在这篇文章中,我们将为您详细介绍pythonnumpyarray与matrix乘方的内容,并且讨论关于pythonarray和matrix的相关问题。此外,我们还会涉及一些关于2021-04-18:给
在这篇文章中,我们将为您详细介绍python numpy array 与 matrix 乘方的内容,并且讨论关于python array和matrix的相关问题。此外,我们还会涉及一些关于2021-04-18:给定一个二维数组 matrix,里面的值不是 1 就是 0,上、下、左、右相邻的 1 认为是一片岛,返回 matrix 中、2021-12-28:给定一个二维数组 matrix,matrix [i][j] = k 代表:从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往右跳<=k 步,或者从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往下跳<=k 步, 如果 matrix [i]、2022-06-11:注意本文件中,graph 不是邻接矩阵的含义,而是一个二部图。 在长度为 N 的邻接矩阵 matrix 中,所有的点有 N 个,matrix [i][j] 表示点 i 到点 j 的距离或者权重, 而在二部、2022-06-25:给定一个正数 n, 表示有 0~n-1 号任务, 给定一个长度为 n 的数组 time,time [i] 表示 i 号任务做完的时间, 给定一个二维数组 matrix, matrix [j] = {a,的知识,以帮助您更全面地了解这个主题。
本文目录一览:- python numpy array 与 matrix 乘方(python array和matrix)
- 2021-04-18:给定一个二维数组 matrix,里面的值不是 1 就是 0,上、下、左、右相邻的 1 认为是一片岛,返回 matrix 中
- 2021-12-28:给定一个二维数组 matrix,matrix [i][j] = k 代表:从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往右跳<=k 步,或者从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往下跳<=k 步, 如果 matrix [i]
- 2022-06-11:注意本文件中,graph 不是邻接矩阵的含义,而是一个二部图。 在长度为 N 的邻接矩阵 matrix 中,所有的点有 N 个,matrix [i][j] 表示点 i 到点 j 的距离或者权重, 而在二部
- 2022-06-25:给定一个正数 n, 表示有 0~n-1 号任务, 给定一个长度为 n 的数组 time,time [i] 表示 i 号任务做完的时间, 给定一个二维数组 matrix, matrix [j] = {a,

python numpy array 与 matrix 乘方(python array和matrix)
python numpy array 与 matrix 乘方
数组 array 的乘方(** 为乘方运算符)是每个元素的乘方,而矩阵 matrix 的乘方遵循矩阵相乘,因此必须是方阵。
2*3 的数组与矩阵
>>> from numpy import * >>> import operator >>> a = array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6]]) >>> a array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) >>> m = mat(a) >>> m matrix([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]) >>> a ** 2 array([[ 1, 4, 9], [16, 25, 36]]) >>> m ** 2 Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> File "D:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\numpy\matrixlib\defmatrix.py", line 356, in __pow__ return matrix_power(self, other) File "D:\anaconda\lib\site-packages\numpy\matrixlib\defmatrix.py", line 173, in matrix_power raise ValueError("input must be a square array") ValueError: input must be a square array >>> (mat () 函数把 array 转化为 matrix)
3*3 的数组与矩阵
>>> A = array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]) >>> A array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]) >>> M = mat(A) >>> M matrix([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]) >>> A ** 2 array([[ 1, 4, 9], [16, 25, 36], [49, 64, 81]]) >>> M ** 2 matrix([[ 30, 36, 42], [ 66, 81, 96], [102, 126, 150]])
2021-04-18:给定一个二维数组 matrix,里面的值不是 1 就是 0,上、下、左、右相邻的 1 认为是一片岛,返回 matrix 中
2021-04-18:给定一个二维数组 matrix,里面的值不是 1 就是 0,上、下、左、右相邻的 1 认为是一片岛,返回 matrix 中岛的数量。
福大大 答案 2021-04-18:
并查集。
代码用 golang 编写。代码如下:
```go
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
arr := [][]byte{
{49, 49, 49, 49, 48},
{49, 49, 48, 49, 48},
{49, 49, 48, 49, 48},
{49, 49, 48, 48, 48},
{48, 48, 48, 48, 48}}
ret := numIslands(arr)
fmt.Println(ret)
}
func numIslands(board [][]byte) int {
row := len(board)
col := len(board[0])
uf := NewUnionFind(board)
for j := 1; j < col; j++ {
if board[0][j-1] == ''1'' && board[0][j] == ''1'' {
uf.union(0, j-1, 0, j)
}
}
for i := 1; i < row; i++ {
if board[i-1][0] == ''1'' && board[i][0] == ''1'' {
uf.union(i-1, 0, i, 0)
}
}
for i := 1; i < row; i++ {
for j := 1; j < col; j++ {
if board[i][j] == ''1'' {
if board[i][j-1] == ''1'' {
uf.union(i, j-1, i, j)
}
if board[i-1][j] == ''1'' {
uf.union(i-1, j, i, j)
}
}
}
}
return uf.getSets()
}
type UnionFind2 struct {
parent []int
size []int
help []int
col int
sets int
}
func NewUnionFind(board [][]byte) *UnionFind2 {
ret := &UnionFind2{}
ret.col = len(board[0])
ret.sets = 0
row := len(board)
length := row * ret.col
ret.parent = make([]int, length)
ret.size = make([]int, length)
ret.help = make([]int, length)
for r := 0; r < row; r++ {
for c := 0; c < ret.col; c++ {
if board[r][c] == ''1'' {
i := ret.index(r, c)
ret.parent[i] = i
ret.size[i] = 1
ret.sets++
}
}
}
return ret
}
// (r,c) -> i
func (this *UnionFind2) index(r int, c int) int {
return r*this.col + c
}
// 原始位置 -> 下标
func (this *UnionFind2) find(i int) int {
hi := 0
for i != this.parent[i] {
this.help[hi] = i
hi++
i = this.parent[i]
}
for hi--; hi >= 0; hi-- {
this.parent[this.help[hi]] = i
}
return i
}
func (this *UnionFind2) union(r1 int, c1 int, r2 int, c2 int) {
i1 := this.index(r1, c1)
i2 := this.index(r2, c2)
f1 := this.find(i1)
f2 := this.find(i2)
if f1 != f2 {
if this.size[f1] >= this.size[f2] {
this.size[f1] += this.size[f2]
this.parent[f2] = f1
} else {
this.size[f2] += this.size[f1]
this.parent[f1] = f2
}
this.sets--
}
}
func (this *UnionFind2) getSets() int {
return this.sets
}
```
执行结果如下:
***
[左神 java 代码](https://github.com/algorithmzuo/algorithmbasic2020/blob/master/src/class15/Code02_NumberOfIslands.java)
[力扣 200. 岛屿数量](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-islands/submissions/)
本文分享自微信公众号 - 福大大架构师每日一题(gh_bbe96e5def84)。
如有侵权,请联系 support@oschina.cn 删除。
本文参与 “OSC 源创计划”,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。
![2021-12-28:给定一个二维数组 matrix,matrix [i][j] = k 代表:从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往右跳<=k 步,或者从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往下跳<=k 步, 如果 matrix [i] 2021-12-28:给定一个二维数组 matrix,matrix [i][j] = k 代表:从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往右跳<=k 步,或者从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往下跳<=k 步, 如果 matrix [i]](http://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/upload/2025/04/dcfe8cac-7de3-451f-ab37-4291477783e11744560955690.jpg)
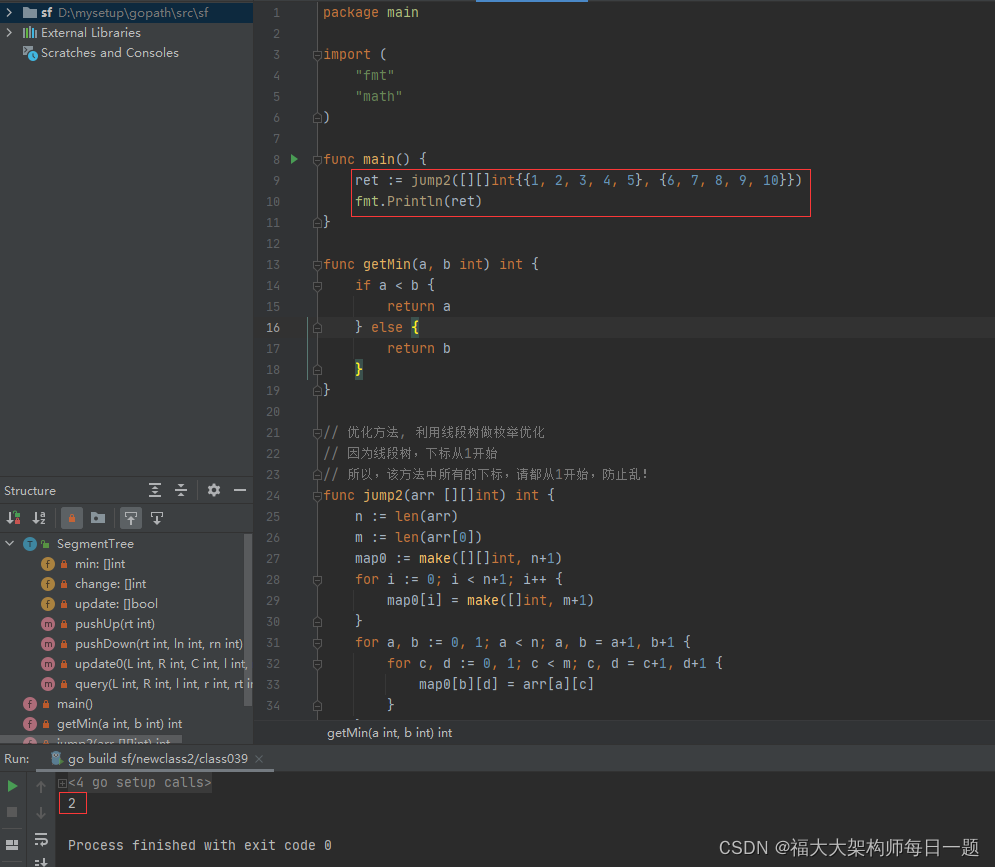
2021-12-28:给定一个二维数组 matrix,matrix [i][j] = k 代表:从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往右跳<=k 步,或者从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往下跳<=k 步, 如果 matrix [i]
2021-12-28:给定一个二维数组 matrix,matrix [i][j] = k 代表:
从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往右跳 <=k 步,或者从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往下跳 <=k 步,
如果 matrix [i][j] = 0,代表来到 (i,j) 位置必须停止,
返回从 matrix 左上角到右下角,至少要跳几次,
已知 matrix 中行数 n <= 5000, 列数 m <= 5000,
matrix 中的值,<= 5000。
来自京东。
答案 2021-12-28:
方法一:自然智慧。递归。复杂度过不了。
方法二:动态规划 + 线段树。
代码用 golang 编写。代码如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
func main() {
ret := jump2([][]int{
{
1, 2, 3, 4, 5}, {
6, 7, 8, 9, 10}})
fmt.Println(ret)
}
func getMin(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
} else {
return b
}
}
// 优化方法, 利用线段树做枚举优化
// 因为线段树,下标从1开始
// 所以,该方法中所有的下标,请都从1开始,防止乱!
func jump2(arr [][]int) int {
n := len(arr)
m := len(arr[0])
map0 := make([][]int, n+1)
for i := 0; i < n+1; i++ {
map0[i] = make([]int, m+1)
}
for a, b := 0, 1; a < n; a, b = a+1, b+1 {
for c, d := 0, 1; c < m; c, d = c+1, d+1 {
map0[b][d] = arr[a][c]
}
}
rowTrees := make([]*SegmentTree, n+1)
for i := 1; i <= n; i++ {
rowTrees[i] = NewSegmentTree(m)
}
colTrees := make([]*SegmentTree, m+1)
for i := 1; i <= m; i++ {
colTrees[i] = NewSegmentTree(n)
}
rowTrees[n].update0(m, m, 0, 1, m, 1)
colTrees[m].update0(n, n, 0, 1, n, 1)
for col := m - 1; col >= 1; col-- {
if map0[n][col] != 0 {
left := col + 1
right := getMin(col+map0[n][col], m)
next := rowTrees[n].query(left, right, 1, m, 1)
if next != math.MaxInt64 {
rowTrees[n].update0(col, col, next+1, 1, m, 1)
colTrees[col].update0(n, n, next+1, 1, n, 1)
}
}
}
for row := n - 1; row >= 1; row-- {
if map0[row][m] != 0 {
up := row + 1
down := getMin(row+map0[row][m], n)
next := colTrees[m].query(up, down, 1, n, 1)
if next != math.MaxInt64 {
rowTrees[row].update0(m, m, next+1, 1, m, 1)
colTrees[m].update0(row, row, next+1, 1, n, 1)
}
}
}
for row := n - 1; row >= 1; row-- {
for col := m - 1; col >= 1; col-- {
if map0[row][col] != 0 {
// (row,col) 往右是什么范围呢?[left,right]
left := col + 1
right := getMin(col+map0[row][col], m)
next1 := rowTrees[row].query(left, right, 1, m, 1)
// (row,col) 往下是什么范围呢?[up,down]
up := row + 1
down := getMin(row+map0[row][col], n)
next2 := colTrees[col].query(up, down, 1, n, 1)
next := getMin(next1, next2)
if next != math.MaxInt64 {
rowTrees[row].update0(col, col, next+1, 1, m, 1)
colTrees[col].update0(row, row, next+1, 1, n, 1)
}
}
}
}
return rowTrees[1].query(1, 1, 1, m, 1)
}
// 区间查询最小值的线段树
// 注意下标从1开始,不从0开始
// 比如你传入size = 8
// 则位置对应为1~8,而不是0~7
type SegmentTree struct {
min []int
change []int
update []bool
}
func NewSegmentTree(size int) *SegmentTree {
ret := &SegmentTree{
}
N := size + 1
ret.min = make([]int, N<<2)
ret.change = make([]int, N<<2)
ret.update = make([]bool, N<<2)
ret.update0(1, size, math.MaxInt64, 1, size, 1)
return ret
}
func (this *SegmentTree) pushUp(rt int) {
this.min[rt] = getMin(this.min[rt<<1], this.min[rt<<1|1])
}
func (this *SegmentTree) pushDown(rt, ln, rn int) {
if this.update[rt] {
this.update[rt<<1] = true
this.update[rt<<1|1] = true
this.change[rt<<1] = this.change[rt]
this.change[rt<<1|1] = this.change[rt]
this.min[rt<<1] = this.change[rt]
this.min[rt<<1|1] = this.change[rt]
this.update[rt] = false
}
}
// 最后三个参数是固定的, 每次传入相同的值即可:
// l = 1(固定)
// r = size(你设置的线段树大小)
// rt = 1(固定)
func (this *SegmentTree) update0(L, R, C, l, r, rt int) {
if L <= l && r <= R {
this.update[rt] = true
this.change[rt] = C
this.min[rt] = C
return
}
mid := (l + r) >> 1
this.pushDown(rt, mid-l+1, r-mid)
if L <= mid {
this.update0(L, R, C, l, mid, rt<<1)
}
if R > mid {
this.update0(L, R, C, mid+1, r, rt<<1|1)
}
this.pushUp(rt)
}
// 最后三个参数是固定的, 每次传入相同的值即可:
// l = 1(固定)
// r = size(你设置的线段树大小)
// rt = 1(固定)
func (this *SegmentTree) query(L, R, l, r, rt int) int {
if L <= l && r <= R {
return this.min[rt]
}
mid := (l + r) >> 1
this.pushDown(rt, mid-l+1, r-mid)
left := math.MaxInt64
right := math.MaxInt64
if L <= mid {
left = this.query(L, R, l, mid, rt<<1)
}
if R > mid {
right = this.query(L, R, mid+1, r, rt<<1|1)
}
return getMin(left, right)
}执行结果如下:
左神 java 代码
![2022-06-11:注意本文件中,graph 不是邻接矩阵的含义,而是一个二部图。 在长度为 N 的邻接矩阵 matrix 中,所有的点有 N 个,matrix [i][j] 表示点 i 到点 j 的距离或者权重, 而在二部 2022-06-11:注意本文件中,graph 不是邻接矩阵的含义,而是一个二部图。 在长度为 N 的邻接矩阵 matrix 中,所有的点有 N 个,matrix [i][j] 表示点 i 到点 j 的距离或者权重, 而在二部](http://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/upload/2025/04/9af37b04-73f6-4cbb-ae3e-8135528369d11744560956430.jpg)
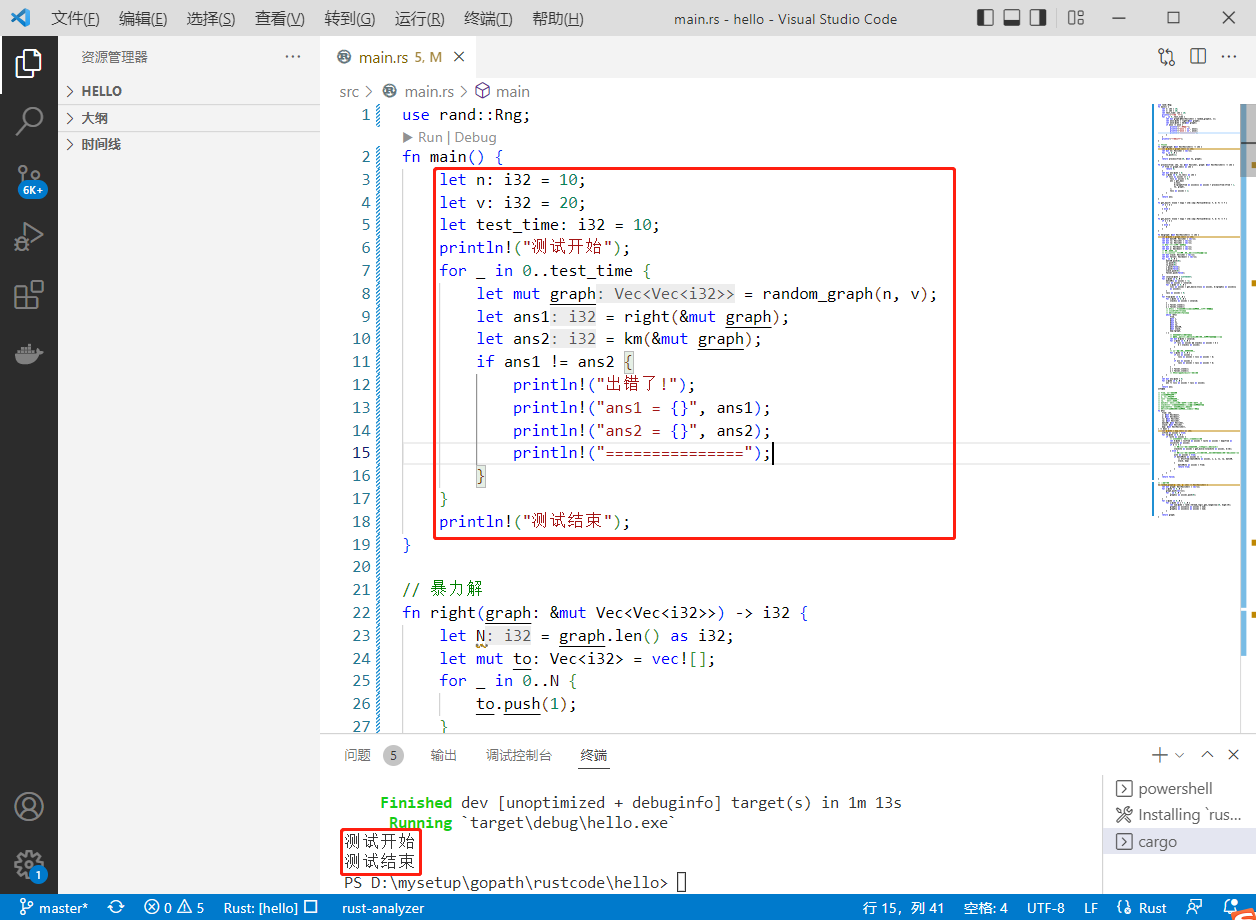
2022-06-11:注意本文件中,graph 不是邻接矩阵的含义,而是一个二部图。 在长度为 N 的邻接矩阵 matrix 中,所有的点有 N 个,matrix [i][j] 表示点 i 到点 j 的距离或者权重, 而在二部
2022-06-11:注意本文件中,graph 不是邻接矩阵的含义,而是一个二部图。 在长度为 N 的邻接矩阵 matrix 中,所有的点有 N 个,matrix [i][j] 表示点 i 到点 j 的距离或者权重, 而在二部图 graph 中,所有的点有 2*N 个,行所对应的点有 N 个,列所对应的点有 N 个。 而且认为,行所对应的点之间是没有路径的,列所对应的点之间也是没有路径的!
答案 2022-06-11:
km 算法。
代码用 rust 编写。代码如下:
use rand::Rng;
fn main() {
let n: i32 = 10;
let v: i32 = 20;
let test_time: i32 = 10;
println!("测试开始");
for _ in 0..test_time {
let mut graph = random_graph(n, v);
let ans1 = right(&mut graph);
let ans2 = km(&mut graph);
if ans1 != ans2 {
println!("出错了!");
println!("ans1 = {}", ans1);
println!("ans2 = {}", ans2);
println!("===============");
}
}
println!("测试结束");
}
// 暴力解
fn right(graph: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let N = graph.len() as i32;
let mut to: Vec<i32> = vec![];
for _ in 0..N {
to.push(1);
}
return process(0, &mut to, graph);
}
fn process(from: i32, to: &mut Vec<i32>, graph: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
if from == graph.len() as i32 {
return 0;
}
let mut ans = 0;
for i in 0..to.len() as i32 {
if to[i as usize] == 1 {
to[i as usize] = 0;
ans = get_max(
ans,
graph[from as usize][i as usize] + process(from + 1, to, graph),
);
to[i as usize] = 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
fn get_max<T: Clone + Copy + std::cmp::PartialOrd>(a: T, b: T) -> T {
if a > b {
a
} else {
b
}
}
fn get_min<T: Clone + Copy + std::cmp::PartialOrd>(a: T, b: T) -> T {
if a < b {
a
} else {
b
}
}
fn km(graph: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let N = graph.len() as i32;
let mut match0: Vec<i32> = vec![];
let mut lx: Vec<i32> = vec![];
let mut ly: Vec<i32> = vec![];
// dfs过程中,碰过的点!
let mut x: Vec<bool> = vec![];
let mut y: Vec<bool> = vec![];
// 降低的预期!
// 公主上,打一个,降低预期的值,只维持最小!
let mut slack: Vec<i32> = vec![];
let mut falsev: Vec<bool> = vec![];
for _ in 0..N {
match0.push(0);
lx.push(0);
ly.push(0);
x.push(false);
y.push(false);
slack.push(0);
falsev.push(false);
}
let invalid = 2147483647;
for i in 0..N {
match0[i as usize] = -1;
lx[i as usize] = -invalid;
for j in 0..N {
lx[i as usize] = get_max(lx[i as usize], graph[i as usize][j as usize]);
}
ly[i as usize] = 0;
}
for from in 0..N {
for i in 0..N {
slack[i as usize] = invalid;
}
x = falsev.clone();
y = falsev.clone();
// dfs() : from王子,能不能不降预期,匹配成功!
// 能:dfs返回true!
// 不能:dfs返回false!
while !dfs(
from,
&mut x,
&mut y,
&mut lx,
&mut ly,
&mut match0,
&mut slack,
graph,
) {
// 刚才的dfs,失败了!
// 需要拿到,公主的slack里面,预期下降幅度的最小值!
let mut d = invalid;
for i in 0..N {
if !y[i as usize] && slack[i as usize] < d {
d = slack[i as usize];
}
}
// 按照最小预期来调整预期
for i in 0..N {
if x[i as usize] {
lx[i as usize] = lx[i as usize] - d;
}
if y[i as usize] {
ly[i as usize] = ly[i as usize] + d;
}
}
x = falsev.clone();
y = falsev.clone();
// 然后回到while里,再次尝试
}
}
let mut ans = 0;
for i in 0..N {
ans += lx[i as usize] + ly[i as usize];
}
return ans;
}
// from, 当前的王子
// x,王子碰没碰过
// y, 公主碰没碰过
// lx,所有王子的预期
// ly, 所有公主的预期
// match,所有公主,之前的分配,之前的爷们!
// slack,连过,但没允许的公主,最小下降的幅度
// map,报价,所有王子对公主的报价
// 返回,from号王子,不降预期能不能配成!
fn dfs(
from: i32,
x: &mut Vec<bool>,
y: &mut Vec<bool>,
lx: &mut Vec<i32>,
ly: &mut Vec<i32>,
match0: &mut Vec<i32>,
slack: &mut Vec<i32>,
map: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>,
) -> bool {
let N = map.len() as i32;
x[from as usize] = true;
for to in 0..N {
if !y[to as usize] {
// 只有没dfs过的公主,才会去尝试
let d = lx[from as usize] + ly[to as usize] - map[from as usize][to as usize];
if d != 0 {
// 如果当前的路不符合预期,更新公主的slack值
slack[to as usize] = get_min(slack[to as usize], d);
} else {
// 如果当前的路符合预期,尝试直接拿下,或者抢夺让之前的安排倒腾去
y[to as usize] = true;
if match0[to as usize] == -1
|| dfs(match0[to as usize], x, y, lx, ly, match0, slack, map)
{
match0[to as usize] = from;
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
// 为了测试
fn random_graph(N: i32, V: i32) -> Vec<Vec<i32>> {
let mut graph: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![];
for i in 0..N {
graph.push(vec![]);
for _ in 0..N {
graph[i as usize].push(0);
}
}
for i in 0..N {
for j in i + 1..N {
let num = rand::thread_rng().gen_range(0, V);
graph[i as usize][j as usize] = num;
graph[j as usize][i as usize] = num;
}
}
return graph;
}
执行结果如下:
左神 java 代码
![2022-06-25:给定一个正数 n, 表示有 0~n-1 号任务, 给定一个长度为 n 的数组 time,time [i] 表示 i 号任务做完的时间, 给定一个二维数组 matrix, matrix [j] = {a, 2022-06-25:给定一个正数 n, 表示有 0~n-1 号任务, 给定一个长度为 n 的数组 time,time [i] 表示 i 号任务做完的时间, 给定一个二维数组 matrix, matrix [j] = {a,](http://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/upload/2025/04/6831037d-f897-41c8-b9fb-fc4924418dac1744560957106.jpg)
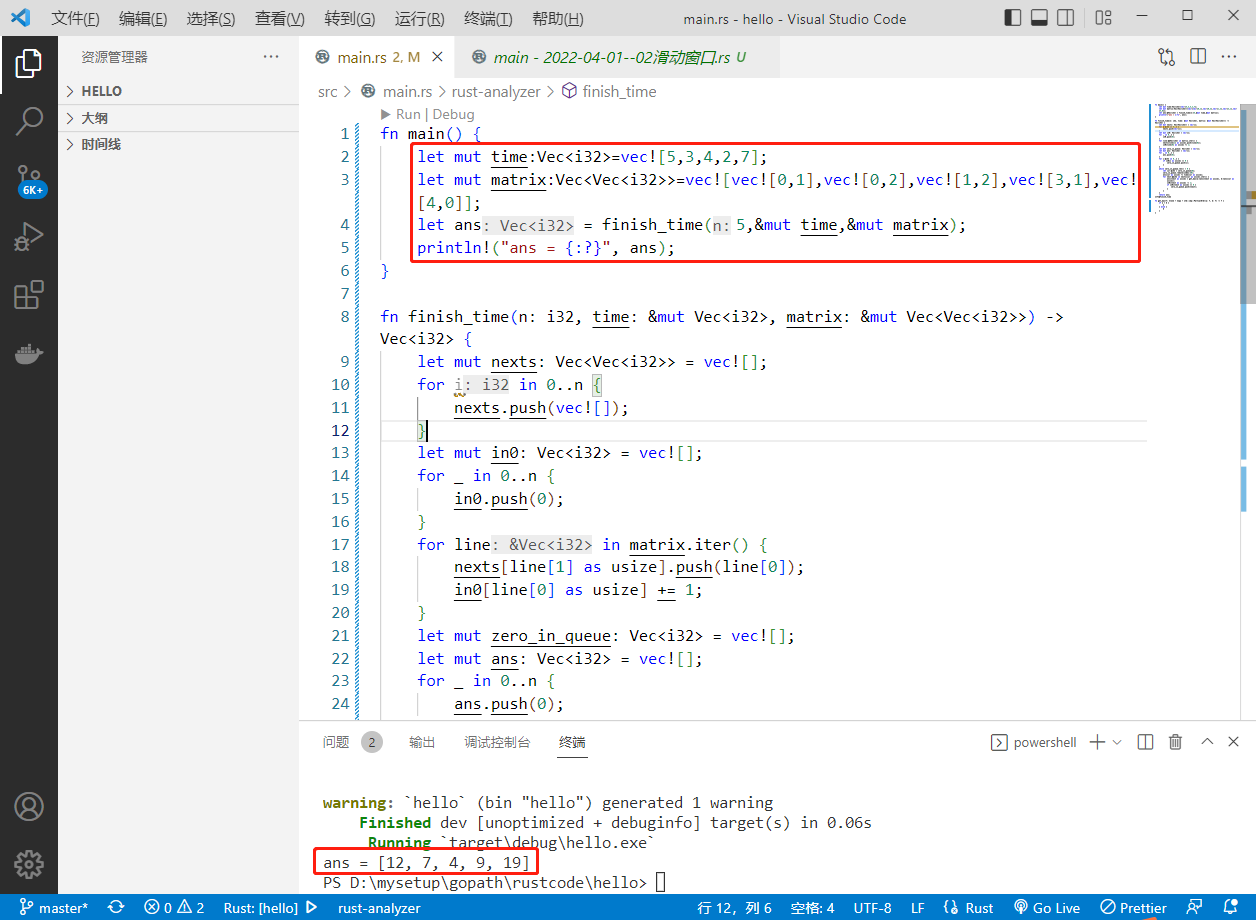
2022-06-25:给定一个正数 n, 表示有 0~n-1 号任务, 给定一个长度为 n 的数组 time,time [i] 表示 i 号任务做完的时间, 给定一个二维数组 matrix, matrix [j] = {a,
2022-06-25:给定一个正数 n, 表示有 0~n-1 号任务, 给定一个长度为 n 的数组 time,time [i] 表示 i 号任务做完的时间, 给定一个二维数组 matrix, matrix [j] = {a, b} 代表:a 任务想要开始,依赖 b 任务的完成, 只要能并行的任务都可以并行,但是任何任务只有依赖的任务完成,才能开始。 返回一个长度为 n 的数组 ans,表示每个任务完成的时间。 输入可以保证没有循环依赖。 来自美团。3.26 笔试。
答案 2022-06-25:
拓扑排序基础上做动态规划。
代码用 rust 编写。代码如下:
fn main() {
let mut time:Vec<i32>=vec![5,3,4,2,7];
let mut matrix:Vec<Vec<i32>>=vec![vec![0,1],vec![0,2],vec![1,2],vec![3,1],vec![4,0]];
let ans = finish_time(5,&mut time,&mut matrix);
println!("ans = {:?}", ans);
}
fn finish_time(n: i32, time: &mut Vec<i32>, matrix: &mut Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut nexts: Vec<Vec<i32>> = vec![];
for i in 0..n {
nexts.push(vec![]);
}
let mut in0: Vec<i32> = vec![];
for _ in 0..n {
in0.push(0);
}
for line in matrix.iter() {
nexts[line[1] as usize].push(line[0]);
in0[line[0] as usize] += 1;
}
let mut zero_in_queue: Vec<i32> = vec![];
let mut ans: Vec<i32> = vec![];
for _ in 0..n {
ans.push(0);
}
for i in 0..n {
if in0[i as usize] == 0 {
zero_in_queue.push(i);
}
}
while zero_in_queue.len() > 0 {
let cur = zero_in_queue[0];
zero_in_queue.remove(0);
ans[cur as usize] += time[cur as usize];
for next in nexts[cur as usize].iter() {
ans[*next as usize] = get_max(ans[*next as usize], ans[cur as usize]);
in0[*next as usize] -= 1;
if in0[*next as usize] == 0 {
zero_in_queue.push(*next);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
fn get_max<T: Clone + Copy + std::cmp::PartialOrd>(a: T, b: T) -> T {
if a > b {
a
} else {
b
}
}
执行结果如下:
左神 java 代码
关于python numpy array 与 matrix 乘方和python array和matrix的介绍已经告一段落,感谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于2021-04-18:给定一个二维数组 matrix,里面的值不是 1 就是 0,上、下、左、右相邻的 1 认为是一片岛,返回 matrix 中、2021-12-28:给定一个二维数组 matrix,matrix [i][j] = k 代表:从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往右跳<=k 步,或者从 (i,j) 位置可以随意往下跳<=k 步, 如果 matrix [i]、2022-06-11:注意本文件中,graph 不是邻接矩阵的含义,而是一个二部图。 在长度为 N 的邻接矩阵 matrix 中,所有的点有 N 个,matrix [i][j] 表示点 i 到点 j 的距离或者权重, 而在二部、2022-06-25:给定一个正数 n, 表示有 0~n-1 号任务, 给定一个长度为 n 的数组 time,time [i] 表示 i 号任务做完的时间, 给定一个二维数组 matrix, matrix [j] = {a,的相关信息,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:





