在这篇文章中,我们将为您详细介绍Pythonnumpy模块-intc()实例源码的内容,并且讨论关于pythonnumpyinterp的相关问题。此外,我们还会涉及一些关于Jupyter中的Numpy
在这篇文章中,我们将为您详细介绍Python numpy 模块-intc() 实例源码的内容,并且讨论关于python numpy interp的相关问题。此外,我们还会涉及一些关于Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()、Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性的知识,以帮助您更全面地了解这个主题。
本文目录一览:- Python numpy 模块-intc() 实例源码(python numpy interp)
- Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
- numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
- numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()
- Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性

Python numpy 模块-intc() 实例源码(python numpy interp)
Python numpy 模块,intc() 实例源码
我们从Python开源项目中,提取了以下50个代码示例,用于说明如何使用numpy.intc()。
- def _validate_X_predict(
- self, X: np.ndarray, check_input: bool) -> np.ndarray:
- if check_input:
- X = check_array(X, dtype=DTYPE, accept_sparse="csr")
- if issparse(X) and (X.indices.dtype != np.intc or
- X.indptr.dtype != np.intc):
- raise ValueError(
- "No support for np.int64 index based sparse matrices")
- n_features = X.shape[1]
- if self.n_features_ != n_features:
- raise ValueError(
- "Number of features of the model must match the input."
- " Model n_features is %s and input n_features is %s "
- % (self.n_features_, n_features))
- return X
- def default(self, obj):
- # convert dates and numpy objects in a json serializable format
- if isinstance(obj, datetime):
- return obj.strftime(''%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%sZ'')
- elif isinstance(obj, date):
- return obj.strftime(''%Y-%m-%d'')
- elif type(obj) in (np.int_, np.intc, np.intp, np.int8, np.int16,
- np.int32, np.int64, np.uint8, np.uint16,
- np.uint32, np.uint64):
- return int(obj)
- elif type(obj) in (np.bool_,):
- return bool(obj)
- elif type(obj) in (np.float_, np.float16, np.float32, np.float64,
- np.complex_, np.complex64, np.complex128):
- return float(obj)
- # Let the base class default method raise the TypeError
- return json.JSONEncoder.default(self, obj)
- def _validate_X_predict(self, X, check_input):
- """Validate X whenever one tries to predict,apply,predict_proba"""
- if self.tree_ is None:
- raise NotFittedError("Estimator not fitted,"
- "call `fit` before exploiting the model.")
- if check_input:
- X = check_array(X, accept_sparse="csr")
- if issparse(X) and (X.indices.dtype != np.intc or
- X.indptr.dtype != np.intc):
- raise ValueError("No support for np.int64 index based "
- "sparse matrices")
- n_features = X.shape[1]
- if self.n_features_ != n_features:
- raise ValueError("Number of features of the model must "
- "match the input. Model n_features is %s and "
- "input n_features is %s "
- % (self.n_features_, n_features))
- return X
- def pairFeatureMatrix(self, elementList):
- """ Construction of pair-distance matrices """
- # Initiate
- nSpecies = len(elementList)
- # Get the molecular structure
- pos = np.array(self.molecule.positions, dtype = float) # Atomic positions
- elInd = np.array(self.molecule.elInd, dtype = np.intc) # Element indices matching to elementList
- natoms = len(self.molecule.names) # Total number of atoms in the molecule
- # Initiate the matrix
- dim1 = natoms * (natoms -1)/2 # First dimension (pairwise distances)
- dim2 = nSpecies * (nSpecies + 1)/2 # Number of possible pairs
- featMat = np.zeros((dim1,dim2)) # To be passed to fun_pairFeatures (compiled C code)
- # Call the C function to store the pairFeatures
- pairFeatures.fun_pairFeatures(nSpecies, natoms, elInd, pos, featMat)
- # Return featMat
- return featMat
- def execute(self, actions):
- """
- Pass action to universe environment,return reward,next step,terminal state and
- additional info.
- :param action: action to execute as numpy array,should have dtype np.intc and should adhere to
- the specification given in DeepMindLabEnvironment.action_spec(level_id)
- :return: dict containing the next state,the reward,and a boolean indicating if the
- next state is a terminal state
- """
- adjusted_actions = list()
- for action_spec in self.level.action_spec():
- if action_spec[''min''] == -1 and action_spec[''max''] == 1:
- adjusted_actions.append(actions[action_spec[''name'']] - 1)
- else:
- adjusted_actions.append(actions[action_spec[''name'']]) # clip?
- actions = np.array(adjusted_actions, dtype=np.intc)
- reward = self.level.step(action=actions, num_steps=self.repeat_action)
- state = self.level.observations()[''RGB_INTERLACED'']
- terminal = not self.level.is_running()
- return state, terminal, reward
- def default(self, date):
- return obj.strftime(''%Y-%m-%d'')
- elif type(obj) in [np.int_, np.uint64]:
- return int(obj)
- elif type(obj) in [np.bool_]:
- return bool(obj)
- elif type(obj) in [np.float_, np.complex128]:
- return float(obj)
- # Let the base class default method raise the TypeError
- return json.JSONEncoder.default(self, obj)
- def predict(self, queries, n_jobs=1):
- ''''''
- Predict the ranking score for each individual document of the given queries.
- n_jobs: int,optional (default is 1)
- The number of working threads that will be spawned to compute
- the ranking scores. If -1,the current number of cpus will be used.
- ''''''
- if self.trained is False:
- raise ValueError(''the model has not been trained yet'')
- predictions = np.zeros(queries.document_count(), dtype=np.float64)
- n_jobs = max(1, min(n_jobs if n_jobs >= 0 else n_jobs + cpu_count() + 1, queries.document_count()))
- indices = np.linspace(0, queries.document_count(), n_jobs + 1).astype(np.intc)
- Parallel(n_jobs=n_jobs, backend="threading")(delayed(parallel_helper, check_pickle=False)
- (LambdarandomForest, ''_LambdarandomForest__predict'', self.estimators,
- queries.feature_vectors[indices[i]:indices[i + 1]],
- predictions[indices[i]:indices[i + 1]]) for i in range(indices.size - 1))
- predictions /= len(self.estimators)
- return predictions
- def perform(self, node, inputs, out):
- # Todo support broadcast!
- # Todo assert all input have the same shape
- z, = out
- if (z[0] is None or
- z[0].shape != inputs[0].shape or
- not z[0].is_c_contiguous()):
- z[0] = theano.sandBox.cuda.Cudandarray.zeros(inputs[0].shape)
- if inputs[0].shape != inputs[1].shape:
- raise TypeError("PycudaElemwiseSourceModuleOp:"
- " inputs don''t have the same shape!")
- if inputs[0].size > 512:
- grid = (int(numpy.ceil(inputs[0].size / 512.)), 1)
- block = (512, 1, 1)
- else:
- grid = (1, 1)
- block = (inputs[0].shape[0], inputs[0].shape[1], 1)
- self.pycuda_fct(inputs[0], inputs[1], z[0],
- numpy.intc(inputs[1].size), block=block, grid=grid)
- def make_thunk(self, storage_map, _, _2):
- mod = SourceModule("""
- __global__ void my_fct(float * i0,float * o0,int size) {
- int i = blockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
- if(i<size){
- o0[i] = i0[i]*2;
- }
- }""")
- pycuda_fct = mod.get_function("my_fct")
- inputs = [ storage_map[v] for v in node.inputs]
- outputs = [ storage_map[v] for v in node.outputs]
- def thunk():
- z = outputs[0]
- if z[0] is None or z[0].shape!=inputs[0][0].shape:
- z[0] = cuda.Cudandarray.zeros(inputs[0][0].shape)
- grid = (int(numpy.ceil(inputs[0][0].size / 512.)),1)
- pycuda_fct(inputs[0][0], numpy.intc(inputs[0][0].size),
- block=(512,1,1), grid=grid)
- return thunk
- def npy2py_type(npy_type):
- int_types = [
- np.int_, np.int32,
- np.uint8, np.uint32, np.uint64
- ]
- float_types = [np.float_, np.float64]
- bytes_types = [np.str_, np.string_]
- if npy_type in int_types:
- return int
- if npy_type in float_types:
- return float
- if npy_type in bytes_types:
- return bytes
- if hasattr(npy_type, ''char''):
- if npy_type.char in [''S'', ''a'']:
- return bytes
- raise TypeError
- return npy_type
- def _validate_X_predict(self, n_features))
- return X
- def _open_and_load(f, dtype, multilabel, zero_based, query_id):
- if hasattr(f, "read"):
- actual_dtype, data, ind, indptr, labels, query = \\
- _load_svmlight_file(f, query_id)
- # XXX remove closing when Python 2.7+/3.1+ required
- else:
- with closing(_gen_open(f)) as f:
- actual_dtype, query = \\
- _load_svmlight_file(f, query_id)
- # convert from array.array,give data the right dtype
- if not multilabel:
- labels = frombuffer_empty(labels, np.float64)
- data = frombuffer_empty(data, actual_dtype)
- indices = frombuffer_empty(ind, np.intc)
- indptr = np.frombuffer(indptr, dtype=np.intc) # never empty
- query = frombuffer_empty(query, np.intc)
- data = np.asarray(data, dtype=dtype) # no-op for float{32,64}
- return data, indices, query
- def to_dense(A):
- """
- Convert a sparse matrix A to dense.
- For debugging only.
- """
- if hasattr(A, "getrow"):
- n = A.size(0)
- m = A.size(1)
- B = np.zeros( (n,m), dtype=np.float64)
- for i in range(0,n):
- [j, val] = A.getrow(i)
- B[i,j] = val
- return B
- else:
- x = Vector()
- Ax = Vector()
- A.init_vector(x,1)
- A.init_vector(Ax,0)
- n = get_local_size(Ax)
- m = get_local_size(x)
- B = np.zeros( (n, dtype=np.float64)
- for i in range(0,m):
- i_ind = np.array([i], dtype=np.intc)
- x.set_local(np.ones(i_ind.shape), i_ind)
- A.mult(x,Ax)
- B[:,i] = Ax.get_local()
- x.set_local(np.zeros(i_ind.shape), i_ind)
- return B
- def _create_lookups(self, X):
- """
- Create document and term lookups for all tokens.
- """
- docs, terms = np.nonzero(X)
- if issparse(X):
- x = np.array(X[docs, terms])[0]
- else:
- x = X[docs, terms]
- doc_lookup = np.ascontiguousarray(np.repeat(docs, x), dtype=np.intc)
- term_lookup = np.ascontiguousarray(np.repeat(terms, dtype=np.intc)
- return doc_lookup, term_lookup
- def _create_edges(self, y, order=''tail''):
- y.sort(order=order)
- _docs, _counts = np.unique(y[order], return_counts=True)
- counts = np.zeros(self.n_docs)
- counts[_docs] = _counts
- docs = np.ascontiguousarray(
- np.concatenate(([0], np.cumsum(counts))), dtype=np.intc)
- edges = np.ascontiguousarray(y[''index''].flatten(), dtype=np.intc)
- return docs, edges
- def fit(self, y):
- """
- Estimate the topic distributions per document (theta),term
- distributions per topic (phi),and regression coefficients (eta).
- Parameters
- ----------
- X : array-like,shape = (n_docs,n_terms)
- The document-term matrix.
- y : array-like,shape = (n_edges,3)
- Each entry of y is an ordered triple (d_1,d_2,y_(d_1,d_2)),
- where d_1 and d_2 are documents and y_(d_1,d_2) is an indicator of
- a directed edge from d_1 to d_2.
- """
- self.doc_term_matrix = X
- self.n_docs, self.n_terms = X.shape
- self.n_tokens = X.sum()
- self.n_edges = y.shape[0]
- doc_lookup, term_lookup = self._create_lookups(X)
- # edge info
- y = np.ascontiguousarray(np.column_stack((range(self.n_edges), y)))
- # we use a view here so that we can sort in-place using named columns
- y_rec = y.view(dtype=list(zip((''index'', ''tail'', ''head'', ''data''),
- 4 * [y.dtype])))
- edge_tail = np.ascontiguousarray(y_rec[''tail''].flatten(),
- dtype=np.intc)
- edge_head = np.ascontiguousarray(y_rec[''head''].flatten(),
- dtype=np.intc)
- edge_data = np.ascontiguousarray(y_rec[''data''].flatten(),
- dtype=np.float64)
- out_docs, out_edges = self._create_edges(y_rec, order=''tail'')
- in_docs, in_edges = self._create_edges(y_rec, order=''head'')
- # iterate
- self.theta, self.phi, self.H, self.loglikelihoods = gibbs_sampler_grtm(
- self.n_iter, self.n_report_iter, self.n_topics, self.n_docs,
- self.n_terms, self.n_tokens, self.n_edges, self.alpha, self.beta,
- self.mu, self.nu2, self.b, doc_lookup, term_lookup, out_docs,
- out_edges, in_docs, in_edges, edge_tail, edge_head, edge_data,
- self.seed)
- def fit(self, hier):
- """
- Estimate the topic distributions per document (theta),n_labels)
- Response values for each document for each labels.
- hier : 1D array-like,size = n_labels
- The index of the list corresponds to the current label
- and the value of the indexed position is the parent of the label.
- Set -1 as the root.
- """
- self.doc_term_matrix = X
- self.n_docs, self.n_terms = X.shape
- self.n_tokens = X.sum()
- doc_lookup, term_lookup = self._create_lookups(X)
- # iterate
- self.theta, self.eta, self.loglikelihoods = gibbs_sampler_blhslda(
- self.n_iter,
- self.n_topics, self.n_terms,
- self.alpha, self.mu,
- term_lookup, np.ascontiguousarray(y, dtype=np.intc),
- np.ascontiguousarray(hier, self.seed)
- def _create_lookups(self, term_lookup
- def fit(self,
- self.seed)
- def fit(self, self.seed)
- def test_dtype(self):
- dt = np.intc
- p = ndpointer(dtype=dt)
- self.assertTrue(p.from_param(np.array([1], dt)))
- dt = ''<i4''
- p = ndpointer(dtype=dt)
- self.assertTrue(p.from_param(np.array([1], dt)))
- dt = np.dtype(''>i4'')
- p = ndpointer(dtype=dt)
- p.from_param(np.array([1], dt))
- self.assertRaises(TypeError, p.from_param,
- np.array([1], dt.newbyteorder(''swap'')))
- dtnames = [''x'', ''y'']
- dtformats = [np.intc, np.float64]
- dtdescr = {''names'': dtnames, ''formats'': dtformats}
- dt = np.dtype(dtdescr)
- p = ndpointer(dtype=dt)
- self.assertTrue(p.from_param(np.zeros((10,), dt)))
- samedt = np.dtype(dtdescr)
- p = ndpointer(dtype=samedt)
- self.assertTrue(p.from_param(np.zeros((10, dt)))
- dt2 = np.dtype(dtdescr, align=True)
- if dt.itemsize != dt2.itemsize:
- self.assertRaises(TypeError, np.zeros((10, dt2))
- else:
- self.assertTrue(p.from_param(np.zeros((10, dt2)))
- def predict(self, check_input=True):
- """Predict class or regression value for X.
- For a classification model,the predicted class for each sample in X is
- returned. For a regression model,the predicted value based on X is
- returned.
- Parameters
- ----------
- X : array-like of shape = [n_samples,n_features]
- The input samples.
- Returns
- -------
- y : array of shape = [n_samples] or [n_samples,n_outputs]
- The predicted classes,or the predict values.
- """
- X = check_array(X, accept_sparse="csr")
- if issparse(X) and (X.indices.dtype != np.intc or
- X.indptr.dtype != np.intc):
- raise ValueError("No support for np.int64 index based "
- "sparse matrices")
- n_samples, n_features = X.shape
- if self.tree_ is None:
- raise Exception("Tree not initialized. Perform a fit first")
- if self.n_features_ != n_features:
- raise ValueError("Number of features of the model must "
- " match the input. Model n_features is %s and "
- " input n_features is %s "
- % (self.n_features_, n_features))
- return (self.tree_.get(''coefficient'') *
- (X[:, self.tree_.get(''best_dim'')] > self.tree_.get(''threshold'')) +
- self.tree_.get(''constant''))
- def _action(*entries):
- return np.array(entries, dtype=np.intc)
- def __init__(self, points, fraction):
- super(Graph, self).__init__(points, fraction)
- self.order = _np.ascontiguousarray(_np.argsort(self.density).astype(_np.intc)[::-1])
- self.delta, self.neighbour = _core.get_delta_and_neighbour(
- self.order, self.distances, self.max_distance)
- def assign(self, min_density, min_delta, border_only=False):
- self.min_density = min_density
- self.min_delta = min_delta
- self.border_only = border_only
- if self.autoplot:
- self.draw_decision_graph(self.min_density, self.min_delta)
- self._get_cluster_indices()
- self.membership = _core.get_membership(self.clusters, self.order, self.neighbour)
- self.border_density, self.border_member = _core.get_border(
- self.kernel_size, self.density, self.membership, self.nclusters)
- self.halo_idx, self.core_idx = _core.get_halo(
- self.density,
- self.border_density, self.border_member.astype(_np.intc), border_only=border_only)
- def _get_cluster_indices(self):
- self.clusters = _np.intersect1d(
- _np.where(self.density > self.min_density)[0],
- _np.where(self.delta > self.min_delta)[0], assume_unique=True).astype(_np.intc)
- self.nclusters = self.clusters.shape[0]
- def _get_membership(self):
- self.membership = -1 * _np.ones(shape=self.order.shape, dtype=_np.intc)
- for i in range(self.ncl):
- self.membership[self.clusters[i]] = i
- for i in range(self.npoints):
- if self.membership[self.order[i]] == -1:
- self.membership[self.order[i]] = self.membership[self.neighbour[self.order[i]]]
- def test_dtype(self):
- dt = np.intc
- p = ndpointer(dtype=dt)
- self.assertTrue(p.from_param(np.array([1], dt2)))
- def MapActions(self, action_raw):
- self.action = np.zeros([self.num_actions])
- if (action_raw == 0):
- self.action[self.indices["LOOK_LEFT_RIGHT_PIXELS_PER_FRAME"]] = -25
- elif (action_raw == 1):
- self.action[self.indices["LOOK_LEFT_RIGHT_PIXELS_PER_FRAME"]] = 25
- """if (action_raw==2):
- self.action[self.indices["LOOK_DOWN_UP_PIXELS_PER_FRAME"]] = -25
- elif (action_raw==3):
- self.action[self.indices["LOOK_DOWN_UP_PIXELS_PER_FRAME"]] = 25
- if (action_raw==4):
- self.action[self.indices["STRAFE_LEFT_RIGHT"]] = -1
- elif (action_raw==5):
- self.action[self.indices["STRAFE_LEFT_RIGHT"]] = 1
- if (action_raw==6):
- self.action[self.indices["MOVE_BACK_FORWARD"]] = -1
- el"""
- if (action_raw == 2): # 7
- self.action[self.indices["MOVE_BACK_FORWARD"]] = 1
- # all binary actions need reset
- """if (action_raw==8):
- self.action[self.indices["FIRE"]] = 0
- elif (action_raw==9):
- self.action[self.indices["FIRE"]] = 1
- if (action_raw==10):
- self.action[self.indices["JUMP"]] = 0
- elif (action_raw==11):
- self.action[self.indices["JUMP"]] = 1
- if (action_raw==12):
- self.action[self.indices["CROUCH"]] = 0
- elif (action_raw==13):
- self.action[self.indices["CROUCH"]] = 1"""
- return np.clip(self.action, self.mins, self.maxs).astype(np.intc)
- def _to_ctypes_array(tup, dtype=numpy.intc):
- return numpy.array(tup, dtype=dtype).ctypes
- def test_dtype(self):
- dt = np.intc
- p = ndpointer(dtype=dt)
- self.assertTrue(p.from_param(np.array([1], dt2)))
- def __init__(self, bins, mapq_thresh=30, clip_thresh=1):
- # set parameters
- self.bins = bins
- self.mapQT = mapq_thresh
- self.clip_thresh = clip_thresh
- # initialise data structures
- self.depth_stats = DepthStats(bins, mapq_thresh=mapq_thresh, dtype=np.intc)
- self.aln_stats = np.zeros((bins.num, len(AlignStats.aln_stats_cols)), dtype=np.intc)
- self.fwd_inserts = np.empty(bins.num, dtype=list)
- self.rvs_inserts = np.empty(bins.num, dtype=list)
- for j in range(0, bins.num):
- self.fwd_inserts[j] = []
- self.rvs_inserts[j] = []
- def generate_data(n_samples, n_features, size_groups, rho=0.5,
- random_state=24):
- """ Data generation process with Toplitz like correlated features:
- this correspond to the synthetic dataset used in our paper
- "GAP Safe Screening Rules for Sparse-Group Lasso".
- """
- rng = check_random_state(random_state)
- n_groups = len(size_groups)
- # g_start = np.zeros(n_groups,order=''F'',dtype=np.intc)
- # for i in range(1,n_groups):
- # g_start[i] = size_groups[i - 1] + g_start[i - 1]
- g_start = np.cumsum(size_groups, dtype=np.intc) - size_groups[0]
- # 10% of groups are actives
- gamma1 = int(np.ceil(n_groups * 0.1))
- selected_groups = rng.random_integers(0, n_groups - 1, gamma1)
- true_beta = np.zeros(n_features)
- for i in selected_groups:
- begin = g_start[i]
- end = g_start[i] + size_groups[i]
- # 10% of features are actives
- gamma2 = int(np.ceil(size_groups[i] * 0.1))
- selected_features = rng.random_integers(begin, end - 1, gamma2)
- ns = len(selected_features)
- s = 2 * rng.rand(ns) - 1
- u = rng.rand(ns)
- true_beta[selected_features] = np.sign(s) * (10 * u + (1 - u) * 0.5)
- vect = rho ** np.arange(n_features)
- covar = toeplitz(vect, vect)
- X = rng.multivariate_normal(np.zeros(n_features), covar, n_samples)
- y = np.dot(X, true_beta) + 0.01 * rng.normal(0, n_samples)
- return X, y
- def test_dtype(self):
- dt = np.intc
- p = ndpointer(dtype=dt)
- self.assertTrue(p.from_param(np.array([1], dt2)))
- def expected_support():
- numpy_datatypes = [numpy.bool_, numpy.bool, numpy.int_,
- numpy.intc, numpy.intp, numpy.int8,
- numpy.int16, numpy.int32, numpy.int64,
- numpy.uint8, numpy.uint16, numpy.uint32,
- numpy.uint64, numpy.float_, numpy.float16,
- numpy.float32, numpy.float64]
- python_datatypes = [bool, int, float, object]
- return numpy_datatypes + python_datatypes
- def test_dtype(self):
- dt = np.intc
- p = ndpointer(dtype=dt)
- self.assertTrue(p.from_param(np.array([1], dt2)))
- def test_dtype(self):
- dt = np.intc
- p = ndpointer(dtype=dt)
- self.assertTrue(p.from_param(np.array([1], dt2)))
- def predict_rankings(self, compact=False, n_jobs=1):
- ''''''
- Predict rankings of the documents for the given queries.
- If `compact` is set to True then the output will be one
- long 1d array containing the rankings for all the queries
- instead of a list of 1d arrays.
- The compact array can be subsequently index using query
- index pointer array,see `queries.query_indptr`.
- query: Query
- The query whose documents should be ranked.
- compact: bool
- Specify to return rankings in compact format.
- n_jobs: int,the current number of cpus will be used.
- ''''''
- # Predict the ranking scores for the documents.
- predictions = self.predict(queries, n_jobs)
- rankings = np.zeros(queries.document_count(), dtype=np.intc)
- ranksort_queries(queries.query_indptr, predictions, rankings)
- if compact or len(queries) == 1:
- return rankings
- else:
- return np.array_split(rankings, queries.query_indptr[1:-1])
- def predict_rankings(self, n_jobs=1):
- ''''''
- Predict rankings of the documents for the given queries.
- If `compact` is set to True then the output will be one
- long 1d array containing the rankings for all the queries
- instead of a list of 1d arrays.
- The compact array can be subsequently index using query
- index pointer array,the current number of cpus will be used.
- ''''''
- if self.trained is False:
- raise ValueError(''the model has not been trained yet'')
- # Predict the ranking scores for the documents.
- predictions = self.predict(queries, rankings)
- if compact or queries.query_count() == 1:
- return rankings
- else:
- return np.array_split(rankings, queries.query_indptr[1:-1])
- def compute_scale(self, relevance_scores=None):
- ''''''
- Return the ideal DCG value for each query. Optionally,external
- relevance assessments can be used instead of the relevances
- present in the queries.
- Parameters
- ----------
- queries: Queries
- The queries for which the ideal DCG should be computed.
- relevance_scores: array of integers,optional,(default is None)
- The relevance scores that should be used instead of the
- relevance scores inside queries. Note,this argument is
- experimental.
- ''''''
- ideal_values = np.empty(queries.query_count(), dtype=np.float64)
- if relevance_scores is not None:
- if queries.document_count() != relevance_scores.shape[0]:
- raise ValueError(''number of documents and relevance scores do not match'')
- # Need to sort the relevance labels first.
- indices = np.empty(relevance_scores.shape[0], dtype=np.intc)
- relevance_argsort_v1(relevance_scores, relevance_scores.shape[0])
- # Creates a copy.
- relevance_scores = relevance_scores[indices]
- else:
- # Assuming these are sorted.
- relevance_scores = queries.relevance_scores
- self.metric_.evaluate_queries_ideal(queries.query_indptr, relevance_scores, ideal_values)
- return ideal_values
- def evaluate(self, ranking=None, labels=None, ranked_labels=None, scales=None):
- ''''''
- Evaluate NDCG metric on the specified ranked list of document relevance scores.
- The function input can be either ranked list of relevance labels (`ranked_labels`),
- which is most convenient from the computational point of view,or it can be in
- the form of ranked list of documents (`ranking`) and corresponding relevance scores
- (`labels`),from which the ranked document relevance labels are computed.
- Parameters:
- -----------
- ranking: array,shape = (n_documents,)
- Specify list of ranked documents.
- labels: array: shape = (n_documents,)
- Specify relevance score for each document.
- ranked_labels: array,)
- Relevance scores of the ranked documents. If not given,then
- `ranking` and `labels` must not be None,`ranked_labels` will
- be than inferred from them.
- scales: float,optional (default is None)
- The ideal DCG value on the given documents. If None is given
- it will be computed from the document relevance scores.
- ''''''
- if ranked_labels is not None:
- return self.get_score_from_labels_list(ranked_labels)
- elif ranking is not None and labels is not None:
- if ranking.shape[0] != labels.shape[0]:
- raise ValueError(''number of ranked documents != number of relevance labels (%d,%d)'' \\
- % (ranking.shape[0], labels.shape[0]))
- ranked_labels = np.array(sorted(labels, key=dict(zip(labels,ranking)).get, reverse=True), dtype=np.intc)
- return self.get_score_from_labels_list(ranked_labels)
- def _get_partition_indices(start, end, n_jobs):
- ''''''
- Get boundary indices for ``n_jobs`` number of sub-arrays dividing
- a (contiguous) array of indices starting with ``start`` (inclusive)
- and ending with ``end`` (exclusive) into equal parts.
- ''''''
- if (end - start) >= n_jobs:
- return np.linspace(start, n_jobs + 1).astype(np.intc)
- else:
- return np.arange(end - start + 1, dtype=np.intc)
- def save_as_text(self, filepath, shuffle=False):
- ''''''
- Save queries into the specified file in svmlight format.
- Parameters:
- -----------
- filepath: string
- The filepath where this object will be saved.
- shuffle: bool
- Specify to shuffle the query document lists prior
- to writing into the file.
- ''''''
- # Inflate the query_ids array such that each id covers
- # the corresponding feature vectors.
- query_ids = np.fromiter(
- chain(*[[qid] * cnt for qid, cnt in zip(self.query_ids, np.diff(self.query_indptr))]),
- dtype=int)
- relevance_scores = self.relevance_scores
- feature_vectors = self.feature_vectors
- if shuffle:
- shuffle_indices = np.random.permutation(self.document_count())
- reshuffle_indices = np.argsort(query_ids[shuffle_indices])
- document_shuffle_indices = np.arange(self.document_count(),
- dtype=np.intc)[shuffle_indices[reshuffle_indices]]
- query_ids = query_ids[document_shuffle_indices]
- relevance_scores = relevance_scores[document_shuffle_indices]
- feature_vectors = feature_vectors[document_shuffle_indices]
- with open(filepath, ''w'') as ofile:
- for score, qid, feature_vector in zip(relevance_scores,
- query_ids,
- feature_vectors):
- ofile.write(''%d'' % score)
- ofile.write('' qid:%d'' % qid)
- for feature in zip(self.feature_indices, feature_vector):
- output = '' %d:%.12f'' % feature
- ofile.write(output.rstrip(''0'').rstrip(''.''))
- ofile.write(''\\n'')
- def _action(*entries):
- return np.array(entries, dtype=np.intc)
- def get_idxs_thread(comm, npoints):
- """ Get indices for processor using Scatterv
- Note:
- -----
- Uppercase mpi4py functions require everything to be in C-compatible
- types or they will return garbage!
- """
- size = comm.Get_size()
- rank = comm.Get_rank()
- npoints_thread = np.zeros(size,dtype=np.intc)
- offsets_thread = np.zeros(size,dtype=np.intc)
- for idx in range(size):
- npoints_thread[idx] = npoints/size
- offsets_thread[idx] = sum(npoints_thread[:idx])
- for idx in range(npoints % size):
- npoints_thread[idx] += 1
- offsets_thread[idx + 1:] += 1
- npoints_thread = tuple(npoints_thread)
- offsets_thread = tuple(offsets_thread)
- idxs_thread = np.zeros(npoints_thread[rank],dtype=np.intc)
- idxs = np.arange(npoints,dtype=np.intc)
- comm.Scatterv((idxs, npoints_thread, offsets_thread, MPI.INT), idxs_thread, root=0)
- return idxs_thread, offsets_thread
- def get_ravel_offsets(npoints_thread,natoms):
- """ Get lengths and offsets for gathering trajectory fragments """
- size = len(npoints_thread)
- ravel_lengths = np.zeros(size,dtype=np.intc)
- ravel_offsets = np.zeros(size,dtype=np.intc)
- for i in range(size):
- ravel_lengths[i] = npoints_thread[i]*3*natoms
- ravel_offsets[i] = sum(ravel_lengths[:i])
- ravel_lengths = tuple(ravel_lengths)
- ravel_offsets = tuple(ravel_offsets)
- return ravel_lengths, ravel_offsets
- def _count_vocab(self, raw_documents, fixed_vocab):
- """Create sparse feature matrix,and vocabulary where fixed_vocab=False
- """
- if fixed_vocab:
- vocabulary = self.vocabulary_
- else:
- # Add a new value when a new vocabulary item is seen
- vocabulary = defaultdict()
- vocabulary.default_factory = vocabulary.__len__
- analyze = self.build_analyzer()
- j_indices = _make_int_array()
- indptr = _make_int_array()
- indptr.append(0)
- for doc in raw_documents:
- for feature in analyze(doc):
- try:
- j_indices.append(vocabulary[feature])
- except KeyError:
- # Ignore out-of-vocabulary items for fixed_vocab=True
- continue
- indptr.append(len(j_indices))
- if not fixed_vocab:
- # disable defaultdict behavIoUr
- vocabulary = dict(vocabulary)
- if not vocabulary:
- raise ValueError("empty vocabulary; perhaps the documents only"
- " contain stop words")
- j_indices = frombuffer_empty(j_indices, dtype=np.intc)
- indptr = np.frombuffer(indptr, dtype=np.intc)
- values = np.ones(len(j_indices))
- X = sp.csr_matrix((values, j_indices, indptr),
- shape=(len(indptr) - 1, len(vocabulary)),
- dtype=self.dtype)
- X.sum_duplicates()
- return vocabulary, X
- def test_dtype(self):
- dt = np.intc
- p = ndpointer(dtype=dt)
- self.assertTrue(p.from_param(np.array([1], dt2)))
- def _count_vocab(self,and vocabulary where fixed_vocab=False
- """
- if fixed_vocab:
- vocabulary = self.vocabulary_
- else:
- # Add a new value when a new vocabulary item is seen
- vocabulary = defaultdict()
- vocabulary.default_factory = vocabulary.__len__
- analyze = self.build_analyzer()
- j_indices = []
- indptr = _make_int_array()
- values = _make_int_array()
- indptr.append(0)
- for doc in raw_documents:
- feature_counter = {}
- for feature in analyze(doc):
- try:
- feature_idx = vocabulary[feature]
- if feature_idx not in feature_counter:
- feature_counter[feature_idx] = 1
- else:
- feature_counter[feature_idx] += 1
- except KeyError:
- # Ignore out-of-vocabulary items for fixed_vocab=True
- continue
- j_indices.extend(feature_counter.keys())
- values.extend(feature_counter.values())
- indptr.append(len(j_indices))
- if not fixed_vocab:
- # disable defaultdict behavIoUr
- vocabulary = dict(vocabulary)
- if not vocabulary:
- raise ValueError("empty vocabulary; perhaps the documents only"
- " contain stop words")
- j_indices = np.asarray(j_indices, dtype=np.intc)
- values = frombuffer_empty(values, dtype=np.intc)
- X = sp.csr_matrix((values,
- dtype=self.dtype)
- X.sort_indices()
- return vocabulary, X
- def _count_vocab_2(self,and vocabulary where fixed_vocab=False
- """
- if fixed_vocab:
- vocabulary = self.vocabulary_
- else:
- # Add a new value when a new vocabulary item is seen
- vocabulary = defaultdict()
- vocabulary.default_factory = vocabulary.__len__
- analyze = self.build_analyzer()
- j_indices = []
- indptr = _make_int_array()
- # values = _make_int_array()
- values = array.array(str("f"))
- indptr.append(0)
- for doc in raw_documents:
- feature_counter = {}
- for feature in analyze(doc):
- try:
- feature_idx = vocabulary[feature]
- if feature_idx not in feature_counter:
- feature_counter[feature_idx] = 1
- else:
- feature_counter[feature_idx] += 1
- except KeyError:
- # Ignore out-of-vocabulary items for fixed_vocab=True
- continue
- j_indices.extend(feature_counter.keys())
- values.extend([i * 1.0 / sum(feature_counter.values()) for i in feature_counter.values()])
- indptr.append(len(j_indices))
- if not fixed_vocab:
- # disable defaultdict behavIoUr
- vocabulary = dict(vocabulary)
- if not vocabulary:
- raise ValueError("empty vocabulary; perhaps the documents only"
- " contain stop words")
- j_indices = np.asarray(j_indices, dtype=np.float32)
- X = sp.csr_matrix((values, len(vocabulary)))
- X.sort_indices()
- return vocabulary, X

Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
如何解决Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable?
晚安, 尝试打印以下内容时,我在 jupyter 中遇到了 numpy 问题,并且得到了一个 错误: 需要注意的是python版本是3.8.8。 我先用 spyder 测试它,它运行正确,它给了我预期的结果
使用 Spyder:
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
Results
0.6604903457995978
0.8236300859753154
0.16067650689842816
0.6967868357083673
0.4231597934445466
现在有了 jupyter
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
-------------------------------------------------- ------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-78-0c6a801b3ea9> in <module>
2 for i in range (5):
3 n = np.random.rand ()
----> 4 print (n)
TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable
感谢您对我如何在 Jupyter 中解决此问题的帮助。
非常感谢您抽出宝贵时间。
阿特,约翰”
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)

numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
今天看到这样一句代码:
xb = np.random.random((nb, d)).astype(''float32'') #创建一个二维随机数矩阵(nb行d列)
xb[:, 0] += np.arange(nb) / 1000. #将矩阵第一列的每个数加上一个值要理解这两句代码需要理解三个函数
1、生成随机数
numpy.random.random(size=None)
size为None时,返回float。
size不为None时,返回numpy.ndarray。例如numpy.random.random((1,2)),返回1行2列的numpy数组
2、对numpy数组中每一个元素进行类型转换
numpy.ndarray.astype(dtype)
返回numpy.ndarray。例如 numpy.array([1, 2, 2.5]).astype(int),返回numpy数组 [1, 2, 2]
3、获取等差数列
numpy.arange([start,]stop,[step,]dtype=None)
功能类似python中自带的range()和numpy中的numpy.linspace
返回numpy数组。例如numpy.arange(3),返回numpy数组[0, 1, 2]

numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()
numpy.ravel(a, order=''C'')
Return a flattened array
numpy.chararray.flatten(order=''C'')
Return a copy of the array collapsed into one dimension
numpy.squeeze(a, axis=None)
Remove single-dimensional entries from the shape of an array.
相同点: 将多维数组 降为 一维数组
不同点:
ravel() 返回的是视图(view),意味着改变元素的值会影响原始数组元素的值;
flatten() 返回的是拷贝,意味着改变元素的值不会影响原始数组;
squeeze()返回的是视图(view),仅仅是将shape中dimension为1的维度去掉;
ravel()示例:
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.ravel()
16 print("a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19
20 print(a)
21 log_type(''a'',a)
flatten()示例
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.flatten()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)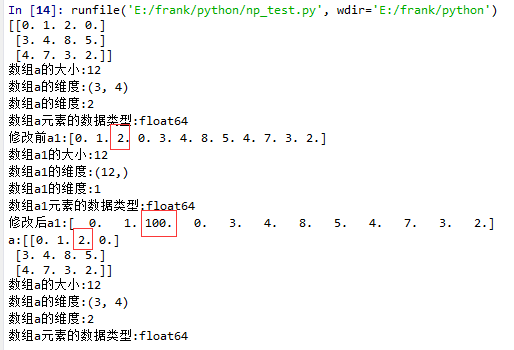
squeeze()示例:
1. 没有single-dimensional entries的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)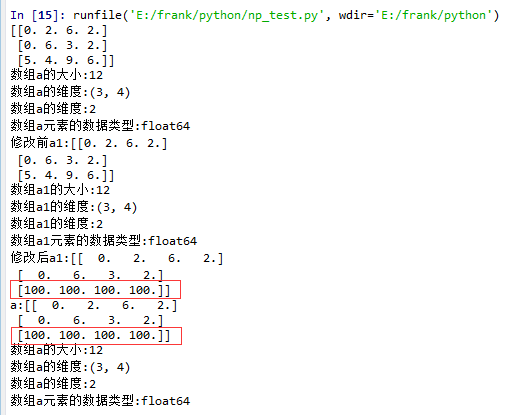
从结果中可以看到,当没有single-dimensional entries时,squeeze()返回额数组对象是一个view,而不是copy。
2. 有single-dimentional entries 的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((1,3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)

Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性
一、Numpy数组创建
part 1:np.linspace(起始值,终止值,元素总个数
import numpy as np
''''''
numpy中的ndarray数组
''''''
ary = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(ary)
ary = ary * 10
print(ary)
''''''
ndarray对象的创建
''''''
# 创建二维数组
# np.array([[],[],...])
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]])
print(a)
# np.arange(起始值, 结束值, 步长(默认1))
b = np.arange(1, 10, 1)
print(b)
print("-------------np.zeros(数组元素个数, dtype=''数组元素类型'')-----")
# 创建一维数组:
c = np.zeros(10)
print(c, ''; c.dtype:'', c.dtype)
# 创建二维数组:
print(np.zeros ((3,4)))
print("----------np.ones(数组元素个数, dtype=''数组元素类型'')--------")
# 创建一维数组:
d = np.ones(10, dtype=''int64'')
print(d, ''; d.dtype:'', d.dtype)
# 创建三维数组:
print(np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int32 ))
# 打印维度
print(np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int32 ).ndim) # 返回:3(维)
结果图:

part 2 :np.linspace ( 起始值,终止值,元素总个数)
import numpy as np
a = np.arange( 10, 30, 5 )
b = np.arange( 0, 2, 0.3 )
c = np.arange(12).reshape(4,3)
d = np.random.random((2,3)) # 取-1到1之间的随机数,要求设置为诶2行3列的结构
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
print(d)
print("-----------------")
from numpy import pi
print(np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 100 ))
print("-------------np.linspace(起始值,终止值,元素总个数)------------------")
print(np.sin(np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 100 )))
结果图:

二、Numpy的ndarray对象属性:
数组的结构:array.shape
数组的维度:array.ndim
元素的类型:array.dtype
数组元素的个数:array.size
数组的索引(下标):array[0]
''''''
数组的基本属性
''''''
import numpy as np
print("--------------------案例1:------------------------------")
a = np.arange(15).reshape(3, 5)
print(a)
print(a.shape) # 打印数组结构
print(len(a)) # 打印有多少行
print(a.ndim) # 打印维度
print(a.dtype) # 打印a数组内的元素的数据类型
# print(a.dtype.name)
print(a.size) # 打印数组的总元素个数
print("-------------------案例2:---------------------------")
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(a)
# 测试数组的基本属性
print(''a.shape:'', a.shape)
print(''a.size:'', a.size)
print(''len(a):'', len(a))
# a.shape = (6, ) # 此格式可将原数组结构变成1行6列的数据结构
# print(a, ''a.shape:'', a.shape)
# 数组元素的索引
ary = np.arange(1, 28)
ary.shape = (3, 3, 3) # 创建三维数组
print("ary.shape:",ary.shape,"\n",ary )
print("-----------------")
print(''ary[0]:'', ary[0])
print(''ary[0][0]:'', ary[0][0])
print(''ary[0][0][0]:'', ary[0][0][0])
print(''ary[0,0,0]:'', ary[0, 0, 0])
print("-----------------")
# 遍历三维数组:遍历出数组里的每个元素
for i in range(ary.shape[0]):
for j in range(ary.shape[1]):
for k in range(ary.shape[2]):
print(ary[i, j, k], end='' '')
结果图:

今天的关于Python numpy 模块-intc() 实例源码和python numpy interp的分享已经结束,谢谢您的关注,如果想了解更多关于Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()、Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性的相关知识,请在本站进行查询。
本文标签:





