库类型
* https://baomidou.com/guide/interceptor-pagination.html
*/
public PaginationInnerInterceptor paginationInnerInterceptor() {
PaginationInnerInterceptor paginationInnerInterceptor = new PaginationInnerInterceptor();
// 设置数据库类型为MysqL
paginationInnerInterceptor.setDbType(DbType.MysqL);
// 设置最大单页限制数量,默认 500 条,-1 不受限制
paginationInnerInterceptor.setMaxLimit(-1L);
return paginationInnerInterceptor;
}
/**
* 乐观锁插件
* https://baomidou.com/guide/interceptor-optimistic-locker.html
*/
public OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor optimisticLockerInnerInterceptor() {
return new OptimisticLockerInnerInterceptor();
}
/**
* 如果是对全表的删除或更新操作,就会终止该操作
* https://baomidou.com/guide/interceptor-block-attack.html
*/
// public BlockAttackInnerInterceptor blockAttackInnerInterceptor() {
// return new BlockAttackInnerInterceptor();
// }
/**
* sql性能规范插件(垃圾sql拦截)
* 如有需要可以启用
*/
// public IllegalsqlInnerInterceptor illegalsqlInnerInterceptor() {
// return new IllegalsqlInnerInterceptor();
// }
/**
* 自定义主键策略
* https://baomidou.com/guide/id-generator.html
*/
// @Bean
// public IdentifierGenerator idGenerator() {
// return new CustomIdGenerator();
// }
/**
* 元对象字段填充控制器
* https://baomidou.com/guide/auto-fill-Metainfo.html
*/
@Bean
public MetaObjectHandler MetaObjectHandler() {
return new CreateAndUpdateMetaObjectHandler();
}
/**
* sql注入器配置
* https://baomidou.com/guide/sql-injector.html
*/
@Bean
public IsqlInjector sqlInjector() {
return new DefaultsqlInjector() {
@Override
public List<AbstractMethod> getmethodList(Class<?> mapperClass) {
List<AbstractMethod> methodList = super.getmethodList(mapperClass);
methodList.add(new InsertAll());
return methodList;
}
};
}
/**
* TenantLineInnerInterceptor 多租户插件
* https://baomidou.com/guide/interceptor-tenant-line.html
* DynamicTableNameInnerInterceptor 动态表名插件
* https://baomidou.com/guide/interceptor-dynamic-table-name.html
*/
}
package com.um.core.config.properties;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
/**
* druid 配置属性
*
* @author um
*/
@Configuration
public class DruidProperties
{
@Value("${spring.datasource.druid.initialSize}")
private int initialSize;
@Value("${spring.datasource.druid.minIdle}")
private int minIdle;
@Value("${spring.datasource.druid.maxActive}")
private int maxActive;
@Value("${spring.datasource.druid.maxWait}")
private int maxWait;
@Value("${spring.datasource.druid.timeBetweenevictionRunsMillis}")
private int timeBetweenevictionRunsMillis;
@Value("${spring.datasource.druid.minevictableIdleTimeMillis}")
private int minevictableIdleTimeMillis;
@Value("${spring.datasource.druid.maxevictableIdleTimeMillis}")
private int maxevictableIdleTimeMillis;
@Value("${spring.datasource.druid.validationQuery}")
private String validationQuery;
@Value("${spring.datasource.druid.testWhileIdle}")
private boolean testWhileIdle;
@Value("${spring.datasource.druid.testOnBorrow}")
private boolean testOnBorrow;
@Value("${spring.datasource.druid.testOnReturn}")
private boolean testOnReturn;
public DruidDataSource dataSource(DruidDataSource datasource)
{
/** 配置初始化大小、最小、最大 */
datasource.setinitialSize(initialSize);
datasource.setMaxActive(maxActive);
datasource.setMinIdle(minIdle);
/** 配置获取连接等待超时的时间 */
datasource.setMaxWait(maxWait);
/** 配置间隔多久才进行一次检测,检测需要关闭的空闲连接,单位是毫秒 */
datasource.setTimeBetweenevictionRunsMillis(timeBetweenevictionRunsMillis);
/** 配置一个连接在池中最小、最大生存的时间,单位是毫秒 */
datasource.setMinevictableIdleTimeMillis(minevictableIdleTimeMillis);
datasource.setMaxevictableIdleTimeMillis(maxevictableIdleTimeMillis);
/**
* 用来检测连接是否有效的sql,要求是一个查询语句,常用select 'x'。如果validationQuery为null,testOnBorrow、testOnReturn、testWhileIdle都不会起作用。
*/
datasource.setValidationQuery(validationQuery);
/** 建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性。申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于timeBetweenevictionRunsMillis,执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。 */
datasource.setTestWhileIdle(testWhileIdle);
/** 申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能。 */
datasource.setTestOnBorrow(testOnBorrow);
/** 归还连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能。 */
datasource.setTestOnReturn(testOnReturn);
return datasource;
}
}
package com.um.core.config;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jackson.Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilderCustomizer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoproxy;
import java.util.TimeZone;
/**
* 程序注解配置
*
* @author um
*/
@Configuration
// 表示通过aop框架暴露该代理对象,AopContext能够访问
@EnableAspectJAutoproxy(exposeProxy = true)
// 指定要扫描的Mapper类的包的路径
//@MapperScan("com.um.project.**.mapper")
public class ApplicationConfig
{
/**
* 时区配置
*/
@Bean
public Jackson2ObjectMapperBuilderCustomizer jacksonObjectMapperCustomization()
{
return jacksonObjectMapperBuilder -> jacksonObjectMapperBuilder.timeZone(TimeZone.getDefault());
}
}
package com.um.core.config;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.servletexception;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource;
import com.alibaba.druid.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DruidDataSourceBuilder;
import com.alibaba.druid.spring.boot.autoconfigure.properties.DruidStatProperties;
import com.alibaba.druid.util.Utils;
import com.um.common.utils.spring.SpringUtils;
import com.um.framework.enums.DataSourceType;
import com.um.core.config.properties.DruidProperties;
import com.um.framework.datasource.DynamicDataSource;
/**
* druid 配置多数据源
*
* @author um
*/
@Configuration
public class DruidConfig
{
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.druid.master")
public DataSource masterDataSource(DruidProperties druidProperties)
{
DruidDataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
return druidProperties.dataSource(dataSource);
}
@Bean
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.druid.slave")
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.datasource.druid.slave", name = "enabled", havingValue = "true")
public DataSource slaveDataSource(DruidProperties druidProperties)
{
DruidDataSource dataSource = DruidDataSourceBuilder.create().build();
return druidProperties.dataSource(dataSource);
}
@Bean(name = "dynamicDataSource")
@Primary
public DynamicDataSource dataSource(DataSource masterDataSource)
{
Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources = new HashMap<>();
targetDataSources.put(DataSourceType.MASTER.name(), masterDataSource);
setDataSource(targetDataSources, DataSourceType.SLAVE.name(), "slaveDataSource");
return new DynamicDataSource(masterDataSource, targetDataSources);
}
/**
* 设置数据源
*
* @param targetDataSources 备选数据源集合
* @param sourceName 数据源名称
* @param beanName bean名称
*/
public void setDataSource(Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources, String sourceName, String beanName)
{
try
{
DataSource dataSource = SpringUtils.getBean(beanName);
targetDataSources.put(sourceName, dataSource);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
}
}
/**
* 去除监控页面底部的广告
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
@Bean
@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "spring.datasource.druid.statViewServlet.enabled", havingValue = "true")
public FilterRegistrationBean removeDruidFilterRegistrationBean(DruidStatProperties properties)
{
// 获取web监控页面的参数
DruidStatProperties.StatViewServlet config = properties.getStatViewServlet();
// 提取common.js的配置路径
String pattern = config.getUrlPattern() != null ? config.getUrlPattern() : "/druid/*";
String commonjsPattern = pattern.replaceAll("\\*", "js/common.js");
final String filePath = "support/http/resources/js/common.js";
// 创建filter进行过滤
Filter filter = new Filter()
{
@Override
public void init(javax.servlet.FilterConfig filterConfig) throws servletexception
{
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, servletexception
{
chain.doFilter(request, response);
// 重置缓冲区,响应头不会被重置
response.resetBuffer();
// 获取common.js
String text = Utils.readFromresource(filePath);
// 正则替换banner, 除去底部的广告信息
text = text.replaceAll("<a.*?banner\"></a><br/>", "");
text = text.replaceAll("powered.*?shrek.wang</a>", "");
response.getWriter().write(text);
}
@Override
public void destroy()
{
}
};
FilterRegistrationBean registrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
registrationBean.setFilter(filter);
registrationBean.addUrlPatterns(commonjsPattern);
return registrationBean;
}
}
package com.um.core.config;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JavaType;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.type.TypeFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.SerializationException;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
/**
* Redis使用FastJson序列化
*
* @author um
*/
public class FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer<T> implements RedisSerializer<T>
{
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
private Class<T> clazz;
static
{
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true);
}
public FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer(Class<T> clazz)
{
super();
this.clazz = clazz;
}
@Override
public byte[] serialize(T t) throws SerializationException
{
if (t == null)
{
return new byte[0];
}
return JSON.toJSONString(t, SerializerFeature.WriteClassName).getBytes(DEFAULT_CHARSET);
}
@Override
public T deserialize(byte[] bytes) throws SerializationException
{
if (bytes == null || bytes.length <= 0)
{
return null;
}
String str = new String(bytes, DEFAULT_CHARSET);
return JSON.parSEObject(str, clazz);
}
public void setobjectMapper(ObjectMapper objectMapper)
{
Assert.notNull(objectMapper, "'objectMapper' must not be null");
this.objectMapper = objectMapper;
}
protected JavaType getJavaType(Class<?> clazz)
{
return TypeFactory.defaultInstance().constructType(clazz);
}
}
package com.um.core.config;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javax.servlet.dispatcherType;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.FilterRegistrationBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import com.um.framework.filter.RepeatableFilter;
import com.um.framework.filter.XssFilter;
import com.um.common.utils.StringUtils;
/**
* Filter配置
*
* @author um
*/
@Configuration
public class FilterConfig
{
@Value("${xss.enabled}")
private String enabled;
@Value("${xss.excludes}")
private String excludes;
@Value("${xss.urlPatterns}")
private String urlPatterns;
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean xssFilterRegistration()
{
FilterRegistrationBean registration = new FilterRegistrationBean();
registration.setdispatcherTypes(dispatcherType.REQUEST);
registration.setFilter(new XssFilter());
registration.addUrlPatterns(StringUtils.split(urlPatterns, ","));
registration.setName("xssFilter");
registration.setorder(FilterRegistrationBean.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
Map<String, String> initParameters = new HashMap<String, String>();
initParameters.put("excludes", excludes);
initParameters.put("enabled", enabled);
registration.setinitParameters(initParameters);
return registration;
}
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean someFilterRegistration()
{
FilterRegistrationBean registration = new FilterRegistrationBean();
registration.setFilter(new RepeatableFilter());
registration.addUrlPatterns("/*");
registration.setName("repeatableFilter");
registration.setorder(FilterRegistrationBean.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE);
return registration;
}
}

ibatis配置类似mybatis的plugins来配置拦截器的问题
ibatis拦截器怎么配置?

MyBatis 学习 之 一、MyBatis 简介与配置 MyBatis+Spring+MySql
一、MyBatis 简介与配置 MyBatis+Spring+MySql
MyBatis 学习 之 一、MyBatis 简介与配置 MyBatis+Spring+MySql
MyBatis 学习 之 二、SQL 语句映射文件 (1) resultMap
MyBatis 学习 之 二、SQL 语句映射文件 (2) 增删改查、参数、缓存
MyBatis 学习 之 三、动态 SQL 语句
MyBatis 学习 之 四、MyBatis 配置文件
1.1MyBatis 简介
MyBatis 是一个可以自定义 SQL、存储过程和高级映射的持久层框架。MyBatis 摒除了大部分的 JDBC 代码、手工设置参数和结果集重获。MyBatis 只使用简单的 XML 和注解来配置和映射基本数据类型、Map 接口和 POJO 到数据库记录。相对 Hibernate 和 Apache OJB 等 “一站式” ORM 解决方案而言,Mybatis 是一种 “半自动化” 的 ORM 实现。
需要使用的 Jar 包:mybatis-3.0.2.jar(mybatis 核心包)。mybatis-spring-1.0.0.jar (与 Spring 结合包)。
下载地址:
http://ibatis.apache.org/tools/ibator
http://code.google.com/p/mybatis/
1.2MyBatis+Spring+MySql 简单配置
1.2.1 搭建 Spring 环境
1, 建立 maven 的 web 项目;
2, 加入 Spring 框架、配置文件;
3, 在 pom.xml 中加入所需要的 jar 包(spring 框架的、mybatis、mybatis-spring、junit 等);
4, 更改 web.xml 和 spring 的配置文件;
5, 添加一个 jsp 页面和对应的 Controller;
6, 测试。
可参照:http://limingnihao.iteye.com/blog/830409。使用 Eclipse 的 Maven 构建 SpringMVC 项目
1.2.2 建立 MySql 数据库
建立一个学生选课管理数据库。
表:学生表、班级表、教师表、课程表、学生选课表。
逻辑关系:每个学生有一个班级;每个班级对应一个班主任教师;每个教师只能当一个班的班主任;
使用下面的 sql 进行建数据库,先建立学生表,插入数据(2 条以上)。
更多 sql 请下载项目源文件,在 resource/sql 中。
/* 建立数据库 */
CREATE DATABASE STUDENT_MANAGER;
USE STUDENT_MANAGER;
/***** 建立student表 *****/
CREATE TABLE STUDENT_TBL
(
STUDENT_ID VARCHAR(255) PRIMARY KEY,
STUDENT_NAME VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
STUDENT_SEX VARCHAR(10),
STUDENT_BIRTHDAY DATE,
CLASS_ID VARCHAR(255)
);
/*插入学生数据*/
INSERT INTO STUDENT_TBL (STUDENT_ID,
STUDENT_NAME,
STUDENT_SEX,
STUDENT_BIRTHDAY,
CLASS_ID)
VALUES (123456,
''某某某'',
''女'',
''1980-08-01'',
121546
)
创建连接 MySql 使用的配置文件 mysql.properties。
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/student_manager?user=root&password=limingnihao&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
1.2.3 搭建 MyBatis 环境
顺序随便,现在的顺序是因为可以尽量的少的修改写好的文件。
1.2.3.1 创建实体类: StudentEntity
public class StudentEntity implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3096154202413606831L;
private ClassEntity classEntity;
private Date studentBirthday;
private String studentID;
private String studentName;
private String studentSex;
public ClassEntity getClassEntity() {
return classEntity;
}
public Date getStudentBirthday() {
return studentBirthday;
}
public String getStudentID() {
return studentID;
}
public String getStudentName() {
return studentName;
}
public String getStudentSex() {
return studentSex;
}
public void setClassEntity(ClassEntity classEntity) {
this.classEntity = classEntity;
}
public void setStudentBirthday(Date studentBirthday) {
this.studentBirthday = studentBirthday;
}
public void setStudentID(String studentID) {
this.studentID = studentID;
}
public void setStudentName(String studentName) {
this.studentName = studentName;
}
public void setStudentSex(String studentSex) {
this.studentSex = studentSex;
}
}
1.2.3.2 创建数据访问接口
Student 类对应的 dao 接口:StudentMapper。
public interface StudentMapper {
public StudentEntity getStudent(String studentID);
public StudentEntity getStudentAndClass(String studentID);
public List<StudentEntity> getStudentAll();
public void insertStudent(StudentEntity entity);
public void deleteStudent(StudentEntity entity);
public void updateStudent(StudentEntity entity);
}
1.2.3.3 创建 SQL 映射语句文件
Student 类的 sql 语句文件 StudentMapper.xml
resultMap 标签:表字段与属性的映射。
Select 标签:查询 sql。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.manager.data.StudentMapper">
<resultMap type="StudentEntity" id="studentResultMap">
<id property="studentID" column="STUDENT_ID"/>
<result property="studentName" column="STUDENT_NAME"/>
<result property="studentSex" column="STUDENT_SEX"/>
<result property="studentBirthday" column="STUDENT_BIRTHDAY"/>
</resultMap>
<!-- 查询学生,根据id -->
<select id="getStudent" parameterType="String" resultType="StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
<![CDATA[
SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL ST
WHERE ST.STUDENT_ID = #{studentID}
]]>
</select>
<!-- 查询学生列表 -->
<select id="getStudentAll" resultType="com.manager.data.model.StudentEntity" resultMap="studentResultMap">
<![CDATA[
SELECT * from STUDENT_TBL
]]>
</select>
</mapper>
1.2.3.4 创建 MyBatis 的 mapper 配置文件
在 src/main/resource 中创建 MyBatis 配置文件:mybatis-config.xml。
typeAliases 标签:给类起一个别名。com.manager.data.model.StudentEntity 类,可以使用 StudentEntity 代替。
Mappers 标签:加载 MyBatis 中实体类的 SQL 映射语句文件。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="StudentEntity" type="com.manager.data.model.StudentEntity"/>
</typeAliases>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/manager/data/maps/StudentMapper.xml" />
</mappers>
</configuration>
1.2.3.5 修改 Spring 的配置文件
主要是添加 SqlSession 的制作工厂类的 bean:SqlSessionFactoryBean,(在 mybatis.spring 包中)。需要指定配置文件位置和 dataSource。
和数据访问接口对应的实现 bean。通过 MapperFactoryBean 创建出来。需要执行接口类全称和 SqlSession 工厂 bean 的引用。
<!-- 导入属性配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:mysql.properties" />
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
</bean>
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml" />
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<!— mapper bean -->
<bean id="studentMapper" class="org.mybatis.spring.MapperFactoryBean">
<property name="mapperInterface" value="com.manager.data.StudentMapper" />
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory" />
</bean>也可以不定义 mapper 的 bean,使用注解:
将 StudentMapper 加入注解
@Repository
@Transactional
public interface StudentMapper {
}对应的需要在 dispatcher-servlet.xml 中加入扫描:
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="annotationClass" value="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/>
<property name="basePackage" value="com.liming.manager"/>
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
1.2.4 测试 StudentMapper
使用 SpringMVC 测试,创建一个 TestController,配置 tomcat,访问 index.do 页面进行测试:
@Controller
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@RequestMapping(value = "index.do")
public void indexPage() {
StudentEntity entity = studentMapper.getStudent("10000013");
System.out.println("name:" + entity.getStudentName());
}
}
使用 Junit 测试:
使用Junit测试:
Java代码
@RunWith(value = SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(value = "test-servlet.xml")
public class StudentMapperTest {
@Autowired
private ClassMapper classMapper;
@Autowired
private StudentMapper studentMapper;
@Transactional
public void getStudentTest(){
StudentEntity entity = studentMapper.getStudent("10000013");
System.out.println("" + entity.getStudentID() + entity.getStudentName());
List<StudentEntity> studentList = studentMapper.getStudentAll();
for( StudentEntity entityTemp : studentList){
System.out.println(entityTemp.getStudentName());
}
}
}

mybatis(二) - mybatis配置文件详解
MyBatis最关键的组成部分是SqlSessionFactory,我们可以从中获取SqlSession, 并执行映射的SQL语句。
SqlSessionFactory对象可以通过基于XML的配置信息或者JavaAPI创建。
1. 使用xml配置Mybatis
构建SqlSessionFactory最常见的方式是基于XML配置。myBatis的配置文件一般命名为mybatis-config.xml,
下面的 mybatis-config.xml展示了一个典型的MyBatis配置文件的样子:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<properties resource="application.properties">
<property name="username" value="db_user" />
<property name="password" value="verysecurepwd" />
</properties>
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true" />
</settings>
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="Student" type="com.briup.pojo.Student" />
<package name="com.briup.pojo" />
</typeAliases>
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler="com.mybatis3.typehandlers.PhoneTypeHandler" />
<package name="com.briup.typehandlers" />
</typeHandlers>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
<environment id="production">
<transactionManager type="MANAGED" />
<dataSource type="JNDI">
<property name="data_source" value="java:comp/jdbc/MyBatisDemoDS" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/briup/mappers/StudentMapper.xml" />
<mapper url="file:///D:/mybatisdemo/mappers/StudentMapper.xml" />
<mapper/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
1.1 myBatis配置文件中的元素
environments元素
environments是配置mybatis当前工作的数据库环境的地方
MyBatis支持配置多个dataSource环境,可以将应用部署到不同的环境上,
比如:DEV(开发环境)、TEST(测试环境)、QA(质量评估环境)、UAT(用户验收环境)、PRODUCTION(生产环境),
不同的环境可能使用的数据库环境不都一样。这时候,我们可以通过将默认environments值(default属性)设置成想要的environment的id值。
有时候,我们可能需要在相同的应用下使用多个数据库,
比如:我们可能用一个shoppingcart数据库来存储所有的订单明细,在使用一个reports数据库存储订单明细的合计,用作报告。(也就是如果系统在运行期间如果有切换数据库环境的需求,mybatis中也可以很轻松的实现)。
如果你的应用需要连接多个数据库,你需要将每个数据库配置成独立的环境,并且为每一个数据库创建一个SqlSessionFactory
例如,现有mybatis-config.xml文件中,配置有两个数据库信息,:
<environments default="shoppingcart">
<environment id="shoppingcart">
<transactionManager type="MANAGED" />
<dataSource type="JNDI">
<property name="data_source" value="java:comp/jdbc/ShoppingcartDS" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
<environment id="reports">
<transaction Managertype="MANAGED" />
<dataSource type="JNDI">
<property name="data_source" value="java:comp/jdbc/ReportsDS" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments> 我们可以为以上每个环境创建一个SqlSessionFactory, java代码:
inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
//默认的环境
defaultSqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
//统计明细的环境
cartSqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream, "shoppingcart");
//统计报表的环境
reportSqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream, "reports"); 注意:对于environments,我们可以在其中配置多个environment子元素,同时还需要在environment中配置dataSource和transactionManager元素。
dataSource元素
dataSource表示的是数据源,至少会包括该连接数据库的各种信息
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</dataSource>
dataSource的类型type属性可以配置成其内置类型之一,如:UNPOOLED,POOLED,JNDI。
UNPOOLED:MyBatis会为每一个数据库操作创建一个新的连接,使用完了并关闭它,该方式适用于只有小规模数量并发用户的简单应用程序上。
POOLED:MyBatis会创建一个数据库连接池,连接池中的一个连接将会被用作数据库操作。一旦数据库操作完成,MyBatis会将此连接返回给连接池。
JNDI(Java Naming and Directory Interface,Java命名和目录接口,是SUN公司提供的一种标准的Java命名系统接口)MyBatis从在应用服务器向配置好的JNDI数据源dataSource获取数据库连接。transactionManager元素 :事务管理器
MyBatis支持两种类型的事务管理器:JDBC 和 MANAGED.
JDBC事务管理器,是在【jdbc程序】负责管理数据库连接的生命周期(提交、回退等等)的时候。如果将TransactionManager 属性设置成JDBC,MyBatis内部将使用JdbcTransactionFactory类创建TransactionManager。
例如,部署到ApacheTomcat的应用程序,需要应用程序自己管理事务。因为ApacheTomcat不会帮我们管理事务。
MANAGED 事务管理器,是在【应用服务器】负责管理数据库连接生命周期的时候。如果将TransactionManager属性设置成MANAGED时,MyBatis内部使用ManagedTransactionFactory 类创建事务管理器TransactionManager。
例如,当一个Java EE的应用程序部署在类似JBoss,WebLogic,GlassFish应用服务器上时,它们会使用 EJB 进行应用服务器的事务管理能力。在这些管理环境中,你可以使用MANAGED事务管理器。
注:Managed 是托管的意思,即我们编写的应用程序本身不去管理事务,而是把事务管理交给应用所在的服务器进行管理。
简单记忆:如果设置为JDBC,则需要程序员自己设置事务提交,如果设置为MANAGED,则会将事务提交委托给web容器,web容器会帮我们事务提交。(不过这要看web容器是否支持,比如,Tomcat不能帮我们手动提交,所以在使用Tomcat的时候,只能设置为JDBC)
properties元素
属性配置元素properties可以将配置值写死到mybatis-config.xml中,
也可以具体到一个属性文件中,并且使用属性文件的key名作为占位符。
在上述的配置中,我们将数据库连接属性配置到了application.properties文件中,
并且为driver,URL等属性使用了占位符.
在applications.properties文件中配置数据库连接参数,如下所示:
jdbc.driverClassName=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
jdbc.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@127.0.0.1:1521:XE
jdbc.username=briup
jdbc.password=briup在mybatis-config.xml文件中,为属性使用application.properties文件中定义的占位符:
<!-- 读取application.properties文件中的数据key-value的形式 -->
<properties resource="application.properties">
<!-- 注意:是applications.properties文件中的值优先级高 -->
<property name="jdbc.username" value="briup" />
<property name="jdbc.password" value="briup" />
</properties>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}" />
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}" />
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}" />
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}" />
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments> typeAliases元素: 类型别名
在SQLMapper配置文件中,对于resultType和parameterType属性值,我们需要使用JavaBean 的完全限定名。
例如:
<select id="findStudentById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.briup.pojo.Student">
SELECT STUD_ID AS ID, NAME, EMAIL, DOB
FROM STUDENTS WHERE STUD_ID=#{Id}
</select>
<update id="updateStudent" parameterType="com.briup.pojo.Student">
UPDATE STUDENTS
SET NAME=#{name}, EMAIL=#{email}, DOB=#{dob}
WHERE STUD_ID=#{id}
</update> 注:parameterType表示,将来调用这个sql语句的时候所传的参数的类型,(参数值或者参数对象里面的属性值 用来替换sql语句中的占位符)
resultType表示,将来调用这个sql语句的时候所返回的结果的类型(方便mybatis给我们自动封装结果集)
这里我们为resultType和parameterType属性值设置为Student类型的完全限定名:com.briup.com.Student
我们可以为完全限定名取一个别名(alias),然后就可以在需要使用完全限定名的地方使用别名,而不是到处使用完全限定名。如果不取别名,会默认按类名去查找
如下例子所示,为完全限定名起一个别名:
<typeAliases>
<typeAlias alias="Student" type="com.briup.pojo.Student" />
<typeAlias alias="Teacher" type="com.briup.pojo.Teacher" />
</typeAliases>
然后在SQLMapper映射文件中,,如下使用Student的别名:
<select id="findStudentById" parameterType="int" resultType="Student">
SELECT STUD_ID AS ID, NAME, EMAIL, DOB
FROM STUDENTS WHERE STUD_ID=#{id}
</select>
<update id="updateStudent" parameterType="Student">
UPDATE STUDENTS
SET NAME=#{name}, EMAIL=#{email}, DOB=#{dob}
WHERE STUD_ID=#{id}
</update> 我们还可以不用为每一个JavaBean单独定义别名,可以为配置出需要取别名的类的所在的包(package),MyBatis会自动扫描包内定义的类,然后分别为每个类注册一个小写字母开头的简单类名形式的别名。
如下所示:
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.briup.pojo" />
</typeAliases> 如果Student.java和 Teacher.java 定义在com.briup.pojo包中,
则 com.briup.pojo.Student的别名会被注册为student,而com.briup.pojo.Teacher别名将会被注册为teacher。
还有另外一种方式为JavaBeans起别名,使用注解 @Alias,
@Alias("stu")
public class Student{
....
} @Alias注解将会覆盖配置文件中的<typeAliases>定义。
typeHandlers元素: 类型处理器
当MyBatis将一个Java对象作为输入参数执行INSERT语句操作时,它会创建一个PreparedStatement对象,并且使用setXXX()方法对占位符设置相应的参数值 。这里,XXX可以是Int,String,Date 等 Java对象属性类型的任意一个。
示例如下:
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="Student">
INSERT INTO STUDENTS(STUD_ID,NAME,EMAIL,DOB)
VALUES(#{stud Id},#{name},#{email},#{dob})
</insert> 为执行这个语句,MyBatis将采取以下一系列动作:
1)创建一个有占位符的PreparedStatement接口,如下:
PreparedStatement ps = connection.prepareStatement ("INSERT INTO STUDENTS(STUD_ID,NAME,EMAIL,DOB) VALUES(?,?,?,?)"); 2)检查Student对象的属性studId的类型,然后使用合适的setXXX方法去设置参数值。
这里studId是integer类型,所以会使用setInt()方法:
ps.setInt(1,student.getStudId()); 类似地,对于name和email属性都是String类型MyBatis使用setString()方法设置参数。
至于dob属性,MyBatis会使用setDate()方法设置dob处占位符位置的值。
MyBaits会将java.util.Date类型转换为java.sql.Timestamp并设值:
ps.setTimestamp(4, new Timestamp((student.getDob()).getTime())); 但MyBatis是怎么知道对于Integer类型属性使用setInt()和String类型属性使用setString()方法呢?
其实MyBatis是通过使用类型处理器typeHandlers来决定这么做的。
MyBatis对于以下的类型使用内建的类型处理器:
所有的 基本数据类型、基本类型的包装类型、 byte[]、java.util.Date、java.sql.Date、java,sql.Time、java.sql.Timestamp、java枚举类型等。
所以当MyBatis发现属性的类型属于上述类型,他会使用对应的类型处理器将值设置到PreparedStatement中,
同样地,当SQL结果集封装成java类对象的时候,也有类似的过程。
那如果有一个自定义的类型,怎么存储存储到数据库呢?
示例如下:
假设表STUDENTS 有一个 PHONE 字段,类型为 VARCHAR2(15),而 Student类有一个自定义类型属性
java代码:PhoneNumber 类定义类型的 phoneNumber 属性。
public class PhoneNumber{
private String countryCode;
private String stateCode;
private String number;
public PhoneNumber(){}
public PhoneNumber(String countryCode, String stateCode, String number) {
this.countryCode = countryCode;
this.stateCode = stateCode;
this.number = number;
}
public PhoneNumber(String str){
if(str!=null){
String[] args = str.split("-");
this.countryCode = args[0];
this.stateCode = args[1];
this.number = args[2];
}
}
public String getAsString() {
return countryCode + "-" + stateCode + "-" + number;
}
// Setters and getters
...
}
//Student类中引入PhoneNumber对象
public class Student{
private Integer id;
private String name;
private String email;
private PhoneNumber phone;
// Setters and getters
...
}
StudentMapper.xml配置:
<insert id="insertStudent" parameterType="Student">
insert into students(name,email,phone)
values(#{name},#{email},#{phone})
</insert> 这里,参数对象中的属性phone的值需要传递给#{phone};参数对象的属性phone是 PhoneNumber类型。
此时,MyBatis 并不知道该怎样来处理这个类型的对象。为了让MyBatis明白怎样处理这个自定义的Java对象类型,如PhoneNumber,我们可以创建一个自定义的类型处理器。
MyBatis提供了抽象类BaseTypeHandler<T> ,我们可以继承此类创建自定义类型处理器。
代码如下所示:
public class PhoneTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<PhoneNumber>{
//遇到PhoneNumber参数的时候应该如何在ps中设置值
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, PhoneNumber parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) throws SQLException {
ps.setString(i, parameter.getAsString());
}
//查询中遇到PhoneNumber类型的应该如何封装(使用列名封装)
@Override
public PhoneNumber getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName)
throws SQLException {
return new PhoneNumber(rs.getString(columnName));
}
//查询中遇到PhoneNumber类型的应该如何封装(使用列的下标)
@Override
public PhoneNumber getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex)
throws SQLException {
return new PhoneNumber(rs.getString(columnIndex));
}
//CallableStatement使用中遇到了PhoneNumber类型的应该如何封装
@Override
public PhoneNumber getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex)
throws SQLException {
return new PhoneNumber(cs.getString(columnIndex));
}
}注意:使用ps.setString()和rs.getString()方法是因为在数据库的表中,phone列是VARCHAR类型。
最后,一旦我们实现了自定义的类型处理器,我们需要在mybatis-config.xml中注册它:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<typeHandlers>
<typeHandler handler="com.briup.typehandlers.PhoneTypeHandler" />
</typeHandlers>
</configuration> 注册PhoneTypeHandler后,MyBatis就能够将Phone类型的对象值存储到VARCHAR类型的列上。
settings元素: 全局参数设置
注意:大多数情况下,【这些参数使用它们的默认值即可】
为满足应用特定的需求,MyBatis默认的全局参数设置可以被覆盖掉,如下所示:
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true" />
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true" />
<setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true" />
<setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true" />
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="false" />
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL" />
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE" />
<setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="25000" />
<setting name="safeRowBoundsEnabled" value="false" />
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="false" />
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION" />
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="OTHER" />
<setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="equals,clone,hash Code ,to String"/>
<setting name="proxyFactory" value="JAVASSIST" />
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="true" />
<setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J " />
<setting name="logPrefix" value="LOG4J " />
<setting name="callSettersOnNulls" value="false " />
</settings> <settings>
<!-- 这个配置使全局的映射器启用或禁用缓存 -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true" />
<!-- 全局启用或禁用延迟加载。当禁用时,所有关联对象都会即时加载 -->
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true" />
<!-- 允许或不允许多种结果集从一个单独的语句中返回(需要适合的驱动) -->
<setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true" />
<!-- 使用列标签代替列名。不同的驱动在这方便表现不同。参考驱动文档或充分测试两种方法来决定所使用的驱动 -->
<setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true" />
<!-- 允许JDBC支持生成的键。需要适合的驱动。 -->
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="false" />
<!-- 指定MyBatis如何自动映射列到字段/属性。PARTIAL只会自动映射简单、没有嵌套的结果。FULL会自动映射任意复杂的结果(嵌套的或其他情况) -->
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL" />
<!-- 配置默认的执行器。SIMPLE执行器没有什么特别之处。REUSE执行器重用预处理语句。BATCH执行器重用语句和批量更新 -->
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE" />
<!-- 设置超时时间,它决定驱动等待一个数据库响应的时间 -->
<setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="25000" />
<!-- 允许在嵌套语句中使用分页(RowBounds)默认false -->
<setting name="safeRowBoundsEnabled" value="false" />
<!-- 是否开启自动驼峰命名规则(camel case)映射,即从经典数据库列名 A_COLUMN 到经典 Java 属性名 aColumn 的类似映射。默认false -->
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="false" />
<!-- MyBatis 利用本地缓存机制(Local Cache)防止循环引用(circular references)和加速重复嵌套查询。 默认值为 SESSION,这种情况下会缓存一个会话中执行的所有查询。 若设置值为 STATEMENT,本地会话仅用在语句执行上,对相同 SqlSession 的不同调用将不会共享数据。 -->
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION" />
<!-- 当没有为参数提供特定的 JDBC 类型时,为空值指定 JDBC 类型。 某些驱动需要指定列的 JDBC 类型,多数情况直接用一般类型即可,比如 NULL、VARCHAR 或 OTHER。 -->
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="OTHER" />
<!-- 指定对象的哪个方法触发一次延迟加载。 -->
<setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="equals,clone,hashCode ,toString" />
<!-- CGLIB | JAVASSIST 默认JAVASSIST(MyBatis 3.3 or above) -->
<!-- 指定 Mybatis 创建具有延迟加载能力的对象所用到的代理工具。 -->
<setting name="proxyFactory" value="JAVASSIST" />
<!-- 当启用时,对任意延迟属性的调用会使带有延迟加载属性的对象完整加载;反之,每种属性将会按需加载。 -->
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="true" />
<!-- 指定 MyBatis 所用日志的具体实现,未指定时将自动查找。 -->
<setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J " />
<!-- 指定 MyBatis 增加到日志名称的前缀。值可以是任意字符串 -->
<setting name="logPrefix" value="LOG4J " />
<!-- 指定当结果集中值为 null 的时候是否调用映射对象的 setter(map 对象时为 put)方法,这对于有 Map.keySet() 依赖或 null 值初始化的时候是有用的。注意基本类型(int、boolean等)是不能设置成 null 的。 默认false-->
<setting name="callSettersOnNulls" value="false " />
</settings> mappers元素: SQL映射
SQLMapper文件中主要是对SQL语句的映射,表明这个sql语句对应哪个方法的调用。
我们需要在mybatis-config.xml文件中配置SQLMapper文件的位置。
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/briup/mappers/StudentMapper.xml" />
<mapper url="file:///D:/mybatisdemo/app/mappers/StudentMapper.xml" />
<mapper/>
<package name="com.briup.mappers" />
</mappers> 以上每一个<mapper> 标签都可以从不同类型的资源中加载映射mapper:
resource属性:用来指定在classpath中的mapper文件。
url属性:用来通过完全文件系统路径或者web URL地址来指向mapper文件
class属性:用来指向一个mapper接口
package属性:用来指向可以找到Mapper接口的包名
2.使用Java API配置MyBatis
(属于了解的内容,因为有了灵活的xml配置方法,这个方式几乎不用)
MyBatis的SqlSessionFactory接口除了使用基于XML的配置创建外也可以通过JavaAPI编程式地被创建。每个在XML中配置的元素,都可以编程式的创建。
因为mybatis框架在读取了我们配置的mybatis-config.xml中配置信息之后,利用这些信息去执行代码创建出我们需要的SqlSessionFactory,再进一步得到sqlSession,最后再进行各种数据库操作。所以其实我们完全可以不去配置任何信息直接把信息写在代码中。 只是这样做再大多数时候都会降低代码的灵活性,所以我们基本上接触的框架都是有相应的配置文件的.
例如:使用Java API创建SqlSessionFactory对象:
之前是读取配置文件之后再创建,现在是自己把信息写到代码中,然后再创建该对象
public static SqlSessionFactory getSqlSessionFactory() {
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = null;
try {
DataSource dataSource = DataSourceFactory.getDataSource();
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = new JdbcTransactionFactory();
Environment environment = new Environment("development", transactionFactory, dataSource);
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(environment);
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAlias("student",Student.class);
configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry().register(PhoneNumber.class, PhoneTypeHandler.class);
configuration.addMapper(StudentMapper.class);
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(configuration);
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return sqlSessionFactory;
} 类似的,每个在XML中配置的元素,都可以编程式的创建.
注:这里就不一一介绍了,因为绝大多数情况下我们还是不会把配置信息直接写到代码中的
3. 自定义MyBatis日志(属于了解的内容)
MyBatis使用其内部LoggerFactory作为真正的日志类库使用的门面。其内部的LaggerFactory会将日志记录任务委托给如下的所示某一个日志实现,
日志记录优先级由上到下顺序递减:
SLF4J
Apache Commons Logging
Log4j2
Log4j
JDK logging
注意:查看org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory源码可知
如果MyBatis未发现上述日志记录实现,则MyBatis的日志记录功能无效,如果你的运行环境中,在classpath中有多个可用的日志类库,并且你希望MyBaits使用某个特定的日志实现,你可以在代码中通过调用以下其中一个方法:
org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory.useSlf4jLogging();
org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory.useLog4JLogging();
org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory.useLog4J2Logging();
org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory.useJdkLogging();
org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory.useCommonsLogging();
org.apache.ibatis.logging.LogFactory.useStdOutLogging(); 注:如果你想自定义MyBatis日志记录,你应该在调用任何其它方法之前调用以上的其中一个方法

MyBatis—02—代替Dao层的mapper映射文件;MyBatis配置文件详解
一. Mapper 映射文件
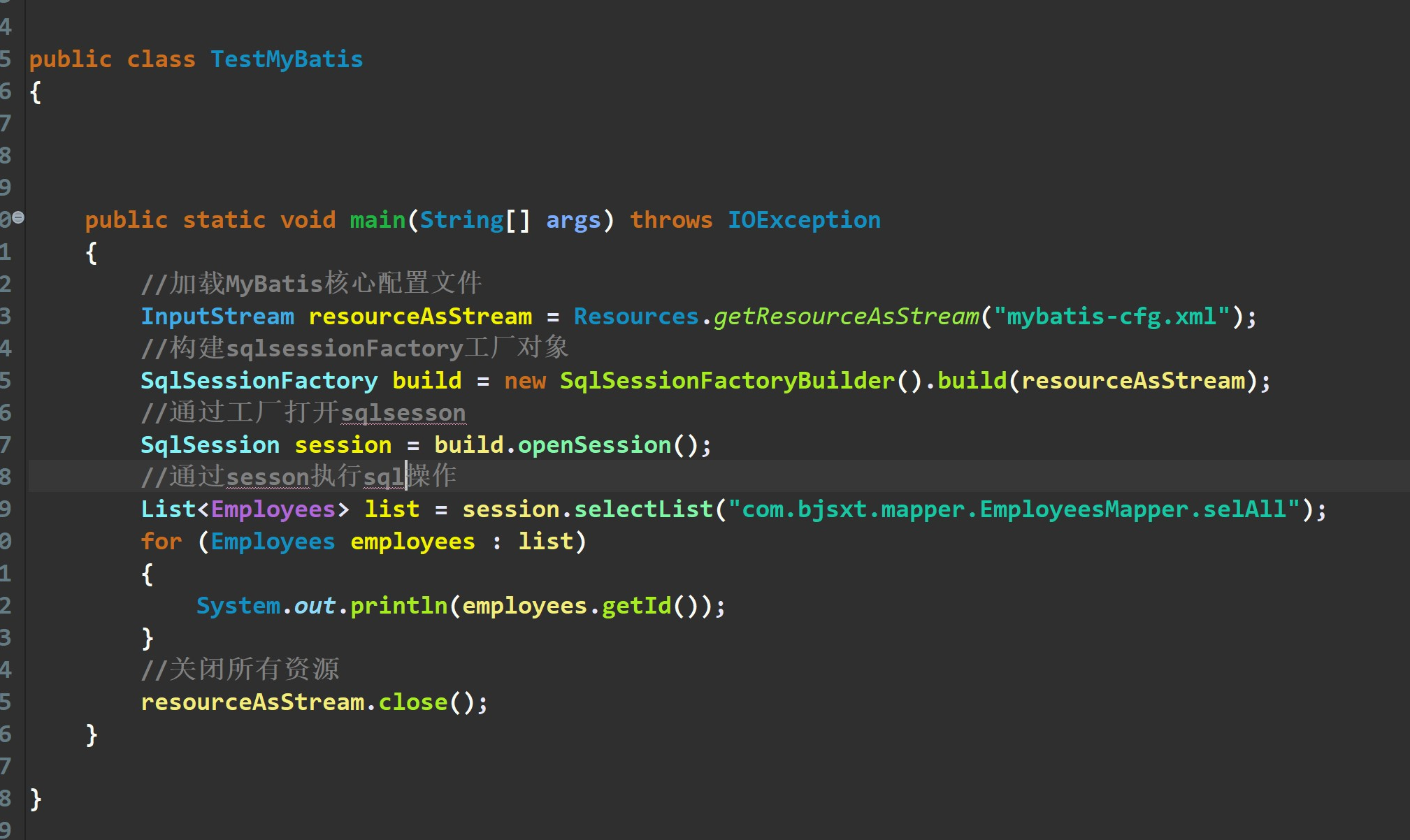
1.编写mapper层的xml映射文件
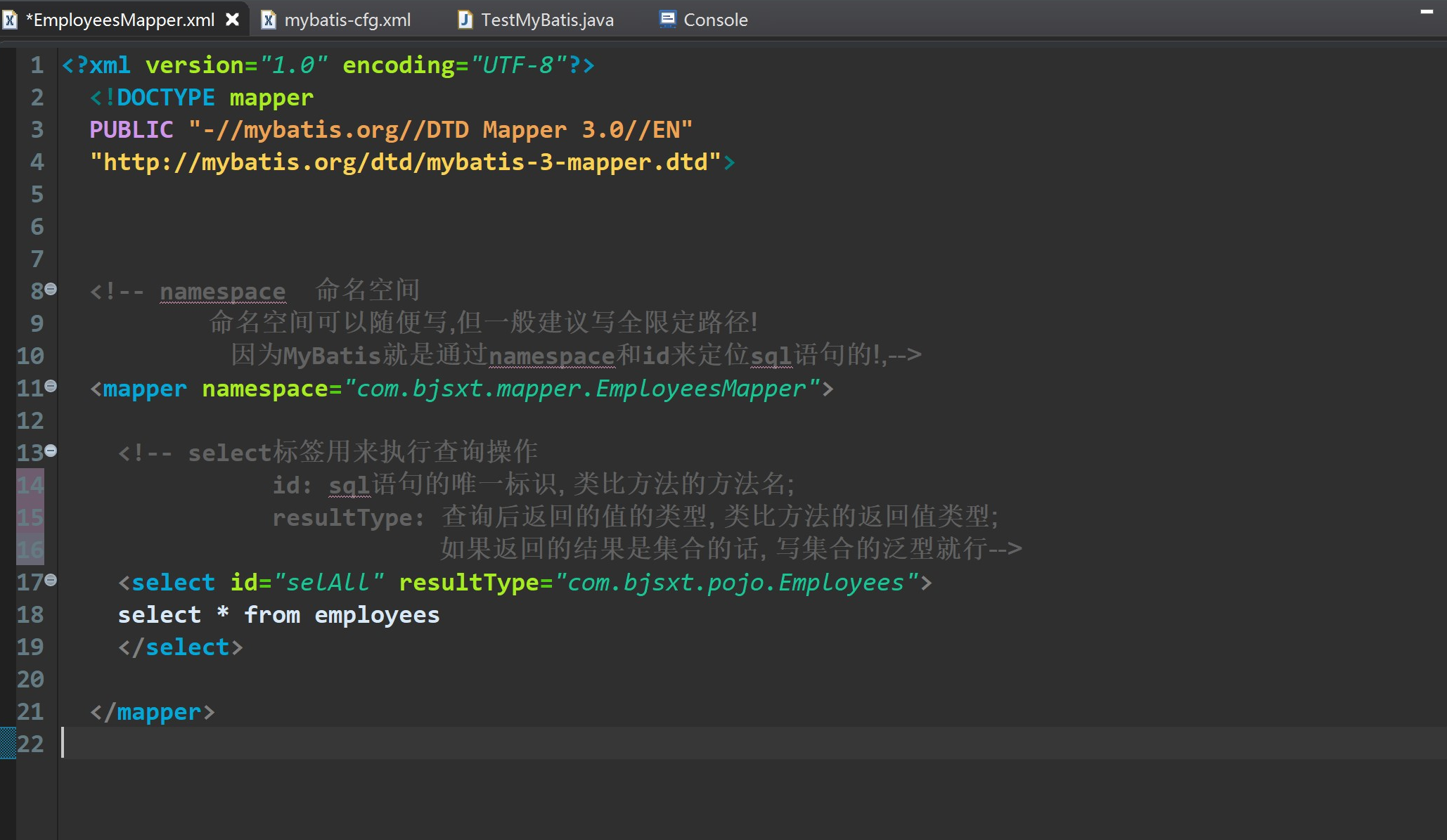
2. 在MyBatis核心配置文件中添加 mapper 扫描
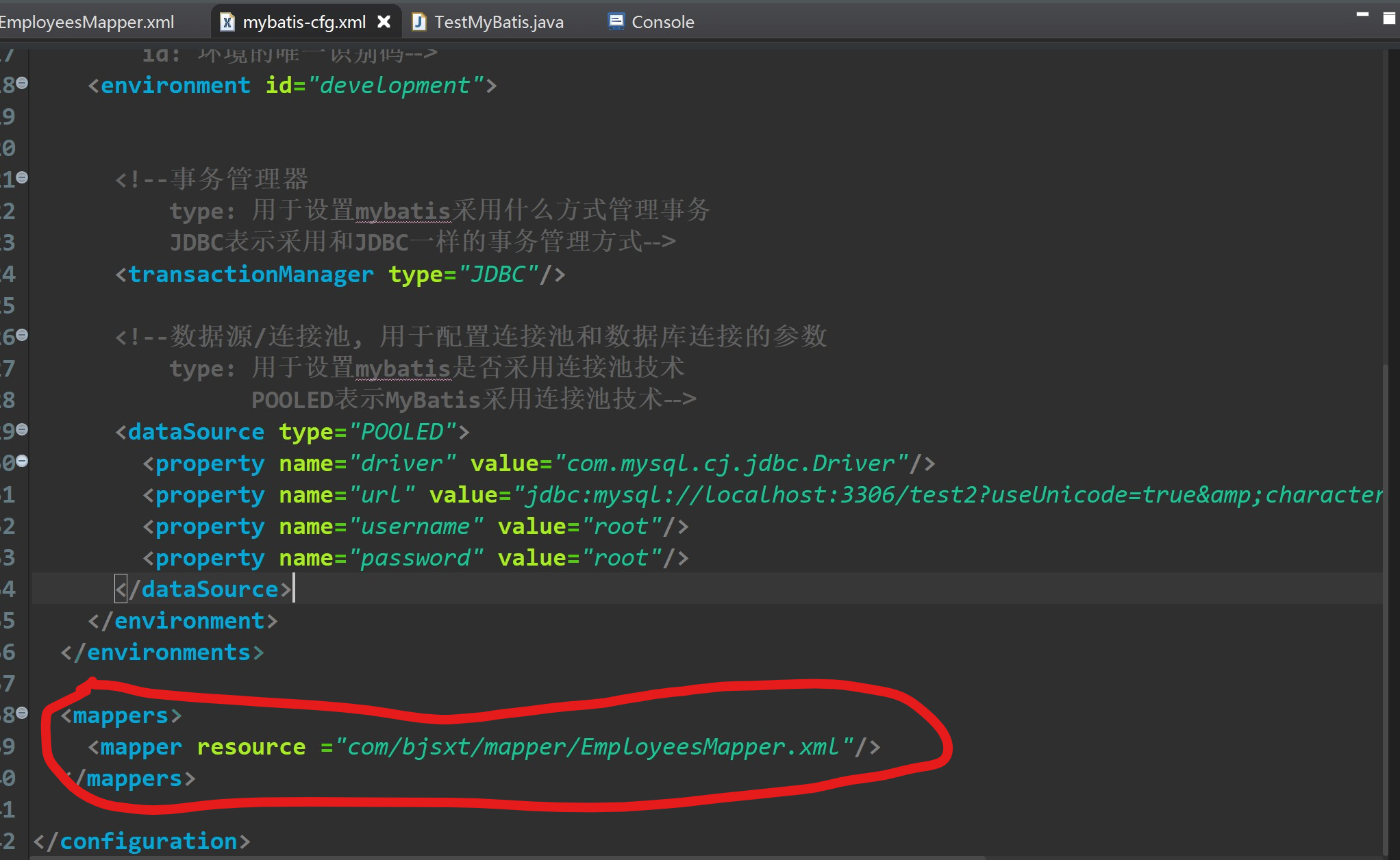
3.测试
二. MyBatis 配置文件详解
1.MyBatis核心配置文件
- 这是配置文件的根元素, 所有的其他元素都要在这个标签下使用.
- 用于管理所有的环境, 并可以指定默认使用哪个环境. 通过default 属性来指定.
- 用于配置环境, id 属性用于唯一标识当前环境
- JDBC: 表示 MyBatis 采用与原生 JDBC 一致的方式管理事务
- MANAGED: 表示将事务管理交给其他容器进行, 例如 Spring1.5用于配置数据源, 设置 MyBatis 是否使用连接池技术, 并且配置数据库连接的四个参数
它的type 属性用于设置 MyBatis 是否使用连接池技术:
- POOLED, 表示采用连接池技术(可以减少每次获取连接的时间)
- UNPOOLED, 表示每次都会开启和关闭连接, 不使用连接池技术
- JNDI, 使用其他容器(例如 Spring)提供数据源
- 用于配置数据库连接参数(driver, url, username, password)
- 用于扫描 mapper 信息

- 在前面声明了properties标签并使用resouce参数指明指向的文件后,我们在<property name= value=>中的value,可以直接使用${}形式获取.properties文件中的值;
- 在configuration 中配置 properties 标签 ,用于加载外部的 properties 文件。常见的是加载数据库的配置文件。想要使用外部文件内的值 要借助 $符号;
- 注意:.properties文件中,存储的文本都是键值对形式, 而${}表示get(key);
(9)settings标签
(10)typeAliases标签
- 给一个类起别名;
- 子标签: <typeAlias type=com.tjpu.mapper.UserMapper alias="u"/>
- 这个时候,我们在文件中再向调用com.tjpu.mapper.UserMapper时,我们只需要写u就可以了;
- 子标签: <package name=com.tjpu.mapper/> 那么这个包下所有类的全限定路径名都被起了个别名, 别名就是他们的类名;
2. mapper 层的映射配置文件
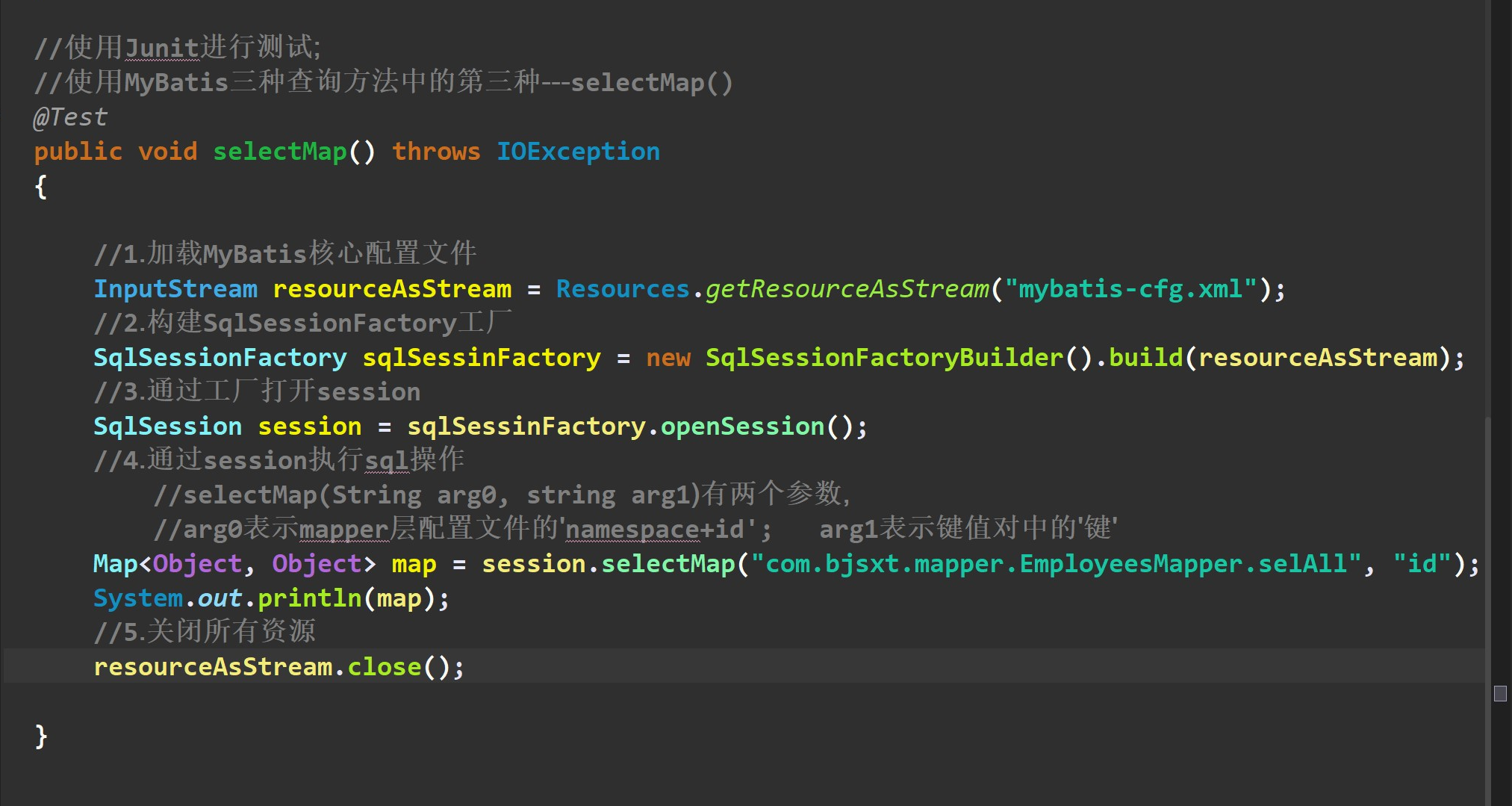
三. MyBatis 中常用的三个查询方法
1.selectList
2. selectOne
3. selectMap
我们今天的关于若依 mybatis配置和若依 mybatisplus的分享就到这里,谢谢您的阅读,如果想了解更多关于ibatis配置类似mybatis的plugins来配置拦截器的问题、MyBatis 学习 之 一、MyBatis 简介与配置 MyBatis+Spring+MySql、mybatis(二) - mybatis配置文件详解、MyBatis—02—代替Dao层的mapper映射文件;MyBatis配置文件详解的相关信息,可以在本站进行搜索。
本文标签: