如果您对Pythonnumpy模块-int0()实例源码感兴趣,那么本文将是一篇不错的选择,我们将为您详在本文中,您将会了解到关于Pythonnumpy模块-int0()实例源码的详细内容,我们还将为
如果您对Python numpy 模块-int0() 实例源码感兴趣,那么本文将是一篇不错的选择,我们将为您详在本文中,您将会了解到关于Python numpy 模块-int0() 实例源码的详细内容,我们还将为您解答python中numpy模块的相关问题,并且为您提供关于Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()、Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性的有价值信息。
本文目录一览:- Python numpy 模块-int0() 实例源码(python中numpy模块)
- Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
- numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
- numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()
- Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性

Python numpy 模块-int0() 实例源码(python中numpy模块)
Python numpy 模块,int0() 实例源码
我们从Python开源项目中,提取了以下31个代码示例,用于说明如何使用numpy.int0()。
- def img_contour_select(ctrs, im):
- # ????????????
- cand_rect = []
- for item in ctrs:
- epsilon = 0.02*cv2.arcLength(item, True)
- approx = cv2.approxpolyDP(item, epsilon, True)
- if len(approx) <= 8:
- rect = cv2.minAreaRect(item)
- if rect[1][0] < 20 or rect[1][1] < 20:
- continue
- if rect[1][0] > 150 or rect[1][1] > 150:
- continue
- #ratio = (rect[1][1]+0.00001) / rect[1][0]
- #if ratio > 1 or ratio < 0.9:
- # continue
- Box = cv2.BoxPoints(rect)
- Box_d = np.int0(Box)
- cv2.drawContours(im, [Box_d], 0, (0,255,0), 3)
- cand_rect.append(Box)
- img_show_hook("????", im)
- return cand_rect
- def draw_markers(img,markers):
- for m in markers:
- centroid = np.array(m[''centroid''],dtype=np.float32)
- origin = np.array(m[''verts''][0],dtype=np.float32)
- hat = np.array([[[0,0],[0,1],[.5,1.25],[1,0]]],dtype=np.float32)
- hat = cv2.perspectiveTransform(hat,m_marker_to_screen(m))
- if m[''id_confidence'']>.9:
- cv2.polylines(img,np.int0(hat),color = (0,0,255),isClosed=True)
- else:
- cv2.polylines(img,isClosed=True)
- # cv2.polylines(img,np.int0(centroid),color = (255,255,int(255*m[''id_confidence''])),isClosed=True,thickness=2)
- m_str = ''id: {:d}''.format(m[''id''])
- org = origin.copy()
- # cv2.rectangle(img,tuple(np.int0(org+(-5,-13))[0,:]),tuple(np.int0(org+(100,30))[0,color=(0,0),thickness=-1)
- cv2.putText(img,m_str,tuple(np.int0(org)[0,fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERShey_SIMPLEX, fontScale=0.4, color=(0,255))
- if ''id_confidence'' in m:
- m_str = ''idc: {:.3f}''.format(m[''id_confidence''])
- org += (0, 12)
- cv2.putText(img,255))
- if ''loc_confidence'' in m:
- m_str = ''locc: {:.3f}''.format(m[''loc_confidence''])
- org += (0, 12 )
- cv2.putText(img,255))
- if ''frames_since_true_detection'' in m:
- m_str = ''otf: {}''.format(m[''frames_since_true_detection''])
- org += (0,255))
- if ''opf_vel'' in m:
- m_str = ''otf: {}''.format(m[''opf_vel''])
- org += (0,255))
- def img_contour_select(ctrs, True)
- if len(approx) <= 8:
- rect = cv2.minAreaRect(item)
- #????????
- if rect[2] < -10 and rect[2] > -80:
- continue
- if rect[1][0] < 10 or rect[1][1] < 10:
- continue
- #ratio = (rect[1][1]+0.00001) / rect[1][0]
- #if ratio > 1 or ratio < 0.9:
- # continue
- Box = cv2.BoxPoints(rect)
- Box_d = np.int0(Box)
- cv2.drawContours(im, im)
- return cand_rect
- def remove_border(contour, ary):
- """Remove everything outside a border contour."""
- # Use a rotated rectangle (should be a good approximation of a border).
- # If it''s far from a right angle,it''s probably two sides of a border and
- # we should use the bounding Box instead.
- c_im = np.zeros(ary.shape)
- r = cv2.minAreaRect(contour)
- degs = r[2]
- if angle_from_right(degs) <= 10.0:
- Box = cv2.BoxPoints(r)
- Box = np.int0(Box)
- cv2.drawContours(c_im, [Box], 255, -1)
- cv2.drawContours(c_im, 4)
- else:
- x1, y1, x2, y2 = cv2.boundingRect(contour)
- cv2.rectangle(c_im, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), -1)
- cv2.rectangle(c_im, 4)
- return np.minimum(c_im, ary)
- def getMask(self, shape):
- p=self.state[''pos'']
- s=self.state[''size'']
- center=p + s / 2
- a=self.state[''angle'']
- # opencv convention:
- shape = (shape[1], shape[0])
- arr1 = np.zeros(shape, dtype=np.uint8)
- arr2 = np.zeros(shape, dtype=np.uint8)
- # draw rotated rectangle:
- vertices = np.int0(cv2.BoxPoints((center, s, a)))
- cv2.drawContours(arr1, [vertices], color=1, thickness=-1)
- # draw ellipse:
- cv2.ellipse(arr2, (int(center[0]), int(center[1])), (int(s[0] / 2 * self._ratioEllispeRectangle),
- int(s[1] / 2 * self._ratioEllispeRectangle)), int(a),
- startAngle=0, endAngle=360, thickness=-1)
- # bring both together:
- return np.logical_and(arr1, arr2).T
- def getMask(self, shape):
- p = self.state[''pos'']
- s = self.state[''size'']
- center = p + s / 2
- a = self.state[''angle'']
- # opencv convention:
- shape = (shape[1], shape[0])
- arr = np.zeros(shape, dtype=np.uint8)
- # draw rotated rectangle:
- vertices = np.int0(cv2.BoxPoints((center, a)))
- cv2.drawContours(arr,
- 0,
- color=1,
- thickness=-1)
- return arr.astype(bool).T
- def deal(self,frame):
- frame=frame.copy()
- track_window=self.track_window
- term_crit = ( cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_EPS | cv2.TERM_CRITERIA_COUNT, 10, 1 )
- roi_hist=self.roi_hist
- dst = cv2.calcBackProject([frame],[0],roi_hist,180],1)
- if self.m==''m'':
- ret, track_window_r = cv2.meanShift(dst, track_window, term_crit)
- x,y,w,h = track_window_r
- img2 = cv2.rectangle(frame, (x,y), (x+w,y+h),2)
- elif self.m==''c'':
- ret, track_window_r = cv2.CamShift(dst, term_crit)
- pts = cv2.BoxPoints(ret)
- pts = np.int0(pts)
- img2 = cv2.polylines(frame,[pts],True,2)
- rectsNew=[]
- center1=(track_window[0]+track_window[2]//2,track_window[1]+track_window[3]//2)
- center2=(track_window_r[0]+track_window_r[2]//2,track_window_r[1]+track_window_r[3]//2)
- img2 = cv2.line(img2,center1,center2,color=0)
- rectsNew=track_window_r
- # x,y,w,h = track_window
- # img2 = cv2.rectangle(frame,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),2)
- cv2.imshow(''img2'',img2)
- cv2.waitKey(0)
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()
- return rectsNew
- def remove_border(contour,it''s probably two sides of a border and
- # we should use the bounding Box instead.
- c_im = np.zeros(ary.shape)
- r = cv2.minAreaRect(contour)
- degs = r[2]
- if angle_from_right(degs) <= 10.0:
- Box = cv2.cv.BoxPoints(r)
- Box = np.int0(Box)
- cv2.drawContours(c_im, ary)
- def density_slice(rast, rel=np.less_equal, threshold=1000, nodata=-9999):
- ''''''
- Returns a density slice from a given raster. Arguments:
- rast A gdal.Dataset or a NumPy array
- rel A NumPy logic function; defaults to np.less_equal
- threshold An integer number
- ''''''
- # Can accept either a gdal.Dataset or numpy.array instance
- if not isinstance(rast, np.ndarray):
- rastr = rast.ReadAsArray()
- else:
- rastr = rast.copy()
- if (len(rastr.shape) > 2 and min(rastr.shape) > 1):
- raise ValueError(''Expected a single-band raster array'')
- return np.logical_and(
- rel(rastr, np.ones(rast.shape) * threshold),
- np.not_equal(rastr, np.ones(rast.shape) * nodata)).astype(np.int0)
- def shapeFiltering(img):
- contours = cv2.findContours(img, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[0]
- if len(contours) == 0:
- return "yoopsie"
- #else:
- #print contours
- """blank_image = np.zeros((img.shape[0],img.shape[1],3),np.uint8)
- cv2.drawContours(blank_image,contours,-1,(255,255))
- cv2.imshow("imagiae",blank_image)
- cv2.waitKey()"""
- good_shape = []
- for c in contours:
- x,h = cv2.boundingRect(c)
- """rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contour)
- Box = cv2.BoxPoints(rect)
- Box = np.int0(Box)
- w = """
- #if h == 0:
- # continue
- ratio = w / h
- ratio_grade = ratio / (TMw / TMh)
- if 0.2 < ratio_grade < 1.8:
- good_shape.append(c)
- """blank_image = np.zeros((img.shape[0],good_shape,255))
- cv2.imshow("imagia",blank_image)
- cv2.waitKey()"""
- return good_shape
- def findCorners(contour):
- """blank_image = np.zeros((img.shape[0],contour,255))
- rows,cols = img.shape[0],img.shape[1]
- M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D((cols/2,rows/2),-45,0.5)
- dst = cv2.warpAffine(blank_image,M,(cols,rows))
- cv2.imshow("rotatio",dst)
- cv2.waitKey()"""
- rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contour)
- Box = cv2.BoxPoints(rect)
- Box = np.int0(Box)
- height_px_1 = Box[0][1] - Box[3][1]
- height_px_2 = Box[1][1] - Box[2][1]
- print height_px_1, height_px_2
- if height_px_1 < height_px_2:
- close_height_px = height_px_2
- far_height_px = height_px_1
- else:
- close_height_px = height_px_1
- far_height_px = height_px_2
- return close_height_px, far_height_px
- def findCorners(contour):
- rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contour)
- Box = cv2.BoxPoints(rect)
- Box = numpy.int0(Box)
- height_px_1 = Box[0][1] - Box[3][1]
- height_px_2 = Box[1][1] - Box[2][1]
- print height_px_1, far_height_px
- def update(roi):
- img1b.setimage(roi.getArrayRegion(arr, img1a), levels=(0, arr.max()))
- img1c.setimage(np.int0(r.getMask(arr.shape)))
- # cell.sigRegionChanged.connect(update)
- # update(cell)
- def get_bounding_rect(contour):
- rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contour)
- Box = cv2.BoxPoints(rect)
- return np.int0(Box)
- def shi_tomasi(gray):
- # image????
- # maxCorners???????
- # qualityLevel?????????????????????
- # mindistance??????????
- corners = cv2.goodFeaturesToTrack(gray,25,0.01,10)
- cv2.computeCorrespondEpilines()
- # ?????? [[ 311.,250.]] ????????
- corners = np.int0(corners)
- return corners
- def calculateFrame(self,cap):
- data = self.getDataPoints()
- #targetCascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(cascPath)
- frame = cap.read()
- gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
- lower_bound = np.array([float(data[''HMIN'']),float(data["SMIN"]),float(data[''VMIN''])])
- upper_bound = np.array([float(data[''HMAX'']),float(data["SMAX"]),float(data[''VMAX''])])
- hsv = cv2.cvtColor(frame,cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
- mask = cv2.inRange(hsv,lower_bound,upper_bound)
- largest_area = 0
- xCenter = -1
- yCenter = -1
- targetRect = None
- ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(mask,200,0)
- contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh,cv2.RETR_TREE,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
- if len(contours) > 1:
- areas = [cv2.contourArea(c) for c in contours]
- max_index = np.argmax(areas)
- cnt = contours[max_index]
- rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt)
- Box = cv2.cv.BoxPoints(rect)
- Box = np.int0(Box)
- xCenter = (Box[0][0] + Box[1][0] + Box[2][0] + Box[3][0]) /4
- yCenter = (Box[0][1] + Box[1][1] + Box[2][1] + Box[3][1]) /4
- cv2.drawContours(frame,[Box],(0,2)
- output = {}
- distance = 0.0025396523 * yCenter**2 + 0.1000098497 *yCenter + 46.8824851568
- theta = math.atan2(xCenter-160, distance)
- output_dict = {"xCenter": xCenter, "yCenter": yCenter,"theta": theta, "distance":distance}
- output = json.dumps(output_dict)
- return frame ,output , True, mask
- def cfmask(mask, mask_values=(1,2,3,4, nodata=-9999):
- ''''''
- Returns a binary mask according to the CFMask algorithm results for the
- image; mask has True for water,cloud,shadow,and sNow (if any) and False
- everywhere else. More information can be found:
- https://landsat.usgs.gov/landsat-surface-reflectance-quality-assessment
- Landsat 4-7 Pre-Collection pixel_qa values to be masked:
- mask_values = (1,2,3,4)
- Landsat 4-7 Collection 1 pixel_qa values to be masked (for "Medium" confidence):
- mask_values = (1,68,72,80,112,132,136,144,160,176,224)
- Landsat 8 Collection 1 pixel_qa values to be masked (for "Medium" confidence):
- mask_values = (1,324,328,386,388,392,400,416,432,480,832,836,840,848,864,880,900,904,912,928,944,992,1024)
- Arguments:
- mask A gdal.Dataset or a NumPy array
- mask_path The path to an EOS HDF4 CFMask raster
- mask_values The values in the mask that correspond to NoData pixels
- nodata The NoData value; defaults to -9999.
- ''''''
- if not isinstance(mask, np.ndarray):
- maskr = mask.ReadAsArray()
- else:
- maskr = mask.copy()
- # Mask according to bit-packing described here:
- # https://landsat.usgs.gov/landsat-surface-reflectance-quality-assessment
- maskr = np.in1d(maskr.reshape((maskr.shape[0] * maskr.shape[1])), mask_values)\\
- .reshape((1, maskr.shape[0], maskr.shape[1])).astype(np.int0)
- return maskr
- def getTargetBox(target):
- minRect = cv2.minAreaRect(target)
- Box = cv2.cv.BoxPoints(minRect)
- #Box = np.int0(Box) # convert points to ints
- return Box
- def validate_contour(contour, img, aspect_ratio_range, area_range):
- rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contour)
- img_width = img.shape[1]
- img_height = img.shape[0]
- Box = cv2.BoxPoints(rect)
- Box = np.int0(Box)
- X = rect[0][0]
- Y = rect[0][1]
- angle = rect[2]
- width = rect[1][0]
- height = rect[1][1]
- angle = (angle + 180) if width < height else (angle + 90)
- output=False
- if (width > 0 and height > 0) and ((width < img_width/2.0) and (height < img_width/2.0)):
- aspect_ratio = float(width)/height if width > height else float(height)/width
- if (aspect_ratio >= aspect_ratio_range[0] and aspect_ratio <= aspect_ratio_range[1]):
- if((height*width > area_range[0]) and (height*width < area_range[1])):
- Box_copy = list(Box)
- point = Box_copy[0]
- del(Box_copy[0])
- dists = [((p[0]-point[0])**2 + (p[1]-point[1])**2) for p in Box_copy]
- sorted_dists = sorted(dists)
- opposite_point = Box_copy[dists.index(sorted_dists[1])]
- tmp_angle = 90
- if abs(point[0]-opposite_point[0]) > 0:
- tmp_angle = abs(float(point[1]-opposite_point[1]))/abs(point[0]-opposite_point[0])
- tmp_angle = rad_to_deg(math.atan(tmp_angle))
- if tmp_angle <= 45:
- output = True
- return output
- def bBoxes_to_xys(bBoxes, image_shape):
- """Convert Seglink bBoxes to xys,i.e.,eight points
- The `image_shape` is used to to make sure all points return are valid,within image area
- """
- if len(bBoxes) == 0:
- return []
- assert np.ndim(bBoxes) == 2 and np.shape(bBoxes)[-1] == 5, ''invalid `bBoxes` param with shape = '' + str(np.shape(bBoxes))
- h, w = image_shape[0:2]
- def get_valid_x(x):
- if x < 0:
- return 0
- if x >= w:
- return w - 1
- return x
- def get_valid_y(y):
- if y < 0:
- return 0
- if y >= h:
- return h - 1
- return y
- xys = np.zeros((len(bBoxes), 8))
- for bBox_idx, bBox in enumerate(bBoxes):
- bBox = ((bBox[0], bBox[1]), (bBox[2], bBox[3]), bBox[4])
- points = cv2.cv.BoxPoints(bBox)
- points = np.int0(points)
- for i_xy, y) in enumerate(points):
- x = get_valid_x(x)
- y = get_valid_y(y)
- points[i_xy, :] = [x, y]
- points = np.reshape(points, -1)
- xys[bBox_idx, :] = points
- return xys
- def __init__(self, fname=None, include_orth=True, include_pols=True):
- if fname is None:
- # fname is the name of the file to read in the design matrix
- self.design = np.zeros([0, 0])
- self.n_col = 0
- # number of columns (conditions) in the design matrix
- self.column_types = np.ones(0)
- self.n_basis = 0
- self.n_stim = 0
- self.n_orth = 0
- self.StimLabels = []
- else:
- # isAFNI = re.match(r''.+[.](1D|1d|txt)$'',fname)
- filename, ext = os.path.splitext(fname)
- # We assume all AFNI 1D files have extension of 1D or 1d or txt
- if ext in [''.1D'', ''.1d'', ''.txt'']:
- self.read_afni(fname=fname)
- self.include_orth = include_orth
- self.include_pols = include_pols
- # The two flags above dictates whether columns corresponding to
- # baseline drift modeled by polynomial functions of time and
- # columns corresponding to other orthogonal signals (usually motion)
- # are included in nuisance regressors.
- self.cols_task = np.where(self.column_types == 1)[0]
- self.design_task = self.design[:, self.cols_task]
- if np.ndim(self.design_task) == 1:
- self.design_task = self.design_task[:, None]
- # part of the design matrix related to task conditions.
- self.n_TR = np.size(self.design_task, axis=0)
- self.cols_nuisance = np.array([])
- if self.include_orth:
- self.cols_nuisance = np.int0(
- np.sort(np.append(self.cols_nuisance,
- np.where(self.column_types == 0)[0])))
- if self.include_pols:
- self.cols_nuisance = np.int0(
- np.sort(np.append(self.cols_nuisance,
- np.where(self.column_types == -1)[0])))
- if np.size(self.cols_nuisance) > 0:
- self.reg_nuisance = self.design[:, self.cols_nuisance]
- if np.ndim(self.reg_nuisance) == 1:
- self.reg_nuisance = self.reg_nuisance[:, None]
- else:
- self.reg_nuisance = None
- # Nuisance regressors for motion,baseline,etc.
- def _find_array_button_thing(self):
- """ Find the array button on the solar array Box """
- """ This uses color to determine if we have a choke """
- lower = np.array([0, 60], dtype = "uint8")
- upper = np.array([20, 20, 255], dtype = "uint8")
- mask = cv2.inRange(self.img, lower, upper)
- blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(mask, (5, 5), 0)
- thresh = cv2.threshold(blurred, 60, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
- contours = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
- contours = contours[0] if is_cv2() else contours[1]
- debug_img = None
- if self.debug:
- debug_img = self.img.copy()
- button_Box = None
- for c in contours:
- Box = cv2.boundingRect(c)
- if button_Box is None:
- button_Box = Box
- else:
- button_Box = self._union_Box(deepcopy(button_Box), Box)
- if button_Box is None:
- return
- top,bottom,left,right,center = self.find_dimensions(np.int0(np.array(self._bound_to_Boxpoints(button_Box))))
- if top is None or left is None or center is None:
- return None
- height = self.find_distance(top, bottom)
- width = self.find_distance(left, right)
- if self.debug:
- for c in contours:
- cv2.drawContours(debug_img, [c], -1, 0), 2)
- cv2.circle(debug_img, top, 5, (255, 0))
- cv2.circle(debug_img, bottom, left, right, 0))
- cv2.rectangle(debug_img, (button_Box[0], button_Box[1]),
- (button_Box[0] + button_Box[2], button_Box[1] + button_Box[3]), (128, 128), 2)
- #cv2.circle(debug_img,center,5,0))
- cv2.imshow("button picture", debug_img)
- cv2.setMouseCallback("button picture", self.handle_mouse)
- cv2.waitKey(0)
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()
- self.array_button = Thing(height, width, center, None)
- self.array_button.set_array_button()
- self.array_button.computed_center = self.compute_center(left, bottom)
- self.things.append(self.array_button)
- def _find_a_thing(self, c, min_height, max_height, min_width, max_width, max_distance, debug_img=None):
- rect = cv2.minAreaRect(c)
- Box = cv2.cv.BoxPoints(rect) if is_cv2() else cv2.BoxPoints(rect)
- top,center = self.find_dimensions(np.int0(np.array(Box)))
- if top is None or left is None or center is None:
- return None
- vertical = self.find_distance(top, bottom)
- horizontal = self.find_distance(left, right)
- away = self.find_distance(center, None)
- if vertical > horizontal:
- height = vertical
- width = horizontal
- flipped = False
- else:
- height = horizontal
- width = vertical
- flipped = True
- if height < min_height or height > max_height:
- return None
- if width < min_width or width > max_height:
- return None
- if away > max_distance:
- return None
- # This page was helpful in understanding angle
- # https://namkeenman.wordpress.com/2015/12/18/open-cv-determine-angle-of-rotatedrect-minarearect/
- angle = rect[2]
- if rect[1][0] < rect[1][1]:
- angle -= 90.0
- if debug_img is not None:
- x,h = cv2.boundingRect(c)
- cv2.drawContours(debug_img, 2)
- cv2.drawContours(debug_img, [np.int0(np.array(Box))], 255), 2)
- cv2.rectangle(debug_img,(x,(x+w,(255,2)
- cv2.circle(debug_img, 0))
- return Thing(height, angle)
- def get_contours(orig_image):
- """
- Get edge points (hopefully corners) from the given opencv image (called
- contours in opencv)
- Parameters:
- :param: `orig_image` - the thresholded image from which to find contours
- """
- new_image = numpy.copy(orig_image)
- # cv2.imshow("Vision",new_image)
- # cv2.waitKey(1000)
- new_image, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(new_image,
- cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL,
- cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
- # print(len(contours))
- # print(len(contours[0]))
- # print(len(contours[0][0]))
- # print(len(contours[0][0][0]))
- largest_contour = 0
- most_matching = 0
- min_score = 0
- max_area = 0
- if len(contours) > 1:
- print("Length of contours:", len(contours))
- max_area = cv2.contourArea(contours[0])
- min_score = average_goal_matching(contours[0])
- for i in range(1, len(contours)):
- # print(contours[i])
- current_score = average_goal_matching(contours[i])
- current_area = cv2.contourArea(contours[i])
- if current_area > max_area:
- max_area = current_area
- largest_contour = i
- if current_score < min_score and current_score != 0 and current_area > 300 and current_area < 1500:
- min_score = current_score
- most_matching = i
- elif len(contours) == 0:
- raise GoalNotFoundException("Goal not found!")
- if min_score >= 9999999999999999:
- raise GoalNotFoundException("Goal not found!")
- print("largest_contour:", largest_contour)
- print("Area:", max_area)
- # print("largest_contour:",largest_contour)
- print("Most matching:", most_matching)
- print("score:", min_score)
- print("Area of most matching:", cv2.contourArea(contours[most_matching]))
- rect = cv2.minAreaRect(contours[most_matching])
- Box = cv2.BoxPoints(rect)
- Box = numpy.int0(Box)
- # print(Box)
- return numpy.array(contours[most_matching]), Box
- def detectAllVertices(self, testImg):
- # Detecting vertices on the newly constructed board
- self.gray = cv2.cvtColor(testImg, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
- tempVertices = cv2.goodFeaturesToTrack(self.gray, int(self.FINAL_VERTICES_COUNT), 0.01, 10)
- tempVertices = np.int0(tempVertices)
- newVertices = []
- for i in tempVertices:
- x, y = i.ravel()
- newVertices.append((x, y))
- # Matrix to store coordinates of vertices on the board
- self.ALL_VERTICES = [[(0, 0) for x in range(self.FACTOR + 2)] for x in range(self.FACTOR + 2)]
- # Filling the matrix
- self.ALL_VERTICES[0][0] = (self.CORNERS[1])
- for i in range(0, self.FACTOR):
- for j in range(0, self.FACTOR):
- predicted_x = self.ALL_VERTICES[i][j][0] + int(
- (self.OUTER_VERTICES[2][self.FACTOR - i][0] - self.OUTER_VERTICES[0][i][0]) / 8)
- predicted_y = self.ALL_VERTICES[i][j][1] + int(
- (self.OUTER_VERTICES[3][self.FACTOR - i][1] - self.OUTER_VERTICES[1][i][1]) / 8)
- minn_dist = self.INT_MAX
- for point in newVertices:
- this_dist = Geometry.getPointsdistance(point, (predicted_x, self.ALL_VERTICES[i][j][1]))
- if this_dist < minn_dist:
- self.ALL_VERTICES[i][j + 1] = point
- minn_dist = this_dist
- minn_dist = self.INT_MAX
- for point in newVertices:
- this_dist = Geometry.getPointsdistance(point, (self.ALL_VERTICES[i][j][0], predicted_y))
- if this_dist < minn_dist:
- self.ALL_VERTICES[i + 1][j] = point;
- minn_dist = this_dist
- self.ALL_VERTICES[self.FACTOR][self.FACTOR] = (self.CORNERS[3])
- def image_callback(self, msg):
- # convert ROS image to OpenCV image
- try:
- image = self.bridge.imgmsg_to_cv2(msg, desired_encoding=''bgr8'')
- except CvBridgeError as e:
- print(e)
- # create hsv image of scene
- hsv = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
- # find pink objects in the image
- lower_pink = numpy.array([139, 240], numpy.uint8)
- upper_pink = numpy.array([159, 121, numpy.uint8)
- mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, lower_pink, upper_pink)
- # dilate and erode with kernel size 11x11
- cv2.morphologyEx(mask, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, numpy.ones((11,11)))
- # find all of the contours in the mask image
- contours, heirarchy = cv2.findContours(mask, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
- self.contourLength = len(contours)
- # Check for at least one target found
- if self.contourLength < 1:
- print "No target found"
- else: # target found
- ## Loop through all of the contours,and get their areas
- area = [0.0]*len(contours)
- for i in range(self.contourLength):
- area[i] = cv2.contourArea(contours[i])
- #### Target #### the largest "pink" object
- target_image = contours[area.index(max(area))]
- # Using moments find the center of the object and draw a red outline around the object
- target_m = cv2.moments(target_image)
- self.target_u = int(target_m[''m10'']/target_m[''m00''])
- self.target_v = int(target_m[''m01'']/target_m[''m00''])
- points = cv2.minAreaRect(target_image)
- Box = cv2.cv.BoxPoints(points)
- Box = numpy.int0(Box)
- cv2.drawContours(image, 2)
- rospy.loginfo("Center of target is x at %d and y at %d", int(self.target_u), int(self.target_v))
- self.target_found = True # set flag for depth_callback processing
- # show image with target outlined with a red rectangle
- cv2.imshow ("Target", image)
- cv2.waitKey(3)
- # This callback function handles processing Kinect depth image,looking for the depth value
- # at the location of the center of the pink target.
- def binary_mask(rast, mask, nodata=-9999, invert=False):
- ''''''
- Applies an arbitrary,binary mask (data in [0,1]) where pixels with
- a value of 1 are pixels to be masked out. Arguments:
- rast A gdal.Dataset or a NumPy array
- mask A gdal.Dataset or a NumPy array
- nodata The NoData value; defaults to -9999.
- invert Invert the mask? (tranpose meaning of 0 and 1); defaults to False.
- ''''''
- # Can accept either a gdal.Dataset or numpy.array instance
- if not isinstance(rast, np.ndarray):
- rastr = rast.ReadAsArray()
- else:
- rastr = rast.copy()
- if not isinstance(mask, np.ndarray):
- maskr = mask.ReadAsArray()
- else:
- maskr = mask.copy()
- if not np.alltrue(np.equal(rastr.shape[-2:], maskr.shape[-2:])):
- raise ValueError(''Raster and mask do not have the same shape'')
- # Convert Boolean arrays to ones and zeros
- if maskr.dtype == bool:
- maskr = maskr.astype(np.int0)
- # Transform into a "1-band" array and apply the mask
- if maskr.shape != rastr.shape:
- maskr = maskr.reshape((1, maskr.shape[-2], maskr.shape[-1]))\\
- .repeat(rastr.shape[0], axis=0) # copy the mask across the "bands"
- # Todo Compare to place(),e.g.,
- # np.place(rastr,mask.repeat(rastr.shape[0],axis=0),(nodata,))
- # Mask out areas that match the mask (==1)
- if invert:
- rastr[maskr < 1] = nodata
- else:
- rastr[maskr > 0] = nodata
- return rastr
- def filterContoursFancy(contours, image=None):
- if len(contours) == 0:
- return []
- numContours = len(contours)
- areas = np.array([cv2.contourArea(contour) for contour in contours])
- boundingRects = [cv2.boundingRect(contour) for contour in contours]
- widths, heights, positions = boundingInfo(boundingRects)
- rotatedRects = [cv2.minAreaRect(contour) for contour in contours]
- if config.withOpenCV3:
- rotatedBoxes = [np.int0(cv2.BoxPoints(rect)) for rect in rotatedRects]
- else:
- rotatedBoxes = [np.int0(cv2.cv.BoxPoints(rect)) for rect in rotatedRects]
- rotatedAreas = [cv2.contourArea(Box) for Box in rotatedBoxes]
- sizescores = [size(area)for area in areas]
- ratioscores = ratios(widths, heights)
- rotationscores = [rotation(rect) for rect in rotatedRects]
- rectangularscores = [distTopolygon(contour, poly) for contour,poly in zip(contours, rotatedBoxes)]
- areascores = polygonAreaDiff(areas, rotatedAreas)
- quadscores = [Quadrify(contour) for contour in contours]
- rectangularscores = np.divide(rectangularscores, widths)
- scores = np.array([sizescores, ratioscores, rotationscores, rectangularscores, areascores, quadscores])
- contourscores = np.dot(weights, scores)
- correctInds, incorrectInds = sortedinds(contourscores)
- correctContours = np.array(contours)[correctInds]
- if config.extra_debug:
- print "size,ratio,rotation,rectangular,area,quad"
- print "Weights:", weights
- print "scores: ", contourscores
- print np.average(scores, axis=1)
- if len(incorrectInds) != 0:
- print "AVG,WORST", test(scores, correctInds, incorrectInds)
- for i in range(numContours):
- print "CONTOUR " + str(i)
- print np.multiply(scores[:, i], weights) #newWeights
- print contourscores[i]
- if image:
- img = copy.deepcopy(image)
- Printing.drawImage(img, contours[:i] + contours[i+1:], contours[i], False)
- Printing.display(img, "contour " + str(i), doResize=True)
- cv2.waitKey(0)
- cv2.destroyAllWindows()
- return correctContours
- def filterContoursAutocalibrate(contours, incorrectInds = sortedinds(contourscores)
- correctContours = np.array(contours)[correctInds]
- averagescore = 0
- for i in range(numContours):
- averagescore += sizescores[i]
- averagescore += ratioscores[i]
- averagescore += rotationscores[i]
- averagescore += rectangularscores[i]
- averagescore += areascores[i]
- averagescore += quadscores[i]
- averagescore /= numContours
- return averagescore
- def image_callback(self,looking for the depth value
- # at the location of the center of the pink target.
- def detect_barcode(imageval):
- # load the image and convert it to grayscale
- file_bytes = np.asarray(bytearray(imageval), dtype=np.uint8)
- img_data_ndarray = cv2.imdecode(file_bytes, cv2.CV_LOAD_IMAGE_UNCHANGED)
- gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_data_ndarray, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
- # compute the Scharr gradient magnitude representation of the images
- # in both the x and y direction
- gradX = cv2.Sobel(gray, ddepth = cv2.cv.CV_32F, dx = 1, dy = 0, ksize = -1)
- gradY = cv2.Sobel(gray, dx = 0, dy = 1, ksize = -1)
- # subtract the y-gradient from the x-gradient
- gradient = cv2.subtract(gradX, gradY)
- gradient = cv2.convertScaleAbs(gradient)
- # blur and threshold the image
- blurred = cv2.blur(gradient, (9, 9))
- (_, thresh) = cv2.threshold(blurred, 225, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
- # construct a closing kernel and apply it to the thresholded image
- kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (21, 7))
- closed = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, kernel)
- # perform a series of erosions and dilations
- closed = cv2.erode(closed, None, iterations = 4)
- closed = cv2.dilate(closed, iterations = 4)
- # find the contours in the thresholded image,then sort the contours
- # by their area,keeping only the largest one
- (cnts, _) = cv2.findContours(closed.copy(),
- cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
- c = sorted(cnts, key = cv2.contourArea, reverse = True)[0]
- # compute the rotated bounding Box of the largest contour
- rect = cv2.minAreaRect(c)
- Box = np.int0(cv2.cv.BoxPoints(rect))
- # draw a bounding Box arounded the detected barcode and display the
- # image
- cv2.drawContours(img_data_ndarray, 3)
- # cv2.imshow("Image",image)
- #cv2.imwrite("uploads/output-"+ datetime.datetime.Now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H:%M:%s") +".jpg",image)
- # cv2.waitKey(0)
- #outputfile = "uploads/output-" + time.strftime("%H:%M:%s") + ".jpg"
- outputfile = "uploads/output.jpg"
- cv2.imwrite(outputfile,img_data_ndarray)

Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
如何解决Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable?
晚安, 尝试打印以下内容时,我在 jupyter 中遇到了 numpy 问题,并且得到了一个 错误: 需要注意的是python版本是3.8.8。 我先用 spyder 测试它,它运行正确,它给了我预期的结果
使用 Spyder:
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
Results
0.6604903457995978
0.8236300859753154
0.16067650689842816
0.6967868357083673
0.4231597934445466
现在有了 jupyter
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
-------------------------------------------------- ------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-78-0c6a801b3ea9> in <module>
2 for i in range (5):
3 n = np.random.rand ()
----> 4 print (n)
TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable
感谢您对我如何在 Jupyter 中解决此问题的帮助。
非常感谢您抽出宝贵时间。
阿特,约翰”
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)

numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
今天看到这样一句代码:
xb = np.random.random((nb, d)).astype(''float32'') #创建一个二维随机数矩阵(nb行d列)
xb[:, 0] += np.arange(nb) / 1000. #将矩阵第一列的每个数加上一个值要理解这两句代码需要理解三个函数
1、生成随机数
numpy.random.random(size=None)
size为None时,返回float。
size不为None时,返回numpy.ndarray。例如numpy.random.random((1,2)),返回1行2列的numpy数组
2、对numpy数组中每一个元素进行类型转换
numpy.ndarray.astype(dtype)
返回numpy.ndarray。例如 numpy.array([1, 2, 2.5]).astype(int),返回numpy数组 [1, 2, 2]
3、获取等差数列
numpy.arange([start,]stop,[step,]dtype=None)
功能类似python中自带的range()和numpy中的numpy.linspace
返回numpy数组。例如numpy.arange(3),返回numpy数组[0, 1, 2]

numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()
numpy.ravel(a, order=''C'')
Return a flattened array
numpy.chararray.flatten(order=''C'')
Return a copy of the array collapsed into one dimension
numpy.squeeze(a, axis=None)
Remove single-dimensional entries from the shape of an array.
相同点: 将多维数组 降为 一维数组
不同点:
ravel() 返回的是视图(view),意味着改变元素的值会影响原始数组元素的值;
flatten() 返回的是拷贝,意味着改变元素的值不会影响原始数组;
squeeze()返回的是视图(view),仅仅是将shape中dimension为1的维度去掉;
ravel()示例:
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.ravel()
16 print("a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19
20 print(a)
21 log_type(''a'',a)
flatten()示例
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.flatten()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)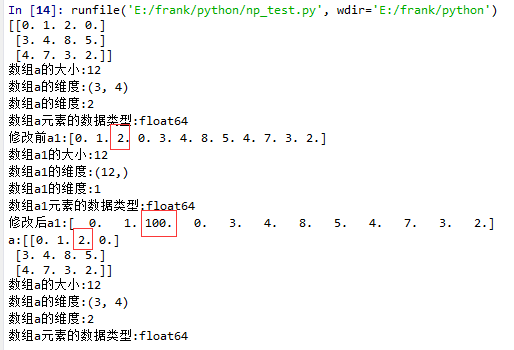
squeeze()示例:
1. 没有single-dimensional entries的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)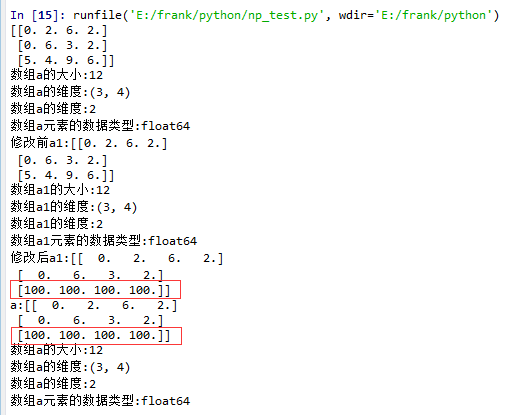
从结果中可以看到,当没有single-dimensional entries时,squeeze()返回额数组对象是一个view,而不是copy。
2. 有single-dimentional entries 的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((1,3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)

Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性
一、Numpy数组创建
part 1:np.linspace(起始值,终止值,元素总个数
import numpy as np
''''''
numpy中的ndarray数组
''''''
ary = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(ary)
ary = ary * 10
print(ary)
''''''
ndarray对象的创建
''''''
# 创建二维数组
# np.array([[],[],...])
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]])
print(a)
# np.arange(起始值, 结束值, 步长(默认1))
b = np.arange(1, 10, 1)
print(b)
print("-------------np.zeros(数组元素个数, dtype=''数组元素类型'')-----")
# 创建一维数组:
c = np.zeros(10)
print(c, ''; c.dtype:'', c.dtype)
# 创建二维数组:
print(np.zeros ((3,4)))
print("----------np.ones(数组元素个数, dtype=''数组元素类型'')--------")
# 创建一维数组:
d = np.ones(10, dtype=''int64'')
print(d, ''; d.dtype:'', d.dtype)
# 创建三维数组:
print(np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int32 ))
# 打印维度
print(np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int32 ).ndim) # 返回:3(维)
结果图:

part 2 :np.linspace ( 起始值,终止值,元素总个数)
import numpy as np
a = np.arange( 10, 30, 5 )
b = np.arange( 0, 2, 0.3 )
c = np.arange(12).reshape(4,3)
d = np.random.random((2,3)) # 取-1到1之间的随机数,要求设置为诶2行3列的结构
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
print(d)
print("-----------------")
from numpy import pi
print(np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 100 ))
print("-------------np.linspace(起始值,终止值,元素总个数)------------------")
print(np.sin(np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 100 )))
结果图:

二、Numpy的ndarray对象属性:
数组的结构:array.shape
数组的维度:array.ndim
元素的类型:array.dtype
数组元素的个数:array.size
数组的索引(下标):array[0]
''''''
数组的基本属性
''''''
import numpy as np
print("--------------------案例1:------------------------------")
a = np.arange(15).reshape(3, 5)
print(a)
print(a.shape) # 打印数组结构
print(len(a)) # 打印有多少行
print(a.ndim) # 打印维度
print(a.dtype) # 打印a数组内的元素的数据类型
# print(a.dtype.name)
print(a.size) # 打印数组的总元素个数
print("-------------------案例2:---------------------------")
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(a)
# 测试数组的基本属性
print(''a.shape:'', a.shape)
print(''a.size:'', a.size)
print(''len(a):'', len(a))
# a.shape = (6, ) # 此格式可将原数组结构变成1行6列的数据结构
# print(a, ''a.shape:'', a.shape)
# 数组元素的索引
ary = np.arange(1, 28)
ary.shape = (3, 3, 3) # 创建三维数组
print("ary.shape:",ary.shape,"\n",ary )
print("-----------------")
print(''ary[0]:'', ary[0])
print(''ary[0][0]:'', ary[0][0])
print(''ary[0][0][0]:'', ary[0][0][0])
print(''ary[0,0,0]:'', ary[0, 0, 0])
print("-----------------")
# 遍历三维数组:遍历出数组里的每个元素
for i in range(ary.shape[0]):
for j in range(ary.shape[1]):
for k in range(ary.shape[2]):
print(ary[i, j, k], end='' '')
结果图:

关于Python numpy 模块-int0() 实例源码和python中numpy模块的问题就给大家分享到这里,感谢你花时间阅读本站内容,更多关于Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()、Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性等相关知识的信息别忘了在本站进行查找喔。
本文标签:





