如果您想了解Pythonnumpy模块-union1d()实例源码的相关知识,那么本文是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将对python中numpy模块进行全面详尽的解释,并且为您提供关于Jupyter中的N
如果您想了解Python numpy 模块-union1d() 实例源码的相关知识,那么本文是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将对python中numpy模块进行全面详尽的解释,并且为您提供关于Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()、Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性的有价值的信息。
本文目录一览:- Python numpy 模块-union1d() 实例源码(python中numpy模块)
- Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
- numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
- numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()
- Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性

Python numpy 模块-union1d() 实例源码(python中numpy模块)
Python numpy 模块,union1d() 实例源码
我们从Python开源项目中,提取了以下39个代码示例,用于说明如何使用numpy.union1d()。
- def __init__(self, source, **params):
- #_Graph.__init__(self)
- self.is_static = False
- if isinstance(source, str): # it is a file
- self._load(source, **params)
- else: # source must be an EventQueue then
- # to do: read from event queue
- # should also get self.starts,...
- pass
- self.t_start = params.get(''t_start'', np.min(self.starts))
- self.t_stop = params.get(''t_stop'', np.max(self.stops))
- # Todo: Ideally only use self.all_nodes
- self.all_nodes = list(np.union1d(self.node1s, self.node2s))
- all_nodes = list(np.union1d(self.node1s, self.node2s))
- n = len(self.all_nodes)
- def get_id(an_id):
- return all_nodes.index(an_id)
- v_get_id = np.vectorize(get_id)
- self.node1s = v_get_id(self.node1s)
- self.node2s = v_get_id(self.node2s)
- # Now we need to remap the node ids
- _Graph.__init__(self, n=n)
- def uunion1d(arr1, arr2):
- """Find the union of two arrays.
- A wrapper around numpy.intersect1d that preserves units. All input arrays
- must have the same units. See the documentation of numpy.intersect1d for
- full details.
- Examples
- --------
- >>> A = yt.YTArray([1,2,3],''cm'')
- >>> B = yt.YTArray([2,3,4],''cm'')
- >>> uunion1d(A,B)
- YTArray([ 1.,2.,3.,4.]) cm
- """
- v = np.union1d(arr1, arr2)
- v = validate_numpy_wrapper_units(v, [arr1, arr2])
- return v
- def __apply_func(self, other, func_name):
- if isinstance(other, Signal):
- time = np.union1d(self.timestamps, other.timestamps)
- s = self.interp(time).samples
- o = other.interp(time).samples
- func = getattr(s, func_name)
- s = func(o)
- elif other is None:
- s = self.samples
- time = self.timestamps
- else:
- func = getattr(self.samples, func_name)
- s = func(other)
- time = self.timestamps
- return Signal(s,
- time,
- self.unit,
- self.name,
- self.info)
- def test_confusion_matrix():
- # Defining numpy implementation of confusion matrix
- def numpy_conf_mat(actual, pred):
- order = numpy.union1d(actual, pred)
- colA = numpy.matrix(actual).T
- colP = numpy.matrix(pred).T
- oneHotA = colA.__eq__(order).astype(''int64'')
- oneHotP = colP.__eq__(order).astype(''int64'')
- conf_mat = numpy.dot(oneHotA.T, oneHotP)
- conf_mat = numpy.asarray(conf_mat)
- return [conf_mat, order]
- x = tensor.vector()
- y = tensor.vector()
- f = theano.function([x, y], confusion_matrix(x, y))
- list_inputs = [[[0, 1, 2, 0], [0, 0, 2]],
- [[2, 1], 2]]]
- for case in list_inputs:
- a = numpy.asarray(case[0])
- b = numpy.asarray(case[1])
- out_exp = numpy_conf_mat(a, b)
- outs = f(case[0], case[1])
- for exp, out in zip(out_exp, outs):
- utt.assert_allclose(exp, out)
- def subtract(curve1, curve2, def_val=0):
- """
- Function calculates difference between curve1 and curve2
- and returns new object which domain is an union
- of curve1 and curve2 domains
- Returned object is of type type(curve1)
- and has same Metadata as curve1 object
- :param curve1: first curve to calculate the difference
- :param curve2: second curve to calculate the difference
- :param def_val: default value for points that cannot be interpolated
- :return: new object of type type(curve1) with element-wise difference
- (using interpolation if necessary)
- """
- coord1 = np.union1d(curve1.x, curve2.x)
- y1 = curve1.evaluate_at_x(coord1, def_val)
- y2 = curve2.evaluate_at_x(coord1, def_val)
- coord2 = y1 - y2
- # the below is explained at the end of curve.Curve.change_domain()
- obj = curve1.__class__(np.dstack((coord1, coord2))[0], **curve1.__dict__[''Metadata''])
- return obj
- def relabelAllSequences(zBySeq, specialStateIDs):
- '''''' Relabel all sequences in provided list.
- Returns
- -------
- zBySeq,relabelled so that each label in specialStateIDs
- Now corresponds to ids 0,1,... L-1
- and all other labels not in that set get ids L,L+1,...
- ''''''
- import copy
- zBySeq = copy.deepcopy(zBySeq)
- L = len(specialStateIDs)
- uniqueVals = []
- for z in zBySeq:
- z += 1000
- for kID, kVal in enumerate(specialStateIDs):
- z[z == 1000 + kVal] = -1000 + kID
- uniqueVals = np.union1d(uniqueVals, np.unique(z))
- for z in zBySeq:
- for kID, kVal in enumerate(sorted(uniqueVals)):
- z[z == kVal] = kID
- return zBySeq
- def multi_x_reader(self, spc_file):
- # use x-values as domain
- all_x = []
- for sub in spc_file.sub:
- x = sub.x
- # assume values in x do not repeat
- all_x = np.union1d(all_x, x)
- domain = Orange.data.Domain([Orange.data.ContinuousVariable.make("%f" % f) for f in all_x], None)
- instances = []
- for sub in spc_file.sub:
- x, y = sub.x, sub.y
- newinstance = np.ones(len(all_x))*np.nan
- ss = np.searchsorted(all_x, x) # find positions to set
- newinstance[ss] = y
- instances.append(newinstance)
- y_data = np.array(instances).astype(float, order=''C'')
- return Orange.data.Table.from_numpy(domain, y_data)
- def pairwisescore(inFile_1, inFile_2, logDebug, outFile):
- (snpCHR1, snpPOS1, snpGT1, snpWEI1, DPmean1) = parseInput(inFile = inFile_1, logDebug = logDebug)
- (snpCHR2, snpPOS2, snpGT2, snpWEI2, DPmean2) = parseInput(inFile = inFile_2, logDebug = logDebug)
- snpmatch_stats = {}
- unique_1, unique_2, common, scores = 0, 0
- chrs = np.union1d(snpCHR1, snpCHR2)
- for i in chrs:
- perchrTarPosInd1 = np.where(snpCHR1 == i)[0]
- perchrTarPosInd2 = np.where(snpCHR2 == i)[0]
- log.info("Analysing chromosome %s positions", i)
- perchrtarSNPpos1 = snpPOS1[perchrTarPosInd1]
- perchrtarSNPpos2 = snpPOS2[perchrTarPosInd2]
- matchedAccInd1 = np.where(np.in1d(perchrtarSNPpos1, perchrtarSNPpos2))[0]
- matchedAccInd2 = np.where(np.in1d(perchrtarSNPpos2, perchrtarSNPpos1))[0]
- unique_1 = unique_1 + len(perchrTarPosInd1) - len(matchedAccInd1)
- unique_2 = unique_2 + len(perchrTarPosInd2) - len(matchedAccInd2)
- common = common + len(matchedAccInd1)
- scores = scores + np.sum(np.array(snpGT1[matchedAccInd1] == snpGT2[matchedAccInd2], dtype = int))
- snpmatch_stats[''unique''] = {"%s" % os.path.basename(inFile_1): [float(unique_1)/len(snpCHR1), len(snpCHR1)], "%s" % os.path.basename(inFile_2): [float(unique_2)/len(snpCHR2), len(snpCHR2)]}
- snpmatch_stats[''matches''] = [float(scores)/common, common]
- if not outFile:
- outFile = "genotyper"
- log.info("writing output in a file: %s" % outFile + ".matches.json")
- with open(outFile + ".matches.json", "w") as out_stats:
- out_stats.write(json.dumps(snpmatch_stats))
- log.info("finished!")
- def union1d(ar1, ar2):
- """
- Find the union of two arrays.
- Return the unique,sorted array of values that are in either of the two
- input arrays.
- Parameters
- ----------
- ar1,ar2 : array_like
- Input arrays. They are flattened if they are not already 1D.
- Returns
- -------
- union1d : ndarray
- Unique,sorted union of the input arrays.
- See Also
- --------
- numpy.lib.arraysetops : Module with a number of other functions for
- performing set operations on arrays.
- Examples
- --------
- >>> np.union1d([-1,1],[-2,2])
- array([-2,-1,2])
- To find the union of more than two arrays,use functools.reduce:
- >>> from functools import reduce
- >>> reduce(np.union1d,([1,4,[3,[6,2]))
- array([1,6])
- """
- return unique(np.concatenate((ar1, ar2)))
- def intersect_sim(array_1, array_2):
- """Calculate the simiarity of two arrays
- by using intersection / union
- """
- sim = float(np.intersect1d(array_1, array_2).size) / \\
- float(np.union1d(array_1, array_2).size)
- return sim
- def union_classes(eval_segm, gt_segm):
- eval_cl, _ = extract_classes(eval_segm)
- gt_cl, _ = extract_classes(gt_segm)
- cl = np.union1d(eval_cl, gt_cl)
- n_cl = len(cl)
- return cl, n_cl
- def __init__(self, edges):
- self.edges = edges
- self.nodes = Nodes(len(numpy.union1d(self.edges.begin, self.edges.end)))
- for i in xrange(len(self.edges)):
- j = i if True else 0
- self.nodes.outgoing[self.edges.begin[i]].append(j)
- self.nodes.incoming[self.edges.end [i]].append(j)
- def union1d(ar1, ar2)))
- def test_numpy_wrappers():
- a1 = YTArray([1, 3], ''cm'')
- a2 = YTArray([2, 3, 4, 5, 6], ''cm'')
- catenate_answer = [1, 6]
- intersect_answer = [2, 3]
- union_answer = [1, 6]
- assert_array_equal(YTArray(catenate_answer, ''cm''), uconcatenate((a1, a2)))
- assert_array_equal(catenate_answer, np.concatenate((a1, a2)))
- assert_array_equal(YTArray(intersect_answer, uintersect1d(a1, a2))
- assert_array_equal(intersect_answer, np.intersect1d(a1, a2))
- assert_array_equal(YTArray(union_answer, uunion1d(a1, a2))
- assert_array_equal(union_answer, np.union1d(a1, a2))
- def test_boolean_spheres_overlap():
- r"""Test to make sure that boolean objects (spheres,overlap)
- behave the way we expect.
- Test overlapping spheres.
- """
- ds = fake_amr_ds()
- sp1 = ds.sphere([0.45, 0.45, 0.45], 0.15)
- sp2 = ds.sphere([0.55, 0.55, 0.55], 0.15)
- # Get indices of both.
- i1 = sp1["index","morton_index"]
- i2 = sp2["index","morton_index"]
- # Make some booleans
- bo1 = sp1 & sp2
- bo2 = sp1 - sp2
- bo3 = sp1 | sp2
- bo4 = ds.union([sp1, sp2])
- bo5 = ds.intersection([sp1, sp2])
- # Now make sure the indices also behave as we expect.
- lens = np.intersect1d(i1, i2)
- apple = np.setdiff1d(i1, i2)
- both = np.union1d(i1, i2)
- b1 = bo1["index","morton_index"]
- b1.sort()
- b2 = bo2["index","morton_index"]
- b2.sort()
- b3 = bo3["index","morton_index"]
- b3.sort()
- assert_array_equal(b1, lens)
- assert_array_equal(b2, apple)
- assert_array_equal(b3, both)
- b4 = bo4["index","morton_index"]
- b4.sort()
- b5 = bo5["index","morton_index"]
- b5.sort()
- assert_array_equal(b3, b4)
- assert_array_equal(b1, b5)
- bo6 = sp1 ^ sp2
- b6 = bo6["index", "morton_index"]
- b6.sort()
- assert_array_equal(b6, np.setxor1d(i1, i2))
- def test_boolean_regions_overlap():
- r"""Test to make sure that boolean objects (regions,overlap)
- behave the way we expect.
- Test overlapping regions.
- """
- ds = fake_amr_ds()
- re1 = ds.region([0.55]*3, [0.5]*3, [0.6]*3)
- re2 = ds.region([0.6]*3, [0.55]*3, [0.65]*3)
- # Get indices of both.
- i1 = re1["index","morton_index"]
- i2 = re2["index","morton_index"]
- # Make some booleans
- bo1 = re1 & re2
- bo2 = re1 - re2
- bo3 = re1 | re2
- bo4 = ds.union([re1, re2])
- bo5 = ds.intersection([re1, re2])
- # Now make sure the indices also behave as we expect.
- cube = np.intersect1d(i1, i2)
- bite_cube = np.setdiff1d(i1, cube)
- assert_array_equal(b2, bite_cube)
- assert_array_equal(b3, b5)
- bo6 = re1 ^ re2
- b6 = bo6["index", i2))
- def test_boolean_slices_overlap():
- r"""Test to make sure that boolean objects (slices,overlap)
- behave the way we expect.
- Test overlapping slices.
- """
- ds = fake_amr_ds()
- sl1 = ds.r[:,:,0.25]
- sl2 = ds.r[:,0.75,:]
- # Get indices of both.
- i1 = sl1["index","morton_index"]
- i2 = sl2["index","morton_index"]
- # Make some booleans
- bo1 = sl1 & sl2
- bo2 = sl1 - sl2
- bo3 = sl1 | sl2
- bo4 = ds.union([sl1, sl2])
- bo5 = ds.intersection([sl1, sl2])
- # Now make sure the indices also behave as we expect.
- line = np.intersect1d(i1, i2)
- orig = np.setdiff1d(i1, line)
- assert_array_equal(b2, orig)
- assert_array_equal(b3, b5)
- bo6 = sl1 ^ sl2
- b6 = bo6["index", i2))
- def union1d(ar1, ar2)))
- def union1d(ar1, ar2)))
- def _wmd(self, i, row, X_train):
- """Compute the WMD between training sample i and given test row.
- Assumes that `row` and train samples are sparse BOW vectors summing to 1.
- """
- union_idx = np.union1d(X_train[i].indices, row.indices) - 1
- W_minimal = self.W_embed[union_idx]
- W_dist = euclidean_distances(W_minimal)
- bow_i = X_train[i, union_idx].A.ravel()
- bow_j = row[:, union_idx].A.ravel()
- return emd(bow_i, bow_j, W_dist)
- def union1d(ar1, ar2)))
- def _match_score(predicted_biclustering, reference_biclustering, bicluster_attr):
- k = len(predicted_biclustering.biclusters)
- return sum(max(len(np.intersect1d(getattr(bp, bicluster_attr), getattr(bt, bicluster_attr))) /
- len(np.union1d(getattr(bp, bicluster_attr)))
- for bt in reference_biclustering.biclusters)
- for bp in predicted_biclustering.biclusters) / k
- def liu_wang_match_score(predicted_biclustering, reference_biclustering):
- """Liu & Wang match score.
- Reference
- ---------
- Liu,X.,& Wang,L. (2006). Computing the maximum similarity bi-clusters of gene expression data.
- Bioinformatics,23(1),50-56.
- Horta,D.,& Campello,R. J. G. B. (2014). Similarity measures for comparing biclusterings.
- IEEE/ACM Transactions on computational Biology and Bioinformatics,11(5),942-954.
- Parameters
- ----------
- predicted_biclustering : biclustlib.model.Biclustering
- Predicted biclustering solution.
- reference_biclustering : biclustlib.model.Biclustering
- Reference biclustering solution.
- Returns
- -------
- lw_match_score : float
- Liu and Wang match score between 0.0 and 1.0.
- """
- check = check_biclusterings(predicted_biclustering, reference_biclustering)
- if isinstance(check, float):
- return check
- k = len(predicted_biclustering.biclusters)
- return sum(max((len(np.intersect1d(bp.rows, br.rows)) + len(np.intersect1d(bp.cols, br.cols))) /
- (len(np.union1d(bp.rows, br.rows)) + len(np.union1d(bp.cols, br.cols)))
- for br in reference_biclustering.biclusters)
- for bp in predicted_biclustering.biclusters) / k
- def union1d(ar1, ar2)))
- def crossGenotyper(args):
- ## Get the VCF file (filtered may be) generated by GATK.
- ## inputs:
- # 1) VCF file
- # 2) Parent1 and Parent2
- # 3) SNP matrix (hdf5 file)
- # 4) Bin length,default as 200Kbp
- # 5) Chromosome length
- log.info("loading genotype data for parents")
- if args[''father''] is not None:
- log.info("input files: %s and %s" % (args[''parents''], args[''father'']))
- if not os.path.isfile(args[''parents'']) and os.path.isfile(args[''father'']):
- die("either of the input files do not exists,please provide VCF/bed file for parent genotype information")
- (p1snpCHR, p1snpPOS, p1snpGT, p1snpWEI, p1DPmean) = snpmatch.parseInput(inFile = args[''parents''], logDebug = args[''logDebug''])
- (p2snpCHR, p2snpPOS, p2snpGT, p2snpWEI, p2DPmean) = snpmatch.parseInput(inFile = args[''father''], logDebug = args[''logDebug''])
- commonCHRs_ids = np.union1d(p1snpCHR, p2snpCHR)
- commonSNPsCHR = np.zeros(0, dtype=commonCHRs_ids.dtype)
- commonSNPsPOS = np.zeros(0, dtype=int)
- snpsP1 = np.zeros(0, dtype=''int8'')
- snpsP2 = np.zeros(0, dtype=''int8'')
- for i in commonCHRs_ids:
- perchrP1inds = np.where(p1snpCHR == i)[0]
- perchrP2inds = np.where(p2snpCHR == i)[0]
- perchrPositions = np.union1d(p1snpPOS[perchrP1inds], p2snpPOS[perchrP2inds])
- commonSNPsCHR = np.append(commonSNPsCHR, np.repeat(i, len(perchrPositions)))
- commonSNPsPOS = np.append(commonSNPsPOS, perchrPositions)
- perchrsnpsP1 = np.repeat(-1, len(perchrPositions)).astype(''int8'')
- perchrsnpsP2 = np.repeat(-1, len(perchrPositions)).astype(''int8'')
- perchrsnpsP1_inds = np.where(np.in1d(p1snpPOS[perchrP1inds], perchrPositions))[0]
- perchrsnpsP2_inds = np.where(np.in1d(p2snpPOS[perchrP2inds], perchrPositions))[0]
- snpsP1 = np.append(snpsP1, snpmatch.parseGT(p1snpGT[perchrsnpsP1_inds]))
- snpsP2 = np.append(snpsP2, snpmatch.parseGT(p2snpGT[perchrsnpsP2_inds]))
- log.info("done!")
- else:
- parents = args[''parents'']
- ## need to filter the SNPs present in C and M
- if not args[''hdf5accFile'']:
- snpmatch.die("needed a HDF5 genotype file and not specified")
- log.info("loading HDF5 file")
- g_acc = genotype.load_hdf5_genotype_data(args[''hdf5accFile''])
- ## die if either parents are not in the dataset
- #import ipdb; ipdb.set_trace()
- try:
- indP1 = np.where(g_acc.accessions == parents.split("x")[0])[0][0]
- indP2 = np.where(g_acc.accessions == parents.split("x")[1])[0][0]
- except:
- snpmatch.die("parents are not in the dataset")
- snpsP1 = g_acc.snps[:,indP1]
- snpsP2 = g_acc.snps[:,indP2]
- commonSNPsCHR = np.array(g_acc.chromosomes)
- commonSNPsPOS = np.array(g_acc.positions)
- log.info("done!")
- log.info("running cross genotyper")
- crossGenotypeWindows(commonSNPsCHR, commonSNPsPOS, snpsP1, snpsP2, args[''inFile''], args[''binLen''], args[''outFile''], args[''logDebug''])
- def test_boolean_cylinders_overlap():
- r"""Test to make sure that boolean objects (cylinders,overlap)
- behave the way we expect.
- Test overlapping cylinders.
- """
- ds = fake_amr_ds()
- cyl1 = ds.disk([0.45]*3, [1, 0.2, 0.2)
- cyl2 = ds.disk([0.55]*3, 0.2)
- # Get indices of both.
- i1 = cyl1["index","morton_index"]
- i2 = cyl2["index","morton_index"]
- # Make some booleans
- bo1 = cyl1 & cyl2
- bo2 = cyl1 - cyl2
- bo3 = cyl1 | cyl2
- bo4 = ds.union([cyl1, cyl2])
- bo5 = ds.intersection([cyl1, cyl2])
- # Now make sure the indices also behave as we expect.
- vlens = np.intersect1d(i1, i2)
- bite_disk = np.setdiff1d(i1, vlens)
- assert_array_equal(b2, bite_disk)
- assert_array_equal(b3, b5)
- bo6 = cyl1 ^ cyl2
- b6 = bo6["index", i2))
- del ds
- def test_boolean_mix_periodicity():
- r"""Test that a hybrid boolean region behaves as we expect.
- This also tests nested logic and that periodicity works.
- """
- ds = fake_amr_ds()
- re = ds.region([0.5]*3, [0.0]*3, [1]*3) # whole thing
- sp = ds.sphere([0.95]*3, 0.3) # wraps around
- cyl = ds.disk([0.05]*3,1,1], 0.1, 0.4) # wraps around
- # Get original indices
- rei = re["index","morton_index"]
- spi = sp["index","morton_index"]
- cyli = cyl["index","morton_index"]
- # Make some booleans
- # whole Box minux spherical bites at corners
- bo1 = re - sp
- # sphere plus cylinder
- bo2 = sp | cyl
- # a jumble,the region minus the sp+cyl
- bo3 = re - (sp | cyl)
- # Now make sure the indices also behave as we expect.
- bo4 = ds.union([re, sp, cyl])
- bo5 = ds.intersection([re, cyl])
- expect = np.setdiff1d(rei, spi)
- ii = bo1["index","morton_index"]
- ii.sort()
- assert_array_equal(expect, ii)
- #
- expect = np.union1d(spi, cyli)
- ii = bo2["index", cyli)
- expect = np.setdiff1d(rei, expect)
- ii = bo3["index", ii)
- b4 = bo4["index","morton_index"]
- b5.sort()
- ii = np.union1d(np.union1d(rei, cyli), spi)
- ii.sort()
- assert_array_equal(ii, b4)
- ii = np.intersect1d(np.intersect1d(rei, b5)
- bo6 = (re ^ sp) ^ cyl
- b6 = bo6["index", np.setxor1d(np.setxor1d(rei, spi), cyli))
- def test_boolean_ray_region_overlap():
- r"""Test to make sure that boolean objects (ray,region,overlap)
- behave the way we expect.
- Test overlapping ray and region. This also checks that the original
- objects don''t change as part of constructing the booleans.
- """
- ds = fake_amr_ds()
- re = ds.Box([0.25]*3, [0.75]*3)
- ra = ds.ray([0]*3, [1]*3)
- # Get indices of both.
- i1 = re["index","morton_index"]
- i2 = ra["index","morton_index"]
- # Make some booleans
- bo1 = re & ra
- bo2 = re - ra
- bo3 = re | ra
- bo4 = ds.union([re, ra])
- bo5 = ds.intersection([re, ra])
- # Now make sure the indices also behave as we expect.
- short_line = np.intersect1d(i1, i2)
- cube_minus_line = np.setdiff1d(i1, short_line)
- assert_array_equal(b2, cube_minus_line)
- assert_array_equal(b3, b5)
- bo6 = re ^ ra
- b6 = bo6["index", i2))
- def test_boolean_rays_overlap():
- r"""Test to make sure that boolean objects (rays,overlap)
- behave the way we expect.
- Test non-overlapping rays.
- """
- ds = fake_amr_ds()
- ra1 = ds.ray([0]*3, [1]*3)
- ra2 = ds.ray([0]*3, [0.5]*3)
- # Get indices of both.
- i1 = ra1["index","morton_index"]
- i1.sort()
- i2 = ra2["index","morton_index"]
- i2.sort()
- ii = np.concatenate((i1, i2))
- ii.sort()
- # Make some booleans
- bo1 = ra1 & ra2
- bo2 = ra1 - ra2
- bo3 = ra1 | ra2
- bo4 = ds.union([ra1, ra2])
- bo5 = ds.intersection([ra1, ra2])
- # Now make sure the indices also behave as we expect.
- short_line = np.intersect1d(i1, i2)
- short_line_b = np.setdiff1d(i1, i2)
- full_line = np.union1d(i1, short_line_b)
- assert_array_equal(b3, full_line)
- b4 = bo4["index", i1)
- assert_array_equal(b3, b5)
- bo6 = ra1 ^ ra2
- b6 = bo6["index", i2))
- def test_boolean_ray_slice_overlap():
- r"""Test to make sure that boolean objects (rays and slices,overlap)
- behave the way we expect.
- Test overlapping rays and slices.
- """
- ds = fake_amr_ds()
- sl = ds.r[:,0.25]
- ra = ds.ray([0, 0.25], 0.25])
- # Get indices of both.
- i1 = sl["index","morton_index"]
- i1.sort()
- i2 = ra["index","morton_index"]
- i1.sort()
- ii = np.concatenate((i1, i2))
- ii.sort()
- # Make some booleans
- bo1 = sl & ra
- bo2 = sl - ra
- bo3 = sl | ra
- bo4 = ds.union([sl, ra])
- bo5 = ds.intersection([sl, ra])
- # Now make sure the indices also behave as we expect.
- line = np.intersect1d(i1, i2)
- sheet_minus_line = np.setdiff1d(i1, i2)
- sheet = np.union1d(i1, sheet_minus_line)
- assert_array_equal(b3, sheet)
- b4 = bo4["index", b5)
- bo6 = sl ^ ra
- b6 = bo6["index", i2))
- def sample_rpn_outputs_wrt_gt_Boxes(Boxes, scores, gt_Boxes, is_training=False, only_positive=False):
- """sample Boxes for refined output"""
- Boxes, batch_inds = sample_rpn_outputs(Boxes, is_training, only_positive)
- if gt_Boxes.size > 0:
- overlaps = cython_bBox.bBox_overlaps(
- np.ascontiguousarray(Boxes[:, 0:4], dtype=np.float),
- np.ascontiguousarray(gt_Boxes[:, dtype=np.float))
- gt_assignment = overlaps.argmax(axis=1) # B
- max_overlaps = overlaps[np.arange(Boxes.shape[0]), gt_assignment] # B
- fg_inds = np.where(max_overlaps >= cfg.FLAGS.fg_threshold)[0]
- mask_fg_inds = np.where(max_overlaps >= cfg.FLAGS.mask_threshold)[0]
- if mask_fg_inds.size > cfg.FLAGS.masks_per_image:
- mask_fg_inds = np.random.choice(mask_fg_inds, size=cfg.FLAGS.masks_per_image, replace=False)
- if True:
- gt_argmax_overlaps = overlaps.argmax(axis=0) # G
- fg_inds = np.union1d(gt_argmax_overlaps, fg_inds)
- fg_rois = int(min(fg_inds.size, cfg.FLAGS.rois_per_image * cfg.FLAGS.fg_roi_fraction))
- if fg_inds.size > 0 and fg_rois < fg_inds.size:
- fg_inds = np.random.choice(fg_inds, size=fg_rois, replace=False)
- # Todo: sampling strategy
- bg_inds = np.where((max_overlaps < cfg.FLAGS.bg_threshold))[0]
- bg_rois = max(min(cfg.FLAGS.rois_per_image - fg_rois, fg_rois * 3), 64)
- if bg_inds.size > 0 and bg_rois < bg_inds.size:
- bg_inds = np.random.choice(bg_inds, size=bg_rois, replace=False)
- keep_inds = np.append(fg_inds, bg_inds)
- else:
- bg_inds = np.arange(Boxes.shape[0])
- bg_rois = min(int(cfg.FLAGS.rois_per_image * (1-cfg.FLAGS.fg_roi_fraction)), 64)
- if bg_rois < bg_inds.size:
- bg_inds = np.random.choice(bg_inds, replace=False)
- keep_inds = bg_inds
- mask_fg_inds = np.arange(0)
- return Boxes[keep_inds, :], scores[keep_inds], batch_inds[keep_inds],\\
- Boxes[mask_fg_inds, scores[mask_fg_inds], batch_inds[mask_fg_inds]
- def fit(self, X, T, max_iter=int(1e3), tol=1e-5):
- """Use training data ``X`` and ``T`` to fit a SVC models."""
- n_samples = X.shape[0]
- n_dual_vars = 2 * n_samples
- # Compute the Gram matrix of training data
- K = self.kernel.inner(X, X)
- # The equality constraints: H(x) = 0
- ones = np.ones(n_samples)
- A = np.concatenate((ones, -ones))
- cons = ({''type'': ''eq'', ''fun'': lambda x: A.dot(x), ''jac'': lambda x: A})
- # The inequality constaints: 0 <= G(x) <= C
- bnds = [(0, self.C) for i in range(n_dual_vars)]
- # The target function: (1/2)*x''*Q*x + p''*x
- Q = np.array(np.bmat([[K, -K], [-K, K]]))
- p = self.eps - A * np.concatenate((T, T))
- lagrange = lambda x: (0.5 * x.dot(Q).dot(x) + p.dot(x), Q.dot(x) + p)
- # Solve the quadratic program
- opt_solution = minimize(lagrange,
- np.zeros(n_dual_vars),
- method=''SLSQP'',
- constraints=cons,
- bounds=bnds,
- tol=tol,
- jac=True,
- options={''maxiter'': max_iter,
- ''disp'': True})
- self.dual_var = np.array([None, None], dtype=np.object)
- self.dual_var[0] = opt_solution.x[:n_samples]
- self.dual_var[1] = opt_solution.x[n_samples:]
- self.sv_indices = np.array([None, dtype=np.object)
- self.sv_indices[0] = np.nonzero((1 - np.isclose(self.dual_var[0], 0)))[
- 0]
- self.sv_indices[1] = np.nonzero((1 - np.isclose(self.dual_var[1], 0)))[
- 0]
- self.union_sv_inices = np.union1d(*self.sv_indices)
- self.inner_sv_indices = np.array([None, dtype=np.object)
- self.inner_sv_indices[0] = np.nonzero(
- (1 - np.isclose(self.dual_var[0], 0)) *
- (1 - np.isclose(self.dual_var[0], self.C)))[0]
- self.inner_sv_indices[1] = np.nonzero(
- (1 - np.isclose(self.dual_var[1], 0)) *
- (1 - np.isclose(self.dual_var[1], self.C)))[0]
- return self
- def select(self, channels, dataframe=False):
- """ return the channels listed in *channels* argument
- Parameters
- ----------
- channels : list
- list of channel names to be filtered
- dataframe: bool
- return a pandas DataFrame instead of a list of Signals; in this
- case the signals will be interpolated using the union of all
- timestamps
- Returns
- -------
- signals : list
- lsit of *Signal* objects based on the input channel list
- """
- # group channels by group index
- gps = {}
- for ch in channels:
- if ch in self.channels_db:
- for group, index in self.channels_db[ch]:
- if group not in gps:
- gps[group] = []
- gps[group].append(index)
- else:
- message = (''MDF filter error: ''
- ''Channel "{}" not found,it will be ignored'')
- warn(message.format(ch))
- continue
- # append filtered channels to new MDF
- signals = {}
- for group in gps:
- grp = self.groups[group]
- data = self._load_group_data(grp)
- for index in gps[group]:
- signal = self.get(group=group, index=index, data=data)
- signals[signal.name] = signal
- signals = [signals[channel] for channel in channels]
- if dataframe:
- times = [s.timestamps for s in signals]
- t = reduce(np.union1d, times).flatten().astype(np.float64)
- signals = [s.interp(t) for s in signals]
- times = None
- pandas_dict = {''t'': t}
- for sig in signals:
- pandas_dict[sig.name] = sig.samples
- signals = DataFrame.from_dict(pandas_dict)
- return signals
- def gesture_overlap_csv(csvpathgt, csvpathpred, seqlenght):
- """ Evaluate this sample against the ground truth file """
- maxGestures = 20
- # Get the list of gestures from the ground truth and frame activation
- gtGestures = []
- binvec_gt = numpy.zeros((maxGestures, seqlenght))
- with open(csvpathgt, ''rb'') as csvfilegt:
- csvgt = csv.reader(csvfilegt)
- for row in csvgt:
- binvec_gt[int(row[0])-1, int(row[1])-1:int(row[2])-1] = 1
- gtGestures.append(int(row[0]))
- # Get the list of gestures from prediction and frame activation
- predGestures = []
- binvec_pred = numpy.zeros((maxGestures, seqlenght))
- with open(csvpathpred, ''rb'') as csvfilepred:
- csvpred = csv.reader(csvfilepred)
- for row in csvpred:
- binvec_pred[int(row[0])-1, int(row[1])-1:int(row[2])-1] = 1
- predGestures.append(int(row[0]))
- # Get the list of gestures without repetitions for ground truth and predicton
- gtGestures = numpy.unique(gtGestures)
- predGestures = numpy.unique(predGestures)
- bgt = (numpy.argmax(binvec_gt,axis=0)+1) * (numpy.max(binvec_gt,axis=0)>0)
- bpred = (numpy.argmax(binvec_pred,axis=0)+1) * (numpy.max(binvec_pred,axis=0)>0)
- # Find false positives
- falsePos=numpy.setdiff1d(gtGestures,numpy.union1d(gtGestures,predGestures)))
- # Get overlaps for each gesture
- overlaps = []
- for idx in gtGestures:
- intersec = sum(binvec_gt[idx-1] * binvec_pred[idx-1])
- aux = binvec_gt[idx-1] + binvec_pred[idx-1]
- union = sum(aux > 0)
- overlaps.append(intersec/union)
- # Use real gestures and false positive gestures to calculate the final score
- return sum(overlaps)/(len(overlaps)+len(falsePos))
- def MergeWaveSets(waveset1, waveset2):
- """Return the union of the two wavelength sets.
- The union is computed using `numpy.union1d`,unless one or
- both of them is `None`.
- The merged result may sometimes contain numbers which are nearly
- equal but differ at levels as small as 1E-14. Having values this
- close together can cause problems due to effectively duplicate
- wavelength values. Therefore,wavelength values having differences
- smaller than or equal to ``pysynphot.spectrum.MERGETHRESH``
- (defaults to 1E-12) are considered as the same.
- Parameters
- ----------
- waveset1,waveset2 : array_like or `None`
- Wavelength sets to combine.
- Returns
- -------
- MergedWaveSet : array_like or `None`
- Merged wavelength set. It is `None` if both inputs are such.
- """
- if waveset1 is None and waveset2 is not None:
- MergedWaveSet = waveset2
- elif waveset2 is None and waveset1 is not None:
- MergedWaveSet = waveset1
- elif waveset1 is None and waveset2 is None:
- MergedWaveSet = None
- else:
- MergedWaveSet = N.union1d(waveset1, waveset2)
- # The merged wave sets may sometimes contain numbers which are nearly
- # equal but differ at levels as small as 1e-14. Having values this
- # close together can cause problems down the line so here we test
- # whether any such small differences are present,with a small
- # difference defined as less than MERGETHRESH.
- #
- # If small differences are present we make a copy of the union''ed array
- # with the lower of the close together pairs removed.
- delta = MergedWaveSet[1:] - MergedWaveSet[:-1]
- if not (delta > MERGETHRESH).all():
- newlen = len(delta[delta > MERGETHRESH]) + 1
- newmerged = N.zeros(newlen, dtype=MergedWaveSet.dtype)
- newmerged[:-1] = MergedWaveSet[:-1][delta > MERGETHRESH]
- newmerged[-1] = MergedWaveSet[-1]
- MergedWaveSet = newmerged
- return MergedWaveSet
- def get_ids_in_region(
- self, cutout_fcn, resource, resolution, corner, extent,
- t_range=[0, version=0):
- """
- Method to get all the ids within a defined region.
- Args:
- cutout_fcn (function): SpatialDB''s cutout method. Provided for naive search of ids in sub-regions
- resource (project.BossResource): Data model info based on the request or target resource
- resolution (int): the resolution level
- corner ((int,int,int)): xyz location of the corner of the region
- extent ((int,int)): xyz extents of the region
- t_range (optional[list[int]]): time range,defaults to [0,1]
- version (optional[int]): Reserved for future use. Defaults to 0
- Returns:
- (dict): { ''ids'': [''1'',''4'',''8''] }
- """
- # Identify sub-region entirely contained by cuboids.
- cuboids = Region.get_cuboid_aligned_sub_region(
- resolution, extent)
- # Get all non-cuboid aligned sub-regions.
- non_cuboid_list = Region.get_all_partial_sub_regions(
- resolution, extent)
- # Do cutouts on each partial region and build id set.
- id_set = np.array([], dtype=''uint64'')
- for partial_region in non_cuboid_list:
- extent = partial_region.extent
- if extent[0] == 0 or extent[1] == 0 or extent[2] == 0:
- continue
- id_arr = self._get_ids_from_cutout(
- cutout_fcn,
- partial_region.corner, partial_region.extent,
- t_range, version)
- # Todo: do a unique first? perf test
- id_set = np.union1d(id_set, id_arr)
- # Get ids from dynamo for sub-region that''s 100% cuboid aligned.
- obj_key_list = self._get_object_keys(
- resource, cuboids, t_range)
- cuboid_ids = self.obj_ind.get_ids_in_cuboids(obj_key_list, version)
- cuboid_ids_arr = np.asarray([int(id) for id in cuboid_ids], dtype=''uint64'')
- # Union ids from cuboid aligned sub-region.
- id_set = np.union1d(id_set, cuboid_ids_arr)
- # Convert ids back to strings for transmission via HTTP.
- ids_as_str = [''%d'' % n for n in id_set]
- return { ''ids'': ids_as_str }
- def sample_rpn_outputs_wrt_gt_Boxes(Boxes, gt_assignment] # B
- fg_inds = np.where(max_overlaps >= cfg.FLAGS.fg_threshold)[0]
- if _DEBUG and np.argmax(overlaps[fg_inds],axis=1).size < gt_Boxes.size/5.0:
- print("gt_size")
- print(gt_Boxes)
- gt_height = (gt_Boxes[:,2]-gt_Boxes[:,0])
- gt_width = (gt_Boxes[:,3]-gt_Boxes[:,1])
- gt_dim = np.vstack((gt_height, gt_width))
- print(np.transpose(gt_dim))
- #print(gt_height)
- #print(gt_width)
- print(''SAMPLE: %d after overlaps by %s'' % (len(fg_inds),cfg.FLAGS.fg_threshold))
- print("detected object no.")
- print(np.argmax(overlaps[fg_inds],axis=1))
- print("total object")
- print(gt_Boxes.size/5.0)
- mask_fg_inds = np.where(max_overlaps >= cfg.FLAGS.mask_threshold)[0]
- if mask_fg_inds.size > cfg.FLAGS.masks_per_image:
- mask_fg_inds = np.random.choice(mask_fg_inds, 8)#64
- if bg_inds.size > 0 and bg_rois < bg_inds.size:
- bg_inds = np.random.choice(bg_inds, replace=False)
- keep_inds = np.append(fg_inds, bg_inds)
- #print(gt_Boxes[np.argmax(overlaps[fg_inds],axis=1),4])
- else:
- bg_inds = np.arange(Boxes.shape[0])
- bg_rois = min(int(cfg.FLAGS.rois_per_image * (1-cfg.FLAGS.fg_roi_fraction)), 8)#64
- if bg_rois < bg_inds.size:
- bg_inds = np.random.choice(bg_inds, batch_inds[mask_fg_inds]
- def _get_points(self):
- # in case only one or no source is enabled
- if not (self.src1 and self.src1.enabled):
- if (self.src2 and self.src2.enabled):
- return self.src2.points
- else:
- return np.zeros((5, 3))
- elif not (self.src2 and self.src2.enabled):
- return self.src1.points
- # Average method
- if self.method == ''Average'':
- if len(np.union1d(self.src1.use, self.src2.use)) < 5:
- error(None, "Need at least one source for each point.",
- "Marker Average Error")
- return np.zeros((5, 3))
- pts = (self.src1.points + self.src2.points) / 2.
- for i in np.setdiff1d(self.src1.use, self.src2.use):
- pts[i] = self.src1.points[i]
- for i in np.setdiff1d(self.src2.use, self.src1.use):
- pts[i] = self.src2.points[i]
- return pts
- # Transform method
- idx = np.intersect1d(self.src1.use, self.src2.use, assume_unique=True)
- if len(idx) < 3:
- error(None, "Need at least three shared points for trans"
- "formation.", "Marker Interpolation Error")
- return np.zeros((5, 3))
- src_pts = self.src1.points[idx]
- tgt_pts = self.src2.points[idx]
- est = fit_matched_points(src_pts, tgt_pts, out=''params'')
- rot = np.array(est[:3]) / 2.
- tra = np.array(est[3:]) / 2.
- if len(self.src1.use) == 5:
- trans = np.dot(translation(*tra), rotation(*rot))
- pts = apply_trans(trans, self.src1.points)
- elif len(self.src2.use) == 5:
- trans = np.dot(translation(* -tra), rotation(* -rot))
- pts = apply_trans(trans, self.src2.points)
- else:
- trans1 = np.dot(translation(*tra), rotation(*rot))
- pts = apply_trans(trans1, self.src1.points)
- trans2 = np.dot(translation(* -tra), rotation(* -rot))
- for i in np.setdiff1d(self.src2.use, self.src1.use):
- pts[i] = apply_trans(trans2, self.src2.points[i])
- return pts
- def sample_rpn_outputs_wrt_gt_Boxes(Boxes, batch_inds[mask_fg_inds]

Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
如何解决Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable?
晚安, 尝试打印以下内容时,我在 jupyter 中遇到了 numpy 问题,并且得到了一个 错误: 需要注意的是python版本是3.8.8。 我先用 spyder 测试它,它运行正确,它给了我预期的结果
使用 Spyder:
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
Results
0.6604903457995978
0.8236300859753154
0.16067650689842816
0.6967868357083673
0.4231597934445466
现在有了 jupyter
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
-------------------------------------------------- ------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-78-0c6a801b3ea9> in <module>
2 for i in range (5):
3 n = np.random.rand ()
----> 4 print (n)
TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable
感谢您对我如何在 Jupyter 中解决此问题的帮助。
非常感谢您抽出宝贵时间。
阿特,约翰”
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)

numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
今天看到这样一句代码:
xb = np.random.random((nb, d)).astype(''float32'') #创建一个二维随机数矩阵(nb行d列)
xb[:, 0] += np.arange(nb) / 1000. #将矩阵第一列的每个数加上一个值要理解这两句代码需要理解三个函数
1、生成随机数
numpy.random.random(size=None)
size为None时,返回float。
size不为None时,返回numpy.ndarray。例如numpy.random.random((1,2)),返回1行2列的numpy数组
2、对numpy数组中每一个元素进行类型转换
numpy.ndarray.astype(dtype)
返回numpy.ndarray。例如 numpy.array([1, 2, 2.5]).astype(int),返回numpy数组 [1, 2, 2]
3、获取等差数列
numpy.arange([start,]stop,[step,]dtype=None)
功能类似python中自带的range()和numpy中的numpy.linspace
返回numpy数组。例如numpy.arange(3),返回numpy数组[0, 1, 2]

numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()
numpy.ravel(a, order=''C'')
Return a flattened array
numpy.chararray.flatten(order=''C'')
Return a copy of the array collapsed into one dimension
numpy.squeeze(a, axis=None)
Remove single-dimensional entries from the shape of an array.
相同点: 将多维数组 降为 一维数组
不同点:
ravel() 返回的是视图(view),意味着改变元素的值会影响原始数组元素的值;
flatten() 返回的是拷贝,意味着改变元素的值不会影响原始数组;
squeeze()返回的是视图(view),仅仅是将shape中dimension为1的维度去掉;
ravel()示例:
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.ravel()
16 print("a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19
20 print(a)
21 log_type(''a'',a)
flatten()示例
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.flatten()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)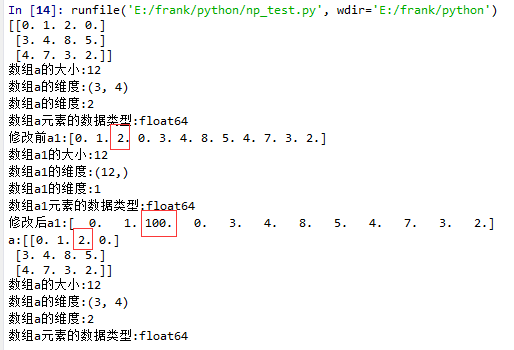
squeeze()示例:
1. 没有single-dimensional entries的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)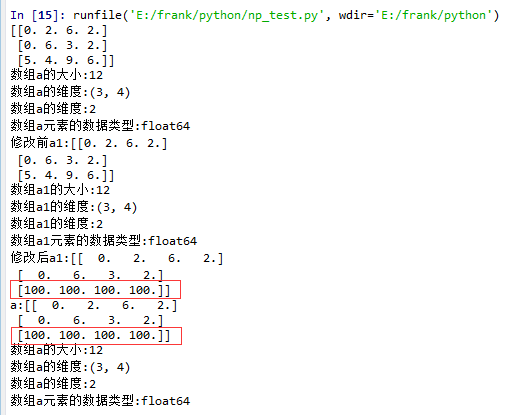
从结果中可以看到,当没有single-dimensional entries时,squeeze()返回额数组对象是一个view,而不是copy。
2. 有single-dimentional entries 的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((1,3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)

Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性
一、Numpy数组创建
part 1:np.linspace(起始值,终止值,元素总个数
import numpy as np
''''''
numpy中的ndarray数组
''''''
ary = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(ary)
ary = ary * 10
print(ary)
''''''
ndarray对象的创建
''''''
# 创建二维数组
# np.array([[],[],...])
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]])
print(a)
# np.arange(起始值, 结束值, 步长(默认1))
b = np.arange(1, 10, 1)
print(b)
print("-------------np.zeros(数组元素个数, dtype=''数组元素类型'')-----")
# 创建一维数组:
c = np.zeros(10)
print(c, ''; c.dtype:'', c.dtype)
# 创建二维数组:
print(np.zeros ((3,4)))
print("----------np.ones(数组元素个数, dtype=''数组元素类型'')--------")
# 创建一维数组:
d = np.ones(10, dtype=''int64'')
print(d, ''; d.dtype:'', d.dtype)
# 创建三维数组:
print(np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int32 ))
# 打印维度
print(np.ones( (2,3,4), dtype=np.int32 ).ndim) # 返回:3(维)
结果图:

part 2 :np.linspace ( 起始值,终止值,元素总个数)
import numpy as np
a = np.arange( 10, 30, 5 )
b = np.arange( 0, 2, 0.3 )
c = np.arange(12).reshape(4,3)
d = np.random.random((2,3)) # 取-1到1之间的随机数,要求设置为诶2行3列的结构
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
print(d)
print("-----------------")
from numpy import pi
print(np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 100 ))
print("-------------np.linspace(起始值,终止值,元素总个数)------------------")
print(np.sin(np.linspace( 0, 2*pi, 100 )))
结果图:

二、Numpy的ndarray对象属性:
数组的结构:array.shape
数组的维度:array.ndim
元素的类型:array.dtype
数组元素的个数:array.size
数组的索引(下标):array[0]
''''''
数组的基本属性
''''''
import numpy as np
print("--------------------案例1:------------------------------")
a = np.arange(15).reshape(3, 5)
print(a)
print(a.shape) # 打印数组结构
print(len(a)) # 打印有多少行
print(a.ndim) # 打印维度
print(a.dtype) # 打印a数组内的元素的数据类型
# print(a.dtype.name)
print(a.size) # 打印数组的总元素个数
print("-------------------案例2:---------------------------")
a = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
print(a)
# 测试数组的基本属性
print(''a.shape:'', a.shape)
print(''a.size:'', a.size)
print(''len(a):'', len(a))
# a.shape = (6, ) # 此格式可将原数组结构变成1行6列的数据结构
# print(a, ''a.shape:'', a.shape)
# 数组元素的索引
ary = np.arange(1, 28)
ary.shape = (3, 3, 3) # 创建三维数组
print("ary.shape:",ary.shape,"\n",ary )
print("-----------------")
print(''ary[0]:'', ary[0])
print(''ary[0][0]:'', ary[0][0])
print(''ary[0][0][0]:'', ary[0][0][0])
print(''ary[0,0,0]:'', ary[0, 0, 0])
print("-----------------")
# 遍历三维数组:遍历出数组里的每个元素
for i in range(ary.shape[0]):
for j in range(ary.shape[1]):
for k in range(ary.shape[2]):
print(ary[i, j, k], end='' '')
结果图:

今天关于Python numpy 模块-union1d() 实例源码和python中numpy模块的介绍到此结束,谢谢您的阅读,有关Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()、Numpy:数组创建 numpy.arrray() , numpy.arange()、np.linspace ()、数组基本属性等更多相关知识的信息可以在本站进行查询。
本文标签:





