在本文中,我们将给您介绍关于ios–我可以安全地删除〜/Library/ApplicationSupport/iPhoneSimulator/6.1/tmp目录的内容吗?的详细内容,此外,我们还将为您
在本文中,我们将给您介绍关于ios – 我可以安全地删除〜/ Library / Application Support / iPhone Simulator / 6.1 / tmp目录的内容吗?的详细内容,此外,我们还将为您提供关于Android Design Support Library - FloatingActionButton、Android Design Support Library--FloatingActionButton 及其 Behavior 的使用、android – ApplicationStatus类E / SysUtils:ApplicationStat中的ApplicationContext为null、Apple Watch Simulator上的watchOS中运行SpriteKit游戏(xCode 8,Swift 3,iOS 10) – libswiftSwiftOnoneSupport错误的知识。
本文目录一览:- ios – 我可以安全地删除〜/ Library / Application Support / iPhone Simulator / 6.1 / tmp目录的内容吗?
- Android Design Support Library - FloatingActionButton
- Android Design Support Library--FloatingActionButton 及其 Behavior 的使用
- android – ApplicationStatus类E / SysUtils:ApplicationStat中的ApplicationContext为null
- Apple Watch Simulator上的watchOS中运行SpriteKit游戏(xCode 8,Swift 3,iOS 10) – libswiftSwiftOnoneSupport错误

ios – 我可以安全地删除〜/ Library / Application Support / iPhone Simulator / 6.1 / tmp目录的内容吗?
通过它的外观3GB是什么,那个文件夹可以轻松架50GB!
我假设我可以删除那里有什么?不应该自动删除?
解决方法
> tmp目录名称似乎表明它们是可删除的.
>其他模拟器(6.0,5.1)工作正常,没有tmp文件夹中的大文件.
>从五月份的this tweet年,越狱开发商Ryan Petrich建议删除这些文件,并没有跟进任何问题.
>他似乎认为这是一个跳板bug,并在this jailbreak tweak修正.
>按照推文,我只删除了gridImages.*,ghostlyIcons.*,iconImages.*和iconLabels_gray.*.离开了IconsCache和lsidentifier plist,因为它们没有占用太多空间(并且存在于其他模拟器版本中).
FWIW,我的模拟器在删除文件后运行正常.

Android Design Support Library - FloatingActionButton
是一个负责显示界面基本操作的圆形按钮。Design library中的FloatingActionButton 实现了一个默认颜色为主题中colorAccent的悬浮操作按钮。 FloatingActionButton——FAB使用非常简单,你可以指定在加强型FrameLayout里面——CoordinatorLayout,这个我们后面再将。 关于FAB的使用,你可以把它当做一个button即可。
- 填充色以来自rippleColor
- 自定义实现参考Android Floating Action Button (FAB) Tutorial
参考资料: http://blog.csdn.net/eclipsexys/article/details/46349721

Android Design Support Library--FloatingActionButton 及其 Behavior 的使用
关于使用
其实我相信很多人都用过了 Material Design 控件了,但是还是要说一下,毕竟有些人接触的晚一些,一些人接触的早一些,先从最简单的使用看起:
| 属性值 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| app:elevation | 设置 FAB 未按下时的景深 |
| app:pressedTranslationZ | 设置 FAB 按下时的景深 |
| app:fabSize | 设置 FAB 的大小,默认只有 normal 和 mini 两种选项 |
| app:borderWidth | 设置 FAB 的边框宽度 |
| android:src | 设置 FAB 的 drawaber |
| app:rippleColor | 设置 FAB 按下时的背景色 |
| app:backgroundTint | 设置 FAB 未按下时的背景色 |
| app:layout_anchor | 设置 FAB 的锚点 |
| app:layout_anchorGravity | 设置 FAB 相对于锚点的位置 |
| app:layout_behavior | 设置 FAB 的 Behavior 行为属性 |
大部分的属性还是很好理解的,这里要提一下几个注意的点
- app:borderWidth : 这个一般设置为 0dp,不然的话在 4.1 的 sdk 上 FAB 会显示为正方形,而且在 5.0 以后的 sdk 没有阴影效果
- app:rippleColor:当我使用
com.android.support:design:23.2.0的时候这个属性会失效,建议使用最新的com.android.support:design:23.3.0''或者适当的降低版本 - android:layout_marginBottom : 由于 FAB 支持库仍然存在一些 bug,在 Kitkat 和 Lollipop 中分别运行示例代码,可以看到如下结果:
Lollipop 中的 FAB:

Lollipop 中的 FAB
Kitkat 中的 FAB:

Kitkat 中的 FAB
很容易看出,Lollipop 中存在边缘显示的问题。为了解决此问题,API21+ 的版本统一定义底部与右边缘空白为 16dp,Lollipop 以下版本统一设置为 0dp. 解决办法:
values/dimens.xml
<dimen name="fab_margin_right">0dp</dimen>
<dimen name="fab_margin_bottom">0dp</dimen>values-v21/dimens.xml
<dimen name="fab_margin_right">16dp</dimen>
<dimen name="fab_margin_bottom">16dp</dimen>布局文件的 FAB 中,也设置相应的值:
<android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton
...
...
android:layout_marginBottom="@dimen/fab_margin_bottom"
android:layout_marginRight="@dimen/fab_margin_right"/>以上这段话出处
- app:layout_anchor:和
app:layout_anchorGravity属性一起搭配使用,可以做出不同的效果:
最简单的使用
<android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton
...
...
app:layout_anchor="@id/mRecycleView"
app:layout_anchorGravity="bottom|right|end"
...
/>
最简单的使用
更酷炫的效果
<android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton
...
app:layout_anchor="@id/collapsingToolbarLayout"
app:layout_anchorGravity="bottom|center"
...
/>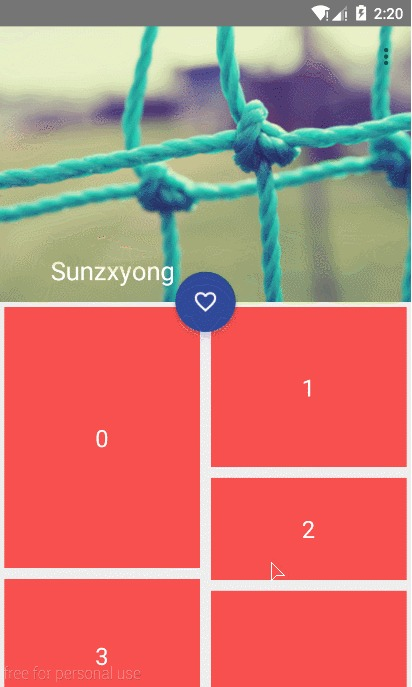
更酷炫的效果
这张图片出处
可以看出我们只要使用 app:layout_anchor 属性设置一个控件作为 FAB 的锚,然后通过 app:layout_anchorGravity 属性放置 FAB 在这个相对的锚的位置,就能做出你想要的效果。
- app:layout_behavior:这个属性接下来会重点讲,也就是这个属性成就了 Material Design 的众多动画交互效果,我们熟知的 SnackBar 配合 FAB 可以侧滑以及 APPBarLayout 等动画效果都是通过 Behavior 做出来的
自定义 Behavior
如果你还记得这张图的话:

交互效果
或者说你见过这种交互效果:
交互效果
其实这些都是通过 Behavior 这个类做出来的,以上的两种动画都是默认自带的 Behavior,在 CoordinatorLayout 内部有对 Behavior 类的描述:
/**
* Interaction behavior plugin for child views of {@link CoordinatorLayout}.
*
* <p>A Behavior implements one or more interactions that a user can take on a child view.
* These interactions may include drags, swipes, flings, or any other gestures.</p>
*
* @param <V> The View type that this Behavior operates on
*/
public static abstract class Behavior<V extends View> {可以看到这是一个抽象类,我们可以在各个 Material Design 去实现这个类,这里提到 FAB,我们可以找一下 FAB 中的默认 Behavior 交互的实现:
/**
* Behavior designed for use with {@link FloatingActionButton} instances. It''s main function
* is to move {@link FloatingActionButton} views so that any displayed {@link Snackbar}s do
* not cover them.
*/
public static class Behavior extends CoordinatorLayout.Behavior<FloatingActionButton> {
// We only support the FAB <> Snackbar shift movement on Honeycomb and above. This is
// because we can use view translation properties which greatly simplifies the code.
private static final boolean SNACKBAR_BEHAVIOR_ENABLED = Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 11;这里只贴出一部分,如果英文不差的话看得懂注释的意思:大致就是说我们这里只提供 API 11 以上的 Snackbar 和 FAB 的运动交互效果,也就是我们上面动图中看到的效果:当出现了一个 SnackBar 时候,FAB 会自动向上移动一段距离,当 SnackBar 消失的时候 FAB 会回到原来位置,那么如何定义一个属于我们自己的 Behavior,先来看看需要用到的知识:
其实细分的话有两种情况:
1、当一个 View 的变化依赖于另一个 View 的尺寸、位置等变化的时候,我们只需要关注以下两种方法:
* @param parent 第一个参数不用解释吧
* @param 你要依赖别的View的那个View
* @param dependency 你要依赖的View
* @return return 如果找到了你依赖的那个View就返回true
* @see #onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout, android.view.View, android.view.View)
*/
public boolean layoutDependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child, View dependency) {
return false;
}* @param parent 同上,不解释
* @param child 同上
* @param dependency 同上
* @return 如果这个Behavior改变了child的位置或者尺寸大小就返回true
*/
public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, V child, View dependency) {
return false;
}其实 FAB 里面就是实现了这两种方法来与 SnackBar 交互的,看一下标准写法:
@Override
public boolean layoutDependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent,
FloatingActionButton child, View dependency) {
// We''re dependent on all SnackbarLayouts (if enabled)
return SNACKBAR_BEHAVIOR_ENABLED && dependency instanceof Snackbar.SnackbarLayout;
}
...
...
@Override
public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, FloatingActionButton child,
View dependency) {
if (dependency instanceof Snackbar.SnackbarLayout) {
updateFabTranslationForSnackbar(parent, child, dependency);
} else if (dependency instanceof AppBarLayout) {
// If we''re depending on an AppBarLayout we will show/hide it automatically
// if the FAB is anchored to the AppBarLayout
updateFabVisibility(parent, (AppBarLayout) dependency, child);
}
return false;
}2、另一种情况是当一个 View 监听 CoordinatorLayout 内部滑动的 View 进行交互时,我们需要关注的方法稍微多一点,这些方法都写在了 NestedScrollingParent 接口里面,而且 CoordinatorLayout 已经对这个接口有了默认实现:
onStartNestedScroll
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param directTargetChild the child view of the CoordinatorLayout that either is or
* contains the target of the nested scroll operation
* @param target the descendant view of the CoordinatorLayout initiating the nested scroll
* @param nestedScrollAxes the axes that this nested scroll applies to. See
* {@link ViewCompat#SCROLL_AXIS_HORIZONTAL},
* {@link ViewCompat#SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL} 滑动时是横轴和纵轴
* @return true if the Behavior wishes to accept this nested scroll
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onStartNestedScroll(View, View, int)
*/
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout,
V child, View directTargetChild, View target, int nestedScrollAxes) {
return false;
}onNestedPreScroll
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param target the descendant view of the CoordinatorLayout performing the nested scroll
* @param dx the raw horizontal number of pixels that the user attempted to scroll
* @param dy the raw vertical number of pixels that the user attempted to scroll
* @param consumed out parameter. consumed[0] should be set to the distance of dx that
* was consumed, consumed[1] should be set to the distance of dy that
* was consumed
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedPreScroll(View, int, int, int[])
*/
public void onNestedPreScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target,
int dx, int dy, int[] consumed) {
// Do nothing
}onNestedFling
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param target the descendant view of the CoordinatorLayout performing the nested scroll
* @param velocityX horizontal velocity of the attempted fling
* @param velocityY vertical velocity of the attempted fling
* @param consumed true if the nested child view consumed the fling
* @return true if the Behavior consumed the fling
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedFling(View, float, float, boolean)
*/
public boolean onNestedFling(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target,
float velocityX, float velocityY, boolean consumed) {
return false;
}onNestedScroll
* @param coordinatorLayout the CoordinatorLayout parent of the view this Behavior is
* associated with
* @param child the child view of the CoordinatorLayout this Behavior is associated with
* @param target the descendant view of the CoordinatorLayout performing the nested scroll
* @param dxConsumed horizontal pixels consumed by the target''s own scrolling operation
* @param dyConsumed vertical pixels consumed by the target''s own scrolling operation
* @param dxUnconsumed horizontal pixels not consumed by the target''s own scrolling
* operation, but requested by the user
* @param dyUnconsumed vertical pixels not consumed by the target''s own scrolling operation,
* but requested by the user
*
* @see NestedScrollingParent#onNestedScroll(View, int, int, int, int)
*/
public void onNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, V child, View target,
int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed) {
// Do nothing
}如果是码农的话上面的英文注释应该不难吧,这四个方法的区别如下:
- onStartNestedScroll :当你想要初始化一个滑动的时候调用
- onNestedPreScroll 和 onNestedScroll:存在着两个方法的原因是一些 Behaviors(比如和 AppBarLayout 使用的)可能会消费掉部分滚动事件,我们可以在 onNestedPreScroll 方法内部计算需要滚动的距离,具体的话请看这里
- onNestedScroll:当 target 正尝试滑动或者已经滑动时候调用这个方法
- onNestedFling:看到 Fling 就明白是这是 Fling 情况下调用的方法,Fling 最直观的体现是你滑动一个 ListView 时松手的时候 ListView 还会因为惯性自动滑动一小段距离
这么看可能太笼统了,看一下这一类 Behavior 的实际体现,我们自己自定义一个 Behavior:
public class FadeBehavior extends FloatingActionButton.Behavior {
/**
* 因为是在XML中使用app:layout_behavior定义静态的这种行为,
* 必须实现一个构造函数使布局的效果能够正常工作。
* 否则 Could not inflate Behavior subclass error messages.
* @param context
* @param attrs
*/
public FadeBehavior(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super();
}
/**
* 处理垂直方向上的滚动事件
*
* @param coordinatorLayout
* @param child
* @param directTargetChild
* @param target
* @param nestedScrollAxes
* @return
*/
@Override
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout,
FloatingActionButton child, View directTargetChild, View target, int nestedScrollAxes) {
// Ensure we react to vertical scrolling
return nestedScrollAxes == ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL ||
super.onStartNestedScroll(coordinatorLayout, child, directTargetChild, target,
nestedScrollAxes);
}
/**
* 检查Y的位置,并决定按钮是否动画进入或退出
* @param coordinatorLayout
* @param child
* @param target
* @param dxConsumed
* @param dyConsumed
* @param dxUnconsumed
* @param dyUnconsumed
*/
@Override
public void onNestedScroll(CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, FloatingActionButton child,
View target, int dxConsumed, int dyConsumed, int dxUnconsumed, int dyUnconsumed) {
super.onNestedScroll(coordinatorLayout, child, target, dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed,
dyUnconsumed);
if (dyConsumed > 0 && child.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE) {
// User scrolled down and the FAB is currently visible -> hide the FAB
child.hide();
} else if (dyConsumed < 0 && child.getVisibility() != View.VISIBLE) {
// User scrolled up and the FAB is currently not visible -> show the FAB
child.show();
}
}
}这里继承了 FAB 的 Behavior 写了一个我们自己的实现,注意实现自己的 Behavior 的时候一定要重写两个参数的构造方法,因为 CoordinatorLayout 会从我们在 XML 中定义的 app:layout_behavior 属性去找这个 Behavior,了解自定义 View 的对这个应该不会陌生,一般的写法是:
app:layout_behavior=".FadeBehavior "在查资料的过程中发现很多人把自定义 Behavior 类所在的包名也写进去了,其实亲测没必要这样做,而且 CoordinatorLayout 里面也有专门的方法去解析:
static Behavior parseBehavior(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, String name) {
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(name)) {
return null;
}
final String fullName;
if (name.startsWith(".")) {
// Relative to the app package. Prepend the app package name.
fullName = context.getPackageName() + name;
} else if (name.indexOf(''.'') >= 0) {
// Fully qualified package name.
fullName = name;
} else {
// Assume stock behavior in this package (if we have one)
fullName = !TextUtils.isEmpty(WIDGET_PACKAGE_NAME)
? (WIDGET_PACKAGE_NAME + ''.'' + name)
: name;
}
try {
Map<String, Constructor<Behavior>> constructors = sConstructors.get();
if (constructors == null) {
constructors = new HashMap<>();
sConstructors.set(constructors);
}
Constructor<Behavior> c = constructors.get(fullName);
if (c == null) {
final Class<Behavior> clazz = (Class<Behavior>) Class.forName(fullName, true,
context.getClassLoader());
c = clazz.getConstructor(CONSTRUCTOR_PARAMS);
c.setAccessible(true);
constructors.put(fullName, c);
}
return c.newInstance(context, attrs);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Could not inflate Behavior subclass " + fullName, e);
}
}可以看到用这种方式的系统会自动给我们加上包名,写太多反而显的累赘,这个自定义 Behavior 应该很好理解,效果就是随着 RecycleView 的滑动 FAB 会隐藏 / 显示,是一个很常见的效果:
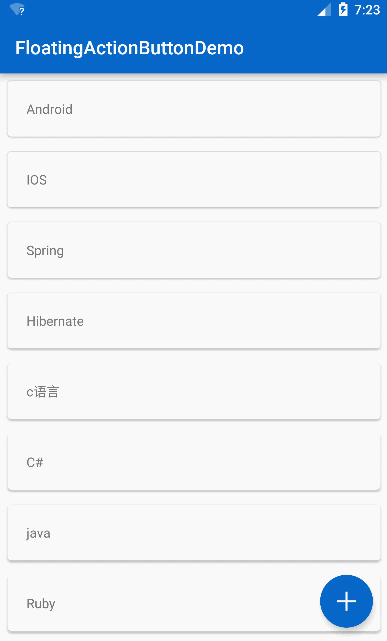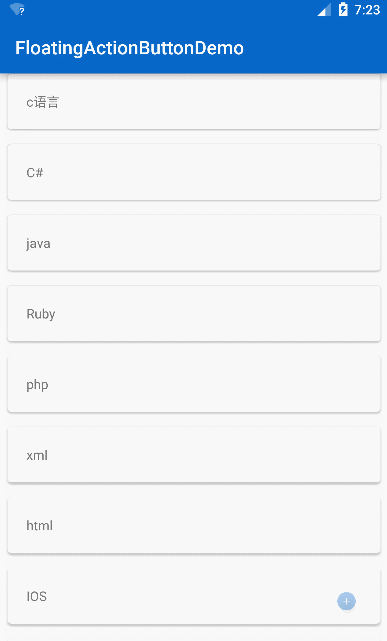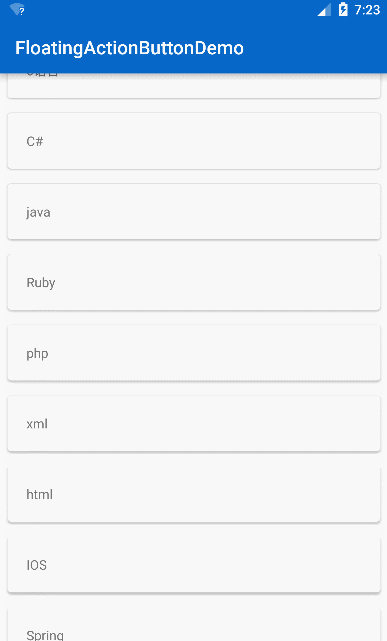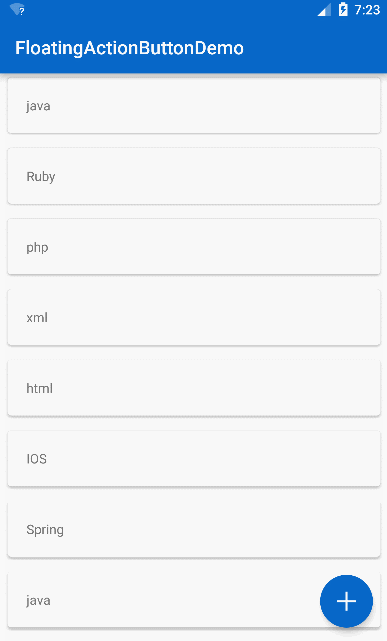
常见效果
只要向上滚动 FAB 就会消失,向下滚动 FAB 就是显示,这里要注意的是 FAB 可以与 RecycleView 形成这种效果,但是暂时并不支持 ListView,没关系,反正 RecycleView 当成 ListView 来用就好,接下来仿照实现知乎的 FAB 效果的实现,先看一下知乎的效果:
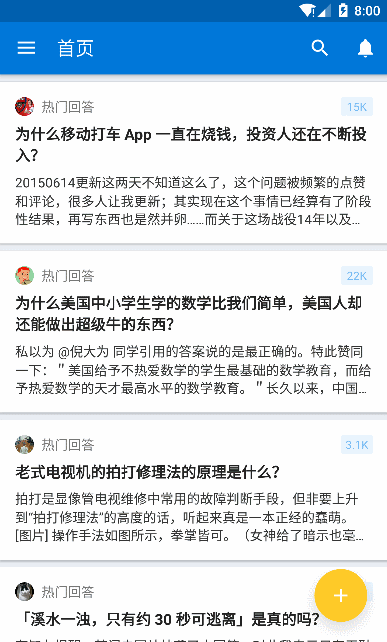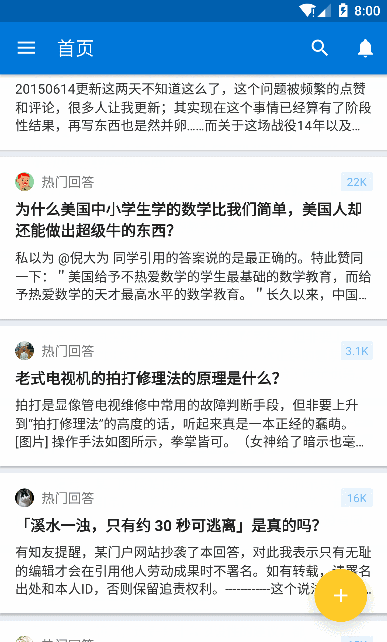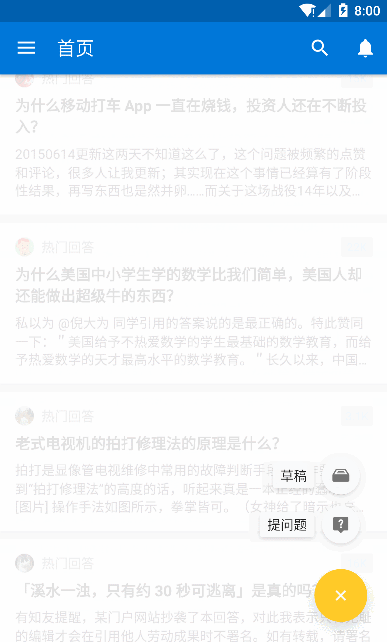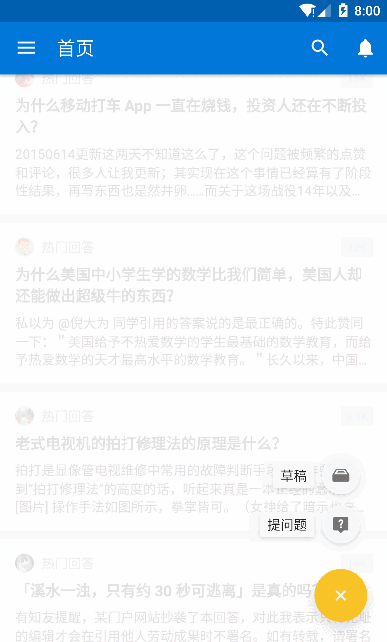
知乎的效果
可以很清楚的看到 FAB 随着 RecycleView 的滑动呈现出滚动推出的效果,并且点击 FAB 会出现旋转效果并且弹出一个蒙版,我们可以先自定义一个用于执行 FAB 旋转的 Behavior,可以看到这里 FAB 是逆时针旋转 135 度,那么代码就可以这么写:
public class RotateBehavior extends CoordinatorLayout.Behavior<FloatingActionButton> {
private static final String TAG = RotateBehavior.class.getSimpleName();
public RotateBehavior() {
}
public RotateBehavior(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
@Override
public boolean layoutDependsOn(CoordinatorLayout parent, FloatingActionButton child, View dependency) {
return dependency instanceof Snackbar.SnackbarLayout;
}
@Override
public boolean onDependentViewChanged(CoordinatorLayout parent, FloatingActionButton child, View dependency) {
float translationY = getFabTranslationYForSnackBar(parent, child);
float percentComplete = -translationY / dependency.getHeight();
child.setRotation(-135 * percentComplete);
child.setTranslationY(translationY);
return true;
}
private float getFabTranslationYForSnackBar(CoordinatorLayout parent,
FloatingActionButton fab) {
float minOffset = 0;
final List<View> dependencies = parent.getDependencies(fab);
for (int i = 0, z = dependencies.size(); i < z; i++) {
final View view = dependencies.get(i);
if (view instanceof Snackbar.SnackbarLayout && parent.doViewsOverlap(fab, view)) {
//view.getHeight()固定为144
//ViewCompat.getTranslationY(view)从144-0,再从0-144
minOffset = Math.min(minOffset,
ViewCompat.getTranslationY(view) - view.getHeight());
Log.d("TranslationY",ViewCompat.getTranslationY(view)+"");
Log.d("Height",view.getHeight()+"");
}
}
return minOffset;
}
}这里可能就这段代码比较难理解:
minOffset = Math.min(minOffset,
ViewCompat.getTranslationY(view) - view.getHeight());我在上面打了两个 Log,分别得出了 ViewCompat.getTranslationY(view) 和 view.getHeight() ,这样看代码就比较容易看懂,但是为什么 ViewCompat.getTranslationY(view) 是正数呢,这里的的 View 我们都知道指的是 SnackBar,我们都知道向上移动的话 getTranslationY 应该是负数啊,其实 SnackBar 的源代码中有一个这样的动作:
ViewCompat.setTranslationY(mView, mView.getHeight());
ViewCompat.animate(mView)
.translationY(0f)
.setInterpolator(FAST_OUT_SLOW_IN_INTERPOLATOR)
.setDuration(ANIMATION_DURATION)也就是说 SnackBar 一开始就向下移动了 mView.getHeight () 的长度,当 SnackBar 出现的时候只是向着它原来的位置移动,本质上还是相当于从它原来的位置移动了一段距离,只是这个距离随着 SnackBar 向上浮动的越来越多而变得越来越小,直至回到原来的位置,这么说应该可以理解了,接下来我们在 XML 文件中加入一个 TextView 作为蒙版:
<TextView
android:id="@+id/hide"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#ffff"
android:visibility="gone" />因为 CoordinatorLayout 相当于帧布局是一层一层叠加的所以这个蒙版放在 RecycleView 和 FAB 中间,整个布局代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:id="@+id/coor"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView
android:id="@+id/mRecycleView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
</android.support.v7.widget.RecyclerView>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/hide"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#ffff"
android:visibility="gone" />
<android.support.design.widget.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/fab"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="@dimen/fab_margin_bottom"
android:layout_marginEnd="@dimen/fab_margin_right"
android:src="@mipmap/plus"
app:backgroundTint="#0767C8"
app:borderWidth="0dp"
app:elevation="6dp"
app:fabSize="normal"
app:layout_anchor="@id/mRecycleView"
app:layout_anchorGravity="bottom|right|end"
app:layout_behavior=".FadeBehavior"
app:pressedTranslationZ="12dp"
app:rippleColor="#0767C8" />
</android.support.design.widget.CoordinatorLayout>看看效果:
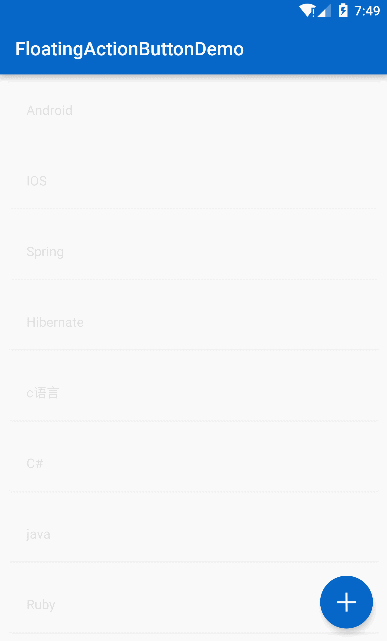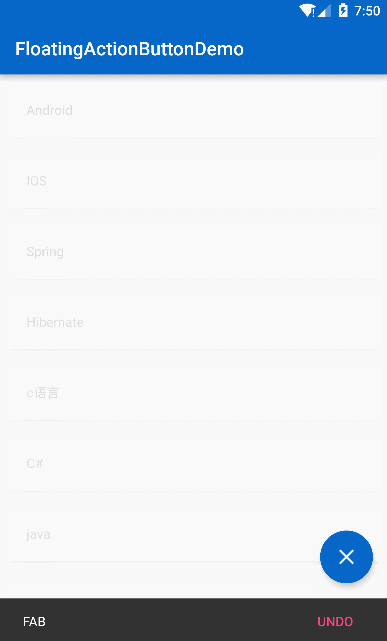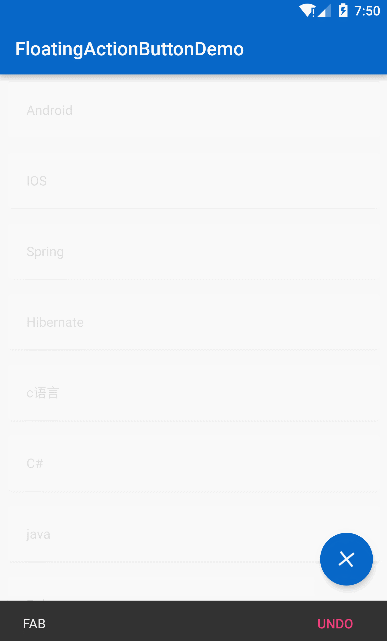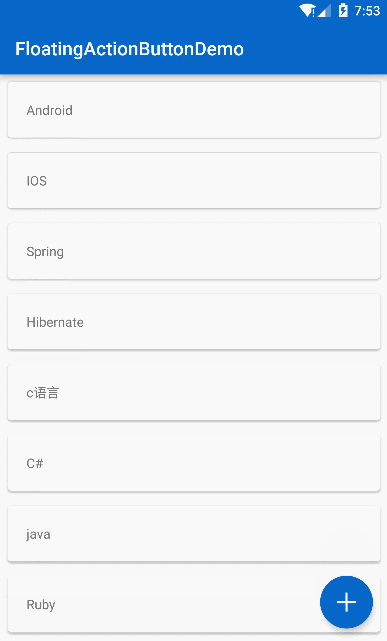
效果
是不是有一个很奇怪的地方,知乎的 FAB 并没有 SnackBar 弹出啊,那就说明一开始的思路错了,但是一个 FAB 只能设置一个 app:layout_behavior ,如果我们把这个 Behavior 用作 FAB 的旋转效果那么 FAB 的滚动移出视图的效果就没了,所以换一种思路,用 Object 动画来做 FAB 的旋转效果:
//开始旋转
public void turnLeft(View v) {
ObjectAnimator objectAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(v, "rotation", 0, -155, -135);
objectAnimator.setDuration(300);
objectAnimator.setInterpolator(new AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator());
objectAnimator.start();
hide.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
AlphaAnimation alphaAnimation = new AlphaAnimation(0, 0.75f);
alphaAnimation.setDuration(300);
alphaAnimation.setFillAfter(true);
hide.startAnimation(alphaAnimation);
hide.setClickable(true);
isOpen = true;
}
//回到起始位置
public void turnRight(View v) {
ObjectAnimator objectAnimator = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(v, "rotation", -135, 20, 0);
objectAnimator.setDuration(300);
objectAnimator.setInterpolator(new AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator());
objectAnimator.start();
hide.setVisibility(View.GONE);
AlphaAnimation alphaAnimation = new AlphaAnimation(0.75f, 0);
alphaAnimation.setDuration(300);
alphaAnimation.setFillAfter(true);
hide.startAnimation(alphaAnimation);
hide.setClickable(false);
isOpen = false;
}
//注:hide就是TextView控件(蒙版)然后实现 FAB 的滚动移出视图效果的 Behavior:
public class ScrollAwareFABBehavior extends FloatingActionButton.Behavior {
//先慢后快再慢
private static final Interpolator INTERPOLATOR = new FastOutSlowInInterpolator();
private boolean mIsAnimatingOut = false;
public ScrollAwareFABBehavior(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super();
}
//初始条件
@Override
public boolean onStartNestedScroll(final CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, final FloatingActionButton child,
final View directTargetChild, final View target, final int nestedScrollAxes) {
//垂直滚动
return nestedScrollAxes == ViewCompat.SCROLL_AXIS_VERTICAL
|| super.onStartNestedScroll(coordinatorLayout, child, directTargetChild, target, nestedScrollAxes);
}
@Override
public void onNestedScroll(final CoordinatorLayout coordinatorLayout, final FloatingActionButton child,
final View target, final int dxConsumed, final int dyConsumed,
final int dxUnconsumed, final int dyUnconsumed) {
super.onNestedScroll(coordinatorLayout, child, target, dxConsumed, dyConsumed, dxUnconsumed, dyUnconsumed);
if (dyConsumed > 0 && !this.mIsAnimatingOut && child.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE) {
// User scrolled down and the FAB is currently visible -> hide the FAB
animateOut(child);
} else if (dyConsumed < 0 && child.getVisibility() != View.VISIBLE) {
// User scrolled up and the FAB is currently not visible -> show the FAB
animateIn(child);
}
}
// Same animation that FloatingActionButton.Behavior uses to hide the FAB when the AppBarLayout exits
private void animateOut(final FloatingActionButton button) {
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 14) {
//withLayer()使动画中的某些操作变得更顺畅,加速渲染,API 14以后
ViewCompat.animate(button).translationY(button.getHeight() + getMarginBottom(button)).setInterpolator(INTERPOLATOR).withLayer()
.setListener(new ViewPropertyAnimatorListener() {
public void onAnimationStart(View view) {
ScrollAwareFABBehavior.this.mIsAnimatingOut = true;
}
public void onAnimationCancel(View view) {
ScrollAwareFABBehavior.this.mIsAnimatingOut = false;
}
public void onAnimationEnd(View view) {
ScrollAwareFABBehavior.this.mIsAnimatingOut = false;
view.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}).start();
} else {
}
}
// Same animation that FloatingActionButton.Behavior uses to show the FAB when the AppBarLayout enters
private void animateIn(FloatingActionButton button) {
button.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= 14) {
ViewCompat.animate(button).translationY(0)
.setInterpolator(INTERPOLATOR).withLayer().setListener(null)
.start();
} else {
}
}
private int getMarginBottom(View v) {
int marginBottom = 0;
final ViewGroup.LayoutParams layoutParams = v.getLayoutParams();
if (layoutParams instanceof ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) {
marginBottom = ((ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams) layoutParams).bottomMargin;
}
return marginBottom;
}最后实现的效果:
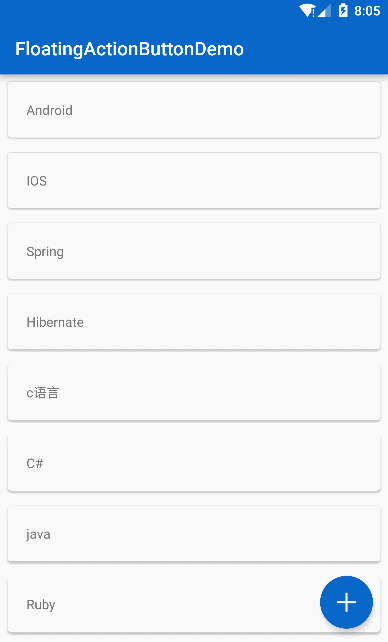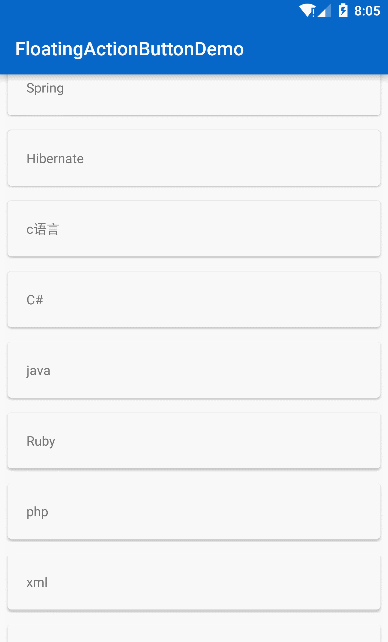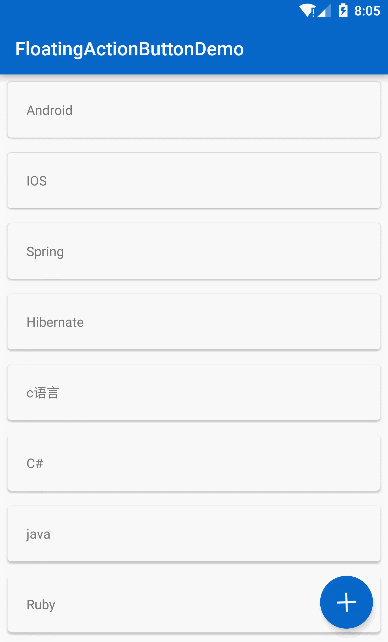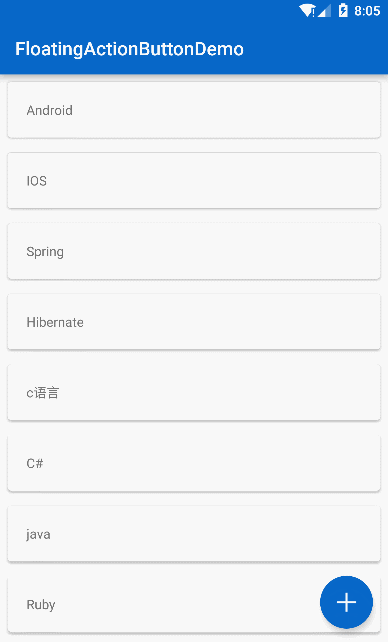
最终效果
这里部分参考了仿知乎 FloatingActionButton 浮动按钮动画效果实现
至于 FAB 弹出的 InBox 这里就不去实现了,比较麻烦,可以参考第三方的实现:
第三方实现
FloatingActionButtonPlus
写在末尾
主要参考:
浮动操作按钮的选择
FloatingActionButton.Behavior
codepath 教程:浮动操作按钮详解
Design Support Library (II): Floating Action Button
CoordinatorLayout 高级用法 - 自定义 Behavior
项目源代码
GitHub 地址
写文章不容易,如果可以的话请给个赞
文/李牧羊(简书作者)
原文链接:http://www.jianshu.com/p/cce743e092ec
著作权归作者所有,转载请联系作者获得授权,并标注 “简书作者”。

android – ApplicationStatus类E / SysUtils:ApplicationStat中的ApplicationContext为null
E / SysUtils:ApplicationStat中的ApplicationContext为null
有谁知道ApplicationStatus类?我没有在我的项目中
它发生在我在openGL中快速渲染纹理时
解决方法
我的问题是在打开新意图时直接传递额外的变量,如下所示.
>调用代码:
intent.putExtra("markerdata: ",assetVO);
>接收代码:
markerdata = (HashMap<String,Object>) getIntent().getSerializableExtra("markerdata");
2天前升级到Android Studio 1.3后,我总是变为空.
所以我的工作是将传递的信息捆绑在一起:
>调用代码:
Bundle b = new Bundle();
b.putSerializable("markerdata",assetVO);
intent.putExtras(b);
>接收代码:
Bundle extras = getIntent().getExtras();
markerdata = (HashMap<String,Object>) extras.getSerializable("markerdata");
现在它的工作原理.希望它可以帮助别人.

Apple Watch Simulator上的watchOS中运行SpriteKit游戏(xCode 8,Swift 3,iOS 10) – libswiftSwiftOnoneSupport错误
然后我通过设置“游戏”为我的项目添加了一个watchOS目标
文件>新>目标:

我检查了WatchExtension中的GameScene.swift,确定所有代码都在那里并设置了一个场景:
import SpriteKit
class GameScene: SKScene {
private var spinnyNode : SKShapeNode?
override func sceneDidLoad() {
if let label = self.childNode(withName: "//helloLabel") as? SKLabelNode {
label.alpha = 0.0
label.run(SKAction.fadeIn(withDuration: 2.0))
}
let w = (self.size.width + self.size.height) * 0.05
let spinnyNode = SKShapeNode(rectOf: CGSize(width: w,height: w),cornerRadius: w * 0.3)
spinnyNode.position = CGPoint(x: 0.0,y: 0.0)
spinnyNode.strokeColor = UIColor.red()
spinnyNode.linewidth = 8.0
spinnyNode.run(SKAction.sequence([SKAction.wait(forDuration: 0.5),SKAction.fadeOut(withDuration: 0.5),SKAction.removeFromParent()]))
spinnyNode.run(SKAction.repeatForever(SKAction.rotate(byAngle: 6.28,duration: 1)))
self.run(SKAction.repeatForever(SKAction.sequence([SKAction.wait(forDuration: 2.0),SKAction.run({
let n = spinnyNode.copy() as! SKShapeNode
self.addChild(n)
})])))
}
override func update(_ currentTime: TimeInterval) {
// Called before each frame is rendered
}
}
不幸的是,我似乎无法在Apple Watch Simulator上安装它.
我已经尝试了我能想到的一切,包括:
>清洁建筑等
>卸载/重新安装,
>查看了info.plist for common errors,
>使用Add Additional Simulators创建一个带有配对Apple Watch的新模拟器,
>已添加Skip Install =否,建议here,
>从iPhone模拟器中的配对iOS Apple Watch App安装(只是不安装),
>甚至添加了用户定义的项目设置,如raywenderlich watchOS教程中所建议的……
我甚至无法安装或出现在Apple Watch上.我不做什么?
UPDATE
我已经为iOS应用程序调整了部署目标到10.0,我终于能够从iPhone模拟器中的Apple Watch应用程序安装它,除了从Apple Watch Simulator启动Apple Watch App之外,我收到以下错误:
dyld: Library not loaded: @rpath/libswiftSwiftOnonesupport.dylib Referenced from: /Users/MYNAME/Library/Developer/CoreSimulator/Devices/XXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX/data/Containers/Bundle/Application/XXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX/MYAPPNAME.app/PlugIns/MYAPPWATCH Extension.appex/MYAPPWATCH Extension Reason: image not found (lldb)
这个错误是什么意思?不应该加载任何图像,因为它是默认的SpriteKit测试…
解决方法
因此,如果您将应用程序转换为Swift 3.0,将watchOS“游戏”目标添加到您的项目中,将iOS部署目标更改为10.0并在WatchOS 3.0模拟器和iPhone 6s iOS 10模拟器上运行,请更新以下设置:
将NO更改为YES:
Project > Targets > App Name > Embed Asset Packs In Product Bundle = YES
并且“你好,世界!”应该出现在Apple Watch上,带有旋转的脉冲spriteNode(屏幕截图中未显示,因为它没有足够快地捕获它).

请注意,您可能必须通过启动Apple Watch App,点击您的应用程序,然后按“Apple Watch上的显示”,从iPhone模拟器安装Apple Watch App中的应用程序.
今天的关于ios – 我可以安全地删除〜/ Library / Application Support / iPhone Simulator / 6.1 / tmp目录的内容吗?的分享已经结束,谢谢您的关注,如果想了解更多关于Android Design Support Library - FloatingActionButton、Android Design Support Library--FloatingActionButton 及其 Behavior 的使用、android – ApplicationStatus类E / SysUtils:ApplicationStat中的ApplicationContext为null、Apple Watch Simulator上的watchOS中运行SpriteKit游戏(xCode 8,Swift 3,iOS 10) – libswiftSwiftOnoneSupport错误的相关知识,请在本站进行查询。
本文标签:





