本文将为您提供关于Oracle等同于PostgreSQLINSERT-ETURNING*;的详细介绍,同时,我们还将为您提供关于function–PostgreSQL–RETURNINGINTO数组、
本文将为您提供关于Oracle等同于PostgreSQL INSERT-ETURNING *;的详细介绍,同时,我们还将为您提供关于function – PostgreSQL – RETURNING INTO数组、JAVA 中使用 PostgreSQL 的 RETURNING 语句来实现插入时快速获取 insert id、Migrating legacy PostgreSQL databases to Amazon RDS or Aurora PostgreSQL using Bucardo、MySQL等同于PostgreSQL的EXPLAIN ANALYZE的实用信息。
本文目录一览:- Oracle等同于PostgreSQL INSERT-ETURNING *;
- function – PostgreSQL – RETURNING INTO数组
- JAVA 中使用 PostgreSQL 的 RETURNING 语句来实现插入时快速获取 insert id
- Migrating legacy PostgreSQL databases to Amazon RDS or Aurora PostgreSQL using Bucardo
- MySQL等同于PostgreSQL的EXPLAIN ANALYZE

Oracle等同于PostgreSQL INSERT-ETURNING *;
我已经将一堆DML(INSERT / UPDATE /
DELETE)查询从Oracle转换为PostgreSQL,现在我需要检查它们是否产生相同的行集,即,假设oracle和postgresql数据库包含相同的行,则delete删除相同的行最初使用相同的数据,更新则更新相同的行,等等。在PostgreSQL方面,我可以将returning子句与DML语句一起使用,即
INSERT INTO test(id, name) VALUES(42, ''foo'') RETURNING *;上面的语句的优点在于,我可以在任何DML语句前添加“返回*”,而无需知道其执行的表的结构甚至表的名称,并且可以像选择语句一样获取所有行。
但是,在Oracle方面似乎并不那么光彩夺目。根据文档,Oracle
8i(我正在使用的那个)支持RETURNING子句,但是它必须将结果存储到变量中,并且似乎没有明显的方法来获取所有结果列,而不是手动指定列名。
因此,问题是是否存在一个oracle语句(或语句序列)来模拟PostgreSQL的“ returning
*”而无需对表或列名进行硬编码。换句话说,有没有办法编写这样的Oracle函数:
fn(''INSERT INTO test(id, name) VALUES(42, ''''foo'''')'')它应返回由SQL语句插入(或在一般情况下进行修改)的行集。
答案1
小编典典目前尚不可能,特别是在旧版本的Oracle(例如8i)中。看到类似问题的答案。

function – PostgreSQL – RETURNING INTO数组
在这个例子中,我给出了一个“parent_ids”列表,我想找到父节点在该数组中的所有子节点.然后,我希望更新它们的一些价值,并做其他的事情.
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION plpgsql_is_really_great(parent_ids bigint[])
RETURNS void AS
$$
DECLARE
found_ids bigint[];
BEGIN
UPDATE child SET
foo = bar
FROM
(SELECT id
FROM child
WHERE parent_id=ANY(parent_ids)
) as children_ids
WHERE
child.id = children_ids.id
RETURNING children_ids.id INTO found_ids; -- ???
-- do more stuff with found_ids
$$LANGUAGE plpgsql
解决方法
在PL / pgsql中:
$$
DECLARE found_id BIGINT;
BEGIN
FOR found_id IN (UPDATE child SET foo=bar RETURNING id) LOOP
PERFORM f(found_id);
END LOOP;
END
$$
在纯sql中:
WITH updated(found_id) AS ( UPDATE child SET foo=bar RETURNING id ) SELECT f(found_id) FROM updated;
如果要收集数组中的所有found_ids,可以简单地:
$$
DECLARE array_var BIGINT[];
BEGIN
WITH updated(found_id) AS (
UPDATE child SET foo=bar RETURNING id
)
SELECT array_agg(found_id) FROM updated INTO array_var;
END
$$

JAVA 中使用 PostgreSQL 的 RETURNING 语句来实现插入时快速获取 insert id
很多时候,当插入一条记录后,希望马上获得插入的主键 id,
不少获得这个 id 的方法是 select max (id) from tablename;
为了获得这个 id 需要多执行一次 sql 语句。
PostgreSQL 提供了 RETURNING 语句在插入后立刻获得这个 id,具体方法如下:
INSERT INTO test(name) values(''name'') RETURNING id;
String sql = "INSERT INTO test(name) VALUES (?)";
PreparedStatement pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
pstmt.setString(1, "name");
pstmt.executeUpdate();
ResultSet generatedKeys = pstmt.getGeneratedKeys();
if (generatedKeys.next()) {
long id = generatedKeys.getLong(1);
//logger.info("insert id :" + id);
}
select max(id)方式:72秒
RETURNING 方式:47秒
RETURNING方式的性能是select max(id)方式的1.5倍
conn.prepareStatement(sql,Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
Migrating legacy PostgreSQL databases to Amazon RDS or Aurora PostgreSQL using Bucardo
https://amazonaws-china.com/blogs/database/migrating-legacy-postgresql-databases-to-amazon-rds-or-aurora-postgresql-using-bucardo/
If you are using PostgreSQL earlier than 9.4, you are using an unsupported version of PostgreSQL, and may have limited options to migrate or replicate your databases in Amazon RDS or Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL. This is primarily because PostgreSQL versions older than 9.4 can’t perform logical replication.
Bucardo is an open-source utility that can replicate data changes asynchronously to multiple secondary or multiple masters. It is a trigger-based replication and proven to be consistent and stable for more extensive migrations and ongoing replications. Bucardo can perform full load for tables without a primary key. However, to replicate delta data changes from Primary, create a primary key before you start the setup.
This post demonstrates how to set up Bucardo and replicate data changes from PostgreSQL 8.4 to PostgreSQL 9.6.
Prerequisites
Before getting started, you must have the following:
- One EC2 instance with Ubuntu 16.04 for Bucardo (Bucardo Server: 172.31.88.4)
- One EC2 instance with RHEL 6 with PostgreSQL 8.4.2 (PostgreSQL 8.4.2: 172.31.16.177)
- One RDS PostgreSQL 9.6 in us-east-1 (RDS 9.6)
This post uses PostgreSQL 8.4.2 on Amazon EC2; however, the PostgreSQL database might be running on-premises.
This solution installs Bucardo 5.4.1 on Ubuntu 16.04, which means that the repository for Bucardo is on the same host running on a PostgreSQL 9.6 instance. The following diagram shows the architecture of the data replication flow.
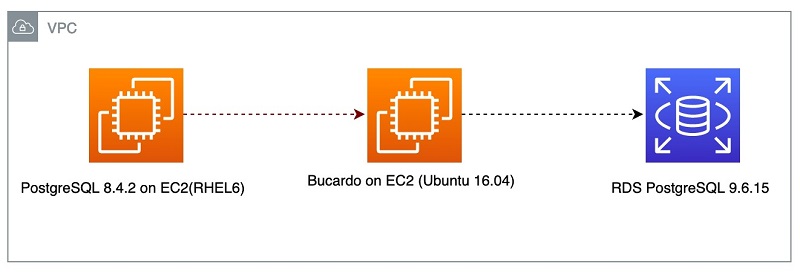
Fig: Replication Architecture to migrate PostgreSQL 8.4 to RDS PostgreSQL 9.6 using Bucardo.
Installing Bucardo binaries
There are several packages that you must install before installing Bucardo. See the following code:
#apt-get install postgresql-plperl-9.6 libdbd-pg-perl libboolean-perl build-essential libdbd-mock-perl libdbd-pg-perl libanyevent-dbd-pg-perl libpg-hstore-perl libpgobject-perlConnect to CPAN and install DBI,DBD::Pg,DBIx::Safe. See the following code:
cpan > install DBI
cpan > install DBD::Pg
cpan > install DBIx::SafeDownload the Bucardo binaries into your local directory and untar. See the following code:
$wget http://bucardo.org/downloads/Bucardo-5.4.1.tar.gz
tar xvfz Bucardo-5.4.1.tar.gz
$perl Makefile.PL
$sudo make install
Creating superusers and the repository database
You must create a Bucardo superuser and repository database to control and track the replications between environments. Connect to DB-APP1 using the PSQL client or pgadmin4 and create the superuser and repository on DR-App1. See the following code:
postgres=# create user bucardo superuser;
CREATE ROLE
postgres=# create database bucardo;
CREATE DATABASE
postgres=# \du
List of roles
Role name | Attributes | Member of
-----------+------------------------------------------------------------+-----------
bucardo | Superuser | {}
postgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS | {}
replica | Replication | {}
postgres=# alter database bucardo owner to bucardo;
ALTER DATABASE
postgres=# \list
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+----------+----------+-------------+-------------+-----------------------
bucardo | bucardo | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 |
postgres | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 |
template0 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
template1 | postgres | UTF8 | en_US.UTF-8 | en_US.UTF-8 | =c/postgres +
| | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres
(4 rows)After you create the superuser and repository database, exit from PSQL and run “bucardo install” from the terminal where Bucardo software is staged. This creates a set of tables in the Bucardo database (the database owner should be a Bucardo superuser).
Installing the Bucardo repository
To install the Bucardo repository, enter the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~/Bucardo-5.4.1$ sudo bucardo install
This installs the Bucardo database into an existing PostgreSQL cluster. You must have compiled PostgreSQL with Perl support, and connect as a superuser. See the following code:
Current connection settings:
1. Host: <none>
2. Port: 5432
3. User: postgres
4. Database: bucardo
5. PID directory: /var/run/bucardo
Enter a number to change it, P to proceed, or Q to quit: p
Postgres version is: 9.6
Attempting to create and populate the bucardo database and schema
Database creation is complete
Updated configuration setting "piddir"
Installation is now complete. If you see errors or need help, you can contact Bucardo support for assistance at bucardo-general@bucardo.org.
You may want to check over the configuration variables next. See the following code:
bucardo show all
Change any setting by using: bucardo set foo=bar
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~/Bucardo-5.4.1$ Whitelisting Bucardo and the PostgreSQL database server to connect with each other
Use pgpass to set up passwordless authentication to connect the source and target databases securely. On the Bucardo server, enter the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ touch ~/.pgpass
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ chmod 0600 ~/.pgpass
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ cat ~/.pgpass
#server:port:database:username:password
127.0.0.1:5432:postgres:postgres:XXXXXX
172.31.88.4:5432:bucardo:postgres:XXXXXX
172.31.16.177:5432:repdb:postgres:XXXXXX
pgrds.cxad2e11vriv.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com:5432:repdb:postgres:XXXXXXVerify that the Bucardo server can connect the source and target databases without a password with the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ psql -h 172.31.16.177 -d repdb -U postgres -w -c "select count(*) from pgbench_branches"
count
-------
1
(1 row)
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ psql --host ''pgrds.cxad2e11vriv.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com'' --port 5432 --username ''postgres'' ''repdb'' -w -c "select count(*) from pgbench_branches"
count
-------
1
(1 row)Resolving a permission denied error
Because RDS is a managed service, AWS doesn’t provide superuser privileges for security reasons. To perform a trigger-based replication, you must enable the parameter session_replication_role.
You can use the security definer function rds_session_replication_role, which helps you to set the parameter to replica when an event occurs. To be consistent across all environments, this post creates the security definer function in EC2 PostgreSQL (8.4.2) and RDS.
Create language plpgsql; with the following code:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.rds_session_replication_role(role text)
RETURNS text
LANGUAGE plpgsql
SECURITY DEFINER
AS $function$
DECLARE
curr_val text := ''unset'';
BEGIN
EXECUTE ''SET session_replication_role = '' || quote_literal(role);
EXECUTE ''SHOW session_replication_role'' INTO curr_val;
RETURN curr_val;
END
$function$;
postgres=> revoke all on function rds_session_replication_role(text) from public;
REVOKE
postgres=> grant execute on function rds_session_replication_role(text) to rds_superuser;
GRANT
postgres=> grant rds_superuser to postgres;
GRANTAlso, make changes to the bucardo.pm file at lines 5397 and 5330 with the following code:
$dbh->do(q{select rds_session_replication_role(''replica'');}); ## Assumes a sane default !
From.
$dbh->do(q{SET session_replication_role = default}); ## Assumes a sane default !Alternatively, you can download the updated bucardo.pm file and move the file to the server where Bucardo is running under the location /usr/local/share/perl/5.22.1/Bucardo.pm. If you are running in production, please test it before using it.
Generating a sample source database and initiating target full load
On the source database, generate some test data using pgbench. This post generates four tables, three with the primary key enabled and one without the primary key enabled. See the following code:
postgres=# create database repdb;
CREATE DATABASE
The following code is the generated sample data in repdb:
[postgres@ip-172-31-16-177 ~]$ pgbench -i repdb
NOTICE: table "pgbench_branches" does not exist, skipping
NOTICE: table "pgbench_tellers" does not exist, skipping
NOTICE: table "pgbench_accounts" does not exist, skipping
NOTICE: table "pgbench_history" does not exist, skipping
creating tables...
10000 tuples done.
20000 tuples done.
30000 tuples done.
40000 tuples done.
50000 tuples done.
60000 tuples done.
70000 tuples done.
80000 tuples done.
90000 tuples done.
100000 tuples done.
set primary key...
NOTICE: ALTER TABLE / ADD PRIMARY KEY will create implicit index "pgbench_branches_pkey" for table "pgbench_branches"
NOTICE: ALTER TABLE / ADD PRIMARY KEY will create implicit index "pgbench_tellers_pkey" for table "pgbench_tellers"
NOTICE: ALTER TABLE / ADD PRIMARY KEY will create implicit index "pgbench_accounts_pkey" for table "pgbench_accounts"
vacuum...done.Verify the data count and table structures. See the following code:
repdb=# select count(*) from pgbench_accounts;
100000
repdb=# select count(*) from pgbench_branches;
1
repdb=# select count(*) from pgbench_history;
0
repdb=# select count(*) from pgbench_tellers;
10Migrating repdb from the source database using pg_dump and pg_restore
Back up the source database using pg_dump. See the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ pg_dump -Fc -v -h ec2-34-229-97-46.compute-1.amazonaws.com -U postgres repdb -w > repdb_bkp1.dump
pg_dump: last built-in OID is 16383
pg_dump: reading extensions
pg_dump: identifying extension members
……
Log in to RDS PostgreSQL and create the database repdb. See the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ psql --host ''pgrds.cxad2e11vriv.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com'' --port 5432 --username ''postgres'' ''postgres''
Password for user postgres:
psql (9.6.15)
SSL connection (protocol: TLSv1.2, cipher: ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384, bits: 256, compression: off)
Type "help" for help.
postgres=> create database repdb;
CREATE DATABASERestore the dump file generated in the newly created repdb in RDS PostgreSQL using pg_restore. See the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ pg_restore -v -h pgrds.cxad2e11vriv.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com -U postgres -d repdb repdb_bkp1.dump
pg_restore: connecting to database for restore
Password:
pg_restore: creating SCHEMA "public"
pg_restore: creating COMMENT "SCHEMA public"
pg_restore: creating PROCEDURAL LANGUAGE "plpgsql"For more information, see Importing Data into PostgreSQL on Amazon RDS.
Configuring Bucardo to replicate tables with a primary key
A typical Bucardo setup consists of steps to add the source and target databases, add tables with a primary key to the group, and create and enable the sync to start replicating the changes from source.
To add the source database, enter the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ bucardo add db pgdb84 dbhost=ec2-34-229-97-46.compute-1.amazonaws.com dbport=5432 dbname=repdb dbuser=postgres
Added database "pgdb84"
To add the target RDS database, enter the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ bucardo add db rds96 dbhost=pgrds.cxad2e11vriv.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com dbport=5432 dbname=repdb dbuser=postgres dbpass=postgres123
Added database "rds96"
To add tables to the herd, enter the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ bucardo add table pgbench_accounts pgbench_branches pgbench_tellers herd=herd_pg84 db=pgdb84
Created the relgroup named "herd_pg84"
The following tables or sequences are now part of the relgroup "herd_pg84":
public.pgbench_accounts
public.pgbench_branches
public.pgbench_tellersTo add the database group, enter the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ bucardo add dbgroup pgdb84_to_rds96 pgdb84:source rds96:target
Created dbgroup "pgdb84_to_rds96"
Added database "pgdb84" to dbgroup "pgdb84_to_rds96" as source
Added database "rds96" to dbgroup "pgdb84_to_rds96" as target
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ bucardo add sync sync_pg84_rds96 relgroup=herd_pg84 db=pgdb84,rds96
Added sync "sync_pg84_rds96"
Using existing dbgroup "dbgrp84_96"You can have multiple databases in a particular database group.
Check the Bucardo sync status before you start to make sure that you see the parameters created. See the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ sudo bucardo status sync_pg84_rds96
[sudo] password for postgres:
======================================================================
Sync name : sync_pg84_rds96
Current state : No records found
Source relgroup/database : herd_pg84 / pgdb84
Tables in sync : 3
Status : Active
Check time : None
Overdue time : 00:00:00
Expired time : 00:00:00
Stayalive/Kidsalive : Yes / Yes
Rebuild index : No
Autokick : Yes
Onetimecopy : No
Post-copy analyze : Yes
Last error: :
======================================================================Start Bucardo and verify its status. See the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ sudo bucardo start
Checking for existing processes
Removing file "/var/run/bucardo/fullstopbucardo"
Starting Bucardo
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ sudo bucardo status sync_pg84_rds96
======================================================================
Last good : Dec 05, 2019 08:30:03 (time to run: 1s)
Rows deleted/inserted : 0 / 0
Sync name : sync_pg84_rds96
Current state : Good
Source relgroup/database : herd_pg84 / pgdb84
Tables in sync : 3
Status : Active
Check time : None
Overdue time : 00:00:00
Expired time : 00:00:00
Stayalive/Kidsalive : Yes / Yes
Rebuild index : No
Autokick : Yes
Onetimecopy : No
Post-copy analyze : Yes
Last error: :
======================================================================The Current State is Good and no inserts, updates, and deletes are happening currently in the source database.
To test the replication, generate a test load in the source database using pgbench and monitor changes on the target. See the following code:
[postgres@ip-172-31-16-177 ~]$ pgbench -t 10000 repdb
starting vacuum...end.
transaction type: TPC-B (sort of)
scaling factor: 1
query mode: simple
number of clients: 1
number of transactions per client: 10000
number of transactions actually processed: 10000/10000
tps = 503.183795 (including connections establishing)
tps = 503.244214 (excluding connections establishing)After you run pgbench, it generates some transactions, but Bucardo can’t move to the target due to a permission issue. Therefore, the status of Current State is Bad. See the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ sudo bucardo status sync_pg84_rds96
======================================================================
Last bad : Dec 05, 2019 08:32:54 (time until fail: 1s)
Sync name : sync_pg84_rds96
Current state : Bad
Source relgroup/database : herd_pg84 / pgdb84
Tables in sync : 3
Status : Active
Check time : None
Overdue time : 00:00:00
Expired time : 00:00:00
Stayalive/Kidsalive : Yes / Yes
Rebuild index : No
Autokick : Yes
Onetimecopy : No
Post-copy analyze : Yes
Last error: : Failed : DBD::Pg::db do failed: ERROR: function rds_session_replication_role(unknown) does not exist LINE 1: select rds_session_replication_role(''replica''); ^ HINT: No function matches the given name and argument types. You might need to add explicit type casts. at /usr/local/share/perl/5.22.1/Bucardo.pm line 5328. Line: 5041 Main DB state: ? Error: none DB pgdb84 state: ? Error: none DB rds96 state: 42883 Error: 7 (KID 14864)
======================================================================If you encounter this error, follow the steps to resolve a permission denied error. In this example, security definer functions were not created in source and target databases and caused the preceding error. After implementing the security definer, restart Bucardo. See the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ sudo bucardo restart
Creating /var/run/bucardo/fullstopbucardo ... Done
Checking for existing processes
Removing file "/var/run/bucardo/fullstopbucardo"
Starting Bucardo
The Current State is now Good, and 294 deletes and inserts happened in the database. This confirms that your Bucardo is healthy. You can ignore the entry for Last error. See the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ sudo bucardo status sync_pg84_rds96
======================================================================
Last good : Dec 05, 2019 08:51:21 (time to run: 1s)
Rows deleted/inserted : 294 / 294
Last bad : Dec 05, 2019 08:35:06 (time until fail: 1s)
Sync name : sync_pg84_rds96
Current state : Good
Source relgroup/database : herd_pg84 / pgdb84
Tables in sync : 3
Status : Active
Check time : None
Overdue time : 00:00:00
Expired time : 00:00:00
Stayalive/Kidsalive : Yes / Yes
Rebuild index : No
Autokick : Yes
Onetimecopy : No
Post-copy analyze : Yes
Last error: : Failed : DBD::Pg::db do failed: ERROR: function rds_session_replication_role(unknown) does not exist LINE 1: select rds_session_replication_role(''replica''); ^ HINT: No function matches the given name and argument types. You might need to add explicit type casts. at /usr/local/share/perl/5.22.1/Bucardo.pm line 5328. Line: 5041 Main DB state: ? Error: none DB pgdb84 state: ? Error: none DB rds96 state: 42883 Error: 7 (KID 15006)
======================================================================To debug the replication, Bucardo logs are located in the /var/log directory. See the following code:
postgres@ip-172-31-88-4:~$ tail -f /var/log/bucardo/log.bucardo
(15337) [Thu Dec 5 08:51:25 2019] KID (sync_pg84_rds96) Delta count for pgdb84.public.pgbench_tellers : 10
(15337) [Thu Dec 5 08:51:25 2019] KID (sync_pg84_rds96) Totals: deletes=297 inserts=297 conflicts=0
(15337) [Thu Dec 5 08:51:25 2019] KID (sync_pg84_rds96) Delta count for pgdb84.public.pgbench_accounts : 109
(15337) [Thu Dec 5 08:51:25 2019] KID (sync_pg84_rds96) Delta count for pgdb84.public.pgbench_branches : 1
(15337) [Thu Dec 5 08:51:25 2019] KID (sync_pg84_rds96) Delta count for pgdb84.public.pgbench_tellers : 10
(15337) [Thu Dec 5 08:51:25 2019] KID (sync_pg84_rds96) Totals: deletes=120 inserts=120 conflicts=0
(15337) [Thu Dec 5 08:51:26 2019] KID (sync_pg84_rds96) Delta count for pgdb84.public.pgbench_accounts : 239
(15337) [Thu Dec 5 08:51:26 2019] KID (sync_pg84_rds96) Delta count for pgdb84.public.pgbench_branches : 1
(15337) [Thu Dec 5 08:51:26 2019] KID (sync_pg84_rds96) Delta count for pgdb84.public.pgbench_tellers : 10
(15337) [Thu Dec 5 08:51:26 2019] KID (sync_pg84_rds96) Totals: deletes=250 inserts=250 conflicts=0
Conclusion
This post demonstrated the complete solution to overcome the challenge of migrating legacy PostgreSQL databases older than 9.4 to Amazon RDS PostgreSQL or Aurora PostgreSQL by using the asynchronous trigger-based replication utility Bucardo.
If you have comments or questions about this solution, please submit them in the comments section.
About the Authors

Rajeshkumar Sabankar is a Database Specialty Architect with Amazon Web Services. He works with internal Amazon customers to build secure, scalable, and resilient architectures in AWS Cloud and help customers perform migrations from on-premise databases to Amazon RDS and Aurora Databases.

Samujjwal Roy is a Database Specialty Architect with the Professional Services team at Amazon Web Services. He has been with Amazon for 15+ years and has led migration projects for internal and external Amazon customers to move their on-premises database environment to AWS Cloud database solutions.

MySQL等同于PostgreSQL的EXPLAIN ANALYZE
我想在MySQL中获得类似于PostgreSQL中EXPLAIN ANALYZE所示的详细查询计划。有等同的吗?
关于Oracle等同于PostgreSQL INSERT-ETURNING *;的问题我们已经讲解完毕,感谢您的阅读,如果还想了解更多关于function – PostgreSQL – RETURNING INTO数组、JAVA 中使用 PostgreSQL 的 RETURNING 语句来实现插入时快速获取 insert id、Migrating legacy PostgreSQL databases to Amazon RDS or Aurora PostgreSQL using Bucardo、MySQL等同于PostgreSQL的EXPLAIN ANALYZE等相关内容,可以在本站寻找。
本文标签:





