对于想了解禁用仅对Elasticsearch上的特定索引创建动态映射?的读者,本文将提供新的信息,我们将详细介绍禁用索引是什么意思,并且为您提供关于ElasticSearch动态映射删除特殊字符和空格
对于想了解禁用仅对Elasticsearch上的特定索引创建动态映射?的读者,本文将提供新的信息,我们将详细介绍禁用索引是什么意思,并且为您提供关于Elastic Search动态映射删除特殊字符和空格、Elasticsearch 2.3.0 索引映射管理、Elasticsearch CentOS6.5下安装ElasticSearch6.2.4+elasticsearch-head+Kibana、Elasticsearch Dynamic Mapping(动态映射机制)的有价值信息。
本文目录一览:- 禁用仅对Elasticsearch上的特定索引创建动态映射?(禁用索引是什么意思)
- Elastic Search动态映射删除特殊字符和空格
- Elasticsearch 2.3.0 索引映射管理
- Elasticsearch CentOS6.5下安装ElasticSearch6.2.4+elasticsearch-head+Kibana
- Elasticsearch Dynamic Mapping(动态映射机制)

禁用仅对Elasticsearch上的特定索引创建动态映射?(禁用索引是什么意思)
我正在尝试仅针对特定索引而不是对所有索引禁用动态映射创建。由于某种原因,我无法将 默认 映射与’dynamic’:’false’
放在一起。因此,在这里我看到了两个选项:
- 指定属性 “index.mapper.dynamic” 文件 elasticsearch.yml 。
- 将 “ index.mapper.dynamic” 放在索引创建时,如此处https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/setup.html#kibana-dynamic-mapping所述
第一个选项只能接受以下值:true,false和strict。所以没有办法像我们用的特性模式做来指定具体指标的子集(
“action.auto_create_index”
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/docs-
index_.html#索引创建)。
第二种选择是行不通的。我已经创建了索引
POST http://localhost:9200/test_idx/{ "settings" : { "mapper" : { "dynamic" : false } }, "mappings" : { "test_type" : { "properties" : { "field1" : { "type" : "string" } } } }}然后检查索引设置:
GET http://localhost:9200/test_idx/_settings { "test_idx" : { "settings" : { "index" : { "mapper" : { "dynamic" : "false" }, "creation_date" : "1445440252221", "number_of_shards" : "1", "number_of_replicas" : "0", "version" : { "created" : "1050299" }, "uuid" : "5QSYSYoORNqCXtdYn51XfA" } } }}和映射:
GET http://localhost:9200/test_idx/_mapping{ "test_idx" : { "mappings" : { "test_type" : { "properties" : { "field1" : { "type" : "string" } } } } }}到目前为止,到目前为止,让我们使用未声明的字段索引文档:
POST http://localhost:9200/test_idx/test_type/1{ "field1" : "it''s ok, field must be in mapping and in source", "somefield" : "but this field must be in source only, not in mapping"}然后,我再次检查了映射:
GET http://localhost:9200/test_idx/_mapping{ "test_idx" : { "mappings" : { "test_type" : { "properties" : { "field1" : { "type" : "string" }, "somefield" : { "type" : "string" } } } } }}如您所见,无论索引设置为“ dynamic”,映射都将扩展:false。我也尝试完全按照文档中的描述创建索引
PUT http://localhost:9200/test_idx{ "index.mapper.dynamic": false}但有相同的行为。
也许我错过了什么?
在此先多谢!
答案1
小编典典您快到了:该值需要设置为strict。正确的用法如下:
PUT /test_idx{ "mappings": { "test_type": { "dynamic":"strict", "properties": { "field1": { "type": "string" } } } }}再进一步说明一下,如果您想甚至禁止创建新类型,不仅要禁止该索引中的字段,请使用以下命令:
PUT /test_idx{ "mappings": { "_default_": { "dynamic": "strict" }, "test_type": { "properties": { "field1": { "type": "string" } } } }}没有_default_模板:
PUT /test_idx{ "settings": { "index.mapper.dynamic": false }, "mappings": { "test_type": { "dynamic": "strict", "properties": { "field1": { "type": "string" } } } }}
Elastic Search动态映射删除特殊字符和空格
如何解决Elastic Search动态映射删除特殊字符和空格?
使用带动态映射的Elasticsearch作为模式是动态的。
对于每个字符串字段,我都需要进行聚合,这可以通过fieldname.keyword上的条款聚合来实现
我还需要在字段上进行搜索,但是查询字符串与原始值不同,为了使其与网址兼容而对其进行了标准化
say:Mac和Cheese-> mac-and-cheese(应仅返回Mac和Cheese,仅Mac和Cheese)不应返回。表示在规范化版本上进行精确搜索。
如何使用动态模板实现?
解决方法
暂无找到可以解决该程序问题的有效方法,小编努力寻找整理中!
如果你已经找到好的解决方法,欢迎将解决方案带上本链接一起发送给小编。
小编邮箱:dio#foxmail.com (将#修改为@)

Elasticsearch 2.3.0 索引映射管理
增加映射
API允许你向索引(index)添加文档类型(type),或者向文档类型(type)中添加字段(field)。
PUT secisland
{
"mappings": {
"log": {
"properties": {
"message": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}
}
}添加索引名为secisland,文档类型为log,其中包含字段message,字段类型是字符串。
PUT secisland/_mapping/user
{
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}向已经存在的索引secisland添加文档类型为user,包含字段name,字段类型是字符串。
PUT secisland/_mapping/log
{
"properties": {
"user_name": {
"type": "string"
}
}
}已经存在的索引secisland,文档类型为log,添加新的字段user_name,字段类型是字符串。
多个索引设置映射,可以一次向多个索引添加文档类型
PUT /{index}/_mapping/{type}
{ body }{index}可以有多种方式,逗号分隔,比如test1,test2,test3
_all,表示所有索引,通配符,*表示所有,test*表示以test开头
{type}需要添加或更新的文档类型
{body}需要添加的字段或字段类型
更新字段映射
在一般情况下,对现有字段的映射不会更新。对这个规则有一些例外。例如:
新的属性被添加到对象数据类型的字段。
新的多域字段被添加到现有的字段。
doc_values可以被禁用。
增加了ignore_above参数。
例如:
请求:PUT my_index
参数:
{
"mappings": {
"user": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"properties": {
"first": {
"type": "string"
}
}
},
"user_id": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
}
}
}
}
}user的第一个name属性是对象数据类型(Object datatype)字段,对上个索引进行修改:
请求:PUT my_index/_mapping/user
参数:
{
"properties": {
"name": {
"properties": {
"last": {
"type": "string"
}
}
},
"user_id": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed",
"ignore_above": 100
}
}
}修改映射,对第一个对象数据类型增加了一个熟悉是last。修改了user_id, 通过设置ignore_above使默认的更新为0。
不同类型之间的冲突
在同一个索引的不同类型(type)中,相同名称的字段中必须有相同的映射,因为他们内部是在同一个领域内,如果试图在这种情况下更新映射参数,系统将会抛出异常。除非在更新的时候指定 update_all_types参数。在这种情况下它将更新在相同的指标参数在所有同名的字段。
例如:
请求:PUT my_index
参数:
{
"mappings": {
"type_one": {
"properties": {
"text": {
"type": "string",
"analyzer": "standard"
}
}
},
"type_two": {
"properties": {
"text": {
"type": "string",
"analyzer": "standard"
}
}
}
}
}修改映射
请求:PUT my_index/_mapping/type_one
参数:
{
"properties": {
"text": {
"type": "string",
"analyzer": "standard",
"search_analyzer": "whitespace"
}
}
}这个时候会抛出异常,然后增加参数,update_all_types,这个时候会同时更新两个类型。
请求:PUT my_index/_mapping/type_one?update_all_types
{
"properties": {
"text": {
"type": "string",
"analyzer": "standard",
"search_analyzer": "whitespace"
}
}
}获取映射
获取文档映射接口允许通过索引或者索引和类型来检索。
curl -XGET ''http://localhost:9200/twitter/_mapping/tweet''
系统同时支持获取多个索引和类型的语法:
获取文档映射接口一次可以获取多个索引或文档映射类型。该接口通常是如下格式:
host:port/{index}/_mapping/{type},{index}和{type}可以接受逗号(,)分隔符,也可以使用_all来表示全部索引。如下所示:
curl -XGET ''http://localhost:9200/_mapping/twitter,kimchy''
curl -XGET ''http://localhost:9200/_all/_mapping/tweet,book''
第一个省略_all,第二个使用_all都是表示全部索引。也就是说,下面两个是等价的:
curl -XGET ''http://localhost:9200/_all/_mapping''
curl -XGET ''http://localhost:9200/_mapping''
获取字段映射
获取文档字段接口允许你检索一个或多个字段。这个用来检索想要检索的字段,而不是某个索引或者文档类型的全部内容。
这段请求只返回字段为text的内容:
curl -XGET ''http://localhost:9200/twitter/_mapping/tweet/field/text''
响应结果如下(假定text为String类型)
{
"twitter": {
"tweet": {
"text": {
"full_name": "text",
"mapping": {
"text": { "type": "string" }
}
}
}
}
}获取多索引和类型的字段映射。
获取文档字段映射接口一次可以获取多个索引或文档映射类型。该接口通常是如下格式:host:port/{index}/{type}/_mapping/field/{field}
{index},{type},{field}可以使用逗号(,)分隔,也可以使用*作为通配符{type},{field}可以使用逗号(,)分隔。
其中{index}可以使用_all表示全部索引,示例如下:
curl -XGET ''http://localhost:9200/twitter,kimchy/_mapping/field/message''
curl -XGET ''http://localhost:9200/_all/_mapping/tweet,book/field/message,user.id''
curl -XGET ''http://localhost:9200/_all/_mapping/tw*/field/*.id''
指定字段
获取文档字段接口,可以使用逗号(,)分隔符或者通配符(*)。
如下文档示例,如果只使用字段名id会产生歧义。
{
"article": {
"properties": {
"id": { "type": "string" },
"title": { "type": "string"},
"abstract": { "type": "string"},
"author": {
"properties": {
"id": { "type": "string" },
"name": { "type": "string" }
}
}
}
}
}如果想要表示author中的id,name,使用author.id,author.name。请求如下:
curl -XGET "http://localhost:9200/publications/_mapping/article/field/
author.id,abstract,author.name"
返回结果如下:
{
"publications": {
"article": {
"abstract": {
"full_name": "abstract",
"mapping": {
"abstract": { "type": "string" }
}
},
"author.id": {
"full_name": "author.id",
"mapping": {
"id": { "type": "string" }
}
},
"author.name": {
"full_name": "author.name",
"mapping": {
"name": { "type": "string" }
}
}
}
}
}判断类型是否存在
检查索引或文档类型是否存在
curl -XHEAD -i ''http://localhost:9200/twitter/tweet''
存在返回200,不存在返回404。
赛克蓝德(secisland)后续会逐步对Elasticsearch的最新版本的各项功能进行分析,近请期待。也欢迎加入secisland公众号进行关注。

Elasticsearch CentOS6.5下安装ElasticSearch6.2.4+elasticsearch-head+Kibana
CentOS6.5下安装ElasticSearch6.2.4
(1)配置JDK环境
配置环境变量
export JAVA_HOME="/opt/jdk1.8.0_144"
export PATH="$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH"
export CLASSPATH=".:$JAVA_HOME/lib"
(2)安装ElasticSearch6.2.4
下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/past-releases/elasticsearch-6-2-4
启动报错:
解决方式:
bin/elasticsearch -Des.insecure.allow.root=true
或者修改bin/elasticsearch,加上ES_JAVA_OPTS属性:
ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Des.insecure.allow.root=true"
再次启动: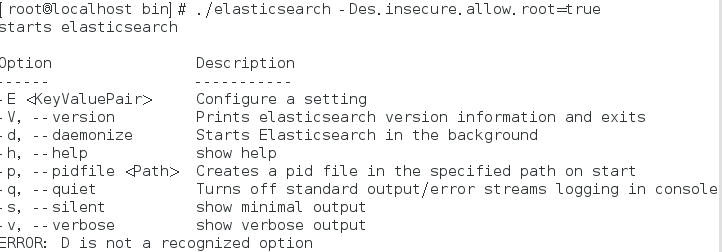
这是出于系统安全考虑设置的条件。由于ElasticSearch可以接收用户输入的脚本并且执行,为了系统安全考 虑,建议创建一个单独的用户用来运行ElasticSearch。
如果没有普通用户就要创建一个普通用户组和普通用户,下面介绍一下怎么创建用户组和普通用户
创建用户组和用户:
groupadd esgroup
useradd esuser -g esgroup -p espassword
更改elasticsearch文件夹及内部文件的所属用户及组:
cd /opt
chown -R esuser:esgroup elasticsearch-6.2.4
切换用户并运行:
su esuser
./bin/elasticsearch
再次启动显示已杀死: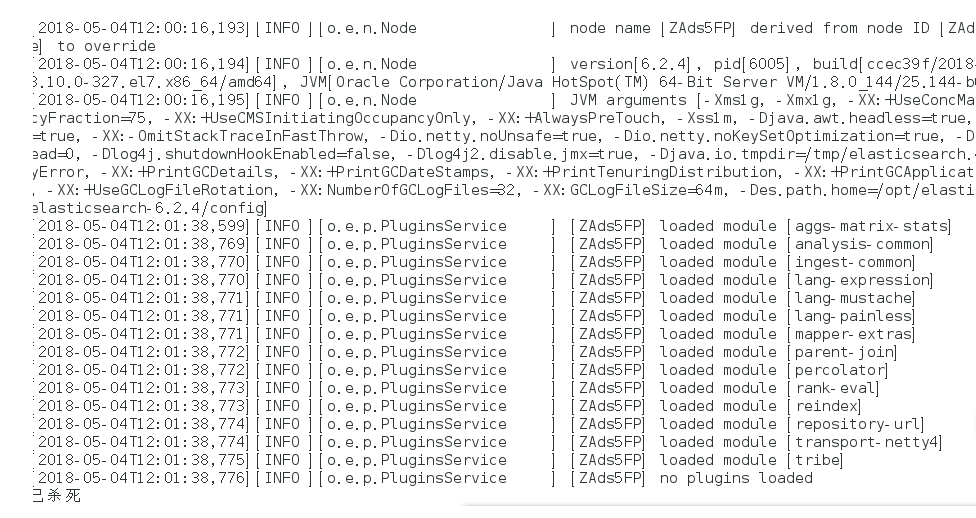
需要调整JVM的内存大小:
vi bin/elasticsearch
ES_JAVA_OPTS="-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
再次启动:启动成功
如果显示如下类似信息:
[INFO ][o.e.c.r.a.DiskThresholdMonitor] [ZAds5FP] low disk watermark [85%] exceeded on [ZAds5FPeTY-ZUKjXd7HJKA][ZAds5FP][/opt/elasticsearch-6.2.4/data/nodes/0] free: 1.2gb[14.2%], replicas will not be assigned to this node
需要清理磁盘空间。
后台运行:./bin/elasticsearch -d
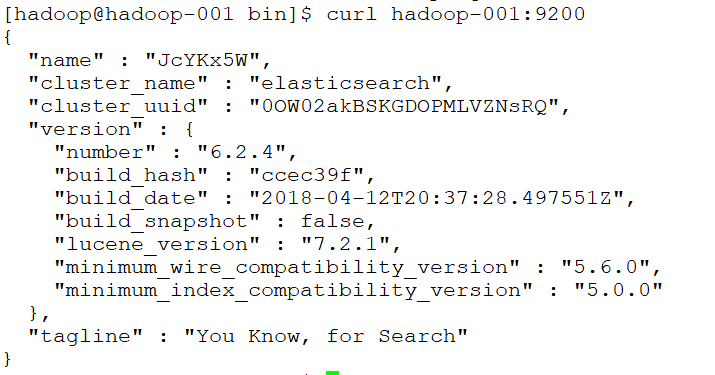
测试连接:curl 127.0.0.1:9200
会看到一下JSON数据:
[root@localhost ~]# curl 127.0.0.1:9200
{
"name" : "rBrMTNx",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "-noR5DxFRsyvAFvAzxl07g",
"version" : {
"number" : "5.1.1",
"build_hash" : "5395e21",
"build_date" : "2016-12-06T12:36:15.409Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "6.3.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}
实现远程访问:
需要对config/elasticsearch.yml进行 配置:
network.host: hadoop-001
再次启动报错:Failed to load settings from [elasticsearch.yml]
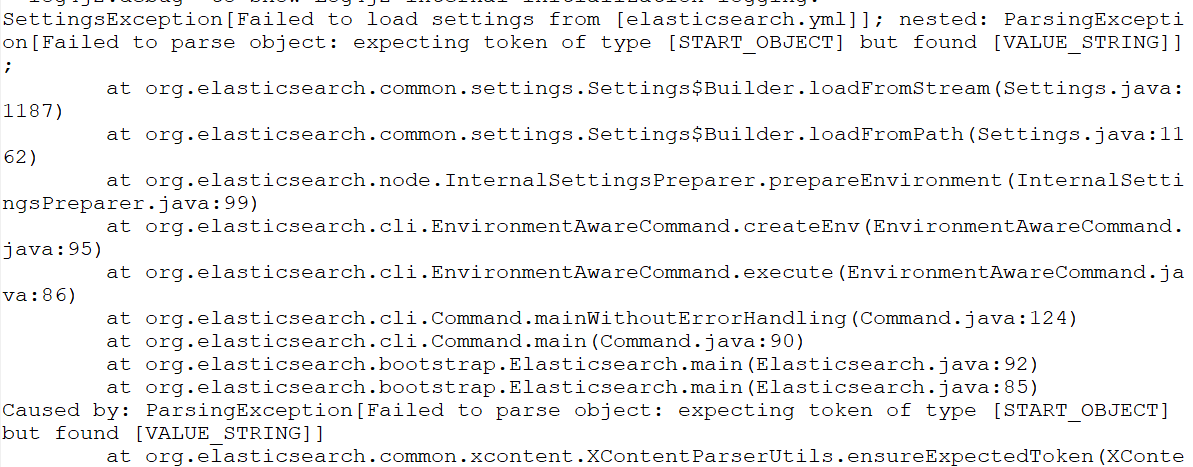
这个错就是参数的冒号前后没有加空格,加了之后就好,我找了好久这个问题;
后来在一个外国网站找到了这句话.
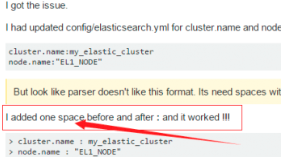
Exception in thread "main" SettingsException[Failed to load settings from [elasticsearch.yml]]; nested: ElasticsearchParseException[malformed, expected end of settings but encountered additional content starting at line number: [3], column number: [1]]; nested: ParserException[expected ''<document start>'', but found BlockMappingStart
in ''reader'', line 3, column 1:
node.rack : r1
^
];
Likely root cause: expected ''<document start>'', but found BlockMappingStart
in ''reader'', line 3, column 1:
node.rack : r1
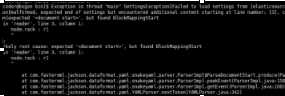
这个是行的开头没有加空格,fuck!
Exception in thread "main" SettingsException[Failed to load settings from [elasticsearch.yml]]; nested: ScannerException[while scanning a simple key
in ''reader'', line 11, column 2:
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts ...
^
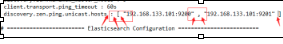
参数冒号后加空格,或者是数组中间加空格
例如:
# discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 3
再次启动
还是报错
max file descriptors [4096] for elasticsearch process is too low
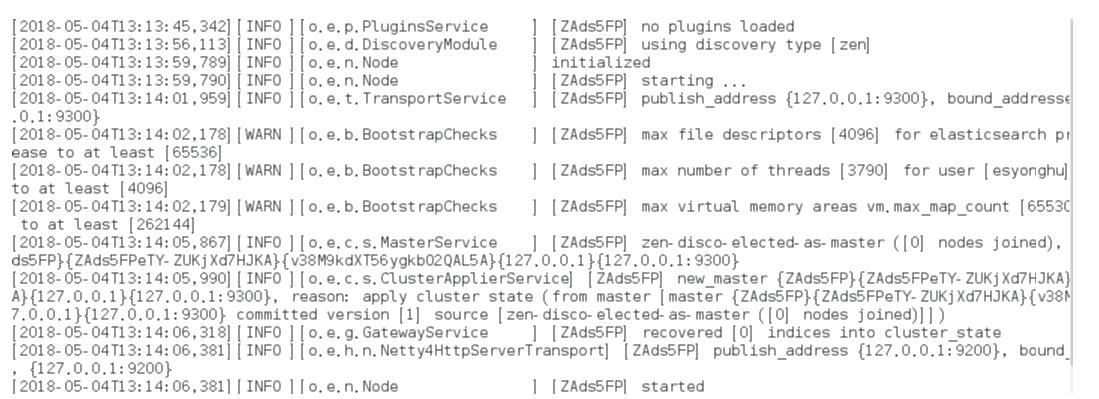
处理第一个错误:
vim /etc/security/limits.conf //文件最后加入
esuser soft nofile 65536
esuser hard nofile 65536
esuser soft nproc 4096
esuser hard nproc 4096
处理第二个错误:
进入limits.d目录下修改配置文件。
vim /etc/security/limits.d/20-nproc.conf
修改为 esuser soft nproc 4096
注意重新登录生效!!!!!!!!
处理第三个错误:
vim /etc/sysctl.conf
vm.max_map_count=655360
执行以下命令生效:
sysctl -p
关闭防火墙:systemctl stop firewalld.service
启动又又又报错
system call filters failed to install; check the logs and fix your configuration or disable sys
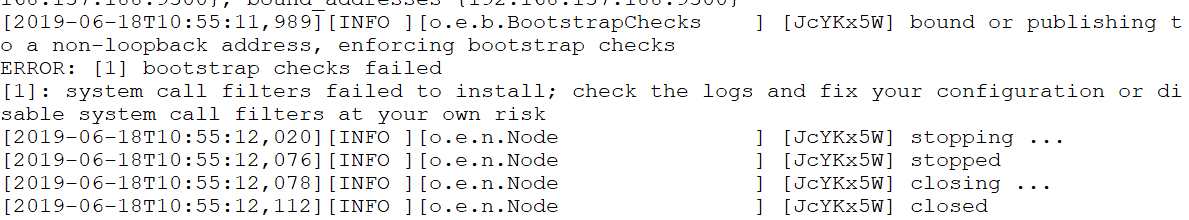
直接在
config/elasticsearch.yml 末尾加上一句
bootstrap.system_call_filter: false再次启动成功!
安装Head插件
Head是elasticsearch的集群管理工具,可以用于数据的浏览和查询
(1)elasticsearch-head是一款开源软件,被托管在github上面,所以如果我们要使用它,必须先安装git,通过git获取elasticsearch-head
(2)运行elasticsearch-head会用到grunt,而grunt需要npm包管理器,所以nodejs是必须要安装的
nodejs和npm安装:
http://blog.java1234.com/blog/articles/354.html
git安装
yum install -y git
(3)elasticsearch5.0之后,elasticsearch-head不做为插件放在其plugins目录下了。
使用git拷贝elasticsearch-head到本地
cd ~
git clone git://github.com/mobz/elasticsearch-head.git
(4)安装elasticsearch-head依赖包
[root@localhost local]# npm install -g grunt-cli
[root@localhost _site]# cd /usr/local/elasticsearch-head/
[root@localhost elasticsearch-head]# cnpm install
(5)修改Gruntfile.js
[root@localhost _site]# cd /usr/local/elasticsearch-head/
[root@localhost elasticsearch-head]# vi Gruntfile.js
在connect-->server-->options下面添加:hostname:’*’,允许所有IP可以访问
(6)修改elasticsearch-head默认连接地址
[root@localhost elasticsearch-head]# cd /usr/local/elasticsearch-head/_site/
[root@localhost _site]# vi app.js
将this.base_uri = this.config.base_uri || this.prefs.get("app-base_uri") || "http://localhost:9200";中的localhost修改成你es的服务器地址
(7)配置elasticsearch允许跨域访问
打开elasticsearch的配置文件elasticsearch.yml,在文件末尾追加下面两行代码即可:
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
(8)打开9100端口
[root@localhost elasticsearch-head]# firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=9100/tcp --permanent
重启防火墙
[root@localhost elasticsearch-head]# firewall-cmd --reload
(9)启动elasticsearch
(10)启动elasticsearch-head
[root@localhost _site]# cd ~/elasticsearch-head/
[root@localhost elasticsearch-head]# node_modules/grunt/bin/grunt server 或者 npm run start
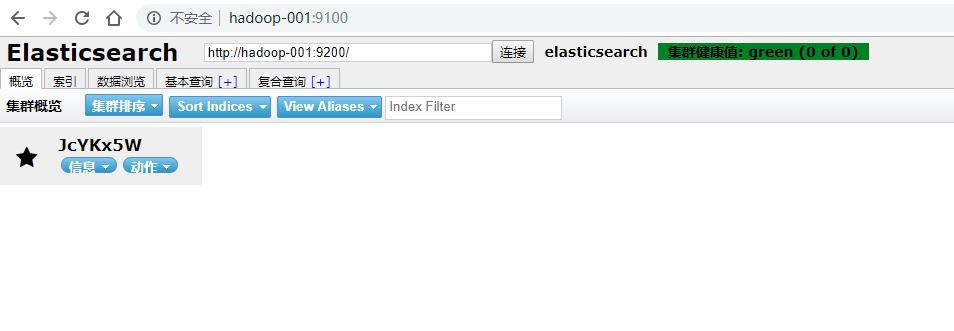
(11)访问elasticsearch-head
关闭防火墙:systemctl stop firewalld.service
浏览器输入网址:hadoop-001:9100/
安装Kibana
Kibana是一个针对Elasticsearch的开源分析及可视化平台,使用Kibana可以查询、查看并与存储在ES索引的数据进行交互操作,使用Kibana能执行高级的数据分析,并能以图表、表格和地图的形式查看数据
(1)下载Kibana
https://www.elastic.co/downloads/kibana
(2)把下载好的压缩包拷贝到/soft目录下
(3)解压缩,并把解压后的目录移动到/user/local/kibana
(4)编辑kibana配置文件
[root@localhost /]# vi /usr/local/kibana/config/kibana.yml
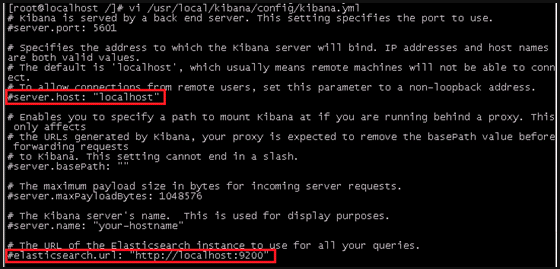
将server.host,elasticsearch.url修改成所在服务器的ip地址
server.port: 5601 //监听端口
server.host: "hadoo-001" //监听IP地址,建议内网ip
elasticsearch.url: "http:/hadoo-001" //elasticsearch连接kibana的URL,也可以填写192.168.137.188,因为它们是一个集群
(5)开启5601端口
Kibana的默认端口是5601
开启防火墙:systemctl start firewalld.service
开启5601端口:firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port=5601/tcp
重启防火墙:firewall-cmd –reload
(6)启动Kibana
[root@localhost /]# /usr/local/kibana/bin/kibana
浏览器访问:http://192.168.137.188:5601
安装中文分词器
一.离线安装
(1)下载中文分词器
https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik
下载elasticsearch-analysis-ik-master.zip
(2)解压elasticsearch-analysis-ik-master.zip
unzip elasticsearch-analysis-ik-master.zip
(3)进入elasticsearch-analysis-ik-master,编译源码
mvn clean install -Dmaven.test.skip=true
(4)在es的plugins文件夹下创建目录ik
(5)将编译后生成的elasticsearch-analysis-ik-版本.zip移动到ik下,并解压
(6)解压后的内容移动到ik目录下
二.在线安装
./elasticsearch-plugin install https://github.com/medcl/elasticsearch-analysis-ik/releases/download/v6.2.4/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-6.2.4.zip

Elasticsearch Dynamic Mapping(动态映射机制)
Elasticsearch可以根据待索引数据自动建立索引、自动定义映射类型。
1PUT data/_doc/1
2{ "count": 5 }执行上述请求时,索引"data"不必预先创建,该API首先会自动创建索引data、类型映射_doc,其映射类型下包含字段count,其类型为long。自动根据文档的值推测其类型的过程,就是本文要重点描述的机制:动态类型映射机制。动态映射机制包含如下两种映射规则:
Dynamic field mappings
Dynamic templates
接下来就分别介绍上述两种动态映射规则。
字段动态映射
动态字段映射规则。默认情况下,当在文档中发现未存在的字段时,Elasticsea-rch将使用动态映射机制为字段添加映射定义。通过将映射参数dynamic设置为f-alse(忽略新字段)或strict(遇到未知字段时抛出异常),可以在文档和对象级别禁用此行为。
类型关系对应表
| JSON datatype | Elasticsearch datatype |
|---|---|
| null | 不会自动增加类型映射 |
| true or false | boolean |
| floating |
float |
| integer | long |
| object | object |
| array | 根据数组中第一个非空值来判断 |
| string | date、double、long、text(带有keyword子字段) |
Date detection
日期类型检测,如果启用了date_dete-ction(默认),那么将检查新增的字符串字段,以查看它们的内容是否匹配dyn-amic_date_format中指定的任何日期模式。如果匹配其中任意一种格式,则添加字段映射时,字段的类型为date,并指定日期的format为匹配的模式。例如-:
1PUT my_index/_doc/1
2{
3 "create_date": "2015/09/02"
4}
由于create_date字段在json中的类型是字符串,但如果date_detection设置为t-rue,则creqate_date会映射为date类型而不是string类型。
可以在类型_type级别设置是否开启日期类型检测(date_detection),示例如下:
1PUT my_index
2{
3 "mappings": {
4 "_doc": {
5 "date_detection": false
6 }
7 }
8}
定制日期类型检测格式
可以通过类型级别(_type)级别通过dyn-amic_date_formats参数来自定义日期检测格式,示例如下:
1PUT my_index
2{
3 "mappings": {
4 "_doc": {
5 "dynamic_date_formats": ["MM/dd/yyyy"]
6 }
7 }
8}
9
10PUT my_index/_doc/1
11{
12 "create_date": "09/25/2015"
13}
numeric detection
数字类型检测。同样如果数字类型的值在JSON中是用字符串表示的话,如果开启日期类型检测,同样在创建映射时会映射为数字类型,而不是字符串类型-。
1PUT my_index
2{
3 "mappings": {
4 "_doc": {
5 "numeric_detection": true
6 }
7 }
8}
默认情况下,numeric_detection为fal-se。
动态映射模板
Dynamic field mappings默认情况下根据elasticsearch支持的数据类型来推测参-数值的类型,而动态模板允许您改变字-段动态映射的默认行为。动态映射模板-通过如下方式进行定义:
1"dynamic_templates": [ // @1
2 {
3 "my_template_name": { // @2
4 ... match conditions ... // @3
5 "mapping": { ... } // @4
6 }
7 },
8 ...
9 ]
代码@1:在类型映射时通过dynamic_-templates属性定义动态映射模板,其类型为数组。
代码@2:定义动态映射模板名称。
代码@3:匹配条件,定义方式包括ma-tch_mapping_type、match、 match_p-attern、unmatch、path_match、path_-unmatch。
代码@4:匹配@3的字段使用的类型映射定义(映射参数为类型映射中支持的参数)。
动态类型映射模板的核心关键是匹配条件与类型映射,接下来按照匹配条件定义方式来重点讲解动态类型模板映射机制。
match_mapping_type
首先使用json解析器解析字段值的类型-,由于JSON不能区分long和integer,也不能区分double和float,所以它总是选-择更广泛的数据类型,例如5,在使用字段动态映射时,elasticsearch会将字段-动态映射为long而不是integer类型,那-如何将数字5动态映射为integer类型呢,利用match_mapping_type可以实现上述需求,例如,如果希望将所有整数字段-映射为整数而不是long,并将所有字符-串字段映射为文本和关键字,可以使用-以下模板:
1PUT my_index
2{
3 "mappings": {
4 "_doc": {
5 "dynamic_templates": [
6 {
7 "integers": {
8 "match_mapping_type": "long",
9 "mapping": {
10 "type": "integer"
11 }
12 }
13 },
14 {
15 "strings": {
16 "match_mapping_type": "string",
17 "mapping": {
18 "type": "text",
19 "fields": {
20 "raw": {
21 "type": "keyword",
22 "ignore_above": 256
23 }
24 }
25 }
26 }
27 }
28 ]
29 }
30 }
31}
一言以蔽之,match_mapping_type为字段动态映射(字段类型检测)得出的类型-建立一个映射关系,将该类型转换为m-apping定义中的类型。
match、unmatch
match参数使用模式匹配字段名,而un-match使用模式排除匹配匹配的字段。
match、unmatch示例如下:
1PUT my_index
2{
3 "mappings": {
4 "_doc": {
5 "dynamic_templates": [
6 {
7 "longs_as_strings": {
8 "match_mapping_type": "string", // @1
9 "match": "long_*", // @2
10 "unmatch": "*_text", // @3
11 "mapping": { // @4
12 "type": "long"
13 }
14 }
15 }
16 ]
17 }
18 }
19}
20PUT my_index/_doc/1
21{
22 "long_num": "5", // @5
23 "long_text": "foo" // @6
24}
代码@1:表示该自动映射模板针对的字段为JSON解析器检测字段的类型为stri-ng的新增字段。
代码@2:字段名称以long_开头的字段-。
代码@3:排除字段名称以text的字段。
代码@4:符合long开头的字段,并且不是以text结尾的字段,如果JSON检测为string类型的新字段,映射为long。
代码@5:long_num,映射类型为lon-g。
代码@6:long_text虽然也满足long开-头,但是以_text结尾,故该字段不会映射为long,而是保留其JSON检测到的类型string,会映射为text字段和keyword-多字段(参考字段动态映射机制)。
match_pattern
使用正则表达式来匹配字段名称。
1"dynamic_templates": [
2 {
3 "longs_as_strings": {
4 "match_mapping_type": "string",
5 "match_pattern": "regex", // @1
6 "match": "^profit_\d+$" // @2
7 "mapping": {
8 "type": "long"
9 }
10 }
11 }
12]
代码@1:设置匹配模式为regex代表ja-va正则表达式
代码@2:java正则表达式
path_match、path_unmatch
path_match与path_unmatch的工作方式与match、unmatch一样,只不过path_-match是针对字段的全路径,特别是针--对嵌套类型(object、nested)。
下面一个示例:将name下的字段除了middle字段为copy到name属性并列的full_name字段中。
1PUT my_index
2{
3 "mappings": {
4 "_doc": {
5 "dynamic_templates": [
6 {
7 "copy_full_name": {
8 "path_match": "name.*",
9 "path_unmatch": "*.middle",
10 "mapping": {
11 "type": "text",
12 "copy_to": "full_name"
13 }
14 }
15 }
16 ]
17 }
18 }
19}
20PUT my_index/_doc/1
21{
22 "name": {
23 "first": "Alice",
24 "middle": "Mary",
25 "last": "White"
26 }
27}
{name}、{dynamic_type}
{name}展位符,表示字段的名称。
{dynamic_type}:JSON解析器解析到的字段类型。
1PUT my_index
2{
3 "mappings": {
4 "_doc": {
5 "dynamic_templates": [
6 {
7 "named_analyzers": { // @1
8 "match_mapping_type": "string",
9 "match": "*",
10 "mapping": {
11 "type": "text",
12 "analyzer": "{name}"
13 }
14 }
15 },
16 {
17 "no_doc_values": { // @2
18 "match_mapping_type":"*",
19 "mapping": {
20 "type": "{dynamic_type}",
21 "doc_values": false
22 }
23 }
24 }
25 ]
26 }
27 }
28}
29
30PUT my_index/_doc/1
31{
32 "english": "Some English text",
33 "count": 5
34}
代码@1:映射模板的含义为:对所有匹配到的字符串类型,类型映射为text,对应的分析器的名称与字段名相同,这个在使用时慎重,可能不存在同名的分析器,本例只是一个展示。
代码@2:对于匹配到的任何类型,其映射定义为类型为自动检测的类型,并且禁用doc_values=false。
更多文章请关注微信公众号:
本文分享自微信公众号 - 中间件兴趣圈(dingwpmz_zjj)。
如有侵权,请联系 support@oschina.cn 删除。
本文参与“OSC源创计划”,欢迎正在阅读的你也加入,一起分享。
关于禁用仅对Elasticsearch上的特定索引创建动态映射?和禁用索引是什么意思的介绍现已完结,谢谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于Elastic Search动态映射删除特殊字符和空格、Elasticsearch 2.3.0 索引映射管理、Elasticsearch CentOS6.5下安装ElasticSearch6.2.4+elasticsearch-head+Kibana、Elasticsearch Dynamic Mapping(动态映射机制)的相关知识,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:





