对于SpringBoot服务注入到doFiler感兴趣的读者,本文将提供您所需要的所有信息,我们将详细讲解springboot注入service,并且为您提供关于5、SpringBoot的Profil
对于Spring Boot服务注入到doFiler感兴趣的读者,本文将提供您所需要的所有信息,我们将详细讲解springboot注入service,并且为您提供关于5、SpringBoot 的 Profile 功能、Consul+Spring boot 的服务注册和服务注销、docker 带参数启动 配合 springboot profile、Maven 之 profile 与Spring boot 的 profile的宝贵知识。
本文目录一览:- Spring Boot服务注入到doFiler(springboot注入service)
- 5、SpringBoot 的 Profile 功能
- Consul+Spring boot 的服务注册和服务注销
- docker 带参数启动 配合 springboot profile
- Maven 之 profile 与Spring boot 的 profile

Spring Boot服务注入到doFiler(springboot注入service)
我正在尝试将身份验证服务注入Filter-
@AutowiredAuthRequestService authService;并在doFiler方法中使用它-
@Overridepublic void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException { HttpServletRequest req = (HttpServletRequest) request; System.out.println("SAPServiceFilter: "+ req.getRequestURI()); //TODO - create auth sender authService.isAuthnticate((HttpServletRequest)request); //null chain.doFilter(request, response);}我的过滤器类位于类的子包中,@SpringBootApplication并带有@service-
@Servicepublic class AuthRequestService { @PostConstruct public void init() { System.out.println("AuthRequestService @PostConstruct"); } public boolean isAuthnticate(HttpServletRequest request) { System.out.println("isAuthnticate"); return true; }}当使用-列出我的所有豆子时,该类也会出现
for (String name : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) { System.out.println(name);}仍然当调试authService为null时,向过滤器注册的最后一件事FilterRegistrationBean-
FilterRegistrationBean<SAPServiceFilter> filterRegBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>();filterRegBean.setFilter(new SAPServiceFilter());答案1
小编典典您可以使用构造函数注入。假设您的过滤器注册Bean位于组件中,并且可以访问该服务,您可以在其中自动进行连接并将其传递给构造函数
@Autowired AuthRequestService authRequestService;[...]FilterRegistrationBean<SAPServiceFilter> filterRegBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>();filterRegBean.setFilter(new SAPServiceFilter(authRequestService));
5、SpringBoot 的 Profile 功能
1.1、功能介绍
配置文件默认使用application.properties、application-default.properties
如果需要指定其他配置文件,可以在命令行参数中指定,spring.profiles.default=xxx
激活profile
spring.profiles.active=xxx
它与default配置文件互斥
希望两个配置文件同时被激活
spring.profiles.include=xxx,xxx
指定profile前缀,在命令行参数中配置,不推荐
spring.config.name=xxx
1.2、Profile 解析
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 发出环境已准备好事件
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(
getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
// ConfigFileApplicationListener
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
List<environmentpostprocessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
postProcessors.add(this);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
// 这边上篇文章已经分析过,最后一个postProcessor就是它自己,ConfigFileApplicationListener,进去看
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
addPropertySources(environment, application.getResourceLoader());
}
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
// 添加一个随机属性源
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
// 这里面会解析profile配置文件
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
public void load() {
this.profiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.activatedProfiles = false;
this.loaded = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// 下面先分析这个方法
initializeProfiles();
while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) {
Profile profile = this.profiles.poll();
if (profile != null && !profile.isDefaultProfile()) {
addProfileToEnvironment(profile.getName());
}
load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false));
this.processedProfiles.add(profile);
}
resetEnvironmentProfiles(this.processedProfiles);
load(null, this::getNegativeProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addFirst, true));
addLoadedPropertySources();
}
private void initializeProfiles() {
// The default profile for these purposes is represented as null. We add it
// first so that it is processed first and has lowest priority.
this.profiles.add(null);
// 判断当前环境有没有配置spring.profiles.active或者spring.profiles.inculde属性,下面先分析这个方法
Set<profile> activatedViaProperty = getProfilesActivatedViaProperty();
this.profiles.addAll(getOtherActiveProfiles(activatedViaProperty));
// Any pre-existing active profiles set via property sources (e.g.
// System properties) take precedence over those added in config files.
// this.profiles.addAll(profiles);该方法只是将activatedViaProperty放入到了profiles中
addActiveProfiles(activatedViaProperty);
// only has null profile
// 如果已经配置了spring.profiles.active属性,就不会再创建default的了
if (this.profiles.size() == 1) {
// this.environment.getDefaultProfiles()默认返回default
for (String defaultProfileName : this.environment.getDefaultProfiles()) {
// 创建一个name为default的Profile
Profile defaultProfile = new Profile(defaultProfileName, true);
this.profiles.add(defaultProfile);
}
}
}
public static final String ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY = "spring.profiles.active";
public static final String INCLUDE_PROFILES_PROPERTY = "spring.profiles.include";
private Set<profile> getProfilesActivatedViaProperty() {
// 如果不包含这两个文件,直接返回一个空集合,默认是没有配置的
if (!this.environment.containsProperty(ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY)
&& !this.environment.containsProperty(INCLUDE_PROFILES_PROPERTY)) {
return Collections.emptySet();
}
// 如果配置了,则获取一些加入到set中,比如在命令行参数中配置--spring.profiles.active=dev,
// 下面就会去创建一个dev的profile
Binder binder = Binder.get(this.environment);
Set<profile> activeProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<>();
activeProfiles.addAll(getProfiles(binder, INCLUDE_PROFILES_PROPERTY));
activeProfiles.addAll(getProfiles(binder, ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY));
return activeProfiles;
}
// 已经添加过的就不添加了
private List<profile> getOtherActiveProfiles(Set<profile> activatedViaProperty) {
return Arrays.stream(this.environment.getActiveProfiles()).map(Profile::new)
.filter((profile) -> !activatedViaProperty.contains(profile)).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public void load() {
this.profiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.processedProfiles = new LinkedList<>();
this.activatedProfiles = false;
this.loaded = new LinkedHashMap<>();
initializeProfiles();
// 上面的已经分析完了,下面分析这个
while (!this.profiles.isEmpty()) {
Profile profile = this.profiles.poll();
if (profile != null && profile.isDefaultProfile()) {
addProfileToEnvironment(profile.getName());
}
// 默认第一个是profile是null,先分析load方法
load(profile, this::getPositiveProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addLast, false));
this.processedProfiles.add(profile);
}
resetEnvironmentProfiles(this.processedProfiles);
load(null, this::getNegativeProfileFilter, addToLoaded(MutablePropertySources::addFirst, true));
addLoadedPropertySources();
}
private void load(Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory, DocumentConsumer consumer) {
getSearchLocations().forEach((location) -> {
boolean isFolder = location.endsWith("/");
Set<string> names = isFolder ? getSearchNames() : NO_SEARCH_NAMES;
names.forEach((name) -> load(location, name, profile, filterFactory, consumer));
});
}
private static final String DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS = "classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/";
private Set<string> getSearchLocations() {
if (this.environment.containsProperty(CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY)) {
return getSearchLocations(CONFIG_LOCATION_PROPERTY);
}
Set<string> locations = getSearchLocations(CONFIG_ADDITIONAL_LOCATION_PROPERTY);
// 默认从这4个路径下去搜索,见下图
locations.addAll(asResolvedSet(ConfigFileApplicationListener.this.searchLocations, DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS));
return locations;
}
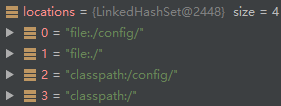
private static final String DEFAULT_NAMES = "application";
// Set<string> names = isFolder ? getSearchNames() : NO_SEARCH_NAMES;
private Set<string> getSearchNames() {
if (this.environment.containsProperty(CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY)) {
String property = this.environment.getProperty(CONFIG_NAME_PROPERTY);
return asResolvedSet(property, null);
}
// 返回默认的配置文件的前缀"application";
return asResolvedSet(ConfigFileApplicationListener.this.names, DEFAULT_NAMES);
}
// names.forEach((name) -> load(location, name, profile, filterFactory, consumer));
private void load(String location, String name, Profile profile, DocumentFilterFactory filterFactory,
DocumentConsumer consumer) {
// name默认是application,跳过
if (!StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) {
if (canLoadFileExtension(loader, location)) {
load(loader, location, profile, filterFactory.getDocumentFilter(profile), consumer);
return;
}
}
}
Set<string> processed = new HashSet<>();
// this.propertySourceLoaders见下图
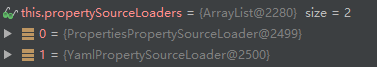
for (PropertySourceLoader loader : this.propertySourceLoaders) {
// 返回每个loader可以处理的扩展名,PropertiesPropertySourceLoader可以处理{.properties,.xml},
// YamlPropertySourceLoader可以处理{.yml,.yaml}格式的文件
for (String fileExtension : loader.getFileExtensions()) {
if (processed.add(fileExtension)) {
loadForFileExtension(loader, location + name, "." + fileExtension, profile, filterFactory, consumer);
}
}
}
}
// 走到这里
private void load(PropertySourceLoader loader, String location, Profile profile, DocumentFilter filter,
DocumentConsumer consumer) {
try {
// 加载资源
Resource resource = this.resourceLoader.getResource(location);
// applicationConfig: [classpath:application.properties]
String name = "applicationConfig: [" + location + "]";
// 下面分析这个方法
List<document> documents = loadDocuments(loader, name, resource);
List<document> loaded = new ArrayList<>();
for (Document document : documents) {
if (filter.match(document)) {
addActiveProfiles(document.getActiveProfiles());
addIncludedProfiles(document.getIncludeProfiles());
loaded.add(document);
}
}
Collections.reverse(loaded);
if (!loaded.isEmpty()) {
loaded.forEach((document) -> consumer.accept(profile, document));
}
}
}
private List<document> loadDocuments(PropertySourceLoader loader, String name, Resource resource)
throws IOException {
// 构造缓存key
DocumentsCacheKey cacheKey = new DocumentsCacheKey(loader, resource);
List<document> documents = this.loadDocumentsCache.get(cacheKey);
if (documents == null) {
List<propertysource<?>> loaded = loader.load(name, resource);
documents = asDocuments(loaded);
this.loadDocumentsCache.put(cacheKey, documents);
}
return documents;
}
public List<propertysource<?>> load(String name, Resource resource) throws IOException {
Map<string, ?> properties = loadProperties(resource);
if (properties.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
// 发现这边就是构造了一个属性源
return Collections.singletonList(new OriginTrackedMapPropertySource(name, properties));
}
private List<document> asDocuments(List<propertysource<?>> loaded) {
if (loaded == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
return loaded.stream().map((propertySource) -> {
Binder binder = new Binder(ConfigurationPropertySources.from(propertySource), this.placeholdersResolver);
return new Document(propertySource, binder.bind("spring.profiles", STRING_ARRAY).orElse(null),
getProfiles(binder, ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY), getProfiles(binder, INCLUDE_PROFILES_PROPERTY));
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
}

Consul+Spring boot 的服务注册和服务注销
一图胜千言
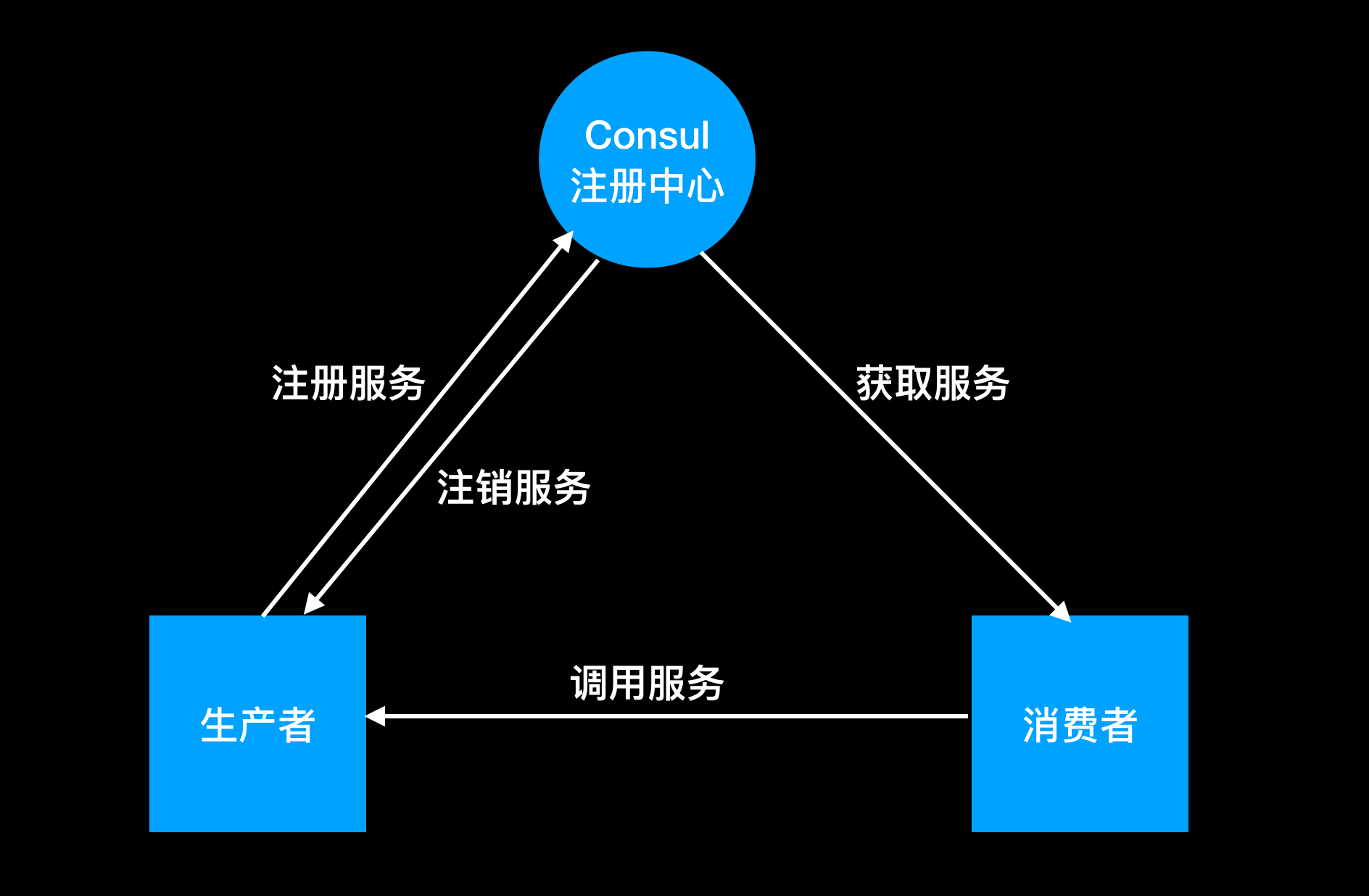
先看一看要做事情,需要在 Consul 上面实现注册中心的功能,并以 2 个 Spring boot 项目分别作为生产者,消费者。
Consul
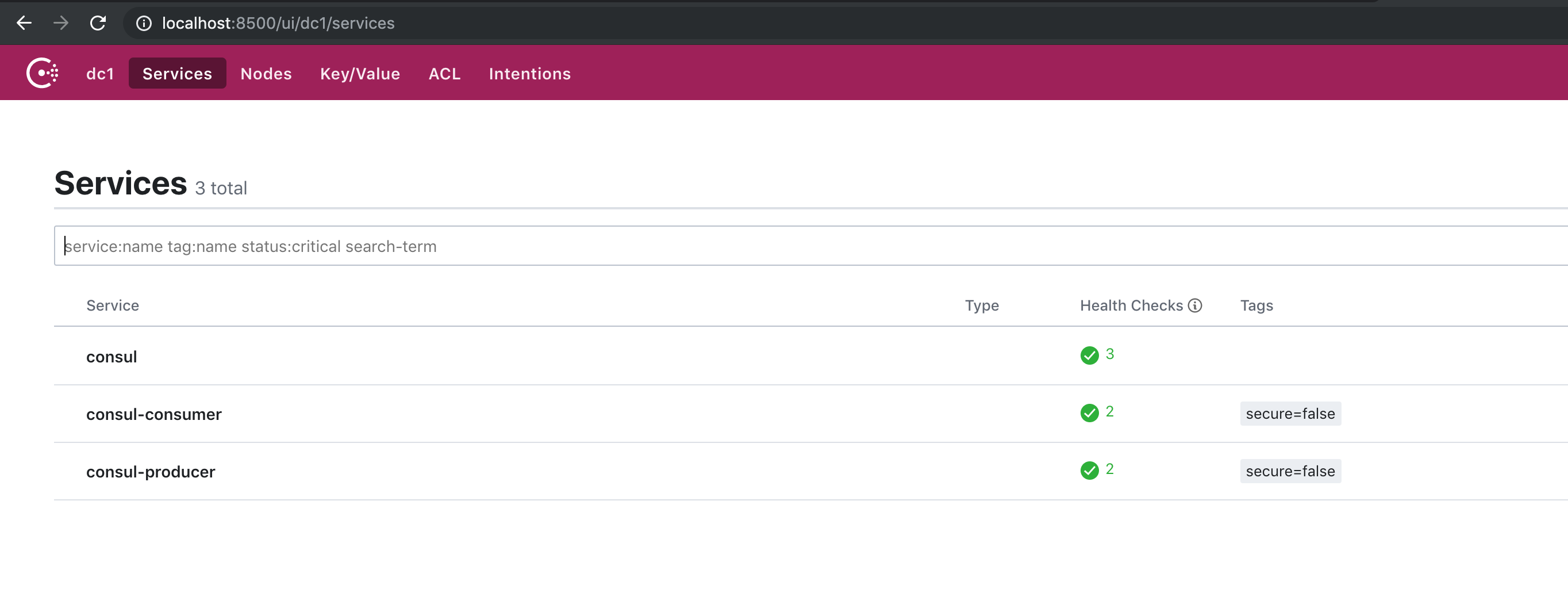
假设已经完成文章《Consul 的开发者模式之 Docker 版》中的所有的配置,并启动了 Consul,访问:http://localhost:8500/ui/dc1/services 即如下图: 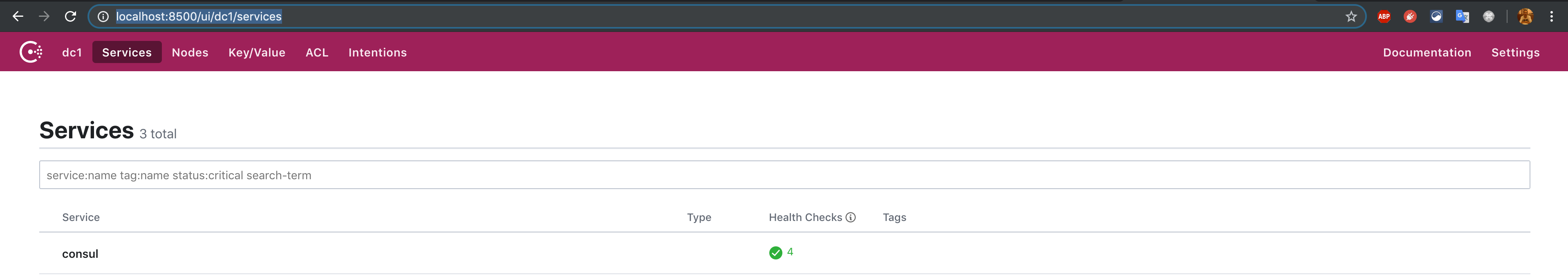
生产者
生产者 - 目录结构
这里就是一个简单的 spring boot 工程。
生产者 - build.gradle
plugins {
id ''org.asciidoctor.convert'' version ''1.5.3''
id ''org.springframework.boot'' version ''2.1.6.RELEASE''
id ''java''
}
apply plugin: ''io.spring.dependency-management''
group = ''com.zyl''
version = ''0.0.1-SNAPSHOT''
sourceCompatibility = ''1.8''
configurations {
developmentOnly
runtimeClasspath {
extendsFrom developmentOnly
}
compileOnly {
extendsFrom annotationProcessor
}
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
ext {
set(''snippetsDir'', file("build/generated-snippets"))
set(''springCloudVersion'', "Greenwich.SR1")
}
dependencies {
implementation ''org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web''
implementation ''org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-starter-consul-discovery''
implementation "org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-actuator"
compileOnly ''org.projectlombok:lombok''
annotationProcessor ''org.projectlombok:lombok''
developmentOnly ''org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-devtools''
annotationProcessor ''org.projectlombok:lombok''
testImplementation ''org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test''
}
dependencyManagement {
imports {
mavenBom "org.springframework.cloud:spring-cloud-dependencies:${springCloudVersion}"
}
}
test {
outputs.dir snippetsDir
}
asciidoctor {
inputs.dir snippetsDir
dependsOn test
}
生产者 - bootstrap.properties
spring.application.name=consul-producer
生产者 - application.properties
server.port=0
spring.cloud.consul.host=localhost
spring.cloud.consul.port=8500
spring.cloud.consul.discovery.prefer-ip-address=true
spring.cloud.consul.discovery.health-check-critical-timeout=90m
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
management.endpoint.health.show-details=always
spring.jackson.serialization.indent_output=true
生产者 - config.properties
这个文件什么都没有,主要是解决一个警告。
生产者 - Application.java
@EnableDiscoveryClient
表示启用服务发现客户端。
消费者
消费者包含以上配置,只是在调用生产者接口都部分有所不同。
消费者 - 目录结构
消费者 - Application.java
package com.zyl.consulconsumer;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.web.client.RestTemplateBuilder;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
import java.time.Duration;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@LoadBalanced
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(RestTemplateBuilder builder) {
return builder.setConnectTimeout(Duration.ofMillis(100))
.setReadTimeout(Duration.ofMillis(500))
.build();
}
}
这里主要就是启用服务发现客户端,和启用 resttemplate 的负载均衡。
消费者 - DemoController.java
package com.zyl.consulconsumer.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
@RestController
public class DemoController {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
public DemoController(RestTemplate restTemplate) {
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
}
@RequestMapping("/")
public String home() {
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://consul-producer/", String.class);
}
}
注意这里调用的时候只要使用 consul 注册中心发现的服务名,进行调用即可。
注册后效果
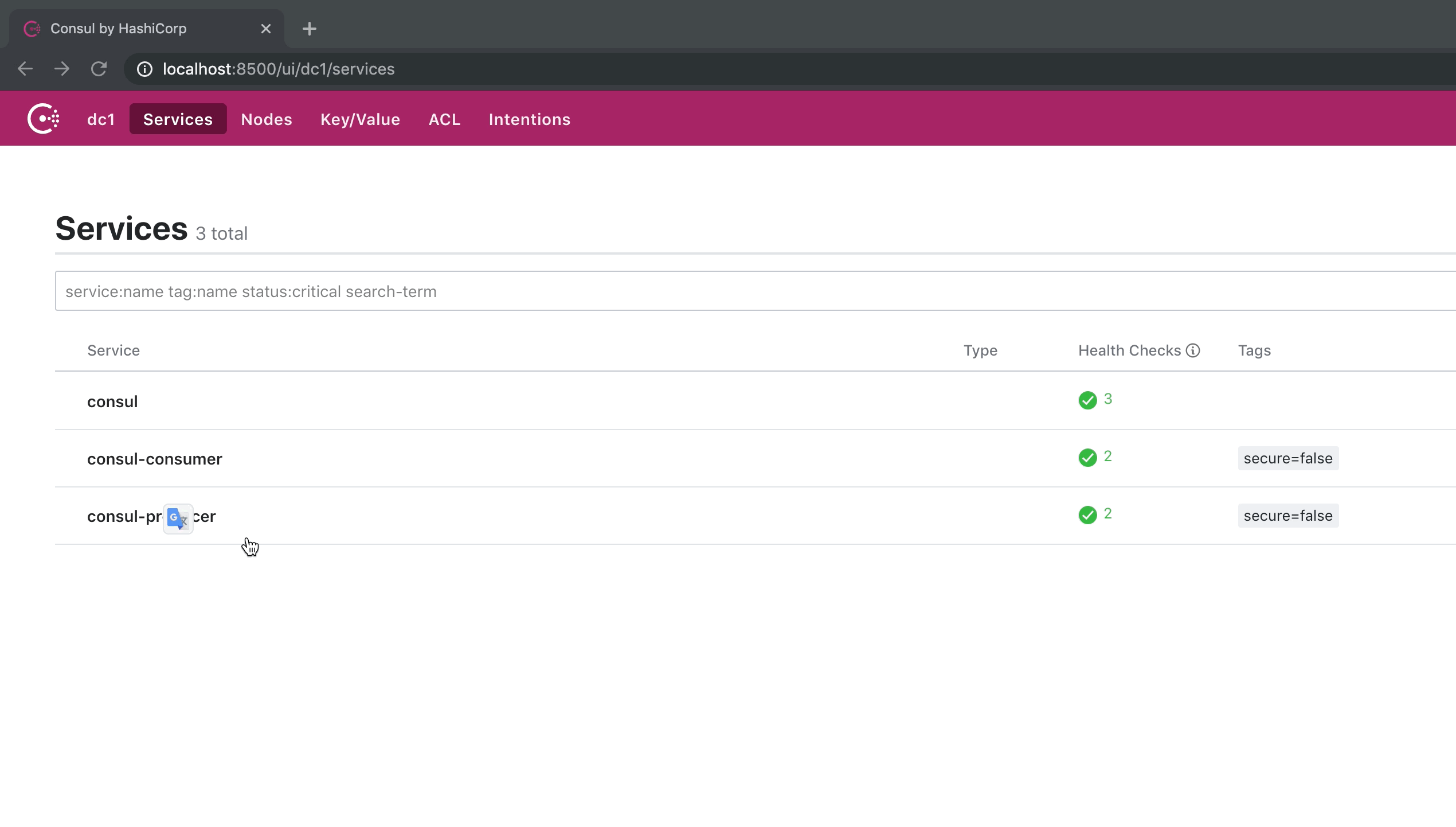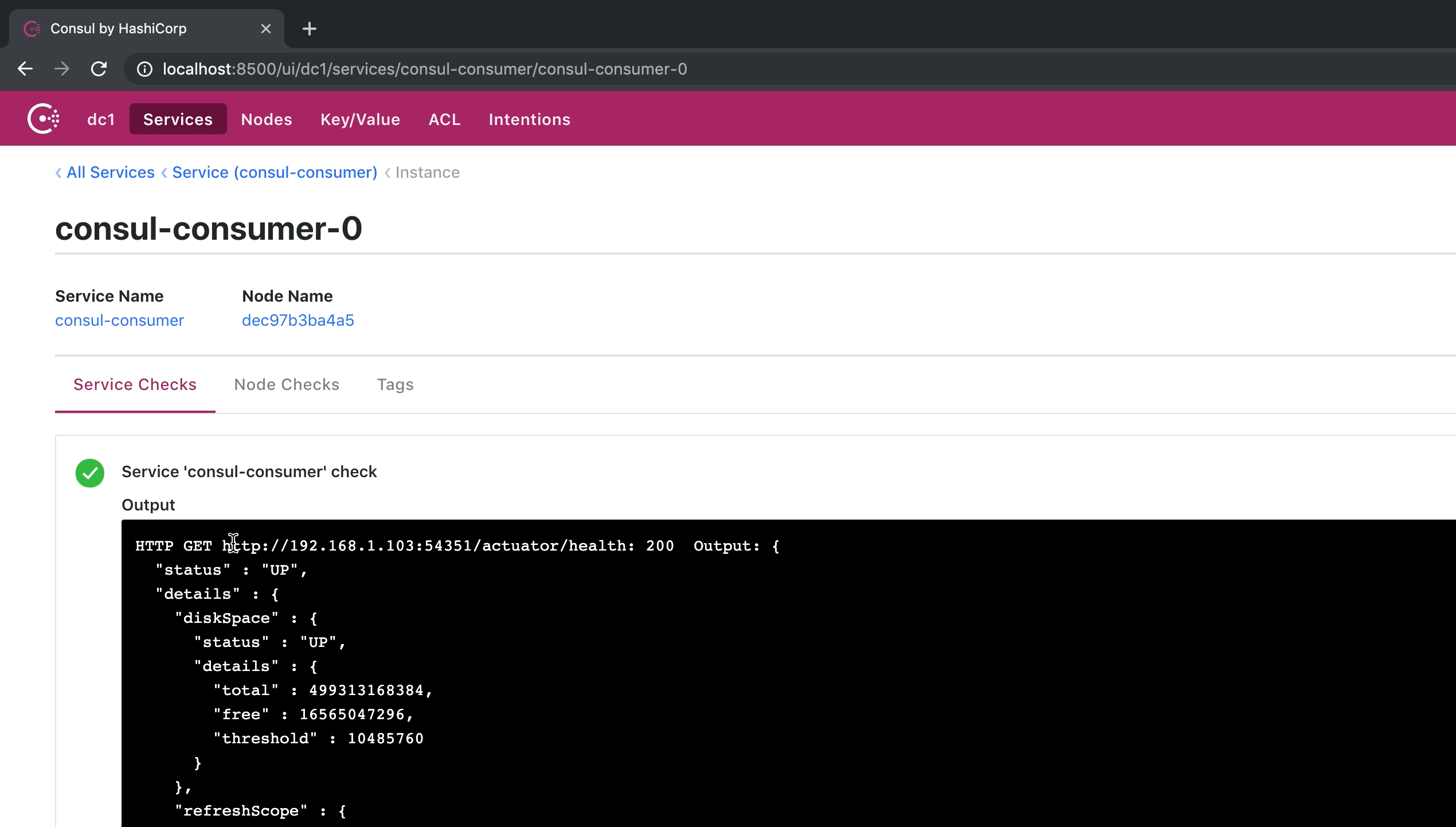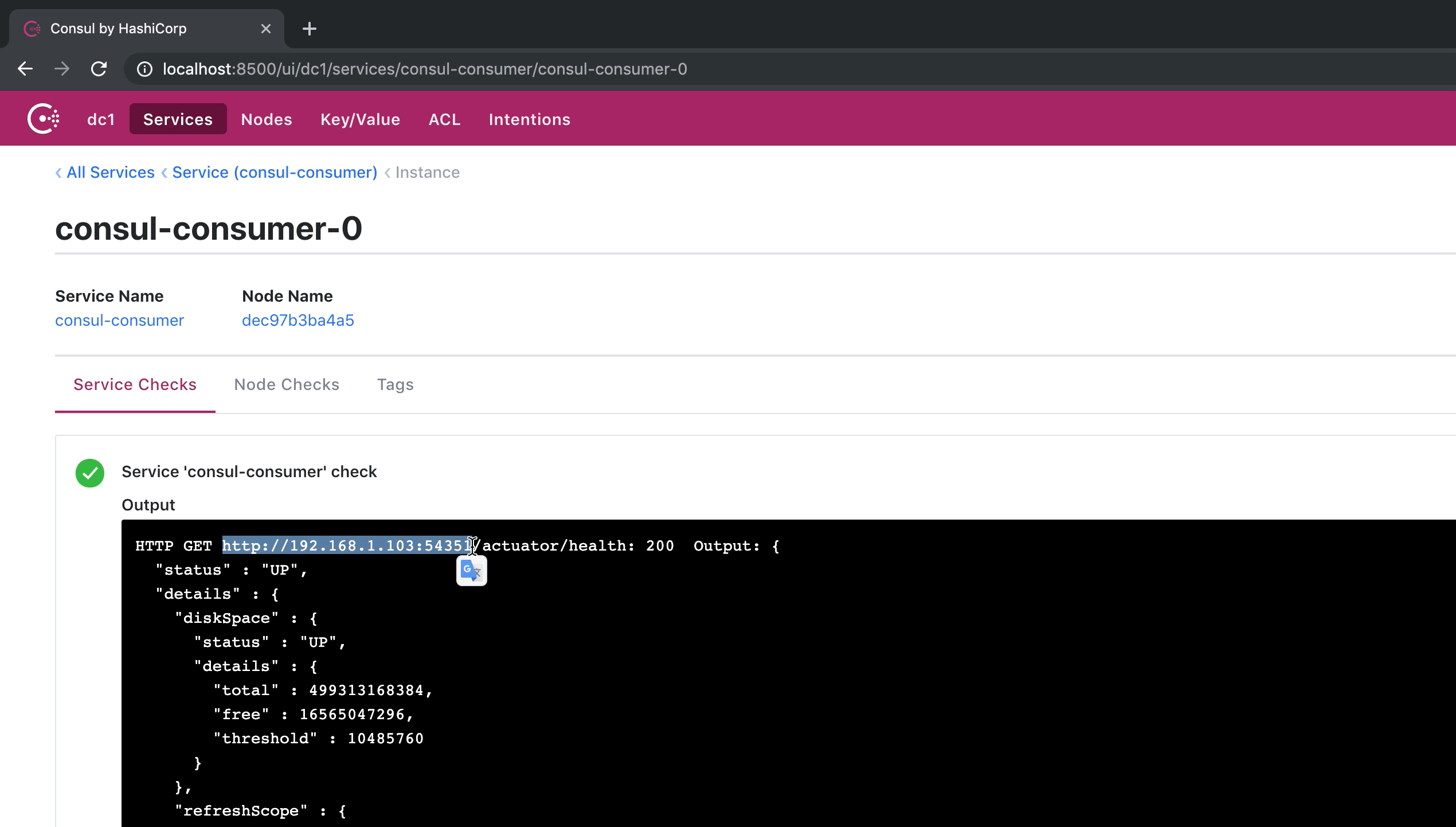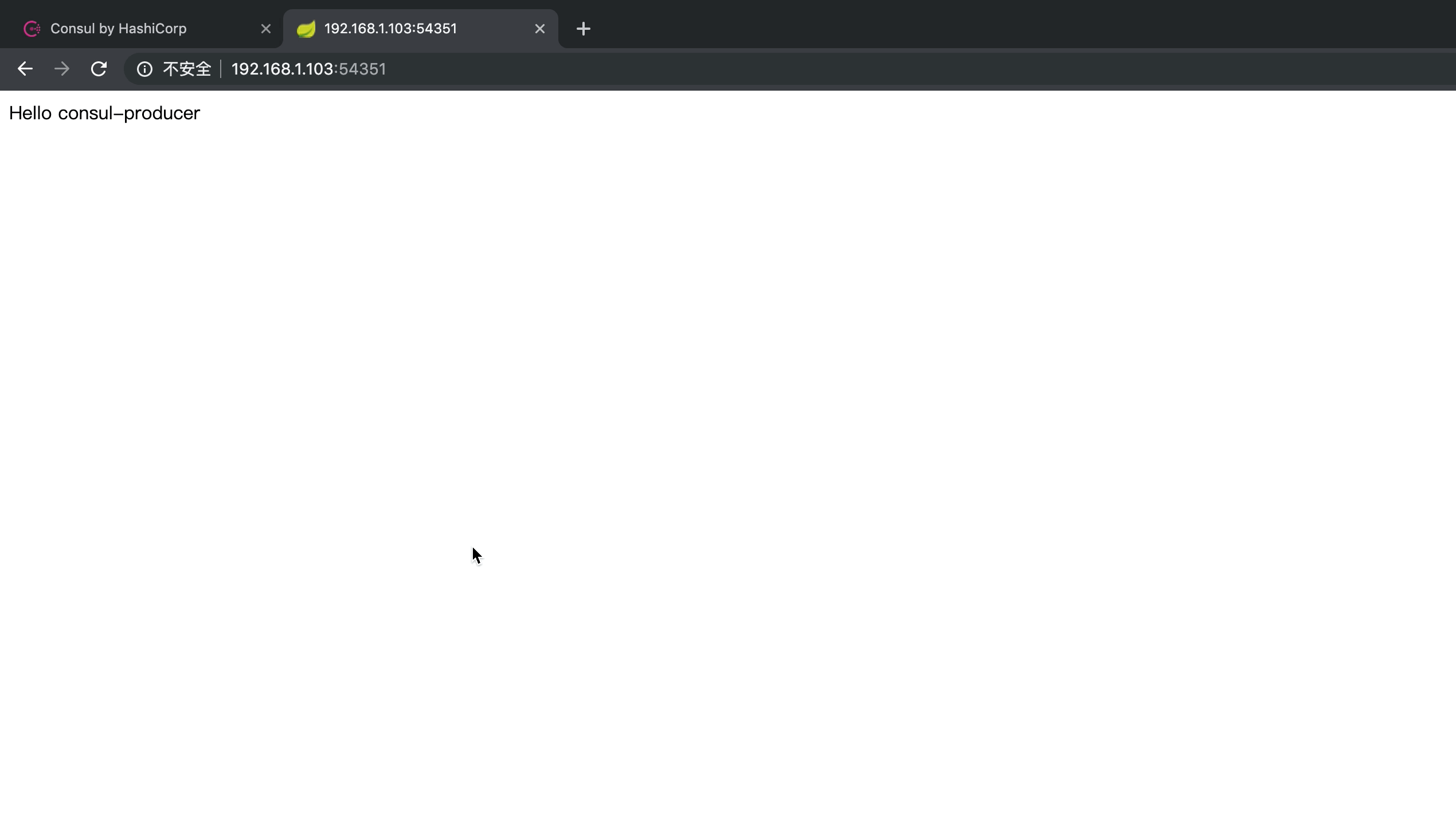
这是 consul 注册中心的页面效果,生产者和消费者都已经注册到 consul 了。
调用效果
源代码
https://github.com/fxtxz2/consul-springboot
参考
- Spring Cloud Consul

docker 带参数启动 配合 springboot profile
dockerfile
FROM frolvlad/alpine-oraclejdk8:slim
VOLUME /tmp
ADD test-push-service-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar app.jar
RUN sh -c ''touch /app.jar''
ENV CE=$CE
ENV JAVA_OPTS=$JAVA_OPTS
ENTRYPOINT [ "sh", "-c", "java $JAVA_OPTS -Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/./urandom -jar /app.jar --spring.config.name=application-$CE" ]
运行镜像:
sudo docker run -it -d --restart unless-stopped -p 8001:8001 --net host -e CE="dev" -e JAVA_OPTS="-Xmx128m -Xss512k" -v /opt/docker/test-push-service/log/:/tmp/ -m 500m --memory-reservation 500m
$Image Name:$Image Tag
QA: CE="dev" ,test= CE="test"

Maven 之 profile 与Spring boot 的 profile
一、概述
不同的环境(测试环境、开发环境)有不同的配置,目前希望在打包的时候,就直接打出针对不同环境的包(内含有某个环境的配置)。Maven本身在 pom.xml 中就提供了 profile 标签进行配置;
spring boot 开发的软件,其也有不同的配置,在结合 maven 打出对应的包的时候,也需要 指定 spring.profiles.active 表示使用的是哪份配置;
二、知识点
1、maven 不同环境配置
(1) profile 的定义位置
我们可以有多个地方定义profile。定义的地方不同,它的作用范围也不同。
- 针对于特定项目的profile配置我们可以定义在该项目的pom.xml中。
- 针对于特定用户的profile配置,我们可以在用户的settings.xml文件中定义profile。该文件在用户家目录下的“.m2”目录下。
- 全局的profile配置。全局的profile是定义在Maven安装目录下的“conf/settings.xml”文件中的。
(2) profile 中能定义的信息
profile中能够定义的配置信息跟profile所处的位置是相关的。以下就分两种情况来讨论,一种是定义在settings.xml中,另一种是定义在pom.xml中。
a) 定义在Setting.xml
当profile定义在settings.xml中时意味着该profile是全局的,它会对所有项目(文件在 Maven 安装目录下)或者某一用户(文件在 用户目录下)的所有项目都产生作用。
此时 Setting.xml 中 profile 下可定义的标签主要有:
- repositories
- pluginRepositories
- properties:定义在<properties>里面的键值对可以在pom.xml中使用
b) 定义在pom.xml中(文件在项目里面)
此时 pom.xml 中标签主要有:
- repositories
- pluginReponsitories
- dependencies
- plugins
- properties
- dependencyManagement
- distributionManagement
(3) profile 的激活方式
a) settings.xml 中 使用 activeProfiles ,指定激活的 profile。
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>profileTest1</id>
<properties>
<hello>world</hello>
</properties>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>profileTest2</id>
<properties>
<hello>andy</hello>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
<activeProfiles>
<activeProfile>profileTest2</activeProfile>
<activeProfile>profileTest1</activeProfile>
</activeProfiles>
一般情况下,activeProfiles 就定义一个 activeProfile ,但会出现如上定义了两个,此时生效两个 profile,pom.xml 在使用 hello 这个 property的时候,是按照 profile 定义的先后顺序来进行覆盖取值的,然后后面定义的会覆盖前面定义的。
而在上面的这个例子中,pom.xml 中 若使用了 ${hello},表示使用 hello 的值,那么此时会使用 andy。
默认激活的 profile 在任何项目打包中都会被激活,它是全局的。
b) pom.xml 中激活方式
- activeByDefault
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>profileTest1</id>
<properties>
<hello>world</hello>
</properties>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
</profile>
</profiles>
当执行maven 命令进行打包时,未指定 -P profile,则表示使用 activeByDefault 声明的 profile,若使用了 吗,mvn clean package -pl artificaId -PanotherProfile,此时就是执行指定的profile,但是settings.xml 中的 默认激活的 profile会默认一致执行,而且是先执行,后执行 pom.xml 中的 profile。
若不想默认执行settings,xml 中激活的 profile,可以使用 mvn -P !profile 命令即可。
- 根据环境来激活 profile
- 根据当前环境中的 jdk 来激活 profile
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>profileTest1</id>
<jdk>1.5</jdk> //JDK版本的前缀匹配,当JDK的版本号以"1.5"开头时, 该配置将被触发
</profile>
<profiles>
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>profileTest1</id>
<jdk>[1.3,1.6)</jdk> //JDK版本的前缀匹配,当JDK的版本号以"1.3\1.4\1.5"开头时, 该配置将被触发
</profile>
<profiles>
-
- 根据操作系统来激活profile
<profiles>
<profile>
<activation>
<os>
<name>Windows XP</name>
<family>Windows</family>
<arch>x86</arch>
<version>5.1.2600</version>
</os>
</activation>
</profile>
</profiles>
-
- 基于环境变量(用户\系统变量)
<profiles>
<profile>
<activation>
<property>
<name>debug</name> //系统属性 debug,无论为何值,都会触发生效该配置
</property>
</activation>
</profile>
</profiles>
<profiles>
<profile>
<activation>
<property>
<name>environment</name>
<value>test</value> //系统属性 environment,值为test 时,会触发生效该配置,可以使用 mvn groupId:artifactId:goal -Denvironment=test 触发
</property>
</activation>
</profile>
</profiles>
-
- 现在\缺失 文件
<profiles>
<profile>
<activation>
<file>
<missing>target/config.xml</missing>
</file>
</activation>
</profile>
</profiles>
- 显示使用命令激活
mvn groupId:artifactId:goal -P profile-1,profile-2
(4) 当settings.xml 和 pom.xml (本工程、从 父pom.xml 继承下来的profile)混合用的时候生效的结果
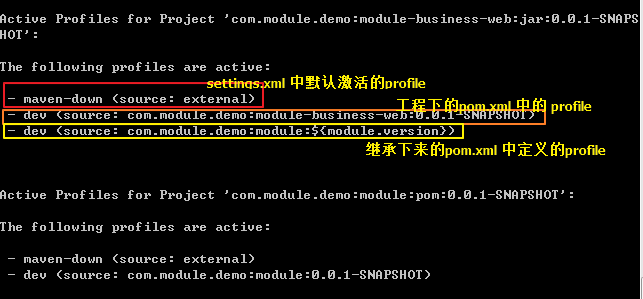
设定场景:
- settings.xml 中 有 profile 为 test1、test2
- 父pom.xml 中有 profile 为 test1、test2、test3
- 本工程 pom.xml 中有 profile 为test1、test2、test3
- 以下表格是 maven 打包时 查找需要执行 profile 的列表,打包时 查找文件顺序为:settings.xml -> 本工程pom.xml -> 父pom.xml
实际生效profile
(顺序 : settings.xml ->
本工程pom.xml ->
父pom.xml)
test1、
test3、
test4
test1、
test2、
teset5
profile 生效规则如下
- 针对每份文件(settings.xml \ 本工程 pom.xml \ 父工程 pom.xml),打包时指定了 profile,若文件 中有指定的 profile 直接激活 指定的 profile,没有则使用默认激活的 profile;
- 针对每份文件(settings.xml \ 本工程 pom.xml \ 父工程 pom.xml),打包时未指定 profile,若文件 中有默认激活的 profile 则使用默认激活的 profile,若没有则不使用该文件中的任何 profile;
- 不同文件激活的多个 profile,出现 property 相同 key时,生效的是第一个激活profile 中的 property;
- pom.xml 中的 activeByDefault 的 profile 若定义了 dependencies ,则依赖的包在任何打包形式下都会被依赖进来;
(5)查看当前处于激活状态的 profile
使用 mvn help:active-profiles
2、spring boot 不同环境配置
(1) 在工程中配置不同环境配置文件

其中:application.yml 内容如下
spring:
application:
name: web
profiles:
active: "@package.env@"
server:
port: 8090
(2) pom.xml 配置如下:
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<filtering>true</filtering>
<includes>
<include>**/*.yml</include>
<include>**/*.yaml</include>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<filtering>false</filtering>
<excludes>
<exclude>**/*.yml</exclude>
<exclude>**/*.yaml</exclude>
<exclude>**/*.properties</exclude>
<exclude>**/*.xml</exclude>
</excludes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/config</directory>
<filtering>true</filtering>
<includes>
<include>**/*.yml</include>
<include>**/*.yaml</include>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/config</directory>
<filtering>false</filtering>
<excludes>
<exclude>**/*.yml</exclude>
<exclude>**/*.yaml</exclude>
<exclude>**/*.properties</exclude>
<exclude>**/*.xml</exclude>
</excludes>
</resource>
</resources>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<executable>true</executable>
</configuration>
</plugin>
可以把 src/main/config 及 src/main/resources 下的配置文件 打包过程中打入。
(3) 激活
在运行的时候,传入参数:-Dspring.profiles.active=dev,表示使用dev 环境配置;
3、不同环境配置 spring boot 与 maven结合
- application.yml 要配置成上图所示的,spring.profiles.active=占位符属性,占位符属性值 在 pom.xml 中的 profile 指定
- pom.xml 中定义 profile ,如下,在本工程中定义内容:
<!-- 多环境的不同配置,在运行时需指明使用哪个环境配置 -->
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>dev</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault> <!-- 运行时未指明 profile,则使用默认的,该配置表示 dev为默认配置 -->
</activation>
<properties>
<package.env>dev</package.env>
</properties>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>release</id>
<properties>
<package.env>release</package.env>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
- pom.xml 中的 resource 标签若没有上面的示例配置复杂,也一定要有以下内容,才能让 maven 将其 property 写入到指定的配置文件中。
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory> // 需要将 maven 的 property 写入 src/main/resources 下所有的配置文件中(只要该配置文件中使用了propetry对应的占位符,如上面 application.yml 配置的那样
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
- 激活
此时,执行命令:mvn groupId:artifactId:goal -P dev 时,maven 的 dev profile 生效,其中定义的 package.env 属性值为dev,此时打开 target 下的 application.yml,其内容已变成,如下:
spring:
application:
name: web
profiles:
active: "dev"
server:
port: 8090
问题:
在做上述例子的时候,发现按照如上配置之后,执行mvn命令,打开 target 下的 application.yml @package.dev@ 还是没有替换成对应值,该原因为:
- maven 默认可识别的配置文件占位符 符号为 ${};
- 若 pom.xml 有通过 parent 标签继承别的 pom.xml ,此时需打开父pom.xml 查看,如,本实例继承了 spring boot 的pom.
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.7.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
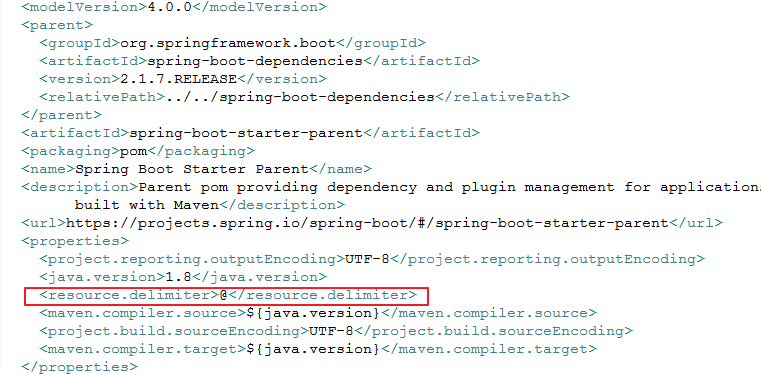
因此 spring boot 继承过来的这种形式,配置文件中要使用 @ 作为占位符,但是若是使用 dependency 这种方式继承 spring boot 的话,直接使用 ${},作为占位符即可。
PS: 以上参考内容:
https://www.cnblogs.com/wxgblogs/p/6696229.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/lddbupt/p/5531885.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/929b9aa70dc8
关于Spring Boot服务注入到doFiler和springboot注入service的问题就给大家分享到这里,感谢你花时间阅读本站内容,更多关于5、SpringBoot 的 Profile 功能、Consul+Spring boot 的服务注册和服务注销、docker 带参数启动 配合 springboot profile、Maven 之 profile 与Spring boot 的 profile等相关知识的信息别忘了在本站进行查找喔。
本文标签:





