本文将分享Pythonnumpy模块-nanargmin()实例源码的详细内容,并且还将对python中numpy模块进行详尽解释,此外,我们还将为大家带来关于Jupyter中的Numpy在打印时出错
本文将分享Python numpy 模块-nanargmin() 实例源码的详细内容,并且还将对python中numpy模块进行详尽解释,此外,我们还将为大家带来关于Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()、Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性的相关知识,希望对你有所帮助。
本文目录一览:- Python numpy 模块-nanargmin() 实例源码(python中numpy模块)
- Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
- numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
- numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()
- Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性

Python numpy 模块-nanargmin() 实例源码(python中numpy模块)
Python numpy 模块,nanargmin() 实例源码
我们从Python开源项目中,提取了以下50个代码示例,用于说明如何使用numpy.nanargmin()。
- def mouse_drag(self, event):
- ''''''
- ''''''
- if event.inaxes == self.ax and event.button == 1:
- # Index of nearest point
- i = np.nanargmin(((event.xdata - self.x) / self.nx) ** 2)
- j = np.nanargmin(((event.ydata - self.y) / self.ny) ** 2)
- if (i == self.last_i) and (j == self.last_j):
- return
- else:
- self.last_i = i
- self.last_j = j
- # Toggle pixel
- if self.aperture[j,i]:
- self.aperture[j,i] = 0
- else:
- self.aperture[j,i] = 1
- # Update the contour
- self.update()
- def mouse_click(self, event):
- ''''''
- ''''''
- if event.mouseevent.inaxes == self.ax:
- # Index of nearest point
- i = np.nanargmin(((event.mouseevent.xdata - self.x) / self.nx) ** 2)
- j = np.nanargmin(((event.mouseevent.ydata - self.y) / self.ny) ** 2)
- self.last_i = i
- self.last_j = j
- # Toggle pixel
- if self.aperture[j,i] = 1
- # Update the contour
- self.update()
- def update(self, arx, xarchive=None, arf=None, evals=None):
- """checks for better solutions in list ``arx``.
- Based on the smallest corresponding value in ``arf``,
- alternatively,`update` may be called with a `BestSolution`
- instance like ``update(another_best_solution)`` in which case
- the better solution becomes the current best.
- ``xarchive`` is used to retrieve the genotype of a solution.
- """
- if isinstance(arx, BestSolution):
- if self.evalsall is None:
- self.evalsall = arx.evalsall
- elif arx.evalsall is not None:
- self.evalsall = max((self.evalsall, arx.evalsall))
- if arx.f is not None and arx.f < np.inf:
- self.update([arx.x], xarchive, [arx.f], arx.evals)
- return self
- assert arf is not None
- # find failsave minimum
- try:
- minidx = np.nanargmin(arf)
- except ValueError:
- return
- if minidx is np.nan:
- return
- minarf = arf[minidx]
- # minarf = reduce(lambda x,y: y if y and y is not np.nan
- # and y < x else x,arf,np.inf)
- if minarf < np.inf and (minarf < self.f or self.f is None):
- self.x, self.f = arx[minidx], arf[minidx]
- if xarchive is not None and xarchive.get(self.x) is not None:
- self.x_geno = xarchive[self.x].get(''geno'')
- else:
- self.x_geno = None
- self.evals = None if not evals else evals - len(arf) + minidx + 1
- self.evalsall = evals
- elif evals:
- self.evalsall = evals
- self.last.x = arx[minidx]
- self.last.f = minarf
- def test_nanargmin(self):
- tgt = np.argmin(self.mat)
- for mat in self.integer_arrays():
- assert_equal(np.nanargmin(mat), tgt)
- def update(self, evals=None):
- """checks for better solutions in list `arx`.
- Based on the smallest corresponding value in `arf`,`update` may be called with a `BestSolution`
- instance like ``update(another_best_solution)`` in which case
- the better solution becomes the current best.
- `xarchive` is used to retrieve the genotype of a solution.
- """
- if isinstance(arx, arx.evals)
- return self
- assert arf is not None
- # find failsave minimum
- minidx = np.nanargmin(arf)
- if minidx is np.nan:
- return
- minarf = arf[minidx]
- # minarf = reduce(lambda x, arf[minidx]
- if xarchive is not None and xarchive.get(self.x) is not None:
- self.x_geno = xarchive[self.x].get(''geno'')
- else:
- self.x_geno = None
- self.evals = None if not evals else evals - len(arf) + minidx + 1
- self.evalsall = evals
- elif evals:
- self.evalsall = evals
- self.last.x = arx[minidx]
- self.last.f = minarf
- def update(self, arf[minidx]
- if xarchive is not None and xarchive.get(self.x) is not None:
- self.x_geno = xarchive[self.x].get(''geno'')
- else:
- self.x_geno = None
- self.evals = None if not evals else evals - len(arf) + minidx + 1
- self.evalsall = evals
- elif evals:
- self.evalsall = evals
- self.last.x = arx[minidx]
- self.last.f = minarf
- def update(self, arf[minidx]
- if xarchive is not None and xarchive.get(self.x) is not None:
- self.x_geno = xarchive[self.x].get(''geno'')
- else:
- self.x_geno = None
- self.evals = None if not evals else evals - len(arf) + minidx + 1
- self.evalsall = evals
- elif evals:
- self.evalsall = evals
- self.last.x = arx[minidx]
- self.last.f = minarf
- def test_nanargmin(self):
- tgt = np.argmin(self.mat)
- for mat in self.integer_arrays():
- assert_equal(np.nanargmin(mat), tgt)
- def figure_mouse_pick(self, event):
- """
- Trigger for when the mouse is used to select an item in the figure.
- :param event:
- The matplotlib event.
- """
- ycol = "abundance"
- xcol = {
- self.ax_excitation_twin: "expot",
- self.ax_line_strength_twin: "reduced_equivalent_width"
- }[event.inaxes]
- xscale = np.ptp(event.inaxes.get_xlim())
- yscale = np.ptp(event.inaxes.get_ylim())
- try:
- distance = np.sqrt(
- ((self._state_transitions[ycol] - event.ydata)/yscale)**2 \\
- + ((self._state_transitions[xcol] - event.xdata)/xscale)**2)
- except AttributeError:
- # Stellar parameters have not been measured yet
- return None
- index = np.nanargmin(distance)
- # Because the state transitions are linked to the parent source model of
- # the table view,we will have to get the proxy index.
- proxy_index = self.table_view.model().mapFromSource(
- self.proxy_spectral_models.sourceModel().createIndex(index, 0)).row()
- self.table_view.selectRow(proxy_index)
- return None
- def find_min(x, bin_width = 10):
- xm = binned_average(x, bin_width=bin_width);
- imin = np.nanargmin(xm);
- return int((imin + 0.5) * bin_width);
- def find_min(x, bin_width=bin_width);
- imin = np.nanargmin(xm);
- return int((imin + 0.5) * bin_width);
- def find_min(x, bin_width=bin_width);
- imin = np.nanargmin(xm);
- return int((imin + 0.5) * bin_width);
- def find_min(x, bin_width=bin_width);
- imin = np.nanargmin(xm);
- return int((imin + 0.5) * bin_width);
- def find_min(x, bin_width=bin_width);
- imin = np.nanargmin(xm);
- return int((imin + 0.5) * bin_width);
- def Variogram(self):
- """
- :return:
- """
- self.run()
- # find the best Variogram
- idx = np.nanargmin(self.e)
- return self.V[idx]
- def _select_best_measure_index(curr_measures, args):
- idx = None
- try:
- if args.measure == ''aicc'':
- # The best score for AICc is the minimum.
- idx = np.nanargmin(curr_measures)
- elif args.measure in [''hmm-distance'', ''wasserstein'', ''mahalanobis'']:
- # The best score for the l-d measure is the maximum.
- idx = np.nanargmax(curr_measures)
- except:
- idx = random.choice(range(len(curr_measures)))
- assert idx is not None
- return idx
- def initial_count(classify, test_set_x, data, valid):
- (valid_st2,valid_st5,valid_st8) = valid
- (ns_test_set_x_st2,ns_test_set_x_st5,ns_test_set_x_st8) = data
- # classify st_2 it is always valid
- (st2_count, st2_res, st2_entropy) = count_in_interval(classify, ns_test_set_x_st2, 0, 81) #100 - 19 etc.
- # check if st5 is valid. if not return st2 count
- if (valid_st5 == 1):
- (st5_count, st5_res, st5_entropy) = count_in_interval(classify, ns_test_set_x_st5, 21)
- else:
- st8_entropy = numpy.inf
- if (valid_st8 == 1):
- (st8_count, st8_res, st8_entropy) = count_in_interval(classify, ns_test_set_x_st8, 6)
- else:
- st8_entropy = numpy.inf
- winner = numpy.nanargmin(numpy.array([st2_entropy, st5_entropy, st8_entropy]))
- if (winner == 0):
- # winner is stride 2
- return (st2_count, (st2_res*2/2,st2_res*2/5, st2_res*2/8))
- if (winner == 1):
- # winner is stride 5
- return (st5_count, (st5_res*5/2,st5_res*5/5, st5_res*5/8))
- if (winner == 2):
- # winner is stride 8
- return (st8_count, (st8_res*8/2,st8_res*8/5, st8_res*8/8))
- def get_next_count(classify, valid, global_count, curr_residue, start_frame):
- (valid_st2,ns_test_set_x_st8) = data
- (curr_residue_st2, curr_residue_st5, curr_residue_st8) = curr_residue
- # classify st_2 it is always valid
- (st2_count, curr_residue_st2, (start_frame/2-19), (start_frame/2-19)+20)
- # check if st5 is valid. if not return st2 count
- if (valid_st5 == 1):
- (st5_count, (start_frame/5-19), (start_frame/5-19)+8)
- else:
- st5_entropy = numpy.inf
- if (valid_st8 == 1):
- (st8_count, curr_residue_st8, (start_frame/8-19), (start_frame/8-19)+5)
- else:
- st8_entropy = numpy.inf
- winner = numpy.nanargmin(numpy.array([st2_entropy, st8_entropy]))
- if (winner == 0):
- # winner is stride 2
- return (global_count + st2_count, st2_res*2/8))
- if (winner == 1):
- # winner is stride 5
- return (global_count + st5_count, st5_res*5/8))
- if (winner == 2):
- # winner is stride 8
- return (global_count + st8_count, st8_res*8/8))
- def get_remain_count(classify, ns_test_set_x_st2.shape[0])
- # check if st5 is valid. if not return st2 count
- if (valid_st5 == 1):
- (st5_count, ns_test_set_x_st5.shape[0])
- else:
- st5_entropy = numpy.inf
- if (valid_st8 == 1):
- (st8_count, ns_test_set_x_st8.shape[0])
- else:
- st8_entropy = numpy.inf
- winner = numpy.nanargmin(numpy.array([st2_entropy, st8_entropy]))
- if (winner == 0):
- # winner is stride 2
- return (global_count + st2_count)
- if (winner == 1):
- # winner is stride 5
- return (global_count + st5_count)
- if (winner == 2):
- # winner is stride 8
- return (global_count + st8_count)
- def count_entire_movie(classify, ns_test_set_x_st8.shape[0])
- else:
- st8_entropy = numpy.inf
- winner = numpy.nanargmin(numpy.array([st2_entropy, st8_entropy]))
- if (winner == 0):
- # winner is stride 2
- return (global_count + st2_count)
- if (winner == 1):
- # winner is stride 5
- return (global_count + st5_count)
- if (winner == 2):
- # winner is stride 8
- return (global_count + st8_count)
- def test_nanargmin(self):
- tgt = np.argmin(self.mat)
- for mat in self.integer_arrays():
- assert_equal(np.nanargmin(mat), tgt)
- def __find_nearest_nodes(self, num, signal, mahar=True):
- #if mahar: return self.__find_nearest_nodes_by_mahar(num,signal)
- n = self.nodes.shape[0]
- indexes = [0.0] * num
- sq_dists = [0.0] * num
- D = util.calc_distance(self.nodes, np.asarray([signal] * n))
- for i in range(num):
- indexes[i] = np.nanargmin(D)
- sq_dists[i] = D[indexes[i]]
- D[indexes[i]] = float(''nan'')
- return indexes, sq_dists
- def update(self, arf[minidx]
- if xarchive is not None and xarchive.get(self.x) is not None:
- self.x_geno = xarchive[self.x].get(''geno'')
- else:
- self.x_geno = None
- self.evals = None if not evals else evals - len(arf) + minidx + 1
- self.evalsall = evals
- elif evals:
- self.evalsall = evals
- self.last.x = arx[minidx]
- self.last.f = minarf
- def test_nanargmin(self):
- tgt = np.argmin(self.mat)
- for mat in self.integer_arrays():
- assert_equal(np.nanargmin(mat), tgt)
- def test_nanargmin(self):
- tgt = np.argmin(self.mat)
- for mat in self.integer_arrays():
- assert_equal(np.nanargmin(mat), tgt)
- def plot(self, ax=None, write_tau=True):
- """
- Returns
- -------
- fig : matplotlib.figure.figure
- figure instance containing the plot.
- """
- check_is_fitted(self, ''neg_log_likelihood_'')
- if ax is None:
- fig = plt.figure()
- ax = fig.gca()
- else:
- fig = ax.figure
- blue, green, red, purple, yellow, cyan = SEABORN_PALETTES[''deep'']
- i_best = np.nanargmin(self.neg_log_likelihood_)
- ax.plot(self.delays_ms_, self.neg_log_likelihood_, color=purple)
- ax.plot(self.delays_ms_[i_best], self.neg_log_likelihood_[i_best], ''D'',
- color=red)
- ax.set_xlabel(''Delay (ms)'')
- ax.set_ylabel(''Neg. log likelihood / T'')
- ax.grid(''on'')
- if write_tau:
- ax.text(0.5, 0.80, r''$\\mathrm{Estimated}$'',
- horizontalalignment=''center'', transform=ax.transAxes)
- ax.text(0.5, 0.66, r''$\\tau_0 = %.0f \\;\\mathrm{ms}$'' %
- (self.delays_ms_[i_best], ), horizontalalignment=''center'',
- transform=ax.transAxes)
- return fig
- def test_delay_shape():
- est = fast_delay()
- assert_equal(est.neg_log_likelihood_.shape, est.delays_ms_.shape)
- assert_greater(est.neg_log_likelihood_.shape[0], 1)
- i_best = np.nanargmin(est.neg_log_likelihood_)
- assert_equal(est.best_delay_ms_, est.delays_ms_[i_best])
- def update(self, arf[minidx]
- if xarchive is not None and xarchive.get(self.x) is not None:
- self.x_geno = xarchive[self.x].get(''geno'')
- else:
- self.x_geno = None
- self.evals = None if not evals else evals - len(arf) + minidx + 1
- self.evalsall = evals
- elif evals:
- self.evalsall = evals
- self.last.x = arx[minidx]
- self.last.f = minarf
- def optimize_threshold_with_f1(f1c, thresholds, criterion=''max''):
- #f1c[np.isnan(f1c)] = 0
- if criterion == ''max'':
- ti = np.nanargmax(f1c)
- else:
- ti = np.nanargmin(np.abs(thresholds-0.5*f1c))
- #assert(np.all(thresholds>=0))
- #idx = (thresholds>=f1c*0.5-mp) & (thresholds<=f1c*0.5+mp)
- #assert(np.any(idx))
- #ti = np.where(idx)[0][f1c[idx].argmax()]
- return thresholds[ti], ti
- def _(artist, event):
- offsets = artist.get_offsets()
- ds = np.hypot(
- *(artist.axes.transData.transform(offsets) - [event.x, event.y]).T)
- argmin = np.nanargmin(ds)
- if ds[argmin] < artist.get_pickradius():
- target = with_attrs(offsets[argmin], index=argmin)
- return Selection(artist, target, ds[argmin], None, None)
- else:
- return None
- def compute_integral(self, x_s, y_s):
- if len(x_s) == 0:
- return np.zeros((y_s.shape[0],)) * np.nan
- closer = np.nanargmin(abs(x_s - self.limits[0]))
- return y_s[:, closer]
- def compute_draw_info(self, x, ys):
- bs = self.compute_baseline(x, ys)
- im = np.array([np.nanargmin(abs(x - self.limits[0]))])
- dx = [self.limits[0], self.limits[0]]
- dys = np.hstack((bs[:, im], ys[:, im]))
- return [("curve", (dx, dys, INTEGRATE_DRAW_EDGE_PENARGS)), # line to value
- ("dot", (x[im], im]))]
- def update(self, arf[minidx]
- if xarchive is not None and xarchive.get(self.x) is not None:
- self.x_geno = xarchive[self.x].get(''geno'')
- else:
- self.x_geno = None
- self.evals = None if not evals else evals - len(arf) + minidx + 1
- self.evalsall = evals
- elif evals:
- self.evalsall = evals
- self.last.x = arx[minidx]
- self.last.f = minarf
- def test_nanargmin(self):
- tgt = np.argmin(self.mat)
- for mat in self.integer_arrays():
- assert_equal(np.nanargmin(mat), tgt)
- def nanmedoid(a, axis=1, indexonly=False):
- """
- Compute the medoid along the specified axis,omitting
- observations containing NaNs.
- Returns the medoid of the array elements.
- Parameters
- ----------
- a : array_like
- Input array or object that can be converted to an array.
- axis : int
- Axis along which the medoid is computed. The default
- is to compute the median along the last axis of the array.
- indexonly : bool,optional
- If this is set to True,only the index of the medoid is returned.
- Returns
- -------
- medoid : ndarray or int
- """
- if axis == 1:
- diff = a.T[:, :] - a.T
- ssum = np.einsum(''ijk,ijk->ij'', diff, diff)
- dist = np.nansum(np.sqrt(ssum), axis=1)
- mask = np.isnan(a).any(axis=0)
- dist[mask] = np.nan
- idx = np.nanargmin(dist)
- if indexonly:
- return idx
- else:
- return a[:, idx]
- if axis == 0:
- diff = a[:, :] - a
- ssum = np.einsum(''ijk, axis=1)
- mask = np.isnan(a).any(axis=1)
- dist[mask] = np.nan
- idx = np.nanargmin(dist)
- if indexonly:
- return idx
- else:
- return a[idx, :]
- raise IndexError("axis {} out of bounds".format(axis))
- def nanargmin(a, axis=None):
- """
- Return the indices of the minimum values in the specified axis ignoring
- NaNs. For all-NaN slices ``ValueError`` is raised. Warning: the results
- cannot be trusted if a slice contains only NaNs and Infs.
- Parameters
- ----------
- a : array_like
- Input data.
- axis : int,optional
- Axis along which to operate. By default flattened input is used.
- Returns
- -------
- index_array : ndarray
- An array of indices or a single index value.
- See Also
- --------
- argmin,nanargmax
- Examples
- --------
- >>> a = np.array([[np.nan,4],[2,3]])
- >>> np.argmin(a)
- 0
- >>> np.nanargmin(a)
- 2
- >>> np.nanargmin(a,axis=0)
- array([1,1])
- >>> np.nanargmin(a,axis=1)
- array([1,0])
- """
- a, mask = _replace_nan(a, np.inf)
- res = np.argmin(a, axis=axis)
- if mask is not None:
- mask = np.all(mask, axis=axis)
- if np.any(mask):
- raise ValueError("All-NaN slice encountered")
- return res
- def nanargmax(a, axis=None):
- """
- Return the indices of the maximum values in the specified axis ignoring
- NaNs. For all-NaN slices ``ValueError`` is raised. Warning: the
- results cannot be trusted if a slice contains only NaNs and -Infs.
- Parameters
- ----------
- a : array_like
- Input data.
- axis : int,optional
- Axis along which to operate. By default flattened input is used.
- Returns
- -------
- index_array : ndarray
- An array of indices or a single index value.
- See Also
- --------
- argmax,nanargmin
- Examples
- --------
- >>> a = np.array([[np.nan,3]])
- >>> np.argmax(a)
- 0
- >>> np.nanargmax(a)
- 1
- >>> np.nanargmax(a,0])
- >>> np.nanargmax(a,1])
- """
- a, -np.inf)
- res = np.argmax(a, axis=axis)
- if np.any(mask):
- raise ValueError("All-NaN slice encountered")
- return res
- def nanargmin(a, axis=axis)
- if np.any(mask):
- raise ValueError("All-NaN slice encountered")
- return res
- def nanargmax(a, axis=axis)
- if np.any(mask):
- raise ValueError("All-NaN slice encountered")
- return res
- def nicecolorbar(self,
- axcb=None,
- reflevel=None,
- label=None,
- vmax=None,
- vmin=None,
- data=None,
- loc=''head right'',
- fontsize=8,
- ticks = None):
- if not axcb:
- axcb = matplotlib.pyplot.gca()
- divider = make_axes_locatable(axcb)
- # this code is from
- # http://matplotlib.org/mpl_toolkits/axes_grid/users/overview.html#axes-grid1
- cax = divider.append_axes("right", size="2%", pad=0.15)
- levels = numpy.asarray([0.001,0.0025,0.005,0.01,0.025,0.05,0.1,0.25,0.5,1,2.5,5,10,25,50,100,250,500,1000])
- if vmax!= None and vmin != None:
- level = levels[numpy.nanargmin(abs((vmax - vmin)/5 - levels))]
- ticks = numpy.arange(vmin, vmax, level)
- elif vmax :
- level = levels[numpy.nanargmin(abs((vmax - numpy.nanmin(data))/5 - levels))]
- ticks = numpy.arange(numpy.nanmin(data), level)
- elif data is not None:
- level = None #levels[numpy.nanargmin(abs((numpy.nanmax(data) - numpy.nanmin(data))/5 - levels))]
- ticks = None #numpy.arange(numpy.nanmin(data),numpy.nanmax(data),level)
- #ticks -= numpy.nanmin(abs(ticks))
- cb = matplotlib.pyplot.colorbar(self,
- cax=cax,
- label=label,
- orientation=''vertical'',
- extend=''both'',
- spacing=''uniform'',
- ticks=ticks)
- if vmax!= None and vmin != None:
- #print(ticks,vmin,vmax)
- cb.set_clim(vmin, vmax)
- cb.ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position(''right'')
- cb.ax.yaxis.set_label_position(''right'')
- cb.ax.set_yticklabels(cb.ax.get_yticklabels(), rotation=''vertical'',fontsize=fontsize)
- #if reflevel:
- # cb.ax.axhline((reflevel-min(cb.get_clim()))/numpy.diff(cb.get_clim()),zorder=999,color=''k'',linewidth=2)
- return cb
- def nanargmin(a, axis=axis)
- if np.any(mask):
- raise ValueError("All-NaN slice encountered")
- return res
- def nanargmax(a, axis=axis)
- if np.any(mask):
- raise ValueError("All-NaN slice encountered")
- return res
- def nanargmin(a, axis=axis)
- if np.any(mask):
- raise ValueError("All-NaN slice encountered")
- return res
- def nanargmax(a, axis=axis)
- if np.any(mask):
- raise ValueError("All-NaN slice encountered")
- return res
- def nanargmin(a, axis=axis)
- if np.any(mask):
- raise ValueError("All-NaN slice encountered")
- return res
- def nanargmax(a, axis=axis)
- if np.any(mask):
- raise ValueError("All-NaN slice encountered")
- return res
- def get_ray_lengths(self,x=None,y=None,PositionTol = 3,Coords=''display''):
- # Work out ray lengths for all raytraced pixels
- RayLength = np.sqrt(np.sum( (self.ray_end_coords - self.ray_start_coords) **2,axis=-1))
- # If no x and y given,return them all
- if x is None and y is None:
- if self.fullchip:
- if Coords.lower() == ''display'':
- return RayLength
- else:
- return self.transform.display_to_original_image(RayLength,binning=self.binning)
- else:
- return RayLength
- else:
- if self.x is None or self.y is None:
- raise Exception(''This ray data does not have x and y pixel indices!'')
- # Otherwise,return the ones at given x and y pixel coords.
- if np.shape(x) != np.shape(y):
- raise ValueError(''x and y arrays must be the same shape!'')
- else:
- if Coords.lower() == ''original'':
- x,y = self.transform.original_to_display_coords(x,y)
- orig_shape = np.shape(x)
- x = np.reshape(x,np.size(x),order=''F'')
- y = np.reshape(y,np.size(y),order=''F'')
- RL = np.zeros(np.shape(x))
- RayLength = RayLength.flatten()
- xflat = self.x.flatten()
- yflat = self.y.flatten()
- for pointno in range(x.size):
- if np.isnan(x[pointno]) or np.isnan(y[pointno]):
- RL[pointno] = np.nan
- continue
- deltaX = xflat - x[pointno]
- deltaY = yflat - y[pointno]
- deltaR = np.sqrt(deltaX**2 + deltaY**2)
- if np.nanmin(deltaR) <= PositionTol:
- RL[pointno] = RayLength[np.nanargmin(deltaR)]
- else:
- raise Exception(''No ray-traced pixel within PositionTol of requested pixel!'')
- return np.reshape(RL,orig_shape,order=''F'')
- # Return unit vectors of sight-line direction for each pixel.
- def _compute_projection_pick(artist, path, xy):
- """Project *xy* on *path* to obtain a `Selection` for *artist*.
- *path* is first transformed to screen coordinates using the artist
- transform,and the target of the returned `Selection` is transformed
- back to data coordinates using the artist *axes* inverse transform. The
- `Selection` `index` is returned as a float. This function returns ``None``
- for degenerate inputs.
- The caller is responsible for converting the index to the proper class if
- needed.
- """
- transform = artist.get_transform().frozen()
- tpath = (path.cleaned(transform) if transform.is_affine
- # `cleaned` only handles affine transforms.
- else transform.transform_path(path).cleaned())
- # `cleaned` should return a path where the first element is `MOVeto`,the
- # following are `LINeto` or `CLOSEpoly`,and the last one is `STOP`,i.e.
- # codes = path.codes
- # assert (codes[0],codes[-1]) == (path.MOVeto,path.STOP)
- # assert np.in1d(codes[1:-1],[path.LINeto,path.CLOSEpoly]).all()
- vertices = tpath.vertices[:-1]
- codes = tpath.codes[:-1]
- vertices[codes == tpath.CLOSEpoly] = vertices[0]
- # Unit vectors for each segment.
- us = vertices[1:] - vertices[:-1]
- ls = np.hypot(*us.T)
- with np.errstate(invalid="ignore"):
- # Results in 0/0 for repeated consecutive points.
- us /= ls[:, None]
- # Vectors from each vertex to the event (overwritten below).
- vs = xy - vertices[:-1]
- # Clipped dot products -- `einsum` cannot be done in place,`clip` can.
- dot = np.clip(np.einsum("ij,ij->i", vs, us), ls, out=vs[:, 0])
- # Projections.
- projs = vertices[:-1] + dot[:, None] * us
- ds = np.hypot(*(xy - projs).T, 1])
- try:
- argmin = np.nanargmin(ds)
- dmin = ds[argmin]
- except (ValueError, IndexError): # See above re: exceptions caught.
- return
- else:
- target = AttrArray(
- artist.axes.transData.inverted().transform_point(projs[argmin]))
- target.index = (
- (argmin + dot[argmin] / ls[argmin])
- / (path._interpolation_steps / tpath._interpolation_steps))
- return Selection(artist, dmin, None)
- def _(artist, event):
- # No need to call `line.contains` because we''re going to redo
- # the work anyways (and it was broken for step plots up to
- # matplotlib/matplotlib#6645).
- # Always work in screen coordinates,as this is how we need to compute
- # distances. Note that the artist transform may be different from the axes
- # transform (e.g.,for axvline).
- xy = event.x, event.y
- data_xy = artist.get_xydata()
- sels = []
- # If markers are visible,find the closest vertex.
- if artist.get_marker() not in ["None", "none", " ", "", None]:
- ds = np.hypot(*(xy - artist.get_transform().transform(data_xy)).T)
- try:
- argmin = np.nanargmin(ds)
- dmin = ds[argmin]
- except (ValueError, IndexError):
- # numpy 1.7.0''s `nanargmin([nan])` returns nan,so
- # `ds[argmin]` raises IndexError. In later versions of numpy,
- # `nanargmin([nan])` raises ValueError (the release notes for 1.8.0
- # are incorrect on this topic).
- pass
- else:
- # More precise than transforming back.
- target = with_attrs(artist.get_xydata()[argmin], index=argmin)
- sels.append(Selection(artist, None))
- # If lines are visible,find the closest projection.
- if (artist.get_linestyle() not in ["None", None]
- and len(artist.get_xydata()) > 1):
- sel = _compute_projection_pick(artist, artist.get_path(), xy)
- if sel is not None:
- sel.target.index = {
- "_draw_lines": lambda _, index: index,
- "_draw_steps_pre": Index.pre_index,
- "_draw_steps_mid": Index.mid_index,
- "_draw_steps_post": Index.post_index}[
- Line2D.drawStyles[artist.get_drawstyle()]](
- len(data_xy), sel.target.index)
- sels.append(sel)
- sel = min(sels, key=lambda sel: sel.dist, default=None)
- return sel if sel and sel.dist < artist.get_pickradius() else None
- def mouseMoved(self, evt):
- pos = evt[0]
- if self.plot.sceneBoundingRect().contains(pos):
- mousePoint = self.plot.vb.mapScenetoView(pos)
- posx, posy = mousePoint.x(), mousePoint.y()
- labels = []
- for a, vs in sorted(self.reports.items()):
- for v in vs:
- if isinstance(v, tuple) and len(v) == 2:
- if v[0] == "x":
- labels.append(("%0." + str(self.important_decimals[0]) + "f") % v[1])
- continue
- labels.append(str(v))
- labels = " ".join(labels)
- self.crosshair_hidden = bool(labels)
- if self.location and not labels:
- fs = "%0." + str(self.important_decimals[0]) + "f %0." + str(self.important_decimals[1]) + "f"
- labels = fs % (posx, posy)
- self.label.setText(labels, color=(0, 0))
- if self.curves and len(self.curves[0][0]): # need non-zero x axis!
- cache = {}
- bd = None
- if self.markclosest and self.plot.vb.action != ZOOMING:
- xpixel, ypixel = self.plot.vb.viewPixelSize()
- distances = distancetocurves(self.curves[0], posx, posy, xpixel, ypixel, r=self.MOUSE_RADIUS,
- cache=cache)
- try:
- mindi = np.nanargmin(distances)
- if distances[mindi] < self.MOUSE_RADIUS:
- bd = mindi
- except ValueError: # if all distances are NaN
- pass
- if self.highlighted != bd:
- QToolTip.hideText()
- if self.highlighted is not None and bd is None:
- self.highlighted = None
- self.highlighted_curve.hide()
- if bd is not None:
- self.highlighted = bd
- x = self.curves[0][0]
- y = self.curves[0][1][self.highlighted]
- self.highlighted_curve.setData(x=x, y=y)
- self.highlighted_curve.show()
- self.vLine.setPos(posx)
- self.hLine.setPos(posy)
- self.viewhelpers_show()
- else:
- self.viewhelpers_hide()

Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
如何解决Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable?
晚安, 尝试打印以下内容时,我在 jupyter 中遇到了 numpy 问题,并且得到了一个 错误: 需要注意的是python版本是3.8.8。 我先用 spyder 测试它,它运行正确,它给了我预期的结果
使用 Spyder:
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
Results
0.6604903457995978
0.8236300859753154
0.16067650689842816
0.6967868357083673
0.4231597934445466
现在有了 jupyter
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
-------------------------------------------------- ------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-78-0c6a801b3ea9> in <module>
2 for i in range (5):
3 n = np.random.rand ()
----> 4 print (n)
TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable
感谢您对我如何在 Jupyter 中解决此问题的帮助。
非常感谢您抽出宝贵时间。
阿特,约翰”
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)
numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
今天看到这样一句代码:
xb = np.random.random((nb, d)).astype(''float32'') #创建一个二维随机数矩阵(nb行d列)
xb[:, 0] += np.arange(nb) / 1000. #将矩阵第一列的每个数加上一个值要理解这两句代码需要理解三个函数
1、生成随机数
numpy.random.random(size=None)
size为None时,返回float。
size不为None时,返回numpy.ndarray。例如numpy.random.random((1,2)),返回1行2列的numpy数组
2、对numpy数组中每一个元素进行类型转换
numpy.ndarray.astype(dtype)
返回numpy.ndarray。例如 numpy.array([1, 2, 2.5]).astype(int),返回numpy数组 [1, 2, 2]
3、获取等差数列
numpy.arange([start,]stop,[step,]dtype=None)
功能类似python中自带的range()和numpy中的numpy.linspace
返回numpy数组。例如numpy.arange(3),返回numpy数组[0, 1, 2]

numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()
numpy.ravel(a, order=''C'')
Return a flattened array
numpy.chararray.flatten(order=''C'')
Return a copy of the array collapsed into one dimension
numpy.squeeze(a, axis=None)
Remove single-dimensional entries from the shape of an array.
相同点: 将多维数组 降为 一维数组
不同点:
ravel() 返回的是视图(view),意味着改变元素的值会影响原始数组元素的值;
flatten() 返回的是拷贝,意味着改变元素的值不会影响原始数组;
squeeze()返回的是视图(view),仅仅是将shape中dimension为1的维度去掉;
ravel()示例:
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.ravel()
16 print("a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19
20 print(a)
21 log_type(''a'',a)
flatten()示例
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.flatten()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)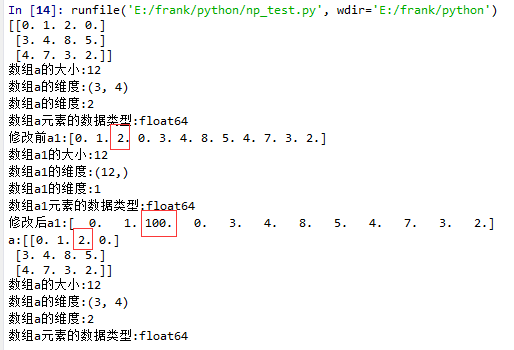
squeeze()示例:
1. 没有single-dimensional entries的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)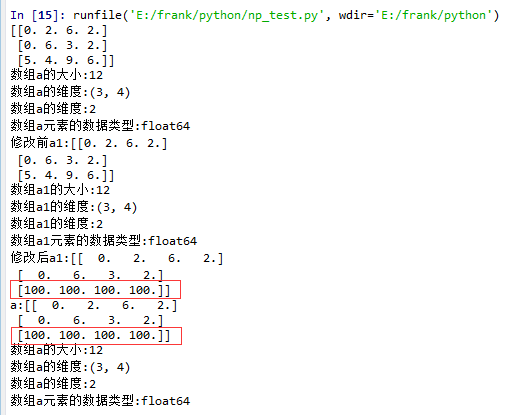
从结果中可以看到,当没有single-dimensional entries时,squeeze()返回额数组对象是一个view,而不是copy。
2. 有single-dimentional entries 的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((1,3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)
Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性
一、Numpy数组创建
part 1:np.linspace(起始值,终止值,元素总个数
import numpy as np
''''''
numpy中的ndarray数组
''''''
ary = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(ary)
ary = ary * 10
print(ary)
''''''
ndarray对象的创建
''''''
# 创建二维数组
# np.array([[],[],...])
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]])
print(a)
# np.arange(起始值, 结束值, 步长(默认1))
b = np.arange(1, 10, 1)
print(b)
print("-------------np.zeros(数组元素个数, dtype=''数组元素类型'')-----")
# 创建一维数组:
c = np.zeros(10)
print(c, ''; c.dtype:'', c.dtype)
# 创建二维数组:
print(np.zeros ((3,4)))
print("----------np.ones(数组元素个数, dtype=''数组元素类型'')--------")
# 创建一维数组:
d = np.ones(10, dtype=''int64'')
print(d, ''; d.dtype:'', d.dtype)
# 创建三维数组:
print(np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int32 ))
# 打印维度
print(np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int32 ).ndim) # 返回:3(维)
结果图:

part 2 :np.linspace ( 起始值,终止值,元素总个数)
import numpy as np
a = np.arange( 10, 30, 5 )
b = np.arange( 0, 2, 0.3 )
c = np.arange(12).reshape(4,3)
d = np.random.random((2,3)) # 取-1到1之间的随机数,要求设置为诶2行3列的结构
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
print(d)
print("-----------------")
from numpy import pi
print(np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 100 ))
print("-------------np.linspace(起始值,终止值,元素总个数)------------------")
print(np.sin(np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 100 )))
结果图:

二、Numpy的ndarray对象属性:
数组的结构:array.shape
数组的维度:array.ndim
元素的类型:array.dtype
数组元素的个数:array.size
数组的索引(下标):array[0]
''''''
数组的基本属性
''''''
import numpy as np
print("--------------------案例1:------------------------------")
a = np.arange(15).reshape(3, 5)
print(a)
print(a.shape) # 打印数组结构
print(len(a)) # 打印有多少行
print(a.ndim) # 打印维度
print(a.dtype) # 打印a数组内的元素的数据类型
# print(a.dtype.name)
print(a.size) # 打印数组的总元素个数
print("-------------------案例2:---------------------------")
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(a)
# 测试数组的基本属性
print(''a.shape:'', a.shape)
print(''a.size:'', a.size)
print(''len(a):'', len(a))
# a.shape = (6, ) # 此格式可将原数组结构变成1行6列的数据结构
# print(a, ''a.shape:'', a.shape)
# 数组元素的索引
ary = np.arange(1, 28)
ary.shape = (3, 3, 3) # 创建三维数组
print("ary.shape:",ary.shape,"\n",ary )
print("-----------------")
print(''ary[0]:'', ary[0])
print(''ary[0][0]:'', ary[0][0])
print(''ary[0][0][0]:'', ary[0][0][0])
print(''ary[0,0,0]:'', ary[0, 0, 0])
print("-----------------")
# 遍历三维数组:遍历出数组里的每个元素
for i in range(ary.shape[0]):
for j in range(ary.shape[1]):
for k in range(ary.shape[2]):
print(ary[i, j, k], end='' '')
结果图:

关于Python numpy 模块-nanargmin() 实例源码和python中numpy模块的介绍现已完结,谢谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()、Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性的相关知识,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:





