本文将带您了解关于Pythonnumpy模块-ComplexWarning()实例源码的新内容,同时我们还将为您解释python中numpy模块的相关知识,另外,我们还将为您提供关于ComplexWa
本文将带您了解关于Python numpy 模块-ComplexWarning() 实例源码的新内容,同时我们还将为您解释python中numpy模块的相关知识,另外,我们还将为您提供关于ComplexWarning:将复数值转换为实数会丢弃虚部、Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()的实用信息。
本文目录一览:- Python numpy 模块-ComplexWarning() 实例源码(python中numpy模块)
- ComplexWarning:将复数值转换为实数会丢弃虚部
- Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
- numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
- numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()

Python numpy 模块-ComplexWarning() 实例源码(python中numpy模块)
Python numpy 模块,ComplexWarning() 实例源码
我们从Python开源项目中,提取了以下40个代码示例,用于说明如何使用numpy.ComplexWarning()。
- def test_ticket_1539(self):
- dtypes = [x for x in np.typeDict.values()
- if (issubclass(x, np.number)
- and not issubclass(x, np.timedelta64))]
- a = np.array([], dtypes[0])
- failures = []
- # ignore complex warnings
- with warnings.catch_warnings():
- warnings.simplefilter(''ignore'', np.ComplexWarning)
- for x in dtypes:
- b = a.astype(x)
- for y in dtypes:
- c = a.astype(y)
- try:
- np.dot(b, c)
- except TypeError:
- failures.append((x, y))
- if failures:
- raise AssertionError("Failures: %r" % failures)
- def test_boolean_index_cast_assign(self):
- # Setup the boolean index and float arrays.
- shape = (8, 63)
- bool_index = np.zeros(shape).astype(bool)
- bool_index[0, 1] = True
- zero_array = np.zeros(shape)
- # Assigning float is fine.
- zero_array[bool_index] = np.array([1])
- assert_equal(zero_array[0, 1], 1)
- # Fancy indexing works,although we get a cast warning.
- assert_warns(np.ComplexWarning,
- zero_array.__setitem__, ([0], [1]), np.array([2 + 1j]))
- assert_equal(zero_array[0, 2) # No complex part
- # Cast complex to float,throwing away the imaginary portion.
- assert_warns(np.ComplexWarning, bool_index, np.array([1j]))
- assert_equal(zero_array[0, 0)
- def test_ticket_1539(self):
- dtypes = [x for x in np.typeDict.values()
- if (issubclass(x, y))
- if failures:
- raise AssertionError("Failures: %r" % failures)
- def test_boolean_index_cast_assign(self):
- # Setup the boolean index and float arrays.
- shape = (8, 0)
- def test_ticket_1539(self):
- dtypes = [x for x in np.typeDict.values()
- if (issubclass(x, y))
- if failures:
- raise AssertionError("Failures: %r" % failures)
- def test_boolean_index_cast_assign(self):
- # Setup the boolean index and float arrays.
- shape = (8, 0)
- def test_ticket_1539(self):
- dtypes = [x for x in np.typeDict.values()
- if (issubclass(x, y))
- if failures:
- raise AssertionError("Failures: %r" % failures)
- def test_boolean_index_cast_assign(self):
- # Setup the boolean index and float arrays.
- shape = (8, 0)
- def test_ticket_1539(self):
- dtypes = [x for x in np.typeDict.values()
- if (issubclass(x, y))
- if failures:
- raise AssertionError("Failures: %r" % failures)
- def test_boolean_index_cast_assign(self):
- # Setup the boolean index and float arrays.
- shape = (8, 0)
- def test_boolean_index_cast_assign(self):
- # Setup the boolean index and float arrays.
- shape = (8, 0)
- def test_dtype_from_dtype(self):
- mat = np.eye(3)
- codes = ''efdgFDG''
- for nf, rf in zip(self.nanfuncs, self.stdfuncs):
- for c in codes:
- with suppress_warnings() as sup:
- if nf in {np.nanstd, np.nanvar} and c in ''FDG'':
- # Giving the warning is a small bug,see gh-8000
- sup.filter(np.ComplexWarning)
- tgt = rf(mat, dtype=np.dtype(c), axis=1).dtype.type
- res = nf(mat, axis=1).dtype.type
- assert_(res is tgt)
- # scalar case
- tgt = rf(mat, axis=None).dtype.type
- res = nf(mat, axis=None).dtype.type
- assert_(res is tgt)
- def test_ddof_too_big(self):
- nanfuncs = [np.nanvar, np.nanstd]
- stdfuncs = [np.var, np.std]
- dsize = [len(d) for d in _rdat]
- for nf, rf in zip(nanfuncs, stdfuncs):
- for ddof in range(5):
- with suppress_warnings() as sup:
- sup.record(RuntimeWarning)
- sup.filter(np.ComplexWarning)
- tgt = [ddof >= d for d in dsize]
- res = nf(_ndat, axis=1, ddof=ddof)
- assert_equal(np.isnan(res), tgt)
- if any(tgt):
- assert_(len(sup.log) == 1)
- else:
- assert_(len(sup.log) == 0)
- def perform(self, node, inputs, outputs):
- # Kalbfleisch and Lawless,J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 80 (1985) Equation 3.4
- # Kind of... You need to do some algebra from there to arrive at
- # this expression.
- (A, gA) = inputs
- (out,) = outputs
- w, V = scipy.linalg.eig(A, right=True)
- U = scipy.linalg.inv(V).T
- exp_w = numpy.exp(w)
- X = numpy.subtract.outer(exp_w, exp_w) / numpy.subtract.outer(w, w)
- numpy.fill_diagonal(X, exp_w)
- Y = U.dot(V.T.dot(gA).dot(U) * X).dot(V.T)
- with warnings.catch_warnings():
- warnings.simplefilter("ignore", numpy.ComplexWarning)
- out[0] = Y.astype(A.dtype)
- def test_ticket_1539(self):
- dtypes = [x for x in np.typeDict.values()
- if (issubclass(x, y))
- if failures:
- raise AssertionError("Failures: %r" % failures)
- def test_boolean_index_cast_assign(self):
- # Setup the boolean index and float arrays.
- shape = (8, 0)
- def test_complex_scalar_warning(self):
- for tp in [np.csingle, np.cdouble, np.clongdouble]:
- x = tp(1+2j)
- assert_warns(np.ComplexWarning, float, x)
- with warnings.catch_warnings():
- warnings.simplefilter(''ignore'')
- assert_equal(float(x), float(x.real))
- def test_iter_buffered_cast_byteswapped():
- # Test that buffering can handle a cast which requires swap->cast->swap
- a = np.arange(10, dtype=''f4'').newbyteorder().byteswap()
- i = nditer(a, [''buffered'', ''external_loop''],
- [[''readwrite'', ''nbo'', ''aligned'']],
- casting=''same_kind'',
- op_dtypes=[np.dtype(''f8'').newbyteorder()],
- buffersize=3)
- for v in i:
- v[...] *= 2
- assert_equal(a, 2*np.arange(10, dtype=''f4''))
- try:
- warnings.simplefilter("ignore", np.ComplexWarning)
- a = np.arange(10, dtype=''f8'').newbyteorder().byteswap()
- i = nditer(a,
- [[''readwrite'',
- casting=''unsafe'',
- op_dtypes=[np.dtype(''c8'').newbyteorder()],
- buffersize=3)
- for v in i:
- v[...] *= 2
- assert_equal(a, dtype=''f8''))
- finally:
- warnings.simplefilter("default", np.ComplexWarning)
- def test_complex_warning(self):
- x = np.array([1, 2])
- y = np.array([1-2j, 1+2j])
- with warnings.catch_warnings():
- warnings.simplefilter("error", np.ComplexWarning)
- assert_raises(np.ComplexWarning, x.__setitem__, slice(None), y)
- assert_equal(x, [1, 2])
- def test_pad_default(self, xp, dtype):
- array = xp.array(self.array, dtype=dtype)
- # Older version of NumPy(<1.12) can emit ComplexWarning
- def f():
- return xp.pad(array, self.pad_width, mode=self.mode)
- if xp is numpy:
- with warnings.catch_warnings():
- warnings.simplefilter(''ignore'', numpy.ComplexWarning)
- return f()
- else:
- return f()
- def test_pad(self, mode=self.mode,
- constant_values=self.constant_values)
- if xp is numpy:
- with warnings.catch_warnings():
- warnings.simplefilter(''ignore'', numpy.ComplexWarning)
- return f()
- else:
- return f()
- def test_complex_scalar_warning(self):
- for tp in [np.csingle, float(x.real))
- def test_iter_buffered_cast_byteswapped():
- # Test that buffering can handle a cast which requires swap->cast->swap
- a = np.arange(10, np.ComplexWarning)
- def test_complex_warning(self):
- x = np.array([1, 2])
- def test_complex_scalar_warning(self):
- for tp in [np.csingle, float(x.real))
- def test_iter_buffered_cast_byteswapped():
- # Test that buffering can handle a cast which requires swap->cast->swap
- a = np.arange(10, np.ComplexWarning)
- def test_complex_warning(self):
- x = np.array([1, 2])
- def test_complex_scalar_warning(self):
- for tp in [np.csingle, float(x.real))
- def test_iter_buffered_cast_byteswapped():
- # Test that buffering can handle a cast which requires swap->cast->swap
- a = np.arange(10, np.ComplexWarning)
- def test_complex_warning(self):
- x = np.array([1, 2])
- def test_complex_scalar_warning(self):
- for tp in [np.csingle, float(x.real))
- def test_iter_buffered_cast_byteswapped():
- # Test that buffering can handle a cast which requires swap->cast->swap
- a = np.arange(10, np.ComplexWarning)
- def test_complex_warning(self):
- x = np.array([1, 2])
- def test_complex_scalar_warning(self):
- for tp in [np.csingle, x)
- with suppress_warnings() as sup:
- sup.filter(np.ComplexWarning)
- assert_equal(float(x), float(x.real))
- def test_iter_buffered_cast_byteswapped():
- # Test that buffering can handle a cast which requires swap->cast->swap
- a = np.arange(10, dtype=''f4''))
- with suppress_warnings() as sup:
- sup.filter(np.ComplexWarning)
- a = np.arange(10, dtype=''f8''))
- def test_complex_warning(self):
- x = np.array([1, 2])
- def test_complex_scalar_warning(self):
- for tp in [np.csingle, float(x.real))
- def test_iter_buffered_cast_byteswapped():
- # Test that buffering can handle a cast which requires swap->cast->swap
- a = np.arange(10, np.ComplexWarning)
- def test_complex_warning(self):
- x = np.array([1, 2])
- def conv(self, img, kern, mode="valid", dilation=1):
- """
- Basic slow Python 2D or 3D convolution for DebugMode
- """
- if not imported_scipy_signal:
- raise NotImplementedError(
- "AbstractConv perform requires the python package"
- " for scipy.signal to be installed.")
- if not (mode in (''valid'', ''full'')):
- raise ValueError(
- ''invalid mode {},which must be either ''
- ''"valid" or "full"''.format(mode))
- if isinstance(dilation, integer_types):
- dilation = (dilation,) * self.convdim
- if len(dilation) != self.convdim:
- raise ValueError(
- ''invalid dilation {},expected {} values''.format(dilation,
- self.convdim))
- out_shape = get_conv_output_shape(img.shape, kern.shape,
- mode, [1] * self.convdim, dilation)
- out = numpy.zeros(out_shape, dtype=img.dtype)
- dil_kern_shp = kern.shape[:-self.convdim] + tuple(
- (kern.shape[-self.convdim + i] - 1) * dilation[i] + 1
- for i in range(self.convdim))
- dilated_kern = numpy.zeros(dil_kern_shp, dtype=kern.dtype)
- dilated_kern[(slice(None), slice(None)) +
- tuple(slice(None, None, dilation[i]) for i in range(self.convdim))
- ] = kern
- if self.convdim == 2:
- val = _valfrommode(mode)
- bval = _bvalfromboundary(''fill'')
- with warnings.catch_warnings():
- warnings.simplefilter(''ignore'', numpy.ComplexWarning)
- for b in xrange(img.shape[0]):
- for n in xrange(kern.shape[0]):
- for im0 in xrange(img.shape[1]):
- # some cast generates a warning here
- out[b, n, ...] += _convolve2d(img[b, im0, ...],
- dilated_kern[n,
- 1, val, bval, 0)
- elif self.convdim == 3:
- for b in xrange(img.shape[0]):
- for n in xrange(kern.shape[0]):
- for im0 in xrange(img.shape[1]):
- out[b, ...] += convolve(img[b,
- dilated_kern[n,
- mode)
- else:
- raise NotImplementedError(''only 2D and 3D convolution are implemented'')
- return out

ComplexWarning:将复数值转换为实数会丢弃虚部
如何解决ComplexWarning:将复数值转换为实数会丢弃虚部?
我想知道如何解决这个问题。
我想用matplotlib.pyplot绘制一个复杂的函数。
Python显示了不正确的图形,因此显示以下内容:
返回数组(a,dtype,copy = False,order = order)
ComplexWarning:将复杂值转换为实数会丢弃虚部
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def f(time):
function=(1+time)+ 1j*(1-time)
return function
x = plt.subplot()
time= np.arange(0,np.pi*2,0.2,dtype="complex_")
plt.plot(time,f(time),lw=2,color="violet",linestyle= "-")
plt.title("Gráfica",fontsize=20,color="violet")
plt.xlabel("Time")
plt.ylabel("Complex Number")
plt.show()
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)

Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable
如何解决Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable?
晚安, 尝试打印以下内容时,我在 jupyter 中遇到了 numpy 问题,并且得到了一个 错误: 需要注意的是python版本是3.8.8。 我先用 spyder 测试它,它运行正确,它给了我预期的结果
使用 Spyder:
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
Results
0.6604903457995978
0.8236300859753154
0.16067650689842816
0.6967868357083673
0.4231597934445466
现在有了 jupyter
import numpy as np
for i in range (5):
n = np.random.rand ()
print (n)
-------------------------------------------------- ------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-78-0c6a801b3ea9> in <module>
2 for i in range (5):
3 n = np.random.rand ()
----> 4 print (n)
TypeError: ''numpy.ndarray'' object is not callable
感谢您对我如何在 Jupyter 中解决此问题的帮助。
非常感谢您抽出宝贵时间。
阿特,约翰”
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)

numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange
今天看到这样一句代码:
xb = np.random.random((nb, d)).astype(''float32'') #创建一个二维随机数矩阵(nb行d列)
xb[:, 0] += np.arange(nb) / 1000. #将矩阵第一列的每个数加上一个值要理解这两句代码需要理解三个函数
1、生成随机数
numpy.random.random(size=None)
size为None时,返回float。
size不为None时,返回numpy.ndarray。例如numpy.random.random((1,2)),返回1行2列的numpy数组
2、对numpy数组中每一个元素进行类型转换
numpy.ndarray.astype(dtype)
返回numpy.ndarray。例如 numpy.array([1, 2, 2.5]).astype(int),返回numpy数组 [1, 2, 2]
3、获取等差数列
numpy.arange([start,]stop,[step,]dtype=None)
功能类似python中自带的range()和numpy中的numpy.linspace
返回numpy数组。例如numpy.arange(3),返回numpy数组[0, 1, 2]

numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()
numpy.ravel(a, order=''C'')
Return a flattened array
numpy.chararray.flatten(order=''C'')
Return a copy of the array collapsed into one dimension
numpy.squeeze(a, axis=None)
Remove single-dimensional entries from the shape of an array.
相同点: 将多维数组 降为 一维数组
不同点:
ravel() 返回的是视图(view),意味着改变元素的值会影响原始数组元素的值;
flatten() 返回的是拷贝,意味着改变元素的值不会影响原始数组;
squeeze()返回的是视图(view),仅仅是将shape中dimension为1的维度去掉;
ravel()示例:
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.ravel()
16 print("a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19
20 print(a)
21 log_type(''a'',a)
flatten()示例
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.flatten()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)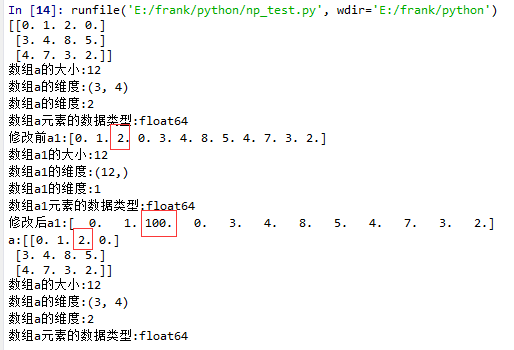
squeeze()示例:
1. 没有single-dimensional entries的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)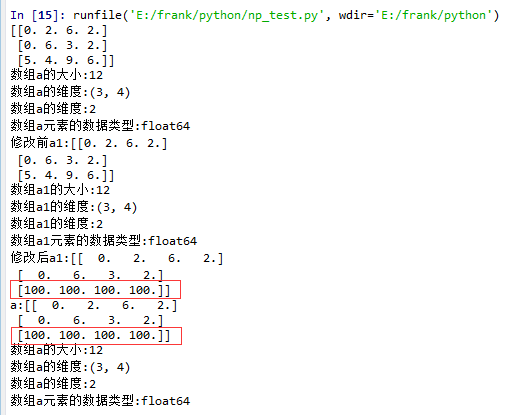
从结果中可以看到,当没有single-dimensional entries时,squeeze()返回额数组对象是一个view,而不是copy。
2. 有single-dimentional entries 的情况
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 import numpy as np
3
4 def log_type(name,arr):
5 print("数组{}的大小:{}".format(name,arr.size))
6 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.shape))
7 print("数组{}的维度:{}".format(name,arr.ndim))
8 print("数组{}元素的数据类型:{}".format(name,arr.dtype))
9 #print("数组:{}".format(arr.data))
10
11 a = np.floor(10*np.random.random((1,3,4)))
12 print(a)
13 log_type(''a'',a)
14
15 a1 = a.squeeze()
16 print("修改前a1:{}".format(a1))
17 log_type(''a1'',a1)
18 a1[2] = 100
19 print("修改后a1:{}".format(a1))
20
21 print("a:{}".format(a))
22 log_type(''a'',a)
我们今天的关于Python numpy 模块-ComplexWarning() 实例源码和python中numpy模块的分享已经告一段落,感谢您的关注,如果您想了解更多关于ComplexWarning:将复数值转换为实数会丢弃虚部、Jupyter 中的 Numpy 在打印时出错(Python 版本 3.8.8):TypeError: 'numpy.ndarray' object is not callable、numpy.random.random & numpy.ndarray.astype & numpy.arange、numpy.ravel()/numpy.flatten()/numpy.squeeze()的相关信息,请在本站查询。
本文标签:





