在本文中,我们将带你了解SpringBoot中的@PathVariable,URL中带有斜线在这篇文章中,我们将为您详细介绍SpringBoot中的@PathVariable,URL中带有斜线的方方面
在本文中,我们将带你了解SpringBoot中的@ PathVariable,URL中带有斜线在这篇文章中,我们将为您详细介绍SpringBoot中的@ PathVariable,URL中带有斜线的方方面面,并解答springboot url attribute is not specified常见的疑惑,同时我们还将给您一些技巧,以帮助您实现更有效的REST控制器spring 4中的可选@Pathvariable、Spring 4中的@PathVariable验证、Spring @Pathvariable、Spring @PathVariable不起作用。
本文目录一览:- SpringBoot中的@ PathVariable,URL中带有斜线(springboot url attribute is not specified)
- REST控制器spring 4中的可选@Pathvariable
- Spring 4中的@PathVariable验证
- Spring @Pathvariable
- Spring @PathVariable不起作用

SpringBoot中的@ PathVariable,URL中带有斜线(springboot url attribute is not specified)
我必须在SpringBoot应用程序中使用@PathValiable从URL获取参数。这些参数通常带有 斜线
。我无法控制用户在URL中输入的内容,因此我想获取他输入的内容,然后我就可以对其进行处理。
我已经在这里浏览了材料和答案,我认为对我而言,好的解决方案不是要求用户以某种方式对输入的参数进行编码。
SpringBoot代码很简单:
@RequestMapping("/modules/{moduleName}")@ResponseBodypublic String moduleStrings (@PathVariable("moduleName") String moduleName) throws Exception { ...}因此,URL例如如下:
http://localhost:3000/modules/...问题在于,参数 moduleName 通常带有斜杠。例如,
metadata-api\cb-metadata-services ORapp-customization-service-impl\\modules\\expand-link-schemes\\common\\app-customization-service-api因此,用户可以输入:
http://localhost:3000/modules/metadata-api\cb-metadata-services是否有可能获得用户在 / modules / 之后在URL中输入的所有内容?
如果有人告诉我什么是解决此类问题的好方法。
答案1
小编典典此代码获取完整路径:
@RequestMapping(value = "/modules/{moduleBaseName}/**", method = RequestMethod.GET)@ResponseBodypublic String moduleStrings(@PathVariable String moduleBaseName, HttpServletRequest request) { final String path = request.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.PATH_WITHIN_HANDLER_MAPPING_ATTRIBUTE).toString(); final String bestMatchingPattern = request.getAttribute(HandlerMapping.BEST_MATCHING_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE).toString(); String arguments = new AntPathMatcher().extractPathWithinPattern(bestMatchingPattern, path); String moduleName; if (null != arguments && !arguments.isEmpty()) { moduleName = moduleBaseName + ''/'' + arguments; } else { moduleName = moduleBaseName; } return "module name is: " + moduleName;}
REST控制器spring 4中的可选@Pathvariable
我正在编写一个Rest服务(HTTP Get端点),在下面的uri中执行以下操作
http://localhost:8080/customers/{customer_id}- 获取在uri中传递的customer_id的详细信息
- 如果没有传递customer_id(http:// localhost:8080 / customers),则获取所有客户详细信息。
码:
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = "customers/{customer_id}")public List<Customer> getCustomers(@PathVariable(name = "customer_id", required = false) final String customerId) {LOGGER.debug("customer_id {} received for getCustomers request", customerId);}但是,使用上面的代码,第二种情况下,控件流向getCustomers()。
注意:我使用的是Java8和spring-web 4.3.10版本
非常感谢对此的任何帮助。
答案1
小编典典@PathVariable仅当您要同时映射GET /customers/{customer_id}和映射GETcustomers到单个java方法时才使用Optional 。
您不能发送的请求将被发送到GET /customers/{customer_id}如果不发送customer_id。
因此,在您的情况下,它将是:
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET, value = {"/customers", "customers/{customer_id}"})public List<Customer> getCustomers(@PathVariable(name = "customer_id", required = false) final String customerId) { LOGGER.debug("customer_id {} received for getCustomers request", customerId);}需要公共抽象布尔值
是否需要path变量。
默认为true,如果传入请求中缺少path变量,则会引发异常。如果您希望使用null或Java 8
java.util,请将其切换为false。例如在用于不同请求的ModelAttribute方法上。
您可以使用java8 null或Optional从java8

Spring 4中的@PathVariable验证
我如何在Spring验证我的路径变量。我想验证id字段,因为我不想将其移到Pojo,因为它只有一个字段
@RestController
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public ResponseEntity method_name(@PathVariable String id) {
/// Some code
}
}
我尝试在路径变量中添加验证,但仍无法正常工作
@RestController
@Validated
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public ResponseEntity method_name(
@Valid
@Nonnull
@Size(max = 2,min = 1,message = "name should have between 1 and 10 characters")
@PathVariable String id) {
/// Some code
}
}
Spring @Pathvariable
先记录下@PathVariable的用法吧:
@RequestMapping("/demo/{id}")
@ResponseBody
public User getUser(@PathVariable("id")Integer id, HttpServletRequest request){
System.out.println(request.getAttribute(RequestMappingHandlerMapping.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE));
List<User> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add(new User(0,"A"));
list.add(new User(1,"B"));
list.add(new User(2,"C"));
list.add(new User(3,"D"));
User user = list.get(id);
return user;
}使用方式一:就像上面那样{}代表占位符,匹配URL中/ /两个之间的内容,通过@PathVariable进行解析
使用方式二:通过request的RequestMappingHandlerMapping.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE这个属性获取到一个Map,然后根据上面的key进行取值
有时候很好奇Spring @Pathvariable怎么解析的,好像无论多少个 {} 都能正确的映射,看起来好像没那么难。 但是我脑子不太行,尝试分析分析看看吧。
就像以前做笔试题:正确答案在下面,虽然我肯定写不出来,但是能看懂也挺为难我哈哈哈哈。
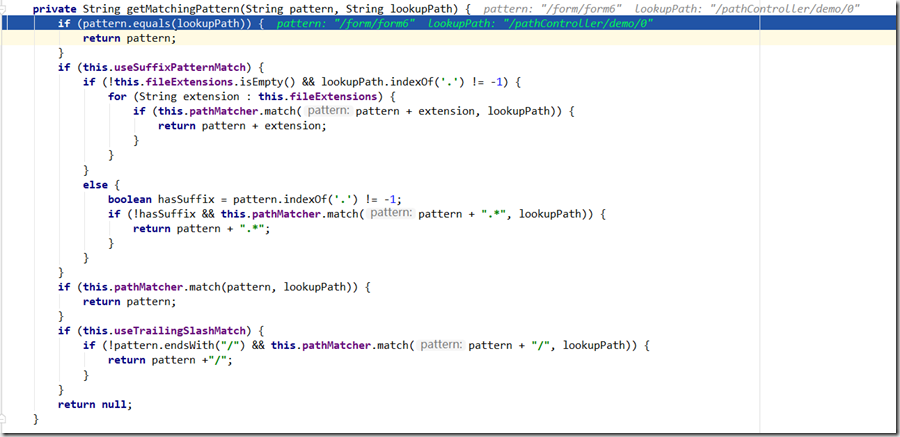
就像给定两个输入, pattern是标准路径 ,就像 /url/{id} , 而lookupPath就是请求路径,就像/url/19 ;
如果pattern和lookupPath一样,就直接返回,这个不难理解,常规URL映射都是这么映射的;
考虑到实际情况以及简化分析,useSuffixPatternMatch 默认为 true , fileExtensions 默认为空 ,以不带后缀名形式分析 ,那就会进入AntPathMatcher分析;
protected boolean doMatch(String pattern, String path, boolean fullMatch, Map<String, String> uriTemplateVariables) {
//pattern为标准路径 /url/{id} path为请求request路径/url/19
//fullMatch默认为true ; uriTemplateVariables默认为null
//pathSeparator默认为 /
//path和pattern刚开始都是/ 开头, 肯定是false ; 这一步算是规则校验 路径不以/开头的 直接返回false
if (path.startsWith(this.pathSeparator) != pattern.startsWith(this.pathSeparator)) {
return false;
}
//标准路径/url/{id}分隔成字符串数组 pattDirs
String[] pattDirs = tokenizePattern(pattern);
//isPotentialMatch方法:
//请求路径 和 @RequestMapping路径匹配 从头匹配刚开始就不相等直接返回false
//解析过程前面相等遇到 { * ?类型返回true 这里逻辑等等再具体描述
if (fullMatch && this.caseSensitive && !isPotentialMatch(path, pattDirs)) {
return false;
}
//请求路径拆分成字符串数组pathDirs
String[] pathDirs = tokenizePath(path);
int pattIdxStart = 0;
int pattIdxEnd = pattDirs.length - 1;
int pathIdxStart = 0;
int pathIdxEnd = pathDirs.length - 1;
//循环遍历是否 请求路径字符数组 和 @RequestMapping路径数组 正则匹配
//{id}的正则表达式被解析为 (.*) 肯定可以匹配上
//字符数组只要有一个元素没匹配上就返回false
while (pattIdxStart <= pattIdxEnd && pathIdxStart <= pathIdxEnd) {
String pattDir = pattDirs[pattIdxStart];
if ("**".equals(pattDir)) {
break;
}
if (!matchStrings(pattDir, pathDirs[pathIdxStart], uriTemplateVariables)) {
return false;
}
pattIdxStart++;
pathIdxStart++;
}
//上面如果匹配完成,pathIdxStart=pathIdxEnd+1 pattIdxStart=pattIdxEnd+1
if (pathIdxStart > pathIdxEnd) {
// Path is exhausted, only match if rest of pattern is * or **''s
if (pattIdxStart > pattIdxEnd) {
// /url/{id} /url/19 就匹配上了到这里 返回true
return (pattern.endsWith(this.pathSeparator) ? path.endsWith(this.pathSeparator) :
!path.endsWith(this.pathSeparator));
}
if (!fullMatch) {
return true;
}
if (pattIdxStart == pattIdxEnd && pattDirs[pattIdxStart].equals("*") && path.endsWith(this.pathSeparator)) {
return true;
}
for (int i = pattIdxStart; i <= pattIdxEnd; i++) {
if (!pattDirs[i].equals("**")) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
else if (pattIdxStart > pattIdxEnd) {
// String not exhausted, but pattern is. Failure.
return false;
}
else if (!fullMatch && "**".equals(pattDirs[pattIdxStart])) {
// Path start definitely matches due to "**" part in pattern.
return true;
}
// up to last ''**''
while (pattIdxStart <= pattIdxEnd && pathIdxStart <= pathIdxEnd) {
String pattDir = pattDirs[pattIdxEnd];
if (pattDir.equals("**")) {
break;
}
if (!matchStrings(pattDir, pathDirs[pathIdxEnd], uriTemplateVariables)) {
return false;
}
pattIdxEnd--;
pathIdxEnd--;
}
if (pathIdxStart > pathIdxEnd) {
// String is exhausted
for (int i = pattIdxStart; i <= pattIdxEnd; i++) {
if (!pattDirs[i].equals("**")) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
while (pattIdxStart != pattIdxEnd && pathIdxStart <= pathIdxEnd) {
int patIdxTmp = -1;
for (int i = pattIdxStart + 1; i <= pattIdxEnd; i++) {
if (pattDirs[i].equals("**")) {
patIdxTmp = i;
break;
}
}
if (patIdxTmp == pattIdxStart + 1) {
// ''**/**'' situation, so skip one
pattIdxStart++;
continue;
}
// Find the pattern between padIdxStart & padIdxTmp in str between
// strIdxStart & strIdxEnd
int patLength = (patIdxTmp - pattIdxStart - 1);
int strLength = (pathIdxEnd - pathIdxStart + 1);
int foundIdx = -1;
strLoop:
for (int i = 0; i <= strLength - patLength; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < patLength; j++) {
String subPat = pattDirs[pattIdxStart + j + 1];
String subStr = pathDirs[pathIdxStart + i + j];
if (!matchStrings(subPat, subStr, uriTemplateVariables)) {
continue strLoop;
}
}
foundIdx = pathIdxStart + i;
break;
}
if (foundIdx == -1) {
return false;
}
pattIdxStart = patIdxTmp;
pathIdxStart = foundIdx + patLength;
}
for (int i = pattIdxStart; i <= pattIdxEnd; i++) {
if (!pattDirs[i].equals("**")) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
isPotentialMatch:进一步的过滤规则
private boolean isPotentialMatch(String path, String[] pattDirs) {
// path 请求路径 pattDirs标准路径以 / 分隔出来的字符数组
if (!this.trimTokens) {
//请求路径转成char数组
char[] pathChars = path.toCharArray();
int pos = 0;
for (String pattDir : pattDirs) {
//请求路径中第一次从0开始找到/的位置,下次就从上次找到的位置开始找下一个/
int skipped = skipSeparator(path, pos, this.pathSeparator);
pos += skipped;
//skipSegment从pathChars找出跳过pattDir的长度
skipped = skipSegment(pathChars, pos, pattDir);
//skipped最理想情况等于pattDir的长度 但是通常通配符形式这里都是小于 //比如映射中包含demo,路径为do,这时候skipped也是2 也会返回true,但是之后的正则表达式校验无法通过
if (skipped < pattDir.length()) {
if (skipped > 0) {
return true;
}
return (pattDir.length() > 0) && isWildcardChar(pattDir.charAt(0));
}
//skipped ==pattDir长度,全匹配上直接匹配下一个/之后内容
pos += skipped;
}
}
return true;
}
//函数作用 待匹配路径字符数组 pos 代表 /所在的下一个位置 prefix标准路径
//标准路径包含wildcardChar { ? * 返回skipped 其他都会返回0
private int skipSegment(char[] chars, int pos, String prefix) {
int skipped = 0;
for (char c : prefix.toCharArray()) {
if (isWildcardChar(c)) {
return skipped;
}
else if (pos + skipped >= chars.length) {
return 0;
}
else if (chars[pos + skipped] == c) {
skipped++;
}
}
return skipped;
}
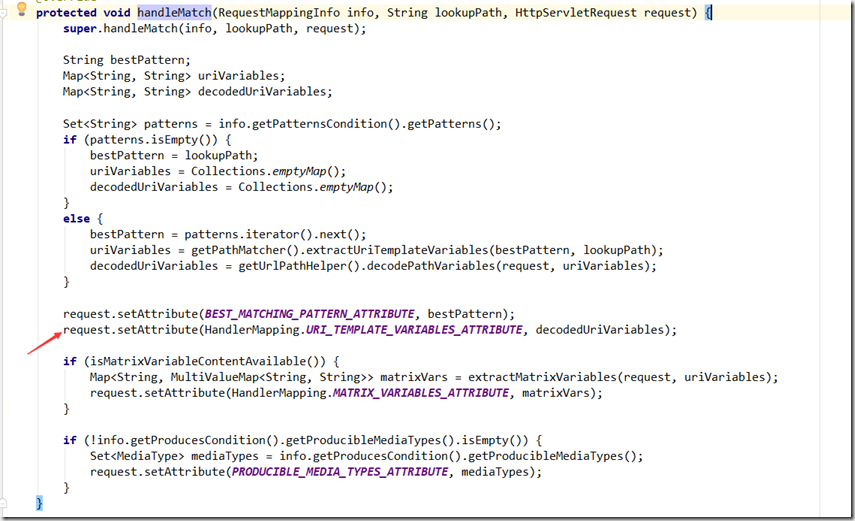
Spring考虑的很全面,最简单的 /url/{id} /url/19这种类型匹配完成了;
转换完成以后,存入request域:以HandlerMapping.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE作为KEY存储
代码位置:org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping#handleMatch
另外还一种特殊写法:{name:正则表达式校验} 比如我只希望URL中id为纯数字 \d*即可
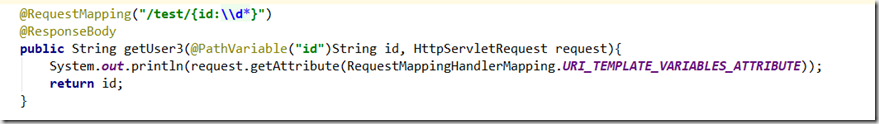
补充:如果正则匹配不了,抛出的错误是404页面找不到. 带:与不带:的区别在于,不带:就默认使用 .* 匹配,其他用法没差别.
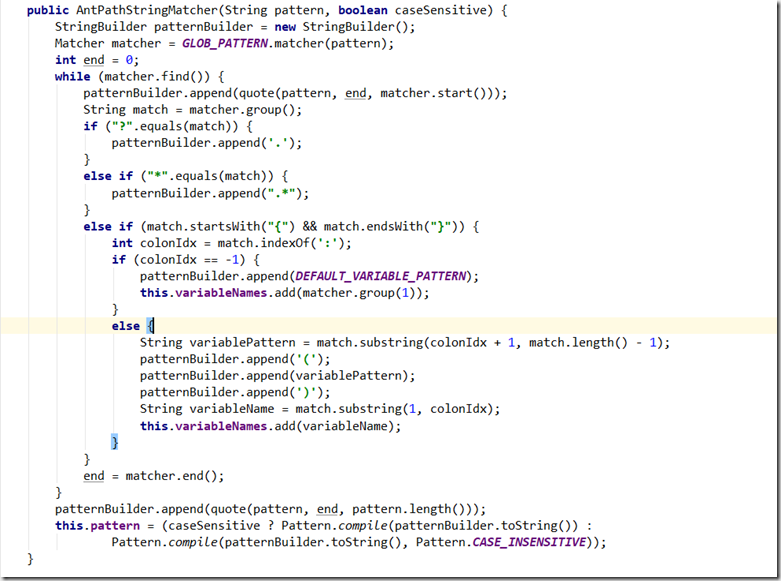
差点忘记记录Spring如何解析@PathVariable注解?
Spring专门的接口HandlerMethodArgumentResolver用来解析方法入参,而PathVariableMethodArgumentResolver就是用来解析 @PathVariable注解的。
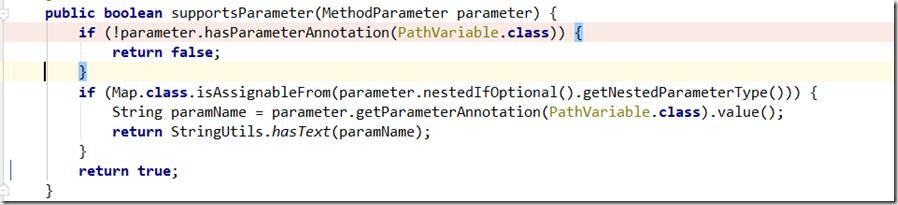
而请求参数绑定到 方法入参的方式:
可以看到也是从request属性域HandlerMapping.URI_TEMPLATE_VARIABLES_ATTRIBUTE中取值,key就是@PathVariable(“yourname”)中的yourname取值.


Spring @PathVariable不起作用
我是springMVC的新手。我的问题是@PathVariable导致404“ 请求的资源()不可用 ”。
例如,这对于URL来说效果很好 http://localhost:8080/Spring/list
@RequestMapping(value = "/list") public String list() { return "WEB-INF/views/list.jsp"; }但是此返回404的URL http://localhost:8080/Spring/list/foo
@RequestMapping(value = "/list/{nameId}") public String list(@PathVariable("nameId") String nameId) { return "WEB-INF/views/list.jsp"; }怎么了?谢谢你的回答
答案1
小编典典错误消息说明了一切。由于它是分层路径,因此需要查找/list/WEB-INF/etc...;尝试使用JSP的绝对路径来避免该问题。
我想这有点违反直觉。
关于SpringBoot中的@ PathVariable,URL中带有斜线和springboot url attribute is not specified的介绍已经告一段落,感谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于REST控制器spring 4中的可选@Pathvariable、Spring 4中的@PathVariable验证、Spring @Pathvariable、Spring @PathVariable不起作用的相关信息,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

