本文将分享检查DataFrame中的哪些列是分类的的详细内容,并且还将对dataframe查看列属性进行详尽解释,此外,我们还将为大家带来关于Pandas-使用一个Dataframe列的子字符串比较两
本文将分享检查DataFrame中的哪些列是分类的的详细内容,并且还将对dataframe查看列属性进行详尽解释,此外,我们还将为大家带来关于Pandas - 使用一个 Dataframe 列的子字符串比较两个 Dataframe、Pandas DataFrame使用另一个DataFrame列过滤行、pandas.DataFrame.from_dict直接从字典构建DataFrame的方法、pandas之dataframe去掉冗余行以及左连接合并dataframe的相关知识,希望对你有所帮助。
本文目录一览:- 检查DataFrame中的哪些列是分类的(dataframe查看列属性)
- Pandas - 使用一个 Dataframe 列的子字符串比较两个 Dataframe
- Pandas DataFrame使用另一个DataFrame列过滤行
- pandas.DataFrame.from_dict直接从字典构建DataFrame的方法
- pandas之dataframe去掉冗余行以及左连接合并dataframe

检查DataFrame中的哪些列是分类的(dataframe查看列属性)
我是Pandas的新手,我想以一种简单通用的方法来查找categorical我的哪些列DataFrame,而无需手动指定每种列类型,这与本SO问题不同。使用以下项df创建:
import pandas as pddf = pd.read_csv("test.csv", header=None)例如
0 1 2 3 40 1.539240 0.423437 -0.687014 Chicago Safari1 0.815336 0.913623 1.800160 Boston Safari2 0.821214 -0.824839 0.483724 New York Safari。
更新(2018/02/04)问题假设数值列不是分类的,@Zero
接受的答案解决了这个问题。
注意-正如@Sagarkar的评论指出的那样,这并不总是正确的。
困难在于数据类型和分类/有序/标称类型是正交的概念,因此在它们之间进行映射并不容易。@Jeff的答案在下面指定了实现手动映射的精确方式。
答案1
小编典典您可以df._get_numeric_data()用来获取数字列,然后找出分类列
In [66]: cols = df.columnsIn [67]: num_cols = df._get_numeric_data().columnsIn [68]: num_colsOut[68]: Index([u''0'', u''1'', u''2''], dtype=''object'')In [69]: list(set(cols) - set(num_cols))Out[69]: [''3'', ''4'']
Pandas - 使用一个 Dataframe 列的子字符串比较两个 Dataframe
我能够使用下面的方法获得所需的输出
df1.merge(df2,left_on = df2.prod_ref.str.extract(''(\d+)'',expand = False),right_on = df1.prod_id.str.extract(''(\d+)'',how = ''left'')

Pandas DataFrame使用另一个DataFrame列过滤行
我会做merge
out = df1.merge(df2[['col1','col2']],on = 'col1',suffixes = ('','1')).query('col3>=col21').drop('col21',1)
out
Out[15]:
col1 col2 col3 col4
1 A 2 0.80 200
2 A 2 0.90 300
3 A 3 0.95 400
4 A 3 0.85 500
5 B 2 0.65 600
6 B 2 0.75 700
9 B 3 0.75 1000
或reindex
out = df1[df1['col3'] >= df2.set_index('col1')['col2'].reindex(df1['col1']).values]
Out[19]:
col1 col2 col3 col4
1 A 2 0.80 200
2 A 2 0.90 300
3 A 3 0.95 400
4 A 3 0.85 500
5 B 2 0.65 600
6 B 2 0.75 700
9 B 3 0.75 1000
您还可以使用map:
df1.loc[df1.col3 >= df1.col1.map(df2.set_index("col1").col2)]
我的方法类似于@Ben_Yo的合并答案,但是代码更多,但也许更直接。
您只需:
- 合并该列并创建新的数据框
ZStack{ Rectangle() .frame(width: geometry.size.width,height: geometry.size.height/3.25) .shadow(radius: 5) .foregroundColor(Color.white) //Words ontop of the Rectangle VStack { HStack { Spacer() Text("Hello World") }.padding(.trailing,40) Spacer() //<-- PROBLEM HERE }//.offset(y: -40) } - 根据条件(在本例中为
s),将数据名人 - 最后,将
s['col3'] >= s['col2']传递给s,结果将排除布尔系列df1中返回False的行:
s更改为返回True或False的布尔系列。
s
pandas.DataFrame.from_dict直接从字典构建DataFrame的方法
pandas函数中pandas.DataFrame.from_dict 直接从字典构建DataFrame 。
参数解析
DataFrame from_dict()方法用于将Dict转换为DataFrame对象。 此方法接受以下参数。
- data: dict or array like object to create DataFrame.data :字典或类似数组的对象来创建DataFrame。
- orient: The orientation of the data. The allowed values are (‘columns’, ‘index’), default is the ‘columns’. orient :数据的方向。 允许值为(“列”,“索引”),默认值为“列”。 Specify orient=''index'' to create the DataFrame using dictionary keys as rows:。 当参数orient为index值时,会将字典的keys作为DataFrame的行。(默认是keys变为列)
- columns: a list of values to use as labels for the DataFrame when orientation is ‘index’. If it’s used with columns orientation, ValueError is raised. columns :当方向为“索引”时,用作DataFrame标签的值的列表。 如果与列方向一起使用,则会引发ValueError 。
实例
1)By default the keys of the dict become the DataFrame columns:
默认是将字典的keys作为列
data = {''col_1'': [3, 2, 1, 0], ''col_2'': [''a'', ''b'', ''c'', ''d'']}
pd.DataFrame.from_dict(data)
col_1 col_2
0 3 a
1 2 b
2 1 c
3 0 d
2) Specify orient=''index'' to create the DataFrame using dictionary keys as rows: 参数orient为index值时,会将字典的keys作为DataFrame的行
data = {''row_1'': [3, 2, 1, 0], ''row_2'': [''a'', ''b'', ''c'', ''d'']}
pd.DataFrame.from_dict(data, orient=''index'')
0 1 2 3
row_1 3 2 1 0
row_2 a b c d
3) orient为index值时, 可以手动命名列名
pd.DataFrame.from_dict(data, orient=''index'',
columns=[''A'', ''B'', ''C'', ''D''])
A B C D
row_1 3 2 1 0
row_2 a b c d
参考: pandas.DataFrame.from_dict — pandas 1.3.4 documentation
到此这篇关于pandas.DataFrame.from_dict直接从字典构建DataFrame的方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关pandas字典构建DataFrame内容请搜索以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持!
- Pandas DataFrame转换为字典的方法
- pandas通过字典生成dataframe的方法步骤
- 从列表或字典创建Pandas的DataFrame对象的方法
- pandas 实现字典转换成DataFrame的方法

pandas之dataframe去掉冗余行以及左连接合并dataframe
去掉冗余行
重现冗余数据
zylMBP:~ zhangyalin$ python3
Python 3.6.5 (v3.6.5:f59c0932b4, Mar 28 2018, 03:03:55)
[GCC 4.2.1 (Apple Inc. build 5666) (dot 3)] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import pandas as pd
>>> df = pd.DataFrame({"A":["foo", "foo", "foo", "bar"]})
>>> print(df)
A
0 foo
1 foo
2 foo
3 bar
三种方式去冗余数据
方式1
>>> df.drop_duplicates(subset=[''A''], keep=False)
A
3 bar
>>>
keep=False表示删除所有冗余行。
方式2
>>> df.drop_duplicates(subset=[''A''], keep=''first'')
A
0 foo
3 bar
>>>
keep==''first''表示保留第一行数据,其他冗余行删除。
方式3
>>> df.drop_duplicates(subset=[''A''], keep=''last'')
A
2 foo
3 bar
>>>
keep==''last''表示保留最后一行数据,其他冗余行删除。
pandas左连接两个dataframe
result = pd.merge(left, right, how=''left'', on=[''key1'', ''key2''])
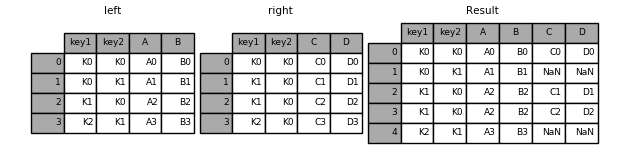
参考
pandas.DataFrame.drop_duplicates Merge, join, and concatenate
我们今天的关于检查DataFrame中的哪些列是分类的和dataframe查看列属性的分享已经告一段落,感谢您的关注,如果您想了解更多关于Pandas - 使用一个 Dataframe 列的子字符串比较两个 Dataframe、Pandas DataFrame使用另一个DataFrame列过滤行、pandas.DataFrame.from_dict直接从字典构建DataFrame的方法、pandas之dataframe去掉冗余行以及左连接合并dataframe的相关信息,请在本站查询。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

