以上就是给各位分享android–如何创建像地图效果的Foursquare:,其中也会对android绘制地图进行解释,同时本文还将给你拓展Android/layout:如何创建标题内容布局、Andr
以上就是给各位分享android – 如何创建像地图效果的Foursquare:,其中也会对android绘制地图进行解释,同时本文还将给你拓展Android / layout:如何创建标题内容布局、Android greenDAO数据库开发梳理 : Android ORM for your SQLite database、Android ProgressBar 模拟进度条效果的实现、Android Studio 3.0:canary 6:启动活动中的android.content.res.Resources $NotFoundException等相关知识,如果能碰巧解决你现在面临的问题,别忘了关注本站,现在开始吧!
本文目录一览:- android – 如何创建像地图效果的Foursquare:(android绘制地图)
- Android / layout:如何创建标题内容布局
- Android greenDAO数据库开发梳理 : Android ORM for your SQLite database
- Android ProgressBar 模拟进度条效果的实现
- Android Studio 3.0:canary 6:启动活动中的android.content.res.Resources $NotFoundException

android – 如何创建像地图效果的Foursquare:(android绘制地图)
我想在我的应用程序中集成Foursquare地图的感觉.
所以我创建了一个MapFragment和一个ListFragment.
我把它们放在我的Activity中,放置地图以占据整个屏幕大小,而列表片段设置一点点,所以你可以看到地图的一部分,另一部分被列表覆盖.现在我的猜测是这就是实现它的方式,因为据我所知,没有办法将MapFragment扩展为全屏幕动画而没有地图再次自我渲染.
首先,这是正确的方法吗?或者我应该将MmapFragment放在Activity的上部并且列表下面呢?如果是这样我怎么会在没有故障的情况下扩展呢?
如果它是第一个选项,那么我需要找到一种方法将地图放置在小视图中(当它被部分看到时)我的位置也在中心,但是因为地图从开始到完全设置屏幕我的位置居中在屏幕的中心,基本上由列表覆盖.
我怎么能实现这样的地图可扩展效果?
解决方法:
选项1 GoogleMap.setPadding.它抵消了被视为VisibleRegion中心的内容.
更多关于它:https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/android/map#map_padding

Android / layout:如何创建标题内容布局
我想要一个“标题”,也就是说,始终保持不变的标题.唯一应该改变的是头部下方的区域.
认为它是一个网页,内容区域在哪里发生=)
+--------------------+ | H E A D E R | +--------------------+ | | | | | | | C O N T E N T | | | | | | | +--------------------+
当然,它容易创建一个LinearLayot,在顶部添加一个视图,然后再添加另一个视图 – tada!但是,Im之后,您如何“设置”或设计项目,以便轻松更改内容中的内容.
我真正想要的是能够“滑动”(参见here)该区域,然后在“内容”区域中“滚动”一个新的View /东西,但保持相同的标题.
我真正想念的是一个综合性的图书馆的例子…
问候
解决方法
<include android:id="@+id/header"
layout="@layout/my_header"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"/>
您如何将标题留在内容布局的顶部将根据您的布局的其余部分而有所不同.您可以使用orientation =“vertical”的LinearLayout,或者在include语句中使用align_parentTop =“true”的相对布局.
这个android documentation有一个很好的基本布局类型的总结.

Android greenDAO数据库开发梳理 : Android ORM for your SQLite database
首先名确一个关键字:Object/relation mapping (ORM):对象/关系映射(ORM)
greenDao是什么?为什么会产生这个框架,也就是说greenDao的诞生是为了解决什么需求的?
关于 Android 中常用的数据存储方式有sharePreference存储、网络存储、文件存储等,但是对于数据量比较大、结构复杂的数据我们想要存储只能通过数据库进行处理,Android 系统中集成了一个轻量级的数据库: sqlite 数据库,但是使用起来比较繁琐和复杂,所以 Android 又新推出了Jetpack 组件库:Room 持久性库,Room 持久性库在 sqlite 的基础上提供了一个抽象层,让用户能够在充分利用 sqlite 的强大功能的同时,获享更强健的数据库访问机制。如果不使用这个新的组件库或者说在jetpack组件库之前,我们怎么能更方便快捷的访问操作sqliteDatabase数据库呢?开源ORM 框架———greenDAO框架。
下面我们来看官网对greenDAO的描述:GreenDAO的本质是为存储在关系数据库sqlite中的数据提供一个面向对象的接口。只需定义数据模型,Green DAO将创建Java数据对象(实体)和DAO(数据访问对象)。这将为您节省大量无聊的代码,只需来回移动数据。除此之外,Green DAO还提供一些高级ORM特性类似于会话缓存、急切加载和活动实体。

greenDAO’s Features at a glance
- Maximum performance (probably the fastest ORM for Android); our benchmarks are open sourced too
- Easy to use powerful APIs covering relations and joins
- Minimal memory consumption
- Small library size (<100KB) to keep your build times low and to avoid the 65k method limit
- Database encryption: greenDAO supports sqlCipher to keep your user’s data safe
- Strong community: More than 5.000 GitHub stars show there is a strong and active community
You want to learn more about greenDAO features like active entities, protocol buffers support, or eager loading? Then have a look at our full feature list.
下面是翻译:
GreenDAO的特点一目了然
- 最大性能(可能是Android最快的ORM);我们的基准测试也是开源的。
- 易用覆盖关系和联接的强大API
- 极小内存消耗
- 小的库大小(<100 kb),以保持较低的构建时间,并避免65k方法限制
- 数据库加密*GreenDAO支持sqlCiPHER,以确保用户数据的安全
- 强群落:5.000多名GitHub明星展示了一个强大而活跃的社区
您想了解有关GreenDAO功能的更多信息,如活动实体、协议缓冲区支持或急切加载?那就来看看我们的特征列表.
官网地址如下:https://greenrobot.org/greendao/
GitHub地址:https://github.com/greenrobot/greenDAO
下面给出使用实例:
首先创建一个项目、添加依赖包:
Add the following Gradle configuration to your Android project. In your root build.gradle file:
buildscript {
repositories {
jcenter()
mavenCentral() // add repository
}
dependencies {
classpath 'com.android.tools.build:gradle:3.5.3'
classpath 'org.greenrobot:greendao-gradle-plugin:3.3.0' // add plugin
}
}In your app modules app/build.gradle file:
apply plugin: 'com.android.application'
apply plugin: 'org.greenrobot.greendao' // apply plugin
dependencies {
implementation 'org.greenrobot:greendao:3.3.0' // add library
}Note that this hooks up the greenDAO Gradle plugin to your build process. When you build your project, it generates classes like DaoMaster, DaoSession and DAOs.
下面来看一个示例效果:在EditText中输入文字(比如做课堂笔记Note),点击添加按钮,就会将输入的文字笔记添加到数据库。下面是一个RecyclerView列表,它将数据库中的内容全部读出并展示,点击item条目会删除该条目同时删除数据库中的记录。

对应数据库字段以及数据:

下面按照实际的开发步骤贴出代码:
1.首先我们需要定义一个实体对象(Entity Object),它是我们映射到数据库中的对象,这里你只需要定义实体对象的字段就可以,其他的getter()\setter()方法等编译器会自动生成:
public class Note {
private Long id;
private String text;
private String comment;
private java.util.Date date;
private NoteType type;
}然后点击Android studio-->build-->Make Project按钮后,编译器就会自动创建完整的实体类:

完整的实体类:
package org.greenrobot.greendao.example;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.annotation.Convert;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.annotation.Entity;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.annotation.Generated;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.annotation.Id;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.annotation.Index;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.annotation.NotNull;
/**
* Entity mapped to table "NOTE".
*/
@Entity(indexes = {
@Index(value = "text, date DESC", unique = true)
})
public class Note {
@Id
private Long id;
@NotNull
private String text;
private String comment;
private java.util.Date date;
@Convert(converter = NoteTypeConverter.class, columnType = String.class)
private NoteType type;
@Generated(hash = 1272611929)
public Note() {
}
public Note(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Generated(hash = 1686394253)
public Note(Long id, @NotNull String text, String comment, java.util.Date date, NoteType type) {
this.id = id;
this.text = text;
this.comment = comment;
this.date = date;
this.type = type;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
@NotNull
public String getText() {
return text;
}
/** Not-null value; ensure this value is available before it is saved to the database. */
public void setText(@NotNull String text) {
this.text = text;
}
public String getComment() {
return comment;
}
public void setComment(String comment) {
this.comment = comment;
}
public java.util.Date getDate() {
return date;
}
public void setDate(java.util.Date date) {
this.date = date;
}
public NoteType getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(NoteType type) {
this.type = type;
}
}
GreenDao并且会自动生成3个核心类如下:

3个核心类介绍
DaoMaster:
使用 greenDAO 的入口点。DaoMaster 负责管理数据库对象(sqliteDatabase)和 DAO 类(对象),我们可以通过它内部类 OpenHelper 和 DevOpenHelper sqliteOpenHelper 创建不同模式的 sqlite 数据库。
DaoSession :
管理指定模式下的所有 DAO 对象,DaoSession提供了一些通用的持久性方法比如插入、负载、更新、更新和删除实体。
XxxDAO :
每个实体类 greenDAO都会生成一个与之对应DAO对象,如:User实体,则会生成一个一个UserDao类,通过这和UserDao对象调用queryBuilder()进而调用查询条件的方法、增删改查的方法等。
Entities
可持久化对象。通常, 实体对象代表一个数据库行使用标准 Java 属性(如一个POJO 或 JavaBean )。
三个核心类与数据实体对象之间的关系:

DaoMaster.class:
package org.greenrobot.greendao.example;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.sqlite.sqliteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.sqliteDatabase.CursorFactory;
import android.util.Log;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.AbstractDaoMaster;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.database.StandardDatabase;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.database.Database;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.database.DatabaSEOpenHelper;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.identityscope.IdentityScopeType;
// THIS CODE IS GENERATED BY greenDAO, DO NOT EDIT.
/**
* Master of DAO (schema version 1000): kNows all DAOs.
*/
public class DaoMaster extends AbstractDaoMaster {
public static final int SCHEMA_VERSION = 1000;
/** Creates underlying database table using DAOs. */
public static void createallTables(Database db, boolean ifNotExists) {
NoteDao.createTable(db, ifNotExists);
}
/** Drops underlying database table using DAOs. */
public static void dropAllTables(Database db, boolean ifExists) {
NoteDao.dropTable(db, ifExists);
}
/**
* WARNING: Drops all table on Upgrade! Use only during development.
* Convenience method using a {@link DevOpenHelper}.
*/
public static DaoSession newDevSession(Context context, String name) {
Database db = new DevOpenHelper(context, name).getWritableDb();
DaoMaster daoMaster = new DaoMaster(db);
return daoMaster.newSession();
}
public DaoMaster(sqliteDatabase db) {
this(new StandardDatabase(db));
}
public DaoMaster(Database db) {
super(db, SCHEMA_VERSION);
registerDaoClass(NoteDao.class);
}
public DaoSession newSession() {
return new DaoSession(db, IdentityScopeType.Session, daoConfigMap);
}
public DaoSession newSession(IdentityScopeType type) {
return new DaoSession(db, type, daoConfigMap);
}
/**
* Calls {@link #createallTables(Database, boolean)} in {@link #onCreate(Database)} -
*/
public static abstract class OpenHelper extends DatabaSEOpenHelper {
public OpenHelper(Context context, String name) {
super(context, name, SCHEMA_VERSION);
}
public OpenHelper(Context context, String name, CursorFactory factory) {
super(context, name, factory, SCHEMA_VERSION);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Database db) {
Log.i("greenDAO", "Creating tables for schema version " + SCHEMA_VERSION);
createallTables(db, false);
}
}
/** WARNING: Drops all table on Upgrade! Use only during development. */
public static class DevOpenHelper extends OpenHelper {
public DevOpenHelper(Context context, String name) {
super(context, name);
}
public DevOpenHelper(Context context, String name, CursorFactory factory) {
super(context, name, factory);
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(Database db, int oldVersion, int newVersion) {
Log.i("greenDAO", "Upgrading schema from version " + oldVersion + " to " + newVersion + " by dropping all tables");
dropAllTables(db, true);
onCreate(db);
}
}
}
DaoSession.class:
package org.greenrobot.greendao.example;
import java.util.Map;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.AbstractDao;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.AbstractDaoSession;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.database.Database;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.identityscope.IdentityScopeType;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.internal.DaoConfig;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.example.Note;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.example.NoteDao;
// THIS CODE IS GENERATED BY greenDAO, DO NOT EDIT.
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @see org.greenrobot.greendao.AbstractDaoSession
*/
public class DaoSession extends AbstractDaoSession {
private final DaoConfig noteDaoConfig;
private final NoteDao noteDao;
public DaoSession(Database db, IdentityScopeType type, Map<Class<? extends AbstractDao<?, ?>>, DaoConfig>
daoConfigMap) {
super(db);
noteDaoConfig = daoConfigMap.get(NoteDao.class).clone();
noteDaoConfig.initIdentityScope(type);
noteDao = new NoteDao(noteDaoConfig, this);
registerDao(Note.class, noteDao);
}
public void clear() {
noteDaoConfig.clearIdentityScope();
}
public NoteDao getNoteDao() {
return noteDao;
}
}
你不用太多的关心上面两个类。我们来看一下数据库的初始化,以及数据库的库名和数据库中与我们这个实体类Note.class对象对应的数据表在哪里命名?
数据库的初始化:自定义MyApplication.class继承Application类,并在Manifest中声明这个MyApplication.class如下:
package org.greenrobot.greendao.example;
import android.app.Application;
import android.content.Context;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.database.Database;
public class MyApplication extends Application {
private DaoSession daoSession;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
/**
* 1、通过DaoMaster内部类OpenHelper获取需要连接的一个标准的数据库对象:sqliteDatabase
*/
ExampleOpenHelper helper = new ExampleOpenHelper(this, "notes-db");
Database db = helper.getWritableDb();
/**
* 2、创建数据库管理对象
* DaoMaster是使用greenDAO的入口点。DaoMaster负责管理数据库对象(sqliteDatabase)和DAO类(对象),
* 我们可以通过它内部类OpenHelper和DevOpenHelper sqliteOpenHelper创建不同模式的sqlite数据库
*/
DaoMaster daoMaster = new DaoMaster(db);
/**
* 3、创建数据库链接会话
* 管理指定模式下的所有DAO对象,DaoSession提供了一些通用的持久性方法比如插入、负载、更新、更新和删除实体。
*/
daoSession = daoMaster.newSession();
}
public DaoSession getDaoSession() {
return daoSession;
}
public static class ExampleOpenHelper extends DaoMaster.OpenHelper {
public ExampleOpenHelper(Context context, String name) {
super(context, name);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(Database db) {
super.onCreate(db);
// Insert some example data.
// INSERT INTO NOTE (_id, DATE, TEXT) VALUES(1, 0, 'Example Note')
db.execsql("INSERT INTO " + NoteDao.TABLENAME + " (" +
NoteDao.Properties.Id.columnName + ", " +
NoteDao.Properties.Date.columnName + ", " +
NoteDao.Properties.Text.columnName +
") VALUES(1, 0, 'Example Note')");
}
}
}
看上面的代码,第1步中获取数据库对象时new ExampleOpenHelper(this, "notes-db");第二个参数用于指定数据库的库名。
你也可以不用像上面那样继承DaoMaster.OpenHelper那样自定义自己的ExampleOpenHelper。可以直接使用DaoMaster.OpenHelper类进行获取数据库对象:
public class MyApplication extends Application {
public static DaoSession mSession;
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
initDb();
}
/**
* 连接数据库并创建会话
*/
public void initDb() {
// 1、获取需要连接的数据库对象
DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper devOpenHelper = new DaoMaster.DevOpenHelper(this, "test.db");
sqliteDatabase db = devOpenHelper.getWritableDatabase();
// 2、创建数据库管理对象
DaoMaster daoMaster = new DaoMaster(db);
// 3、创建数据库会话
mSession = daoMaster.newSession();
}
// 供外接使用
public DaoSession getDaoSession() {
return mSession;
}
}
我们还有一个自动生成的类没说,NoteDao.class:
package org.greenrobot.greendao.example;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.sqliteStatement;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.AbstractDao;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.Property;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.internal.DaoConfig;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.database.Database;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.database.DatabaseStatement;
// THIS CODE IS GENERATED BY greenDAO, DO NOT EDIT.
/**
* DAO for table "NOTE".
*/
public class NoteDao extends AbstractDao<Note, Long> {
public static final String TABLENAME = "NOTE";
/**
* Properties of entity Note.<br/>
* Can be used for QueryBuilder and for referencing column names.
*/
public static class Properties {
public final static Property Id = new Property(0, Long.class, "id", true, "_id");
public final static Property Text = new Property(1, String.class, "text", false, "TEXT");
public final static Property Comment = new Property(2, String.class, "comment", false, "COMMENT");
public final static Property Date = new Property(3, java.util.Date.class, "date", false, "DATE");
public final static Property Type = new Property(4, String.class, "type", false, "TYPE");
}
private final NoteTypeConverter typeConverter = new NoteTypeConverter();
public NoteDao(DaoConfig config) {
super(config);
}
public NoteDao(DaoConfig config, DaoSession daoSession) {
super(config, daoSession);
}
/** Creates the underlying database table. */
public static void createTable(Database db, boolean ifNotExists) {
String constraint = ifNotExists? "IF NOT EXISTS ": "";
db.execsql("CREATE TABLE " + constraint + "\"NOTE\" (" + //
"\"_id\" INTEGER PRIMARY KEY ," + // 0: id
"\"TEXT\" TEXT NOT NULL ," + // 1: text
"\"COMMENT\" TEXT," + // 2: comment
"\"DATE\" INTEGER," + // 3: date
"\"TYPE\" TEXT);"); // 4: type
// Add Indexes
db.execsql("CREATE UNIQUE INDEX " + constraint + "IDX_NOTE_TEXT_DATE_DESC ON \"NOTE\"" +
" (\"TEXT\" ASC,\"DATE\" DESC);");
}
/** Drops the underlying database table. */
public static void dropTable(Database db, boolean ifExists) {
String sql = "DROP TABLE " + (ifExists ? "IF EXISTS " : "") + "\"NOTE\"";
db.execsql(sql);
}
@Override
protected final void bindValues(DatabaseStatement stmt, Note entity) {
stmt.clearBindings();
Long id = entity.getId();
if (id != null) {
stmt.bindLong(1, id);
}
stmt.bindString(2, entity.getText());
String comment = entity.getComment();
if (comment != null) {
stmt.bindString(3, comment);
}
java.util.Date date = entity.getDate();
if (date != null) {
stmt.bindLong(4, date.getTime());
}
NoteType type = entity.getType();
if (type != null) {
stmt.bindString(5, typeConverter.convertToDatabaseValue(type));
}
}
@Override
protected final void bindValues(sqliteStatement stmt, Note entity) {
stmt.clearBindings();
Long id = entity.getId();
if (id != null) {
stmt.bindLong(1, id);
}
stmt.bindString(2, entity.getText());
String comment = entity.getComment();
if (comment != null) {
stmt.bindString(3, comment);
}
java.util.Date date = entity.getDate();
if (date != null) {
stmt.bindLong(4, date.getTime());
}
NoteType type = entity.getType();
if (type != null) {
stmt.bindString(5, typeConverter.convertToDatabaseValue(type));
}
}
@Override
public Long readKey(Cursor cursor, int offset) {
return cursor.isNull(offset + 0) ? null : cursor.getLong(offset + 0);
}
@Override
public Note readEntity(Cursor cursor, int offset) {
Note entity = new Note( //
cursor.isNull(offset + 0) ? null : cursor.getLong(offset + 0), // id
cursor.getString(offset + 1), // text
cursor.isNull(offset + 2) ? null : cursor.getString(offset + 2), // comment
cursor.isNull(offset + 3) ? null : new java.util.Date(cursor.getLong(offset + 3)), // date
cursor.isNull(offset + 4) ? null : typeConverter.convertToEntityProperty(cursor.getString(offset + 4)) // type
);
return entity;
}
@Override
public void readEntity(Cursor cursor, Note entity, int offset) {
entity.setId(cursor.isNull(offset + 0) ? null : cursor.getLong(offset + 0));
entity.setText(cursor.getString(offset + 1));
entity.setComment(cursor.isNull(offset + 2) ? null : cursor.getString(offset + 2));
entity.setDate(cursor.isNull(offset + 3) ? null : new java.util.Date(cursor.getLong(offset + 3)));
entity.setType(cursor.isNull(offset + 4) ? null : typeConverter.convertToEntityProperty(cursor.getString(offset + 4)));
}
@Override
protected final Long updateKeyAfterInsert(Note entity, long rowId) {
entity.setId(rowId);
return rowId;
}
@Override
public Long getKey(Note entity) {
if(entity != null) {
return entity.getId();
} else {
return null;
}
}
@Override
public boolean hasKey(Note entity) {
return entity.getId() != null;
}
@Override
protected final boolean isEntityUpdateable() {
return true;
}
}
这个类中第一行一个静态变量就定义了与我们数据实体对象对应的数据表的表名。
在NoteActivity中查询数据并显示:(请不要复制这个例子到项目中运行,因为这里还有一些类我没有贴出。)
/*
* copyright (C) 2011 Markus Junginger, greenrobot (http://greenrobot.de)
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.greenrobot.greendao.example;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.text.Editable;
import android.text.TextWatcher;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.inputmethod.EditorInfo;
import android.widget.EditText;
import org.greenrobot.greendao.query.Query;
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.linearlayoutmanager;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;
public class NoteActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private EditText editText;
private View addNoteButton;
private NoteDao noteDao;
private Query<Note> notesQuery;
private NotesAdapter notesAdapter;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
setUpViews();
// get the note DAO
DaoSession daoSession = ((MyApplication) getApplication()).getDaoSession();
noteDao = daoSession.getNoteDao();
/**
* 查询数据库对应表中所有的笔记数据
* query all notes, sorted a-z by their text
*/
notesQuery = noteDao.queryBuilder().orderAsc(NoteDao.Properties.Text).build();
updateNotes();
}
private void updateNotes() {
List<Note> notes = notesQuery.list();
notesAdapter.setNotes(notes);
}
protected void setUpViews() {
RecyclerView recyclerView = findViewById(R.id.recyclerViewNotes);
recyclerView.setHasFixedSize(true);
recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new linearlayoutmanager(this));
notesAdapter = new NotesAdapter(noteClickListener);
recyclerView.setAdapter(notesAdapter);
addNoteButton = findViewById(R.id.buttonAdd);
addNoteButton.setEnabled(false);
editText = findViewById(R.id.editTextNote);
editText.setonEditorActionListener((v, actionId, event) -> {
if (actionId == EditorInfo.IME_ACTION_DONE) {
addNote();
return true;
}
return false;
});
editText.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() {
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int before, int count) {
boolean enable = s.length() != 0;
addNoteButton.setEnabled(enable);
}
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence s, int start, int count, int after) {
}
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable s) {
}
});
}
public void onAddButtonClick(View view) {
addNote();
}
private void addNote() {
String noteText = editText.getText().toString();
editText.setText("");
final DateFormat df = DateFormat.getDateTimeInstance(DateFormat.MEDIUM, DateFormat.MEDIUM);
String comment = "Added on " + df.format(new Date());
Note note = new Note();
note.setText(noteText);
note.setComment(comment);
note.setDate(new Date());
note.setType(NoteType.TEXT);
noteDao.insert(note);
Log.d("DaoExample", "Inserted new note, ID: " + note.getId());
updateNotes();
}
NotesAdapter.NoteClickListener noteClickListener = new NotesAdapter.NoteClickListener() {
@Override
public void onNoteClick(int position) {
Note note = notesAdapter.getNote(position);
Long noteId = note.getId();
noteDao.deleteByKey(noteId);
Log.d("DaoExample", "Deleted note, ID: " + noteId);
updateNotes();
}
};
}NoteActivity的布局文件:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context="org.greenrobot.greendao.example.NoteActivity"
tools:ignore="RtlHardcoded">
<Button
android:id="@+id/buttonAdd"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:onClick="onAddButtonClick"
android:text="@string/add"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editTextNote"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/buttonAdd"
android:hint="@string/enter_new_note"
android:imeOptions="actionDone"
android:inputType="text"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textViewNoteInstructions"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/editTextNote"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:paddingBottom="8dp"
android:paddingLeft="8dp"
android:paddingRight="8dp"
android:text="@string/click_to_remove"
android:textSize="12sp"/>
<androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/recyclerViewNotes"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_below="@id/textViewNoteInstructions"
android:scrollbars="vertical"/>
</RelativeLayout>
RecyclerView适配器代码如下:
package org.greenrobot.greendao.example;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import androidx.annotation.NonNull;
import androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView;
public class NotesAdapter extends RecyclerView.Adapter<NotesAdapter.NoteViewHolder> {
private NoteClickListener clickListener;
private List<Note> dataset;
public interface NoteClickListener {
void onNoteClick(int position);
}
static class NoteViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder {
public TextView text;
public TextView comment;
public NoteViewHolder(View itemView, final NoteClickListener clickListener) {
super(itemView);
text = itemView.findViewById(R.id.textViewNoteText);
comment = itemView.findViewById(R.id.textViewNoteComment);
itemView.setonClickListener(view -> {
if (clickListener != null) {
clickListener.onNoteClick(getAdapterPosition());
}
});
}
}
public NotesAdapter(NoteClickListener clickListener) {
this.clickListener = clickListener;
this.dataset = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void setNotes(@NonNull List<Note> notes) {
dataset = notes;
notifyDataSetChanged();
}
public Note getNote(int position) {
return dataset.get(position);
}
@NonNull
@Override
public NotesAdapter.NoteViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(ViewGroup parent, int viewType) {
View view = LayoutInflater.from(parent.getContext())
.inflate(R.layout.item_note, parent, false);
return new NoteViewHolder(view, clickListener);
}
@Override
public void onBindViewHolder(NotesAdapter.NoteViewHolder holder, int position) {
Note note = dataset.get(position);
holder.text.setText(note.getText());
holder.comment.setText(note.getComment());
}
@Override
public int getItemCount() {
return dataset.size();
}
}
上面只是梳理了GreenDao的使用流程,以及我们需要知道的知识点。当然这并不是所有的知识点,我们需要学习的还很多。这个例子请不要复制到项目中运行,因为这里还有一些类我没有贴出。如果想看完整的代码、并运行上面的实例,请至GreenDao的GitHub地址:https://github.com/greenrobot/greenDAO下载demo示例。上面的例子就是来自官网给的实例。


在说会上面的NoteActivity.class,一般对数据的增删改查,正式的项目开发中我们并不会直接在Activity中直接那么写。而是把它封装到一个诸如NoteDBManager.class的类中,这里贴出一个示例:
public class MessageManager {
private static MessageManager messageManager;
/**
* DaoSession
*/
private DaoSession mDaoSession;
private MessageDao messageDao;
private MessageManager() {
}
@Deprecated
public static MessageManager getMMInstance(Context context) {
return getInstance();
}
public static MessageManager getInstance() {
if (null == messageManager) {
synchronized (MessageManager.class) {
if (messageManager == null) {
messageManager = new MessageManager();
messageManager.mDaoSession = MyApplication.getDaoSession();
messageManager.messageDao = messageManager.mDaoSession.getMessageDao();
}
}
}
return messageManager;
}
/**
* 每天执行一次删除无效过期消息
*/
public static void oneDayDelInvalidMsg() {
Context context = MyApplication.getInstance().getApplicationContext();
final SharedPreferences msgSp = context.getSharedPreferences(MsgCenteractivity.MSG_SP_NAME,
Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd", Locale.getDefault());
final String curDay = format.format(new Date());
String deleteDay = msgSp.getString("delete_day", "");
if (!curDay.equals(deleteDay)) {
MessageManager.getInstance().deleteInvalidMessage();
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = msgSp.edit();
editor.putString("delete_day", curDay);
editor.commit();
}
}
/**
* 根据id删除推送消息
*
* @param mid
*/
public void deleteMessageByMid(String mid) {
try {
QueryBuilder<Message> qb = messageDao.queryBuilder();
DeleteQuery<Message> bd = qb.where(Properties.Mid.eq(mid)).buildDelete();
bd.executeDeleteWithoutDetachingEntities();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
/**
* 根据id删除推送消息(假删除)
*
* @param mid
*/
public void deleteMessageNewByMid(String mid) {
try {
QueryBuilder<Message> qb = messageDao.queryBuilder();
List<Message> msgList ;
msgList = qb.where(Properties.Mid.eq(mid)).list();
if (null != msgList && !msgList.isEmpty()) {
Message msg = msgList.get(0);
if (null != msg) {
msg.setIsdelete(1);
messageDao.insertOrReplace(msg);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
public void deleteMessageByMid(String mid, String mobile) {
try {
QueryBuilder<Message> qb = messageDao.queryBuilder();
DeleteQuery<Message> bd = qb.where(qb.and(Properties.Mid.eq(mid), Properties.Mobile.eq(mobile)))
.buildDelete();
bd.executeDeleteWithoutDetachingEntities();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
/**
* 根据类型id删除所有消息
*
* @param typeId
*/
public void deleteMessageByType(String typeId) {
try {
QueryBuilder<Message> qb = messageDao.queryBuilder();
DeleteQuery<Message> bd = qb.where(Properties.MsgType.eq(typeId)).buildDelete();
bd.executeDeleteWithoutDetachingEntities();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
/**
* 根据类型id删除该用户手机号
*
* @param typeId
* @param mobile
*/
public void deleteTypeMessageByTypeMob(String typeId, String mobile) {
try {
QueryBuilder<Message> qb = messageDao.queryBuilder();
DeleteQuery<Message> bd = qb.where(qb.and(Properties.MsgType.eq(typeId), Properties.Mobile.eq(mobile)))
.buildDelete();
bd.executeDeleteWithoutDetachingEntities();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
public void deleteInvalidMessage() {
try {
QueryBuilder<Message> qb = messageDao.queryBuilder();
DeleteQuery<Message> bd = qb.where(qb.and(Properties.EffectiveTime.lt(System.currentTimeMillis()),
Properties.EffectiveTime.isNotNull())).buildDelete();
bd.executeDeleteWithoutDetachingEntities();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
public void updateMessageStatus(String mobile) {
try {
String curTime = getCurTime();
QueryBuilder<Message> qb = messageDao.queryBuilder();
List<Message> msgList ;
msgList = qb.where(qb.and(Properties.Status.eq(0),
Properties.Mobile.eq(mobile), Properties.Isdelete.notEq(1))).list();
if (null != msgList && !msgList.isEmpty()) {
int size = msgList.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
Message msg = msgList.get(i);
if (null != msg) {
msg.setStatus(1);
msg.setReadTime(curTime);
messageDao.update(msg);
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
然后通过管理类的单例在Activity中调用封装后的增删改查方法!。
忠言逆耳:对于初学者请一定先运行GitHub官网给的dome示例。而不是盲目的找示例demo,那样只会放慢你学习的脚步。
岁月鎏金,用知识铭刻生命的每分每秒!

Android ProgressBar 模拟进度条效果的实现
进度条的使用
圆形进度条
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/pb"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
/>
如图

长条不显示进度进度条
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/pb2"
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"android:indeterminate="true"
/>
//表示进度条风格是长条形的//表示此进度条不显示进度 android:indeterminate="true"
如图
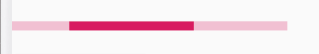
在Java代码中实现点击按钮使进度条增加,并且增加到100就隐藏
在xml布局文件中设置进度条最大值为100android:max="100"创建按钮并设置监听
//将progress1现有进度get并且赋值给一个int
//判断进度是否与最大进度一致,一致就隐藏,否则就加10
button1.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int progress = progressBar1.getProgress();
if (progress==progressBar1.getMax()){
progressBar1.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}else{
progress += 10;
progressBar1.setProgress(progress);
}
}
});
在Java代码中progress对象的
.setVisibility(View.GONE);则表示隐藏该进度条
.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);表示显示该进度条
到此这篇关于Android ProgressBar 模拟进度条效果的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Android ProgressBar进度条内容请搜索以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持!
- android自定义进度条移动效果
- Android实现简单的加载进度条
- Android实现带有指示器的进度条
- Android Studio实现进度条效果
- Android自定义圆环式进度条
- Android自定义分段式进度条
- Android自定义圆形进度条效果
- Android自定义View实现圆形进度条
- Android实现进度条(ProgressBar)的功能与用法
- Android实现下载进度条效果

Android Studio 3.0:canary 6:启动活动中的android.content.res.Resources $NotFoundException
我将android-studio 3.0从canary 5更新为canary 6,然后突然我的应用程序在KitKat(API 19)上发生崩溃,下面是stacktrace.
Main2Activity.java:10行是我的活动onCreate()方法的第一行.
07-11 13:00:39.523 8913-8913/dcpl.com.myapplication E/AndroidRuntime: FATAL EXCEPTION: main
Process: dcpl.com.myapplication, PID: 8913
java.lang.RuntimeException: Unable to start activity ComponentInfo{dcpl.com.myapplication/dcpl.com.myapplication.Main2Activity}: android.content.res.Resources$NotFoundException: Resource ID #0x7f070058
at android.app.ActivityThread.performlaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2318)
at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2396)
at android.app.ActivityThread.access$800(ActivityThread.java:139)
at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1293)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:102)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:149)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5257)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invokeNative(Native Method)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:515)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:817)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:633)
at dalvik.system.NativeStart.main(Native Method)
Caused by: android.content.res.Resources$NotFoundException: Resource ID #0x7f070058
at android.content.res.Resources.getValue(Resources.java:1173)
at android.support.v7.widget.AppCompatDrawableManager.loadDrawableFromDelegates(AppCompatDrawableManager.java:332)
at android.support.v7.widget.AppCompatDrawableManager.getDrawable(AppCompatDrawableManager.java:197)
at android.support.v7.widget.AppCompatDrawableManager.getDrawable(AppCompatDrawableManager.java:190)
at android.support.v7.widget.AppCompatDrawableManager.checkVectorDrawableSetup(AppCompatDrawableManager.java:711)
at android.support.v7.widget.AppCompatDrawableManager.getDrawable(AppCompatDrawableManager.java:195)
at android.support.v7.widget.TintTypedArray.getDrawableIfKNown(TintTypedArray.java:81)
at android.support.v7.app.AppCompatDelegateImplBase.<init>(AppCompatDelegateImplBase.java:131)
at android.support.v7.app.AppCompatDelegateImplV9.<init>(AppCompatDelegateImplV9.java:155)
at android.support.v7.app.AppCompatDelegateImplV11.<init>(AppCompatDelegateImplV11.java:31)
at android.support.v7.app.AppCompatDelegateImplV14.<init>(AppCompatDelegateImplV14.java:55)
at android.support.v7.app.AppCompatDelegate.create(AppCompatDelegate.java:205)
at android.support.v7.app.AppCompatDelegate.create(AppCompatDelegate.java:185)
at android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity.getDelegate(AppCompatActivity.java:519)
at android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity.setContentView(AppCompatActivity.java:140)
at dcpl.com.myapplication.Main2Activity.onCreate(Main2Activity.java:10)
at android.app.Activity.performCreate(Activity.java:5411)
at android.app.Instrumentation.callActivityOnCreate(Instrumentation.java:1087)
at android.app.ActivityThread.performlaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2270)
at android.app.ActivityThread.handleLaunchActivity(ActivityThread.java:2396)
at android.app.ActivityThread.access$800(ActivityThread.java:139)
at android.app.ActivityThread$H.handleMessage(ActivityThread.java:1293)
at android.os.Handler.dispatchMessage(Handler.java:102)
at android.os.Looper.loop(Looper.java:149)
at android.app.ActivityThread.main(ActivityThread.java:5257)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invokeNative(Native Method)
at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:515)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit$MethodAndArgsCaller.run(ZygoteInit.java:817)
at com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.main(ZygoteInit.java:633)
at dalvik.system.NativeStart.main(Native Method)
我该如何解决?
解决方法:
似乎这个问题与Aapt 2有关.
放
android.enableAapt2 = FALSE
在您的gradle.properties文件中,它为我修复了问题.
关于android – 如何创建像地图效果的Foursquare:和android绘制地图的介绍已经告一段落,感谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于Android / layout:如何创建标题内容布局、Android greenDAO数据库开发梳理 : Android ORM for your SQLite database、Android ProgressBar 模拟进度条效果的实现、Android Studio 3.0:canary 6:启动活动中的android.content.res.Resources $NotFoundException的相关信息,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:





