最近很多小伙伴都在问[Swift]LeetCode682.棒球比赛|BaseballGame和棒球比赛2021这两个问题,那么本篇文章就来给大家详细解答一下,同时本文还将给你拓展2023-08-10:
最近很多小伙伴都在问[Swift]LeetCode682. 棒球比赛 | Baseball Game和棒球比赛2021这两个问题,那么本篇文章就来给大家详细解答一下,同时本文还将给你拓展2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组 景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数: game [i] = { Ki, Bi } Ki 一定是负数,、682. Baseball Game 棒球游戏 按字母处理、Acer Swift 3笔记本怎么样 Acer Swift 3笔记本上手图赏、Codeforces Round #426 (Div. 2) C. The Meaningless Game C. The Meaningless Game等相关知识,下面开始了哦!
本文目录一览:- [Swift]LeetCode682. 棒球比赛 | Baseball Game(棒球比赛2021)
- 2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组 景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数: game [i] = { Ki, Bi } Ki 一定是负数,
- 682. Baseball Game 棒球游戏 按字母处理
- Acer Swift 3笔记本怎么样 Acer Swift 3笔记本上手图赏
- Codeforces Round #426 (Div. 2) C. The Meaningless Game C. The Meaningless Game
![[Swift]LeetCode682. 棒球比赛 | Baseball Game(棒球比赛2021) [Swift]LeetCode682. 棒球比赛 | Baseball Game(棒球比赛2021)](http://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/upload/2025/04/265952c2-62a3-48b8-89b4-9742927e00421744859723045.jpg)
[Swift]LeetCode682. 棒球比赛 | Baseball Game(棒球比赛2021)
You‘re Now a baseball game point recorder.
Given a list of strings,each string can be one of the 4 following types:
-
Integer(one round‘s score): Directly represents the number of points you get in this round. -
"+"(one round‘s score): Represents that the points you get in this round are the sum of the last twovalidround‘s points. -
"D"(one round‘s score): Represents that the points you get in this round are the doubled data of the lastvalidround‘s points. -
"C"(an operation,which isn‘t a round‘s score): Represents the lastvalidround‘s points you get were invalid and should be removed.
Each round‘s operation is permanent and Could have an impact on the round before and the round after.
You need to return the sum of the points you Could get in all the rounds.
Example 1:
Input: ["5","2","C","D","+"] Output: 30 Explanation: Round 1: You Could get 5 points. The sum is: 5. Round 2: You Could get 2 points. The sum is: 7. Operation 1: The round 2‘s data was invalid. The sum is: 5. Round 3: You Could get 10 points (the round 2‘s data has been removed). The sum is: 15. Round 4: You Could get 5 + 10 = 15 points. The sum is: 30.
Example 2:
Input: ["5","-2","4","9","+","+"] Output: 27 Explanation: Round 1: You Could get 5 points. The sum is: 5. Round 2: You Could get -2 points. The sum is: 3. Round 3: You Could get 4 points. The sum is: 7. Operation 1: The round 3‘s data is invalid. The sum is: 3. Round 4: You Could get -4 points (the round 3‘s data has been removed). The sum is: -1. Round 5: You Could get 9 points. The sum is: 8. Round 6: You Could get -4 + 9 = 5 points. The sum is 13. Round 7: You Could get 9 + 5 = 14 points. The sum is 27.
Note:
- The size of the input list will be between 1 and 1000.
- Every integer represented in the list will be between -30000 and 30000.
你现在是棒球比赛记录员。
给定一个字符串列表,每个字符串可以是以下四种类型之一:
1.整数(一轮的得分):直接表示您在本轮中获得的积分数。
2. "+"(一轮的得分):表示本轮获得的得分是前两轮有效 回合得分的总和。
3. "D"(一轮的得分):表示本轮获得的得分是前一轮有效 回合得分的两倍。
4. "C"(一个操作,这不是一个回合的分数):表示您获得的最后一个有效 回合的分数是无效的,应该被移除。
每一轮的操作都是永久性的,可能会对前一轮和后一轮产生影响。
你需要返回你在所有回合中得分的总和。
示例 1:
输入: ["5","+"] 输出: 30 解释: 第1轮:你可以得到5分。总和是:5。 第2轮:你可以得到2分。总和是:7。 操作1:第2轮的数据无效。总和是:5。 第3轮:你可以得到10分(第2轮的数据已被删除)。总数是:15。 第4轮:你可以得到5 + 10 = 15分。总数是:30。
示例 2:
输入: ["5","+"] 输出: 27 解释: 第1轮:你可以得到5分。总和是:5。 第2轮:你可以得到-2分。总数是:3。 第3轮:你可以得到4分。总和是:7。 操作1:第3轮的数据无效。总数是:3。 第4轮:你可以得到-4分(第三轮的数据已被删除)。总和是:-1。 第5轮:你可以得到9分。总数是:8。 第6轮:你可以得到-4 + 9 = 5分。总数是13。 第7轮:你可以得到9 + 5 = 14分。总数是27。
注意:
- 输入列表的大小将介于1和1000之间。
- 列表中的每个整数都将介于-30000和30000之间。
1 class Solution { 2 func calPoints(_ ops: [String]) -> Int { 3 var v:[Int] = [Int]() 4 for op in ops 5 { 6 if op == "+" 7 { 8 v.append(v.last! + v[v.count - 2]) 9 } 10 else if op == "D" 11 { 12 v.append(2 * v.last!) 13 } 14 else if op == "C" 15 { 16 v.popLast() 17 } 18 else 19 { 20 v.append(Int(op)!) 21 } 22 } 23 return v.reduce(0,+) 24 } 25 }
28ms
1 class Solution { 2 func calPoints(_ ops: [String]) -> Int { 3 var points:Int = 0 4 var poStack:[Int] = [] 5 6 for i in 0..<ops.count { 7 if ops[i] == "+" { 8 let n:Int = poStack.count - 2 9 points = points + poStack[n] + poStack.last! 10 poStack.append(poStack[n] + poStack.last!) 11 12 }else if ops[i] == "C"{ 13 let temp:Int = poStack.last! 14 poStack.removeLast() 15 points = points - temp 16 17 }else if ops[i] == "D" { 18 points = points + poStack.last! * 2 19 let po = poStack.last! * 2 20 poStack.append(po) 21 22 }else{ 23 points = points + Int(ops[i])! 24 poStack.append(Int(ops[i])!) 25 } 26 } 27 28 return points 29 } 30 }
32ms
1 class Solution { 2 func calPoints(_ ops: [String]) -> Int { 3 var stack = [Int]() 4 var sum = 0 5 for ch in ops { 6 switch ch { 7 case "C": 8 let x = stack.removeLast() 9 sum -= x 10 case "D": 11 if let x = stack.last { 12 stack.append(x * 2) 13 sum += x * 2 14 } 15 case "+": 16 if stack.count >= 2 { 17 let x = stack[stack.count - 1] 18 let y = stack[stack.count - 2] 19 stack.append(x + y) 20 sum += (x + y) 21 } 22 default: 23 if let x = Int(ch) { 24 stack.append(x) 25 sum += x 26 } 27 } 28 } 29 return sum 30 } 31 }
36ms
1 class Solution { 2 func calPoints(_ ops: [String]) -> Int { 3 var stack = [String]() 4 for op in ops { 5 if Int(op) != nil { 6 stack.append(op) 7 } else if op == "C" && stack.count > 0 { 8 stack.removeLast() 9 } else if op == "D" && stack.count > 0 { 10 stack.append(String(Int(stack.last!)! * 2)) 11 } else if stack.count >= 2 { 12 let sum = String(Int(stack.last!)! + Int(stack[stack.count - 2])!) 13 stack.append(sum) 14 } 15 } 16 17 var ans = 0 18 for item in stack { 19 ans += Int(item)! 20 } 21 return ans 22 } 23 }
40ms
1 struct Stack<T: Equatable> { 2 private var list: [T] 3 init() { 4 list = [T]() 5 } 6 var isEmpty:Bool { 7 return list.count == 0 8 } 9 var count: Int { 10 return list.count 11 } 12 mutating func push(_ value: T) { 13 list.append(value) 14 } 15 16 mutating func pop() -> T? { 17 guard !isEmpty else { return nil } 18 return list.removeLast() 19 } 20 21 func peek() -> T? { 22 return list.last 23 } 24 func peekLastButOne() -> T? { 25 guard !isEmpty else { return nil } 26 guard count > 1 else { return nil } 27 return list[count-2] 28 } 29 } 30 31 class Solution { 32 func calPoints(_ ops: [String]) -> Int { 33 var dataStack = Stack<Int>() 34 var totalSum = 0 35 for element in ops { 36 if let number = Int(element) { 37 // handle integers 38 dataStack.push(number) 39 totalSum += number 40 } 41 else { 42 if element == "C" { 43 // cancel case operation 44 let val = dataStack.pop() ?? 0 45 totalSum -= val 46 } else if element == "D" { 47 // double round 48 var val = dataStack.peek() ?? 0 49 val *= 2 50 dataStack.push(val) 51 totalSum += val 52 } else { 53 var val1 = dataStack.peek() ?? 0 54 let val2 = dataStack.peekLastButOne() ?? 0 55 val1 += val2 56 dataStack.push(val1) 57 totalSum += val1 58 // sum of last 2 rounds results 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 return totalSum 63 } 64 }
60ms
1 class Solution { 2 func calPoints(_ ops: [String]) -> Int { 3 var history = [Int]() 4 for op in ops { 5 if op == "+" { 6 history.append(history[history.count-1] + history[history.count-2]) 7 } else if op == "D" { 8 history.append(history[history.count-1] * 2) 9 } else if op == "C" { 10 history.removeLast() 11 } else { 12 history.append(Int(op)!) 13 } 14 } 15 16 return history.reduce(0) { $0 + $1 } 17 } 18 }
76ms
1 class Solution { 2 func calPoints(_ ops: [String]) -> Int { 3 if ops.count < 1 { 4 return 0 5 } 6 var result = 0 7 var statckArray : [Int] = [] 8 var temp = 0 9 for score in ops { 10 if score == "C" && statckArray.count > 0{ 11 statckArray.removeLast() 12 }else if score == "D" && statckArray.count > 0 { 13 temp = statckArray.last! 14 statckArray.append(temP*2) 15 }else if score == "+" && statckArray.count > 1 { 16 temp = statckArray.last! + statckArray[statckArray.count-2] 17 statckArray.append(temp) 18 }else if score == "+" && statckArray.count == 1 { 19 temp = statckArray.last! 20 statckArray.append(temp) 21 }else if isPurnInt(string: score) { 22 statckArray.append(Int(score)!) 23 } 24 } 25 while statckArray.count > 0 { 26 result = result + statckArray.last! 27 statckArray.removeLast() 28 } 29 return result 30 } 31 func isPurnInt(string: String) -> Bool { 32 let scan: Scanner = Scanner(string: string) 33 var val:Int = 0 34 return scan.scanInt(&val) && scan.isAtEnd 35 36 } 37 }
![2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组 景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数: game [i] = { Ki, Bi } Ki 一定是负数, 2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组 景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数: game [i] = { Ki, Bi } Ki 一定是负数,](http://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/upload/2025/04/248381e3-7eff-4f50-bf9c-ebddc0d8438c1744859725561.jpg)
2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组 景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数: game [i] = { Ki, Bi } Ki 一定是负数,
2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组
景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数:
game[i] = { Ki, Bi }
Ki 一定是负数,Bi 一定是正数
举个例子 :
Ki = -2, Bi = 10
如果只有 1 个人买票,单张门票的价格为 : Ki * 1 + Bi = 8
所以这 1 个人游玩该项目要花 8 元
如果有 2 个人买票,单张门票的价格为 : Ki * 2 + Bi = 6
所以这 2 个人游玩该项目要花 6 * 2 = 12 元
如果有 5 个人买票,单张门票的价格为 : Ki * 2 + Bi = 0
所以这 5 个人游玩该项目要花 0 * 5 = 0 元
如果有更多人买票,都认为花 0 元 (因为你让项目倒贴钱实在是太操蛋了)
于是可以认为,如果有 x 个人买票,单张门票的价格为 : Ki * x + Bi
x 个人游玩这个项目的总花费是 : max {(Ki * x + Bi) * x , 0 }
你作为领导,单位一共有 n 个人,每个人最多可以选 1 个项目来游玩,也可以不选任何项目
所有员工将在明晚提交选择,然后由你去按照上面的规则,统一花钱,统一购票
但是现在,你想知道自己需要准备多少钱,就可以应付可能的各种情况,
支持各种可能下的开销,返回这个最保险的钱数。
数据量描述 :
1 <= N、M、Bi <= 10^5,
-(10^5) <= Ki < 0。
来自左程云。
答案 2023-08-10:
步骤描述:
1. 创建一个优先队列(堆)h,用于存储游戏项目。我们使用 GameHeap 类型来定义优先队列,并实现 Len、Less、Swap、Push 和 Pop 方法。
2. 遍历每个项目 g,在遍历过程中将 Ki 和 Bi 作为参数创建 Game 结构体 game,并将其添加到优先队列 h 中。
3. 初始化结果变量 ans 为 0,用于记录总花费。
4. 迭代 n 次,表示有 n 个人进行选择游戏项目的操作。
4.1. 检查当前优先队列 h 的第一个项目的 Earn 值(单张门票的价格乘以人数)。如果 Earn 值小于等于 0,即项目不再划算,跳出循环。
4.2. 从优先队列 h 中弹出一个项目,并将其赋值给变量 cur。
4.3. 将当前项目的 Earn 值累加到结果变量 ans 中。
4.4. 增加当前项目的人数 cur.People。
4.5. 将更新后的项目 cur 添加回优先队列 h 中。
5. 返回结果变量 ans,即准备的最保险的金额。
总的时间复杂度:O (nlog (m)),其中 n 为人数,m 为项目数。遍历 n 次,每次从优先队列中弹出最大值,时间复杂度为 log (m)。
总的空间复杂度:O (m),优先队列 h 的大小取决于项目数 m。
go 完整代码如下:
package main
import (
"container/heap"
"fmt"
)
type Game struct {
Ki int
Bi int
People int
}
type GameHeap []Game
func (h GameHeap) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h GameHeap) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].Earn() > h[j].Earn() }
func (h GameHeap) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *GameHeap) Push(x interface{}) { *h = append(*h, x.(Game)) }
func (h *GameHeap) Pop() interface{} {
old := *h
n := len(old)
x := old[n-1]
*h = old[0 : n-1]
return x
}
func (g Game) Earn() int {
return (2*g.People+1)*g.Ki + g.Bi
}
func EnoughMoney(n int, games [][]int) int {
h := &GameHeap{}
heap.Init(h)
for _, g := range games {
game := Game{Ki: g[0], Bi: g[1]}
heap.Push(h, game)
}
ans := 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
if (*h)[0].Earn() <= 0 {
break
}
cur := heap.Pop(h).(Game)
ans += cur.Earn()
cur.People++
heap.Push(h, cur)
}
return ans
}
func main() {
games := [][]int{{-2, 10}, {-1, 5}, {-3, 15}}
n := 5
result := EnoughMoney(n, games)
fmt.Println(result)
}
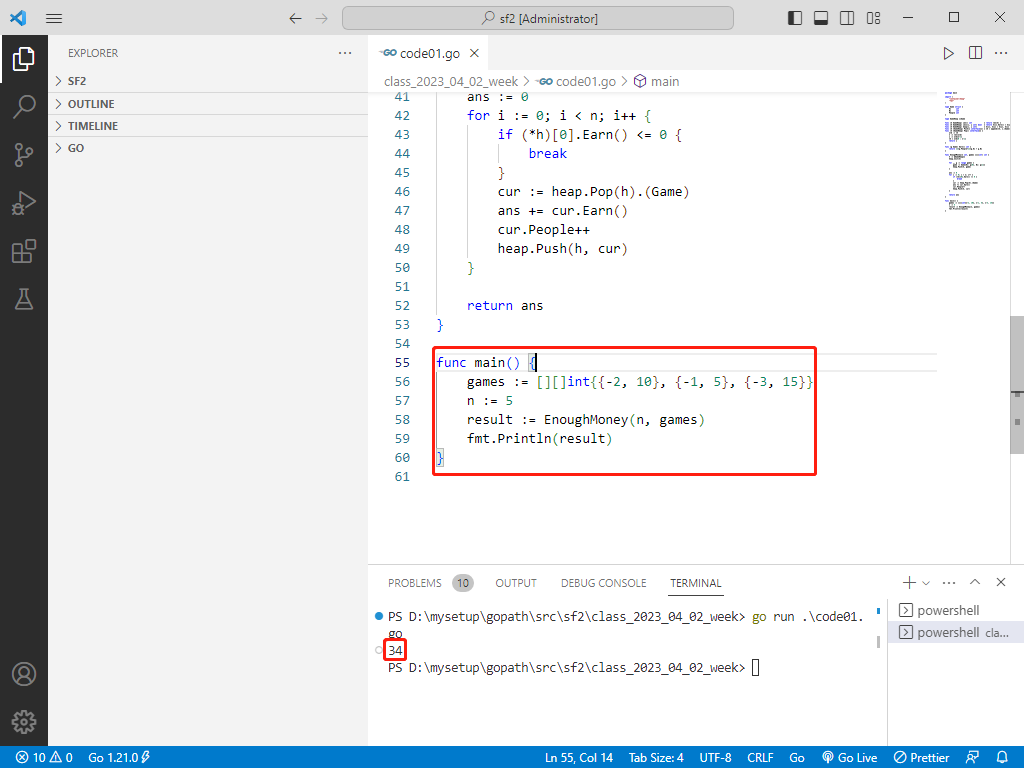
c++ 完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct Game {
int Ki;
int Bi;
int people;
Game(int k, int b) {
Ki = k;
Bi = b;
people = 0;
}
int earn() const {
return (2 * people + 1) * Ki + Bi;
}
};
struct CompareGame {
bool operator()(const Game& a, const Game& b) {
return a.earn() < b.earn();
}
};
int enoughMoney(int n, vector<vector<int>>& games) {
priority_queue<Game, vector<Game>, CompareGame> heap;
for (auto& g : games) {
heap.push(Game(g[0], g[1]));
}
int ans = 0;
while (n > 0 && heap.top().earn() > 0) {
Game cur = heap.top();
heap.pop();
ans += cur.earn();
cur.people++;
heap.push(cur);
n--;
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> games = { {-2, 10}, {-1, 5}, {-3, 15} };
int n = 5;
int result = enoughMoney(n, games);
cout << "Amount needed: " << result << endl;
return 0;
}
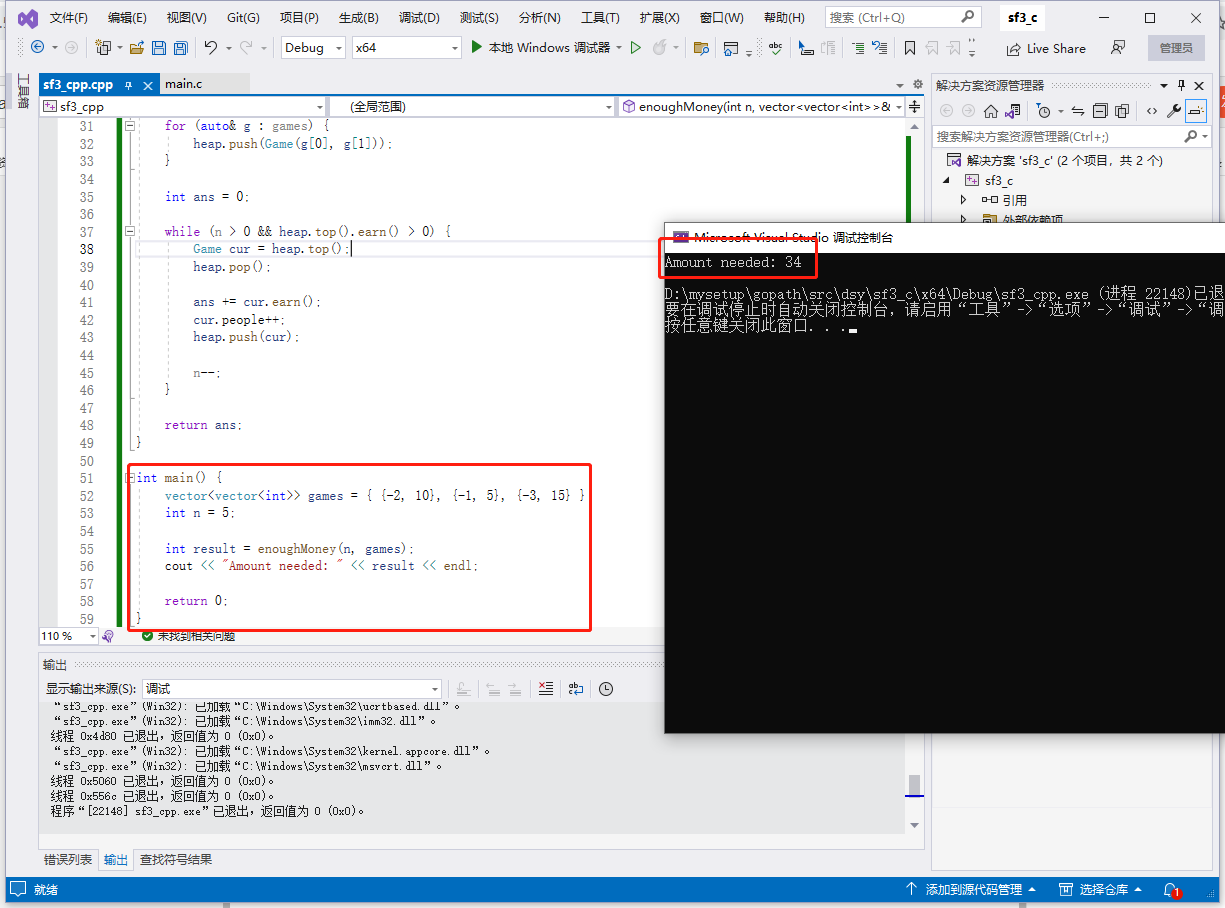
c 语言完整代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Game {
int Ki;
int Bi;
int people;
};
typedef struct Game Game;
int cmp(const void* a, const void* b) {
Game* gameA = (Game*)a;
Game* gameB = (Game*)b;
return (2 * gameB->people + 1) * gameB->Ki + gameB->Bi - (2 * gameA->people + 1) * gameA->Ki - gameA->Bi;
}
int enoughMoney(int n, int games[][2], int m) {
Game* heap = (Game*)malloc(m * sizeof(Game));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
heap[i].Ki = games[i][0];
heap[i].Bi = games[i][1];
heap[i].people = 0;
}
qsort(heap, m, sizeof(Game), cmp);
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if ((2 * heap[0].people + 1) * heap[0].Ki + heap[0].Bi <= 0) {
break;
}
ans += (2 * heap[0].people + 1) * heap[0].Ki + heap[0].Bi;
heap[0].people++;
qsort(heap, m, sizeof(Game), cmp);
}
free(heap);
return ans;
}
int main() {
int games[][2] = { {-2, 10}, {-1, 5}, {-3, 15} };
int n = 5;
int m = sizeof(games) / sizeof(games[0]);
int result = enoughMoney(n, games, m);
printf("Total money needed: %d\n", result);
return 0;
}

682. Baseball Game 棒球游戏 按字母处理
[抄题]:
You''re now a baseball game point recorder.
Given a list of strings, each string can be one of the 4 following types:
Integer(one round''s score): Directly represents the number of points you get in this round."+"(one round''s score): Represents that the points you get in this round are the sum of the last twovalidround''s points."D"(one round''s score): Represents that the points you get in this round are the doubled data of the lastvalidround''s points."C"(an operation, which isn''t a round''s score): Represents the lastvalidround''s points you get were invalid and should be removed.
Each round''s operation is permanent and could have an impact on the round before and the round after.
You need to return the sum of the points you could get in all the rounds.
Example 1:
Input: ["5","2","C","D","+"]
Output: 30
Explanation:
Round 1: You could get 5 points. The sum is: 5.
Round 2: You could get 2 points. The sum is: 7.
Operation 1: The round 2''s data was invalid. The sum is: 5.
Round 3: You could get 10 points (the round 2''s data has been removed). The sum is: 15.
Round 4: You could get 5 + 10 = 15 points. The sum is: 30.
Example 2:
Input: ["5","-2","4","C","D","9","+","+"]
Output: 27
Explanation:
Round 1: You could get 5 points. The sum is: 5.
Round 2: You could get -2 points. The sum is: 3.
Round 3: You could get 4 points. The sum is: 7.
Operation 1: The round 3''s data is invalid. The sum is: 3.
Round 4: You could get -4 points (the round 3''s data has been removed). The sum is: -1.
Round 5: You could get 9 points. The sum is: 8.
Round 6: You could get -4 + 9 = 5 points. The sum is 13.
Round 7: You could get 9 + 5 = 14 points. The sum is 27.[暴力解法]:
时间分析:
空间分析:
[优化后]:
时间分析:
空间分析:
[奇葩输出条件]:
[奇葩corner case]:
[思维问题]:
[一句话思路]:
[输入量]:空: 正常情况:特大:特小:程序里处理到的特殊情况:异常情况(不合法不合理的输入):
[画图]:
[一刷]:
- string数组中的元素是string,不是char。用双引号。但是字符串也可以用一个c字母来表示。
- 两倍的情况不能忘了push回原来的值
[二刷]:
[三刷]:
[四刷]:
[五刷]:
[五分钟肉眼debug的结果]:
[总结]:
stack起作用的时候,不外乎就是push pop方法
[复杂度]:Time complexity: O(n) Space complexity: O(n)
[英文数据结构或算法,为什么不用别的数据结构或算法]:
Integer.parseInt 用整数类,把字符转化成整数了
[关键模板化代码]:
int temp1 = stack.pop();
int temp2 = stack.pop();
int tempSum = temp1 + temp2;
sum += tempSum;
stack.push(temp2);
stack.push(temp1);
stack.push(tempSum);
[其他解法]:
[Follow Up]:
[LC给出的题目变变变]:
[代码风格] :


class Solution {
public int calPoints(String[] ops) {
//cc
if (ops.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
//ini: stack, sum
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int sum = 0;
//4 states
for (String c : ops) {
if (c.equals("+")) {
int temp1 = stack.pop();
int temp2 = stack.pop();
int tempSum = temp1 + temp2;
sum += tempSum;
stack.push(temp2);
stack.push(temp1);
stack.push(tempSum);
}
else if (c.equals("D")) {
int temp = stack.pop();
int temp_d = temp * 2;
sum += temp_d;
stack.push(temp);
stack.push(temp_d);
}
else if (c.equals("C")) {
int del = stack.pop();
sum -= del;
}
else {
int temp = Integer.parseInt(c);
sum += temp;
stack.push(temp);
}
}
return sum;
}
}
Acer Swift 3笔记本怎么样 Acer Swift 3笔记本上手图赏
Acer Swift 3是宏碁推出的笔记本电脑,具有轻薄时尚等元素,这里为大家带来 Acer Swift 3笔记本上手图赏 ,一起来看看。
14英寸1920*1080的显示屏幕、2.5GHz的英特尔酷睿酷睿i3、i5-7200u/i7处理器、图形128mb英特尔高清显卡620、8GB/256GB的SSD、Windows Hello、指纹识别器,处理速度快可媲美MacBook,售价仅为1398美元(约£1090/1760美元),性价比方面还是不错的。







以上就是 Acer Swift 3笔记本上手图赏 相关内容,希望对你有帮助。

Codeforces Round #426 (Div. 2) C. The Meaningless Game C. The Meaningless Game
总结
以上是小编为你收集整理的Codeforces Round #426 (Div. 2) C. The Meaningless Game C. The Meaningless Game全部内容。
如果觉得小编网站内容还不错,欢迎将小编网站推荐给好友。
关于[Swift]LeetCode682. 棒球比赛 | Baseball Game和棒球比赛2021的介绍已经告一段落,感谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于2023-08-10:景区里有 m 个项目,也就是项目数组为 int [][] game,这是一个 m*2 的二维数组 景区的第 i 个项目有如下两个参数: game [i] = { Ki, Bi } Ki 一定是负数,、682. Baseball Game 棒球游戏 按字母处理、Acer Swift 3笔记本怎么样 Acer Swift 3笔记本上手图赏、Codeforces Round #426 (Div. 2) C. The Meaningless Game C. The Meaningless Game的相关信息,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:





