对于docker-composev3版本命令详解参考感兴趣的读者,本文将会是一篇不错的选择,我们将详细介绍docker-composeversion,并为您提供关于DockerCLI实战指南:从基础命
对于docker-compose v3 版本命令详解参考感兴趣的读者,本文将会是一篇不错的选择,我们将详细介绍docker-compose version,并为您提供关于Docker CLI 实战指南:从基础命令到 Dockerfile 构建和 Docker Compose、Docker Compose 命令详解、Docker Compose 版本过高(Docker 版本不匹配),降低 docker-compose 版本、Docker Compose 部署 Nexus3 时的 docker-compose,yml 代码的有用信息。
本文目录一览:- docker-compose v3 版本命令详解参考(docker-compose version)
- Docker CLI 实战指南:从基础命令到 Dockerfile 构建和 Docker Compose
- Docker Compose 命令详解
- Docker Compose 版本过高(Docker 版本不匹配),降低 docker-compose 版本
- Docker Compose 部署 Nexus3 时的 docker-compose,yml 代码
docker-compose v3 版本命令详解参考(docker-compose version)
参考和指南
这些主题描述了 Compose 文件格式的第 3 版。这是最新的版本.
Compose and Docker 兼容性矩阵
有几个版本的 Compose 文件格式 - 1,2,2.x 和 3.x. 下表是快速浏览。有关每个版本包含和如何升级的详细信息,请参阅关于版本和升级.
Compose 文件结构和示例
version: "3"
services:
redis:
image: redis:alpine
ports:
- "6379"
networks:
- frontend
deploy:
replicas: 2
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
db:
image: postgres:9.4
volumes:
- db-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
networks:
- backend
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
vote:
image: dockersamples/examplevotingapp_vote:before
ports:
- 5000:80
networks:
- frontend
depends_on:
- redis
deploy:
replicas: 2
update_config:
parallelism: 2
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
result:
image: dockersamples/examplevotingapp_result:before
ports:
- 5001:80
networks:
- backend
depends_on:
- db
deploy:
replicas: 1
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
worker:
image: dockersamples/examplevotingapp_worker
networks:
- frontend
- backend
deploy:
mode: replicated
replicas: 1
labels: [APP=VOTING]
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
delay: 10s
max_attempts: 3
window: 120s
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
visualizer:
image: dockersamples/visualizer:stable
ports:
- "8080:8080"
stop_grace_period: 1m30s
volumes:
- "/var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock"
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
networks:
frontend:
backend:
volumes:
db-data:
此参考页面上的主题按顶级按键按字母顺序组织,以反映撰写文件本身的结构。定义配置文件中的一部分,如顶级键 build,deploy,depends_on, networks,等等,都与所有支持他们的子课题的选项中列出。这将映射到 <key>: <option>: <value>Compose 文件的缩进结构。
一个好的开始是入门教程,它使用版本 3 编写堆栈文件来实现多容器应用程序,服务定义和群组模式。以下是本教程中使用的一些撰写文件。,
-
你的第一个 docker-compose.yml 文件
-
添加新服务并重新部署
另一个很好的参考是在 Docker for Beginners 实验室 主题 将应用程序部署到 Swarm. 上的投票应用程序示例的 compose 文件 。这也在本节顶部上展示。
服务配置参考
Compose 文件是一个定义 服务 , 网络 和 卷的 YAML 文件. Compose 文件的默认路径是 ./docker-compose.yml.
提示:您可以对此文件使用
.yml或.yaml扩展名。他们都工作.
服务定义包含将应用于为该服务启动的每个容器的配置,就像传递命令行参数一样 docker run。同样,网络和卷的定义类似于 docker network create 和 docker volume create。
正如 docker run 在 Dockerfile 指定选项(例如,CMD, EXPOSE,VOLUME,ENV)是默认的尊重 - 你不需要再次指定它们 docker-compose.yml。
您可以使用类似 Bash 的 ${VARIABLE} 语法在配置值中使用环境变量 - 有关详细信息,请参阅 变量替换 for full details.
本节包含版本 3 中服务定义支持的所有配置选项的列表。
build
build 可以指定为包含构建上下文的路径的字符串:
version: ''2''
services:
webapp:
build: ./dir
或者,作为一个对象,具有 上下文 和可选的 Dockerfile 和 args 下指定的路径:
version: ''2''
services:
webapp:
build:
context: ./dir
dockerfile: Dockerfile-alternate
args:
buildno: 1
如果指定 image 以及 build,然后撰写的名称与内置的图像 webapp 和可选的 tag 规定 image:
build: ./dir
image: webapp:tag
这将导致命名的镜像 webapp 和标签 tag,从建成./dir。
注意:在使用(版本 3)Compose 文件以群组模式部署堆栈 时,将忽略此选项 。该
docker stack命令仅接受预建图像。
上下文
到包含 Dockerfile 的目录的路径,或者是 git 仓库的 URL。
当提供的值是相对路径时,它被解释为相对于撰写文件的位置。该目录也是发送到 Docker 守护程序的构建上下文。
Compose 将使用生成的名称构建并标记它,然后使用该映像。
build:
context: ./dir
Dockerfile
备用 Docker 文件。
Compose 将使用备用文件来构建。还必须指定构建路径。
build:
context: .
dockerfile: Dockerfile-alternate
Args
添加构建参数,环境变量只能在构建过程中访问。
首先,在 Dockerfile 中指定参数:
ARG buildno
ARG password
RUN echo "Build number: $buildno"
RUN script-requiring-password.sh "$password"
然后在 build 密钥下指定参数。您可以传递映射或列表:
build:
context: .
args:
buildno: 1
password: secret
build:
context: .
args:
- buildno=1
- password=secret
您可以在指定构建参数时省略该值,在这种情况下,构建时的值是运行 Compose 的环境中的值。
args:
- buildno
- password
注:YAML 布尔值(
true,false,yes,no,on,off)必须用引号括起来,这样分析器会将它们解释为字符串。
cache_from
注意:此选项在 v3.2 中是新增功能
引擎将用于缓存解析的图像列表。
build:
context: .
cache_from:
- alpine:latest
- corp/web_app:3.14
labels
注意:此选项在 v3.3 中是新增的
使用 Docker labels 将元数据添加到生成的图像。您可以使用数组或字典。
建议您使用反向 DNS 符号来防止标签与其他软件使用的标签相冲突。
build:
context: .
labels:
com.example.description: "Accounting webapp"
com.example.department: "Finance"
com.example.label-with-empty-value: ""
build:
context: .
labels:
- "com.example.description=Accounting webapp"
- "com.example.department=Finance"
- "com.example.label-with-empty-value"
cap_add, cap_drop
添加或删除容器功能。查看 man 7 capabilities 完整列表。
cap_add:
- ALL
cap_drop:
- NET_ADMIN
- SYS_ADMIN
注意:在 使用(版本 3)Compose 文件以群组模式部署堆栈 时,将忽略这些选项 。
command
覆盖默认命令。
command: bundle exec thin -p 3000
该命令也可以是一个列表,类似于 dockerfile:
command: ["bundle", "exec", "thin", "-p", "3000"]
configs
使用每个服务 configs 配置在每个服务的基础上授予对配置的访问权限。支持两种不同的语法变体。
注意:该配置必须已经存在或 在 configs 该堆栈文件的 顶级配置 中定义,否则堆栈部署将失败
Short syntax
短语法变体只指定配置名称。这允许容器访问该配置并将其安装在 /<config_name> 容器内。源名称和目标安装点都设置为配置名称。
以下示例使用简短的语法来授予 redis 对 my_config 和 my_other_config 配置的服务访问权限。将值 my_config 设置为文件的内容./my_config.txt,并将 my_other_config 其定义为外部资源,这意味着它已经在 Docker 中定义,无论是通过运行 docker config create 命令还是通过其他堆栈部署。如果外部配置不存在,则堆栈部署失败并出现 config not found 错误。
注意:
config定义仅在版本 3.3 及更高版本的组合文件格式中受支持。
version: "3.3"
services:
redis:
image: redis:latest
deploy:
replicas: 1
configs:
- my_config
- my_other_config
configs:
my_config:
file: ./my_config.txt
my_other_config:
external: true
Long syntax
长语法在服务的任务容器中如何创建配置提供了更多的粒度。
source:Docker 中存在的配置名称。target:将要装入服务任务容器的文件的路径和名称。默认为/<source>未指定。uid和gid:数字 UID 或 GID,它将拥有服务的任务容器中的挂载配置文件。0如果没有指定,则默认为 Linux。Windows 不支持mode:将在服务的任务容器中装载的文件的权限,以八进制符号表示。例如,0444代表世界可读。默认是0444。配置不能被写入,因为它们被安装在临时文件系统中,所以如果设置可写位,则忽略它。可执行位可以设置。如果您不熟悉 UNIX 文件权限模式,您可能会发现此 权限计算器 很有用.
下面的示例设置的名称 my_config,以 redis_config 在容器内,将模式设定为 0440(组可读),并且将所述用户和组 103。该 redis 服务无法访问该 my_other_config 配置。
version: "3.3"
services:
redis:
image: redis:latest
deploy:
replicas: 1
configs:
- source: my_config
target: /redis_config
uid: ''103''
gid: ''103''
mode: 0440
configs:
my_config:
file: ./my_config.txt
my_other_config:
external: true
您可以授予对多个配置的服务访问权限,您可以混合长短语法。定义配置并不意味着授予对其的访问权限。
cgroup_parent
为容器指定一个可选的父 cgroup。
cgroup_parent: m-executor-abcd
注意:在 使用(版本 3)Compose 文件以群组模式部署堆栈 时,将忽略此选项 。
container_name
指定自定义容器名称,而不是生成的默认名称。
container_name: my-web-container
因为 Docker 容器名称必须是唯一的,如果您指定了自定义名称,则无法将服务扩展到超过 1 个容器。尝试这样做会导致错误。
注意:在 使用(版本 3)Compose 文件以群组模式部署堆栈 时,将忽略此选项 。
credential_spec
注意:此选项已在 v3.3 中添加
配置托管服务帐户的凭据规范。此选项仅用于使用 Windows 容器的服务。在 credential_spec 必须在格式 file://<filename> 或 registry://<value-name>。
在使用时 file:,引用的文件必须存在于 CredentialSpecs docker 数据目录的子目录中,这 C:\ProgramData\Docker\ 在 Windows 上是默认的。以下示例从名为 C:\ProgramData\Docker\CredentialSpecs\my-credential-spec.json 以下文件的文件加载凭据规范 :
credential_spec:
file: my-credential-spec.json
使用时 registry:,凭据规范从守护程序主机上的 Windows 注册表中读取。具有给定名称的注册表值必须位于:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\Virtualization\Containers\CredentialSpecs
以下示例从 my-credential-spec 注册表中指定的值加载凭据规范:
credential_spec:
registry: my-credential-spec
deploy
仅限版本 3
指定与部署和运行相关的配置。这只能部署到时生效 swarm 与 docker stack deploy, 并且被忽略 docker-compose up 和 docker-compose run。
version: ''3''
services:
redis:
image: redis:alpine
deploy:
replicas: 6
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
有几个子选项可用:
endpoint_mode
为连接到群组的外部客户端指定服务发现方法。
版本 3.3 .
-
endpoint_mode: vip- Docker 为服务分配虚拟 IP(VIP),作为客户端到达网络服务的 “前端”。Docker 在服务的客户端和可用的工作者节点之间路由请求,而无需客户端了解有多少个节点参与服务或其 IP 地址或端口。(这是默认值。) -
endpoint_mode: dnsrr- DNS 循环(DNSRR)服务发现不使用单个虚拟 IP。Docker 为服务设置 DNS 条目,以便服务名称的 DNS 查询返回 IP 地址列表,客户端直接连接到其中一个。如果要使用自己的负载均衡器,或混合 Windows 和 Linux 应用程序,则 DNS 循环是非常有用的。
version: "3.3"
services:
wordpress:
image: wordpress
ports:
- 8080:80
networks:
- overlay
deploy:
mode: replicated
replicas: 2
endpoint_mode: vip
mysql:
image: mysql
volumes:
- db-data:/var/lib/mysql/data
networks:
- overlay
deploy:
mode: replicated
replicas: 2
endpoint_mode: dnsrr
volumes:
db-data:
networks:
overlay:
endpoint_mode 在 swarm 模式 CLI 命令 docker service create 也可用作标志 的选项。有关所有群集相关 docker 命令的快速列表,请参阅 Swarm 模式 CLI 命令.
labels
指定服务的标签。这些标签只能在服务上设置,而不能在服务的任何容器上设置。
version: "3"
services:
web:
image: web
deploy:
labels:
com.example.description: "This label will appear on the web service"
要在容器上设置标签,请使用以下 labels 键 deploy:
version: "3"
services:
web:
image: web
labels:
com.example.description: "This label will appear on all containers for the web service"
mode
任一 global(正好一个每群节点容器)或 replicated(一个指定的数量的容器)。默认是 replicated。
version: ''3''
services:
worker:
image: dockersamples/examplevotingapp_worker
deploy:
mode: global
placement
指定布局约束
version: ''3''
services:
db:
image: postgres
deploy:
placement:
constraints:
- node.role == manager
- engine.labels.operatingsystem == ubuntu 14.04
replicas
如果服务是 replicated(默认为),请指定在任何给定时间应运行的容器数。
version: ''3''
services:
worker:
image: dockersamples/examplevotingapp_worker
networks:
- frontend
- backend
deploy:
mode: replicated
replicas: 6
resources
配置资源约束。
注意:这取代了旧的资源约束选项在撰写非群模式文件之前版本 3(
cpu_shares,cpu_quota,cpuset, mem_limit,memswap_limit,mem_swappiness 如在 升级版本 2.x 到 3.x.
这些都是一个单一的值,类似于 docker service create 对应的.
在这个通用示例中,redis 服务被限制为使用不超过 50M 的内存和 0.001(0.1%)的可用处理时间(CPU),并且具有 保留 20M 的内存和 0.0001CPU 时间(一直可用)。
version: ''3''
services:
redis:
image: redis:alpine
deploy:
resources:
limits:
cpus: ''0.001''
memory: 50M
reservations:
cpus: ''0.0001''
memory: 20M
下面的主题描述了为群集中的服务或容器设置资源约束的可用选项。
内存异常 (OOME)
如果您的服务或容器尝试使用比系统可用的更多内存,则可能会遇到内存异常(OOME),并且容器或 Docker 守护程序可能被内核 OOM 杀手杀死。为了防止这种情况发生,请确保您的应用程序在具有足够内存的主机上运行,并且了解内存不足的风险。
restart_policy
配置在退出时是否以及如何重新启动容器。替换 restart.
condition: 其中之一none,on-failure或any(默认:)any。delay: 在重新启动尝试之间等待多长时间,指定为持续时间(默认值:0)。max_attempts: 在放弃之前尝试重新启动一个容器多少次(默认:永不放弃).window: 在决定重新启动成功之前等待多长时间,指定为持续时间(默认:立即决定).
version: "3"
services:
redis:
image: redis:alpine
deploy:
restart_policy:
condition: on-failure
delay: 5s
max_attempts: 3
window: 120s
update_config
配置服务如何更新。用于配置滚动更新。
parallelism: 一次更新的容器数量。delay: 更新一组容器之间等待的时间。failure_action: 如果更新失败,该怎么办?其中之一continue,rollback或pause(默认:)pause。monitor: 每个任务更新后的持续时间来监视失败(ns|us|ms|s|m|h)(默认为 0)。max_failure_ratio: 更新期间容忍的故障率。order: 更新期间的操作顺序。其中一个stop-first(旧任务,开始新的一个前停止),或者start-first(新的任务首先启动,并且正在运行的任务将简要重叠)(默认 stop-first)注:仅支持 V3.4 及更高版本。
注意:order 仅支持 v3.4 及更高版本的撰写文件格式。
version: ''3.4''
services:
vote:
image: dockersamples/examplevotingapp_vote:before
depends_on:
- redis
deploy:
replicas: 2
update_config:
parallelism: 2
delay: 10s
order: stop-first
不支持 docker stack deploy
下面的子选项(支持 docker compose up 和 docker compose run)是不支持的 docker stack deploy 或 deploy 键的。
- build
- cgroup_parent
- container_name
- devices
- dns
- dns_search
- tmpfs
- external_links
- links
- network_mode
- security_opt
- stop_signal
- sysctls
- userns_mode
devices
设备映射列表 使用与 --devicedocker 客户端创建选项相同的格式。
devices:
- "/dev/ttyUSB0:/dev/ttyUSB0"
注意:在使用(版本 3)Compose 文件以群组模式部署堆栈 时,将忽略此选项 。
depends_on
服务之间的快速依赖,有两个作用:
-
docker-compose up将依依次顺序启动服务。在下面的例子中,db 并 redis 会开始之前 web。 -
docker-compose up SERVICE将自动包含 SERVICE 的依赖关系。在下面的例子中,docker-compose up web 也将创建和启动 db 和 redis。
简单的例子:
version: ''3''
services:
web:
build: .
depends_on:
- db
- redis
redis:
image: redis
db:
image: postgres
使用时需要注意几件事情
depends_on:
depends_on在开始之前不会等待db并且redis“准备好”,web直到它们被启动为止版本 3 不再支持的
condition形式depends_on
depends_on使用(版本 3)Compose 文件以群组模式部署堆栈 时,将忽略此选项 。
DNS
自定义 DNS 服务器。可以是单个值或列表。
dns: 8.8.8.8
dns:
- 8.8.8.8
- 9.9.9.9
注意: 使用(版本 3)Compose 文件以群组模式部署堆栈 时,将忽略此选项 。
dns_search
自定义 DNS 搜索域。可以是单个值或列表。
dns_search: example.com
dns_search:
- dc1.example.com
- dc2.example.com
注意: 使用(版本 3)Compose 文件以群组模式部署堆栈 时,将忽略此选项 。
tmpfs
版本 2 文件格式 and up.
在容器内安装临时文件系统。可以是单个值或列表。
tmpfs: /run
tmpfs:
- /run
- /tmp
注意: 使用(版本 3)Compose 文件以群组模式部署堆栈 时,将忽略此选项 。
entrypoint
覆盖默认入口点。
entrypoint: /code/entrypoint.sh
entrypoint 也可以是一个列表,类似于 dockerfile:
entrypoint:
- php
- -d
- zend_extension=/usr/local/lib/php/extensions/no-debug-non-zts-20100525/xdebug.so
- -d
- memory_limit=-1
- vendor/bin/phpunit
注意:设置
entrypoint将使用ENTRYPOINTDockerfile指令覆盖服务映像上的任何默认入口点集,并 清除映像上的任何默认命令 - 这意味着如果CMDDockerfile 中有指令,则将忽略它。
env_file
从文件添加环境变量。可以是单个值或列表。
如果您指定了一个 Compose 文件 docker-compose -f FILE,则路径 env_file 相对于该文件所在的目录。
环境变量 部分中 声明的环境变量将覆盖这些值 - 即使这些值为空或未定义,这也将成立。
env_file: .env
env_file:
- ./common.env
- ./apps/web.env
- /opt/secrets.env
Compose 期望 env 文件中的每一行都是 VAR=VAL 格式化的。以#(即注释)开始的行将被忽略,空白行也将被忽略。
# Set Rails/Rack environment
RACK_ENV=development
注意:如果您的服务指定构建选项,则在构建期间将不会自动显示在环境文件中定义的变量。使用
args子选项build定义构建时环境变量。
该值 VAL 是按原样使用的,完全没有修改。例如,如果值被引号包围(通常是 shell 变量的情况),引号将包含在传递给 Compose 的值中。
请记住,在确定分配给显示多次的变量的值时,列表中文件的顺序很重要。列表中的文件从上到下处理。对于在文件中指定的相同变量,a.env 并在文件中 分配了不同的值 b.env,如果 b.env 在下面列出(之后),则来自 b.envstand 的值。例如,给出以下声明 docker_compose.yml:
services:
some-service:
env_file:
- a.env
- b.env
和以下文件:
# a.env
VAR=1
和
# b.env
VAR=hello
$ VAR 将会 hello
environment
添加环境变量。您可以使用数组或字典。任何布尔值;true,false,yes no,需要用引号括起来,以确保它们不被 YML 解析器转换为 True 或 False。
仅具有密钥的环境变量将被解析为其正在运行的机器上的值,这对于秘密或主机特定值有帮助。
environment:
RACK_ENV: development
SHOW: ''true''
SESSION_SECRET:
environment:
- RACK_ENV=development
- SHOW=true
- SESSION_SECRET
注意:如果您的服务指定构建选项,environment 则在构建期间不会自动显示定义的变量。使用 args 子选项 build 定义构建时环境变量。
expose
暴露端口而不将它们发布到主机 - 它们只能被链接服务访问。只能指定内部端口。
expose:
- "3000"
- "8000"
external_links
连接到组合之外 docker-compose.yml 或甚至外部的容器,尤其是提供共享或公共服务的容器。 在指定容器名称和链接别名()时,external_links 遵循与 legacy 选项相似的语义。linksCONTAINER:ALIAS
external_links:
- redis_1
- project_db_1:mysql
- project_db_1:postgresql
注意: 如果您使用的是版本 2 或以上的文件格式,外部创建的容器必须连接至至少一个与要链接的服务相同的网络。链接是遗留选项。我们建议使用网络。
使用(版本 3)Compose 文件在群集模式下部署堆栈时,将忽略此选项。
extra_hosts
添加主机名映射。使用与 docker 客户端 --add-host 参数相同的值。
extra_hosts:
- "somehost:162.242.195.82"
- "otherhost:50.31.209.229"
将在 /etc/hosts 此服务的内部容器中创建具有 ip 地址和主机名的条目,例如:
162.242.195.82 somehost
50.31.209.229 otherhost
healthcheck
配置运行的支票以确定此服务的容器是否 “健康”。
healthcheck:
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://localhost"]
interval: 1m30s
timeout: 10s
retries: 3
interval 并被 timeout 指定为持续时间。
test 必须是字符串或列表。如果它是一个列表,第一项必须是 NONE,CMD 或 CMD-SHELL。如果它是一个字符串,则相当于指定 CMD-SHELL 该字符串。
# Hit the local web app
test: ["CMD", "curl", "-f", "http://localhost"]
# As above, but wrapped in /bin/sh. Both forms below are equivalent.
test: ["CMD-SHELL", "curl -f http://localhost || exit 1"]
test: curl -f https://localhost || exit 1
要禁用图像设置的任何默认的健康检查,可以使用 disable: true。这相当于指定 test: ["NONE"]。
healthcheck:
disable: true
image
指定要从中启动容器的图像。可以是存储库 / 标签或部分映像 ID。
image: redis
image: ubuntu:14.04
image: tutum/influxdb
image: example-registry.com:4000/postgresql
image: a4bc65fd
如果图像不存在,Compose 尝试拉它,除非您也指定了构建,在这种情况下,它使用指定的选项构建它,并使用指定的标签进行标记。
isolation
指定容器的隔离技术。在 Linux 上,唯一支持的值是 default。在 Windows 中,可接受的值是 default,process 和 hyperv。有关详细信息,请参阅 Docker Engine docs .
labels
使用 Docker 标签将元数据添加到容器。您可以使用数组或字典。
建议您使用反向 DNS 符号来防止标签与其他软件使用的标签相冲突。
labels:
com.example.description: "Accounting webapp"
com.example.department: "Finance"
com.example.label-with-empty-value: ""
labels:
- "com.example.description=Accounting webapp"
- "com.example.department=Finance"
- "com.example.label-with-empty-value"
links
链接到另一个服务中的容器。指定服务名称和链接别名(SERVICE:ALIAS)或仅指定服务名称。
web:
links:
- db
- db:database
- redis
链接服务的容器将以与别名相同的主机名或者未指定别名的服务名称可访问。
链接不需要启用服务进行通信 - 默认情况下,任何服务都可以达到该服务名称的任何其他服务。
链接还以与 depends_on 相同的方式表示服务之间的依赖关系 ,因此它们确定服务启动的顺序。
Notes
如果您定义了链接和网络,那么它们之间链接的服务必须至少共享一个网络以进行通信。
使用(版本 3)Compose 文件在群集模式下部署堆栈时,将忽略此选项
logging
记录该服务的配置。
logging:
driver: syslog
options:
syslog-address: "tcp://192.168.0.42:123"
该 driver 名称指定服务的容器的日志记录驱动程序,以及 --log-driverdocker 运行的选项(在此记录)。
默认值为 json-file。
driver: "json-file"
driver: "syslog"
driver: "none"
Note: 只有 json-file 和 journald 驱动程序可以直接从 docker-compose up 和 docker-compose logs。使用任何其他驱动程序不会打印任何日志。
使用 options 键指定记录驱动程序的日志记录选项,与 --log-opt 选项一样 docker run。
记录选项是键值对。syslog 选项示例:
driver: "syslog"
options:
syslog-address: "tcp://192.168.0.42:123"
默认驱动程序 json-file 具有限制存储的日志数量的选项。为此,请使用键值对来获取最大存储大小和最大文件数:
options:
max-size: "200k"
max-file: "10"
上面显示的示例将存储日志文件,直到它们达到 max-size200kB,然后旋转它们。存储的各个日志文件的数量由 max-file 值指定。当日志超出最大限制时,会删除较旧的日志文件以允许存储新日志。
这是一个 docker-compose.yml 限制日志存储的示例文件:
services:
some-service:
image: some-service
logging:
driver: "json-file"
options:
max-size: "200k"
max-file: "10"
上述用于控制日志文件和大小的示例使用特定于 json 文件驱动程序的选项。这些特定选项在其他日志记录驱动程序中不可用。
network_mode
网络模式。使用与 docker 客户端 --net 参数相同的值,加上特殊格式 service:[service name]。
network_mode: "bridge"
network_mode: "host"
network_mode: "none"
network_mode: "service:[service name]"
network_mode: "container:[container name/id]"
Notes
使用(版本 3)Compose 文件在群集模式下部署堆栈时,将忽略此选项 。
network_mode: "host"不能与 links 混合.
networks
加入网络,引用顶级 networks 密钥下的条目
services:
some-service:
networks:
- some-network
- other-network
aliases
网络上此服务的别名(替代主机名)。同一网络上的其他容器可以使用服务名称或此别名来连接到其中一个服务的容器。
由于 aliases 是网络范围的,相同的服务可以在不同的网络上有不同的别名。
Note: 全网域别名可由多个容器共享,甚至可以由多个服务共享。如果是,则不能保证名称解决的哪个容器。
一般格式如下所示。
services:
some-service:
networks:
some-network:
aliases:
- alias1
- alias3
other-network:
aliases:
- alias2
在下面的例子中,提供了三种服务(web,worker,和 db),其中两个网络(沿 new 和 legacy)。该 db 服务是在到达的主机名 db 或 database 上 new 网络,并 db 或 mysql 将上 legacy 网络。
version: ''2''
services:
web:
build: ./web
networks:
- new
worker:
build: ./worker
networks:
- legacy
db:
image: mysql
networks:
new:
aliases:
- database
legacy:
aliases:
- mysql
networks:
new:
legacy:
ipv4_address, ipv6_address
在加入网络时为该服务指定容器的静态 IP 地址。
顶级网络部分中的相应网络配置 必须具有 ipam 覆盖每个静态地址的子网配置的 块。如果需要 IPv6 寻址,则 enable_ipv6 必须设置该选项,您必须使用版本 2.x Compose 文件,如下所示。
一个例子:
version: ''2.1''
services:
app:
image: busybox
command: ifconfig
networks:
app_net:
ipv4_address: 172.16.238.10
ipv6_address: 2001:3984:3989::10
networks:
app_net:
driver: bridge
enable_ipv6: true
ipam:
driver: default
config:
-
subnet: 172.16.238.0/24
-
subnet: 2001:3984:3989::/64
pid
pid: "host"
将 PID 模式设置为主机 PID 模式。这将打开容器和主机操作系统之间的共享 PID 地址空间。使用此标志启动的容器将能够访问和操作裸机机器的命名空间中的其他容器,反之亦然。
ports
Expose ports.
Short syntax
既可以指定端口(HOST:CONTAINER),也可以指定容器端口(将选择随机的主机端口)。
Note: 以 HOST:CONTAINER 格式映射端口时,使用低于 60 的容器端口时,可能会遇到错误的结果,因为 YAML 会将格式的数字解析 xx:yy 为六进制(基数为 60)。因此,我们建议您始终将端口映射明确指定为字符串。
ports:
- "3000"
- "3000-3005"
- "8000:8000"
- "9090-9091:8080-8081"
- "49100:22"
- "127.0.0.1:8001:8001"
- "127.0.0.1:5000-5010:5000-5010"
- "6060:6060/udp"
Long syntax
长格式语法允许配置不能以简短形式表达的其他字段。
target: 容器内的端口published: 公开端港口protocol: 端口协议(tcp 或 udp)mode: host 用于在每个节点上发布主机端口,或者 ingress 用于在负载均衡的群集模式端口上发布主机端口。
ports:
- target: 80
published: 8080
protocol: tcp
mode: host
Note: v3.2 中的长语法是新的
secrets
使用每个服务 secrets 配置在每个服务的基础上授予访问权限。支持两种不同的语法变体。
Note: 该秘密必须已经存在或者 在 secrets 该堆栈文件的顶级配置中定义,否则堆栈部署将失败
For more information on secrets, see secrets.
Short syntax
短语法变体仅指定秘密名称。这允许容器访问秘密,并将其安装在 /run/secrets/<secret_name> 容器内。源名称和目标挂载点都设置为秘密名称。
以下示例使用简短的语法来授予 redis 对该 my_secret 和 my_other_secret 机密的服务访问权限。将值 my_secret 设置为文件的内容./my_secret.txt,并将 my_other_secret 其定义为外部资源,这意味着它已经在 Docker 中定义,无论是通过运行 docker secret create 命令还是通过其他堆栈部署。如果外部机密不存在,则堆栈部署失败并出现 secret not found 错误。
version: "3.1"
services:
redis:
image: redis:latest
deploy:
replicas: 1
secrets:
- my_secret
- my_other_secret
secrets:
my_secret:
file: ./my_secret.txt
my_other_secret:
external: true
Long syntax
The long syntax provides more granularity in how the secret is created within the service''s task containers.
source: The name of the secret as it exists in Docker.target: The name of the file that will be mounted in/run/secrets/in the service''s task containers. Defaults tosourceif not specified.uidandgid: The numeric UID or GID which will own the file within/run/secrets/in the service''s task containers. Both default to0if not specified.mode: The permissions for the file that will be mounted in/run/secrets/in the service''s task containers, in octal notation. For instance,0444represents world-readable. The default in Docker 1.13.1 is0000, but will be0444in the future. Secrets cannot be writable because they are mounted in a temporary filesystem, so if you set the writable bit, it is ignored. The executable bit can be set. If you aren''t familiar with UNIX file permission modes, you may find this permissions calculator{: target="blank"} useful.
The following example sets name of the my_secret to redis_secret within the container, sets the mode to 0440 (group-readable) and sets the user and group to 103. The redis service does not have access to the my_other_secret secret.
version: "3.1"
services:
redis:
image: redis:latest
deploy:
replicas: 1
secrets:
- source: my_secret
target: redis_secret
uid: ''103''
gid: ''103''
mode: 0440
secrets:
my_secret:
file: ./my_secret.txt
my_other_secret:
external: true
You can grant a service access to multiple secrets and you can mix long and short syntax. Defining a secret does not imply granting a service access to it.
security_opt
Override the default labeling scheme for each container.
security_opt:
- label:user:USER
- label:role:ROLE
Note: This option is ignored when deploying a stack in swarm mode with a (version 3) Compose file.
stop_grace_period
Specify how long to wait when attempting to stop a container if it doesn''t handle SIGTERM (or whatever stop signal has been specified with stop_signal), before sending SIGKILL. Specified as a duration.
stop_grace_period: 1s
stop_grace_period: 1m30s
By default, stop waits 10 seconds for the container to exit before sending SIGKILL.
stop_signal
Sets an alternative signal to stop the container. By default stop uses SIGTERM. Setting an alternative signal using stop_signal will cause stop to send that signal instead.
stop_signal: SIGUSR1
Note: This option is ignored when deploying a stack in swarm mode with a (version 3) Compose file.
sysctls
Kernel parameters to set in the container. You can use either an array or a dictionary.
sysctls:
net.core.somaxconn: 1024
net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies: 0
sysctls:
- net.core.somaxconn=1024
- net.ipv4.tcp_syncookies=0
Note: This option is ignored when deploying a stack in swarm mode with a (version 3) Compose file.
ulimits
Override the default ulimits for a container. You can either specify a single limit as an integer or soft/hard limits as a mapping.
ulimits:
nproc: 65535
nofile:
soft: 20000
hard: 40000
userns_mode
userns_mode: "host"
Disables the user namespace for this service, if Docker daemon is configured with user namespaces. See dockerd for more information.
Note: This option is ignored when deploying a stack in swarm mode with a (version 3) Compose file.
volumes
挂载主机路径或命名卷,指定为服务的子选项。
您可以将主机路径作为单个服务的定义的一部分进行安装,并且不需要在顶级 volumes 密钥中定义它。
但是,如果要跨多个服务重用卷,请在顶级 volumes 密钥中定义一个命名卷。使用命名卷与服务,群组和堆栈文件。
Note: 顶级 卷键定义一个命名卷,并从每个服务的 volumes 列表中引用它。这将替代 volumes_from 早期版本的撰写文件格式。
该实施例显示了一个名为体积(mydata)正在使用的 web 服务,和一个绑定安装为一个单一的服务(下第一路径定义 db 的服务 volumes)。该 db 服务还使用一个名为 dbdata(称为 db 服务的第二个路径 volumes)的命名卷,但使用旧的字符串格式来定义它,用于安装一个命名卷。命名卷必须列在顶级 volumes 密钥下,如图所示。
version: "3.2"
services:
web:
image: nginx:alpine
volumes:
- type: volume
source: mydata
target: /data
volume:
nocopy: true
- type: bind
source: ./static
target: /opt/app/static
db:
image: postgres:latest
volumes:
- "/var/run/postgres/postgres.sock:/var/run/postgres/postgres.sock"
- "dbdata:/var/lib/postgresql/data"
volumes:
mydata:
dbdata:
Short syntax
可选地指定主机(HOST:CONTAINER)或访问模式(HOST:CONTAINER:ro)上的路径。
您可以在主机上安装相对路径,该路径将相对于正在使用的 Compose 配置文件的目录进行扩展。相对路径应该始于。或..。
volumes:
# Just specify a path and let the Engine create a volume
- /var/lib/mysql
# Specify an absolute path mapping
- /opt/data:/var/lib/mysql
# Path on the host, relative to the Compose file
- ./cache:/tmp/cache
# User-relative path
- ~/configs:/etc/configs/:ro
# Named volume
- datavolume:/var/lib/mysql
Long syntax
长格式语法允许配置不能以简短形式表达的其他字段。
type: 安装类型 volume,bind 或 tmpfssource: 安装的源,主机上的绑定安装路径,或顶级 volumes 密钥中定义的卷的名称 。不适用于 tmpfs mount。target: 容器中将要装入卷的路径read_only: 将卷设置为只读的标志bind: 配置其他绑定选项propagation: 用于绑定的传播模式
volume: 配置其他卷选项nocopy: 在创建卷时禁止从容器复制数据的标志
version: "3.2"
services:
web:
image: nginx:alpine
ports:
- "80:80"
volumes:
- type: volume
source: mydata
target: /data
volume:
nocopy: true
- type: bind
source: ./static
target: /opt/app/static
networks:
webnet:
volumes:
mydata:
Note: v3.2 中的长语法是新的
Volumes for services, swarms, and stack files
当使用服务,群集和 docker-stack.yml 文件时,请记住,支持服务的任务(容器)可以部署在群集中的任何节点上,每当节点更新时,它们可能是不同的节点。
在没有指定源的命名卷的情况下,Docker 为支持服务的每个任务创建一个匿名卷。删除关联的容器后,匿名卷不会持久。
如果要使数据持久存在,请使用多主机感知的命名卷和卷驱动程序,以便可以从任何节点访问数据。或者,对服务设置约束,使其任务部署在存在卷的节点上。
作为示例,Docker Labs 中 docker-stack.yml 的表决应用程序示例的文件 定义了一个名为 db 运行 postgres 数据库的服务。它被配置为命名卷,以便将数据保留在群集中, 并且被限制为仅在 manager 节点上运行。这是从该文件的相关剪辑:
version: "3"
services:
db:
image: postgres:9.4
volumes:
- db-data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
networks:
- backend
deploy:
placement:
constraints: [node.role == manager]
restart
no 是默认的重新启动策略,它不会在任何情况下重新启动容器。当 always 指定时,容器总是重新启动。on-failure 如果退出代码指示故障错误,该 策略将重新启动容器。
restart: "no"
restart: always
restart: on-failure
restart: unless-stopped
domainname, hostname, ipc, mac_address, privileged, read_only, shm_size, stdin_open, tty, user, working_dir
这些都是一个单一的值,类似于其 docker run 对应物
user: postgresql
working_dir: /code
domainname: foo.com
hostname: foo
ipc: host
mac_address: 02:42:ac:11:65:43
privileged: true
read_only: true
shm_size: 64M
stdin_open: true
tty: true
Specifying durations
一些配置选项,如 interval 和 timeout 子选项 check,接受一个持续时间为看起来像这样的格式的字符串:
2.5s
10s
1m30s
2h32m
5h34m56s
The supported units are us, ms, s, m and h.
Volume configuration reference
虽然可以在文件中声明卷作为服务声明的一部分,但本节允许您创建 volumes_from 可以跨多个服务重复使用的命名卷(不依赖),并且可以使用 docker 命令行轻松地检索和检查 API。有关更多信息,请参阅 docker volume 子命令文档。
以下是一个双服务设置的示例,其中将数据库的数据目录与其他服务共享为卷,以便可以定期备份数据库的数据目录:
version: "3"
services:
db:
image: db
volumes:
- data-volume:/var/lib/db
backup:
image: backup-service
volumes:
- data-volume:/var/lib/backup/data
volumes:
data-volume:
顶级 volumes 密钥下的条目可以为空,在这种情况下,它将使用引擎配置的默认驱动程序(在大多数情况下,这是 local 驱动程序)。
driver
指定该卷使用哪个卷驱动程序。默认为 Docker Engine 配置为使用的任何驱动程序,这在大多数情况下是这样 local。如果驱动程序不可用,引擎将在 docker-compose up 尝试创建卷时返回错误 。
driver: foobar
driver_opts
指定选项列表作为键值对,以传递给此卷的驱动程序。这些选项与驱动程序相关 - 有关详细信息,请参阅驱动程序文档。可选的。
driver_opts:
foo: "bar"
baz: 1
external
如果设置为 true,则指定此卷已在 Compose 之外创建。docker-compose up 不会尝试创建它,如果不存在则会引发错误。
external 不能与其他卷配置键(driver,driver_opts)结合使用。
在下面的示例中,[projectname]_dataCompose 不是尝试创建一个名为的卷,而是 会查找一个简单调用的现有卷,data 并将其安装到 db 服务的容器中。
version: ''2''
services:
db:
image: postgres
volumes:
- data:/var/lib/postgresql/data
volumes:
data:
external: true
您还可以在 Compose 文件中与用于引用卷的名称分开指定卷的名称:
volumes:
data:
external:
name: actual-name-of-volume
总是使用 docker stack deploy 创建外部卷
如果使用 docker stack deploy 以 swarm 模式启动应用程序 (而不是 docker 组合),则将创建不存在的外部卷。在群集模式下,当由服务定义时,会自动创建一个卷。由于服务任务在新节点上安排, 所以 swarmkit 会在本地节点上创建卷。
labels
使用 Docker 标签将元数据添加到容器 。您可以使用数组或字典。
建议您使用反向 DNS 符号来防止标签与其他软件使用的标签相冲突。
labels:
com.example.description: "Database volume"
com.example.department: "IT/Ops"
com.example.label-with-empty-value: ""
labels:
- "com.example.description=Database volume"
- "com.example.department=IT/Ops"
- "com.example.label-with-empty-value"
Network configuration reference
顶级 networks 密钥允许您指定要创建的网络。
-
For a full explanation of Compose''s use of Docker networking features and all network driver options, see the Networking guide.
-
For Docker Labs tutorials on networking, start with Designing Scalable, Portable Docker Container Networks
driver
指定该网络应使用哪个驱动程序。
默认驱动程序取决于您使用的 Docker Engine 是如何配置的,但在大多数情况下,它将 bridge 位于单个主机和 overlaySwarm 上。
如果驱动程序不可用,Docker Engine 将返回一个错误。
driver: overlay
bridge
Docker 默认 bridge 在单个主机上使用网络。
overlay
该 overlay 驱动程序创建一个跨多个节点命名的网络 swarm.
-
For a working example of how to build and use an
overlaynetwork with a service in swarm mode, see the Docker Labs tutorial on Overlay networking and service discovery. -
For an in-depth look at how it works under the hood, see the networking concepts lab on the Overlay Driver Network Architecture.
host or none
使用主机的网络堆栈,或没有网络。等同于 docker run --net=host 或 docker run --net=none。仅在使用 docker stack 命令时使用 。如果使用该 docker-compose 命令,请改用 network_mode。
使用内置的网络,如语法 host 和 none 稍有不同。使用名称 host 或 none(Docker 已经自动创建的)和 Compose 可以使用的别名(hostnet 或 nonet 在这些示例中)定义外部网络,然后使用别名授予对该网络的服务访问权限。
services:
web:
...
networks:
hostnet: {}
networks:
hostnet:
external:
name: host
services:
web:
...
networks:
nonet: {}
networks:
nonet:
external:
name: none
driver_opts
指定选项列表作为键值对,以传递给此网络的驱动程序。这些选项与驱动程序相关 - 有关详细信息,请参阅驱动程序文档。可选的。
driver_opts:
foo: "bar"
baz: 1
attachable
Note: Only supported for v3.2 and higher.
仅在 driver 设置时使用 overlay。如果设置为 true,则除了服务之外,独立容器可以附加到此网络。如果独立的容器附加到覆盖网络,则它可以与服务和独立容器通信,这些容器也从其他 Docker 守护程序连接到覆盖网络。
networks:
mynet1:
driver: overlay
attachable: true
enable_ipv6
在此网络上启用 IPv6 网络。
Compose File 版本 3 中不支持
enable_ipv6要求您使用版本 2 Compose 文件,因为在 Swarm 模式下此命令尚不支持。
ipam
Specify custom IPAM config. This is an object with several properties, each of which is optional:
driver: Custom IPAM driver, instead of the default.config: A list with zero or more config blocks, each containing any of the following keys:subnet: Subnet in CIDR format that represents a network segment
A full example:
ipam:
driver: default
config:
- subnet: 172.28.0.0/16
Note: Additional IPAM configurations, such as
gateway, are only honored for version 2 at the moment.
internal
By default, Docker also connects a bridge network to it to provide external connectivity. If you want to create an externally isolated overlay network, you can set this option to true.
labels
Add metadata to containers using Docker labels. You can use either an array or a dictionary.
It''s recommended that you use reverse-DNS notation to prevent your labels from conflicting with those used by other software.
labels:
com.example.description: "Financial transaction network"
com.example.department: "Finance"
com.example.label-with-empty-value: ""
labels:
- "com.example.description=Financial transaction network"
- "com.example.department=Finance"
- "com.example.label-with-empty-value"
external
If set to true, specifies that this network has been created outside of Compose. docker-compose up will not attempt to create it, and will raise an error if it doesn''t exist.
external cannot be used in conjunction with other network configuration keys (driver, driver_opts, ipam, internal).
In the example below, proxy is the gateway to the outside world. Instead of attempting to create a network called [projectname]_outside, Compose will look for an existing network simply called outside and connect the proxy service''s containers to it.
version: ''2''
services:
proxy:
build: ./proxy
networks:
- outside
- default
app:
build: ./app
networks:
- default
networks:
outside:
external: true
You can also specify the name of the network separately from the name used to refer to it within the Compose file:
networks:
outside:
external:
name: actual-name-of-network
configs configuration reference
The top-level configs declaration defines or references configs which can be granted to the services in this stack. The source of the config is either file or external.
file: The config is created with the contents of the file at the specified path.external: If set to true, specifies that this config has already been created. Docker will not attempt to create it, and if it does not exist, aconfig not founderror occurs.
In this example, my_first_config will be created (as <stack_name>_my_first_config)when the stack is deployed, and my_second_config already exists in Docker.
configs:
my_first_config:
file: ./config_data
my_second_config:
external: true
Another variant for external configs is when the name of the config in Docker is different from the name that will exist within the service. The following example modifies the previous one to use the external config called redis_config.
configs:
my_first_config:
file: ./config_data
my_second_config:
external:
name: redis_config
You still need to grant access to the config to each service in the stack.
secrets configuration reference
The top-level secrets declaration defines or references secrets which can be granted to the services in this stack. The source of the secret is either file or external.
file: The secret is created with the contents of the file at the specified path.external: If set to true, specifies that this secret has already been created. Docker will not attempt to create it, and if it does not exist, asecret not founderror occurs.
In this example, my_first_secret will be created (as <stack_name>_my_first_secret)when the stack is deployed, and my_second_secret already exists in Docker.
secrets:
my_first_secret:
file: ./secret_data
my_second_secret:
external: true
Another variant for external secrets is when the name of the secret in Docker is different from the name that will exist within the service. The following example modifies the previous one to use the external secret called redis_secret.
secrets:
my_first_secret:
file: ./secret_data
my_second_secret:
external:
name: redis_secret
You still need to grant access to the secrets to each service in the stack.
Variable substitution
{% include content/compose-var-sub.md %}
Compose documentation
- User guide
- Installing Compose
- Compose file versions and upgrading
- Get started with Docker
- Samples
- Command line reference

Docker CLI 实战指南:从基础命令到 Dockerfile 构建和 Docker Compose
Docker 学习路线 11:Docker命令行
Docker CLI (命令行界面) 是一个强大的工具,可让您与 Docker 容器、映像、卷和网络进行交互和管理。它为用户提供了广泛的命令,用于在其开发和生产工作流中创建、运行和管理 Docker 容器和其他 Docker 资源。
安装
要开始使用 Docker CLI,您需要在计算机上安装 Docker。您可以从 Docker 文档的官方安装指南中按照您所使用的操作系统进行安装。
基本命令
以下是一些基本的 Docker CLI 命令,供您熟悉:
docker run:从 Docker 映像创建并启动容器docker container:列出正在运行的容器docker image:列出系统中所有可用的映像docker pull:从 Docker Hub 或其他注册表拉取映像docker push:将映像推送到 Docker Hub 或其他注册表docker build:从 Dockerfile 构建映像docker exec:在正在运行的容器中运行命令docker logs:显示容器的日志
Docker Run 选项
docker run 是 Docker CLI 中最重要的命令之一。您可以使用各种选项自定义容器的行为,例如:
d, --detach:在后台运行容器e, --env:为容器设置环境变量v, --volume:绑定挂载卷p, --publish:将容器的端口发布到主机name:为容器指定名称restart:指定容器的重启策略rm:容器退出时自动删除容器
Dockerfile
Dockerfile 是一个包含构建 Docker 映像的指令的脚本。您可以使用 Docker CLI 使用 Dockerfile 构建、更新和管理 Docker 映像。
以下是 Dockerfile 的一个简单示例:
# Set the base image to use
FROM alpine:3.7
# Update the system and install packages
RUN apk update && apk add curl
# Set the working directory
WORKDIR /app
# Copy the application file
COPY app.sh .
# Set the entry point
ENTRYPOINT ["./app.sh"]
要构建映像,请使用以下命令:
docker build -t my-image .
Docker Compose
Docker Compose 是一个 CLI 工具,用于使用 YAML 文件定义和管理多容器 Docker 应用程序。它与 Docker CLI 协作,提供了一种一致的方式来管理多个容器及其依赖项。
使用官方的安装指南安装 Docker Compose,然后您可以创建一个 docker-compose.yml 文件来定义和运行多容器应用程序:
version: ''3''
services:
web:
image: webapp-image
ports: - "80:80"
database:
image: mysql
environment: - MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=my-secret-pw
使用以下命令运行应用程序:
docker-compose up
总之,Docker CLI 是管理 Docker 容器和资源的强大而多才多艺的工具。一旦熟悉其命令和功能,您将能够轻松开发、维护和部署使用 Docker 的应用程序。
Docker镜像
Docker镜像是一种轻量级、独立、可执行的软件包,其包含了运行应用程序所需的所有组件。这些组件包括:依赖项、库、运行时、系统工具和代码等,以确保应用程序在不同的环境中可以保持一致地运行。
Docker镜像是使用Dockerfile进行构建和管理的。Dockerfile是一个包含了创建Docker镜像所需指令的脚本,提供了一个逐步设置应用程序环境的指南。
使用Docker镜像
Docker CLI提供了多个命令来管理和使用Docker镜像。其中一些重要的命令包括:
docker image ls:列出本地系统上所有可用的镜像。docker build:从Dockerfile构建镜像。docker image rm:删除一个或多个镜像。docker pull:从注册表(如Docker Hub)将镜像拉到本地系统。docker push:将镜像推送到仓库。
例如,要从Docker Hub拉取官方的Ubuntu镜像,可以运行以下命令:
docker pull ubuntu:latest
拉取镜像后,可以使用docker run命令创建和运行一个使用该镜像的容器:
docker run -it ubuntu:latest /bin/bash
这个命令将创建一个新的容器,并使用**/bin/bash** shell在容器内启动一个交互式会话。
共享镜像
Docker镜像可以使用容器注册表(如Docker Hub、Google Container Registry或Amazon Elastic Container Registry(ECR))共享和分发。一旦将您的镜像推送到注册表中,其他人就可以轻松地访问和使用它们。
要共享您的镜像,您首先需要使用适当的命名格式对其进行标记:
docker tag <image-id> <username>/<repository>:<tag>
然后,您可以使用以下命令将标记的镜像推送到注册表中:
docker push <username>/<repository>:<tag>
总之,Docker镜像是Docker生态系统中不可或缺的一部分,允许开发人员打包其应用程序、轻松地共享它们,并在不同的环境中确保一致性。通过理解Docker镜像和管理它们的命令,您可以利用容器化的力量,增强您的开发工作流程。在您的开发过程中使用Docker镜像可以大大提高开发效率,减少开发过程中的问题,让您能够更好地专注于应用程序的核心开发。
容器
容器可以被视为轻量级的、独立的可执行软件包,包括运行所需的所有东西,包括代码、运行时、库、环境变量和配置文件。容器将软件与其环境隔离开来,确保其在不同环境下工作一致。
为什么使用容器?
- 可移植性:容器确保应用程序在不同平台上一致工作,无论是开发人员的笔记本电脑还是生产服务器。这消除了“它在我的机器上运行”的问题。
- 效率:容器很轻量级,因为它们使用共享资源,没有完整操作系统的开销。这使得启动时间更快,减少资源使用。
- 可扩展性:容器可以根据工作量轻松地进行缩放,因此非常适合分布式应用程序和微服务。
- 一致性:容器使得开发人员、QA 和运维团队在整个应用程序生命周期中拥有一致的环境,从而加快了部署流程。
- 安全性:容器提供了一定程度的隔离,使其与其他容器和底层主机系统隔离开来,有助于维护应用程序的安全性。
使用 Docker CLI 工作
Docker CLI 提供了多个命令,可帮助您创建、管理和与容器交互。一些常用命令包括:
docker run:用于创建和启动新容器。docker container ls:列出运行中的容器。docker container stop:停止运行中的容器。docker container rm:删除已停止的容器。docker exec:在运行中的容器中执行命令。docker logs:获取容器的日志,有助于调试问题。
Docker卷
Docker卷是一种用于存储Docker容器生成和使用的数据的机制。它们允许您将数据与容器本身分开,从而轻松备份、迁移和管理持久性数据。
卷的重要性
Docker容器本质上是暂时的,这意味着它们可以轻松地停止、删除或替换。尽管这对应用程序开发和部署非常有利,但处理持久性数据时会带来挑战。这就是卷的作用。它们提供了一种将数据存储和管理与容器的生命周期分开的方法。
卷的类型
Docker中有三种类型的卷:
- 主机卷:它们存储在主机机器的文件系统中,通常位于
/var/lib/docker/volumes目录中。这些可以很容易地访问,但可能会带来可移植性或文件系统兼容性问题。 - 匿名卷:这些是在运行容器时没有指定卷时自动生成的。它们的ID由Docker生成,也存储在主机机器的文件系统中。
- 命名卷:与匿名卷类似,命名卷也存储在主机机器的文件系统中。但是,您可以提供自定义名称,这样在其他容器中引用或备份时更容易。
使用Docker CLI管理卷
Docker CLI提供了各种命令来管理卷:
docker volume create: 使用给定的名称创建新卷。docker volume ls: 列出系统中的所有卷。docker volume inspect: 提供有关特定卷的详细信息。docker volume rm: 删除卷。docker volume prune: 删除所有未使用的卷。
要在容器中使用卷,可以在docker run命令期间使用-v或--volume标志。例如:
docker run -d --name my-container -v my-named-volume:/var/lib/data my-image
此命令使用“my-image”映像创建一个名为“my-container”的新容器,并在容器内部将“my-named-volume”卷挂载到/var/lib/data路径。
Docker 网络
Docker 网络提供了管理容器通信的重要方法。它允许容器使用各种网络驱动程序相互通信并与主机机器通信。通过理解和利用不同类型的网络驱动程序,您可以设计容器网络以适应特定的场景或应用程序需求。
网络驱动程序
Docker 中有几个可用的网络驱动程序。这里,我们将介绍四个最常见的驱动程序:
- bridge:容器的默认网络驱动程序。它创建了一个私有网络,容器可以相互通信并与主机机器通信。在此网络上的容器可以通过主机网络访问外部资源。
- host:该驱动程序取消了网络隔离并允许容器共享主机的网络。在网络性能至关重要的情况下,它非常有用,因为它最小化了容器网络的开销。
- none:该网络驱动程序禁用容器网络。使用此驱动程序的容器在没有任何网络访问的隔离环境下运行。
- overlay:该网络驱动程序使部署在不同主机上的容器能够相互通信。它专为 Docker Swarm 设计,并且非常适合多主机或基于集群的容器部署。
管理 Docker 网络
Docker CLI 提供了各种命令来管理网络。以下是一些有用的命令:
- 列出所有网络:
docker network ls - 检查网络:
docker network inspect <network_name> - 创建新网络:
docker network create --driver <driver_type> <network_name> - 将容器连接到网络:
docker network connect <network_name> <container_name> - 将容器与网络断开连接:
docker network disconnect <network_name> <container_name> - 删除网络:
docker network rm <network_name>
最后
为了方便其他设备和平台的小伙伴观看往期文章:
微信公众号搜索:Let us Coding,关注后即可获取最新文章推送
看完如果觉得有帮助,欢迎 点赞、收藏、关注

Docker Compose 命令详解
1.Docker compose 的使用非常类似于 docker 命令的使用,但是需要注意的是大部分的 compose 命令都需要到 docker-compose.yml 文件所在的目录下才能执行。
2.compose 以守护进程模式运行加 - d 选项
$ docker-compose up -d
3. 查看有哪些服务,使用 docker-compose ps 命令,非常类似于 docker 的 ps 命令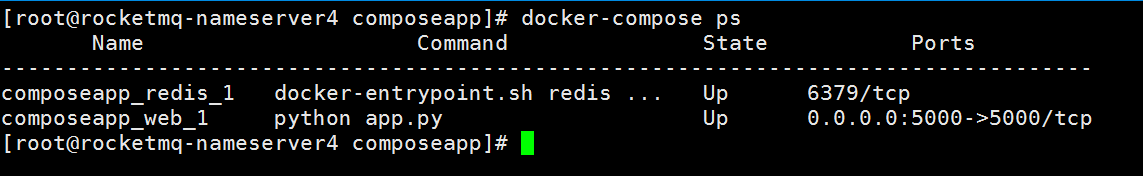
4. 查看 compose 日志
$ docker-compose logs web
$ docker-compose logs redis
5. 停止 compose 服务
$ docker-compose stop
$ docker-compose ps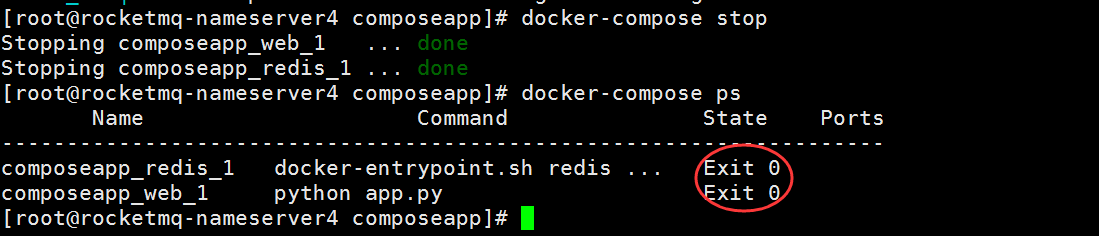
看到服务的状态为 Exit 退出状态
6. 重启 compose 服务
$ docker-compose restart
$ docker-compose ps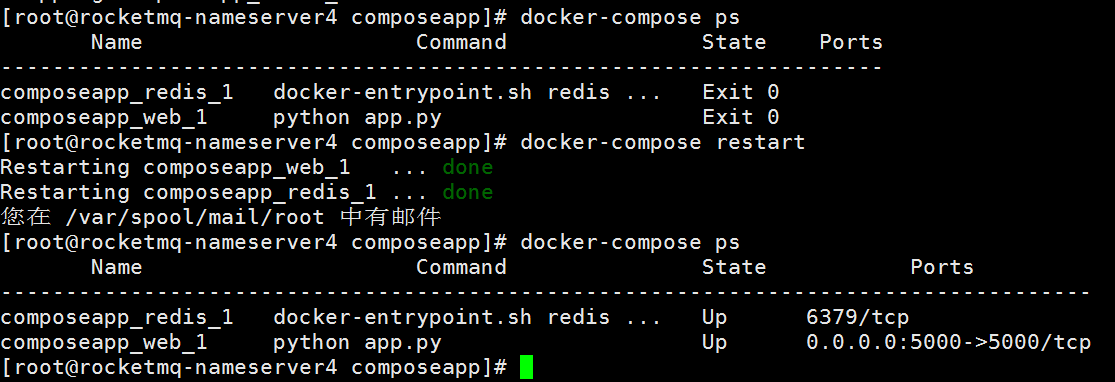
7.kill compose 服务
$ docker-compose kill
$ docker-compose ps
状态码为 137
8. 删除 compose 服务
$ docker-compose rm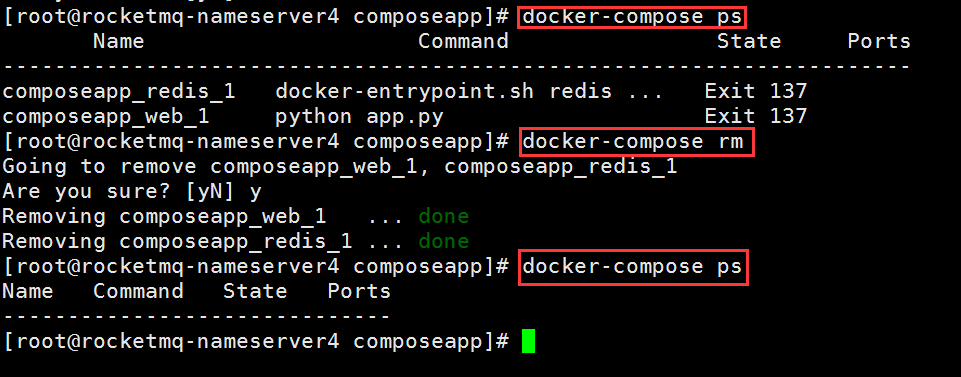
9. 更多的 docker-compose 命令可以使用 docker-compose --help 查看

Docker Compose 版本过高(Docker 版本不匹配),降低 docker-compose 版本
通过 docker-compose 启动容器,报错:
ERROR: The Docker Engine version is less than the minimum required by Compose. Your current project requires a Docker Engine of version 1.10.0 or greater.
升级 Docker 过于麻烦,只能降 docker-compose 的版本。
先看一下我们已经安装的 Docker 版本:
[root@Redmine-186 docker-compose]# docker -v
Docker version 1.7.1, build 786b29d/1.7.1 经查 Docker Compose Github Docs,发现 docker-compose 1.5.2 版本是兼容 Docker 1.7.1 的:Note that Compose 1.5.2 requires Docker 1.7.1 or later.。
好了,开始降级 docker-compose,先卸载:
# pip uninstall docker-compose
再安装指定版本:
# pip install docker-compose==1.5.2至此,docker-compose 降版本成功!
docker-compose.yml 版本问题
解决完 docker-compse 版本问题适配之后,对着已有的 docker-compose.yml 执行 “,会提示不能正常识别 docker-compose.yml 文件中的内容。究其原因,是因为我们的 docker-compose 1.5.2 只支持 V1 版本的 docker-compose.yml ,那么好,把现在 V2 版本的 docker-compose.yml 改成 V1 版本的格式。
V1 版本的 docker-compose.yml 只被支持到 docker-compose 1.6.x。再往后的 docker-compose 版本就不再支持 V1 版本的 docker-compose.yml。
先看文档:Compose file versions and upgrading。
V1 版本的 docker-compose.yml 文件格式主要区别就是:
- 没有开头的 version 声明
- 没有 services 声明
- 不支持 depends_on
- 不支持命名的 volumes, networks, build arguments 声明
- 其他我没用到的所以没细究的区别
附录
- How To Install Docker on CentOS 6
- Docker and docker-compose in CentOS 6
- 关于 pip 安装时提示 pkg_resources.DistributionNotFound 错误问题
- CentOS 升级 Python2.7
- ERROR: The Docker Engine version is less than the minimum required by Compose
- Docker Compose Github Docs
- Compose file versions and upgrading

Docker Compose 部署 Nexus3 时的 docker-compose,yml 代码
场景
Docker-Compose 简介与 Ubuntu Server 上安装 Compose:
https://blog.csdn.net/BADAO_LIUMANG_QIZHI/article/details/100902301
Docker Compose 基本使用 - 使用 Compose 启动 Tomcat 为例:
https://blog.csdn.net/BADAO_LIUMANG_QIZHI/article/details/100904080
Docker Compose 部署项目到容器 - 基于 Tomcat 和 mysql 的商城项目 (附源码和 sql 下载):
https://blog.csdn.net/BADAO_LIUMANG_QIZHI/article/details/100941366
在上面实现基本的 Compose 的操作的基础上,实现使用 Docker Compose 搭建 Nexus3。
注:
博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/badao_liumang_qizhi
关注公众号
霸道的程序猿
获取编程相关电子书、教程推送与免费下载。
实现
version: ''3''
services:
nexus:
restart: always
image: sonatype/nexus3
container_name: nexus3
ports:
- 8081:8081
volumes:
- /usr/local/docker/nexus/nexus-data:/nexus-data
今天关于docker-compose v3 版本命令详解参考和docker-compose version的分享就到这里,希望大家有所收获,若想了解更多关于Docker CLI 实战指南:从基础命令到 Dockerfile 构建和 Docker Compose、Docker Compose 命令详解、Docker Compose 版本过高(Docker 版本不匹配),降低 docker-compose 版本、Docker Compose 部署 Nexus3 时的 docker-compose,yml 代码等相关知识,可以在本站进行查询。
本文标签:





