如果您想了解使用BigIntegerMultiply运算符的相关知识,那么本文是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将对biginteger赋值进行全面详尽的解释,并且为您提供关于(OK)Graphviz-MAN
如果您想了解使用BigInteger Multiply运算符的相关知识,那么本文是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将对biginteger赋值进行全面详尽的解释,并且为您提供关于(OK) Graphviz - MANET - multiple interfaces multiple paths、(OK) MPTCP & quagga - multi-interface, multi-routing, multi-hop (fullpath) in MANETs、(OK) quagga - multi-interface, multi-routing, multi-hop (partpath) in MANETs、17_java之Integer|System|Arrays|Math|BigInteger|BigDecimal的有价值的信息。
本文目录一览:- 使用BigInteger Multiply运算符(biginteger赋值)
- (OK) Graphviz - MANET - multiple interfaces multiple paths
- (OK) MPTCP & quagga - multi-interface, multi-routing, multi-hop (fullpath) in MANETs
- (OK) quagga - multi-interface, multi-routing, multi-hop (partpath) in MANETs
- 17_java之Integer|System|Arrays|Math|BigInteger|BigDecimal

使用BigInteger Multiply运算符(biginteger赋值)
我想知道是否存在一种将BigInteger变量相乘的方法,因为*运算符无法应用于BigInteger。
所以我想知道是否可以在BigIntegers不使用*运算符的情况下将两个相乘。
答案1
小编典典您可以这样使用BigIntegersmultiply()方法:
BigInteger int1 = new BigInteger("131224324234234234234313");BigInteger int2 = new BigInteger("13345663456346435648234313");BigInteger result = int1.multiply(int2)我早就应该指出这BigInteger是一成不变的。因此,任何运算结果都必须存储到变量中。运算符或操作数永远不会更改。

(OK) Graphviz - MANET - multiple interfaces multiple paths
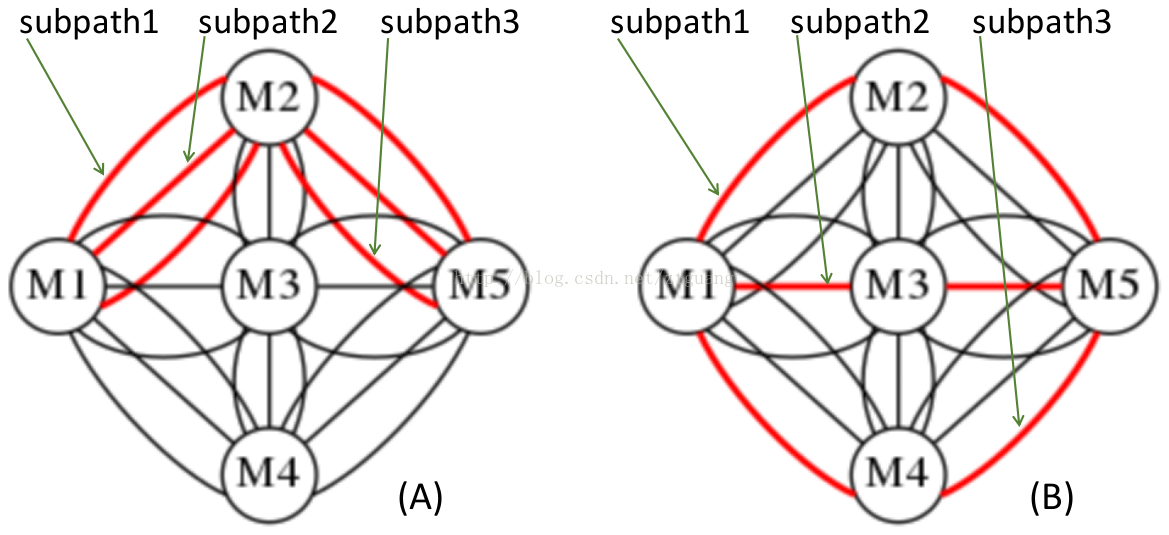
/*
dot example3.dot -Tpng -o example3.png
*/
digraph G {
size="10,10";
rankdir=LR // set graph direction rankdir="TB", "LR", "BT", "RL"
//ranksep="1.0 equally"
//splines=line
nodesep=0.4;
//node [label=""];
subgraph cluster_1 {
color=white;
node [style=solid, color=black, shape=circle, width=.4 height=.4, fixedsize=true];
M1;
//label = "layer 1";
}
subgraph cluster_2 {
color=white;
node [style=solid, color=black, shape=circle, width=.4 height=.4, fixedsize=true];
M2;
//label = "layer 2";
}
subgraph cluster_3 {
color=white;
node [style=solid, color=black, shape=circle, width=.4 height=.4, fixedsize=true];
M3;
//label = "layer 2";
}
subgraph cluster_4 {
color=white;
node [style=solid, color=black, shape=circle, width=.4 height=.4, fixedsize=true];
M4;
//label = "layer 2";
}
subgraph cluster_5 {
color=white;
node [style=solid, color=black, shape=circle, width=.4 height=.4, fixedsize=true];
M5;
//label = "layer 3";
}
//At present, the recognized style names are "dashed", "dotted", "solid", "invis" and "bold" for nodes and edges, "tapered" for edges only, and "filled", "striped", "wedged", "diagonals" and "rounded" for nodes only. The styles "filled", "striped" and "rounded" are recognized for clusters. The style "radial" is recognized for nodes, clusters and graphs, and indicates a radial-style gradient fill if applicable.
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// original MPTCP
/*
M1 -> M2 [style=bold, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, color=red]
M1 -> M2 [style=bold, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, color=red]
M1 -> M2 [style=bold, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, color=red]
M1 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M1 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M1 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M1 -> M4 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M1 -> M4 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M1 -> M4 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M2 -> M5 [style=bold, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, color=red]
M2 -> M5 [style=bold, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, color=red]
M2 -> M5 [style=bold, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, color=red]
M3 -> M5 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M3 -> M5 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M3 -> M5 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M4 -> M5 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M4 -> M5 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M4 -> M5 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M2 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, constraint=false]
M2 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, constraint=false]
M2 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, constraint=false]
M4 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, constraint=false]
M4 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, constraint=false]
M4 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, constraint=false]
//*/
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// original MPTCP
//*
M1 -> M2 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M1 -> M2 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M1 -> M2 [style=bold, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, color=red]
M1 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M1 -> M3 [style=bold, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, color=red]
M1 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M1 -> M4 [style=bold, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, color=red]
M1 -> M4 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M1 -> M4 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M2 -> M5 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M2 -> M5 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M2 -> M5 [style=bold, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, color=red]
M3 -> M5 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M3 -> M5 [style=bold, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, color=red]
M3 -> M5 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M4 -> M5 [style=bold, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, color=red]
M4 -> M5 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M4 -> M5 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none]
M2 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, constraint=false]
M2 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, constraint=false]
M2 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, constraint=false]
M4 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, constraint=false]
M4 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, constraint=false]
M4 -> M3 [style=solid, dir="both", arrowhead=none, arrowtail=none, constraint=false]
//*/
//-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
}
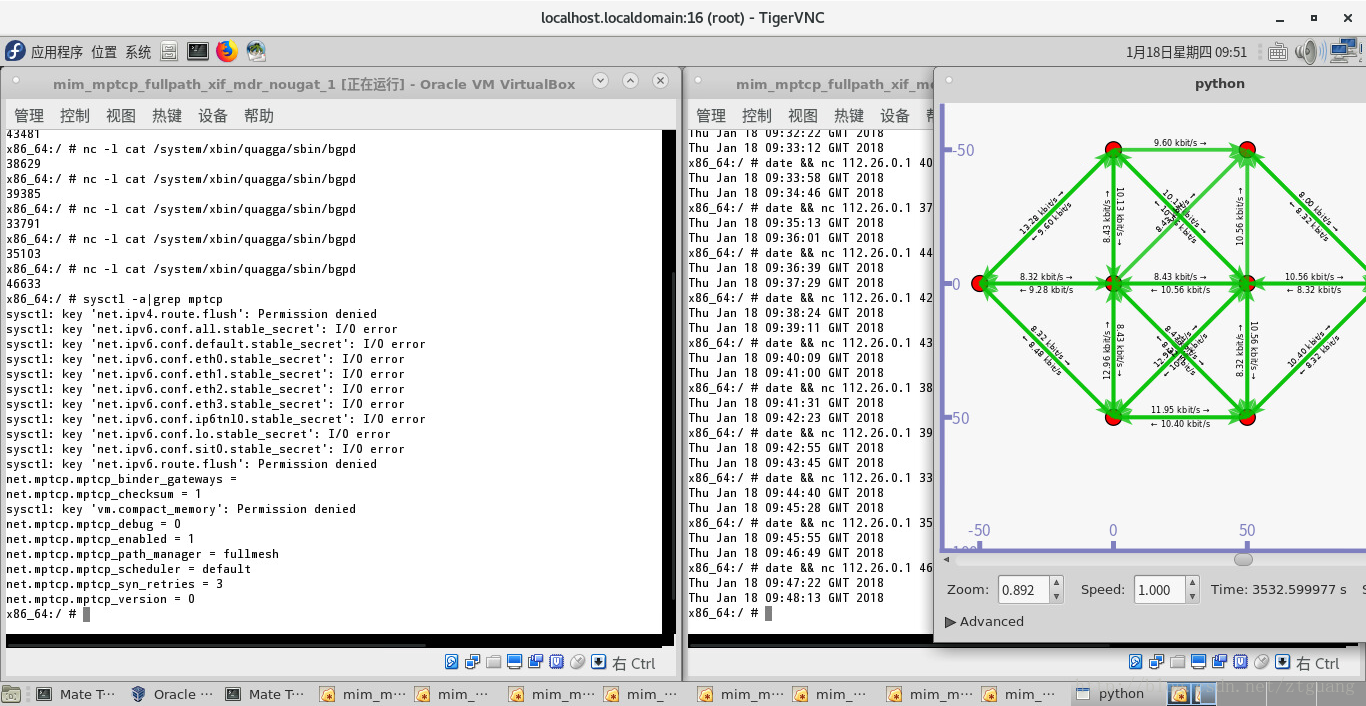
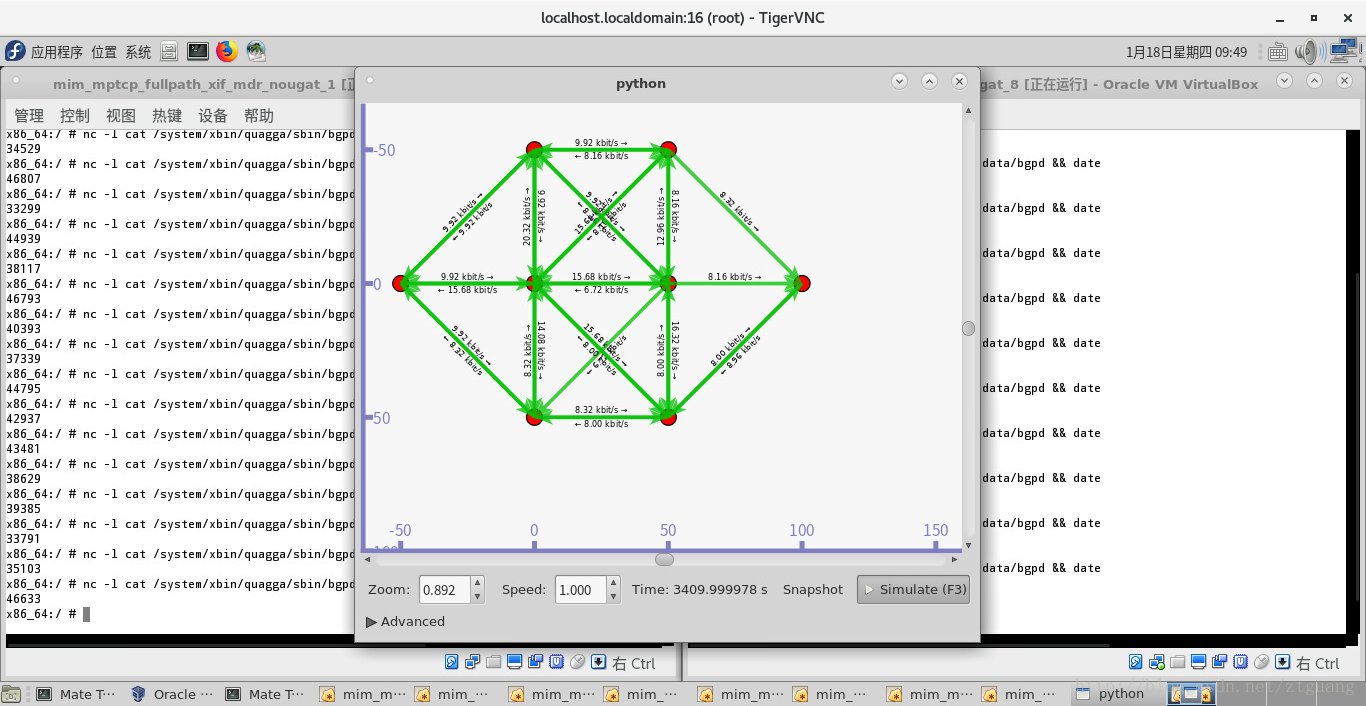
(OK) MPTCP & quagga - multi-interface, multi-routing, multi-hop (fullpath) in MANETs
第一张图为测试视频截图,视频文件下载地址:
https://github.com/ztguang/MiM/blob/master/MiM-screenrecord/mim-mptcp-fullpath-xif-mdr---mptcp-tcpdump-on-xif---screenrecord.mp4
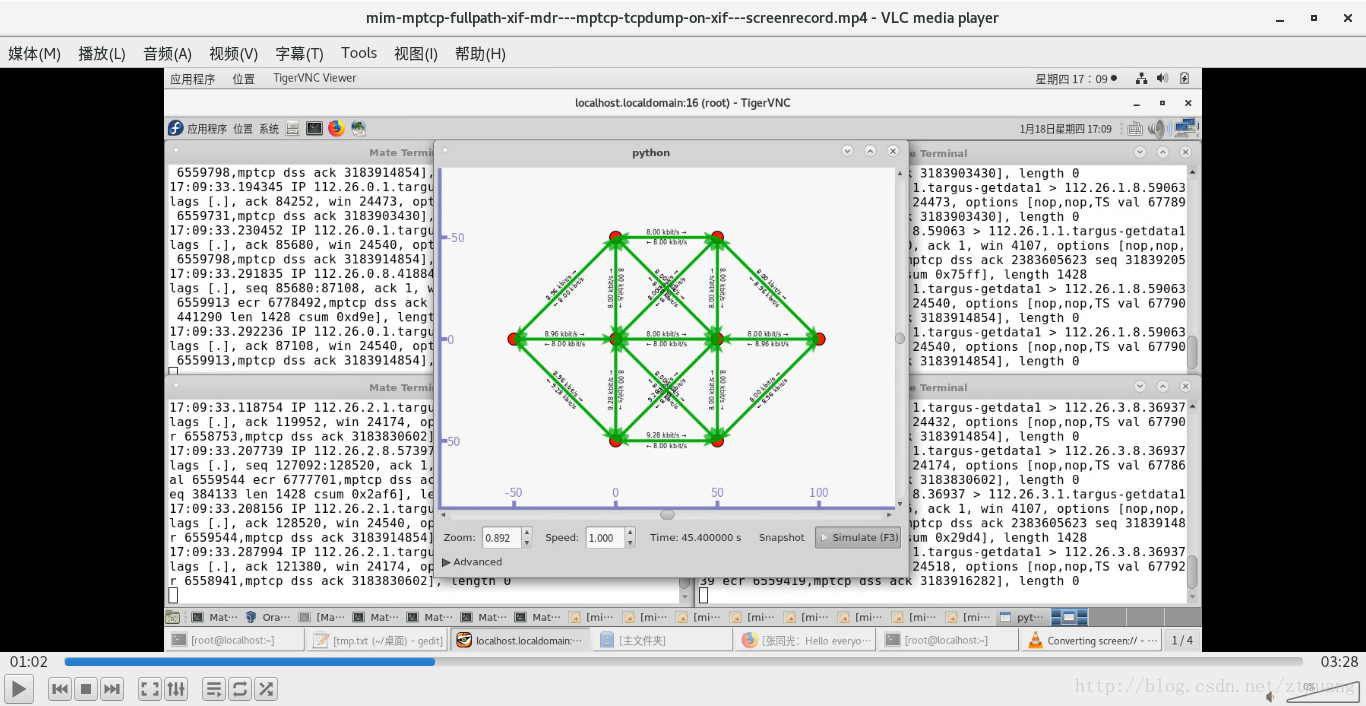
下图对 第一个结点的 四个 网络接口 进行抓包
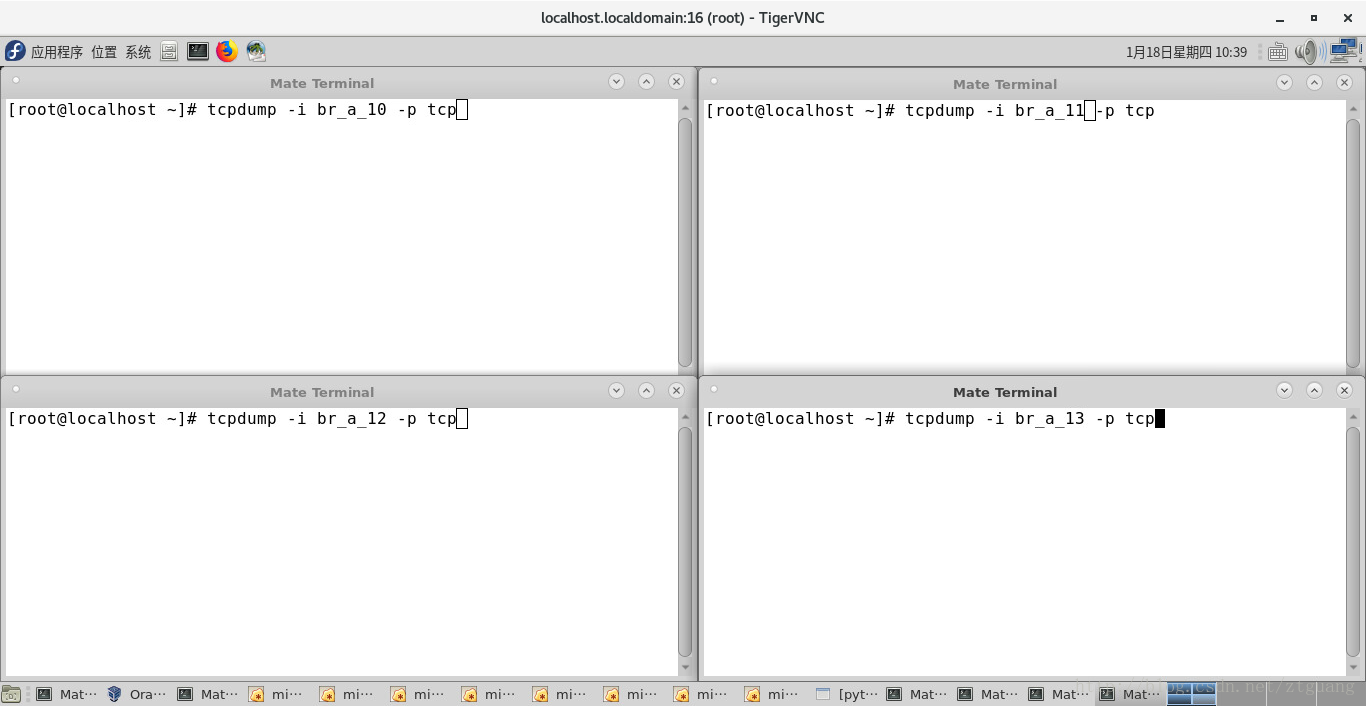
下图对 第一个结点的 四个 网络接口 进行抓包,结果说明,结点1 和 结点8 的数据传输是通过 MPTCP
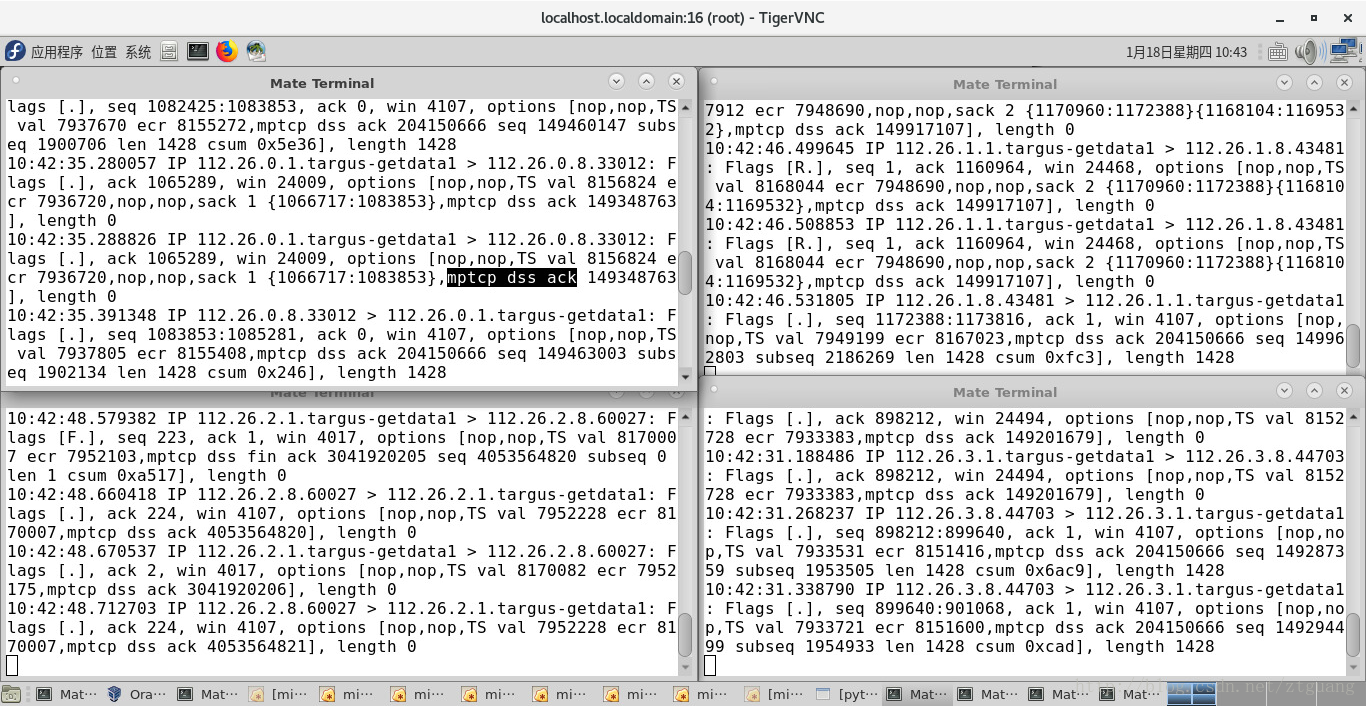
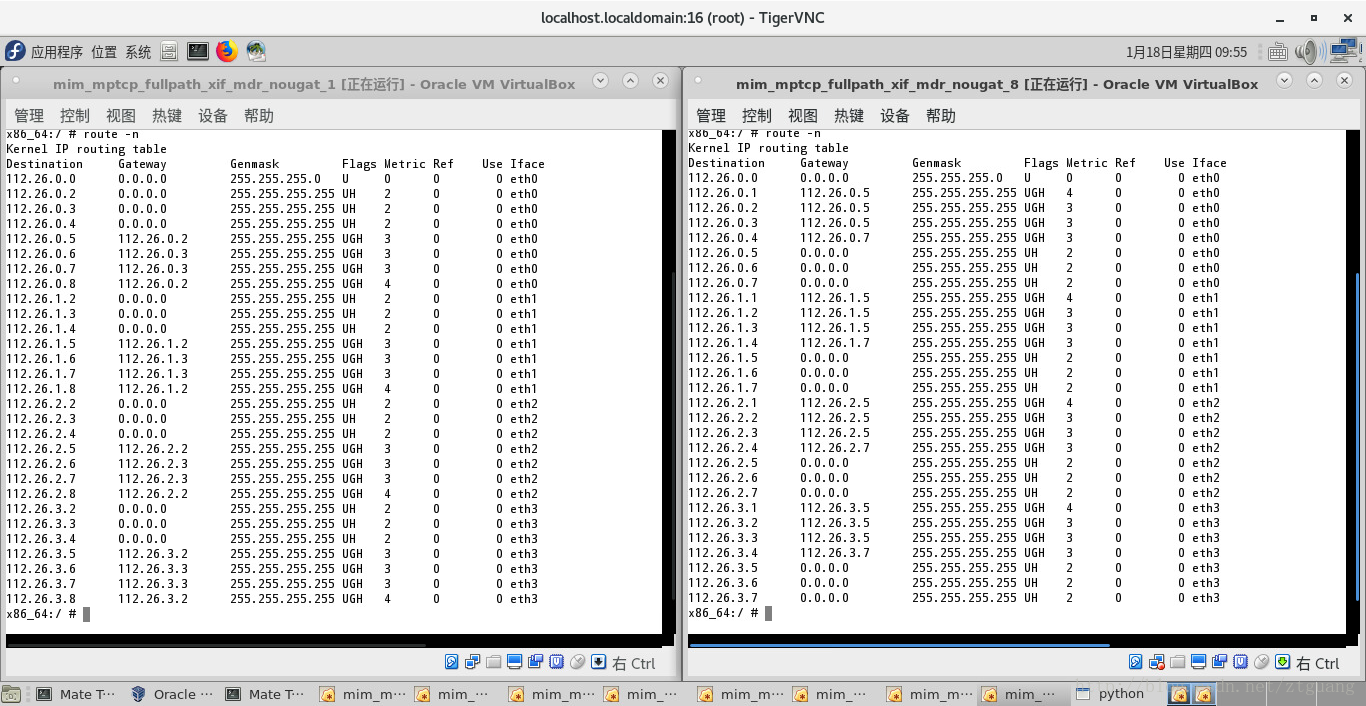
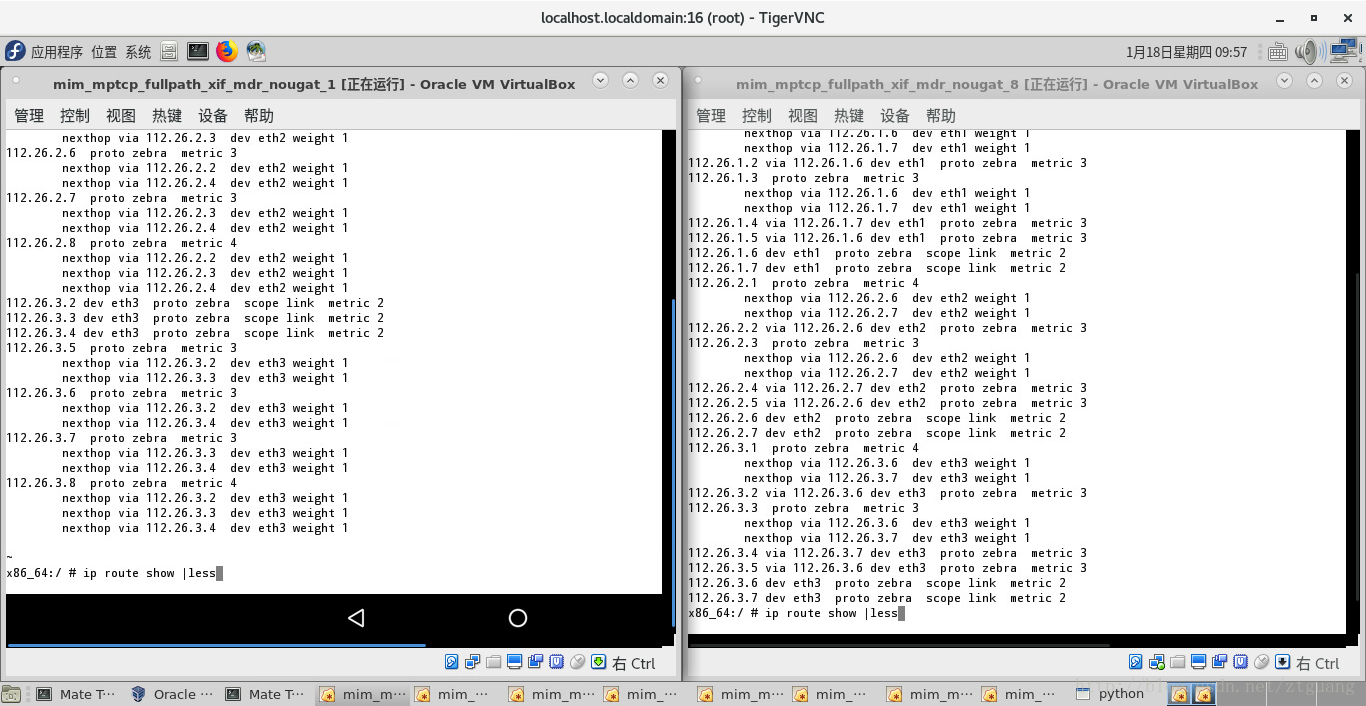
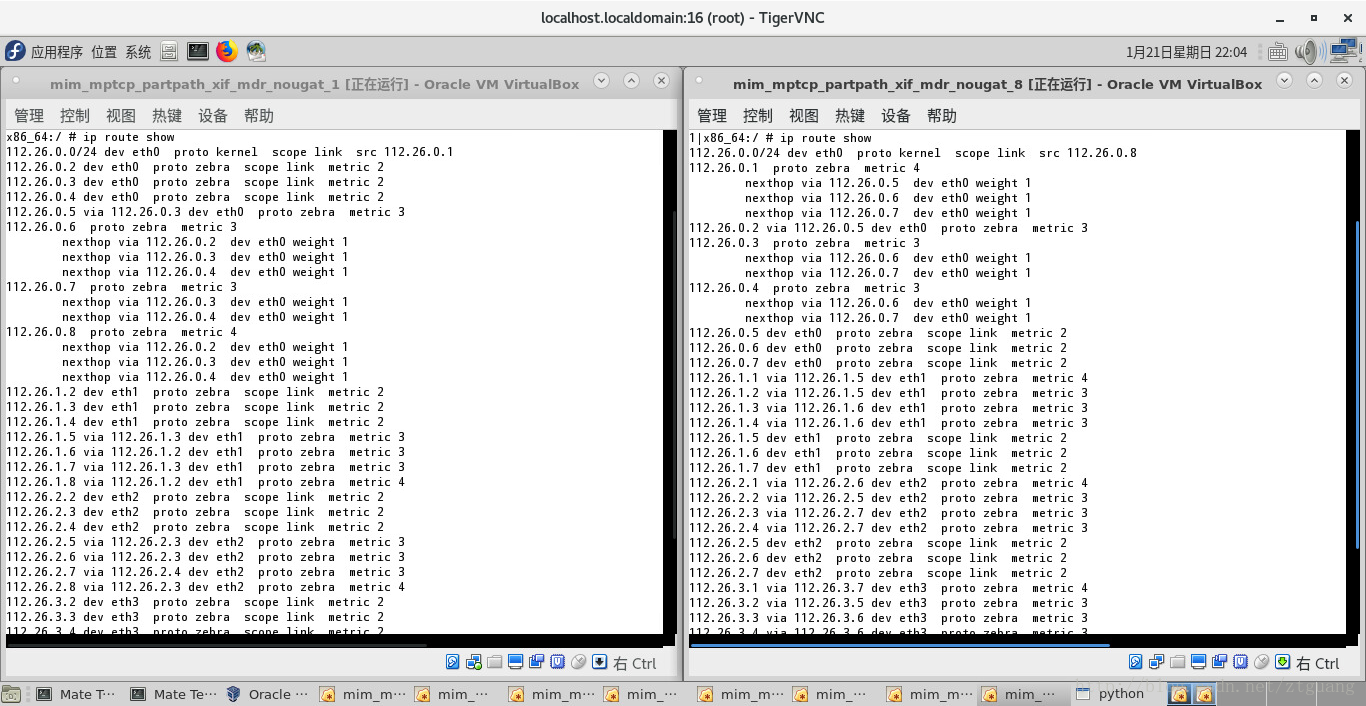
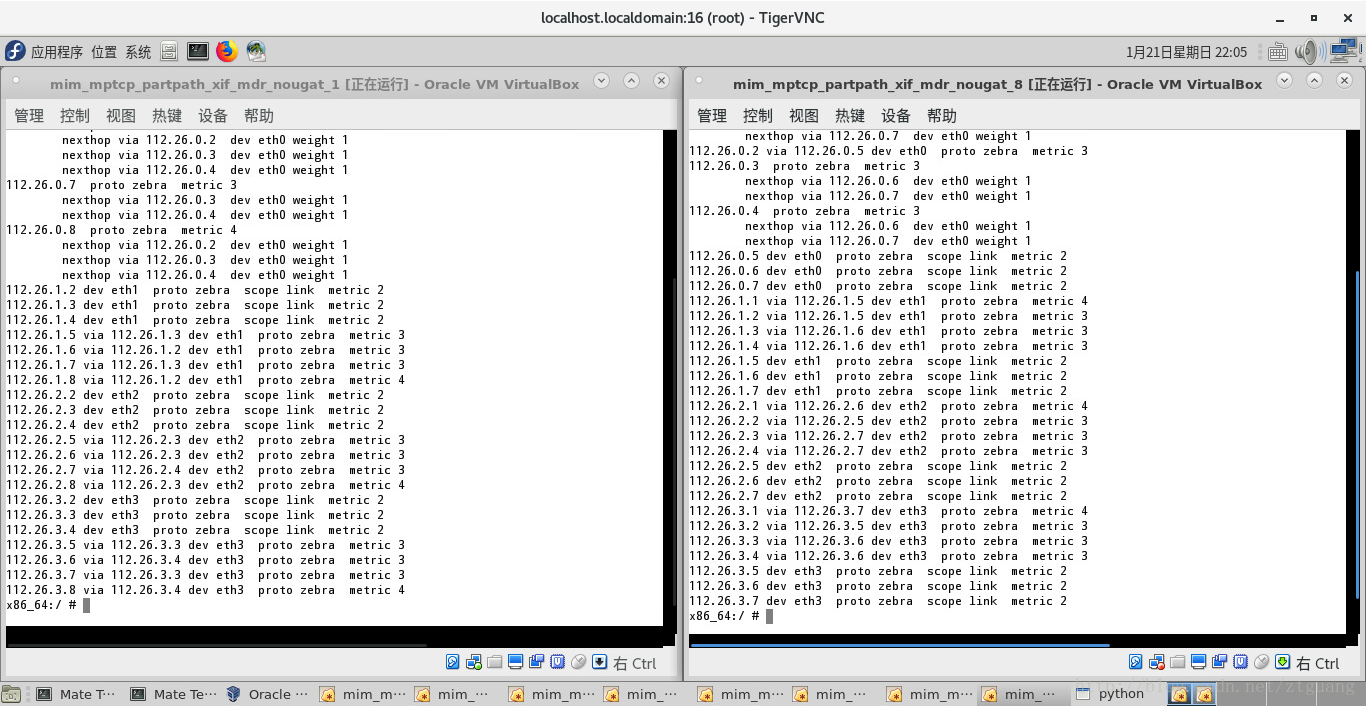
下图是 第一个结点、第八个结点的路由表
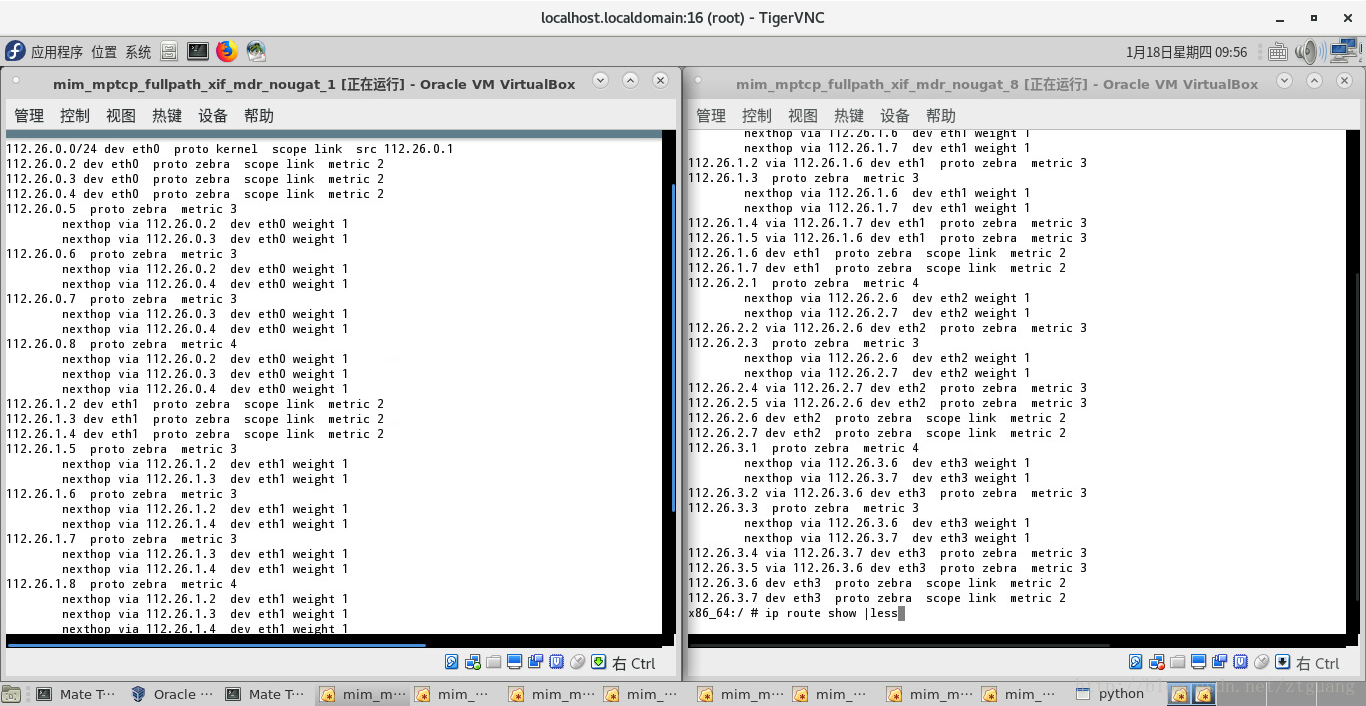
下图是 第一个结点、第八个结点的路由表中的多跳路由
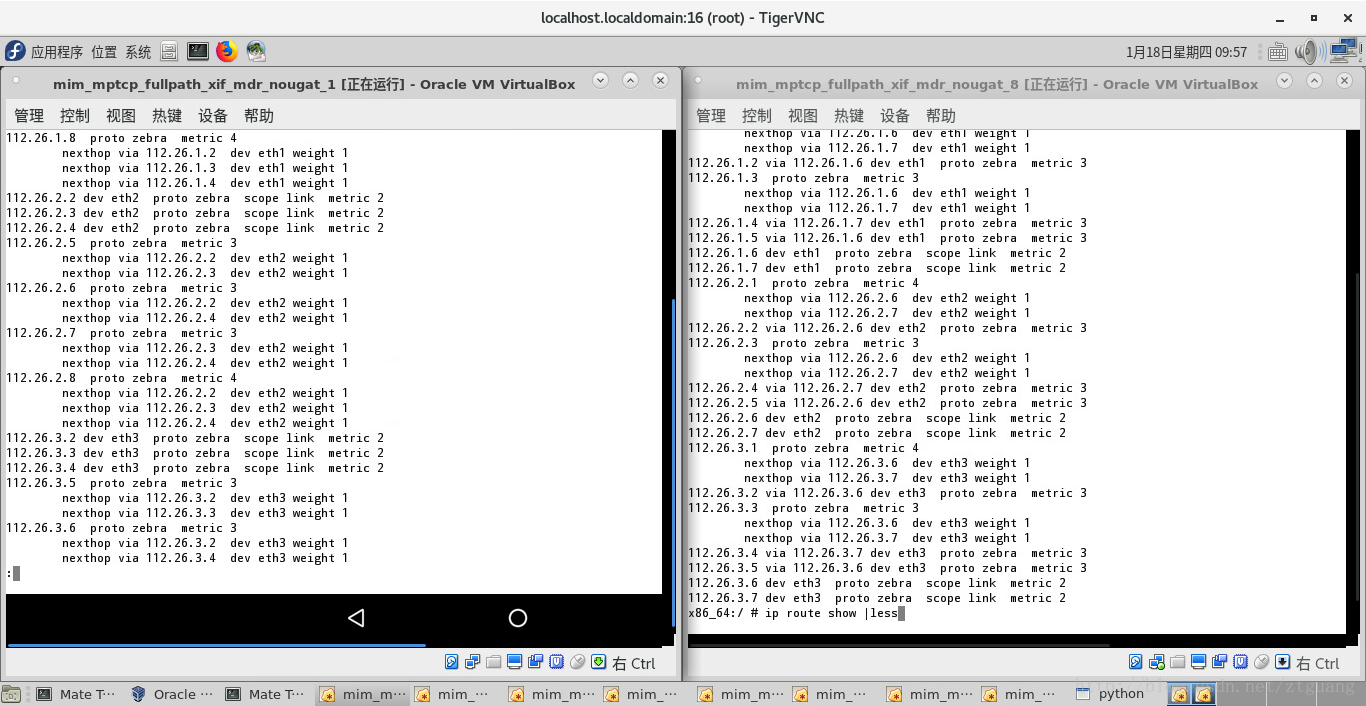
下图是 第一个结点、第八个结点的路由表中的多跳路由
下图是 第一个结点、第八个结点的路由表中的多跳路由

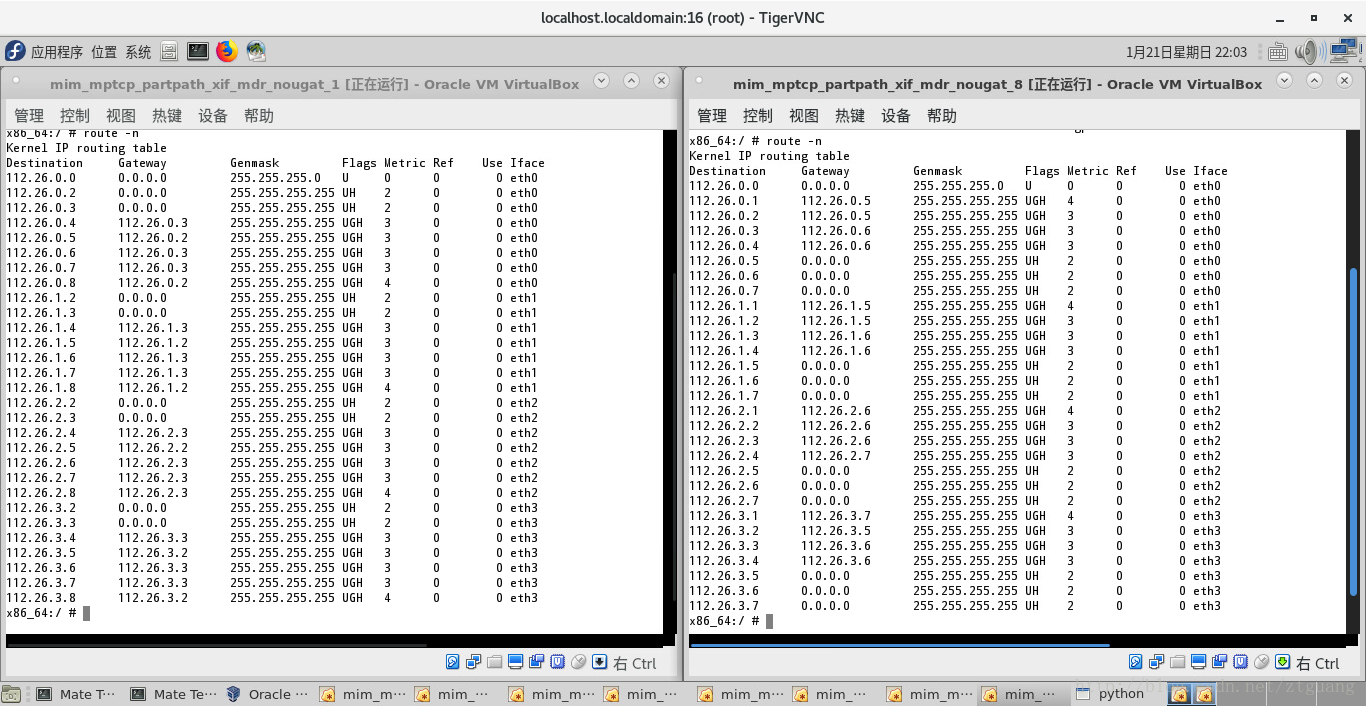
(OK) quagga - multi-interface, multi-routing, multi-hop (partpath) in MANETs

17_java之Integer|System|Arrays|Math|BigInteger|BigDecimal
01基本数据类型对象包装类概述
*A:基本数据类型对象包装类概述
*a.基本类型包装类的产生
在实际程序使用中,程序界面上用户输入的数据都是以字符串类型进行存储的。而程序开发中,我们需要把字符串数据,
根据需求转换成指定的基本数据类型,如年龄需要转换成int类型,考试成绩需要转换成double类型等
*b.八种基本类型对应的包装类
char Character
int Integer
byte Byte
short Short
long Long
float Float
double Double
boolean Boolean02Integer类parseInt方法
*A:Integer类parseInt方法:
*a:parseInt()
int i = Integer.parseInt("12");
System.out.println(i/2);//6
*b:parseInt(String s, int radix)
/*
* Integer类静态方法parseInt(String s, int radix)
* radix基数,进制
* "110",2 含义 前面的数字是二进制的,但是方法parseInt运行结果都是十进制
* 指定进制的字符串转换为十进制的整数
*/
public static void function_1(){
int i = Integer.parseInt("110", 2);
System.out.println(i);
}03Integer类int转成字符串
*A:Integer类int转成字符串:
*a:使用+与字符串拼接
int i = 3;
String s = i+"";
System.out.println(s+1);//"31"
*b:toString(int ,int 进制),任意进制整数转成任意进制的字符串 (了解)
String s1 = Integer.toString(5,2);
System.out.println(s1);04Integer类构造方法
*A:Integer类构造方法
/*
* Integer类构造方法
* Integer (String s)
* 将数字格式的字符串,传递到Integer类的构造方法中
* 创建Integer对象,包装的是一个字符串
* 将构造方法中的字符串,转成基本数据类型,调用方法,非静态的, intValue()
*/
public static void function_3(){
Integer in = new Integer("100");
int i = in.intValue();
System.out.println(--i);//99
}05Integer类其他方法
*A:Integer类其他方法
/*
* Integer类的3个静态方法
* 做进制的转换
* 十进制转成二进制 toBinarString(int)
* 十进制转成八进制 toOctalString(int)
*十进制转成十六进制 toHexString(int)
* 三个方法,返回值都是以String形式出现
*/
a:十进制转二,八,十六进制
public static void function_1(){
System.out.println(Integer.toBinaryString(99));
System.out.println(Integer.toOctalString(99));
System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(999));
}
b:获取int的最大值和最小值
/*
* Integer类的静态成员变量
* MAX_VALUE * MIN_VALUE
*/
public static void function(){
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}06自动装箱和自动拆箱
*A:自动装箱与自动拆箱:
//JDK1.5新特性
//自动装箱,拆箱的 好处: 基本类型和引用类直接运算
//自动装箱:使用Integer.valueOf(整数值)返回一个封装了该整数值的Integer对象
//自动拆箱:使用Integer对象.intValue()返回Integer对象中封装的整数值 public static void function(){
//引用类型 , 引用变量一定指向对象 //自动装箱, 基本数据类型1, 直接变成了对象
Integer in = 1; // Integer in = new Integer(1)
//in 是引用类型,不能和基本类型运算, 自动拆箱,引用类型in,转换基本类型
//in+1 ==> in.inValue()+1 = 2
//in = 2 自动装箱
in = in + 1;
System.out.println(in);
}07自动装箱和自动拆箱(当心陷阱!!!)
*A:自动装箱与自动拆箱:
Integer i = new Integer(1);
Integer j = new Integer(1);
System.out.println(i==j); // false 比较的是地址
System.out.println(i.equals(j)); // true 继承的是Object重写equals,比较的对象的数据值
System.out.println("===================");
Integer a = 500;//Integer integer=Integer.valueOf(500)
//integer=new Integer(500);
Integer b = 500;
System.out.println(a==b);//false
System.out.println(a.equals(b));//true
System.out.println("===================");
//数据在byte(-128~127)范围内,JVM不会从新new对象
Integer aa = 127; // Integer aa = new Integer(127)
Integer bb = 127; // Integer bb = aa;
System.out.println(aa==bb); //true
System.out.println(aa.equals(bb));//true08System类方法currentTimeMillis
A:System类方法currentTimeMillis():用于计算程序的执行时间 /* * 获取系统当前毫秒值 * static long currentTimeMillis() * 对程序执行时间测试 */
public static void function(){ long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//当前时间x-1970年1月1日零时零分零秒 for(int i = 0 ; i < 10000; i++){ System.out.println(i); } long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
//当前时间y-1970年1月1日零时零分零秒 System.out.println(end - start);//当前时间y-当前时间x }09System类方法exit
*A:System类方法exit()方法
/*
* 退出虚拟机,所有程序全停止
* static void exit(0)
*/
public static void function_1(){
while(true){
System.out.println("hello");
System.exit(0);//该方法会在以后的finally代码块中使用(讲到再说)
}
}10System类方法gc
A:System类方法gc public class Person { public void finalize(){ System.out.println("垃圾收取了"); } }
/*
* JVM在内存中,收取对象的垃圾
* 当没有更多引用指向该对象时,会自动调用垃圾回收机制回收堆中的对象
* 同时调用回收对象所属类的finalize方法()
* static void gc()
*/
public static void function_2(){
new Person();
new Person();
new Person();
new Person();
new Person();
new Person();
new Person();
new Person();
System.gc();
}11System类方法getProperties
A:System类方法getProperties(了解)
/*
* 获取当前操作系统的属性:例如操作系统名称,
* static Properties getProperties()
*/
public static void function_3(){
System.out.println( System.getProperties() );
}12System类方法arraycopy
A:System类方法arraycopy:
/*
* System类方法,复制数组
* arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length)
* Object src, 要复制的源数组
* int srcPos, 数组源的起始索引
* Object dest,复制后的目标数组
* int destPos,目标数组起始索引
* int length, 复制几个
*/
public static void function_4(){
int[] src = {11,22,33,44,55,66};
int[] desc = {77,88,99,0};
System.arraycopy(src, 1, desc, 1, 2);//将src数组的1位置开始(包含1位置)的两个元素,拷贝到desc的1,2位置上
for(int i = 0 ; i < desc.length ; i++){
System.out.println(desc[i]);
}
}13Math类的方法_1
A:Math类中的方法 /*
static double sqrt(double d)
返回参数的平方根*/public static void function_4(){ double d = Math.sqrt(-2); System.out.println(d);}
/*0
static double pow(double a, double b)
a的b次方*/public static void function_3(){double d = Math.pow(2, 3);System.out.println(d);}
/*
static double floor(double d)
返回小于或者等于参数d的最大整数*/public static void function_2(){double d = Math.floor(1.5);System.out.println(d);}
/*
static double ceil(double d)
返回大于或者等于参数d的最小整数*/public static void function_1(){double d = Math.ceil(5.1);System.out.println(d);}
/*
static int abs(int i)
获取参数的绝对值*/ public static void function(){int i = Math.abs(0);System.out.println(i); }14Math类的方法_2
A:Math类的方法_2 /*
static double round(doubl d)
获取参数的四舍五入,取整数*/ public static void function_6(){ double d = Math.round(5.4195); System.out.println(d); }
/*
static double random() 返回随机数 0.0-1.0之间
来源,也是Random类*/
public static void function_5(){
for(int i = 0 ; i < 10 ;i++){
double d = Math.random(); System.out.println(d);
} }15Arrays工具类
A:Arrays工具类: public class ArraysDemo { public static void main(String[] args) {
function_2(); int[] arr = {56,65,11,98,57,43,16,18,100,200};
int[] newArray = test(arr); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(newArray));
}
/*
* 定义方法,接收输入,存储的是10个人考试成绩 * 将最后三个人的成绩,存储到新的数组中,返回新的数组
*/ public static int[] test(int[] arr){
//对数组排序 Arrays.sort(arr);
//将最后三个成绩存储到新的数组中 int[] result = new int[3];
//成绩数组的最后三个元素,复制到新数组中
// System.arraycopy(arr, 0, result, 0, 3); for(int i = 0 ; i < 3 ;i++){ result[i] = arr[i]; } return result; }
/*
* static String toString(数组)
* 将数组变成字符串
*/
public static void function_2(){
int[] arr = {5,1,4,6,8,9,0};
String s = Arrays.toString(arr);
System.out.println(s);
}
/*
* static int binarySearch(数组, 被查找的元素)
* 数组的二分搜索法
* 返回元素在数组中出现的索引
* 元素不存在, 返回的是 (-插入点-1)
*/
public static void function_1(){
int[] arr = {1,4,7,9,11,15,18};
int index = Arrays.binarySearch(arr, 10);
System.out.println(index);
}
/*
* static void sort(数组)
* 对数组升序排列
*/
public static void function(){
int[] arr = {5,1,4,6,8,9,0};
Arrays.sort(arr);
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
} 16数组复制练习
*A:数组复制练习:
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {56,65,11,98,57,43,16,18,100,200};
int[] newArray = test(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(newArray));
}
/*
* 定义方法,接收输入,存储的是10个人考试成绩
* 将最后三个人的成绩,存储到新的数组中,返回新的数组
*/
public static int[] test(int[] arr){
//对数组排序 Arrays.sort(arr);
//将最后三个成绩存储到新的数组中 int[] result = new int[3];
//成绩数组的最后三个元素,复制到新数组中
//System.arraycopy(arr, 0, result, 0, 3); for(int i = 0 ; i < 3 ;i++){ result[i] = arr[i]; } return result; }17BigInteger类概述和构造方法
A:BigInteger类概述和构造方法
public static void main(String[] args) { function(); }
/*
*BigInteger类的构造方法
*传递字符串,要求数字格式,没有长度限制
**/
public static void function(){
BigInteger b = new BigInteger("8465846668464684562385634168451684568645684564564");
System.out.println(b);
BigInteger b1 = new BigInteger("5861694569514568465846668464684562385634168451684568645684564564");
System.out.println(b1);
}18BigInteger类四则运算
A:BigInteger类四则运算 public static void main(String[] args) { function_1(); }
/*
* BigInteger对象的四则运算
* 调用方法计算,计算结果也只能是BigInteger对象
*/
public static void function_1(){
BigInteger b1 = new BigInteger("5665464516451051581613661405146");
BigInteger b2 = new BigInteger("965855861461465516451051581613661405146");
//计算 b1+b2对象的和,调用方法 add
BigInteger bigAdd = b1.add(b2);//965855867126930032902103163227322810292
System.out.println(bigAdd);
//计算b1-b2对象的差,调用方法subtract
BigInteger bigSub = b1.subtract(b2);
System.out.println(bigSub);
//计算b1*b2对象的乘积,调用方法multiply
BigInteger bigMul = b1.multiply(b2);
System.out.println(bigMul);
//计算b2/b1对象商,调用方法divied
BigInteger bigDiv = b2.divide(b1);
System.out.println(bigDiv);
}19员工案例的子类的编写
A:BigDecimal类概述
/*
* 计算结果,未知
* 原因: 计算机二进制中,表示浮点数不精确造成
* 超级大型的浮点数据,提供高精度的浮点运算, BigDecimal
System.out.println(0.09 + 0.01);//0.09999999999999999
System.out.println(1.0 - 0.32);//0.6799999999999999
System.out.println(1.015 * 100);//101.49999999999999
System.out.println(1.301 / 100);//0.013009999999999999
*/20BigDecimal类实现加法减法乘法
A:BigDecimal类实现加法减法乘法 /*
BigDecimal实现三则运算
**/
public static void function(){
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal("0.09");
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal("0.01");
//计算b1+b2的和,调用方法addBigDecimal bigAdd = b1.add(b2);System.out.println(bigAdd);
BigDecimal b3 = new BigDecimal("1");
BigDecimal b4 = new BigDecimal("0.32");
//计算b3-b2的差,调用方法subtractBigDecimal
bigSub = b3.subtract(b4);
System.out.println(bigSub);
BigDecimal b5 = new BigDecimal("1.015");
BigDecimal b6 = new BigDecimal("100");
//计算b5*b6的成绩,调用方法
multiplyBigDecimal bigMul = b5.multiply(b6);
System.out.println(bigMul);}21BigDecimal类实现除法
A:BigDecimal类实现除法
/*
* BigDecimal实现除法运算
* divide(BigDecimal divisor, int scale, int roundingMode)
* int scale : 保留几位小数
* int roundingMode : 保留模式
* 保留模式 阅读API文档
* static int ROUND_UP 向上+1
* static int ROUND_DOWN 直接舍去
* static int ROUND_HALF_UP >= 0.5 向上+1
* static int ROUND_HALF_DOWN > 0.5 向上+1 ,否则直接舍去
*/
public static void function_1(){
BigDecimal b1 = new BigDecimal("1.0301");
BigDecimal b2 = new BigDecimal("100");
//计算b1/b2的商,调用方法divied
BigDecimal bigDiv = b1.divide(b2,2,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);//0.01301
System.out.println(bigDiv);
}
今天关于使用BigInteger Multiply运算符和biginteger赋值的介绍到此结束,谢谢您的阅读,有关(OK) Graphviz - MANET - multiple interfaces multiple paths、(OK) MPTCP & quagga - multi-interface, multi-routing, multi-hop (fullpath) in MANETs、(OK) quagga - multi-interface, multi-routing, multi-hop (partpath) in MANETs、17_java之Integer|System|Arrays|Math|BigInteger|BigDecimal等更多相关知识的信息可以在本站进行查询。
本文标签:



![[转帖]Ubuntu 安装 Wine方法(ubuntu如何安装wine)](https://www.gvkun.com/zb_users/cache/thumbs/4c83df0e2303284d68480d1b1378581d-180-120-1.jpg)

