对于防止itertools.permutation中的内存错误感兴趣的读者,本文将会是一篇不错的选择,我们将详细介绍防止handler内存泄漏,并为您提供关于784.LetterCasePermuta
对于防止itertools.permutation中的内存错误感兴趣的读者,本文将会是一篇不错的选择,我们将详细介绍防止handler内存泄漏,并为您提供关于784. Letter Case Permutation、c++ STL 中的 next_permutation、C++的全排列函数--next_permutation,prev_permutation、C. Polycarp Restores Permutation的有用信息。
本文目录一览:- 防止itertools.permutation中的内存错误(防止handler内存泄漏)
- 784. Letter Case Permutation
- c++ STL 中的 next_permutation
- C++的全排列函数--next_permutation,prev_permutation
- C. Polycarp Restores Permutation

防止itertools.permutation中的内存错误(防止handler内存泄漏)
首先,我想提一下,我有一个3 GB的内存。
我正在研究一种在节点上时间呈指数形式的算法,因此在代码中已经有了
perm = list( itertools.permutations(list(graph.Nodes))) # graph.Nodes is a tuple of 1,2,... n integers
生成列表中所有顶点的组合,然后我可以处理其中一种排列。
但是,当我为40个顶点运行程序时,它给出了内存错误。
有没有一种更简单的实现方式可以通过它生成顶点的所有组合而不会出现此错误。

784. Letter Case Permutation
Given a string S, we can transform every letter individually to be lowercase or uppercase to create another string. Return a list of all possible strings we could create.
Examples:
Input: S = "a1b2"
Output: ["a1b2", "a1B2", "A1b2", "A1B2"]
Input: S = "3z4"
Output: ["3z4", "3Z4"]
Input: S = "12345"
Output: ["12345"]把字符串里的字母任意改为大写或小写,求能获得的所有字符。
我的解决思路是一个个遍历字符,碰到数字直接加上,碰的字母的,就把已经有的字符串复制一遍,前面一半字符串尾补加小写字母,后面一半字符串尾补加大写字母。
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> letterCasePermutation(string S) {
vector<string> res(1);
for (int i=0; i<S.length(); ++i) {
char c = S[i];
int len = res.size();
if ((c>=''a'' && c <=''z'') || (c>=''A'' && c<=''Z'')) {
for (int j=0; j<len; ++j) {
res.push_back(res[j]);
res[j].push_back(tolower(c));
res[j+len].push_back(toupper(c));
}
}
else
for (int j=0; j<len; ++j)
res[j].push_back(c);
}
return res;
}
};

c++ STL 中的 next_permutation
| default (1) | |
|---|---|
| custom (2) | |
next_permutation 是 <algorithm> 头文件中的一个函数。
STL 提供了两个用来计算排列组合关系的算法,分别是 next_permutation 和 prev_permutation。首先我们必须了解什么是 “下一个” 排列组合,什么是 “前一个” 排列组合。考虑三个字符所组成的序列 {a,b,c}。
这个序列有六个可能的排列组合:abc,acb,bac,bca,cab,cba。这些排列组合根据 less-than 操作符做字典顺序 (lexicographical) 的排序。也就是说,abc 名列第一,因为每一个元素都小于其后的元素。acb 是次一个排列组合,因为它是固定了 a (序列内最小元素) 之后所做的新组合。
同样道理,那些固定 b (序列中次小元素) 而做的排列组合,在次序上将先于那些固定 c 而做的排列组合。以 bac 和 bca 为例,bac 在 bca 之前,因为次序 ac 小于序列 ca。面对 bca,我们可以说其前一个排列组合是 bac,而其后一个排列组合是 cab。序列 abc 没有 “前一个” 排列组合,cba 没有 “后一个” 排列组合。
next_permutation () 会取得 [first,last) 所标示之序列的下一个排列组合,如果没有下一个排列组合,便返回 false; 否则返回 true。这个算法有两个版本。版本一使用元素型别所提供的 less-than 操作符来决定下一个排列组合,版本二则是以仿函数 comp 来决定。
示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n)&&n){
int a[1000];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
}
sort(a,a+n);
do{
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%d ",a[i]);
printf("\n");
}while(next_permutation(a,a+n));
}
return 0;
}输入
3
0 1 2
输出
0 1 2
0 2 1
1 0 2
1 2 0
2 0 1
2 1 0

C++的全排列函数--next_permutation,prev_permutation
以下博客转载自:https://blog.csdn.net/howardemily/article/details/68064377 ,在此感谢前辈们的经验分享。
全排列参考了两位的博客 感谢!
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_9f7ea4390101101u.html
http://blog.csdn.net/ac_gibson/article/details/45308645
早就听说了了next_permutation 产生全排列的强大,一直到昨晚遇到一个对字符串产生全排列的问题才知道这个函数的强大,我们队是按照dfs去搞全排列,然后在进行字符串的匹配,结果写的很长,过程中还各种debug。。。于是决定今天学一下next_permutation函数
组合数学中经常用到排列,这里介绍一个计算序列全排列的函数:next_permutation(start,end)(千万注意,两个参数分别表示全排列的起始地址还有结束地址),和prev_permutation(start,end)。这两个函数作用是一样的,区别就在于前者求的是当前排列的下一个排列,后一个求的是当前排列的上一个排列。至于这里的“前一个”和“后一个”,我们可以把它理解为序列的字典序的前后,严格来讲,就是对于当前序列pn,他的下一个序列pn+1满足:不存在另外的序列pm,使pn<pm<pn+1.
对于next_permutation函数,其函数原型为:
#include <algorithm>
bool next_permutation(iterator start,iterator end)
当当前序列不存在下一个排列时,函数返回false,否则返回true
我们来看下面这个例子:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num[3]={1,2,3};
do
{
cout<<num[0]<<" "<<num[1]<<" "<<num[2]<<endl;
}while(next_permutation(num,num+3));
return 0;
} 输出结果为:
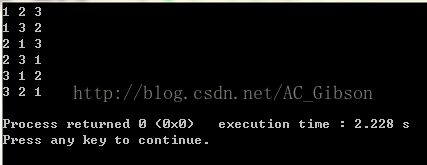
当我们把while(next_permutation(num,num+3))中的3改为2时,输出就变为了:
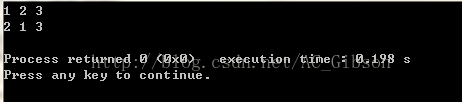
由此可以看出,next_permutation(num,num+n)函数是对数组num中的前n个元素进行全排列,同时并改变num数组的值。
另外,需要强调的是,next_permutation()在使用前需要对欲排列数组按升序排序,否则只能找出该序列之后的全排列数。比如,如果数组num初始化为2,3,1,那么输出就变为了:
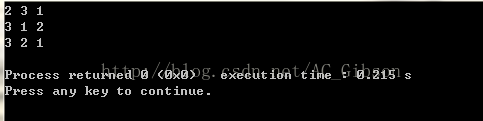
此外,next_permutation(node,node+n,cmp)可以对结构体num按照自定义的排序方式cmp进行排序。
也可以对字符...
next_permutation 自定义比较函数 POJ 1256
题目中要求的字典序是
//''A''<''a''<''B''<''b''<...<''Z''<''z''.#include<iostream> //poj 1256 Anagram
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int cmp(char a,char b)
{
if(tolower(a)!=tolower(b))//tolower 是将大写字母转化为小写字母.
return tolower(a)<tolower(b);
else
return a<b;
}
int main()
{
char ch[20];
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--)
{
scanf("%s",ch);
sort(ch,ch+strlen(ch),cmp);
do
{
printf("%s\n",ch);
}while(next_permutation(ch,ch+strlen(ch),cmp));
}
return 0;
}
在上面的基础上,补充以下:
- 一道蓝桥杯的题目:https://blog.csdn.net/ryo_218/article/details/79682803
- prev_permutation函数:
std::next_permutation与std::prev_permutation可以获取数字或者是字符的全排列,其std::next_permutation提供升序、std::prev_permutation提供降序。

C. Polycarp Restores Permutation

链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1141/problem/C
题意:
给 n-1 个数,
qi=pi+1−pi
p 为 1-n 的排列序列
q 为给的序列。
根据 q 求出 p, 求不出时为 - 1。
思路:
另 p 数组首个为 0. 求出 p 数组,再得到 p 数组中最小的值,将 p 中所有数减掉最小值再加 1 得到原 p。
同时记录原 p 中每个数出现的次数。超过一次,说明不能还原 。
代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10;
LL a[MAXN];
map<LL, int> b;
int main()
{
int n, v;
cin >> n;
a[0] = 0;
LL sum = 0, mmin = 0;
for (int i = 2;i <= n;i++)
{
cin >> v;
a[i] = a[i - 1] + v;
sum += a[i];
mmin = min(mmin, a[i]);
}
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
a[i] = a[i] - mmin + 1;
if (b[a[i]] == 1 || a[i] > n)
{
cout << -1 << endl;
return 0;
}
b[a[i]] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
cout << a[i] << '' '' ;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
关于防止itertools.permutation中的内存错误和防止handler内存泄漏的问题我们已经讲解完毕,感谢您的阅读,如果还想了解更多关于784. Letter Case Permutation、c++ STL 中的 next_permutation、C++的全排列函数--next_permutation,prev_permutation、C. Polycarp Restores Permutation等相关内容,可以在本站寻找。
本文标签:





