对于想了解PythonMatplotlib基础:常用用法及示例的读者,本文将是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将详细介绍python中matplotlib用法,并且为您提供关于CMake不断从cygwinpy
对于想了解Python Matplotlib基础:常用用法及示例的读者,本文将是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将详细介绍python中matplotlib用法,并且为您提供关于CMake 不断从 cygwin python 中获取 Python,如何从 Windows 安装的 Python 中获取、Core Python | 2 - Core Python: Getting Started | 2.5 - Modularity | 2.5.5 - The Python Execution Mod、Error: Can‘t find Python executable “python“, you can set the PYTHON env variable、ERROR: Command "python setup.py egg_info" python-nss的有价值信息。
本文目录一览:- Python Matplotlib基础:常用用法及示例(python中matplotlib用法)
- CMake 不断从 cygwin python 中获取 Python,如何从 Windows 安装的 Python 中获取
- Core Python | 2 - Core Python: Getting Started | 2.5 - Modularity | 2.5.5 - The Python Execution Mod
- Error: Can‘t find Python executable “python“, you can set the PYTHON env variable
- ERROR: Command "python setup.py egg_info" python-nss

Python Matplotlib基础:常用用法及示例(python中matplotlib用法)
Matplotlib
matplotlib 是
1. 认识Matploblib
1.1 Figure
在任何绘图之前,我们需要一个Figure对象,可以理解成我们需要一张画板才能开始绘图。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt fig = plt.figure()
1.2 Axes
在拥有Figure对象之后,在作画前我们还需要轴,没有轴的话就没有绘图基准,所以需要添加Axes。也可以理解成为真正可以作画的纸。
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
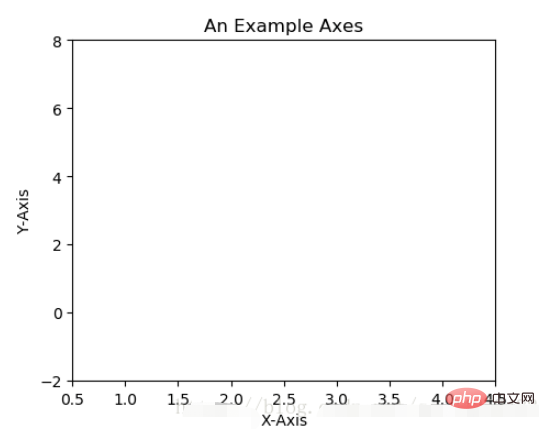
ax.set(xlim=[0.5, 4.5], ylim=[-2, 8], title='An Example Axes',
ylabel='Y-Axis', xlabel='X-Axis')
plt.show()上的代码,在一幅图上添加了一个Axes,然后设置了这个Axes的X轴以及Y轴的取值范围(这些设置并不是强制的,后面会再谈到关于这些设置),效果如下图:
立即学习“Python免费学习笔记(深入)”;
对于上面的fig.add_subplot(111)就是添加Axes的,参数的解释的在画板的第1行第1列的第一个位置生成一个Axes对象来准备作画。也可以通过fig.add_subplot(2, 2, 1)的方式生成Axes,前面两个参数确定了面板的划分,例如 2, 2会将整个面板划分成 2 * 2 的方格,第三个参数取值范围是 [1, 2*2] 表示第几个Axes。如下面的例子:
fig = plt.figure() ax1 = fig.add_subplot(221) ax2 = fig.add_subplot(222) ax3 = fig.add_subplot(224)
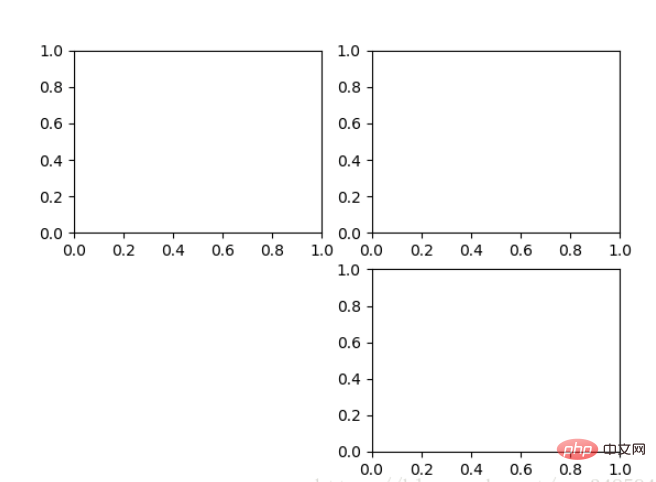
1.3 Multiple Axes
可以发现我们上面添加 Axes 似乎有点弱鸡,所以提供了下面的方式一次性生成所有 Axes:
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2) axes[0,0].set(title='Upper Left') axes[0,1].set(title='Upper Right') axes[1,0].set(title='Lower Left') axes[1,1].set(title='Lower Right')
fig 还是我们熟悉的画板, axes 成了我们常用二维数组的形式访问,这在循环绘图时,额外好用。
1.4 Axes Vs .pyplot
相信不少人看过下面的代码,很简单并易懂,但是下面的作画方式只适合简单的绘图,快速的将图绘出。在处理复杂的绘图工作时,我们还是需要使用 Axes 来完成作画的。
plt.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [10, 20, 25, 30], color='lightblue', linewidth=3) plt.xlim(0.5, 4.5) plt.show()
2. 基本绘图2D
2.1 线
plot()函数画出一系列的点,并且用线将它们连接起来。看下例子:
x = np.linspace(0, np.pi) y_sin = np.sin(x) y_cos = np.cos(x) ax1.plot(x, y_sin) ax2.plot(x, y_sin, 'go--', linewidth=2, markersize=12) ax3.plot(x, y_cos, color='red', marker='+', linestyle='dashed')
在上面的三个Axes上作画。plot,前面两个参数为x轴、y轴数据。ax2的第三个参数是 MATLAB风格的绘图,对应ax3上的颜色,marker,线型。
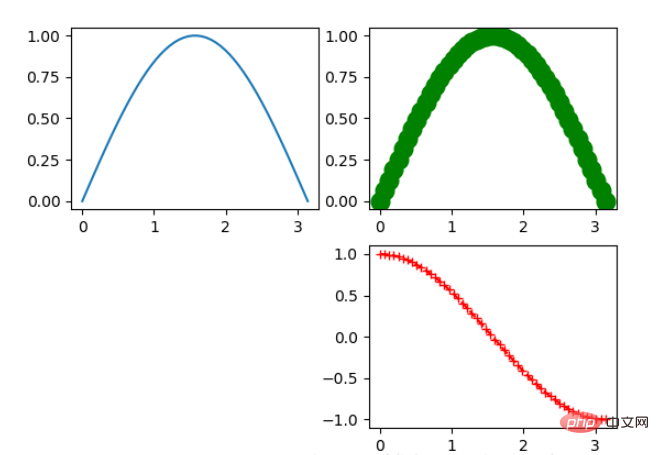
另外,我们可以通过关键字参数的方式绘图,如下例:
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 200)
data_obj = {'x': x,
'y1': 2 * x + 1,
'y2': 3 * x + 1.2,
'mean': 0.5 * x * np.cos(2*x) + 2.5 * x + 1.1}
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
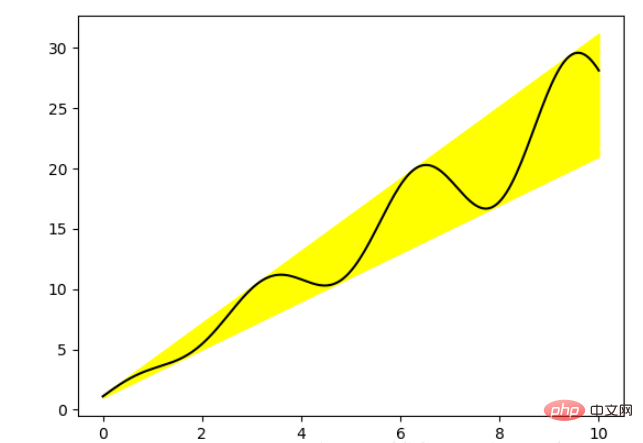
#填充两条线之间的颜色
ax.fill_between('x', 'y1', 'y2', color='yellow', data=data_obj)
# Plot the "centerline" with `plot`
ax.plot('x', 'mean', color='black', data=data_obj)
plt.show()发现上面的作图,在数据部分只传入了字符串,这些字符串对一个这 data_obj 中的关键字,当以这种方式作画时,将会在传入给 data 中寻找对应关键字的数据来绘图。
2.2 散点图
只画点,但是不用线连接起来。
x = np.arange(10) y = np.random.randn(10) plt.scatter(x, y, color='red', marker='+') plt.show()
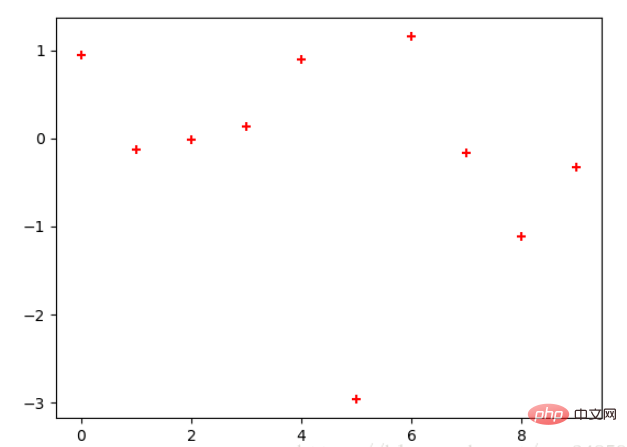
2.3 条形图
条形图分两种,一种是水平的,一种是垂直的,见下例子:
np.random.seed(1) x = np.arange(5) y = np.random.randn(5) fig, axes = plt.subplots(ncols=2, figsize=plt.figaspect(1./2)) vert_bars = axes[0].bar(x, y, color='lightblue', align='center') horiz_bars = axes[1].barh(x, y, color='lightblue', align='center') #在水平或者垂直方向上画线 axes[0].axhline(0, color='gray', linewidth=2) axes[1].axvline(0, color='gray', linewidth=2) plt.show()
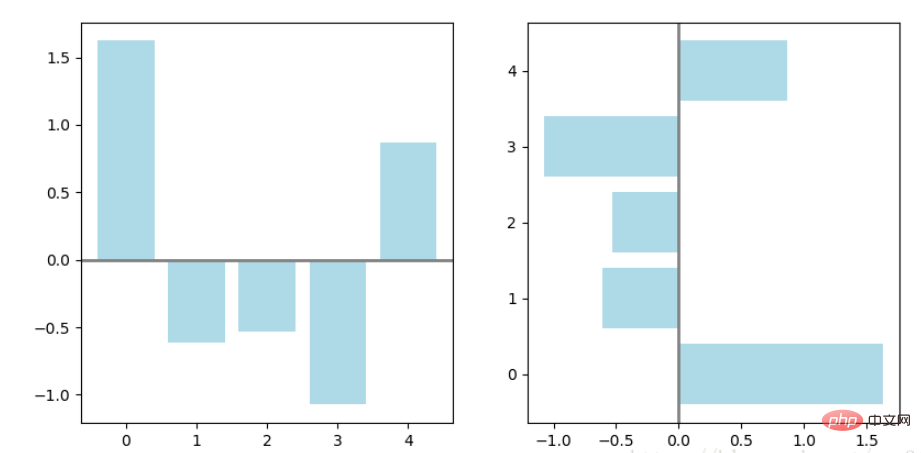
条形图还返回了一个Artists 数组,对应着每个条形,例如上图 Artists 数组的大小为5,我们可以通过这些 Artists 对条形图的样式进行更改,如下例:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
vert_bars = ax.bar(x, y, color='lightblue', align='center')
# We could have also done this with two separate calls to `ax.bar` and numpy boolean indexing.
for bar, height in zip(vert_bars, y):
if height < 0:
bar.set(edgecolor='darkred', color='salmon', linewidth=3)
plt.show()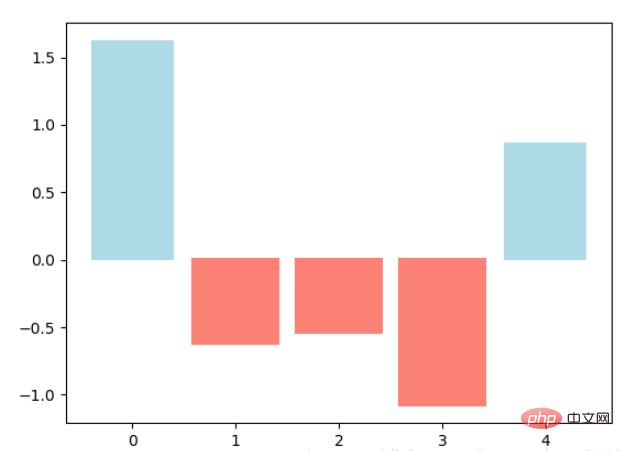
2.4 直方图
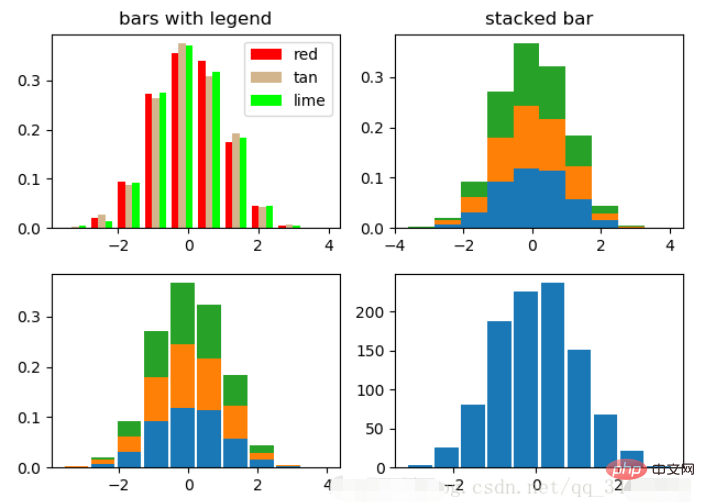
直方图用于统计数据出现的次数或者频率,有多种参数可以调整,见下例:
np.random.seed(19680801)
n_bins = 10
x = np.random.randn(1000, 3)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2)
ax0, ax1, ax2, ax3 = axes.flatten()
colors = ['red', 'tan', 'lime']
ax0.hist(x, n_bins, density=True, histtype='bar', color=colors, label=colors)
ax0.legend(prop={'size': 10})
ax0.set_title('bars with legend')
ax1.hist(x, n_bins, density=True, histtype='barstacked')
ax1.set_title('stacked bar')
ax2.hist(x, histtype='barstacked', rwidth=0.9)
ax3.hist(x[:, 0], rwidth=0.9)
ax3.set_title('different sample sizes')
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()参数中density控制Y轴是概率还是数量,与返回的第一个的变量对应。histtype控制着直方图的样式,默认是 ‘bar’,对于多个条形时就相邻的方式呈现如子图1, ‘barstacked’ 就是叠在一起,如子图2、3。 rwidth 控制着宽度,这样可以空出一些间隙,比较图2、3. 图4是只有一条数据时。
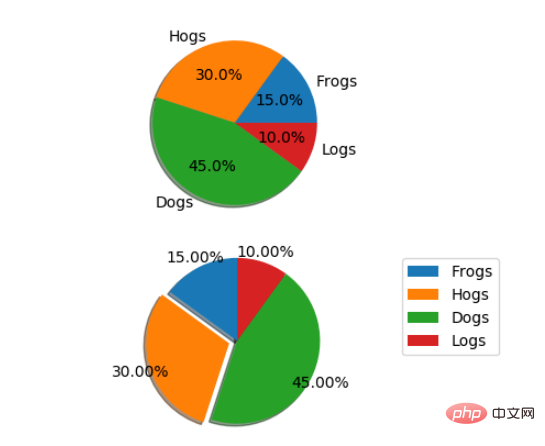
2.5 饼图
labels = 'Frogs', 'Hogs', 'Dogs', 'Logs'
sizes = [15, 30, 45, 10]
explode = (0, 0.1, 0, 0) # only "explode" the 2nd slice (i.e. 'Hogs')
fig1, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2)
ax1.pie(sizes, labels=labels, autopct='%1.1f%%', shadow=True)
ax1.axis('equal')
ax2.pie(sizes, autopct='%1.2f%%', shadow=True, startangle=90, explode=explode,
pctdistance=1.12)
ax2.axis('equal')
ax2.legend(labels=labels, loc='upper right')
plt.show()饼图自动根据数据的百分比画饼.。labels是各个块的标签,如子图一。autopct=%1.1f%%表示格式化百分比精确输出,explode,突出某些块,不同的值突出的效果不一样。pctdistance=1.12百分比距离圆心的距离,默认是0.6.
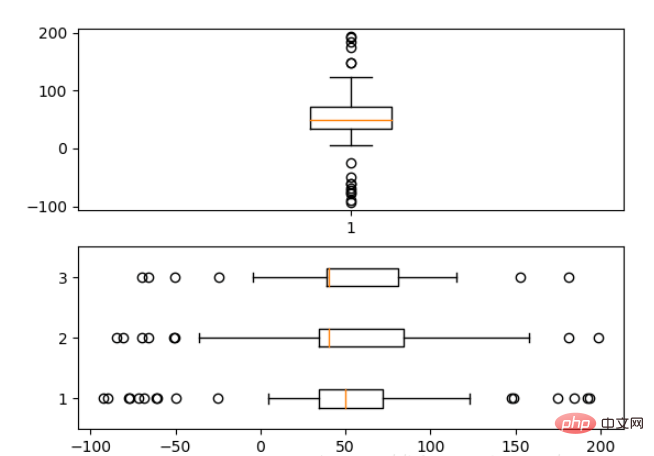
2.6 箱形图
为了专注于如何画图,省去数据的处理部分。 data 的 shape 为 (n, ), data2 的 shape 为 (n, 3)。
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2) ax1.boxplot(data) ax2.boxplot(data2, vert=False) #控制方向
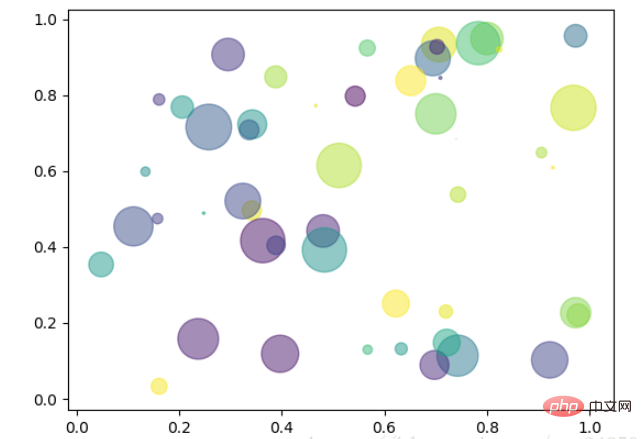
2.7 泡泡图
散点图的一种,加入了第三个值 s 可以理解成普通散点,画的是二维,泡泡图体现了Z的大小,如下例:
np.random.seed(19680801) N = 50 x = np.random.rand(N) y = np.random.rand(N) colors = np.random.rand(N) area = (30 * np.random.rand(N))**2 # 0 to 15 point radii plt.scatter(x, y, s=area, c=colors, alpha=0.5) plt.show()
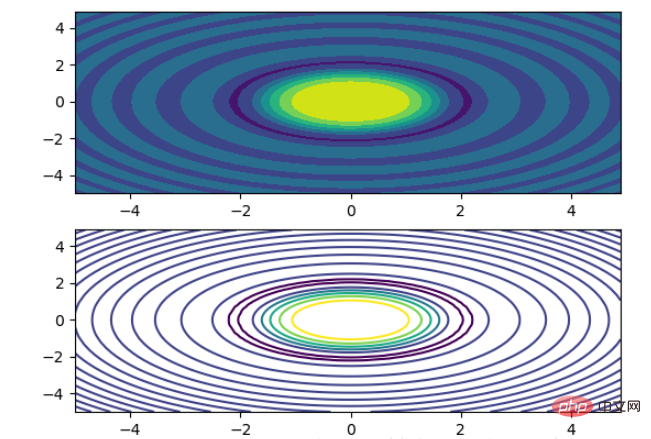
2.8 等高线(轮廓图)
有时候需要描绘边界的时候,就会用到轮廓图,机器学习用的决策边界也常用轮廓图来绘画,见下例:
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2) x = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.1) y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.1) xx, yy = np.meshgrid(x, y, sparse=True) z = np.sin(xx**2 + yy**2) / (xx**2 + yy**2) ax1.contourf(x, y, z) ax2.contour(x, y, z)
上面画了两个一样的轮廓图,contourf会填充轮廓线之间的颜色。数据x, y, z通常是具有相同 shape 的二维矩阵。x, y 可以为一维向量,但是必需有 z.shape = (y.n, x.n) ,这里 y.n 和 x.n 分别表示x、y的长度。Z通常表示的是距离X-Y平面的距离,传入X、Y则是控制了绘制等高线的范围。
3 布局、图例说明、边界等
3.1区间上下限
当绘画完成后,会发现X、Y轴的区间是会自动调整的,并不是跟我们传入的X、Y轴数据中的最值相同。为了调整区间我们使用下面的方式:
ax.set_xlim([xmin, xmax]) #设置X轴的区间 ax.set_ylim([ymin, ymax]) #Y轴区间 ax.axis([xmin, xmax, ymin, ymax]) #X、Y轴区间 ax.set_ylim(bottom=-10) #Y轴下限 ax.set_xlim(right=25) #X轴上限
具体效果见下例:
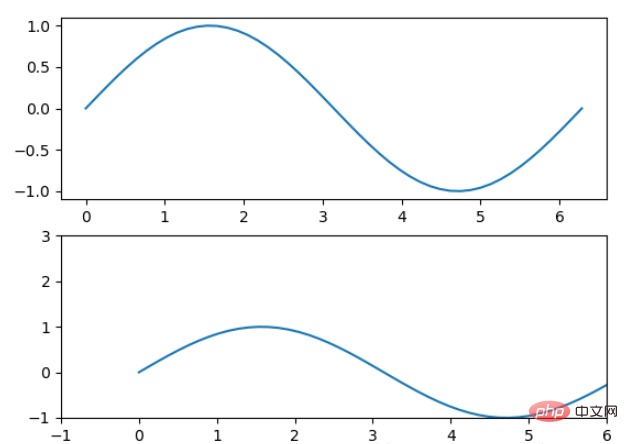
x = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi) y = np.sin(x) fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2) ax1.plot(x, y) ax2.plot(x, y) ax2.set_xlim([-1, 6]) ax2.set_ylim([-1, 3]) plt.show()
可以看出修改了区间之后影响了图片显示的效果。
3.2 图例说明
我们如果我们在一个Axes上做多次绘画,那么可能出现分不清哪条线或点所代表的意思。这个时间添加图例说明,就可以解决这个问题了,见下例:
fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [10, 20, 25, 30], label='Philadelphia') ax.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [30, 23, 13, 4], label='Boston') ax.scatter([1, 2, 3, 4], [20, 10, 30, 15], label='Point') ax.set(ylabel='Temperature (deg C)', xlabel='Time', title='A tale of two cities') ax.legend() plt.show()
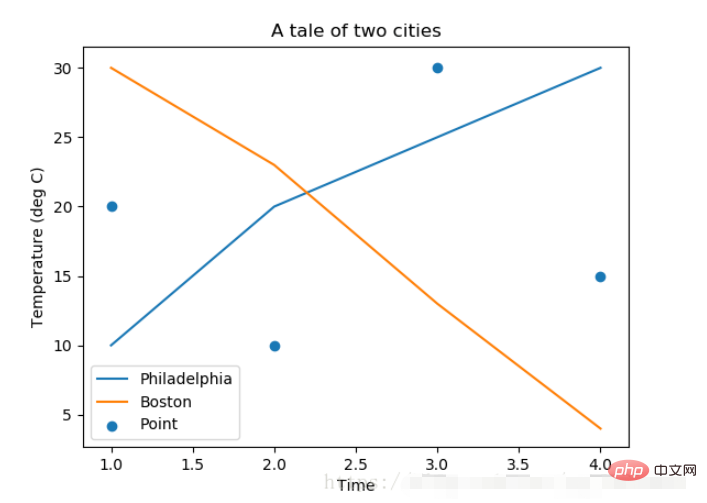
在绘图时传入 label 参数,并最后调用ax.legend()显示体力说明,对于 legend 还是传入参数,控制图例说明显示的位置:
| Location String | Location Code |
|---|---|
| ‘best’ | 0 |
| ‘upper right’ | 1 |
| ‘upper left’ | 2 |
| ‘lower left’ | 3 |
| ‘lower right’ | 4 |
| ‘right’ | 5 |
| ‘center left’ | 6 |
| ‘center right’ | 7 |
| ‘lower center’ | 8 |
| ‘upper center’ | 9 |
| ‘center’ | 10 |
3.3 区间分段
默认情况下,绘图结束之后,Axes 会自动的控制区间的分段。见下例:
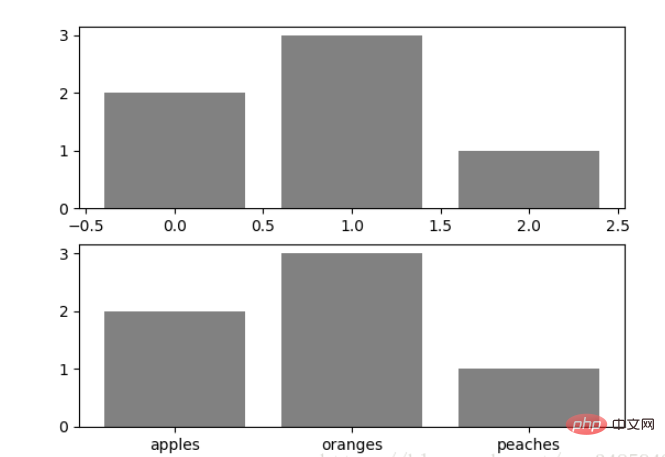
data = [('apples', 2), ('oranges', 3), ('peaches', 1)] fruit, value = zip(*data) fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2) x = np.arange(len(fruit)) ax1.bar(x, value, align='center', color='gray') ax2.bar(x, value, align='center', color='gray') ax2.set(xticks=x, xticklabels=fruit) #ax.tick_params(axis='y', direction='inout', length=10) #修改 ticks 的方向以及长度 plt.show()
上面不仅修改了X轴的区间段,并且修改了显示的信息为文本。
3.4 布局
当我们绘画多个子图时,就会有一些美观的问题存在,例如子图之间的间隔,子图与画板的外边间距以及子图的内边距,下面说明这个问题:
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(9, 9))
fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.5, hspace=0.3,
left=0.125, right=0.9,
top=0.9, bottom=0.1)
#fig.tight_layout() #自动调整布局,使标题之间不重叠
plt.show()通过fig.subplots_adjust()我们修改了子图水平之间的间隔wspace=0.5,垂直方向上的间距hspace=0.3,左边距left=0.125 等等,这里数值都是百分比的。以 [0, 1] 为区间,选择left、right、bottom、top 注意 top 和 right 是 0.9 表示上、右边距为百分之10。不确定如果调整的时候,fig.tight_layout()是一个很好的选择。之前说到了内边距,内边距是子图的,也就是 Axes 对象,所以这样使用 ax.margins(x=0.1, y=0.1),当值传入一个值时,表示同时修改水平和垂直方向的内边距。
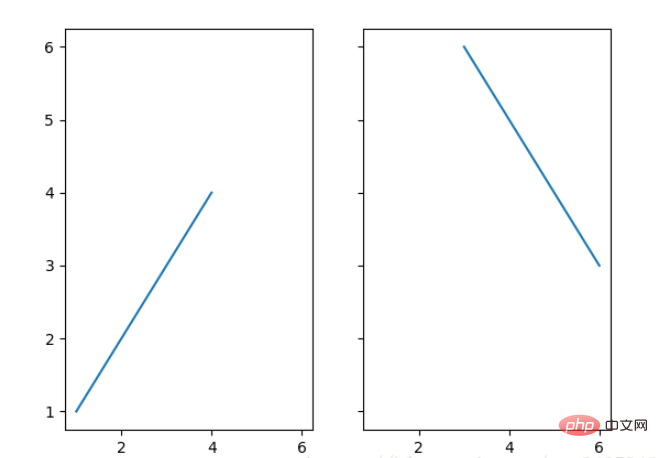
观察上面的四个子图,可以发现他们的X、Y的区间是一致的,而且这样显示并不美观,所以可以调整使他们使用一样的X、Y轴:
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, sharex=True, sharey=True) ax1.plot([1, 2, 3, 4], [1, 2, 3, 4]) ax2.plot([3, 4, 5, 6], [6, 5, 4, 3]) plt.show()
3.5 轴相关
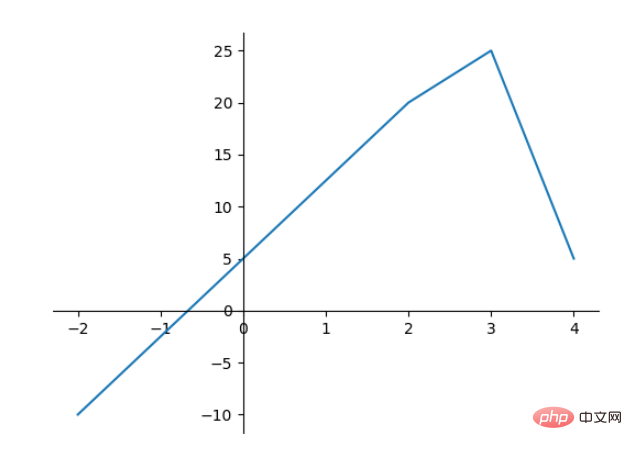
改变边界的位置,去掉四周的边框:
fig, ax = plt.subplots() ax.plot([-2, 2, 3, 4], [-10, 20, 25, 5]) ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False) #顶边界不可见 ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom') # ticks 的位置为下方,分上下的。 ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False) #右边界不可见 ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left') # "outward" # 移动左、下边界离 Axes 10 个距离 #ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('outward', 10)) #ax.spines['left'].set_position(('outward', 10)) # "data" # 移动左、下边界到 (0, 0) 处相交 ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0)) ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', 0)) # "axes" # 移动边界,按 Axes 的百分比位置 #ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('axes', 0.75)) #ax.spines['left'].set_position(('axes', 0.3)) plt.show()
以上就是Python Matplotlib基础:常用用法及示例的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

CMake 不断从 cygwin python 中获取 Python,如何从 Windows 安装的 Python 中获取
如何解决CMake 不断从 cygwin python 中获取 Python,如何从 Windows 安装的 Python 中获取
我有一个看起来像这样的 CMake 脚本:
find_program(PYTHON_COMMAND NAMES python3 python)
问题是它检测到安装在 Cygwin 安装中的 python。 输出总是:
-- PYTHON_PATH:C:/cygwin64/bin/python3
我希望它取自:
c:\\python36-64\\python
在windows PATH变量中,Cygwin bin在路径的最后一个,windows安装在第一个
但它只检测到 Cygwin python,
怎么改?

Core Python | 2 - Core Python: Getting Started | 2.5 - Modularity | 2.5.5 - The Python Execution Mod
It's important to understand the Python execution model and precisely when function deFinitions and other important events occur when a module is imported or executed. Here, we show execution of our Python module as it's imported in a graphical debugging environment. We step through the top‑level statements in the module. What's important to realize here is that the def used for the fetch_words function isn't merely a declaration. It's actually a statement, which when executed in sequence with the other top‑level model scope code, causes the code within the function to be bound to the name of the function. When modules are imported or run, all of the top‑level statements are run, and this is the means by which the function within the module namespace are defined. We are sometimes asked about the difference between Python modules, Python scripts, and Python programs. Any .py file constitutes a Python module. But as we've seen, modules can be written for convenient import, convenient execution, or using the if dunder name = dunder main idiom, both. We strongly recommend making even simple scripts importable since it eases development and testing so much if you can access your code from within the REPL. Likewise, even modules, which are only ever meant to be imported in production settings, benefit from having executable test code. For this reason, nearly all modules we create have this form of defining one or more importable functions with a postscript to facilitate execution. Whether you consider a module to be a Python script or Python program is a matter of context and usage. It's certainly wrong to consider Python to be merely a scripting tool, in the vein of Windows batch files or UNIX Shell scripts, as many large and complex applications are built exclusively with python.
- def不仅仅是一个declaration声明,更是一条statement语句。它将其中的python代码于函数名绑定在一起
- 一个py文件就是一个模块,这个模块包含类或函数。你写python,要尽量将代码包装成函数和类,方便各种import
- 一个py文件也可看作是一个脚本,在系统命令行中运行
- python不仅仅是脚本语言,很多大型程序都是用python构建的

Error: Can‘t find Python executable “python“, you can set the PYTHON env variable
在启动vue项目的时候,安装node.js组件node-sass过程中报错了,错误提示如下
Error: Can’t find Python executable “python”, you can set the PYTHON env variable
由错误提示可知:Node.js 在安装模块组件node-sass的时候,node.js缺少Visual Studio2015 Build Tools相关的组件和python的环境,如果安装了vs2015组件的小伙伴们就不用安装Visual Studio2015 Build Tools相应的组件,只用安装python2.7即可解决缺少的python组件的问题。
欲安装python2.7,请至python官网:www.python.org 下载,然后配置好python的环境变量即可。
不过博主我并不推荐上述的解决方案,因为对于程序员来说,效率第一,上述的问题一个命令就可以轻松解决你所遇到的麻烦,前面说了那么多,无非就是想告诉在看本篇博客的同仁们放下浮躁的心,遇到问题首先不是急着去解决问题,而是分析为什么会这样,然后才能水到聚成的去找到解决问题的方法。
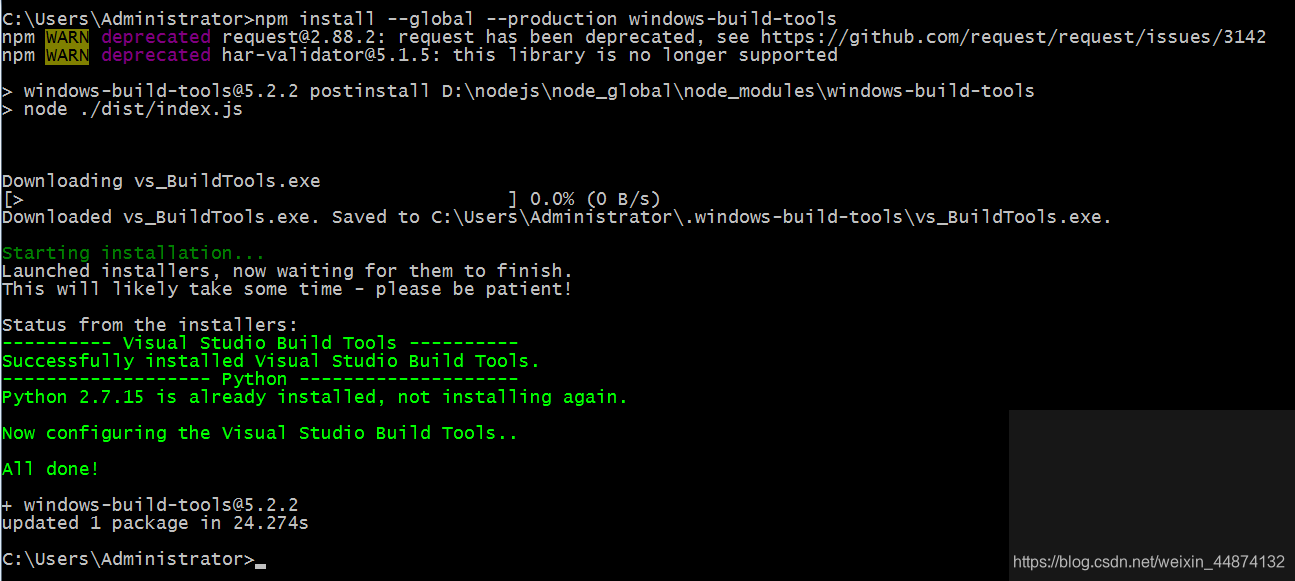
运行下面这个命令即可解决你们遇到的Error问题
npm install --global --production windows-build-tools
注:上面讲述了一堆就是为了讲述此命令是干嘛的,上面已经描述很详细了,就不再赘述了,该操作与上述的一堆操作无异,效果却是一样的。
然后运气不好的小伙伴可能接着会遇到一个坑,那就是执行了:npm install --global --production windows-build-tools这个命令的人细心点会发现执行到一半就卡住了,这个卡住了没有红字重点提示,而且下方还有英文在等待中,粗心的小伙伴可能以为是命令执行完了,组件安装好了,其实不然,我这边已经解决了,就无法复现了,具体点就是中文的提示,提示我们由于有类似组件在运行或者下载导致无法继续下载安装组件了。稳妥点的解决办法是,将电脑重启,将底层正在运行的模块干掉,待电脑重启后再执行npm install --global --production windows-build-tools这条命令即可,博主我就是这样解决的,稳稳的幸福就会浮现在你面前如下图所示,你的可能和我不一样,因为我已经跑成功过一次了,没有你的那么多细节的log打印。
然后就是在你的项目下shift+鼠标右击你的项目运行npm run dev即可启动vue项目了。
ERROR: Command "python setup.py egg_info" python-nss
[root@localhost ~]# pip install python-nss
DEPRECATION: Python 2.7 will reach the end of its life on January 1st, 2020. Please upgrade your Python as Python 2.7 won''t be maintained after that date. A future version of pip will drop support for Python 2.7.
Looking in indexes: http://pypi.douban.com/simple
Collecting python-nss
Downloading http://pypi.doubanio.com/packages/6b/29/629098e34951c358b1f04f13a70b3590eb0cf2df817d945bd05c4169d71b/python-nss-1.0.1.tar.bz2 (222kB)
|████████████████████████████████| 225kB 31kB/s
ERROR: Complete output from command python setup.py egg_info:
ERROR: Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<string>", line 1, in <module>
File "/tmp/pip-install-JGnrT5/python-nss/setup.py", line 409, in <module>
sys.exit(main(sys.argv))
File "/tmp/pip-install-JGnrT5/python-nss/setup.py", line 333, in main
nss_include_dir = find_include_dir([''nss3'', ''nss''], [''nss.h'', ''pk11pub.h''], include_roots=include_roots)
File "/tmp/pip-install-JGnrT5/python-nss/setup.py", line 94, in find_include_dir
raise ValueError("unable to locate include directory containing header files %s" % include_files)
ValueError: unable to locate include directory containing header files [''nss.h'', ''pk11pub.h'']
ERROR: Command "python setup.py egg_info" failed with error code 1 in /tmp/pip-install-JGnrT5/python-nss/
查看错误日志缺少头文件
进入python-nss官网,写着To build python-nss you the C language header files and libraries for both NSPR and NSS will need to be installed. This is system and distribution specific, as such we cannot give you explicit instructions. On Linux typically these packages are called:
- nss-devel
- nspr-devel
yum install nss-devel -y
yum install nspr-devel -y
关于Python Matplotlib基础:常用用法及示例和python中matplotlib用法的问题就给大家分享到这里,感谢你花时间阅读本站内容,更多关于CMake 不断从 cygwin python 中获取 Python,如何从 Windows 安装的 Python 中获取、Core Python | 2 - Core Python: Getting Started | 2.5 - Modularity | 2.5.5 - The Python Execution Mod、Error: Can‘t find Python executable “python“, you can set the PYTHON env variable、ERROR: Command "python setup.py egg_info" python-nss等相关知识的信息别忘了在本站进行查找喔。
本文标签:





