对于想了解c#–从IntPtr(16位)数组复制到托管的ushort的读者,本文将是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将详细介绍c#数组复制到另一个数组,并且为您提供关于c–将shortint复制到char数组
对于想了解c# – 从IntPtr(16位)数组复制到托管的ushort的读者,本文将是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将详细介绍c#数组复制到另一个数组,并且为您提供关于c – 将short int复制到char数组、c# – 将字节数组复制到通用类型而不进行装箱、C# 中 int short Int16 Int32 Int64 区别、C语言将数组复制到另一个数组的有价值信息。
本文目录一览:- c# – 从IntPtr(16位)数组复制到托管的ushort(c#数组复制到另一个数组)
- c – 将short int复制到char数组
- c# – 将字节数组复制到通用类型而不进行装箱
- C# 中 int short Int16 Int32 Int64 区别
- C语言将数组复制到另一个数组

c# – 从IntPtr(16位)数组复制到托管的ushort(c#数组复制到另一个数组)
public const int width = 2056;
public const int height = 2048;
public const int depth = 2;
public system.intPtr rawbits;
public ushort[] bits()
{
ushort[] output = new ushort[width * height];
short[] temp = new short[width * height];
Marshal.copy(rawbits,temp,width * height);
System.Buffer.Blockcopy(temp,output,width * height * depth);
return output;
}
以下问题中给出的建议没有帮助. (编译错误).
C# Marshal.Copy Intptr to 16 bit managed unsigned integer array
[顺便说一句,短阵列中确实有无符号的16位数据. Marshal.copy()不尊重标志,这就是我想要的.但我宁愿不只是假装短[]是一个ushort []]
解决方法
[DllImport("kernel32.dll",SetLastError = false)]
static extern void copyMemory(IntPtr destination,IntPtr source,UIntPtr length);
public static void copy<T>(IntPtr source,T[] destination,int startIndex,int length)
where T : struct
{
var gch = GCHandle.Alloc(destination,GCHandleType.Pinned);
try
{
var targetPtr = Marshal.UnsafeAddrOfPinnedArrayElement(destination,startIndex);
var bytesTocopy = Marshal.SizeOf(typeof(T)) * length;
copyMemory(targetPtr,source,(UIntPtr)bytesTocopy);
}
finally
{
gch.Free();
}
}
不便携,但性能不错.
选项2 – 不安全和指针:
public static void copy(IntPtr source,ushort[] destination,int length)
{
unsafe
{
var sourcePtr = (ushort*)source;
for(int i = startIndex; i < startIndex + length; ++i)
{
destination[i] = *sourcePtr++;
}
}
}
需要在项目构建属性中启用不安全选项.
选项3 – 反思(只是为了好玩,不要在生产中使用):
Marshal类在内部对所有copy(IntPtr,< array>,int,int)重载使用copyToManaged(IntPtr,object,int)方法(至少在.NET 4.5中).使用反射我们可以直接调用该方法:
private static readonly Action<IntPtr,int> _copyToManaged =
GetcopyToManagedMethod();
private static Action<IntPtr,int> GetcopyToManagedMethod()
{
var method = typeof(Marshal).getmethod("copyToManaged",System.Reflection.BindingFlags.Static | System.Reflection.BindingFlags.NonPublic);
return (Action<IntPtr,int>)method.CreateDelegate(
typeof(Action<IntPtr,int>),null);
}
public static void copy<T>(IntPtr source,int length)
where T : struct
{
_copyToManaged(source,destination,startIndex,length);
}
由于Marshal类的内部结构可以更改,因此该方法不可靠且不应使用,尽管此实现可能最接近其他Marshal.copy()方法重载.

c – 将short int复制到char数组
unsighed short s_int = 2;
我想将这个数字复制到char数组到char数组的第一个和第二个位置.
假设我们有char缓冲区[10];我们希望将s_int的两个字节复制到缓冲区[0]和缓冲区[1].
我该怎么做?
解决方法
b[0] = si & 0xff; b[1] = (si >> 8) & 0xff;
虽然这应该完成在unsigned char中,而不是普通的char,因为它们在大多数系统上都已签名.
存储较大的整数可以以类似的方式或循环来完成.

c# – 将字节数组复制到通用类型而不进行装箱
MyClass<T>
{
public T Value = default(T);
public MyClass(byte[] bytes)
{
// how to copy `bytes` into `Value`?
}
}
我宁愿不使用拳击.有没有办法使用编组,反射或非托管/不安全代码?
我确实找到了this other post,但唯一建议的答案是行不通的,因为它使用拳击.
解决方法
class MyClass<T> where T : struct
{
public T Value = default(T);
public MyClass(byte[] bytes)
{
Value = MemoryMarshal.Cast<byte,T>(bytes)[0];
}
}
您还可以在最近的C#版本中使用unsafe(对于T:非托管约束):
class MyClass<T> where T : unmanaged
{
public T Value = default(T);
public unsafe MyClass(byte[] bytes)
{
fixed (byte* ptr = bytes)
{
Value = *(T*)ptr; // note: no out-of-range check here; dangerous
}
}
}
你也可以使用Unsafe.*方法(System.Runtime.CompilerServices.Unsafe)做一些事情.例如(注意没有约束):
class MyClass<T>
{
public T Value = default(T);
public unsafe MyClass(byte[] bytes)
{
T local = default(T);
fixed (byte* ptr = bytes)
{
Unsafe.copy(ref local,ptr); // note: no out-of-range check here; dangerous
}
Value = local;
}
}
如果要检查超出范围的问题:
if (bytes.Length < Unsafe.SizeOf<T>())
throw new InvalidOperationException("Not enough data,fool!");
或者如果你有T:unmanaged约束,你可以使用sizeof(T).您不需要使用Span< T>解决方案(第一个),因为原始的Cast< byte,T>在这种情况下,将产生一个长度为零的跨度,[0]将适当地抛出.
我认为这也应该有效!
public unsafe MyClass(byte[] bytes)
{
Value = Unsafe.As<byte,T>(ref bytes[0]); // note: no out-of-range check here; dangerous
}
完整示例(适用于net462):
using System;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
struct Foo
{
public int x,y;
}
class MyClass<T>
{
public T Value = default(T);
public unsafe MyClass(byte[] bytes)
{
if (bytes.Length < Unsafe.SizeOf<T>())
throw new InvalidOperationException("not enough data");
Value = Unsafe.As<byte,T>(ref bytes[0]);
}
}
static class P
{
static void Main() {
byte[] bytes = new byte[] { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8 };
var obj = new MyClass<Foo>(bytes);
var val = obj.Value;
Console.WriteLine(val.x); // 67305985 = 0x04030201
Console.WriteLine(val.y); // 134678021 = 0x08070605
}
}

C# 中 int short Int16 Int32 Int64 区别
Java 中没有 Int32,Int64,,java 中只有 int,short,long
Java 中 int 就代表 Int32 ,short 就代表 Int16,long 就代表 Int64
首先,几个基本的关键字:
Int16 = short, 占 2 个字节. -32768 ~ 32767
Int32 = int, 占 4 个字节. -2147483648 ~ 2147483647
Int64 = long, 占 8 个字节. -9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807
这样,看起来比 short,int,long 更加直观些
MSDN 中说 int 就是 Int32 的别名,是等价的,short,long 同理也是别名
详解 Int32
为什么 Int32 就等于 int, 很简单,在 VS 中写 int a=1; 选中 a , F12 转到定义就是 System.Int32.
Int32 就是代表一共能存储 2^32 次方,一共有 42,9496,7296 个数
从 - 21,4748,3648 到 +21,4748,3647 为止,为什么正数比负数小一个数,因为 0 占了一个数
所以 Int32 的最大数并不是 42,9496,7296,而是 (2^31)-1=+21,4748,3647,为什么是 31 次方,因为是有符号整型,最高位要空出来判断是不是负数,所以是 31 次方,-1 是因为 0 占了一个数。
但是一共还是能存储 2^32 次方 既 42,9496,7296 个数,因为有正负数,其实一样的,还是 2 的 32 次方个数
如图:

所以 Int16 和 Int64 也是同理的。只不过是把 2^32 换成 2^16 或者 2^64 而已....
无符号整形 Uint32
上面说的都是有符号整数,既 signed integer, 就是可以储存正负数的,而无符号整数就是只能存储正数,既 unsigned integer
在 C# 中用 Uint16,UInt32,Uint64 等表示
跟上面同理
ushort =UInt16
uint =UInt32 ,0 ~ 4364967295
ulong =UInt64
UInt32 和 Int32 一样 ,也是代表一共能存储 2^32 次方,一共有 42,9496,7296 个数
但是因为只有正数和 0,所以最大值为 4364967295, 既 2^32-1,-1 是因为 0 占了一个数
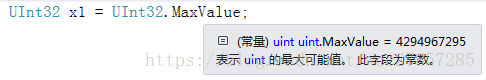
溢出会如何
更进一步,尝试 Int32 a=Int32.MaxValue+1 , 会不会报错?
答案是不会,至少在 VS 中不会,编译器会自动把 a 赋值成 - 21,4748,3648,既最小数值,若加 2,则为 - 21,4748,3647,依次递加。。。
同理,UInt32 a=UInt32.MaxValue+1 ,a 就是 0,既,若 + 2,a=1, 依次递加。。。
https://www.cnblogs.com/EEEE1/p/8098876.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/raytheweak/p/7290617.html

C语言将数组复制到另一个数组
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int original[10] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 0};
int copied[10];
int loop;
for(loop = 0; loop < 10; loop++) {
copied[loop] = original[loop];
}
printf(original -> copied \n);
for(loop = 0; loop < 10; loop++) {
printf( %2d %2d\n, original[loop], copied[loop]);
}
return 0;
}
我们今天的关于c# – 从IntPtr(16位)数组复制到托管的ushort和c#数组复制到另一个数组的分享已经告一段落,感谢您的关注,如果您想了解更多关于c – 将short int复制到char数组、c# – 将字节数组复制到通用类型而不进行装箱、C# 中 int short Int16 Int32 Int64 区别、C语言将数组复制到另一个数组的相关信息,请在本站查询。
本文标签:





