如果您想了解thinkinginSwift:重新审视装饰器模式的相关知识,那么本文是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将对重试装饰器进行全面详尽的解释,并且为您提供关于d3.js学习笔记--MikeBostoc
如果您想了解thinking in Swift:重新审视装饰器模式的相关知识,那么本文是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将对重试装饰器进行全面详尽的解释,并且为您提供关于d3.js学习笔记--Mike Bostock: Thinking with Joins、Effective Python (Pythonic Thinking)、iOS Swift 应用程序随机 EXC_BAD_ACCESS 崩溃:swift_bridgeObjectRetain swift_retain swift::RefCounts
- thinking in Swift:重新审视装饰器模式(重试装饰器)
- d3.js学习笔记--Mike Bostock: Thinking with Joins
- Effective Python (Pythonic Thinking)
- iOS Swift 应用程序随机 EXC_BAD_ACCESS 崩溃:swift_bridgeObjectRetain swift_retain swift::RefCounts
- java 线程 原子类相关操作示例 thinking in java4 目录21.3.4

thinking in Swift:重新审视装饰器模式(重试装饰器)
(点击上方公众号,可快速关注)
来源:没故事的卓同学
链接:http://www.jianshu.com/p/65463cd65a92
如果在swift中按部就班的谈Gof设计模式,这在一开始就是错误的命题。原因主要有两个:
设计模式是基于面向对象的编程范式
实现基于当时的主流编程语言:C++ 和 Java
如今的swift的推荐编程范式并不是面向对象,很多人都大谈面向协议、函数式编程我就不展开了;现代的swift中有一些语法特性是当时的语言所不具备的,比如protocol extension,高阶函数等。
所以本文将利用swift的语法来谈下装饰器模式在swift下的解决思路。
Decorator pattern
有人翻作装饰器模式,也有翻成装饰者模式,英文的名称就是Decorator pattern。
装饰器模式能够实现动态的为对象添加功能,是从一个对象外部来给对象添加功能。装饰器模式就是基于对象组合的方式,可以很灵活的给对象添加所需要的功能。
直接用代码来说明。
用dish表示菜肴,一道菜有两个属性,名称和价格。然后为了方便测试重写了description属性,返回名称和价格。
class dish: customstringconvertible {
var name: String
priceInt
init(String,Int) {
self.name = name
selfprice = price
}
descriptionString get return "\(name): price)元"
}
}
}
再假设有一个菜的订单对象,接收一个dish对象后,最后可以通过total方法返回这些菜的总价钱。具体就不实现了,大概这个逻辑。
dishOrder func appenddish: dish func total() -> Int}
假设在一个饭馆里,老板发现这里的客人点菜的时候喜欢让厨师多放点盐,大家都知道非典时期盐很贵,所以老板觉得很亏,决定如果一道菜多加盐就要贵一块钱。接着又来了一个需求,如果打包带走,一道菜再加两块钱。如果我们不能改变dish的源码(在实际项目中常会遇到这种情况,可能这类定义在第三方的库里),要怎么实现这两个需求呢?
可以定义两个装饰器,注意这两个装饰器都要继承dish:
// 加盐的装饰器
classSaltdishDecorator: dish super.init:"加糖 dish.)"dish + 1)
}
}
// 外带打包的装饰器
PackagedishDecorator"打包 2}
现在我们要表示一道打包带走的松鼠桂鱼就这样表示了:
let dish = PackagedishDecorator(dish: SaltdishDecorator(dish: dish(name: "松鼠桂鱼", price: 15)))
这样我们就可以给任意一道菜增加一些装饰性的功能。也有人用咖啡举例子,一杯咖啡可能要加糖,加奶,加巧克力等等。一层包一层。如果取名字的是中国人可能就叫洋葱模式了。最后使用的时候行为和dish是一样的。因为这些Decorator是继承自dish的。只是在初始化过程中改变了原有的一些属性。
缺陷:继承不是一个优秀的解决方案
编程时常常提到的一个指导思想就是组合优于继承。
继承最大的问题就在于你只能有一个爹。一个爹的结果就是能力有限,不够灵活。所以最后还得认一些干爹。
就拿上面的例子来讲,现在是给dish做了几个装饰功能,如果有一天说店里的点心也要支持这两个功能(给我来一个加盐的馒头!),是不是有要继承点心类写两个装饰器呢?
利用Swift中的Extension
我们可以这么理解这个需求,需要有这么一个方法,接受一个dish类型的参数,经过处理后返回一个dish。我们完全可以把这个方法通过extension写在dish身上。
extension dish func salted -> dish return dish"加盐 func packaged}
然后我们就可以链式调用:
let exteneddish = dish(name: "松鼠桂鱼", price: 15).salted().packaged()
更进一步:protocol extension
如果为了将来的扩展灵活,也可以把这个装饰写到protocol的extension里。
protocol Product{ get set}
protocol Salteable: Product func salted -> Self
}
上面先定义了一个产品的协议,有名称和价格两个属性。
接着再定义了一个继承Product的Salteable的协议。里面有一个返回自身的salted方法。接着给这个protocol增加扩展实现:
extension Salteable func salted -> Self newProduct = self
newProduct = )"
= 1
newProduct
}
然后我们再定义一个表示小吃的Snack,和菜一样也有两个属性。
structSnack}
如果我们要给这个Snack增加加盐的效果,只要声明他实现Salteable协议就可以了。
extension : Salteable{
}
这样就够啦!
看下输出:
欢迎关注我的微博:@没故事的卓同学
关注「 iOS大全 」
看更多精选 iOS 技术文章
↓↓↓


d3.js学习笔记--Mike Bostock: Thinking with Joins
我们可以使用append方法, 来创建一个单一元素:
var svg = d3.select(''svg''),
d = {"x": 50, "y": 50};
svg.append("circle")
.attr("cx", d.x)
.attr("cy", d.y)
.attr("r", 25);如果想传递多条数据, 则需要这样编写:
var svg = d3.select(''svg''),
data = [{"x": 50, "y": 50}, {"x": 120, "y": 50}];
svg.selectAll("circle")
.data(data)
.enter()
.append("circle")
.attr("cx", function(d) { return d.x; })
.attr("cy", function(d) { return d.y; })
.attr("r", 25);这里代码主要的疑惑点在于:
svg.selectAll("circle")为什么我们要选择要新创建的DOM元素呢?
以下是处理方式. 我们不必告诉D3如何实现, 而是告诉D3我们所想要的. 我想要一个circle绑定到一个data上, 即每个circle和data数组中的元素一一对应. 这种概念叫做: data join
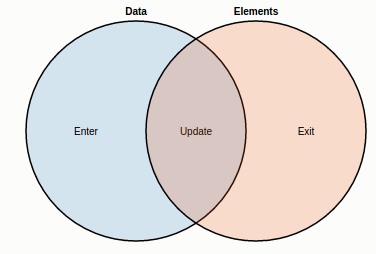
数据 join to 存在的DOM元素, 产生一个update操作. 坐标非update的数据产生enter的操作, 而右边的DOM元素由于没有绑定, 则处于Exit状态, 代表被删除.
现在我们来解释以下神奇的enter-append 的代码是如何data join:
1. 首先, svg.selectAll("circle")返回一个空的选择器, 它的父节点是svg.
2. 空的选择器绑定于数据data, 产生三个新的选择器分别代表Eneter, update 和 exit. 这三个选择器都是空的, 只有Enter为每个新的元素保留占位符.
3. selection.data返回update选择器, 当enter/exit均解绑于update的时候. selection.enter返回enter选择器.
4.

Effective Python (Pythonic Thinking)
Know the differences Between bytes,str and unicode
In Python 3, there are two types that represent sequences of characters: bytes and str. Instances of bytes contain raw 8-bit values. Instances of str contain Unicode characters.
# to_str
def to_str(bytes_or_str):
if isinstance(bytes_to_str, bytes):
value = bytes_or_str.decode(''utf-8'')
else:
value = bytes_or_str
return value # Instance of str
# to_bytes
def to_bytes(bytes_or_str):
if isinstance(bytes_to_str, str):
value = bytes_to_str.encode(''utf-8'')
else:
value = bytes_to_str
return value # Instance of bytesIn Python 2, there are two types that represent sequences of characters: str andunicode. In contrast to Python 3, instances of str contain raw 8-bit values. Instances ofunicode contain Unicode characters.
# to_unicode
def to_unicode(unicode_or_str):
if isinstance(unicode_or_str, str):
value = unicode_or_str.encode(''utf-8'')
else:
value = unicode_or_str
return value # Instance of unicode
# to_str
def to_str(unicode_or_str):
if isinstance(unicode_or_str, unicode):
value = unicode_or_str.decode(''utf-8'')
else:
value = unicode_or_str
return value # Instance of str如果你要读取/写入二进制数据至文件中,请使用”rb“或者”wb“:
import os
with open(''/tmp/random.bin'', ''wb'') as f:
f.write(os.urandom(10))Use List Comprehensions Instead of map and filter (用列表解析代替map和filter)
a = [1, 2, 3, 4]
squares = [x ** 2 for x in a]
squares = map(lambda x: x ** 2, a)
even_squares = [x ** 2 for x in a if x % 2 == 0]
alt = map(lambda x: x ** 2, filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, a))
# 对调字典的key与value
chile_ranks = {''ghost'': 1, ''habanero'': 2, ''cayenne'': 3}
rank_dict = {rank: name for name, rank in chile_ranks.items()}
chile_len_set = {len(name) for name in rank_dict.values()}Consider Generator Expressions for Large Comprehensions(用生成器表达式代替大的列表解析)
value = [len(x) for x in open(''/tmp/my_file.txt'')]
print(value)
it = (len(x) for x in open(''/tmp/my_file.txt''))
print(next(it))
# 生成器表达式可以由另外一个生成器表达式构成
roots = ((x, x**0.5) for x in it)
print(next(roots))Prefer enumerate Over range
# 当迭代一个列表,同时想知道当前元素的索引(计数)时;使用enumerate而不是range
flavor_list = [''vanilla'', ''chocolate'', ''pecan'', ''strawberry'']
# use range
for i in range(len(flavor_list)):
print(''%d: %s'' % (i, flavor_list[i]))
# use enumerate
for i, flavor in enumerate(flavor_list): # enumerate(flavor_list, 1)可为enumerate指定开始计数值
print(''%d: %s'' % (i, flavor))Use zip to Process Iterators in Parallel
# 使用zip并行处理迭代器
names = [''Cecilia'', ''Lise'', ''Marie'']
letters = [len(n) for n in names]
max_letters = 0
for name, count in zip(names, letters):
if count > max_letters:
longest_name = name
max_letters = count
# 注意:在Python3中zip是一个元组生成器;在Python2中zip是一个由元组组成的列表。Avoid else Blocks After for and while Loops
# 避免在for与while循环之后使用else
# 1,在没有break的for/while循环结束后,会马上执行else中的语句
# 2,避免在循环之后使用else,因为else不确定是否执行
for i in in range(5):
print i
else:
print ''else run''
for i in range(5):
break
else:
print ''else not run''Take Advantage of Each Block in try/except/else/finally
# 使用finally 去可靠的关机文件句柄、socket等
handle = open(''/tmp/random_data.txt'') # May raise IOError
try:
data = handle.read() # May raise UnicodeDecodeError
finally:
try:
handle.close() # Always runs after try
except Exception:
pass
# 使用else 减少try block里面的代码量、提高可读性
# 如:从字符串中加载一个json dict并返回某个key的value
def load_json_key(data, key):
try:
result_dict = json.loads(data) # May raise ValueError
except ValueError as e:
raise KeyError from e
else:
return result_dict[key] # May raise KeyError
#
UNDEFINED = object()
def divide_json(path):
handle = open(path, ''r+'') # May raise IOError
try:
data = handle.read() # May raise UnicodeDecodeError
op = json.loads(data) # May raise ValueError
value = (op[''numerator''] / op[''denominator'']) # May raise ZeroDivisonError
except ZeroDivisionError as e:
return UNDEFINED
else:
op[''result''] = value
result = json.dumps(op)
handle.seek(0)
handle.write(result) # May raise IOError
return value
finally:
try:
handle.close() # Always runs
except Exception:
pass
iOS Swift 应用程序随机 EXC_BAD_ACCESS 崩溃:swift_bridgeObjectRetain swift_retain swift::RefCounts
如何解决iOS Swift 应用程序随机 EXC_BAD_ACCESS 崩溃:swift_bridgeObjectRetain swift_retain swift::RefCounts<swift::RefCountBitsT<(swift::RefCountInlinedness)1>
我不断收到来自随机用户的随机崩溃报告。不幸的是,我无法定期重现这一点。用户说崩溃是在 discussionViewController 中随机发生的。所有崩溃报告都有类似的内容:
0 libswiftCore.dylib 0x00000001a53face4 swift::RefCounts<swift::RefCountBitsT<(swift::RefCountInlinedness)1> >::incrementSlow(swift::RefCountBitsT<(swift::RefCountInlinedness)1>,unsigned int) + 60 (atomic:1003)
1 libswiftCore.dylib 0x00000001a53c59e0 swift_retain + 124 (RefCount.h:813)
2 libswiftCore.dylib 0x00000001a5401d60 swift_bridgeObjectRetain + 56 (SwiftObject.mm:585)
3 APPNAME 0x0000000102b59734 closure #1 in discussionViewController.fetchPostData() + 7916
这是完整的崩溃日志和崩溃的线程:
Hardware Model: iphone11,6
Process: APPNAME [11770]
Path: /private/var/containers/Bundle/Application/.../APPNAME.app/APPNAME
Identifier: ----
Version: 62 (62)
AppStoretools: 12E262
AppVariant: 1:iphone11,6:13
Code Type: ARM-64 (Native)
Role: Foreground
Parent Process: launchd [1]
Coalition: ---- [1824]
Date/Time: 2021-06-17 12:07:01.4346 +1000
Launch Time: 2021-06-17 12:06:56.4993 +1000
OS Version: iPhone OS 14.6 (18F72)
Release Type: User
Baseband Version: 3.04.01
Report Version: 104
Exception Type: EXC_BAD_ACCESS (SIGSEGV)
Exception Subtype: KERN_INVALID_ADDRESS at 0x8000000000000010 -> 0x0000000000000010 (possible pointer authentication failure)
VM Region Info: 0x10 is not in any region. Bytes before following region: 4339515376
REGION TYPE START - END [ VSIZE] PRT/MAX SHRMOD REGION DETAIL
UNUSED SPACE AT START
--->
__TEXT 102a7c000-102a94000 [ 96K] r-x/r-x SM=COW ...APPNAME.app/APPNAME
Termination Signal: Segmentation fault: 11
Termination Reason: Namespace SIGNAL,Code 0xb
Terminating Process: exc handler [11770]
Triggered by Thread: 3
Thread 3 name:
Thread 3 Crashed:
0 libswiftCore.dylib 0x00000001a53face4 swift::RefCounts<swift::RefCountBitsT<(swift::RefCountInlinedness)1> >::incrementSlow(swift::RefCountBitsT<(swift::RefCountInlinedness)1>,unsigned int) + 60 (atomic:1003)
1 libswiftCore.dylib 0x00000001a53c59e0 swift_retain + 124 (RefCount.h:813)
2 libswiftCore.dylib 0x00000001a5401d60 swift_bridgeObjectRetain + 56 (SwiftObject.mm:585)
3 APPNAME 0x0000000102b59734 closure #1 in discussionViewController.fetchPostData() + 7916
4 APPNAME 0x0000000102ad09d4 thunk for @escaping @callee_guaranteed (@guaranteed Data?,@guaranteed NSURLResponse?,@guaranteed Error?) -> () + 132 (<compiler-generated>:0)
5 CFNetwork 0x00000001a1b0a3dc __40-[__NSURLSessionLocal taskForClassInfo:]_block_invoke + 540 (LocalSession.mm:687)
6 CFNetwork 0x00000001a1b1c768 __49-[__NSCFLocalSessionTask _task_onqueue_didFinish]_block_invoke + 244 (LocalSessionTask.mm:584)
7 libdispatch.dylib 0x00000001a10d1a84 _dispatch_call_block_and_release + 32 (init.c:1466)
8 libdispatch.dylib 0x00000001a10d381c _dispatch_client_callout + 20 (object.m:559)
9 libdispatch.dylib 0x00000001a10db004 _dispatch_lane_serial_drain + 620 (inline_internal.h:2557)
10 libdispatch.dylib 0x00000001a10dbc34 _dispatch_lane_invoke + 456 (queue.c:3862)
11 libdispatch.dylib 0x00000001a10e64bc _dispatch_workloop_worker_thread + 764 (queue.c:6589)
12 libsystem_pthread.dylib 0x00000001ed04a7a4 0x1ed047000 + 14244
13 libsystem_pthread.dylib 0x00000001ed05174c 0x1ed047000 + 42828
我已验证 discussionViewController.fetchPostData() 不会强制解开任何可选选项,没有 try! 并且在任何地方都使用 [weak self] 和 self?。该函数非常大,所以我很难缩小崩溃发生的范围。

java 线程 原子类相关操作示例 thinking in java4 目录21.3.4
java 线程 原子类相关操作示例
package org.rui.thread.volatiles;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
/**
* 原子类,
* java SE5引入了诸如AtomicInteger AtomicLong AtomicReference
* 等特殊的原子性变量类,它们提供下面形式的原子性条件更新操作:
*
* boolean compareAndSet(expectedValue,updateValue);
*
* 这些类被调整为可以使用在某些现代处理器上的可获得的,并且是在机器级别上的原子性,
* 因此在使用它们时,通常不需要担心。对于常规编程来说,它们很少会派上用场,但是在涉级性能调优时,
* 它们就大有用武之地了,例如,我们可以使用AtomicInteger来重写AtomictyTest.java
* @author lenovo
*
*/
public class AtomicIntegerTest implements Runnable {
/**
* 这里我们通过使用AtomicInteger而消除了synchronized关键字。
* 因为这个程序不会失败,所以添加了一个timer,以便在5秒钟之后自动地终止
*/
private AtomicInteger i=new AtomicInteger(0);
public int getValue(){return i.get();}
private void evenIncrement(){i.addAndGet(2);}
@Override
public void run()
{
while(true)
{
evenIncrement();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//订时器
new Timer().schedule(new TimerTask()
{
@Override
public void run()
{
System.err.println("Aborting");
System.exit(0);
}
}, 5000);
//线程池
ExecutorService exec=Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
AtomicIntegerTest at=new AtomicIntegerTest();
exec.execute(at);
while(true)
{
int val=at.getValue();
if(val%2!=0)
{
System.out.println(val);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
}
/**
* output:
* Aborting
*/package org.rui.thread.volatiles;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import org.rui.thread.res.EvenChecker;
import org.rui.thread.res.IntGenerator;
/**
* 下面是用AtomicInteger重写MutexEvenGenerator.java:
* 所有其他形式的同步再次通过使用AtomicInteger得到了根除
*
*
*
* 应该强调的是,atomic类被设计用来构建java.util.concureent中的类,
* 因此只有在特殊情况下才在自己的代码中使用它们,即便使用了也需要确保不存在其他可能出现的问题。
* 通常依赖于锁要更安全一些(要么是synchronized关键字,要么是显式的lock对象)
* @author lenovo
*
*/
public class AtomicEvenGenerator extends IntGenerator{
private AtomicInteger currentEvenValue=new AtomicInteger(0);
@Override
public int next() {
return currentEvenValue.addAndGet(2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EvenChecker.test(new AtomicEvenGenerator());
}
}关于thinking in Swift:重新审视装饰器模式和重试装饰器的介绍现已完结,谢谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于d3.js学习笔记--Mike Bostock: Thinking with Joins、Effective Python (Pythonic Thinking)、iOS Swift 应用程序随机 EXC_BAD_ACCESS 崩溃:swift_bridgeObjectRetain swift_retain swift::RefCounts
本文标签:





