如果您想了解[Swift]LeetCode433.最小基因变化|MinimumGeneticMutation的相关知识,那么本文是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将对最小基因组是什么进行全面详尽的解释,并且为
如果您想了解[Swift]LeetCode433. 最小基因变化 | Minimum Genetic Mutation的相关知识,那么本文是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将对最小基因组是什么进行全面详尽的解释,并且为您提供关于(Java) LeetCode 433. Minimum Genetic Mutation —— 最小基因变化、barplot3d | 圣诞节送你一个 mutation signature 搭建的 “乐高”、Codeforces 76C Mutation、Codeforces 86C Genetic engineering 题解《挑战程序设计竞赛》的有价值的信息。
本文目录一览:- [Swift]LeetCode433. 最小基因变化 | Minimum Genetic Mutation(最小基因组是什么)
- (Java) LeetCode 433. Minimum Genetic Mutation —— 最小基因变化
- barplot3d | 圣诞节送你一个 mutation signature 搭建的 “乐高”
- Codeforces 76C Mutation
- Codeforces 86C Genetic engineering 题解《挑战程序设计竞赛》
![[Swift]LeetCode433. 最小基因变化 | Minimum Genetic Mutation(最小基因组是什么) [Swift]LeetCode433. 最小基因变化 | Minimum Genetic Mutation(最小基因组是什么)](http://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/upload/2025/04/1b86f426-eaf4-4cf0-a0bf-ab45e542c2f31745469255146.jpg)
[Swift]LeetCode433. 最小基因变化 | Minimum Genetic Mutation(最小基因组是什么)
A gene string can be represented by an 8-character long string,with choices from "A", "C", "G", "T".
Suppose we need to investigate about a mutation (mutation from "start" to "end"),where ONE mutation is defined as ONE single character changed in the gene string.
For example, "AACCGGTT" -> "AACCGGTA" is 1 mutation.
Also,there is a given gene "bank",which records all the valid gene mutations. A gene must be in the bank to make it a valid gene string.
Now,given 3 things - start,end,bank,your task is to determine what is the minimum number of mutations needed to mutate from "start" to "end". If there is no such a mutation,return -1.
Note:
- Starting point is assumed to be valid,so it might not be included in the bank.
- If multiple mutations are needed,all mutations during in the sequence must be valid.
- You may assume start and end string is not the same.
Example 1:
start: "AACCGGTT" end: "AACCGGTA" bank: ["AACCGGTA"] return: 1
Example 2:
start: "AACCGGTT" end: "AAACGGTA" bank: ["AACCGGTA","AACCGCTA","AAACGGTA"] return: 2
Example 3:
start: "AAAAACCC" end: "AACCCCCC" bank: ["AAAACCCC","AAACCCCC","AACCCCCC"] return: 3
一条基因序列由一个带有8个字符的字符串表示,其中每个字符都属于 "A", "T"中的任意一个。
假设我们要调查一个基因序列的变化。一次基因变化意味着这个基因序列中的一个字符发生了变化。
例如,基因序列由"AACCGGTT" 变化至 "AACCGGTA" 即发生了一次基因变化。
与此同时,每一次基因变化的结果,都需要是一个合法的基因串,即该结果属于一个基因库。
现在给定3个参数 — start,bank,分别代表起始基因序列,目标基因序列及基因库,请找出能够使起始基因序列变化为目标基因序列所需的最少变化次数。如果无法实现目标变化,请返回 -1。
注意:
- 起始基因序列默认是合法的,但是它并不一定会出现在基因库中。
- 所有的目标基因序列必须是合法的。
- 假定起始基因序列与目标基因序列是不一样的。
示例 1:
start: "AACCGGTT" end: "AACCGGTA" bank: ["AACCGGTA"] 返回值: 1
示例 2:
start: "AACCGGTT" end: "AAACGGTA" bank: ["AACCGGTA","AAACGGTA"] 返回值: 2
示例 3:
start: "AAAAACCC" end: "AACCCCCC" bank: ["AAAACCCC","AACCCCCC"] 返回值: 3
8ms
1 class Solution { 2 func minMutation(_ start: String,_ end: String,_ bank: [String]) -> Int { 3 var bank = bank 4 var explored:[Bool] = [Bool](repeating:false,count:bank.count) 5 if bank.isEmpty {return -1} 6 return minMutation(&explored,start,&bank) 7 } 8 9 func minMutation(_ explored:inout [Bool],_ start:String,_ end:String,_ bank:inout[String]) -> Int 10 { 11 if start == end {return 0} 12 var step:Int = bank.count + 1 13 for i in 0..<bank.count 14 { 15 if diffOne(start,bank[i]) && !explored[i] 16 { 17 explored[i] = true 18 var temp:Int = minMutation(&explored,bank[i],&bank) 19 if temp != -1 20 { 21 step = min(step,temp) 22 } 23 explored[i] = false 24 } 25 } 26 return step == bank.count + 1 ? -1 : 1 + step 27 } 28 29 func diffOne(_ s1:String,_ s2:String) -> Bool 30 { 31 var count:Int = 0 32 for i in 0..<s1.count 33 { 34 if s1[i] != s2[i] 35 { 36 count += 1 37 } 38 if count >= 2 39 { 40 return false 41 } 42 } 43 return count == 1 44 } 45 } 46 47 extension String { 48 //subscript函数可以检索数组中的值 49 //直接按照索引方式截取指定索引的字符 50 subscript (_ i: Int) -> Character { 51 //读取字符 52 get {return self[index(startIndex,offsetBy: i)]} 53 54 } 55 }
10ms
1 class Solution { 2 func minMutation(_ start: String,_ bank: [String]) -> Int { 3 let geneChoice = [Character("A"),Character("C"),Character("G"),Character("T")] 4 var bankArray = Set(bank.map { Array($0) }) 5 var startArray = Array(start) 6 var endarray = Array(end) 7 var queue = [startArray] 8 var mutationCount = 0 9 while queue.count > 0 { 10 var nextQueue = [[Character]]() 11 for i in 0 ..< queue.count { 12 var curr = queue[i] 13 if curr == endarray { 14 return mutationCount 15 } 16 for j in 0 ..< 8 { 17 var c = curr[j] 18 for k in 0 ..< geneChoice.count { 19 if c != geneChoice[k] { 20 curr[j] = geneChoice[k] 21 if bankArray.contains(curr) { 22 nextQueue.append(curr) 23 bankArray.remove(curr) 24 } 25 } 26 } 27 curr[j] = c 28 } 29 } 30 queue = nextQueue 31 mutationCount += 1 32 } 33 return -1 34 } 35 }
12ms
1 class Solution { 2 func minMutation(_ start: String,_ bank: [String]) -> Int { 3 if !bank.contains(end){ 4 return -1 5 } 6 if start == end{ 7 return 0 8 } 9 var max :Int = 0 10 11 var arr = [String]() 12 var vists = [String]() 13 var temp = [String]() 14 arr.append(start) 15 while arr.count > 0 { 16 17 for j in 0..<arr.count{ 18 for k in 0..<bank.count{ 19 if vists.contains(bank[k]){continue} 20 var dif :Int = 0 21 for i in 0..<8{ 22 let s = arr[j].index(arr[j].startIndex,offsetBy: i) 23 let b = bank[k].index(bank[k].startIndex,offsetBy: i) 24 if arr[j][s] != bank[k][b] { 25 dif = dif + 1 26 } 27 if(i == 7 && dif == 1){ 28 if bank[k] == end {return max + 1} 29 temp.append(bank[k]) 30 vists.append(bank[k]) 31 } 32 } 33 34 35 } 36 } 37 if temp.count == 0 {return -1}else{ max = max + 1 } 38 arr = temp;temp = []; 39 } 40 return max 41 } 42 }

(Java) LeetCode 433. Minimum Genetic Mutation —— 最小基因变化
A gene string can be represented by an 8-character long string, with choices from "A", "C", "G", "T".
Suppose we need to investigate about a mutation (mutation from "start" to "end"), where ONE mutation is defined as ONE single character changed in the gene string.
For example, "AACCGGTT" -> "AACCGGTA" is 1 mutation.
Also, there is a given gene "bank", which records all the valid gene mutations. A gene must be in the bank to make it a valid gene string.
Now, given 3 things - start, end, bank, your task is to determine what is the minimum number of mutations needed to mutate from "start" to "end". If there is no such a mutation, return -1.
Note:
- Starting point is assumed to be valid, so it might not be included in the bank.
- If multiple mutations are needed, all mutations during in the sequence must be valid.
- You may assume start and end string is not the same.
Example 1:
start: "AACCGGTT"
end: "AACCGGTA"
bank: ["AACCGGTA"]
return: 1Example 2:
start: "AACCGGTT"
end: "AAACGGTA"
bank: ["AACCGGTA", "AACCGCTA", "AAACGGTA"]
return: 2Example 3:
start: "AAAAACCC"
end: "AACCCCCC"
bank: ["AAAACCCC", "AAACCCCC", "AACCCCCC"]
return: 3
本题和LeetCode 127. Word Ladder —— 单词接龙完全一样,没有任何区别,利用广度优先搜索查找最短路径。欣慰自己写代码一遍过,直接AC。
Java
class Solution {
public int minMutation(String start, String end, String[] bank) {
if (bank == null || bank.length == 0) return -1;
char[] gen = {''A'',''C'',''G'',''T''};
HashSet<String> bankSet = new HashSet<>();
for (String s : bank)
bankSet.add(s);
Queue<String> q = new LinkedList<>();
HashMap<String, Integer> res = new HashMap<>();
res.put(start, 0);
q.add(start);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
String s = q.poll();
bankSet.remove(s);
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char[] next = s.toCharArray();
for (char c : gen) {
next[i] = c;
String nextS = new String(next);
if (bankSet.contains(nextS)) {
res.put(nextS, res.get(s) + 1);
if (nextS.equals(end)) return res.get(nextS);
q.add(nextS);
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}

barplot3d | 圣诞节送你一个 mutation signature 搭建的 “乐高”
本文首发于 “生信补给站”,https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/VNLIFzc9OysepGrE3lJrkw
更多关于 R 语言,ggplot2 绘图,生信分析的内容,敬请关注小号。
上次通过 deconstructSigs | 探寻 cosmic 的独特 “气质”-mutation signature !学会了如何利用 deconstructSigs-R 包进行 mutation signature 分析。
在文章最后利用每个样本的 96 种三碱基类型在最后绘制了柱形图,本文利用同样的数据绘制乐高图,下图为文献插图
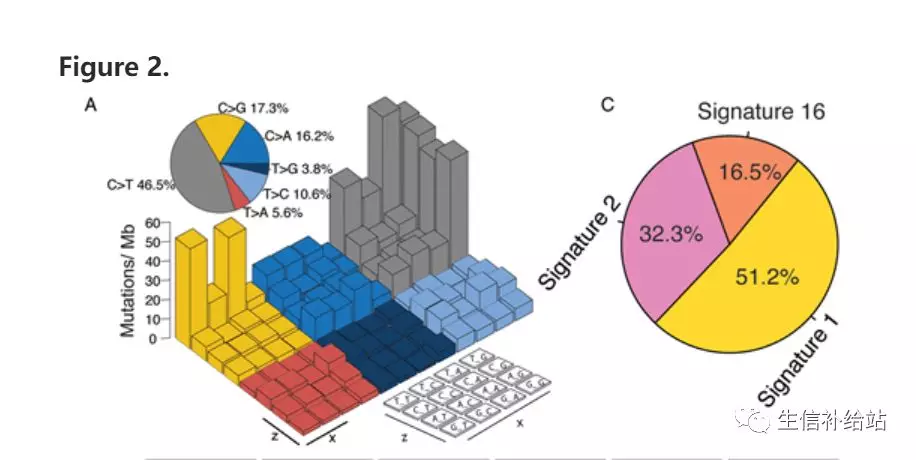
一 mutation signature 分析
快速实现 mutation signature 分析,得到每个样本的三碱基序列结果,详细参数详见 deconstructSigs | 探寻 cosmic 的独特 “气质”-mutation signature !
library(deconstructSigs)
#查看数据
head(sample.mut.ref)
# Convert to deconstructSigs input
sigs.input <- mut.to.sigs.input(mut.ref = sample.mut.ref,
sample.id = "Sample",
chr = "chr",
pos = "pos",
ref = "ref",
alt = "alt")
# Determine the signatures contributing to the example sample1
sample_1 = whichSignatures(tumor.ref = sigs.input,
signatures.ref = signatures.cosmic,
sample.id = 1,
contexts.needed = TRUE,
tri.counts.method = ''default'')
#输出tumor的三碱基序列百分比
sample_1$tumor
二 搭 “乐高”
利用上部分得到的三碱基序列比例进行绘制:
需要注意的自己的数据与 COSMIC 数据的顺序要相同 !
library(barplot3d)
# Read in COSMIC signature probabilities
x=system.file("extdata", "signature_probabilities.txt", package = "barplot3d")
sigdata=read.table(x,header=TRUE,stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
# 输入文件的顺序必须与此一致
cat(sigdata$Somatic_mutation_type,sep="\n")
#使用自己的数据绘制乐高图
legoplot3d(contextdata=sample_1$tumor,labels=FALSE,scalexy=0.03)
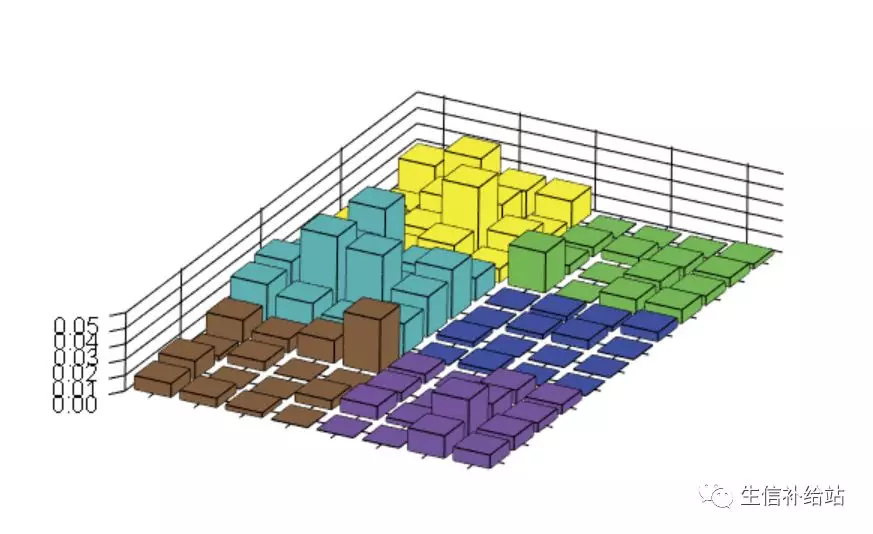
#参数调整
legoplot3d(contextdata=sample_1$tumor,labels=FALSE,scalexy=0.01,sixcolors="broad",alpha=0.4)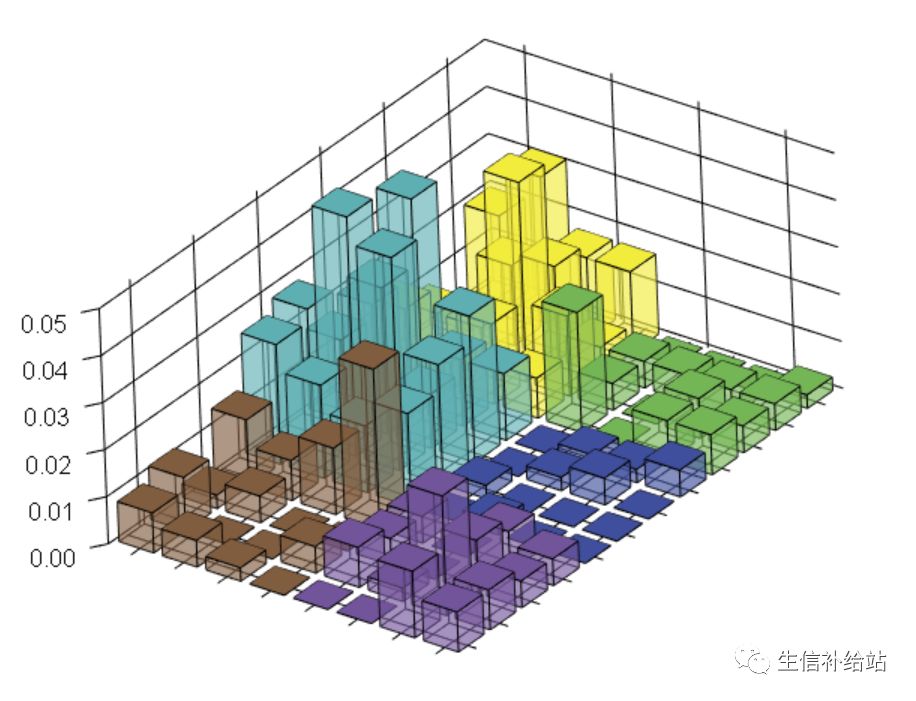
scalexy:适当调整获得适当缩放的图像;
alpha:柱子的透明度;
sixcolors:默认颜色与 Sanger 的 signature 一致,可以设置为原始的 Broad Institute 颜色,也可以其他 6 种颜色。
对了,图是 3D 的,可以自己转,,,![]()
参考资料:
A mutational signature associated with alcohol consumption and prognostically significantly mutated driver genes in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/barplot3d/vignettes/barplot3d.html
◆ ◆ ◆ ◆ ◆
精心整理(含图版)| 你要的全拿走!有备无患 (R 统计,ggplot2 绘图,生信图形可视化汇总)
【觉得不错,右下角点个 “在看”,期待您的转发,谢谢!】

Codeforces 76C Mutation
Description
描述
给出一个由前 $k$ 个大写字母组成的字符串,每次可以花费 $t_i$ 代价删去该字符串中所有的第 $i$ 个大写字母,一个字符串的代价为该字符串每对相邻字符的代价,给出一 $k\times k$ 的矩阵表示两个相邻的大写字母的代价矩阵,问有多少种删除方案使得删除的代价以及剩余字符串的代价之和不超过 $T$ ,注意剩余字符串需非空。
输入
第一行三个整数 $n,k,T$ 表示字符串长度,所用字母种类以及代价上限,之后输入一个由前 $k$ 个大写字母组成的长度为 $n$ 的字符串,以及 $n$ 个整数 $t_i$ 表示删去第 $i$ 种字符的代价,最后输入一个 $k\times k$ 的矩阵 $m_{x,y}$ 表示相邻两字母的代价矩阵 ($1≤n≤2⋅10^5$,$1≤k≤22$,$1≤T≤2⋅10^9$,$1≤t_i,a_{x,y}≤10^9$)。
输出
输出满足条件的方案数。
样例
输入
5 3 13
BACAC
4 1 2
1 2 3
2 3 4
3 4 10输出
5
解释
下面是合法的方案:
$\text{BACAC} (11), \text{ACAC} (10), \text{BAA} (5), \text{B}(6), \text{AA}(4)$。
Solution
考虑前缀和。
用一个 $k$ 位 $01$ 集合表示删字母情况,$0$ 表示不删,$1$ 表示删。
令 $f_i$ 表示删去集合为 $i$ 后的字符串代价,如果我们求出了每一个 $f_i$,就可以像这样统计答案:
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 1 << k; i++)
if((i & all) == i /* 删去字符在集合中 */ && f[i] <= T /* 符合代价要求 */ && i != all /* 剩余字符串不为空 */)
ans++;
printf("%d\n", ans);其中 $all$ 表示所有出现字符全集,$T$ 为代价上限。
以下为读入及预处理:
scanf("%d%d%d%s", &n, &k, &T, s);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
s[i] -= ''A'';
all |= 1 << s[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) scanf("%d", &t[i]);
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
memset(can, -1, sizeof(can));
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) f[1 << i] = t[i];将每一种字符的损耗 $t_i$ 存进 $f_{2^i}$ 里,最后使用前缀和累加就可以将其加入每一种情况了。
累加 $f_i$ 就是从每一个比 $f_i$ 少一个元素的子集里累加(当然还有自己本来存储的值)。
例如 $f_{10110} = f_{10110} + f_{00110} + f_{10010} + f_{10100}$。
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 1 << k; j++)
if((j >> i) & 1)
f[j] += f[j ^ (1 << i)];注意这里累加的其实是 $f_j$。
前方高能
下面考虑如何求出每一个 $f$ 。
用 $can_i$ 表示从最近的字符 $i$,到当前字符之间的字符集(两端不含),$can$ 初始化为 $-1$,表示该字符自身还没出现过。
我们遍历这个字符串,对于每一个字符 $s_i$,将它视为删去字符集的右端点(不含),再枚举所有的 $k$ 个字符 $j$,将离 $s_i$ 最近的 $j$ 视为删去字符集的左端点(不含),则删去的字符状态即为它们之间的所有种类的字符。
注意,并不是所有的 $j$ 都可以和 $s_i$ 匹配,一个合法的 $j$ 应有如下条件:
1. 在 $s_i$ 之前出现了字符 $j$,代码中体现为 can[j] >= 0 ;
2. $can_j$ 中不包含字符 $j$ 和 $s_i$,代码中体现为 !((can[j] >> j) & 1) && !((can[j] >> s[i]) & 1) 。
如果合法,那么删去两者之间的字符集后,该两个字符将会产生一个新的代价 $a_{s_i,j}$,将这个代价加入 $f_{can_j}$ 中,但需要注意的是 $f_{can_j|2^{s_i}}$ 和 $f_{can_j|2^j}$ 这两个不应该存在这个代价的状态将在最终被累加这个代价,所以将它们都减去 $a_{s_i,j}$,那此时 $f_{can_j|2^j|2^{s_i}}$ 其实被减去了两遍代价,那么将它加上 $a_{s_i,j}$。
也就是一个容斥啦。
f[can[j]] += a[j][s[i]];
f[can[j] | (1 << j)] -= a[j][s[i]];
f[can[j] | (1 << s[i])] -= a[j][s[i]];
f[can[j] | (1 << j) | (1 << s[i])] += a[j][s[i]];还有两个细节,一是一个 $s_i$ 处理完后,就要将该 $can_{s_i}$ 清空,因为出现了一个新的 $s_i$,就是 can[s[i]] = 0 。
二是在遍历 $k$ 个字符时,只要该字符出现了,则在容斥(也有可能不容斥)后要标记 $j$ 可以和 $s_i$ 匹配,即 can[j] |= (1 << s[i]) 。
有一个问题:初始代价好像并没有预处理啊?
这是因为当访问到 $s_i$ 时 $can_{s_{i-1}}$ 必定为 $0$,这时就会把 $a_{s_i,s_{i-1}}$ 加入 $f_0$ 中啦,其它情况也同理。
那么 AC 代码就出来了,时间复杂度 $\mathcal O (nk+k\times 2^k)$。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
const int K = 25;
int n, k, T, all, can[K], t[K], a[K][K], f[1 << K];
char s[200005];
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d%d%s", &n, &k, &T, s);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
s[i] -= ''A'';
all |= 1 << s[i];
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) scanf("%d", &t[i]);
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) scanf("%d", &a[i][j]);
memset(can, -1, sizeof(can));
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++) f[1 << i] = t[i];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for(int j = 0; j < k; j++)
if(can[j] >= 0)
{
if(!((can[j] >> j) & 1) && !((can[j] >> s[i]) & 1))
{
f[can[j]] += a[j][s[i]];
f[can[j] | (1 << j)] -= a[j][s[i]];
f[can[j] | (1 << s[i])] -= a[j][s[i]];
f[can[j] | (1 << j) | (1 << s[i])] += a[j][s[i]];
}
can[j] |= (1 << s[i]);
}
can[s[i]] = 0;
}
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < 1 << k; j++)
if((j >> i) & 1)
f[j] += f[j ^ (1 << i)];
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 1 << k; i++)
if((i & all) == i && f[i] <= T && i != all)
ans++;
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}参考文献:
v5zsq.CodeForces 76 C.Mutation(状压 DP + 容斥原理 + 高维前缀和).CSDN

Codeforces 86C Genetic engineering 题解《挑战程序设计竞赛》
本文由码农场 同步,最新版本请查看原文:http://www.hankcs.com/program/algorithm/codeforces-86c-genetic-engineering.html

Codeforces 86C Genetic engineering 基因工程:给定m个子串,求构造长n的母串的方案数。母串中每个字符都至少来自一个子串。4.7华丽地处理字符串 动态规划算法 用AC自动机(后缀树)维护子串,处理出每个节点的最长后缀模式串长度max_match。定义动态规划数组:dp[i][j][k] := 构造长i的母串,trie树节点为j,后缀从后往前数最远第k个字符不满足要求时的方案数于是搜索状态一共有ijk这三个元素,假设当前节点为c...
继续阅读:码农场 » Codeforces 86C Genetic engineering 题解《挑战程序设计竞赛》
原文链接:http://www.hankcs.com/program/algorithm/codeforces-86c-genetic-engineering.html
感谢阅读本文,欢迎 查看原文或访问 码农场 获取更多内容
关于[Swift]LeetCode433. 最小基因变化 | Minimum Genetic Mutation和最小基因组是什么的介绍现已完结,谢谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于(Java) LeetCode 433. Minimum Genetic Mutation —— 最小基因变化、barplot3d | 圣诞节送你一个 mutation signature 搭建的 “乐高”、Codeforces 76C Mutation、Codeforces 86C Genetic engineering 题解《挑战程序设计竞赛》的相关知识,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:






