在这里,我们将给大家分享关于Android基础-(整体布局添加进度条和Toast)的知识,让您更了解android加载布局的本质,同时也会涉及到如何更有效地AndroidProgressBar进度条和
在这里,我们将给大家分享关于Android基础-(整体布局添加进度条和Toast)的知识,让您更了解android加载布局的本质,同时也会涉及到如何更有效地Android ProgressBar进度条和ProgressDialog进度框的展示DEMO、Android Toast 自定义布局、Android UI 系列 ----- 时间、日期、Toasts 和进度条 Dialog、Android XML 布局添加到 Window 的过程的内容。
本文目录一览:- Android基础-(整体布局添加进度条和Toast)(android加载布局)
- Android ProgressBar进度条和ProgressDialog进度框的展示DEMO
- Android Toast 自定义布局
- Android UI 系列 ----- 时间、日期、Toasts 和进度条 Dialog
- Android XML 布局添加到 Window 的过程

Android基础-(整体布局添加进度条和Toast)(android加载布局)
1.添加Toast 如果当前名字和密码为空就报Toast
//1.判断姓名, 密码是否为空
EditText nameEdt = findViewById(R.id.name);
EditText pwdEdt = findViewById(R.id.pwd);
ProgressBar proBar = findViewById(R.id.pro_bar);
String name = nameEdt.getText().toString();
String pwd = pwdEdt.getText().toString();
if (name.equals("") || pwd.equals("")) {
//2.如果为空,则提示
//无焦点提示
//参数1: 环境上下文
Toast.makeText(this, "姓名或者密码不能为空", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
2.否者就显示进度条,并且刷新进度条
else {
//3.都不为空, 则出现进度条
proBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
proBar.setProgress(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(30);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
整体代码和xml布局
1.xml布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="@mipmap/bg"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:gravity="center_horizontal">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Sign up"
android:layout_marginTop="70dp"
android:visibility="invisible"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Imooc Imooc Imooc Imooc\n Imooc Imooc"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"/>
<!--
android:src="" 指定前景图片资源
android:backgroud="" 设置背景
-->
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@mipmap/add_photo"
android:layout_margin="10dp"/>
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/pro_bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:visibility="invisible"
android:layout_margin="10dp"/>
<!--
android:inputType 输入类型
textPassowrd 密码
number 只能有正整数
numberSigned 只能输入整数
numberDecimal 小数
-->
<EditText
android:id="@+id/name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="68dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:layout_marginRight="30dp"
android:layout_marginTop="25dp"
android:hint="Name and Surname"
android:gravity="center"
android:textColorHint="#cccccc"
android:background="@mipmap/border"/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="68dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:layout_marginRight="30dp"
android:layout_marginTop="25dp"
android:hint="Emial Address"
android:gravity="center"
android:textColorHint="#cccccc"
android:background="@mipmap/border"/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="68dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:layout_marginRight="30dp"
android:layout_marginTop="25dp"
android:hint="Phone"
android:gravity="center"
android:textColorHint="#cccccc"
android:inputType="phone"
android:background="@mipmap/border"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/pwd"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="68dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:layout_marginRight="30dp"
android:layout_marginTop="25dp"
android:hint="Password"
android:gravity="center"
android:textColorHint="#cccccc"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:maxLength="12"
android:background="@mipmap/border"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="68dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="30dp"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:layout_marginRight="30dp"
android:background="@mipmap/btn"
android:text="Register"
android:onClick="register"
app:backgroundTint="@color/teal_700" />
</LinearLayout>
整体代码
package com.example.uidemo;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.ProgressBar;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
public void register(View v) {
//1.判断姓名, 密码是否为空
EditText nameEdt = findViewById(R.id.name);
EditText pwdEdt = findViewById(R.id.pwd);
ProgressBar proBar = findViewById(R.id.pro_bar);
String name = nameEdt.getText().toString();
String pwd = pwdEdt.getText().toString();
if (name.equals("") || pwd.equals("")) {
//2.如果为空,则提示
//无焦点提示
//参数1: 环境上下文
Toast.makeText(this, "姓名或者密码不能为空", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
} else {
//3.都不为空, 则出现进度条
proBar.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
proBar.setProgress(i);
try {
Thread.sleep(30);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printstacktrace();
}
}
}
}.start();
}
}
}


Android ProgressBar进度条和ProgressDialog进度框的展示DEMO
本篇文章是对Android中ProgressBar进度条和ProgressDialog进度框的展示DEMO进行了详细的分析介绍,需要的朋友参考下
在做手机开发时,经常碰到一些比较耗时的操作,这个时候进度条就开始派上用场了。
这个demo展示了ProgressBar进度条和ProgressDialog进度框。
一、ProgressDialog进度框,效果如图所示:

代码如下:
复制代码 代码如下:
//进度对话框按钮监听
class ProssButtonListener implements OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
myDialog = ProgressDialog.show(ProgressbarDemo.this, "进度条标题",
"进度条内容", true);
new Thread() {
public void run() {
try {
/* 在这里写上要背景运行的程序片段 */
/* 为了明显看见效果,以暂停3秒作为示范 */
sleep(3000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 卸载所创建的myDialog对象。
myDialog.dismiss();
}
}
}.start(); /* 开始运行运行线程 */
}
}
二、进度条对话框,这里用两种情况来动态显示进度条刻度
1、handle方法
效果图如下:

代码如下:
复制代码 代码如下:
//进度条handle按钮监听
class ProssBarHandleButtonListener implements OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
progressBarHandle.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
myProssBarhandleText.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
progressBarHandle.setMax(1000);
new Thread() {
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i
try {
/* 在这里写上运行的进度条 */
Message msg = new Message();
msg.what = 1;
msg.getData().putInt("size", i);
handler.sendMessage(msg);//handle发送消息
/* 为了明显看见效果,以暂停1秒作为示范 */
sleep(100);
i+=10;
} catch (Exception e) {
handler.obtainMessage(-1).sendToTarget();
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}.start(); /* 开始运行运行线程 */
}
}
//handle接收消息
private Handler handler = new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case 1:
progressBarHandle.setProgress(msg.getData().getInt("size"));
float num = (float)progressBarHandle.getProgress()/(float)progressBarHandle.getMax();
int result = (int)(num*100);
System.out.println("progressBarHandle.getProgress()======="+progressBarHandle.getProgress());
myProssBarhandleText.setText(result+ "%");
if(progressBarHandle.getProgress()==progressBarHandle.getMax()){
Toast.makeText(ProgressbarDemo.this, "下载成功", 1).show();
progressBarHandle.setVisibility(View.GONE);
myProssBarhandleText.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
break;
case -1:
Toast.makeText(ProgressbarDemo.this,"下载失败", 1).show();
break;
}
}
};
2、使用AsyncTask方法,网站空间,效果图与handle效果一样
具体代码如下:
复制代码 代码如下:
//进度条synctask按钮监听
class ProssBarSyncButtonListener implements OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
new AsyncLoader().execute((Void)null);
}
}
//AsyncTask 任务执行
class AsyncLoader extends AsyncTask
@Override
//
在doInBackground方法执行前执行
protected void onPreExecute(){
progressBarHandle.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
myProssBarhandleText.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
progressBarHandle.setMax(100000);
}
//
做具体的耗时操作
protected Integer doInBackground(Void... params) {
//这里以1万的进度条刻度来显示
int totalSize = 100000;
for (int i = 0; i
publishProgress(i); //通过推送消息传递数据给onProgressUpdate方法执行
i+=10;
}
return totalSize;
}
//
在doInBackground方法执行过程中执行
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... progress) {
progressBarHandle.setProgress(progress[0]);
float num = (float)progressBarHandle.getProgress()/(float)progressBarHandle.getMax();
int result = (int)(num*100);
myProssBarhandleText.setText(result+ "%");
}
//
在doInBackground方法结束后执行
protected void onPostExecute(Integer result) {
Toast.makeText(ProgressbarDemo.this, "下载成功,下载了"+result, 1).show();
myProssBarhandleText.setVisibility(View.GONE);
progressBarHandle.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}
点击下载DEMO示例
,香港服务器租用,虚拟主机

Android Toast 自定义布局
在Toast工具类中添加一个子项,用来添加自定义布局的方法,直接上代码
/**
* toast 自定义
*/
public Toast showToastFree(Context ctx,String str,int resID){
toast = Toast.makeText(ctx, str, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT);
LinearLayout toastView = (LinearLayout)
LayoutInflater.from(ctx).inflate(R.layout.toast_hor_view, null);
ImageView iv = toastView.findViewById(R.id.toast_iv);
iv.setImageResource(resID);
TextView tv = toastView.findViewById(R.id.toast_tv);
tv.setText(str);
toast.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER,0,0);
toast.setView(toastView);
toast.show();
return toast;
}布局 toast_hor_view.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:background="@drawable/shape_corner"
android:paddingEnd="12dp"
android:paddingStart="8dp"
android:paddingTop="6dp"
android:paddingBottom="6dp"
android:layout_height="50dp">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/toast_iv"
android:layout_width="35dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_height="35dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/toast_tv"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:text="00000"/>
</LinearLayout>布局圆角背景 shape_corner.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<shape xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<solid android:color="#9703A9F4" />
<corners android:topLeftRadius="12dp"
android:topRightRadius="12dp"
android:bottomRightRadius="12dp"
android:bottomLeftRadius="12dp"/>
<stroke android:width="1dp" android:color="#000000" />
</shape>

Android UI 系列 ----- 时间、日期、Toasts 和进度条 Dialog

您可以通过点击 右下角 的按钮 来对文章内容作出评价, 也可以通过左下方的 关注按钮 来关注我的博客的最新动态。
如果文章内容对您有帮助, 不要忘记点击右下角的 推荐按钮 来支持一下哦
如果您对文章内容有任何疑问, 可以通过评论或发邮件的方式联系我: 501395377@qq.com / lzp501395377@gmail.com
如果需要转载,请注明出处,谢谢!!
本篇随笔将继续学习 Android UI 系列中的 Dialog,包括 DatePickerDialog、TimePickerDialog、Toasts 以及 ProgressDialog。下面让我们来看看这几种不同的 Dialog 对话框的使用.
一、DatePickerDialog 和 TimePickerDialog
DatePickerDialog 和 TimePickerDialog 是 Android 提供的可以弹出一个日期、时间选择的对话框,我们可以在程序中通过实例化 DatePickerDialog 和 TimePickerDialog 来得到一个日期、时间对话框。这两个类都是 AlertDialog 的子类:

java.lang.Object
↳ android.app.Dialog
↳ android.app.AlertDialog
↳ android.app.DatePickerDialog
java.lang.Object
↳ android.app.Dialog
↳ android.app.AlertDialog
↳ android.app.TimePickerDialog
这两个控件的使用非常的简单,下面我们直接通过例子来看看 DatePickerDialog 和 TimePickerDialog 的使用:

我们在布局上定义两个 Button 和两个 EditText,当点击第一个按钮,弹出一个 DatePickerDialog,并得到选择的日期显示在第一个 EditText 上,点击第二个按钮,弹出一个 TimePickerDialog,得到选择的时间显示在第二个 EditText 上。
activity_main.xml:

<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<Button android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="99dp"
android:text="DatePickerDialog" />
<EditText android:id="@+id/editText1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="29dp"
android:ems="10" >
</EditText>
<EditText android:id="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/button1"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="31dp"
android:ems="10" >
<requestFocus />
</EditText>
<Button android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/editText2"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="24dp"
android:text="TimePickerDialog" /></RelativeLayout>
MainActivity 类:

public class MainActivity extends Activity
{ private Button button; private Button button2; private EditText editText; private EditText editText2; private int year, monthOfYear, dayOfMonth, hourOfDay, minute;
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{ super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
button = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button1);
button2 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button2);
editText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText1);
editText2 = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.editText2);
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR);
monthOfYear = calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH);
dayOfMonth = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);
hourOfDay = calendar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);
minute = calendar.get(Calendar.MINUTE);
button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
@Override public void onClick(View view)
{ /**
* 实例化一个DatePickerDialog的对象
* 第二个参数是一个DatePickerDialog.OnDateSetListener匿名内部类,当用户选择好日期点击done会调用里面的onDateSet方法 */
DatePickerDialog datePickerDialog = new DatePickerDialog(MainActivity.this, new DatePickerDialog.OnDateSetListener()
{
@Override public void onDateSet(DatePicker view, int year, int monthOfYear, int dayOfMonth)
{
editText.setText("日期:" + year + "-" + (monthOfYear + 1) + "-" + dayOfMonth);
}
}, year, monthOfYear, dayOfMonth);
datePickerDialog.show();
}
});
button2.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
@Override public void onClick(View v)
{ /**
* 实例化一个TimePickerDialog的对象
* 第二个参数是一个TimePickerDialog.OnTimeSetListener匿名内部类,当用户选择好时间后点击done会调用里面的onTimeset方法 */
TimePickerDialog timePickerDialog = new TimePickerDialog(MainActivity.this, new TimePickerDialog.OnTimeSetListener()
{
@Override public void onTimeSet(TimePicker view, int hourOfDay, int minute)
{
editText2.setText("Time: " + hourOfDay + ":" + minute);
}
}, hourOfDay, minute, true);
timePickerDialog.show();
}
});
}
@Override public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu)
{ // Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present. getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu); return true;
}
}
我们看到,我们如果要得到一个日期或者时间弹出框,只需要实例化一个 DatePickerDialog 和 TimePickerDialog 对象即可,我们来看看日期和时间弹出框的样子是什么:


当点击 Done 后,就会分别调用绑定到得监听器,得到我们设置的时间

二、Toasts
Toasts 对话框也是非常的简单,其实在之前的一些随笔里面我们已经大量的看到使用了 Toast 这种对话框来弹出一个信息给我们用户,要注意的是,Toast 框是不能够与用户进行交互的,当超过我们设定的时间后,Toast 对话框会自动的消失,我们可以直接使用 Toast 的 makeText 这个静态方法来实例化一个默认的 Toast 对象
public static Toast makeText (Context context, CharSequence text, int duration)
Parameterscontext The context to use. Usually your Application or Activity object.text The text to show. Can be formatted text.duration How long to display the message. Either LENGTH_SHORT or LENGTH_LONG第一个参数指定了在哪个窗口下弹出这个 Toast 框,第二个参数指定了弹出框显示的文本内容,第三个参数指定了弹出框显示的时间。
默认的 Toast 弹出框是弹出一个黑色的框,弹出的位置位于屏幕的下方,我们还可以设置我们自定义的 Toast 弹出框,并可以通过 setGravity () 的方法来设置弹出框的位置。
下面我们也通过一个实例来看看 Toast 框的使用方法:

<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="32dp"
android:text="弹出一个普通Toast框" />
<Button android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/button1"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="29dp"
android:text="弹出一个自定义的Toast框" /></RelativeLayout>
同样定义两个 Button,当点击 Button,弹出一个 Toast 框

button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
@Override public void onClick(View v)
{ // 实例化一个Toast的对话框
Toast toast = Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Hello World", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT); /*
* setGravity方法来设定Toast框的弹出位置,第一个参数指定弹出的方位,第二个参数指定X轴的偏移量
* 第三个参数指定Y轴的偏移量 */
toast.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER, 0, 0);
}
});
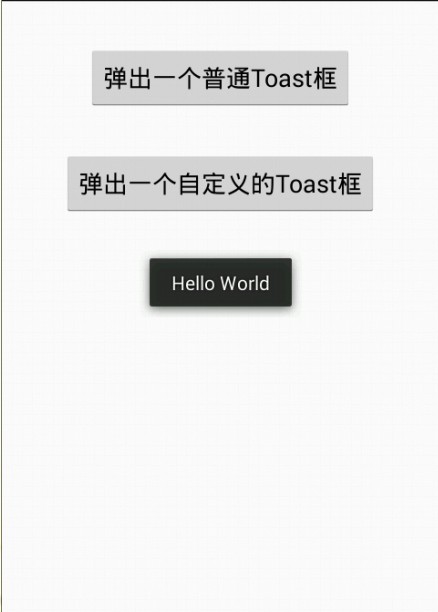
我们看到当我们设置了 setGravity () 方法后,Toast 的弹出框位置就会根据我们的设置发生变化

button2.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
@Override public void onClick(View v)
{ // 通过LayoutInflater方法来加载我们自定义的xml布局文件
View view = LayoutInflater.from(MainActivity.this).inflate(R.layout.toast, null); // 直接通过new的方式得到一个Toast对象
Toast toast = new Toast(MainActivity.this); // 设置我们Toast框的弹出内容为我们自定义的Toast toast.setView(view);
toast.show();
}
});

我们也可以通过自定义一个 xml 布局文件,然后通过 Toast 的 setView 方法来弹出一个我们自定义的 Toast 框。
三、ProgressDialog
最后我们来看一看 ProgressDialog,这是一个进度条的弹出框,其也是 AlertDialog 的一个子类
java.lang.Object
↳ android.app.Dialog
↳ android.app.AlertDialog
↳ android.app.ProgressDialogProgressDialog 可以显示一个包含一个文本 message 或者是一个自定义的 View 的带进度条的弹出框。注意:文本 message 和自定义的 View 只能存在一个。
如果要创建一个 ProgressDialog,我们可以直接通过 new 的方式来创建,因为进度条有两种样式,一种是水平的进度条,一种是圆圈进度条,所以我们还可以设置进度条弹出框的显示样式。下面我们通过一个实例来分别看看这两种样式的进度条弹出框:

<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="42dp"
android:text="弹出一个圆形的进度条框" />
<Button android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/button1"
android:layout_below="@+id/button1"
android:layout_marginTop="44dp"
android:text="弹出一个水平的进度条框" />
</RelativeLayout>
圆形的进度条框:

button.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
@Override public void onClick(View v)
{ // 实例化一个ProgressDialog
ProgressDialog progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(MainActivity.this);
progressDialog.setTitle("提示信息");
progressDialog.setMessage("正在下载中,请稍后......"); // 设置ProgressDialog的显示样式,ProgressDialog.STYLE_SPINNER代表的是圆形进度条 progressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_SPINNER);
progressDialog.show();
}
});

我们可以点击屏幕其他部分,然后这个进度条弹出框就会消失,如果希望其不消失可以调用
progressDialog.setCancelable(false); // 设置弹出框不能被取消再来看看水平的进度条框:

button2.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener()
{
@Override public void onClick(View v)
{ // 实例化一个ProgressDialog
ProgressDialog progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(MainActivity.this);
progressDialog.setTitle("提示信息");
progressDialog.setMessage("正在下载中,请稍后......"); // 设置最大进度,ProgressDialog的进度范围是从1-10000
progressDialog.setMax(100); // 设置主进度
progressDialog.setProgress(50); // 设置第二进度
progressDialog.setSecondaryProgress(70); // 设置ProgressDialog的显示样式,ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL代表的是水平进度条 progressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL);
progressDialog.show();
}
});

以上就是两种进度条的使用方法
总结:本篇随便主要讲解了 DatePickerDialog、TimePickerDialog、Toasts 和 ProgressDialog 这四种弹出框的使用方法,在后续的随笔当中,将会继续记录学习 Android 的点点滴滴。

Android XML 布局添加到 Window 的过程
第一步:XML 布局添加到 DecorView 的过程
我们都知道添加布局的方式,调用 setContentView (R.layout.main)
Activity.java
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
//向window中添加布局
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
//初始化ActionBar
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}向 Window 中添加布局
1. 获取 Window 对象
Activity.java
private Window mWindow;
public Window getWindow() {
return mWindow;
}
/**
*
*使依附
*/
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor) {
//这里初始化窗口对象
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this);
}2.PhoneWindows.setContentView(int)
PhoneWindow.java
@Override
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
// Note: FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS may be set in the process of installing the window
// decor, when theme attributes and the like are crystalized. Do not check the feature
// before this happens.
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
if (hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
final Scene newScene = Scene.getSceneForLayout(mContentParent, layoutResID,
getContext());
transitionTo(newScene);
} else {
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
}
mContentParent.requestApplyInsets();
final Callback cb = getCallback();
if (cb != null && !isDestroyed()) {
cb.onContentChanged();
}
}3.XML 解析其来解析 XML 内容
LayoutInflater.java
public View inflate(@LayoutRes int resource, @Nullable ViewGroup root) {
return inflate(resource, root, root != null);
}
public View inflate(@LayoutRes int resource, @Nullable ViewGroup root, boolean attachToRoot) {
final Resources res = getContext().getResources();
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "INFLATING from resource: \"" + res.getResourceName(resource) + "\" ("
+ Integer.toHexString(resource) + ")");
}
//XML解析器解析
final XmlResourceParser parser = res.getLayout(resource);
try {
return inflate(parser, root, attachToRoot);
} finally {
parser.close();
}
}
4. 如何解析就不深究了
5. 解析 XML 过程需要通过函数 inflate 传递一个参数对象 root,该对象是一个 ViewGroup
ViewGroup mContentParent;
初始化该对象 mContentParent
PhoneWindow.java
private void installDecor() {
if (mDecor == null) {
mDecor = generateDecor();
mDecor.setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS);
mDecor.setIsRootNamespace(true);
if (!mInvalidatePanelMenuPosted && mInvalidatePanelMenuFeatures != 0) {
mDecor.postOnAnimation(mInvalidatePanelMenuRunnable);
}
}
if (mContentParent == null) {
mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor);
}
}
/***/
protected DecorView generateDecor() {
return new DecorView(getContext(), -1);
}
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) {
else {
// Embedded, so no decoration is needed.
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple;
// System.out.println("Simple!");
}
View in = mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResource, null);
decor.addView(in, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
mContentRoot = (ViewGroup) in;
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);
return contentParent;
}
private final class DecorView extends FrameLayout implements RootViewSurfaceTaker {
}
screen_simple.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:fitsSystemWindows="true"
android:orientation="vertical">
<ViewStub android:id="@+id/action_mode_bar_stub"
android:inflatedId="@+id/action_mode_bar"
android:layout="@layout/action_mode_bar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:theme="?attr/actionBarTheme" />
<!--这个就是ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);-->
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:foregroundInsidePadding="false"
android:foregroundGravity="fill_horizontal|top"
android:foreground="?android:attr/windowContentOverlay" />
</LinearLayout>
今天的关于Android基础-(整体布局添加进度条和Toast)和android加载布局的分享已经结束,谢谢您的关注,如果想了解更多关于Android ProgressBar进度条和ProgressDialog进度框的展示DEMO、Android Toast 自定义布局、Android UI 系列 ----- 时间、日期、Toasts 和进度条 Dialog、Android XML 布局添加到 Window 的过程的相关知识,请在本站进行查询。
本文标签:





