关于解析大于hdfs块大小的XmlInputFormat元素和hdfs小于单个块大小的文件的问题就给大家分享到这里,感谢你花时间阅读本站内容,更多关于DBInputFormat、FileInputFo
关于解析大于hdfs块大小的XmlInputFormat元素和hdfs小于单个块大小的文件的问题就给大家分享到这里,感谢你花时间阅读本站内容,更多关于DBInputFormat、FileInputFormat 的实现之TextInputFormat、Flutter:在TextInputFormatter中使用NumberFormat、hadoop map reduce程序,注意引入FileOutputFormat类和FileInputFormat类等相关知识的信息别忘了在本站进行查找喔。
本文目录一览:- 解析大于hdfs块大小的XmlInputFormat元素(hdfs小于单个块大小的文件)
- DBInputFormat
- FileInputFormat 的实现之TextInputFormat
- Flutter:在TextInputFormatter中使用NumberFormat
- hadoop map reduce程序,注意引入FileOutputFormat类和FileInputFormat类

解析大于hdfs块大小的XmlInputFormat元素(hdfs小于单个块大小的文件)
我是Hadoop
MapReduce的新手(准确地说是4天),并且被要求在集群上执行分布式XML解析。根据我在Internet上的(重新)搜索,使用Mahout的XmlInputFormat应该相当容易,但是我的任务是确保该系统适用于大型(〜5TB)XML文件。
据我所知,发送到映射器的文件拆分不能大于hdfs块大小(或每个作业块大小)。[如果我弄错了,请纠正我]。
我面临的问题是,某些XML元素很大(〜200MB),而有些很小(〜1MB)
所以我的问题是:XmlInputFormat创建的XML元素块大于块大小时会发生什么?它将整个大文件(例如200MB)发送到映射器,还是将元素分成三部分(64
+ 64 + 64 + 8)发送出去?
我目前无法访问公司的hadoop集群(并且直到某个时候才可以访问),所以我无法执行测试并找出答案。请帮我。
答案1
小编典典所以要清除一些东西:
Mahout的XMLInputFormat将处理XML文件,并在两个已配置的开始/结束标记之间提取XML。因此,如果您的XML如下所示:
<main> <person> <name>Bob</name> <dob>1970/01/01</dob> </person></main>并且您已将开始/结束标记配置为<person>和</person>,那么您的映射器将通过以下<LongWritable,Text>对传递到其map方法:
LongWritable: 10Text: "<person>\n <name>Bob</name>\n <dob>1970/01/01</dob>\n </person>"然后,您就可以在映射器中处理此数据。
关于splits,XmlInputFormatextendsTextInputFormat,因此,如果您输入的文件是可拆分的(即未压缩或使用可拆分的编解码器(例如snappy)压缩),则该文件将由一个或多个映射器处理,如下所示:
- 如果输入文件的大小(比如说48 MB)小于HDFS中的单个块(比如说64MB),并且您没有配置最小/最大拆分大小属性,那么您将获得一个映射器来处理文件
- 和上面一样,但是您将最大拆分大小配置为10MB(
mapred.max.split.size=10485760),那么您将获得5个映射任务来处理文件 - 如果文件大于块大小,那么您将获得每个块的映射任务,或者如果配置了最大拆分大小,则将文件划分为该拆分大小的每个部分的映射
当文件拆分为这些块或拆分大小的块时,XmlInputFormat将寻求对块的字节地址/偏移量/拆分边界进行查找,然后向前扫描,直到找到配置的XML起始标记或到达块的字节地址为止/分割边界。如果找到开始标签,它将消耗数据直到找到结束标签(或文件末尾)。如果找到结束标记,则记录将被传递到您的映射器,否则您的映射器将不会收到任何输入。要强调的是,在尝试找到结束标签时,地图可能会扫描到块/拆分的末尾,但只有找到开始标签后才会执行此操作,否则扫描将在块/拆分的末尾停止。
因此,要(最终)回答您的问题,如果您尚未配置映射器(并且正在使用默认值或标识映射器,因为它是众所周知的),那么是的,XML块的大小(MB,GB)无关紧要,TB!)它将被发送到减速器。
我希望这是有道理的。
编辑
跟进您的评论:
- 是的,每个映射器都会尝试处理文件的拆分(字节范围)
- 是的,无论您也设置了最大拆分大小是多少,映射器都会收到记录,这些记录代表开始/结束标记之间(包括两端)的数据。无论person元素的大小如何,都不会拆分它(显然,如果start和end元素之间存在GB的数据,则很可能会用尽内存来尝试将其缓冲到Text对象中)
- 从上面继续,您的数据将永远不会在开始元素和结束元素之间分割,人员元素将以其完整性发送到映射器,因此您应该始终可以使用SAX解析器之类的东西来进一步处理它而不必担心您只会看到person元素的一部分。

DBInputFormat
代码未做测试,先做记录
package com.test;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URI;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configured;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.db.DBConfiguration;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.db.DBInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.db.DBWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.Tool;
import org.apache.hadoop.util.ToolRunner;
/**
* 要运行本示例
* 1、把mysql的jdbc驱动放到taskTracker的lib目录下,重启集群
*
*/
public class WordCountDB extends Configured implements Tool {
private String OUT_PATH = "hdfs://grid131:9000/output";
public static class Map extends Mapper<LongWritable, MyUser, LongWritable, Text> {
public void map(LongWritable key, MyUser value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
context.write(key, new Text(value.toString()));
}
}
public int run(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = this.getConf();
DBConfiguration.configureDB(conf, "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver", "jdbc:mysql://grid131:3306/test", "root", "admin");
//输出路径如果存在,则删除
FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(new URI(OUT_PATH), conf);
fs.delete(new Path(OUT_PATH), true);
Job job = new Job(conf, WordCountDB.class.getSimpleName());
job.setJarByClass(WordCountDB.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
//指定不需要reduce,直接把map输出写入到hdfs中
job.setNumReduceTasks(0);
job.setInputFormatClass(DBInputFormat.class);
//指定表、字段
//DBInputFormat.setInput(job, inputClass, tableName, conditions, orderBy, fieldNames)
DBInputFormat.setInput(job, MyUser.class, "myuser", null, null, "id", "name");
job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
//当reduce输出类型与map输出类型一致时,map的输出类型可以不设置
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
return job.isSuccessful()?0:1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
int exit = ToolRunner.run(new WordCount(), args);
System.exit(exit);
}
}
class MyUser implements Writable, DBWritable {
private Long id;
private String name;
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(this.id);
Text.writeString(out, this.name);
}
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.id = in.readLong();
this.name = Text.readString(in);
}
@Override
public void write(PreparedStatement statement) throws SQLException {
statement.setLong(1, this.id);
statement.setString(2, this.name);
}
@Override
public void readFields(ResultSet resultSet) throws SQLException {
this.id = resultSet.getLong(1);
this.name = resultSet.getString(2);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.id + "\t" + this.name;
}
}
FileInputFormat 的实现之TextInputFormat
##说明 TextInputFormat默认是按行切分记录record,本篇在于理解,对于同一条记录record,如果被切分在不同的split时是怎么处理的。首先getSplits是在逻辑上划分,并没有物理切分,也就是只是记录每个split从文件的个位置读到哪个位置,文件还是一个整体。所以在LineRecordReader中,它的处理方式是每个split多读一行,也就是读到下一个split的第一行。然后除了每个文件的第一个split,其他split都跳过第一行,进而避免重复读取,这种方式去处理。
##FileInputFomat 之 getSplits TextInputFormat 继承TextInputFormat,并没有重写getSplits,而是沿用父类的getSplits方法,下面看下该方法的源码
public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job) throws IOException {
StopWatch sw = new StopWatch().start();
//getFormatMinSplitSize() == 1,getMinSplitSize(job)为用户设置的切片最小值,默认1。 job.getConfiguration().getLong("mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.minsize", 1L);
long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job));
// getMaxSplitSize(job)为用户设置的切片最大值,context.getConfiguration().getLong("mapreduce.input.fileinputformat.split.maxsize", Long.MAX_VALUE);
long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job);
// generate splits
List<InputSplit> splits = new ArrayList<InputSplit>();
List<FileStatus> files = listStatus(job);
for (FileStatus file: files) {
Path path = file.getPath();
long length = file.getLen();
if (length != 0) {
BlockLocation[] blkLocations;
//LocatedFileStatus带有blockLocation信息
if (file instanceof LocatedFileStatus) {
blkLocations = ((LocatedFileStatus) file).getBlockLocations();
} else {
FileSystem fs = path.getFileSystem(job.getConfiguration());
blkLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(file, 0, length);
}
//判断文件是否可切分
if (isSplitable(job, path)) {
long blockSize = file.getBlockSize();
//真正的切片设置大小判断,computeSplitSize方法中的实现,返回值 Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize));
long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize);
long bytesRemaining = length;
while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) {
int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize,
blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
bytesRemaining -= splitSize;
}
if (bytesRemaining != 0) {
int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining,
blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
}
} else { // not splitable
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
// Log only if the file is big enough to be splitted
if (length > Math.min(file.getBlockSize(), minSize)) {
LOG.debug("File is not splittable so no parallelization "
+ "is possible: " + file.getPath());
}
}
splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, blkLocations[0].getHosts(),
blkLocations[0].getCachedHosts()));
}
} else {
//Create empty hosts array for zero length files
splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, new String[0]));
}
}
// Save the number of input files for metrics/loadgen
job.getConfiguration().setLong(NUM_INPUT_FILES, files.size());
sw.stop();
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Total # of splits generated by getSplits: " + splits.size()
+ ", TimeTaken: " + sw.now(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
return splits;
}
##FileInputFomat 之 createRecordReader,主要是看LineRecordReader
public RecordReader<LongWritable, Text>
createRecordReader(InputSplit split,
TaskAttemptContext context) {
//设置record的分隔符
String delimiter = context.getConfiguration().get(
"textinputformat.record.delimiter");
byte[] recordDelimiterBytes = null;
if (null != delimiter)
recordDelimiterBytes = delimiter.getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8);
return new LineRecordReader(recordDelimiterBytes);
}
##LineRecordReader的方法initialize和nextKeyValue方法
public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit,
TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException {
FileSplit split = (FileSplit) genericSplit;
Configuration job = context.getConfiguration();
this.maxLineLength = job.getInt(MAX_LINE_LENGTH, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
start = split.getStart();
end = start + split.getLength();
final Path file = split.getPath();
// open the file and seek to the start of the split
final FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(job);
fileIn = fs.open(file);
//判断是否压缩,赋值对应的SplitLineReader
CompressionCodec codec = new CompressionCodecFactory(job).getCodec(file);
if (null!=codec) {
isCompressedInput = true;
decompressor = CodecPool.getDecompressor(codec);
if (codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec) {
final SplitCompressionInputStream cIn =
((SplittableCompressionCodec)codec).createInputStream(
fileIn, decompressor, start, end,
SplittableCompressionCodec.READ_MODE.BYBLOCK);
in = new CompressedSplitLineReader(cIn, job,
this.recordDelimiterBytes);
start = cIn.getAdjustedStart();
end = cIn.getAdjustedEnd();
filePosition = cIn;
} else {
in = new SplitLineReader(codec.createInputStream(fileIn,
decompressor), job, this.recordDelimiterBytes);
filePosition = fileIn;
}
} else {
fileIn.seek(start);
in = new UncompressedSplitLineReader(
fileIn, job, this.recordDelimiterBytes, split.getLength());
filePosition = fileIn;
}
//这句是关键,由于getSplits的时候,并不能保证一条record记录,不被切分到不同的split。所以处理方式是,除了每个文件的第一个split,其他每个split多读一行
//所以避免重复读,不是开始的split都跳过第一行。
// If this is not the first split, we always throw away first record
// because we always (except the last split) read one extra line in
// next() method.
if (start != 0) {
start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start));
}
this.pos = start;
}
##接下来是nextKeyValue
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException {
if (key == null) {
key = new LongWritable();
}
key.set(pos);
if (value == null) {
value = new Text();
}
int newSize = 0;
// We always read one extra line, which lies outside the upper
// split limit i.e. (end - 1)
//这个in具体看是CompressedSplitLineReader还是UncompressedSplitLineReader,重写了其中的readerLine方法
while (getFilePosition() <= end || in.needAdditionalRecordAfterSplit()) {
if (pos == 0) {
//跳过utf的开头
newSize = skipUtfByteOrderMark();
} else {
//readerLine有两种实现方法,一种readCustomLine这种是自己定义了record的分隔符,还有一种是readDefaultLine,这种是没有自定义分隔符,默认的读取数据的方式,用\r,\n或者\r\n分割
newSize = in.readLine(value, maxLineLength, maxBytesToConsume(pos));
pos += newSize;
}
if ((newSize == 0) || (newSize < maxLineLength)) {
break;
}
// line too long. try again
LOG.info("Skipped line of size " + newSize + " at pos " +
(pos - newSize));
}
if (newSize == 0) {
key = null;
value = null;
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}

Flutter:在TextInputFormatter中使用NumberFormat
如何解决Flutter:在TextInputFormatter中使用NumberFormat?
这是因为在格式化值之后,您要添加一个新字符,但文本选择保持在同一位置,少一个字符,这会导致预期的行为
您可以TextInputFormatter这样修改:
class Numerictextformatter extends TextInputFormatter {
TextEditingValue formatEditUpdate(
TextEditingValue oldValue, TextEditingValue newValue) {
if (newValue.text.length == 0) {
return newValue.copyWith(text: '''');
} else if (newValue.text.compareto(oldValue.text) != 0) {
int selectionIndexFromTheRight = newValue.text.length - newValue.selection.end;
final f = new NumberFormat("#,###");
int num = int.parse(newValue.text.replaceAll(f.symbols.GROUP_SEP, ''''));
final newString = f.format(num);
return new TextEditingValue(
text: newString,
selection: TextSelection.collapsed(offset: newString.length - selectionIndexFromTheRight),
);
} else {
return newValue;
}
}
}
解决方法
我试图使用NumberFromatter的TextInputFormatter,但是当我尝试使用它,它完全搞砸了!这是我的TextInputFormatter实现代码:
class NumericTextFormatter extends TextInputFormatter {
TextEditingValue formatEditUpdate(TextEditingValue oldValue,TextEditingValue newValue) {
if(newValue.text.length > 0) {
int num = int.parse(newValue.text.replaceAll('','',''''));
final f = new NumberFormat("#,###");
return newValue.copyWith(text: f.format(num));
} else {
return newValue.copyWith(text: '''');
}
}
}
因此,当我将此格式化程序添加到TextField并尝试输入1到9时,我希望看到的内容如下:123,456,789
但这显示在TextField:
1
12
123
1,234
12,354 <- this is where it starts
123,564
1,235,674
12,356,874 <- and it happends again
似乎在添加一个字符后光标移动了。那么有人可以帮我吗?

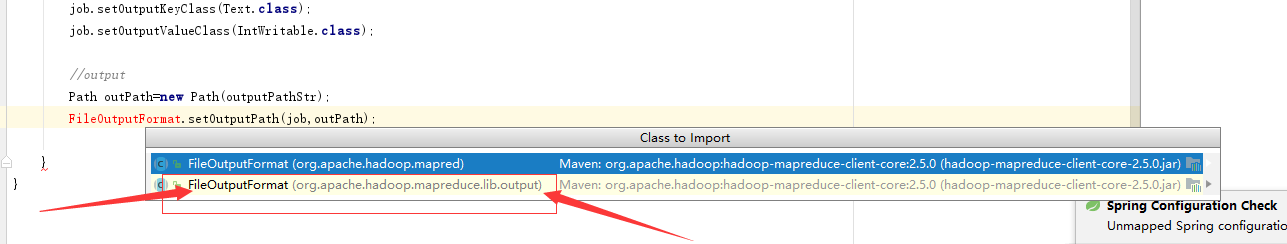
hadoop map reduce程序,注意引入FileOutputFormat类和FileInputFormat类
写map reduce程序时,引入
FileOutputFormat类时,必须注意,一定是:
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
同时
FileInputFormat也是一样,必须是
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
今天关于解析大于hdfs块大小的XmlInputFormat元素和hdfs小于单个块大小的文件的介绍到此结束,谢谢您的阅读,有关DBInputFormat、FileInputFormat 的实现之TextInputFormat、Flutter:在TextInputFormatter中使用NumberFormat、hadoop map reduce程序,注意引入FileOutputFormat类和FileInputFormat类等更多相关知识的信息可以在本站进行查询。
本文标签:





