对于想了解飘刃0.2.1发布,比Parcel更易上手的极速WEB打包工具的读者,本文将是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将详细介绍飘刀加速器怎么使用效果最佳,并且为您提供关于Android中的Parcel机制
对于想了解飘刃 0.2.1 发布,比 Parcel 更易上手的极速 WEB 打包工具的读者,本文将是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将详细介绍飘刀加速器怎么使用效果最佳,并且为您提供关于Android 中的 Parcel 机制 (上)、Android 进阶 ——Android 跨进程通讯机制之 Binder、IBinder、Parcel、AIDL、DHH 锐评 “打包工具”:前端根本不需要构建 (No Build)、esbuild, 一个用 GO 语言写的 Javascript 打包工具,比 Webpack 快接近 100 倍的有价值信息。
本文目录一览:- 飘刃 0.2.1 发布,比 Parcel 更易上手的极速 WEB 打包工具(飘刀加速器怎么使用效果最佳)
- Android 中的 Parcel 机制 (上)
- Android 进阶 ——Android 跨进程通讯机制之 Binder、IBinder、Parcel、AIDL
- DHH 锐评 “打包工具”:前端根本不需要构建 (No Build)
- esbuild, 一个用 GO 语言写的 Javascript 打包工具,比 Webpack 快接近 100 倍

飘刃 0.2.1 发布,比 Parcel 更易上手的极速 WEB 打包工具(飘刀加速器怎么使用效果最佳)
祝大家五一不用加班!!!
更新内容:
- 添加支持 `import a, { b, c } ...` 和 `export { a } from ...` 语法
- 添加支持少于4k的图片压缩成base64
- 添加 html 和 css 里的图片资源自动拷贝到相应的静态文件夹的功能
- 添加 html2VueRender 选项,默认开启,即 html 和 js 同级目录且同名 html 会转成 Vue render 函数
- 解决 sass 使用 `@import` 导入路径问题
- 添加支持 rollup 插件的 `resolveId` 方法
- 优化项目文件结构
飘刃 v0.2.1 是个较为完善的版本,作者已经去天桥底找风水靓位了,近期都不会更新,除非发现重大 bug。如果你拿人民币来砸我的话,收回上面那句话。
为什么不更新了?
我自己已经够用了,没必须折腾去实现那些不常用又容易出 bug 的功能。
为什么要开源?
为了造福全人类。你信?说来也奇怪,一个跑下快速上手示例就能入门的工具为什么那么少人尝试?一个几个文件加起来才一千来行代码的工具已经实现了别人的核心功能,不值得研究吗?为什么要开源?为了把我的最新研究成果分享给大家啊!不扯,主要是为了装逼。
怎样看待别人对飘刃的埋汰?
那些说飘刃坚持不了两年的人听着,我昨天已经给阿里云续费3年了,只要阿里云不倒,我就让飘刃官网至少飘3年。而且码云是不可能倒的,我就让飘刃一直搁码云这里。
“大厂的工具有团队多年维护,经得起考验,你的个人小玩意谁用?”谁用?我真没想过除了我自己还会有谁用,分享,只是想让大家看到 WEB 构建工具还可以这样写。已经 9012 年了,谷歌浏览器对 ES6+ 的支持十分稳妥,完全可以利用这个优势让开发更快更稳,真没必须开发环境都自己建 AST。
听说作者已经创业有一段时间,好久没上过班了,不会是闭门造车吧?
项目我就搁这里,希望能抛砖引玉吧

Android 中的 Parcel 机制 (上)
一.先从 Serialize 说起
我们都知道 JAVA 中的 Serialize 机制,译成串行化、序列化……,其作用是能将数据对象存入字节流当中,在需要时重新生成对象。主要应用是利用外部存储设备保存对象状态,以及通过网络传输对象等。
二.Android 中的新的序列化机制
在 Android 系统中,定位为针对内存受限的设备,因此对性能要求更高,另外系统中采用了新的 IPC(进程间通信)机制,必然要求使用性能更出色的对象传输方式。在这样的环境下,Parcel 被设计出来,其定位就是轻量级的高效的对象序列化和反序列化机制。
三.Parcel 类的背后
在 Framework 中有 parcel 类,源码路径是:
Frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Parcel.java
典型的源码片断如下:
/**
* Write an integer value into the parcel at the current dataPosition(),
* growing dataCapacity() if needed.
*/
public final native void writeInt(int val);
/**
* Write a long integer value into the parcel at the current dataPosition(),
* growing dataCapacity() if needed.
*/
public final native void writeLong(long val);从中我们看到,从这个源程序文件中我们看不到真正的功能是如何实现的,必须透过 JNI 往下走了。于是,Frameworks/base/core/jni/android_util_Binder.cpp 中找到了线索
static void android_os_Parcel_writeInt(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz, jint val)
{
Parcel* parcel = parcelForJavaObject(env, clazz);
if (parcel != NULL) {
const status_t err = parcel->writeInt32(val);
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/OutOfMemoryError", NULL);
}
}
}
static void android_os_Parcel_writeLong(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz, jlong val)
{
Parcel* parcel = parcelForJavaObject(env, clazz);
if (parcel != NULL) {
const status_t err = parcel->writeInt64(val);
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
jniThrowException(env, "java/lang/OutOfMemoryError", NULL);
}
}
}从这里我们可以得到的信息是函数的实现依赖于 Parcel 指针,因此还需要找到 Parcel 的类定义,注意,这里的类已经是用 C++ 语言实现的了。
找到 Frameworks/base/include/binder/parcel.h 和 Frameworks/base/libs/binder/parcel.cpp。终于找到了最终的实现代码了。
有兴趣的朋友可以自己读一下,不难理解,这里把基本的思路总结一下:
1. 整个读写全是在内存中进行,主要是通过 malloc ()、realloc ()、memcpy () 等内存操作进行,所以效率比 JAVA 序列化中使用外部存储器会高很多;
2. 读写时是 4 字节对齐的,可以看到 #define PAD_SIZE (s) (((s)+3)&~3) 这句宏定义就是在做这件事情;
3. 如果预分配的空间不够时 newSize = ((mDataSize+len)*3)/2; 会一次多分配 50%;
4. 对于普通数据,使用的是 mData 内存地址,对于 IBinder 类型的数据以及 FileDescriptor 使用的是 mObjects 内存地址。后者是通过 flatten_binder () 和 unflatten_binder () 实现的,目的是反序列化时读出的对象就是原对象而不用重新 new 一个新对象。
好了,这就是 Parcel 背后的动作,全是在一块内存里进行读写操作,就不啰嗦了,把 parcel 的代码贴在这供没有源码的朋友参考吧。接下来我会用一个小 DEMO 演示一下 Parcel 类在应用程序中的使用,详见《Android 中的 Parcel 机制(下)》。
/*
* Copyright (C) 2005 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
#ifndef ANDROID_PARCEL_H
#define ANDROID_PARCEL_H
#include <cutils/native_handle.h>
#include <utils/Errors.h>
#include <utils/RefBase.h>
#include <utils/String16.h>
#include <utils/Vector.h>
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
namespace android {
class IBinder;
class ProcessState;
class String8;
class TextOutput;
class Flattenable;
struct flat_binder_object; // defined in support_p/binder_module.h
class Parcel
{
public:
Parcel();
~Parcel();
const uint8_t* data() const;
size_t dataSize() const;
size_t dataAvail() const;
size_t dataPosition() const;
size_t dataCapacity() const;
status_t setDataSize(size_t size);
void setDataPosition(size_t pos) const;
status_t setDataCapacity(size_t size);
status_t setData(const uint8_t* buffer, size_t len);
status_t appendFrom(Parcel *parcel, size_t start, size_t len);
bool hasFileDescriptors() const;
status_t writeInterfaceToken(const String16& interface);
bool enforceInterface(const String16& interface) const;
bool checkInterface(IBinder*) const;
void freeData();
const size_t* objects() const;
size_t objectsCount() const;
status_t errorCheck() const;
void setError(status_t err);
status_t write(const void* data, size_t len);
void* writeInplace(size_t len);
status_t writeUnpadded(const void* data, size_t len);
status_t writeInt32(int32_t val);
status_t writeInt64(int64_t val);
status_t writeFloat(float val);
status_t writeDouble(double val);
status_t writeIntPtr(intptr_t val);
status_t writeCString(const char* str);
status_t writeString8(const String8& str);
status_t writeString16(const String16& str);
status_t writeString16(const char16_t* str, size_t len);
status_t writeStrongBinder(const sp<IBinder>& val);
status_t writeWeakBinder(const wp<IBinder>& val);
status_t write(const Flattenable& val);
// Place a native_handle into the parcel (the native_handle''s file-
// descriptors are dup''ed, so it is safe to delete the native_handle
// when this function returns).
// Doesn''t take ownership of the native_handle.
status_t writeNativeHandle(const native_handle* handle);
// Place a file descriptor into the parcel. The given fd must remain
// valid for the lifetime of the parcel.
status_t writeFileDescriptor(int fd);
// Place a file descriptor into the parcel. A dup of the fd is made, which
// will be closed once the parcel is destroyed.
status_t writeDupFileDescriptor(int fd);
status_t writeObject(const flat_binder_object& val, bool nullMetaData);
void remove(size_t start, size_t amt);
status_t read(void* outData, size_t len) const;
const void* readInplace(size_t len) const;
int32_t readInt32() const;
status_t readInt32(int32_t *pArg) const;
int64_t readInt64() const;
status_t readInt64(int64_t *pArg) const;
float readFloat() const;
status_t readFloat(float *pArg) const;
double readDouble() const;
status_t readDouble(double *pArg) const;
intptr_t readIntPtr() const;
status_t readIntPtr(intptr_t *pArg) const;
const char* readCString() const;
String8 readString8() const;
String16 readString16() const;
const char16_t* readString16Inplace(size_t* outLen) const;
sp<IBinder> readStrongBinder() const;
wp<IBinder> readWeakBinder() const;
status_t read(Flattenable& val) const;
// Retrieve native_handle from the parcel. This returns a copy of the
// parcel''s native_handle (the caller takes ownership). The caller
// must free the native_handle with native_handle_close() and
// native_handle_delete().
native_handle* readNativeHandle() const;
// Retrieve a file descriptor from the parcel. This returns the raw fd
// in the parcel, which you do not own -- use dup() to get your own copy.
int readFileDescriptor() const;
const flat_binder_object* readObject(bool nullMetaData) const;
// Explicitly close all file descriptors in the parcel.
void closeFileDescriptors();
typedef void (*release_func)(Parcel* parcel,
const uint8_t* data, size_t dataSize,
const size_t* objects, size_t objectsSize,
void* cookie);
const uint8_t* ipcData() const;
size_t ipcDataSize() const;
const size_t* ipcObjects() const;
size_t ipcObjectsCount() const;
void ipcSetDataReference(const uint8_t* data, size_t dataSize,
const size_t* objects, size_t objectsCount,
release_func relFunc, void* relCookie);
void print(TextOutput& to, uint32_t flags = 0) const;
private:
Parcel(const Parcel& o);
Parcel& operator=(const Parcel& o);
status_t finishWrite(size_t len);
void releaseObjects();
void acquireObjects();
status_t growData(size_t len);
status_t restartWrite(size_t desired);
status_t continueWrite(size_t desired);
void freeDataNoInit();
void initState();
void scanForFds() const;
template<class T>
status_t readAligned(T *pArg) const;
template<class T> T readAligned() const;
template<class T>
status_t writeAligned(T val);
status_t mError;
uint8_t* mData;
size_t mDataSize;
size_t mDataCapacity;
mutable size_t mDataPos;
size_t* mObjects;
size_t mObjectsSize;
size_t mObjectsCapacity;
mutable size_t mNextObjectHint;
mutable bool mFdsKnown;
mutable bool mHasFds;
release_func mOwner;
void* mOwnerCookie;
};
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
inline TextOutput& operator<<(TextOutput& to, const Parcel& parcel)
{
parcel.print(to);
return to;
}
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
// Generic acquire and release of objects.
void acquire_object(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const flat_binder_object& obj, const void* who);
void release_object(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const flat_binder_object& obj, const void* who);
void flatten_binder(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const sp<IBinder>& binder, flat_binder_object* out);
void flatten_binder(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const wp<IBinder>& binder, flat_binder_object* out);
status_t unflatten_binder(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const flat_binder_object& flat, sp<IBinder>* out);
status_t unflatten_binder(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const flat_binder_object& flat, wp<IBinder>* out);
}; // namespace android
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#endif // ANDROID_PARCEL_H下面是函数的实现
/*
* Copyright (C) 2005 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
#define LOG_TAG "Parcel"
//#define LOG_NDEBUG 0
#include <binder/Parcel.h>
#include <binder/Binder.h>
#include <binder/BpBinder.h>
#include <utils/Debug.h>
#include <binder/ProcessState.h>
#include <utils/Log.h>
#include <utils/String8.h>
#include <utils/String16.h>
#include <utils/TextOutput.h>
#include <utils/misc.h>
#include <utils/Flattenable.h>
#include <private/binder/binder_module.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#ifndef INT32_MAX
#define INT32_MAX ((int32_t)(2147483647))
#endif
#define LOG_REFS(...)
//#define LOG_REFS(...) LOG(LOG_DEBUG, "Parcel", __VA_ARGS__)
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
#define PAD_SIZE(s) (((s)+3)&~3)
// XXX This can be made public if we want to provide
// support for typed data.
struct small_flat_data
{
uint32_t type;
uint32_t data;
};
namespace android {
void acquire_object(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const flat_binder_object& obj, const void* who)
{
switch (obj.type) {
case BINDER_TYPE_BINDER:
if (obj.binder) {
LOG_REFS("Parcel %p acquiring reference on local %p", who, obj.cookie);
static_cast<IBinder*>(obj.cookie)->incStrong(who);
}
return;
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER:
if (obj.binder)
static_cast<RefBase::weakref_type*>(obj.binder)->incWeak(who);
return;
case BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE: {
const sp<IBinder> b = proc->getStrongProxyForHandle(obj.handle);
if (b != NULL) {
LOG_REFS("Parcel %p acquiring reference on remote %p", who, b.get());
b->incStrong(who);
}
return;
}
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE: {
const wp<IBinder> b = proc->getWeakProxyForHandle(obj.handle);
if (b != NULL) b.get_refs()->incWeak(who);
return;
}
case BINDER_TYPE_FD: {
// intentionally blank -- nothing to do to acquire this, but we do
// recognize it as a legitimate object type.
return;
}
}
LOGD("Invalid object type 0x%08lx", obj.type);
}
void release_object(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const flat_binder_object& obj, const void* who)
{
switch (obj.type) {
case BINDER_TYPE_BINDER:
if (obj.binder) {
LOG_REFS("Parcel %p releasing reference on local %p", who, obj.cookie);
static_cast<IBinder*>(obj.cookie)->decStrong(who);
}
return;
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER:
if (obj.binder)
static_cast<RefBase::weakref_type*>(obj.binder)->decWeak(who);
return;
case BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE: {
const sp<IBinder> b = proc->getStrongProxyForHandle(obj.handle);
if (b != NULL) {
LOG_REFS("Parcel %p releasing reference on remote %p", who, b.get());
b->decStrong(who);
}
return;
}
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE: {
const wp<IBinder> b = proc->getWeakProxyForHandle(obj.handle);
if (b != NULL) b.get_refs()->decWeak(who);
return;
}
case BINDER_TYPE_FD: {
if (obj.cookie != (void*)0) close(obj.handle);
return;
}
}
LOGE("Invalid object type 0x%08lx", obj.type);
}
inline static status_t finish_flatten_binder(
const sp<IBinder>& binder, const flat_binder_object& flat, Parcel* out)
{
return out->writeObject(flat, false);
}
status_t flatten_binder(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const sp<IBinder>& binder, Parcel* out)
{
flat_binder_object obj;
obj.flags = 0x7f | FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS;
if (binder != NULL) {
IBinder *local = binder->localBinder();
if (!local) {
BpBinder *proxy = binder->remoteBinder();
if (proxy == NULL) {
LOGE("null proxy");
}
const int32_t handle = proxy ? proxy->handle() : 0;
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE;
obj.handle = handle;
obj.cookie = NULL;
} else {
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
obj.binder = local->getWeakRefs();
obj.cookie = local;
}
} else {
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
obj.binder = NULL;
obj.cookie = NULL;
}
return finish_flatten_binder(binder, obj, out);
}
status_t flatten_binder(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const wp<IBinder>& binder, Parcel* out)
{
flat_binder_object obj;
obj.flags = 0x7f | FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS;
if (binder != NULL) {
sp<IBinder> real = binder.promote();
if (real != NULL) {
IBinder *local = real->localBinder();
if (!local) {
BpBinder *proxy = real->remoteBinder();
if (proxy == NULL) {
LOGE("null proxy");
}
const int32_t handle = proxy ? proxy->handle() : 0;
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE;
obj.handle = handle;
obj.cookie = NULL;
} else {
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER;
obj.binder = binder.get_refs();
obj.cookie = binder.unsafe_get();
}
return finish_flatten_binder(real, obj, out);
}
// XXX How to deal? In order to flatten the given binder,
// we need to probe it for information, which requires a primary
// reference... but we don''t have one.
//
// The OpenBinder implementation uses a dynamic_cast<> here,
// but we can''t do that with the different reference counting
// implementation we are using.
LOGE("Unable to unflatten Binder weak reference!");
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
obj.binder = NULL;
obj.cookie = NULL;
return finish_flatten_binder(NULL, obj, out);
} else {
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
obj.binder = NULL;
obj.cookie = NULL;
return finish_flatten_binder(NULL, obj, out);
}
}
inline static status_t finish_unflatten_binder(
BpBinder* proxy, const flat_binder_object& flat, const Parcel& in)
{
return NO_ERROR;
}
status_t unflatten_binder(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const Parcel& in, sp<IBinder>* out)
{
const flat_binder_object* flat = in.readObject(false);
if (flat) {
switch (flat->type) {
case BINDER_TYPE_BINDER:
*out = static_cast<IBinder*>(flat->cookie);
return finish_unflatten_binder(NULL, *flat, in);
case BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE:
*out = proc->getStrongProxyForHandle(flat->handle);
return finish_unflatten_binder(
static_cast<BpBinder*>(out->get()), *flat, in);
}
}
return BAD_TYPE;
}
status_t unflatten_binder(const sp<ProcessState>& proc,
const Parcel& in, wp<IBinder>* out)
{
const flat_binder_object* flat = in.readObject(false);
if (flat) {
switch (flat->type) {
case BINDER_TYPE_BINDER:
*out = static_cast<IBinder*>(flat->cookie);
return finish_unflatten_binder(NULL, *flat, in);
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER:
if (flat->binder != NULL) {
out->set_object_and_refs(
static_cast<IBinder*>(flat->cookie),
static_cast<RefBase::weakref_type*>(flat->binder));
} else {
*out = NULL;
}
return finish_unflatten_binder(NULL, *flat, in);
case BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE:
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE:
*out = proc->getWeakProxyForHandle(flat->handle);
return finish_unflatten_binder(
static_cast<BpBinder*>(out->unsafe_get()), *flat, in);
}
}
return BAD_TYPE;
}
// ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Parcel::Parcel()
{
initState();
}
Parcel::~Parcel()
{
freeDataNoInit();
}
const uint8_t* Parcel::data() const
{
return mData;
}
size_t Parcel::dataSize() const
{
return (mDataSize > mDataPos ? mDataSize : mDataPos);
}
size_t Parcel::dataAvail() const
{
// TODO: decide what to do about the possibility that this can
// report an available-data size that exceeds a Java int''s max
// positive value, causing havoc. Fortunately this will only
// happen if someone constructs a Parcel containing more than two
// gigabytes of data, which on typical phone hardware is simply
// not possible.
return dataSize() - dataPosition();
}
size_t Parcel::dataPosition() const
{
return mDataPos;
}
size_t Parcel::dataCapacity() const
{
return mDataCapacity;
}
status_t Parcel::setDataSize(size_t size)
{
status_t err;
err = continueWrite(size);
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
mDataSize = size;
LOGV("setDataSize Setting data size of %p to %d/n", this, mDataSize);
}
return err;
}
void Parcel::setDataPosition(size_t pos) const
{
mDataPos = pos;
mNextObjectHint = 0;
}
status_t Parcel::setDataCapacity(size_t size)
{
if (size > mDataSize) return continueWrite(size);
return NO_ERROR;
}
status_t Parcel::setData(const uint8_t* buffer, size_t len)
{
status_t err = restartWrite(len);
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
memcpy(const_cast<uint8_t*>(data()), buffer, len);
mDataSize = len;
mFdsKnown = false;
}
return err;
}
status_t Parcel::appendFrom(Parcel *parcel, size_t offset, size_t len)
{
const sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
status_t err;
uint8_t *data = parcel->mData;
size_t *objects = parcel->mObjects;
size_t size = parcel->mObjectsSize;
int startPos = mDataPos;
int firstIndex = -1, lastIndex = -2;
if (len == 0) {
return NO_ERROR;
}
// range checks against the source parcel size
if ((offset > parcel->mDataSize)
|| (len > parcel->mDataSize)
|| (offset + len > parcel->mDataSize)) {
return BAD_VALUE;
}
// Count objects in range
for (int i = 0; i < (int) size; i++) {
size_t off = objects[i];
if ((off >= offset) && (off < offset + len)) {
if (firstIndex == -1) {
firstIndex = i;
}
lastIndex = i;
}
}
int numObjects = lastIndex - firstIndex + 1;
// grow data
err = growData(len);
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
return err;
}
// append data
memcpy(mData + mDataPos, data + offset, len);
mDataPos += len;
mDataSize += len;
if (numObjects > 0) {
// grow objects
if (mObjectsCapacity < mObjectsSize + numObjects) {
int newSize = ((mObjectsSize + numObjects)*3)/2;
size_t *objects =
(size_t*)realloc(mObjects, newSize*sizeof(size_t));
if (objects == (size_t*)0) {
return NO_MEMORY;
}
mObjects = objects;
mObjectsCapacity = newSize;
}
// append and acquire objects
int idx = mObjectsSize;
for (int i = firstIndex; i <= lastIndex; i++) {
size_t off = objects[i] - offset + startPos;
mObjects[idx++] = off;
mObjectsSize++;
flat_binder_object* flat
= reinterpret_cast<flat_binder_object*>(mData + off);
acquire_object(proc, *flat, this);
if (flat->type == BINDER_TYPE_FD) {
// If this is a file descriptor, we need to dup it so the
// new Parcel now owns its own fd, and can declare that we
// officially know we have fds.
flat->handle = dup(flat->handle);
flat->cookie = (void*)1;
mHasFds = mFdsKnown = true;
}
}
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
bool Parcel::hasFileDescriptors() const
{
if (!mFdsKnown) {
scanForFds();
}
return mHasFds;
}
status_t Parcel::writeInterfaceToken(const String16& interface)
{
// currently the interface identification token is just its name as a string
return writeString16(interface);
}
bool Parcel::checkInterface(IBinder* binder) const
{
return enforceInterface(binder->getInterfaceDescriptor());
}
bool Parcel::enforceInterface(const String16& interface) const
{
const String16 str(readString16());
if (str == interface) {
return true;
} else {
LOGW("**** enforceInterface() expected ''%s'' but read ''%s''/n",
String8(interface).string(), String8(str).string());
return false;
}
}
const size_t* Parcel::objects() const
{
return mObjects;
}
size_t Parcel::objectsCount() const
{
return mObjectsSize;
}
status_t Parcel::errorCheck() const
{
return mError;
}
void Parcel::setError(status_t err)
{
mError = err;
}
status_t Parcel::finishWrite(size_t len)
{
//printf("Finish write of %d/n", len);
mDataPos += len;
LOGV("finishWrite Setting data pos of %p to %d/n", this, mDataPos);
if (mDataPos > mDataSize) {
mDataSize = mDataPos;
LOGV("finishWrite Setting data size of %p to %d/n", this, mDataSize);
}
//printf("New pos=%d, size=%d/n", mDataPos, mDataSize);
return NO_ERROR;
}
status_t Parcel::writeUnpadded(const void* data, size_t len)
{
size_t end = mDataPos + len;
if (end < mDataPos) {
// integer overflow
return BAD_VALUE;
}
if (end <= mDataCapacity) {
restart_write:
memcpy(mData+mDataPos, data, len);
return finishWrite(len);
}
status_t err = growData(len);
if (err == NO_ERROR) goto restart_write;
return err;
}
status_t Parcel::write(const void* data, size_t len)
{
void* const d = writeInplace(len);
if (d) {
memcpy(d, data, len);
return NO_ERROR;
}
return mError;
}
void* Parcel::writeInplace(size_t len)
{
const size_t padded = PAD_SIZE(len);
// sanity check for integer overflow
if (mDataPos+padded < mDataPos) {
return NULL;
}
if ((mDataPos+padded) <= mDataCapacity) {
restart_write:
//printf("Writing %ld bytes, padded to %ld/n", len, padded);
uint8_t* const data = mData+mDataPos;
// Need to pad at end?
if (padded != len) {
#if BYTE_ORDER == BIG_ENDIAN
static const uint32_t mask[4] = {
0x00000000, 0xffffff00, 0xffff0000, 0xff000000
};
#endif
#if BYTE_ORDER == LITTLE_ENDIAN
static const uint32_t mask[4] = {
0x00000000, 0x00ffffff, 0x0000ffff, 0x000000ff
};
#endif
//printf("Applying pad mask: %p to %p/n", (void*)mask[padded-len],
// *reinterpret_cast<void**>(data+padded-4));
*reinterpret_cast<uint32_t*>(data+padded-4) &= mask[padded-len];
}
finishWrite(padded);
return data;
}
status_t err = growData(padded);
if (err == NO_ERROR) goto restart_write;
return NULL;
}
status_t Parcel::writeInt32(int32_t val)
{
return writeAligned(val);
}
status_t Parcel::writeInt64(int64_t val)
{
return writeAligned(val);
}
status_t Parcel::writeFloat(float val)
{
return writeAligned(val);
}
status_t Parcel::writeDouble(double val)
{
return writeAligned(val);
}
status_t Parcel::writeIntPtr(intptr_t val)
{
return writeAligned(val);
}
status_t Parcel::writeCString(const char* str)
{
return write(str, strlen(str)+1);
}
status_t Parcel::writeString8(const String8& str)
{
status_t err = writeInt32(str.bytes());
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
err = write(str.string(), str.bytes()+1);
}
return err;
}
status_t Parcel::writeString16(const String16& str)
{
return writeString16(str.string(), str.size());
}
status_t Parcel::writeString16(const char16_t* str, size_t len)
{
if (str == NULL) return writeInt32(-1);
status_t err = writeInt32(len);
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
len *= sizeof(char16_t);
uint8_t* data = (uint8_t*)writeInplace(len+sizeof(char16_t));
if (data) {
memcpy(data, str, len);
*reinterpret_cast<char16_t*>(data+len) = 0;
return NO_ERROR;
}
err = mError;
}
return err;
}
status_t Parcel::writeStrongBinder(const sp<IBinder>& val)
{
return flatten_binder(ProcessState::self(), val, this);
}
status_t Parcel::writeWeakBinder(const wp<IBinder>& val)
{
return flatten_binder(ProcessState::self(), val, this);
}
status_t Parcel::writeNativeHandle(const native_handle* handle)
{
if (!handle || handle->version != sizeof(native_handle))
return BAD_TYPE;
status_t err;
err = writeInt32(handle->numFds);
if (err != NO_ERROR) return err;
err = writeInt32(handle->numInts);
if (err != NO_ERROR) return err;
for (int i=0 ; err==NO_ERROR && i<handle->numFds ; i++)
err = writeDupFileDescriptor(handle->data[i]);
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
LOGD("write native handle, write dup fd failed");
return err;
}
err = write(handle->data + handle->numFds, sizeof(int)*handle->numInts);
return err;
}
status_t Parcel::writeFileDescriptor(int fd)
{
flat_binder_object obj;
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_FD;
obj.flags = 0x7f | FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS;
obj.handle = fd;
obj.cookie = (void*)0;
return writeObject(obj, true);
}
status_t Parcel::writeDupFileDescriptor(int fd)
{
flat_binder_object obj;
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_FD;
obj.flags = 0x7f | FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS;
obj.handle = dup(fd);
obj.cookie = (void*)1;
return writeObject(obj, true);
}
status_t Parcel::write(const Flattenable& val)
{
status_t err;
// size if needed
size_t len = val.getFlattenedSize();
size_t fd_count = val.getFdCount();
err = this->writeInt32(len);
if (err) return err;
err = this->writeInt32(fd_count);
if (err) return err;
// payload
void* buf = this->writeInplace(PAD_SIZE(len));
if (buf == NULL)
return BAD_VALUE;
int* fds = NULL;
if (fd_count) {
fds = new int[fd_count];
}
err = val.flatten(buf, len, fds, fd_count);
for (size_t i=0 ; i<fd_count && err==NO_ERROR ; i++) {
err = this->writeDupFileDescriptor( fds[i] );
}
if (fd_count) {
delete [] fds;
}
return err;
}
status_t Parcel::writeObject(const flat_binder_object& val, bool nullMetaData)
{
const bool enoughData = (mDataPos+sizeof(val)) <= mDataCapacity;
const bool enoughObjects = mObjectsSize < mObjectsCapacity;
if (enoughData && enoughObjects) {
restart_write:
*reinterpret_cast<flat_binder_object*>(mData+mDataPos) = val;
// Need to write meta-data?
if (nullMetaData || val.binder != NULL) {
mObjects[mObjectsSize] = mDataPos;
acquire_object(ProcessState::self(), val, this);
mObjectsSize++;
}
// remember if it''s a file descriptor
if (val.type == BINDER_TYPE_FD) {
mHasFds = mFdsKnown = true;
}
return finishWrite(sizeof(flat_binder_object));
}
if (!enoughData) {
const status_t err = growData(sizeof(val));
if (err != NO_ERROR) return err;
}
if (!enoughObjects) {
size_t newSize = ((mObjectsSize+2)*3)/2;
size_t* objects = (size_t*)realloc(mObjects, newSize*sizeof(size_t));
if (objects == NULL) return NO_MEMORY;
mObjects = objects;
mObjectsCapacity = newSize;
}
goto restart_write;
}
void Parcel::remove(size_t start, size_t amt)
{
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("Parcel::remove() not yet implemented!");
}
status_t Parcel::read(void* outData, size_t len) const
{
if ((mDataPos+PAD_SIZE(len)) >= mDataPos && (mDataPos+PAD_SIZE(len)) <= mDataSize) {
memcpy(outData, mData+mDataPos, len);
mDataPos += PAD_SIZE(len);
LOGV("read Setting data pos of %p to %d/n", this, mDataPos);
return NO_ERROR;
}
return NOT_ENOUGH_DATA;
}
const void* Parcel::readInplace(size_t len) const
{
if ((mDataPos+PAD_SIZE(len)) >= mDataPos && (mDataPos+PAD_SIZE(len)) <= mDataSize) {
const void* data = mData+mDataPos;
mDataPos += PAD_SIZE(len);
LOGV("readInplace Setting data pos of %p to %d/n", this, mDataPos);
return data;
}
return NULL;
}
template<class T>
status_t Parcel::readAligned(T *pArg) const {
COMPILE_TIME_ASSERT_FUNCTION_SCOPE(PAD_SIZE(sizeof(T)) == sizeof(T));
if ((mDataPos+sizeof(T)) <= mDataSize) {
const void* data = mData+mDataPos;
mDataPos += sizeof(T);
*pArg = *reinterpret_cast<const T*>(data);
return NO_ERROR;
} else {
return NOT_ENOUGH_DATA;
}
}
template<class T>
T Parcel::readAligned() const {
T result;
if (readAligned(&result) != NO_ERROR) {
result = 0;
}
return result;
}
template<class T>
status_t Parcel::writeAligned(T val) {
COMPILE_TIME_ASSERT_FUNCTION_SCOPE(PAD_SIZE(sizeof(T)) == sizeof(T));
if ((mDataPos+sizeof(val)) <= mDataCapacity) {
restart_write:
*reinterpret_cast<T*>(mData+mDataPos) = val;
return finishWrite(sizeof(val));
}
status_t err = growData(sizeof(val));
if (err == NO_ERROR) goto restart_write;
return err;
}
status_t Parcel::readInt32(int32_t *pArg) const
{
return readAligned(pArg);
}
int32_t Parcel::readInt32() const
{
return readAligned<int32_t>();
}
status_t Parcel::readInt64(int64_t *pArg) const
{
return readAligned(pArg);
}
int64_t Parcel::readInt64() const
{
return readAligned<int64_t>();
}
status_t Parcel::readFloat(float *pArg) const
{
return readAligned(pArg);
}
float Parcel::readFloat() const
{
return readAligned<float>();
}
status_t Parcel::readDouble(double *pArg) const
{
return readAligned(pArg);
}
double Parcel::readDouble() const
{
return readAligned<double>();
}
status_t Parcel::readIntPtr(intptr_t *pArg) const
{
return readAligned(pArg);
}
intptr_t Parcel::readIntPtr() const
{
return readAligned<intptr_t>();
}
const char* Parcel::readCString() const
{
const size_t avail = mDataSize-mDataPos;
if (avail > 0) {
const char* str = reinterpret_cast<const char*>(mData+mDataPos);
// is the string''s trailing NUL within the parcel''s valid bounds?
const char* eos = reinterpret_cast<const char*>(memchr(str, 0, avail));
if (eos) {
const size_t len = eos - str;
mDataPos += PAD_SIZE(len+1);
LOGV("readCString Setting data pos of %p to %d/n", this, mDataPos);
return str;
}
}
return NULL;
}
String8 Parcel::readString8() const
{
int32_t size = readInt32();
// watch for potential int overflow adding 1 for trailing NUL
if (size > 0 && size < INT32_MAX) {
const char* str = (const char*)readInplace(size+1);
if (str) return String8(str, size);
}
return String8();
}
String16 Parcel::readString16() const
{
size_t len;
const char16_t* str = readString16Inplace(&len);
if (str) return String16(str, len);
LOGE("Reading a NULL string not supported here.");
return String16();
}
const char16_t* Parcel::readString16Inplace(size_t* outLen) const
{
int32_t size = readInt32();
// watch for potential int overflow from size+1
if (size >= 0 && size < INT32_MAX) {
*outLen = size;
const char16_t* str = (const char16_t*)readInplace((size+1)*sizeof(char16_t));
if (str != NULL) {
return str;
}
}
*outLen = 0;
return NULL;
}
sp<IBinder> Parcel::readStrongBinder() const
{
sp<IBinder> val;
unflatten_binder(ProcessState::self(), *this, &val);
return val;
}
wp<IBinder> Parcel::readWeakBinder() const
{
wp<IBinder> val;
unflatten_binder(ProcessState::self(), *this, &val);
return val;
}
native_handle* Parcel::readNativeHandle() const
{
int numFds, numInts;
status_t err;
err = readInt32(&numFds);
if (err != NO_ERROR) return 0;
err = readInt32(&numInts);
if (err != NO_ERROR) return 0;
native_handle* h = native_handle_create(numFds, numInts);
for (int i=0 ; err==NO_ERROR && i<numFds ; i++) {
h->data[i] = dup(readFileDescriptor());
if (h->data[i] < 0) err = BAD_VALUE;
}
err = read(h->data + numFds, sizeof(int)*numInts);
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
native_handle_close(h);
native_handle_delete(h);
h = 0;
}
return h;
}
int Parcel::readFileDescriptor() const
{
const flat_binder_object* flat = readObject(true);
if (flat) {
switch (flat->type) {
case BINDER_TYPE_FD:
//LOGI("Returning file descriptor %ld from parcel %p/n", flat->handle, this);
return flat->handle;
}
}
return BAD_TYPE;
}
status_t Parcel::read(Flattenable& val) const
{
// size
const size_t len = this->readInt32();
const size_t fd_count = this->readInt32();
// payload
void const* buf = this->readInplace(PAD_SIZE(len));
if (buf == NULL)
return BAD_VALUE;
int* fds = NULL;
if (fd_count) {
fds = new int[fd_count];
}
status_t err = NO_ERROR;
for (size_t i=0 ; i<fd_count && err==NO_ERROR ; i++) {
fds[i] = dup(this->readFileDescriptor());
if (fds[i] < 0) err = BAD_VALUE;
}
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
err = val.unflatten(buf, len, fds, fd_count);
}
if (fd_count) {
delete [] fds;
}
return err;
}
const flat_binder_object* Parcel::readObject(bool nullMetaData) const
{
const size_t DPOS = mDataPos;
if ((DPOS+sizeof(flat_binder_object)) <= mDataSize) {
const flat_binder_object* obj
= reinterpret_cast<const flat_binder_object*>(mData+DPOS);
mDataPos = DPOS + sizeof(flat_binder_object);
if (!nullMetaData && (obj->cookie == NULL && obj->binder == NULL)) {
// When transferring a NULL object, we don''t write it into
// the object list, so we don''t want to check for it when
// reading.
LOGV("readObject Setting data pos of %p to %d/n", this, mDataPos);
return obj;
}
// Ensure that this object is valid...
size_t* const OBJS = mObjects;
const size_t N = mObjectsSize;
size_t opos = mNextObjectHint;
if (N > 0) {
LOGV("Parcel %p looking for obj at %d, hint=%d/n",
this, DPOS, opos);
// Start at the current hint position, looking for an object at
// the current data position.
if (opos < N) {
while (opos < (N-1) && OBJS[opos] < DPOS) {
opos++;
}
} else {
opos = N-1;
}
if (OBJS[opos] == DPOS) {
// Found it!
LOGV("Parcel found obj %d at index %d with forward search",
this, DPOS, opos);
mNextObjectHint = opos+1;
LOGV("readObject Setting data pos of %p to %d/n", this, mDataPos);
return obj;
}
// Look backwards for it...
while (opos > 0 && OBJS[opos] > DPOS) {
opos--;
}
if (OBJS[opos] == DPOS) {
// Found it!
LOGV("Parcel found obj %d at index %d with backward search",
this, DPOS, opos);
mNextObjectHint = opos+1;
LOGV("readObject Setting data pos of %p to %d/n", this, mDataPos);
return obj;
}
}
LOGW("Attempt to read object from Parcel %p at offset %d that is not in the object list",
this, DPOS);
}
return NULL;
}
void Parcel::closeFileDescriptors()
{
size_t i = mObjectsSize;
if (i > 0) {
//LOGI("Closing file descriptors for %d objects...", mObjectsSize);
}
while (i > 0) {
i--;
const flat_binder_object* flat
= reinterpret_cast<flat_binder_object*>(mData+mObjects[i]);
if (flat->type == BINDER_TYPE_FD) {
//LOGI("Closing fd: %ld/n", flat->handle);
close(flat->handle);
}
}
}
const uint8_t* Parcel::ipcData() const
{
return mData;
}
size_t Parcel::ipcDataSize() const
{
return (mDataSize > mDataPos ? mDataSize : mDataPos);
}
const size_t* Parcel::ipcObjects() const
{
return mObjects;
}
size_t Parcel::ipcObjectsCount() const
{
return mObjectsSize;
}
void Parcel::ipcSetDataReference(const uint8_t* data, size_t dataSize,
const size_t* objects, size_t objectsCount, release_func relFunc, void* relCookie)
{
freeDataNoInit();
mError = NO_ERROR;
mData = const_cast<uint8_t*>(data);
mDataSize = mDataCapacity = dataSize;
//LOGI("setDataReference Setting data size of %p to %lu (pid=%d)/n", this, mDataSize, getpid());
mDataPos = 0;
LOGV("setDataReference Setting data pos of %p to %d/n", this, mDataPos);
mObjects = const_cast<size_t*>(objects);
mObjectsSize = mObjectsCapacity = objectsCount;
mNextObjectHint = 0;
mOwner = relFunc;
mOwnerCookie = relCookie;
scanForFds();
}
void Parcel::print(TextOutput& to, uint32_t flags) const
{
to << "Parcel(";
if (errorCheck() != NO_ERROR) {
const status_t err = errorCheck();
to << "Error: " << (void*)err << " /"" << strerror(-err) << "/"";
} else if (dataSize() > 0) {
const uint8_t* DATA = data();
to << indent << HexDump(DATA, dataSize()) << dedent;
const size_t* OBJS = objects();
const size_t N = objectsCount();
for (size_t i=0; i<N; i++) {
const flat_binder_object* flat
= reinterpret_cast<const flat_binder_object*>(DATA+OBJS[i]);
to << endl << "Object #" << i << " @ " << (void*)OBJS[i] << ": "
<< TypeCode(flat->type & 0x7f7f7f00)
<< " = " << flat->binder;
}
} else {
to << "NULL";
}
to << ")";
}
void Parcel::releaseObjects()
{
const sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
size_t i = mObjectsSize;
uint8_t* const data = mData;
size_t* const objects = mObjects;
while (i > 0) {
i--;
const flat_binder_object* flat
= reinterpret_cast<flat_binder_object*>(data+objects[i]);
release_object(proc, *flat, this);
}
}
void Parcel::acquireObjects()
{
const sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
size_t i = mObjectsSize;
uint8_t* const data = mData;
size_t* const objects = mObjects;
while (i > 0) {
i--;
const flat_binder_object* flat
= reinterpret_cast<flat_binder_object*>(data+objects[i]);
acquire_object(proc, *flat, this);
}
}
void Parcel::freeData()
{
freeDataNoInit();
initState();
}
void Parcel::freeDataNoInit()
{
if (mOwner) {
//LOGI("Freeing data ref of %p (pid=%d)/n", this, getpid());
mOwner(this, mData, mDataSize, mObjects, mObjectsSize, mOwnerCookie);
} else {
releaseObjects();
if (mData) free(mData);
if (mObjects) free(mObjects);
}
}
status_t Parcel::growData(size_t len)
{
size_t newSize = ((mDataSize+len)*3)/2;
return (newSize <= mDataSize)
? (status_t) NO_MEMORY
: continueWrite(newSize);
}
status_t Parcel::restartWrite(size_t desired)
{
if (mOwner) {
freeData();
return continueWrite(desired);
}
uint8_t* data = (uint8_t*)realloc(mData, desired);
if (!data && desired > mDataCapacity) {
mError = NO_MEMORY;
return NO_MEMORY;
}
releaseObjects();
if (data) {
mData = data;
mDataCapacity = desired;
}
mDataSize = mDataPos = 0;
LOGV("restartWrite Setting data size of %p to %d/n", this, mDataSize);
LOGV("restartWrite Setting data pos of %p to %d/n", this, mDataPos);
free(mObjects);
mObjects = NULL;
mObjectsSize = mObjectsCapacity = 0;
mNextObjectHint = 0;
mHasFds = false;
mFdsKnown = true;
return NO_ERROR;
}
status_t Parcel::continueWrite(size_t desired)
{
// If shrinking, first adjust for any objects that appear
// after the new data size.
size_t objectsSize = mObjectsSize;
if (desired < mDataSize) {
if (desired == 0) {
objectsSize = 0;
} else {
while (objectsSize > 0) {
if (mObjects[objectsSize-1] < desired)
break;
objectsSize--;
}
}
}
if (mOwner) {
// If the size is going to zero, just release the owner''s data.
if (desired == 0) {
freeData();
return NO_ERROR;
}
// If there is a different owner, we need to take
// posession.
uint8_t* data = (uint8_t*)malloc(desired);
if (!data) {
mError = NO_MEMORY;
return NO_MEMORY;
}
size_t* objects = NULL;
if (objectsSize) {
objects = (size_t*)malloc(objectsSize*sizeof(size_t));
if (!objects) {
mError = NO_MEMORY;
return NO_MEMORY;
}
// Little hack to only acquire references on objects
// we will be keeping.
size_t oldObjectsSize = mObjectsSize;
mObjectsSize = objectsSize;
acquireObjects();
mObjectsSize = oldObjectsSize;
}
if (mData) {
memcpy(data, mData, mDataSize < desired ? mDataSize : desired);
}
if (objects && mObjects) {
memcpy(objects, mObjects, objectsSize*sizeof(size_t));
}
//LOGI("Freeing data ref of %p (pid=%d)/n", this, getpid());
mOwner(this, mData, mDataSize, mObjects, mObjectsSize, mOwnerCookie);
mOwner = NULL;
mData = data;
mObjects = objects;
mDataSize = (mDataSize < desired) ? mDataSize : desired;
LOGV("continueWrite Setting data size of %p to %d/n", this, mDataSize);
mDataCapacity = desired;
mObjectsSize = mObjectsCapacity = objectsSize;
mNextObjectHint = 0;
} else if (mData) {
if (objectsSize < mObjectsSize) {
// Need to release refs on any objects we are dropping.
const sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
for (size_t i=objectsSize; i<mObjectsSize; i++) {
const flat_binder_object* flat
= reinterpret_cast<flat_binder_object*>(mData+mObjects[i]);
if (flat->type == BINDER_TYPE_FD) {
// will need to rescan because we may have lopped off the only FDs
mFdsKnown = false;
}
release_object(proc, *flat, this);
}
size_t* objects =
(size_t*)realloc(mObjects, objectsSize*sizeof(size_t));
if (objects) {
mObjects = objects;
}
mObjectsSize = objectsSize;
mNextObjectHint = 0;
}
// We own the data, so we can just do a realloc().
if (desired > mDataCapacity) {
uint8_t* data = (uint8_t*)realloc(mData, desired);
if (data) {
mData = data;
mDataCapacity = desired;
} else if (desired > mDataCapacity) {
mError = NO_MEMORY;
return NO_MEMORY;
}
} else {
mDataSize = desired;
LOGV("continueWrite Setting data size of %p to %d/n", this, mDataSize);
if (mDataPos > desired) {
mDataPos = desired;
LOGV("continueWrite Setting data pos of %p to %d/n", this, mDataPos);
}
}
} else {
// This is the first data. Easy!
uint8_t* data = (uint8_t*)malloc(desired);
if (!data) {
mError = NO_MEMORY;
return NO_MEMORY;
}
if(!(mDataCapacity == 0 && mObjects == NULL
&& mObjectsCapacity == 0)) {
LOGE("continueWrite: %d/%p/%d/%d", mDataCapacity, mObjects, mObjectsCapacity, desired);
}
mData = data;
mDataSize = mDataPos = 0;
LOGV("continueWrite Setting data size of %p to %d/n", this, mDataSize);
LOGV("continueWrite Setting data pos of %p to %d/n", this, mDataPos);
mDataCapacity = desired;
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
void Parcel::initState()
{
mError = NO_ERROR;
mData = 0;
mDataSize = 0;
mDataCapacity = 0;
mDataPos = 0;
LOGV("initState Setting data size of %p to %d/n", this, mDataSize);
LOGV("initState Setting data pos of %p to %d/n", this, mDataPos);
mObjects = NULL;
mObjectsSize = 0;
mObjectsCapacity = 0;
mNextObjectHint = 0;
mHasFds = false;
mFdsKnown = true;
mOwner = NULL;
}
void Parcel::scanForFds() const
{
bool hasFds = false;
for (size_t i=0; i<mObjectsSize; i++) {
const flat_binder_object* flat
= reinterpret_cast<const flat_binder_object*>(mData + mObjects[i]);
if (flat->type == BINDER_TYPE_FD) {
hasFds = true;
break;
}
}
mHasFds = hasFds;
mFdsKnown = true;
}
}; // namespace android本文的源码使用的是 Android 2.1 版本。

Android 进阶 ——Android 跨进程通讯机制之 Binder、IBinder、Parcel、AIDL
前言
Binder 机制是 Android 系统提供的跨进程通讯机制,这篇文章开始会从 Linux 相关的基础概念知识开始介绍,从基础概念知识中引出 Binder 机制,归纳 Binder 机制与 Linux 系统的跨进程机制的优缺点,接着分析 Binder 的通信模型和原理,而 Binder 机制最佳体现就是 AIDL,所以在后面会分析 AIDL 的实现原理,最后简单的提下 AMS 的 Binder 体系,整篇文章中间会穿插有 IBinder、Binder、Parcel 的介绍,整篇文章阅读难度不大,不会涉及到 framework 层的 Binder 原理,AIDL 部分需要有 AIDL 的使用基础
基础概念
基础概念部分介绍 Linux 的某些机制,主要想表达 Binder 驱动的出现的原因,如果对 Linux 熟悉的可以直接跳过这部分,看第五点即可
一、进程隔离
出于安全考虑,一个进程不能操作另一个进程的数据,进而一个操作系统必须具备进程隔离这个特性。在 Linux 系统中,虚拟内存机制为每个进程分配了线性连续的内存空间,操作系统将这种虚拟内存空间映射到物理内存空间,每个进程有自己的虚拟内存空间,进而不能操作其他进程的内存空间,每个进程只能操作自己的虚拟内存空间,只有操作系统才有权限操作物理内存空间。进程隔离保证了每个进程的内存安全,但是在大多数情形下,不同进程间的数据通讯是不可避免的,因此操作系统必须提供跨进程通信机制
二、用户空间和内核空间
- 用户空间:表示进程运行在一个特定的操作模式中,没有接触物理内存或设备的权限
- 内核空间:表示独立于普通的应用程序,可以访问受保护的内存空间,也有访问底层硬件设备的所有权限
三、系统调用 / 内核态 / 用户态
抽象来看,操作系统中安全边界的概念就像环路的概念一样 (前提是系统支持这种特性),一个环上持有一个特定的权限组,Intel 支持四层环,但是 Linux 只使用了其中的两环 (0 号环持有全部权限,3 号环持有最少权限,1 号和 2 号环未使用),系统进程运行在 1 号环,用户进程运行在3号环,如果一个用户进程需要其他高级权限,其必须从3号环过渡成0号环,过渡需要通过一个安全参数检查的网关,这种过渡被称为系统调用,在执行过程中会产生一定数量的计算开销。所以,用户空间要访问内核空间的唯一方式就是系统调用 (System Call)
四、内核模块 / 驱动
通过系统调用,用户空间可以访问内核空间,它是怎么做到访问内核空间的呢?Linux 的动态可加载内核模块机制解决了这个问题,模块是具有独立功能的程序,它可以被单独编译,但不能独立运行。这样,Android 系统可以通过添加一个内核模块运行在内核空间,用户进程之间的通过这个模块作为桥梁,就可以完成通信了。在 Android 系统中,这个运行在内核空间的,负责各个用户进程通过 Binder 通信的内核模块叫做 Binder 驱动
五、简单的总结
将前面的所有概念连接起来理解就会非常好消化知识点:
- Linux 的虚拟内存机制导致内存的隔离,进而导致进程隔离
- 进程隔离的出现导致对内存的操作被划分为用户空间和内核空间
- 用户空间需要跨权限去访问内核空间,必须使用系统调用去实现
- 系统调用需要借助内核模块 / 驱动去完成
前三步决定了进程间通讯需要借助内核模块 / 驱动去实现,而 Binder 驱动就是内核模块 / 驱动中用来实现进程间通讯的
为什么要用 Binder
Linux 提供有管道、消息队列、信号量、内存共享、套接字等跨进程方式,那为什么 Android 要选择 Binder 另起炉灶呢?
一、传输性能好
- Socket:是一个通用接口,导致其传输效率低,开销大
- 共享内存:虽然在传输时不需要拷贝数据,但其控制机制复杂
- Binder:复杂数据类型传递可以复用内存,需要拷贝 1 次数据
- 管道和消息队列:采用存储转发方式,至少需要拷贝 2 次数据,效率低
二、安全性高
- 传统的进程:通信方式对于通信双方的身份并没有做出严格的验证,只有在上层协议上进行架设
- Binder 机制:从协议本身就支持对通信双方做身份校检,因而大大提升了安全性
Binder 通信模型
首先在理解模型之前先熟悉这几个概念:
- Client 进程:跨进程通讯的客户端(运行在某个进程)
- Server 进程:跨进程通讯的服务端(运行在某个进程)
- Binder 驱动:跨进程通讯的介质
- ServiceManager:跨进程通讯中提供服务的注册和查询(运行在 System 进程)
这里只是个简单的模型而已,只需理解模型的通讯流程:
- Server 端通过 Binder 驱动在 ServiceManager 中注册
- Client 端通过 Binder 驱动获取 ServiceManager 中注册的 Server 端
- Client 端通过 Binder 驱动和 Server 端进行通讯
Binder 通信原理
理解完模型流程之后,开始理解模型的通讯原理:
- Service 端通过 Binder 驱动在 ServiceManager 的查找表中注册 Object 对象的 add 方法
- Client 端通过 Binder 驱动在 ServiceManager 的查找表中找到 Object 对象的 add 方法,并返回 proxy 对象的 add 方法,add 方法是个空实现,proxy 对象也不是真正的 Object 对象,是通过 Binder 驱动封装好的代理类的 add 方法
- 当 Client 端调用 add 方法时,Client 端会调用 proxy 对象的 add 方法,通过 Binder 驱动去请求 ServiceManager 来找到 Service 端真正对象,然后调用 Service 端的 add 方法
Binder 对象和 Binder 驱动
- Binder 对象:Binder 机制中进行进程间通讯的对象,对于 Service 端为 Binder 本地对象,对于 Client 端为 Binder 代理对象
- Binder 驱动:Binder 机制中进行进程间通讯的介质,Binder 驱动会对具有跨进程传递能力的对象做特殊处理,自动完成代理对象和本地对象的转换
由于 Binder 驱动会对具有跨进程传递能力的对象做特殊处理,自动完成代理对象和本地对象的转换,因此在驱动中保存了每一个跨越进程的 Binder 对象的相关信息,Binder 本地对象(或 Binder 实体)保存在 binder_node 的数据结构,Binder 代理对象(或 Binder 引用 / 句柄)保存在 binder_ref 的数据结构
Java 层的 Binder
- Binder 类:是 Binder 本地对象
- BinderProxy 类:是 Binder 类的内部类,它代表远程进程的 Binder 对象的本地代理
- Parcel 类:是一个容器,它主要用于存储序列化数据,然后可以通过 Binder 在进程间传递这些数据
- IBinder 接口:代表一种跨进程传输的能力,实现这个接口,就能将这个对象进行跨进程传递
- IInterface 接口:client 端与 server 端的调用契约,实现这个接口,就代表远程 server 对象具有什么能力,因为 IInterface 接口的 asBinder 方法的实现可以将 Binder 本地对象或代理对象进行返回
Binder 类和 BinderProxy 类都继承自 IBinder,因而都具有跨进程传输的能力,在跨越进程的时候,Binder 驱动会自动完成这两个对象的转换。IBinder 是远程对象的基本接口,是为高性能而设计的轻量级远程调用机制的核心部分,但它不仅用于远程调用,也用于进程内调用。IBinder 接口定义了与远程对象交互的协议,建议不要直接实现这个接口,而应该从 Binder 派生。Binder 实现了 IBinder 接口,但是一般不需要直接实现此类,而是跟据你的需要由开发包中的工具生成,这个工具叫 aidi。你通过 aidi 语言定义远程对象的方法,然后用 aidi 工具生成 Binder 的派生类,然后使用它
AIDL
由于编译工具会给我们生成一个 Stub 的静态内部类,这个类继承了 Binder, 说明它是一个 Binder 本地对象,它实现了 IInterface 接口,表明它具有远程 Server 承诺给 Client 的能力
一、服务端
在服务端中,我们只要实现 Stub 抽象类,和实现其方法即可
private IBinder myS = new IMyAidlInterface.Stub() {
@Override
public void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, String aString) throws RemoteException {
}
@Override
public int add(int num1, int num2) throws RemoteException {
Log.i("Hensen", "从客户端发来的AIDL请求:num1->" + num1 + "::num2->" + num2);
return num1 + num2;
}
}; - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
二、客户端
在客户端中,可以通过 bindService 的回调中获取 AIDL 接口
private ServiceConnection conn = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
iMyAidlInterface = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service);
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
iMyAidlInterface = null;
}
};
public void add(View view) {
try {
int res = iMyAidlInterface.add(1, 2);
Log.i("Hensen", "从服务端调用成功的结果:" + res);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
梳理客户端的调用流程:
- 调用 Stub.asInterface 获取 BinderProxy 对象
- 调用 BinderProxy 对象的 add 方法
三、分析原理
1、Stub
Stub 类继承自 Binder,意味着这个 Stub 其实自己是一个 Binder 本地对象,然后实现了 IMyAidlInterface 接口,IMyAidlInterface 本身是一个 IInterface,因此他携带某种客户端需要的能力(这里是方法 add)。此类有一个内部类 Proxy,也就是 Binder 代理对象
/*
* This file is auto-generated. DO NOT MODIFY.
* Original file: D:\\workspace5\\Boke\\app\\src\\main\\aidl\\com\\handsome\\boke\\IMyAidlInterface.aidl
*/
package com.handsome.boke;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
public interface IMyAidlInterface extends android.os.IInterface {
/**
* Local-side IPC implementation stub class.
*/
public static abstract class Stub extends android.os.Binder implements com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface {
private static final java.lang.String DESCRIPTOR = "com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface";
/**
* Construct the stub at attach it to the interface.
*/
public Stub() {
this.attachInterface(this, DESCRIPTOR);
}
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface))) {
return ((com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface) iin);
}
return new com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return this;
}
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: {
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_basicTypes: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
int _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readInt();
long _arg1;
_arg1 = data.readLong();
boolean _arg2;
_arg2 = (0 != data.readInt());
float _arg3;
_arg3 = data.readFloat();
double _arg4;
_arg4 = data.readDouble();
java.lang.String _arg5;
_arg5 = data.readString();
this.basicTypes(_arg0, _arg1, _arg2, _arg3, _arg4, _arg5);
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_add: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
int _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readInt();
int _arg1;
_arg1 = data.readInt();
int _result = this.add(_arg0, _arg1);
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(_result);
return true;
}
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
}
private static class Proxy implements com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface {
private android.os.IBinder mRemote;
Proxy(android.os.IBinder remote) {
mRemote = remote;
}
@Override
public android.os.IBinder asBinder() {
return mRemote;
}
public java.lang.String getInterfaceDescriptor() {
return DESCRIPTOR;
}
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
@Override
public void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, java.lang.String aString) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeInt(anInt);
_data.writeLong(aLong);
_data.writeInt(((aBoolean) ? (1) : (0)));
_data.writeFloat(aFloat);
_data.writeDouble(aDouble);
_data.writeString(aString);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_basicTypes, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
}
@Override
public int add(int num1, int num2) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
int _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeInt(num1);
_data.writeInt(num2);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_add, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readInt();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
}
}
static final int TRANSACTION_basicTypes = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 0);
static final int TRANSACTION_add = (android.os.IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION + 1);
}
/**
* Demonstrates some basic types that you can use as parameters
* and return values in AIDL.
*/
public void basicTypes(int anInt, long aLong, boolean aBoolean, float aFloat, double aDouble, java.lang.String aString) throws android.os.RemoteException;
public int add(int num1, int num2) throws android.os.RemoteException;
} - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
- 112
- 113
- 114
- 115
- 116
- 117
- 118
- 119
- 120
- 121
- 122
- 123
- 124
- 125
- 126
- 127
- 128
- 129
- 130
- 131
- 132
- 133
- 134
- 135
- 136
- 137
- 138
- 139
- 140
- 141
- 142
- 143
- 144
- 145
- 146
- 147
- 148
- 149
- 150
- 151
- 152
- 153
2、asInterface
当客户端 bindService 的 onServiceConnecttion 的回调里面,通过 asInterface 方法获取远程的 service 的。其函数的参数 IBinder 类型的 obj,这个对象是驱动给我们的,如果是 Binder 本地对象,那么它就是 Binder 类型,如果是 Binder 代理对象,那就是 BinderProxy 类型。asInterface 方法中会调用 queryLocalInterface,查找 Binder 本地对象,如果找到,说明 Client 和 Server 都在同一个进程,这个参数直接就是本地对象,直接强制类型转换然后返回,如果找不到,说明是远程对象那么就需要创建 Binder 代理对象,让这个 Binder 代理对象实现对于远程对象的访问
/**
* Cast an IBinder object into an com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface interface,
* generating a proxy if needed.
*/
public static com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface asInterface(android.os.IBinder obj) {
if ((obj == null)) {
return null;
}
android.os.IInterface iin = obj.queryLocalInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
if (((iin != null) && (iin instanceof com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface))) {
return ((com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface) iin);
}
return new com.handsome.boke.IMyAidlInterface.Stub.Proxy(obj);
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
3、add
当客户端调用 add 方法时,首先用 Parcel 把数据序列化,然后调用 mRemote.transact 方法,mRemote 就是 new Stub.Proxy (obj) 传进来的,即 BinderProxy 对象
@Override
public int add(int num1, int num2) throws android.os.RemoteException {
android.os.Parcel _data = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
android.os.Parcel _reply = android.os.Parcel.obtain();
int _result;
try {
_data.writeInterfaceToken(DESCRIPTOR);
_data.writeInt(num1);
_data.writeInt(num2);
mRemote.transact(Stub.TRANSACTION_add, _data, _reply, 0);
_reply.readException();
_result = _reply.readInt();
} finally {
_reply.recycle();
_data.recycle();
}
return _result;
} - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
4、transact
BinderProxy 的 transact 方法是 native 方法,它的实现在 native 层,它会去借助 Binder 驱动完成数据的传输,当完成数据传输后,会唤醒 Server 端,调用了 Server 端本地对象的 onTransact 函数
public native boolean transact(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply,
int flags) throws RemoteException;- 1
- 2
5、onTransact
在 Server 进程里面,onTransact 根据调用 code 会调用相关函数,接着将结果写入 reply 并通过 super.onTransact 返回给驱动,驱动唤醒挂起的 Client 进程里面的线程并将结果返回
@Override
public boolean onTransact(int code, android.os.Parcel data, android.os.Parcel reply, int flags) throws android.os.RemoteException {
switch (code) {
case INTERFACE_TRANSACTION: {
reply.writeString(DESCRIPTOR);
return true;
}
case TRANSACTION_add: {
data.enforceInterface(DESCRIPTOR);
int _arg0;
_arg0 = data.readInt();
int _arg1;
_arg1 = data.readInt();
int _result = this.add(_arg0, _arg1);
reply.writeNoException();
reply.writeInt(_result);
return true;
}
}
return super.onTransact(code, data, reply, flags);
} - 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
AMS 的 Binder 体系
AMS 是 Android 中最核心的服务,主要负责系统中四大组件的启动、切换、调度及应用进程的管理和调度等工作,从图中可以看出:
| AMS | Binder 角色 |
|---|---|
| IActivityManager | IInterface |
| ActivityManagerNative | Binder 本地对象 |
| ActivityManagerProxy | Binder 代理对象 |
| ActivityManagerService | Service 端 |
| ActivityManager | 普通管理类 |
结语
这里只是简单的理解下 Binder 机制的基本原理,后续有时间会研究 framework 层的知识,如果有兴趣的同学可以不依赖 AIDL 工具,手写远程 Service 完成跨进程通信,这样就可以加深对 AIDL 和 Binder 的理解,个人觉得这样是最好的记忆方式,一起来写吧

DHH 锐评 “打包工具”:前端根本不需要构建 (No Build)

继 “移除 TypeScript” 后,Ruby on Rails 作者 DHH 近日又在公开场合发表了一番 “暴论”—— 称最快的打包工具就是没有打包 (No Build),有了 HTTP/2 以及浏览器原生支持 ES Modules ,前端根本不需要构建。
在上周举办的 Rails World 大会上,DHH 说道:“最先进的(打包)技术不再是寻找更复杂的方法来构建 JavaScript 或 CSS,因为前端根本不需要构建。现在可以依靠 HTTP/2 和对 import map 的普遍支持来避免打包。”
via https://twitter.com/dhh/status/1712145950397841826
对于 DHH 提出的「No Build」,Vercel CTO Malte Ubl 称他们已尝试过,结果是行不通。因为在 HTTP2 中,每个请求的开销仍然非常大,并且存在并发限制,此外还会出现瀑布流和低效压缩。 目前,“打包” 对于高性能网站来说是无法绕过的。
via https://twitter.com/cramforce/status/1712265070213050390
DHH 不认可 Malte Ubl 所说的 “行不通”。他说道,这就是技术讨论的奇怪之处。即便已经有案例证明项目能完成大规模任务(如 Rails 之于 Shopify),但人们也会声称它不能进行扩展。或者已顺利使用某种方法多年(如 no build JS 之于 HEY 网站),也会有人说这套 “行不通”。
最后,DHH 展示了其公司主站 https://www.hey.com/world/ 的性能表现。他表示 HEY 主要应用运行的 JavaScript 代码没有经过构建。
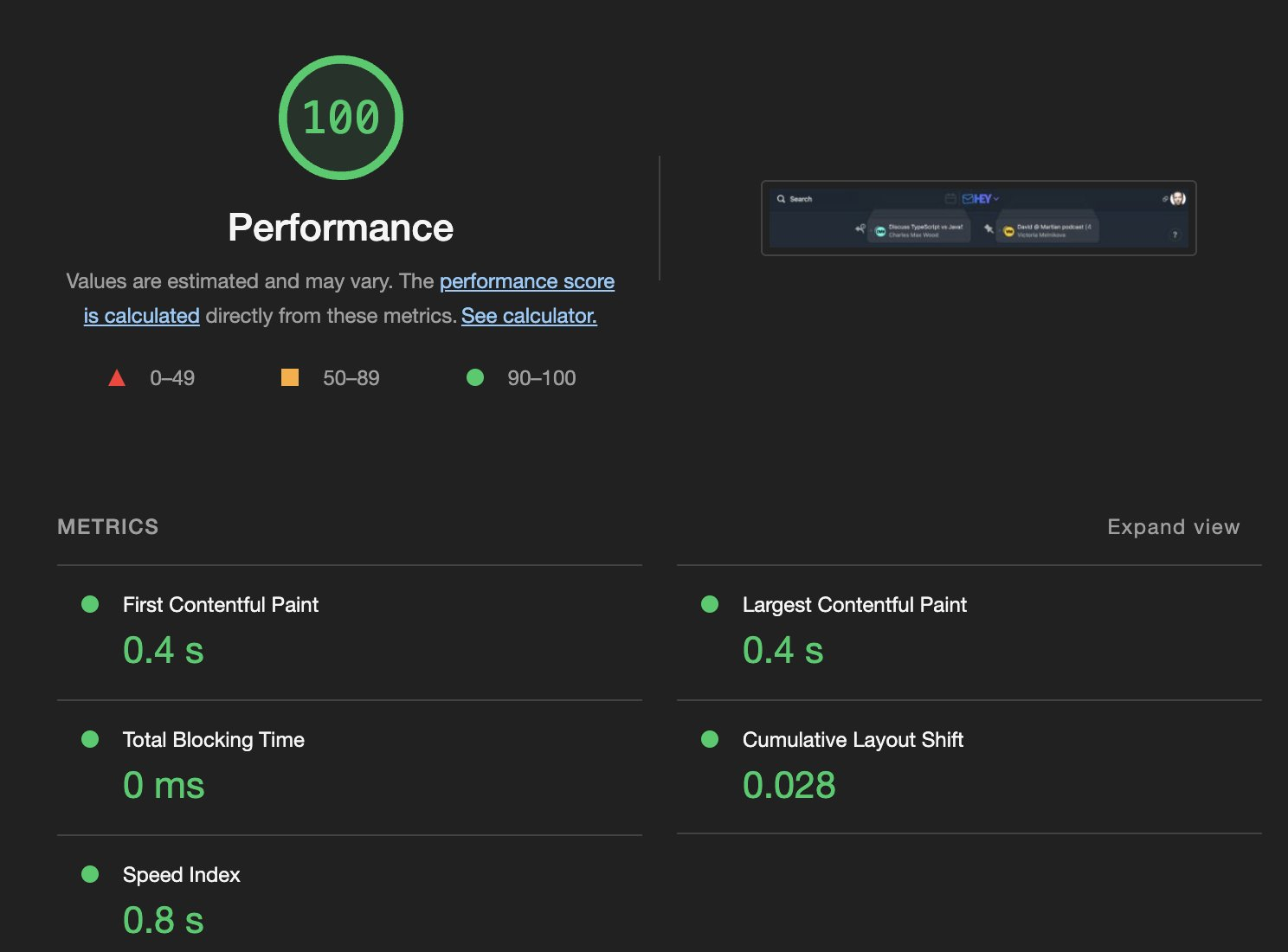
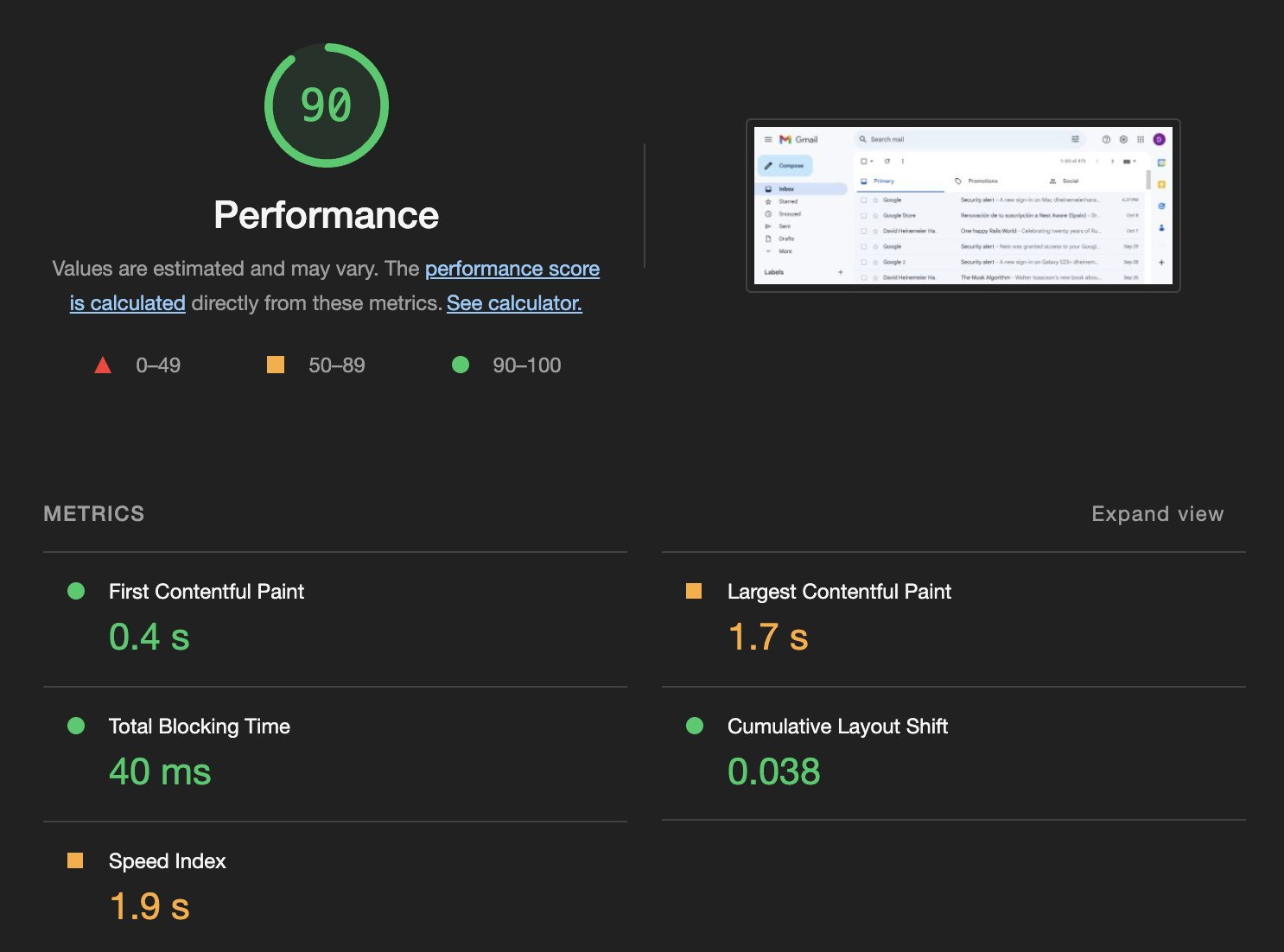

esbuild, 一个用 GO 语言写的 Javascript 打包工具,比 Webpack 快接近 100 倍
如题所述,esbuild 是一个用 Go 语言编写的用于打包,压缩 Javascript 代码的工具库。它最突出的特点就是打包速度极快 (extremely fast),下图是 esbuild 跟 webpack, rollup, Parcel 等打包工具打包效率的一个 benchmark:
图片取自 esbuild Github 仓库。
为什么它能做到那么快?
有以下几个原因:
- 它是用 Go 语言编写的,该语言可以编译为本地代码
- 解析,生成最终打包文件和生成 source maps 的操作全部完全并行化
- 无需昂贵的数据转换,只需很少的几步即可完成所有操作
- 该库以提高编译速度为编写代码时的第一原则,并尽量避免不必要的内存分配
更多详细介绍,详见 Breword 翻译的 esbuild 官方文档:http://docs.breword.com/evanw...
该文档同时提供中英双语版本供查看,可通过右下角切换器进行切换。
友情提示:
esbuild 目前在 Github 上已经拥有超过 8k stars,且它要解决的是当前前端开发中一个非常棘手及必要的问题,个人认为是一个非常有潜力的项目,大家可以踊跃试用、参与贡献、关注。
文档中还包含 esbuild 的整体架构详解及架构图,如有对其内部实现感兴趣或想要参与贡献代码的朋友来说,非常值得一看。
最后,该文档翻译由 Breword 驱动:https://www.breword.com/proje...
关于飘刃 0.2.1 发布,比 Parcel 更易上手的极速 WEB 打包工具和飘刀加速器怎么使用效果最佳的介绍已经告一段落,感谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于Android 中的 Parcel 机制 (上)、Android 进阶 ——Android 跨进程通讯机制之 Binder、IBinder、Parcel、AIDL、DHH 锐评 “打包工具”:前端根本不需要构建 (No Build)、esbuild, 一个用 GO 语言写的 Javascript 打包工具,比 Webpack 快接近 100 倍的相关信息,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:













