关于Hosts/W32qemucompile的问题就给大家分享到这里,感谢你花时间阅读本站内容,更多关于:org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.CompilationRe
关于Hosts/W32 qemu compile的问题就给大家分享到这里,感谢你花时间阅读本站内容,更多关于: org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.CompilationResult.getProblems()[Lorg/eclipse/jdt/core/compiler/IProblem;、Angular self study 2 - compile how is hello {{ name }} compiled、asp.net – system.web.compilation.debug与system.codedom.compilers.compiler.compilerOptions / define:Debug = True、c# – LINQ-SQL – 在CompiledQuery.Compile中使用静态只读字段?等相关知识的信息别忘了在本站进行查找喔。
本文目录一览:- Hosts/W32 qemu compile
- : org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.CompilationResult.getProblems()[Lorg/eclipse/jdt/core/compiler/IProblem;
- Angular self study 2 - compile how is hello {{ name }} compiled
- asp.net – system.web.compilation.debug与system.codedom.compilers.compiler.compilerOptions / define:Debug = True
- c# – LINQ-SQL – 在CompiledQuery.Compile中使用静态只读字段?

Hosts/W32 qemu compile
https://wiki.qemu.org/Documentation/GettingStartedDevelopers
https://wiki.qemu.org/Documentation/Debugging
Contents
- 1 QEMU on W32 and W64 hosts
- 1.1 Building QEMU for W32
- 1.1.1 Cross builds
- 1.1.1.1 Debian based cross builds
- 1.1.1.2 Linux Mint based cross builds
- 1.1.1.3 OpenSUSE based cross builds
- 1.1.1.4 Fedora based cross builds
- 1.1.1.5 Docker based cross builds
- 1.1.2 Native builds with Mingw-w64
- 1.1.2.1 Libraries (also needed for cross builds)
- 1.1.2.2 Tools (only needed for native builds)
- 1.1.3 Native builds with Cygwin
- 1.1.3.1 Required packages
- 1.1.3.2 Recommended packages
- 1.1.3.3 Optional packages
- 1.1.1 Cross builds
- 1.2 Building QEMU for W64
- 1.2.1 Cross builds
- 1.2.1.1 Debian based cross builds
- 1.2.1.2 Fedora based cross builds
- 1.2.1.3 Libraries (also needed for cross builds)
- 1.2.2 Native builds with MSYS2
- 1.2.1 Cross builds
- 1.3 Installation
- 1.4 Running QEMU for W32
- 1.4.1 System emulation
- 1.4.2 Special W32 devices
- 1.5 Links
- 1.1 Building QEMU for W32
QEMU on W32 and W64 hosts
This documentation is work in progress - more information will be added as needed. It will finally replace the old documentation from the QEMU user manual. I think that a wiki is better in keeping evolving documentation like this one up to date.
While QEMU''s main host platform is Linux, it is sometimes also useful to build or run it on members of the W32 / W64 family of operating systems (MS Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, Windows 7, ...) or on ReactOS (a W32 clone).
Running QEMU on the 64-bit variants is similar but needs additional documentation and currently some code patches. Support for W64 was added in QEMU 1.1.
Please note that less developers work on QEMU for W32 / W64 hosts, so it might be less stable (but I don''t think it is).
Some system emulations on Linux use KVM, a special emulation mode which claims to reach nearly native speed. KVM is mainly used for x86 (32 and 64 bit) emulation on x86 hosts running Linux. There exists a highly experimental KVM for W32, but it is unknown whether it works with QEMU. Starting with QEMU 2.9, there is also a working acceleration similar to KVM, but based on Intel HAXM.
Building QEMU for W32
QEMU for W32 needs a fairly complete Mingw-w64 based development environment with tools (make, compiler, linker, ...) and some additional libraries. Building with the older MinGW does not work!
Cross builds
Compilation of QEMU for W32 on non-W32 hosts (e.g. Linux hosts) is called cross compilation. Some Linux distributions (Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora and maybe others) already include packages needed for cross compilation, so the installation of these packages is the first step.
Debian based cross builds
# Debian squeeze for W32: apt-get install gcc-mingw32 mingw32-binutils mingw32-runtime
# Debian (squeeze?) for W64: apt-get install gcc-mingw32 mingw32-binutils mingw-w64
SDL support is not included in standard MinGW, but packages for MinGW are available on the SDL homepage. POSIX thread support is not included in Debian or Ubuntu. Latest QEMU will need it, so you have to get it from MinGW (see links below).
Cross compilers usually are installed in /usr/bin with a prefix. For Debian, the cross gcc is called i586-mingw32msvc-gcc. This cross prefix must be passed to QEMU''s configure.
# Debian cross configuration for W32: configure --cross-prefix=i586-mingw32msvc- [--extra-cflags=-mthreads]
Compiler option is needed for gcc versions which don''t support TLS (thread local storage) without it (version 4.4 which is Debian''s default needs it!).
Debian does not include a cross pkg-config, but it is required for cross builds. The following script can be saved as /usr/bin/i586-mingw32msvc-pkg-config and optionally be linked to /usr/bin/amd64-mingw32msvc-pkg-config.
#!/bin/sh basename=`basename $0` prefix=/usr/`echo $basename|sed s/-pkg-config//` PKG_CONFIG_LIBDIR=$prefix/lib/pkgconfig export PKG_CONFIG_LIBDIR pkg-config --define-variable=prefix=$prefix $@
Linux Mint based cross builds
These instructions were tested with the Linux Mint Debian Edition on 2012-06-02.
# Linux Mint for W32 and W64 (about 463 MiB): apt-get install mingw-w64
OpenSUSE based cross builds
Add http://download.opensuse.org/repositories/windows:/mingw:/win32/openSUSE_11.4 (update with your release version) to the list of software repositories. Then install at least the following packets (most of them are pulled via dependencies):
mingw32-binutils
mingw32-cpp
mingw32-cross-binutils
mingw32-cross-cpp
mingw32-cross-gcc
mingw32-cross-pkg-config
mingw32-filesystem
mingw32-gcc
mingw32-glib2
mingw32-glib2-devel
mingw32-glib2-lang
mingw32-headers
mingw32-libgcc
mingw32-libgmp
mingw32-libintl
mingw32-libintl-devel
mingw32-libmpc
mingw32-libmpfr
mingw32-libSDL
mingw32-libSDL-devel
mingw32-libssp
mingw32-runtime
mingw32-zlib
mingw32-zlib-devel
This toolchain does not include libiberty.a in its binutils package, but it also does not need to. If building against a QEMU version that still pulls this in unconditionally, simply drop the -liberty from configure.
For W64 use the corresponding win64 repository and mingw64- packages.
Fedora based cross builds
Fedora supports both W64 and W32 cross builds.
# Fedora for W32 cross build: dnf install mingw32-pixman dnf install mingw32-glib2 dnf install mingw32-gmp dnf install mingw32-SDL dnf install mingw32-pkg-config
# Fedora for W64 cross build: dnf install mingw64-pixman dnf install mingw64-glib2 dnf install mingw64-gmp dnf install mingw64-SDL dnf install mingw64-pkg-config
Cross compilers usually are installed in /usr/bin with a prefix. This cross prefix must be passed to QEMU''s configure. The prefix depends on your target platform.
For Fedora W64 builds, the cross gcc is called x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc.
# Fedora cross configuration for W64: ./configure --cross-prefix=x86_64-w64-mingw32-
For Fedora W32 builds, the cross gcc is called i686-w64-mingw32-gcc.
# Fedora cross configuration for W32: ./configure --cross-prefix=i686-w64-mingw32-
Note that "-mingw32-w64" appears in prefix for both W32 and W64 builds.
Docker based cross builds
As of June 2016, the master tree supports "docker based compiling", which can be used for convenient windows cross build.
Make sure your docker command works ("docker ps" or "sudo docker ps" reports no error), then cd into the root of QEMU source tree and run
make docker-test-mingw@fedora V=1 DEBUG=1 J=4
, it will download and initialize the needed docker image for you, and drop you into a shell in the started container. Run
cd $QEMU_SRC
then
./configure --cross-prefix=x86_64-w64-mingw32-
or
./configure --cross-prefix=i686-w64-mingw32-
for 64bit/32bit builds respectively.
Native builds with Mingw-w64
Get and install Mingw-w64. In addition, some more packages are needed:
Libraries (also needed for cross builds)
- GLib Run-time (http://ftp.gnome.org/pub/gnome/binaries/win32/glib/2.28/glib_2.28.1-1_win32.zip)
- GLib Development (http://ftp.gnome.org/pub/gnome/binaries/win32/glib/2.28/glib-dev_2.28.1-1_win32.zip)
- gettext-runtime Development (http://ftp.gnome.org/pub/gnome/binaries/win32/dependencies/gettext-runtime-dev_0.18.1.1-2_win32.zip)
Tools (only needed for native builds)
- pkg-config (http://ftp.gnome.org/pub/gnome/binaries/win32/dependencies/pkg-config_0.23-3_win32.zip)
Get the QEMU source code (git or tarball), then run configure and make.
Native builds with Cygwin
Builds with the normal Cygwin compiler are not supported. Nevertheless, cygwin can be used as a build environment because it also contains all necessary Mingw-w64 packages.
# Don''t build in the QEMU source directory. Using a subdirectory is better. # Here is an example of a debug build. SRC_PATH=$PWD BUILD_DIR=$PWD/bin/debug/i686-w64-mingw32 mkdir -p $BUILD_DIR cd $BUILD_DIR $SRC_PATH/configure'' ''--enable-debug'' ''--cross-prefix=i686-w64-mingw32-'' make
For 32 bit builds, these packages should be installed:
Required packages
- mingw64-i686-gcc-g++
- mingw64-i686-glib2.0
- mingw64-i686-pixman
- mingw64-i686-pkg-config
Recommended packages
- mingw64-i686-curl
- mingw64-i686-gtk3
- mingw64-i686-libssh2
- mingw64-i686-libtasn1
- mingw64-i686-nettle
- mingw64-i686-ncurses
- mingw64-i686-gnutls
Optional packages
- mingw64-i686-SDL2
- mingw64-i686-libgcrypt
- mingw64-i686-libusb1.0
- mingw64-i686-usbredir
注意如果编译 x64 版本的,还要安装:mingw64-x86_64-xxx 的库
经测试,还需要:
- flex
- bison
Building QEMU for W64
QEMU for W64 needs a fairly complete MinGW-w64 based development environment with tools (make, compiler, linker, ...) and some additional libraries.
Cross builds
Compilation of QEMU for W64 on non-W64 hosts (e.g. Linux hosts) is called cross compilation. Some Linux distributions (Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora and maybe others) already include packages needed for cross compilation, so the installation of these packages is the first step.
Debian based cross builds
# Debian cross configuration for W64: configure --cross-prefix=amd64-mingw32msvc-
Fedora based cross builds
# Fedora cross configuration for W64: ./configure --cross-prefix=x86_64-w64-mingw32-
Libraries (also needed for cross builds)
- GLib Run-time (http://ftp.gnome.org/pub/gnome/binaries/win64/glib/2.22/glib_2.22.4-1_win64.zip)
- GLib Development (http://ftp.gnome.org/pub/gnome/binaries/win64/glib/2.22/glib-dev_2.22.4-1_win64.zip) - newer versions don''t work because leading underscores for global symbols are missing
- gettext-runtime Development (http://ftp.gnome.org/pub/gnome/binaries/win64/dependencies/gettext-runtime-dev_0.18.1.1-2_win64.zip)
Native builds with MSYS2
MSYS2 provides a convenient environment to produce native builds for W64.
- Download and run the MSYS2 installer from msys2.org.
- As per the MSYS2 documentation, download the latest repository updates with:
pacman -Syu
- If required, restart the MSYS2 console. Then update the remaining packages with:
pacman -Su
- Next install the basic set of developer tools:
pacman -S base-devel mingw-w64-x86_64-toolchain git python
- Then install any required QEMU-specific packages. For a basic setup you can use:
pacman -S mingw-w64-x86_64-glib2 mingw64/mingw-w64-x86_64-gtk3 mingw64/mingw-w64-x86_64-SDL2
- Initialise the git repository:
git clone git://git.qemu-project.org/qemu.git cd qemu git submodule update --init ui/keycodemapdb git submodule update --init capstone git submodule update --init dtc
- Finally build QEMU as normal:
./configure --enable-gtk --enable-sdl make
Installation
Installation is easy with the installers from https://qemu.weilnetz.de/.
Running QEMU for W32
User mode emulation is unsupported: it only works on BSD and Linux.
System emulation
All QEMU system emulation should be working (that simply means I don''t know of emulations which don''t work, and those which I tried, namely x86 and mips, work well).
Hardware acceleration for x86 can be enabled with the command line option --enable-hax. This requires at least QEMU 1.9 and an installed Intel HAXM driver.
Special W32 devices
QEMU is based on Mingw-w64, so some commonly used UNIX device names like /dev/null or /dev/zero can be used. W32 device names also work, especially names like //./PhysicalDrive0 for the first hard disk of the host (this name must be used with extreme care or you will likely crash your system).
Text which is normally printed by QEMU to the console output channels (normally known as standard output = stdout and standard error output = stderr) might be written to files called stdout.txt and stderr.txt if QEMU was linked with SDL 1.2. If you want to see QEMU''s help messages or if it does not work as expected, you should look for these files in the directory where your exe file is installed.
Links
MinGW Website (old, no longer supported by QEMU)
http://www.mingw.org/
Mingw-w64 Website (supports both 32 and 64 bit builds)
http://mingw-w64.sourceforge.net/
GLib-2.0 for MinGW
http://www.gtk.org/download/win32.php
http://www.gtk.org/download/win64.php
POSIX thread support for MinGW (old, no longer needed)
http://sourceforge.net/projects/mingw/files/MinGW/pthreads-w32/
libSDL 1.2 for MinGW (old, no longer needed)
http://www.libsdl.org/download-1.2.php
Intel Hardware Accelerated Execution Manager (HAXM)
https://software.intel.com/en-us/android/articles/intel-hardware-accelerated-execution-manager

: org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.CompilationResult.getProblems()[Lorg/eclipse/jdt/core/compiler/IProblem;
java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.CompilationResult.getProblems()[Lorg/eclipse/jdt/core/compiler/IProblem;at org.apache.jasper.compiler.JDTCompiler$2.acceptResult(JDTCompiler.java:354)
at org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.Compiler.compile(Compiler.java:480)
at org.apache.jasper.compiler.JDTCompiler.generateClass(JDTCompiler.java:425)
at org.apache.jasper.compiler.Compiler.compile(Compiler.java:298)
at org.apache.jasper.compiler.Compiler.compile(Compiler.java:277)
at org.apache.jasper.compiler.Compiler.compile(Compiler.java:265)
at org.apache.jasper.JspCompilationContext.compile(JspCompilationContext.java:564)
at org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServletWrapper.service(JspServletWrapper.java:299)
at org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet.serviceJspFile(JspServlet.java:315)
at org.apache.jasper.servlet.JspServlet.service(JspServlet.java:265)
at javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet.service(HttpServlet.java:731)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:303)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:208)
at org.apache.tomcat.websocket.server.WsFilter.doFilter(WsFilter.java:52)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:241)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:208)
at org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter.doFilterInternal(CharacterEncodingFilter.java:88)
at org.springframework.web.filter.OncePerRequestFilter.doFilter(OncePerRequestFilter.java:107)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.internalDoFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:241)
at org.apache.catalina.core.ApplicationFilterChain.doFilter(ApplicationFilterChain.java:208)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve.invoke(StandardWrapperValve.java:220)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextValve.invoke(StandardContextValve.java:122)
at org.apache.catalina.authenticator.AuthenticatorBase.invoke(AuthenticatorBase.java:505)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve.invoke(StandardHostValve.java:170)
at org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve.invoke(ErrorReportValve.java:103)
at org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve.invoke(AccessLogValve.java:956)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngineValve.invoke(StandardEngineValve.java:116)
at org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.service(CoyoteAdapter.java:423)
at org.apache.coyote.http11.AbstractHttp11Processor.process(AbstractHttp11Processor.java:1079)
at org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol$AbstractConnectionHandler.process(AbstractProtocol.java:625)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint$SocketProcessor.run(JIoEndpoint.java:316)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(Unknown Source)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(Unknown Source)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.TaskThread$WrappingRunnable.run(TaskThread.java:61)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Unknown Source)
十二月 26, 2016 4:43:02 下午 org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve invoke
严重: Servlet.service() for servlet [jsp] in context with path [/shake] threw exception [java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.CompilationResult.getProblems()[Lorg/eclipse/jdt/core/compiler/IProblem;] with root cause
java.lang.NoSuchMethodError: org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.CompilationResult.getProblems()[Lorg/eclipse/jdt/core/compiler/IProblem;
at org.apache.jasper.compiler.JDTCompiler$2.acceptResult(JDTCompiler.java:354)

Angular self study 2 - compile how is hello {{ name }} compiled
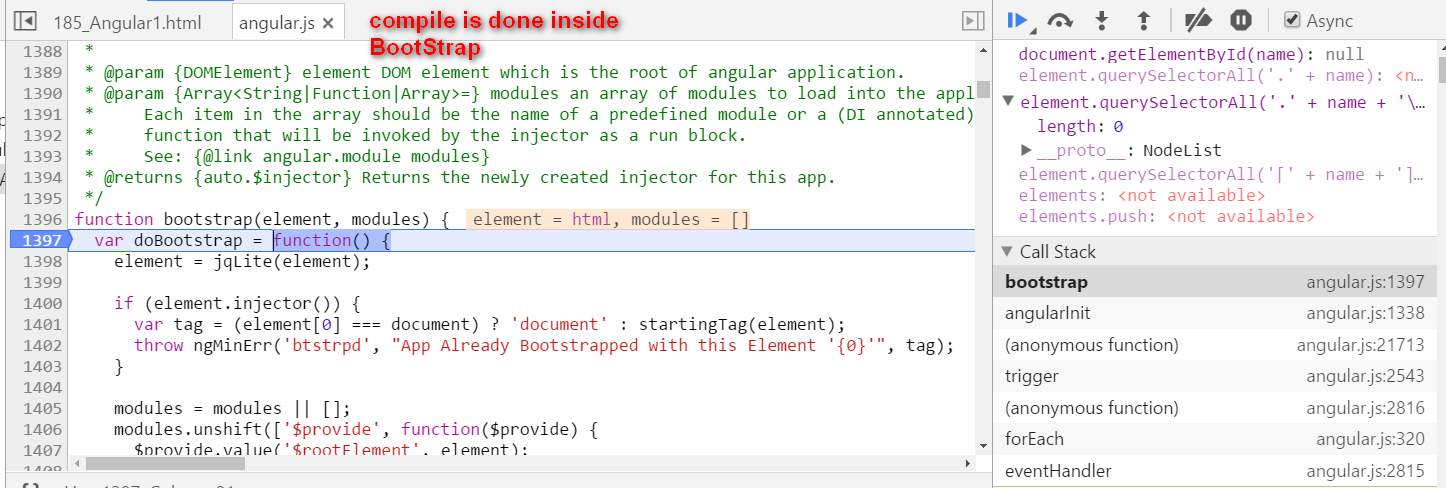
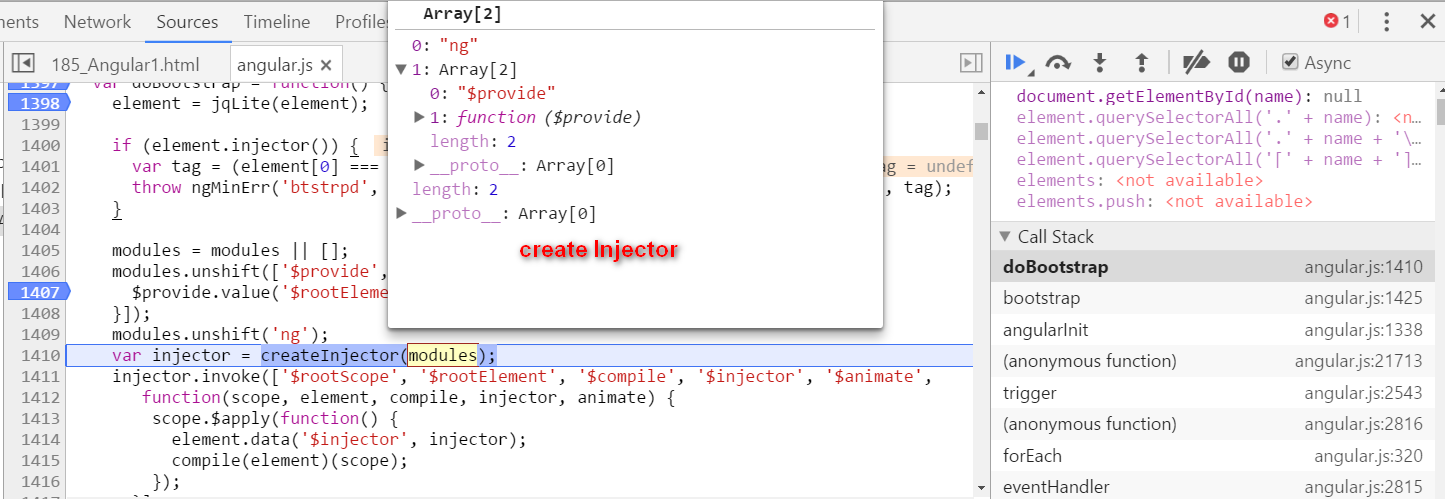
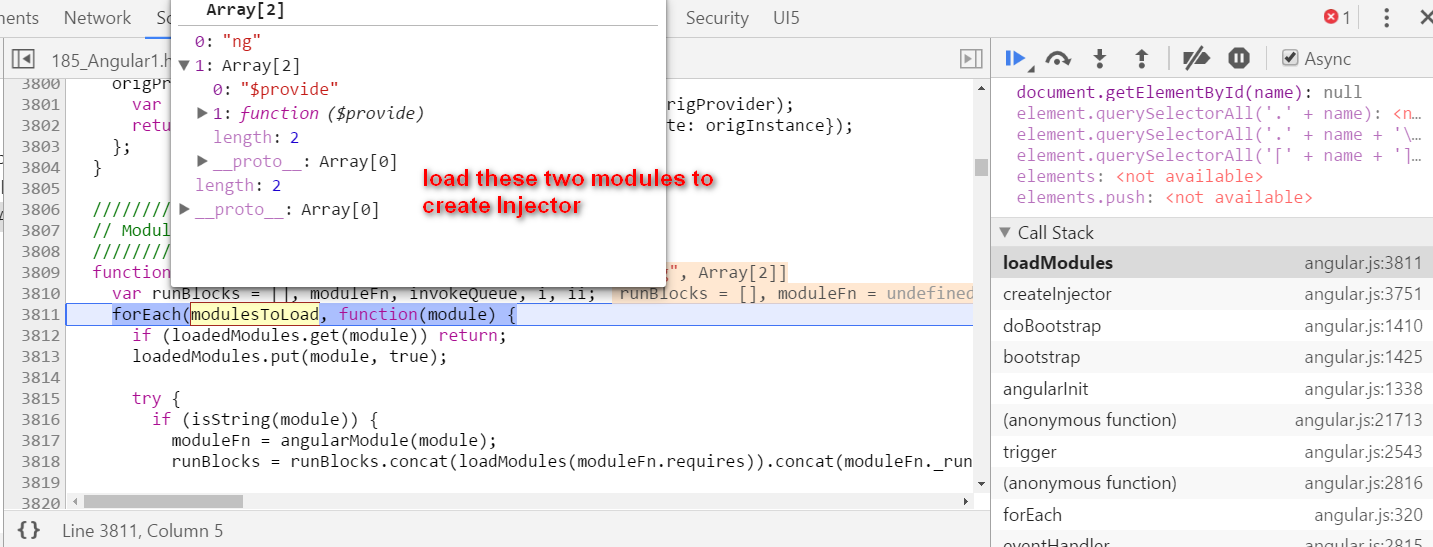
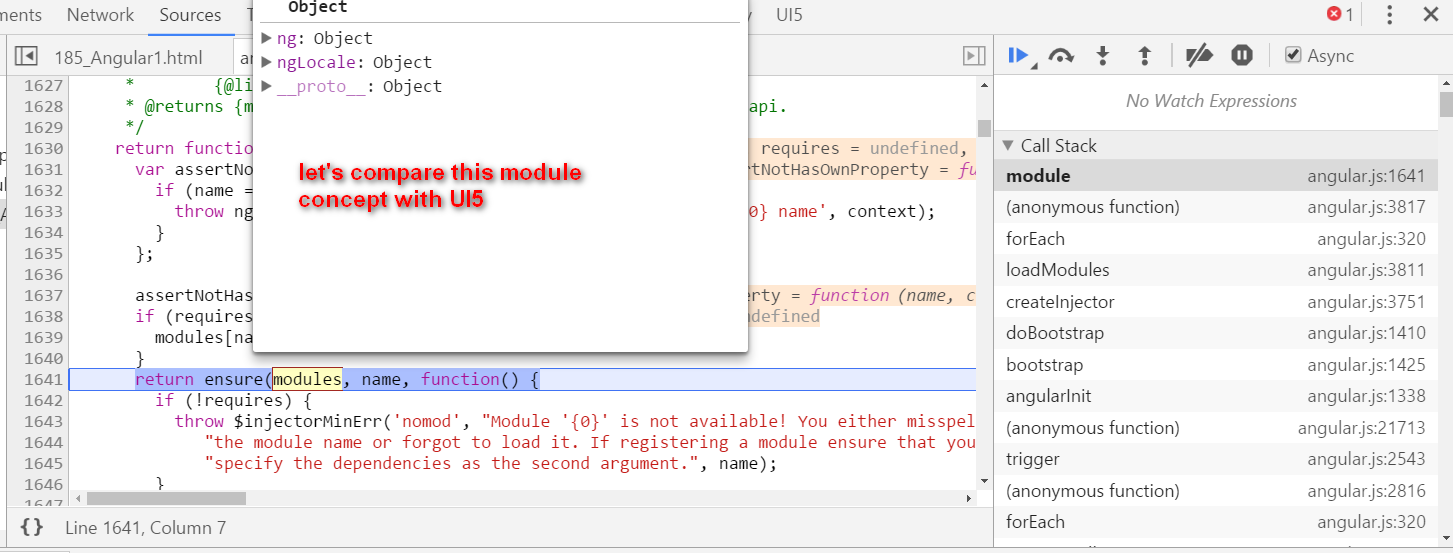
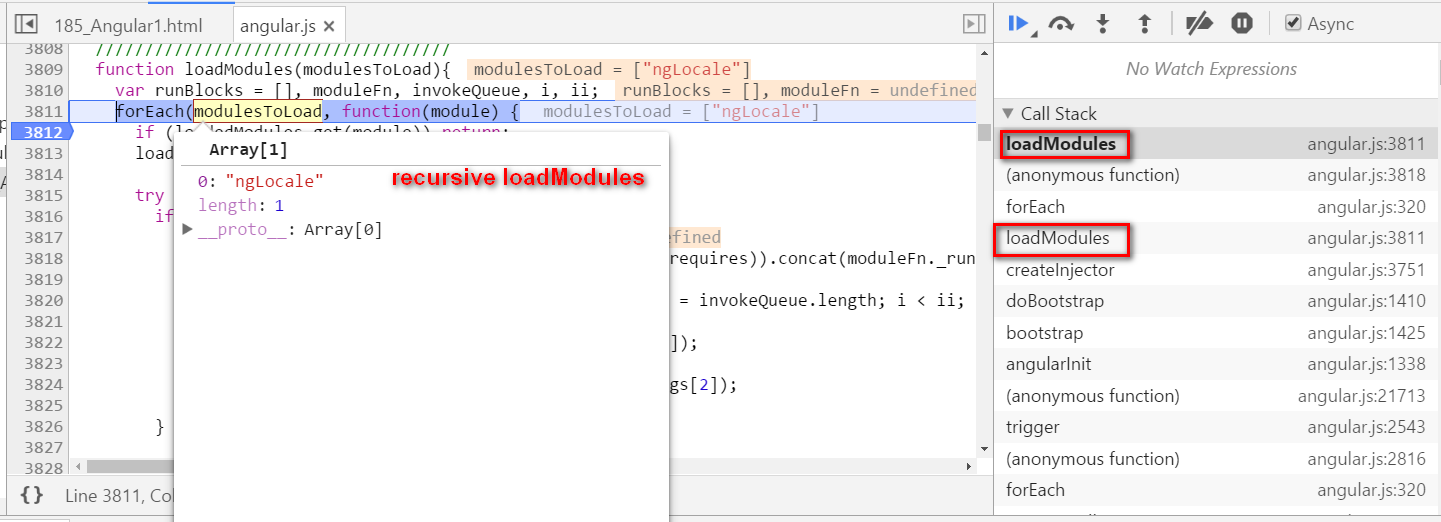
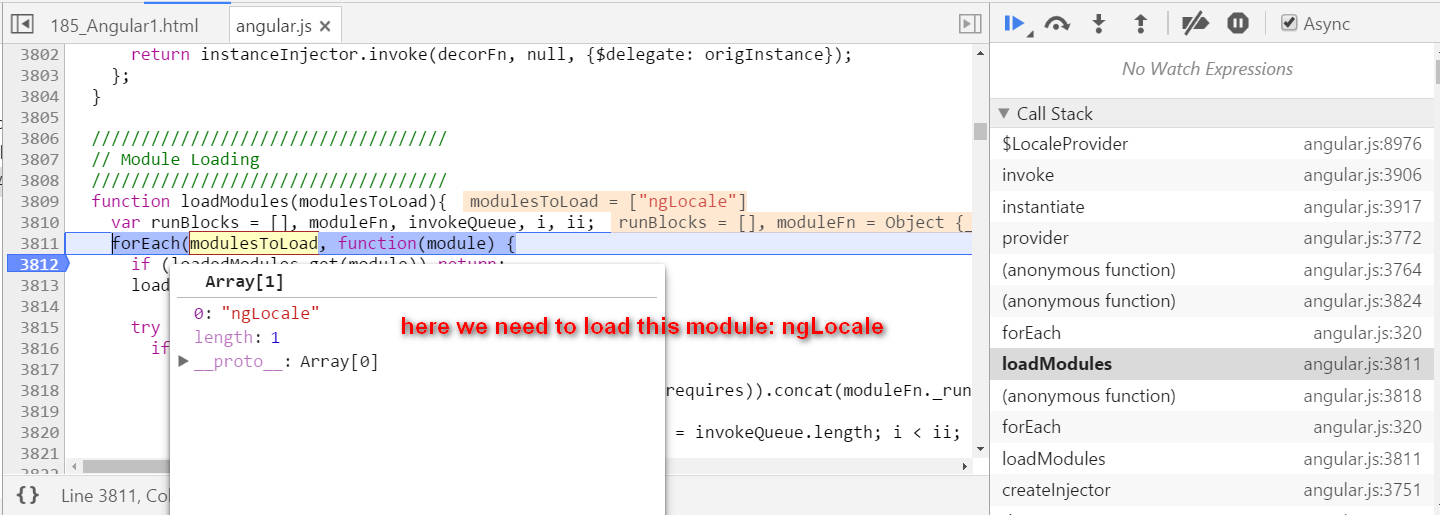
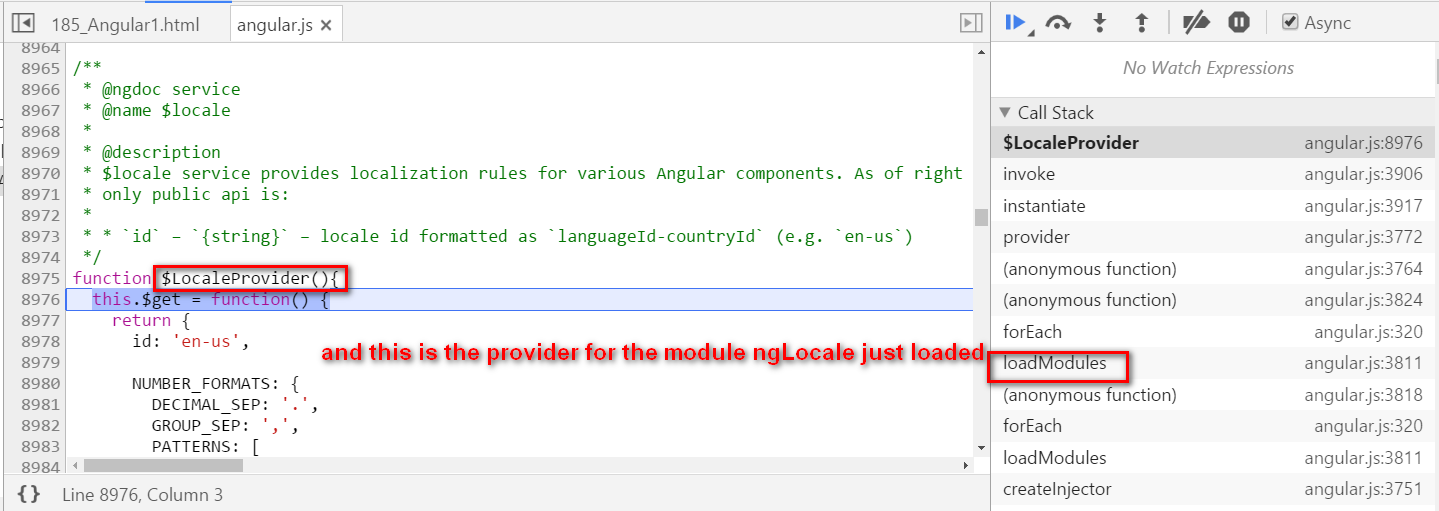
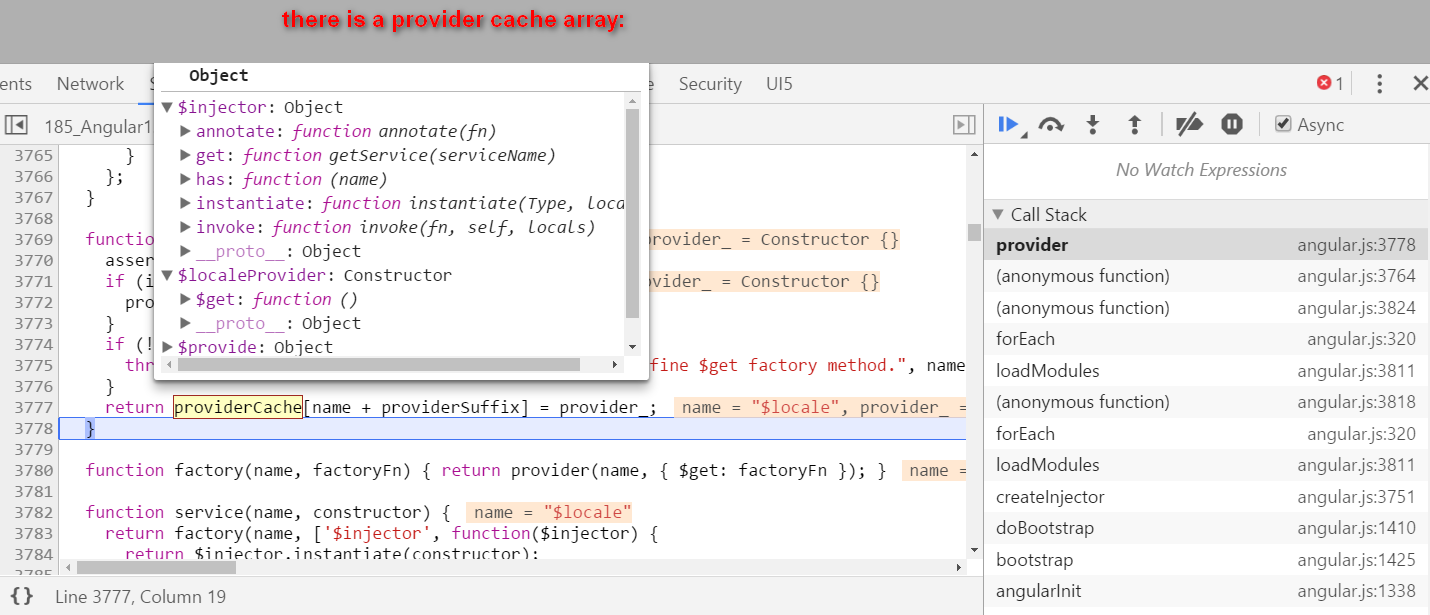
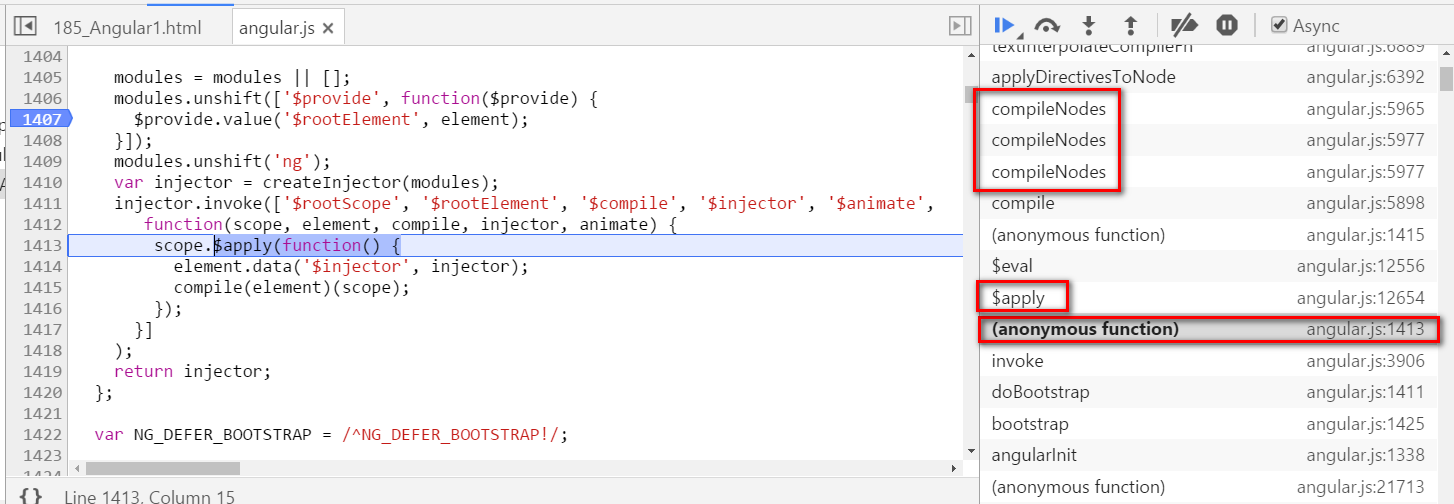
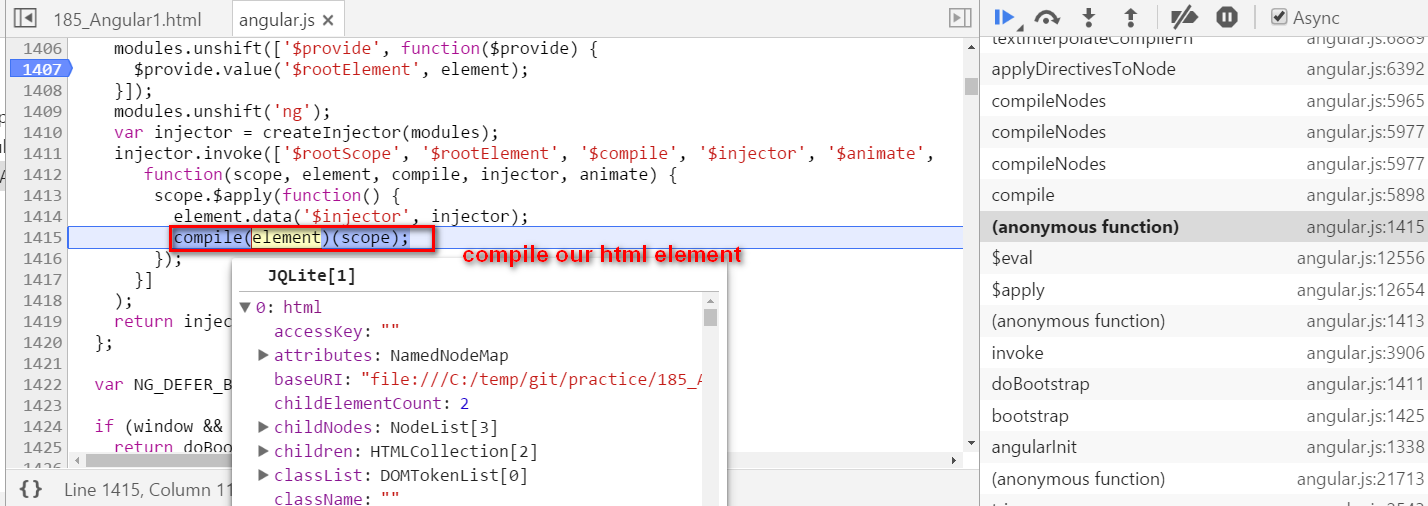
本文同步分享在 博客 “汪子熙”(CSDN)。
如有侵权,请联系 support@oschina.cn 删除。
本文参与 “OSC 源创计划”,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。

asp.net – system.web.compilation.debug与system.codedom.compilers.compiler.compilerOptions / define:Debug = True
<system.codedom>
<compilers>
<compiler compilerOptions="/define:Debug=True" />
</compilers>
</system.codedom>
这是什么?事实是,那就是打败了从< compilation>中删除它的目的吗?如果我删除上面显示的属性会怎样?
解决方法
Is the fact that that’s there defeating the purpose
of removing it from<compilation>
从MSDN C# Compiler Options起
要打开调试,编译器上的标志是/ debug而不是/ define:Debug = True
/debug : Instruct the compiler to emit debugging information.
/define : Defines preprocessor symbols.
因此,当您定义Debug = True时,您只能将此情况设为true:
#if DEBUG == true // Compile what is inside here ! #endif
/ define:Debug = True不会添加任何其他调试信息,除非您使用上述代码手动包含它们.
测试页面
我使用以下代码进行测试,看看发生了什么.
txtDebug.Text = HttpContext.Current.IsDebuggingEnabled.ToString();
#if DEBUG
txtDebug.Text += "<br>defined Debug is on";
#endif
#if DEBUG == true
txtDebug.Text += "<br>defined Debug = true is on";
#endif
结果1
现在,如果debug =“false”并且使用compilerOptions =“/ define:Debug = True”,结果是
false
defined Debug = true is on
结果2
如果debug =“true”和compilerOptions =“/ define:Debug = True”结果是
true
defined Debug is on
defined Debug = true is on
结果3
现在我再做一次测试,我在web.config上添加了这一行
<compiler language="c#;cs;csharp" extension=".cs"
compilerOptions="/define:Debug=True /D:DEBUG,TESTFLAG"
type="Microsoft.CSharp.CSharpCodeProvider,System,Version=4.0.0.0,Culture=neutral,PublicKeyToken=b77a5c561934e089"
warningLevel="4" />
结果是debug = false
False (debug is false)
defined Debug is on (but the defined DEBUG Now is runs)
defined Debug = true is on (This is also runs)
test flag (but the defined extra flag is also runs)
MSDN
看看MSDN for the /define (Preprocessor Definition)我看那个宣言
/define:Debug=True
只适用于这种代码的情况
#if DEBUG == true txtDebug.Text += "<br>defined Debug = true is on"; #endif

c# – LINQ-SQL – 在CompiledQuery.Compile中使用静态只读字段?
Class member X is unmapped
如果我将字段decleration从partial类移到另一个与LINQ-sql无关的类中,那么我得到以下内容:
Object reference not set to an instance of an object
如果我将字段作为参数传递,那么我看到没有错误,查询工作正常并生成预期的sql.
一个例子如下:
partial class Order
{
public static readonly string Complete = "Complete";
public static readonly string Pending = "Pending";
public static readonly Func<DataContext,Order,bool> IsComplete =
CompiledQuery.Compile((DataContext context,Order o) =>
Complete == o.Status);
}
用法:
var test = from o in db.Orders
select new
{
IsComplete = Order.IsComplete(db,o)
};
这会产生上述错误.如果我将一个字符串[]作为另一个参数添加到CompiledQuery,那么我看到没有错误.此外,如果我将字符串修改为const而不是静态只读,这也可以,但我想这是由于在编译时分配的值.
有没有办法让静态只读字段工作?
解决方法
我建议你创建一个包装属性来为你完成工作
partial class Order {
public static readonly string Complete = "Complete";
public static readonly string Pending = "Pending";
private static readonly Func<DataContext,bool> _isComplete;
public static Func<DataContext,bool> IsComplete {
get {
if (_isComplete == null) {
var complete=Complete;
_isComplete CompiledQuery.Compile((DataContext context,Order o) =>
complete == o.Status);
}
return _isComplete;
}
}
}
}
今天关于Hosts/W32 qemu compile的讲解已经结束,谢谢您的阅读,如果想了解更多关于: org.eclipse.jdt.internal.compiler.CompilationResult.getProblems()[Lorg/eclipse/jdt/core/compiler/IProblem;、Angular self study 2 - compile how is hello {{ name }} compiled、asp.net – system.web.compilation.debug与system.codedom.compilers.compiler.compilerOptions / define:Debug = True、c# – LINQ-SQL – 在CompiledQuery.Compile中使用静态只读字段?的相关知识,请在本站搜索。
本文标签:





