对于想了解Pythonnumpy模块-logical_xor()实例源码的读者,本文将是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将详细介绍python中numpy模块,并且为您提供关于Jupyter中的Numpy在打
对于想了解Python numpy 模块-logical_xor() 实例源码的读者,本文将是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将详细介绍python中numpy模块,并且为您提供关于Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()、Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性的有价值信息。
本文目录一览:- Python numpy 模块-logical_xor() 实例源码(python中numpy模块)
- Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
- numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
- numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()
- Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性

Python numpy 模块-logical_xor() 实例源码(python中numpy模块)
Python numpy 模块,logical_xor() 实例源码
我们从Python开源项目中,提取了以下50个代码示例,用于说明如何使用numpy.logical_xor()。
- def calculate_plane_histogram(plane, doseplane, dosegridpoints,
- maxdose, dd, id, structure, hist):
- """Calculate the DVH for the given plane in the structure."""
- contours = [[x[0:2] for x in c[''data'']] for c in plane]
- # If there is no dose for the current plane,go to the next plane
- if not len(doseplane):
- return (np.arange(0, maxdose), 0)
- # Create a zero valued bool grid
- grid = np.zeros((dd[''rows''], dd[''columns'']), dtype=np.uint8)
- # Calculate the histogram for each contour in the plane
- # and boolean xor to remove holes
- for i, contour in enumerate(contours):
- m = get_contour_mask(dd, contour)
- grid = np.logical_xor(m.astype(np.uint8), grid).astype(np.bool)
- hist, vol = calculate_contour_dvh(
- grid, maxdose, structure)
- return (hist, vol)
- def _gene_signature(self,wm,size,key):
- ''''''????????????????????????''''''
- wm = cv2.resize(wm,(size,size))
- wU,_,wV = np.linalg.svd(np.mat(wm))
- sumU = np.sum(np.array(wU),axis=0)
- sumV = np.sum(np.array(wV),axis=0)
- sumU_mid = np.median(sumU)
- sumV_mid = np.median(sumV)
- sumU=np.array([1 if sumU[i] >sumU_mid else 0 for i in range(len(sumU)) ])
- sumV=np.array([1 if sumV[i] >sumV_mid else 0 for i in range(len(sumV)) ])
- uv_xor=np.logical_xor(sumU,sumV)
- np.random.seed(key)
- seq=np.random.randint(2,size=len(uv_xor))
- signature = np.logical_xor(uv_xor, seq)
- sqrts = int(np.sqrt(size))
- return np.array(signature,dtype=np.int8).reshape((sqrts,sqrts))
- def _gene_signature(self,(256,256))
- wU, seq)
- return np.array(signature,dtype=np.int8)
- def _gene_signature(self,wU,wV,key):
- ''''''????????????????????????''''''
- sumU = np.sum(wU,axis=0)
- sumV = np.sum(wV,dtype=np.int8)
- def test_truth_table_logical(self):
- # 2,3 and 4 serves as true values
- input1 = [0, 0, 3, 2]
- input2 = [0, 4, 2]
- typecodes = (np.typecodes[''AllFloat'']
- + np.typecodes[''AllInteger'']
- + ''?'') # boolean
- for dtype in map(np.dtype, typecodes):
- arg1 = np.asarray(input1, dtype=dtype)
- arg2 = np.asarray(input2, dtype=dtype)
- # OR
- out = [False, True, True]
- for func in (np.logical_or, np.maximum):
- assert_equal(func(arg1, arg2).astype(bool), out)
- # AND
- out = [False, False, True]
- for func in (np.logical_and, np.minimum):
- assert_equal(func(arg1, out)
- # XOR
- out = [False, False]
- for func in (np.logical_xor, np.not_equal):
- assert_equal(func(arg1, out)
- def test_NotImplemented_not_returned(self):
- # See gh-5964 and gh-2091. Some of these functions are not operator
- # related and were fixed for other reasons in the past.
- binary_funcs = [
- np.power, np.add, np.subtract, np.multiply, np.divide,
- np.true_divide, np.floor_divide, np.bitwise_and, np.bitwise_or,
- np.bitwise_xor, np.left_shift, np.right_shift, np.fmax,
- np.fmin, np.fmod, np.hypot, np.logaddexp, np.logaddexp2,
- np.logical_and, np.logical_or, np.logical_xor, np.maximum,
- np.minimum, np.mod
- ]
- # These functions still return NotImplemented. Will be fixed in
- # future.
- # bad = [np.greater,np.greater_equal,np.less,np.less_equal,np.not_equal]
- a = np.array(''1'')
- b = 1
- for f in binary_funcs:
- assert_raises(TypeError, f, a, b)
- def calculate_plane_histogram(plane,
- id, hist):
- """Calculate the DVH for the given plane in the structure."""
- contours = [[x[0:2] for x in c[''data'']] for c in plane]
- # Create a zero valued bool grid
- grid = np.zeros((dd[''rows''], dtype=np.uint8)
- # Calculate the dose plane mask for each contour in the plane
- # and boolean xor to remove holes
- for i, vol = calculate_contour_dvh(grid,
- structure)
- return (hist, vol)
- def test_truth_table_logical(self):
- # 2, out)
- def test_NotImplemented_not_returned(self):
- # See gh-5964 and gh-2091. Some of these functions are not operator
- # related and were fixed for other reasons in the past.
- binary_funcs = [
- np.power, b)
- def test_truth_table_logical(self):
- # 2, out)
- def test_NotImplemented_not_returned(self):
- # See gh-5964 and gh-2091. Some of these functions are not operator
- # related and were fixed for other reasons in the past.
- binary_funcs = [
- np.power, b)
- def data_cleaning(file_path):
- data = pd.read_csv(file_path, index_col=False)
- data.drop([''Street'', ''Utilities'', ''Condition2'', ''RoofMatl'', ''Alley'',
- ''GarageYrBlt'', ''GarageCond'', ''PoolQC'', ''MiscFeature''],
- axis=1, inplace=True)
- # marked as NA in BsmtExposure and not NA in other Bsmt Attributes
- data.loc[np.logical_xor(data[''BsmtCond''].isnull(), data[''BsmtExposure''].isnull()), ''BsmtExposure''] = ''No''
- # LotFrontage''s N/A is assigned zero,will it cause problem?
- data.fillna(value={''MasVnrType'': ''None'', ''MasVnrArea'': 0, ''BsmtQual'': ''NoBsmt'', ''BsmtCond'': ''NoBsmt'',
- ''BsmtExposure'': ''NoBsmt'', ''BsmtFinType1'': ''NoBsmt'', ''BsmtFinType2'': ''NoBsmt'',
- ''Electrical'': ''SBrkr'', ''FireplaceQu'': ''NoFP'', ''GarageType'': ''Noga'',
- ''GarageFinish'': ''Noga'', ''GarageQual'': ''Noga'', ''Fence'': ''NoFence'', ''LotFrontage'': 0},
- inplace=True)
- data.loc[:, ''YrSold''] = 2016 - data.loc[:, ''YrSold'']
- data.loc[data.loc[:, ''PoolArea''] != 0, ''PoolArea''] = 1
- data.loc[:, ''Porch''] = np.sum(data.loc[:, [''EnclosedPorch'', ''3SsnPorch'', ''ScreenPorch'']], axis=1)
- data.drop([''EnclosedPorch'', ''ScreenPorch''], axis=1, inplace=True)
- data.replace({''BsmtFullBath'': {3: 2},
- ''LotShape'': {''IR3'': ''IR2''}},
- inplace=True)
- data.columns
- # examine columns containing NA value
- print(data)
- print(data.columns[np.sum(data.isnull(), axis=0) != 0])
- def test_truth_table_logical(self):
- # 2, out)
- def test_NotImplemented_not_returned(self):
- # See gh-5964 and gh-2091. Some of these functions are not operator
- # related and were fixed for other reasons in the past.
- binary_funcs = [
- np.power, b)
- def m_menu(self):
- """Runs the Mathmatically defined sculpture menu item."""
- sin, cos = np.sin, np.cos
- res = raw_input("Enter a functional deFinition of a volume (x**2+y**2+z**2 < 1) \\n")
- self.user_text = res
- self.volume_data = self.bool_ops()
- self.create_iso_surface(.7)
- while True:
- res = raw_input("Enter another functional deFinition of a volume (x**2+y**2+z**2 < 1) \\n")
- self.user_text = res
- self.sec_volume_data = self.bool_ops()
- self.create_iso_surface(.7, second=True)
- res = raw_input("Enter a boolean operation to do with the prevIoUs solid (a = and,o = or,n = not,x = xor):\\n")
- if res == "a":
- self.sec_volume_data = 0+ np.logical_and(my_sculpture.volume_data, my_sculpture.bool_ops())
- elif res == "o":
- self.sec_volume_data = 0+ np.logical_or(my_sculpture.volume_data, my_sculpture.bool_ops())
- elif res == "n":
- self.sec_volume_data = 0+ np.logical_not(my_sculpture.volume_data, my_sculpture.bool_ops())
- elif res == "x":
- self.sec_volume_data = 0+ np.logical_xor(my_sculpture.volume_data, my_sculpture.bool_ops())
- self.create_iso_surface(.7, second=True)
- def test_truth_table_logical(self):
- # 2, out)
- def test_NotImplemented_not_returned(self):
- # See gh-5964 and gh-2091. Some of these functions are not operator
- # related and were fixed for other reasons in the past.
- binary_funcs = [
- np.power, b)
- def test_truth_table_logical(self):
- # 2, out)
- def test_NotImplemented_not_returned(self):
- # See gh-5964 and gh-2091. Some of these functions are not operator
- # related and were fixed for other reasons in the past.
- binary_funcs = [
- np.power, b)
- def selectShell(ref_coords, coords, R, sw):
- """
- Return indices of the particles within the spherical shell of
- inner radius (R-sw) and outer radius R,ie the shell.
- Parameters
- ----------
- ref_coords : array_like (n_atoms,n_dim)
- Reference atoms positions
- coords : array_like (n_atoms,n_dim)
- atoms positions
- R : float
- distance to any atoms
- Returns
- -------
- array
- particle indices within shell
- """
- if R < sw:
- raise RuntimeError("selection radius smaller then shell width")
- body_query = get_selection(coords, ref_coords, R=R)
- core_query = get_selection(coords, R=R - sw)
- query = np.logical_xor(body_query, core_query)
- return np.where(query)
- def test_truth_table_logical(self):
- # 2, out)
- def test_NotImplemented_not_returned(self):
- # See gh-5964 and gh-2091. Some of these functions are not operator
- # related and were fixed for other reasons in the past.
- binary_funcs = [
- np.power, b)
- def encodeMask(M):
- """
- Encode binary mask M using run-length encoding.
- :param M (bool 2D array) : binary mask to encode
- :return: R (object RLE) : run-length encoding of binary mask
- """
- [h, w] = M.shape
- M = M.flatten(order=''F'')
- N = len(M)
- counts_list = []
- pos = 0
- # counts
- counts_list.append(1)
- diffs = np.logical_xor(M[0:N-1], M[1:N])
- for diff in diffs:
- if diff:
- pos +=1
- counts_list.append(1)
- else:
- counts_list[pos] += 1
- # if array starts from 1. start with 0 counts for 0
- if M[0] == 1:
- counts_list = [0] + counts_list
- return {''size'': [h, w],
- ''counts'': counts_list ,
- }
- def _gene_signature(wm,key):
- ''''''
- ????????????????????????
- wm : ????
- size ??????????
- key ????????
- ''''''
- wm = cv2.resize(wm,wV = np.linalg.svd(np.mat(wm))
- sumU = np.sum(np.array(wU),sqrts))
- def test_logical_and_or_xor(self):
- assert_array_equal(self.t | self.t, self.t)
- assert_array_equal(self.f | self.f, self.f)
- assert_array_equal(self.t | self.f, self.t)
- assert_array_equal(self.f | self.t, self.t)
- np.logical_or(self.t, self.t, out=self.o)
- assert_array_equal(self.o, self.t)
- assert_array_equal(self.t & self.t, self.t)
- assert_array_equal(self.f & self.f, self.f)
- assert_array_equal(self.t & self.f, self.f)
- assert_array_equal(self.f & self.t, self.f)
- np.logical_and(self.t, self.t)
- assert_array_equal(self.t ^ self.t, self.f)
- assert_array_equal(self.f ^ self.f, self.f)
- assert_array_equal(self.t ^ self.f, self.t)
- assert_array_equal(self.f ^ self.t, self.t)
- np.logical_xor(self.t, self.f)
- assert_array_equal(self.nm & self.t, self.nm)
- assert_array_equal(self.im & self.f, False)
- assert_array_equal(self.nm & True, self.nm)
- assert_array_equal(self.im & False, self.f)
- assert_array_equal(self.nm | self.t, self.t)
- assert_array_equal(self.im | self.f, self.im)
- assert_array_equal(self.nm | True, self.t)
- assert_array_equal(self.im | False, self.im)
- assert_array_equal(self.nm ^ self.t, self.im)
- assert_array_equal(self.im ^ self.f, self.im)
- assert_array_equal(self.nm ^ True, self.im)
- assert_array_equal(self.im ^ False, self.im)
- def encodeMask(M):
- """
- Encode binary mask M using run-length encoding.
- :param M (bool 2D array) : binary mask to encode
- :return: R (object RLE) : run-length encoding of binary mask
- """
- [h,
- }
- def xor_(a: Bool = True, b: Bool = False) -> Bool:
- return np.logical_xor(a, b)
- def count_matrices(data, start_state=None, threshold=None, display=False):
- num_clusters = 2
- if threshold is None:
- clust = clusterer(data)
- state = clust.fit_predict(data.reshape(-1, 1)).reshape(data.shape)
- else:
- logger.debug("Cluster data based on threshold = {}".format(threshold))
- state = data > threshold
- init_state = state[:,:,0]
- final_state = state[:,1]
- switched = np.logical_xor(init_state, final_state)
- init_state_frac = [np.mean(init_state == ct) for ct in range(num_clusters)]
- for ct, fraction in enumerate(init_state_frac):
- logger.debug("Initial fraction of state %d: %f" %(ct, fraction))
- if start_state is not None and start_state in range(num_clusters):
- start_stt = start_state
- else:
- start_stt = np.argmax(init_state_frac)
- logger.debug("Start state set to state: {}".format(start_stt))
- logger.debug("Switched state is state: {}".format(1-start_stt))
- # This array contains a 2x2 count_matrix for each coordinate tuple
- count_mat = np.zeros((init_state.shape[0], 2, 2))
- # count_mat = np.zeros((2,2),dtype=np.int)
- count_mat[:,0,0] = np.logical_and(init_state == 0, np.logical_not(switched)).sum(axis=-1)
- count_mat[:,1] = np.logical_and(init_state == 0, switched).sum(axis=-1)
- count_mat[:,1,0] = np.logical_and(init_state == 1,1] = np.logical_and(init_state == 1, np.logical_not(switched)).sum(axis=-1)
- return count_mat, start_stt
- def count_matrices_ber(data, display=None):
- num_clusters = 2
- if threshold is None:
- clust = clusterer(data)
- state = clust.fit_predict(data.reshape(-1, 1)).reshape((-1,2))
- else:
- logger.debug("Cluster data based on threshold = {}".format(threshold))
- state = data > threshold
- state = state.reshape((-1,2))
- init_state = state[:, fraction))
- if start_state is not None and start_state in range(num_clusters):
- start_stt = start_state
- else:
- start_stt = np.argmax(init_state_frac)
- logger.debug("Start state set to state: {}".format(start_stt))
- logger.debug("Switched state is state: {}".format(1-start_stt))
- # This array contains a 2x2 count_matrix for each coordinate tuple
- count_mat = np.zeros((2,dtype=np.int)
- count_mat[0, np.logical_not(switched)).sum()
- count_mat[0, switched).sum()
- count_mat[1, np.logical_not(switched)).sum()
- return count_mat, start_stt
- def encodeMask(M):
- """
- Encode binary mask M using run-length encoding.
- :param M (bool 2D array) : binary mask to encode
- :return: R (object RLE) : run-length encoding of binary mask
- """
- [h, w] = M.shape
- M = M.flatten(order=''F'')
- N = len(M)
- counts_list = []
- pos = 0
- # counts
- counts_list.append(1)
- diffs = np.logical_xor(M[0:N - 1], M[1:N])
- for diff in diffs:
- if diff:
- pos += 1
- counts_list.append(1)
- else:
- counts_list[pos] += 1
- # if array starts from 1. start with 0 counts for 0
- if M[0] == 1:
- counts_list = [0] + counts_list
- return {''size'': [h,
- ''counts'': counts_list,
- }
- def encodeMask(M):
- """
- Encode binary mask M using run-length encoding.
- :param M (bool 2D array) : binary mask to encode
- :return: R (object RLE) : run-length encoding of binary mask
- """
- [h,
- }
- def encodeMask(M):
- """
- Encode binary mask M using run-length encoding.
- :param M (bool 2D array) : binary mask to encode
- :return: R (object RLE) : run-length encoding of binary mask
- """
- [h,
- }
- def encodeMask(M):
- """
- Encode binary mask M using run-length encoding.
- :param M (bool 2D array) : binary mask to encode
- :return: R (object RLE) : run-length encoding of binary mask
- """
- [h,
- }
- def compute_accuracy(scores, labels):
- is_pos = (labels != 0)
- is_neg = np.logical_not(is_pos)
- num_pos = np.sum(is_pos)
- num_neg = np.sum(is_neg)
- num_all = num_pos + num_neg
- is_correct = np.logical_xor(scores < 0, is_pos)
- accuracy_all = np.sum(is_correct) / num_all
- accuracy_pos = np.sum(is_correct[is_pos]) / (num_pos + 1)
- accuracy_neg = np.sum(is_correct[is_neg]) / num_neg
- return accuracy_all, accuracy_pos, accuracy_neg
- def test_logical_and_or_xor(self):
- assert_array_equal(self.t | self.t, self.im)
- def calcAnomaly(self, actual, predicted):
- """
- Calculates the anomaly of two SDRs
- Uses the equation presented on the wiki:
- https://github.com/numenta/nupic/wiki/Anomaly-score-Memo
- To put this in terms of the temporal pooler:
- A is the actual input array at a given timestep
- P is the predicted array that was produced from the prevIoUs timestep(s)
- [A - (A && P)] / [A]
- Rephrasing as questions:
- What bits are on in A that are not on in P?
- How does that compare to total on bits in A?
- Outputs 0 is there''s no difference between P and A.
- Outputs 1 if P and A are totally distinct.
- Not a perfect metric - it doesn''t credit proximity
- Next step: combine with a metric for a spatial pooler
- """
- combined = numpy.logical_and(actual, predicted)
- delta = numpy.logical_xor(actual,combined)
- delta_score = sum(delta)
- actual_score = float(sum(actual))
- return delta_score / actual_score
- def points_in_polys(points, polys, polyy=None):
- """
- :param points: Numpy array of Nx2 points
- :param polys: Numpy array of N polygons of degree M represented
- by Mx2 points (NxMx2) for each point,see if respective poly
- contains it. Returns array of True/False
- """
- result = np.zeros((points.shape[0],), dtype=bool)
- if isinstance(points, np.ma.masked_array):
- points = points.data
- if isinstance(polys, np.ma.masked_array):
- polys = polys.data
- if polyy is not None and isinstance(polyy, np.ma.masked_array):
- polyy = polyy.data
- pointsx = points[:, 0]
- pointsy = points[:, 1]
- v1x = v1y = v2x = v2y = -1
- for i in range(0, polys.shape[1]):
- if polyy is not None:
- v1x = polys[:, i - 1]
- v1y = polyy[:, i - 1]
- v2x = polys[:, i]
- v2y = polyy[:, i]
- else:
- v1x = polys[:, i - 1, 0]
- v1y = polys[:, 1]
- v2x = polys[:, i, 0]
- v2y = polys[:, 1]
- test1 = (v2y > pointsy) != (v1y > pointsy)
- test2 = np.zeros(points.shape[0], dtype=bool)
- m = np.where(test1 == 1)[0]
- test2[m] = pointsx[m] < \\
- (v1x[m] - v2x[m]) * (pointsy[m] - v2y[m]) / \\
- (v1y[m] - v2y[m]) + v2x[m]
- np.logical_and(test1, test2, test1)
- np.logical_xor(result, test1, result)
- return result
- def gold(bits, idx):
- """Generate the idx-th Gold code of length 2^bits - 1.
- Parameters
- ----------
- bits : int
- Length of LFSR. The length of the gold code will be
- :math:`2^{\\\\mathtt{bits}} - 1`.
- idx : int
- Index of the code to generate within the set of gold codes,where
- :math:`0 \\\\le \\\\mathtt{idx} < 2^{\\\\mathtt{bits}} + 1`.
- """
- bits = int(bits)
- if bits not in TAPS:
- raise ValueError(''Preferred pairs for %d bits unkNown.'' % bits)
- seed = np.ones(bits, dtype=bool)
- seq1 = lfsr(TAPS[bits][0], seed)
- seq2 = lfsr(TAPS[bits][1], seed)
- if idx == 0:
- return seq1
- elif idx == 1:
- return seq2
- else:
- return np.logical_xor(seq1, np.roll(seq2, -idx + 2))
- def test_logical_and_or_xor(self):
- assert_array_equal(self.t | self.t, self.im)
- def read_train(file_path):
- data = pd.read_csv(file_path, index_col=False)
- data.drop([''Street'', inplace=True)
- # marked as NA in BsmtExposure and not NA in other Bsmt Attributes
- data.loc[np.logical_xor(data[''BsmtCond''].isnull(), ''BsmtExposure''] = ''No''
- # LotFrontage''s N/A is assigned zero,
- inplace=True)
- data.loc[:, ''YrSold'']
- data.loc[data.loc[:, ''PoolArea''] = 1
- data.loc[:, inplace=True)
- data.replace({''BsmtFullBath'': {3: 2}, ''LotShape'': {''IR3'': ''IR2''}}, inplace=True)
- return data
- def data_cleaning(file_path):
- data = pd.read_csv(file_path, ''YrSold'']
- data.loc[:, ''YearBuilt''] = 2016 - data.loc[:, ''YearBuilt'']
- data.loc[:, ''YearRemodAdd''] = 2016 - data.loc[:, ''YearRemodAdd'']
- data.loc[data.loc[:, ''PoolArea''] = ''Y''
- data.loc[data.loc[:, ''PoolArea''] == 0, ''PoolArea''] = ''N''
- data.loc[:,
- inplace=True)
- return data
- # data.columns
- # examine columns containing NA value
- # print(data)
- # print(data.columns[np.sum(data.isnull(),axis=0) != 0])
- def test_logical_and_or_xor(self):
- assert_array_equal(self.t | self.t, self.im)
- def test_logical_and_or_xor(self):
- assert_array_equal(self.t | self.t, self.im)
- def plot_xor():
- np.random.seed(0)
- X_xor = np.random.randn(200, 2)
- y_xor = np.logical_xor(X_xor[:, 0] > 0, X_xor[:, 1] > 0)
- y_xor = np.where(y_xor, 1, -1)
- svm = SVC(kernel=''rbf'', random_state=0, gamma=0.1, C=10.0)
- svm.fit(X_xor, y_xor)
- plot_decision_regions(X_xor, y_xor, classifier=svm)
- plt.legend(loc=''upper left'')
- plt.show()
- def test_logical_and_or_xor(self):
- assert_array_equal(self.t | self.t, self.im)
- def shortest_path(mgrid, domain, targets, obstacles, buffer_radius):
- """Vector field guiding towards targets."""
- obstacles_buffered = obstacles.buffer(buffer_radius).intersection(domain)
- dmap_targets = distance_map(mgrid, obstacles_buffered)
- dir_map_targets = direction_map(dmap_targets)
- # Fill values between buffered region and obstacles
- mask = np.full(mgrid.shape, dtype=np.bool_)
- draw_geom(obstacles, mask, mgrid.indicer, True)
- fill_missing(np.logical_xor(mask, dir_map_targets[0].mask),
- *mgrid.values, *dir_map_targets)
- return dir_map_targets, dmap_targets
- def from_xyxy(cls, xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, correct_flipped=False):
- x_flipped = True if xmax >= 0 and xmin > xmax else False
- y_flipped = True if ymax >= 0 and ymin > ymax else False
- if correct_flipped:
- if np.logical_xor(x_flipped, y_flipped):
- assert False, "Invalid bounding Box"
- elif x_flipped and y_flipped:
- xmin, xmax = xmax, xmin
- ymin, ymax = ymax, ymin
- return cls(xmin, xmax - xmin + 1, ymax - ymin + 1)
- def xor_data(num_examples, noise=None):
- X = randn(num_examples, 2)
- if noise is None:
- X_ = X
- else:
- X_ = X + noise * randn(num_examples, 2)
- y = np.logical_xor(X_[:, X_[:, 1] > 0).astype(int)
- return X, y
- def test_logical_and_or_xor(self):
- assert_array_equal(self.t | self.t, self.im)
- def test_half_ufuncs(self):
- """Test the varIoUs ufuncs"""
- a = np.array([0, 2], dtype=float16)
- b = np.array([-2, 5, 3], dtype=float16)
- c = np.array([0, -1, -np.inf, np.nan, 6], dtype=float16)
- assert_equal(np.add(a, b), [-2, 6, 8, 5])
- assert_equal(np.subtract(a, [2, -4, -1])
- assert_equal(np.multiply(a, [0, 16, 6])
- assert_equal(np.divide(a, 0.199951171875, 0.66650390625])
- assert_equal(np.equal(a, [False, False])
- assert_equal(np.not_equal(a, [True, True])
- assert_equal(np.less(a, True])
- assert_equal(np.less_equal(a, True])
- assert_equal(np.greater(a, False])
- assert_equal(np.greater_equal(a, False])
- assert_equal(np.logical_and(a, True])
- assert_equal(np.logical_or(a, True])
- assert_equal(np.logical_xor(a, False])
- assert_equal(np.logical_not(a), False])
- assert_equal(np.isnan(c), False])
- assert_equal(np.isinf(c), False])
- assert_equal(np.isfinite(c), True])
- assert_equal(np.signbit(b), False])
- assert_equal(np.copysign(b, a), 3])
- assert_equal(np.maximum(a, 3])
- x = np.maximum(b, c)
- assert_(np.isnan(x[3]))
- x[3] = 0
- assert_equal(x, 6])
- assert_equal(np.minimum(a, 2])
- x = np.minimum(b, 3])
- assert_equal(np.fmax(a, 3])
- assert_equal(np.fmax(b, c), 6])
- assert_equal(np.fmin(a, 2])
- assert_equal(np.fmin(b, 3])
- assert_equal(np.floor_divide(a, 0])
- assert_equal(np.remainder(a, 2])
- assert_equal(np.square(b), [4, 25, 9])
- assert_equal(np.reciprocal(b), [-0.5, 0.25, 0.333251953125])
- assert_equal(np.ones_like(b), [1, 1])
- assert_equal(np.conjugate(b), b)
- assert_equal(np.absolute(b), 3])
- assert_equal(np.negative(b), -5, -3])
- assert_equal(np.sign(b), [-1, 1])
- assert_equal(np.modf(b), ([0, 0], b))
- assert_equal(np.frexp(b), ([-0.5, 0.625, 0.5, 0.75], 2]))
- assert_equal(np.ldexp(b, 2]), 10, 64, 12])

Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
如何解决Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable?
晚安, 尝试打印以下内容时,我在 jupyter 中遇到了 numpy 问题,并且得到了一个 错误: 需要注意的是python版本是3.8.8。 我先用 spyder 测试它,它运行正确,它给了我预期的结果
使用 Spyder:
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
Results
0.6604903457995978
0.8236300859753154
0.16067650689842816
0.6967868357083673
0.4231597934445466
现在有了 jupyter
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
-------------------------------------------------- ------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-78-0c6a801b3ea9> in <module>
2 for i in range (5):
3 n = np.random.rand ()
----> 4 print (n)
TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable
感谢您对我如何在 Jupyter 中解决此问题的帮助。
非常感谢您抽出宝贵时间。
阿特,约翰”
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)

numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
今天看到这样一句代码:
xb = np.random.random((nb, d)).astype(''float32'') #创建一个二维随机数矩阵(nb行d列)
xb[:, 0] += np.arange(nb) / 1000. #将矩阵第一列的每个数加上一个值要理解这两句代码需要理解三个函数
1、生成随机数
numpy.random.random(size=None)
size为None时,返回float。
size不为None时,返回numpy.ndarray。例如numpy.random.random((1,2)),返回1行2列的numpy数组
2、对numpy数组中每一个元素进行类型转换
numpy.ndarray.astype(dtype)
返回numpy.ndarray。例如 numpy.array([1, 2, 2.5]).astype(int),返回numpy数组 [1, 2, 2]
3、获取等差数列
numpy.arange([start,]stop,[step,]dtype=None)
功能类似python中自带的range()和numpy中的numpy.linspace
返回numpy数组。例如numpy.arange(3),返回numpy数组[0, 1, 2]

numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()
numpy.ravel(a, order=''C'')
Return a flattened array
numpy.chararray.flatten(order=''C'')
Return a copy of the array collapsed into one dimension
numpy.squeeze(a, axis=None)
Remove single-dimensional entries from the shape of an array.
相同点: 将多维数组 降为 一维数组
不同点:
ravel() 返回的是视图(view),意味着改变元素的值会影响原始数组元素的值;
flatten() 返回的是拷贝,意味着改变元素的值不会影响原始数组;
squeeze()返回的是视图(view),仅仅是将shape中dimension为1的维度去掉;
ravel()示例:
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.ravel()
16 print("a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19
20 print(a)
21 log_type(''a'',a)
flatten()示例
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.flatten()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)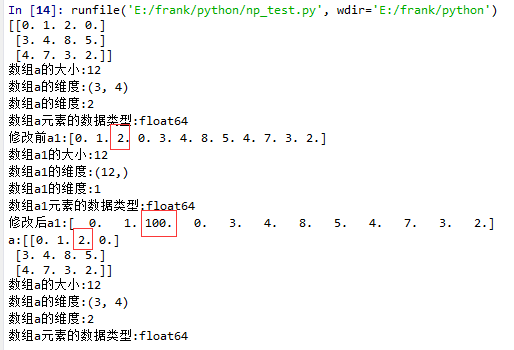
squeeze()示例:
1. 没有single-dimensional entries的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)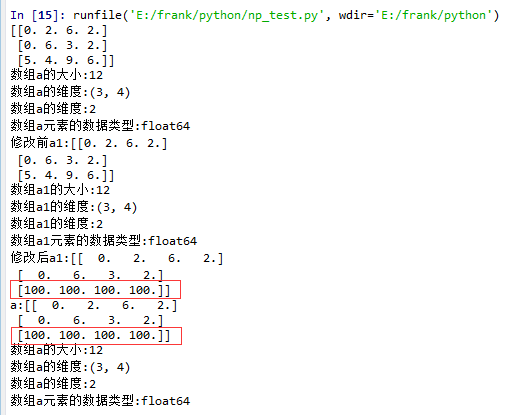
从结果中可以看到,当没有single-dimensional entries时,squeeze()返回额数组对象是一个view,而不是copy。
2. 有single-dimentional entries 的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((1,3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)

Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性
一、Numpy数组创建
part 1:np.linspace(起始值,终止值,元素总个数
import numpy as np
''''''
numpy中的ndarray数组
''''''
ary = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(ary)
ary = ary * 10
print(ary)
''''''
ndarray对象的创建
''''''
# 创建二维数组
# np.array([[],[],...])
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]])
print(a)
# np.arange(起始值, 结束值, 步长(默认1))
b = np.arange(1, 10, 1)
print(b)
print("-------------np.zeros(数组元素个数, dtype=''数组元素类型'')-----")
# 创建一维数组:
c = np.zeros(10)
print(c, ''; c.dtype:'', c.dtype)
# 创建二维数组:
print(np.zeros ((3,4)))
print("----------np.ones(数组元素个数, dtype=''数组元素类型'')--------")
# 创建一维数组:
d = np.ones(10, dtype=''int64'')
print(d, ''; d.dtype:'', d.dtype)
# 创建三维数组:
print(np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int32 ))
# 打印维度
print(np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int32 ).ndim) # 返回:3(维)
结果图:

part 2 :np.linspace ( 起始值,终止值,元素总个数)
import numpy as np
a = np.arange( 10, 30, 5 )
b = np.arange( 0, 2, 0.3 )
c = np.arange(12).reshape(4,3)
d = np.random.random((2,3)) # 取-1到1之间的随机数,要求设置为诶2行3列的结构
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
print(d)
print("-----------------")
from numpy import pi
print(np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 100 ))
print("-------------np.linspace(起始值,终止值,元素总个数)------------------")
print(np.sin(np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 100 )))
结果图:

二、Numpy的ndarray对象属性:
数组的结构:array.shape
数组的维度:array.ndim
元素的类型:array.dtype
数组元素的个数:array.size
数组的索引(下标):array[0]
''''''
数组的基本属性
''''''
import numpy as np
print("--------------------案例1:------------------------------")
a = np.arange(15).reshape(3, 5)
print(a)
print(a.shape) # 打印数组结构
print(len(a)) # 打印有多少行
print(a.ndim) # 打印维度
print(a.dtype) # 打印a数组内的元素的数据类型
# print(a.dtype.name)
print(a.size) # 打印数组的总元素个数
print("-------------------案例2:---------------------------")
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(a)
# 测试数组的基本属性
print(''a.shape:'', a.shape)
print(''a.size:'', a.size)
print(''len(a):'', len(a))
# a.shape = (6, ) # 此格式可将原数组结构变成1行6列的数据结构
# print(a, ''a.shape:'', a.shape)
# 数组元素的索引
ary = np.arange(1, 28)
ary.shape = (3, 3, 3) # 创建三维数组
print("ary.shape:",ary.shape,"\n",ary )
print("-----------------")
print(''ary[0]:'', ary[0])
print(''ary[0][0]:'', ary[0][0])
print(''ary[0][0][0]:'', ary[0][0][0])
print(''ary[0,0,0]:'', ary[0, 0, 0])
print("-----------------")
# 遍历三维数组:遍历出数组里的每个元素
for i in range(ary.shape[0]):
for j in range(ary.shape[1]):
for k in range(ary.shape[2]):
print(ary[i, j, k], end='' '')
结果图:

关于Python numpy 模块-logical_xor() 实例源码和python中numpy模块的问题我们已经讲解完毕,感谢您的阅读,如果还想了解更多关于Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()、Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性等相关内容,可以在本站寻找。
本文标签:





