如果您想了解Android3D效果图片库的相关知识,那么本文是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将对android3d效果实现进行全面详尽的解释,并且为您提供关于3D翻转效果介绍,Android动画分析、And
如果您想了解Android 3D效果图片库的相关知识,那么本文是一篇不可错过的文章,我们将对android3d效果实现进行全面详尽的解释,并且为您提供关于3D翻转效果介绍,Android动画分析、Android 3D 图片滚动效果怎么适应不同安卓版本、Android 3D 旋转动画效果、Android GPS定位测试(附效果图和示例)的有价值的信息。
本文目录一览:- Android 3D效果图片库(android3d效果实现)
- 3D翻转效果介绍,Android动画分析
- Android 3D 图片滚动效果怎么适应不同安卓版本
- Android 3D 旋转动画效果
- Android GPS定位测试(附效果图和示例)

Android 3D效果图片库(android3d效果实现)
我有一个android应用,我需要制作一个看起来像这张图片的图片库
但我不知道如何实现此库以及如何对其产生影响.我只需要遵循以下步骤或任何代码即可理解
任何帮助请
谢谢
解决方法:
在这里为您演示.希望对您有所帮助.
http://www.inter-fuser.com/2010/01/android-coverflow-widget.html
http://www.studyoverflow.org/2013/07/cover-flow-type-gallery-layout-in.html

3D翻转效果介绍,Android动画分析
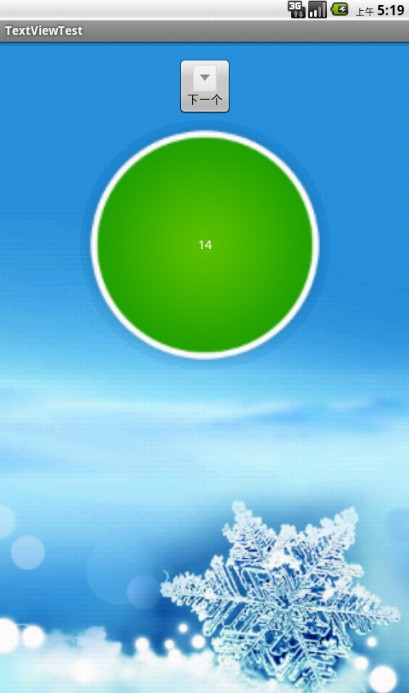
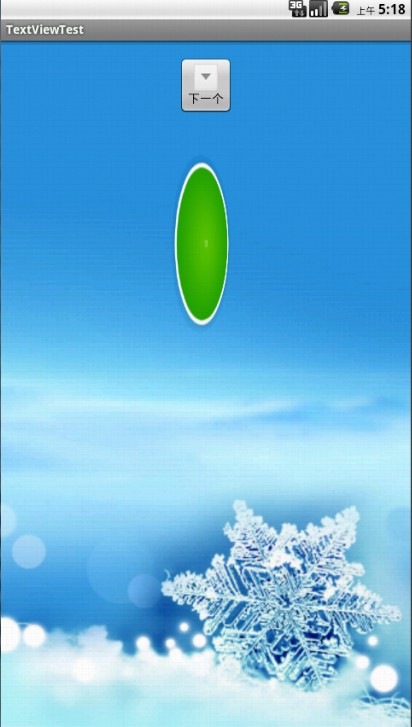
android中的翻转动画效果的实现,首先看一下运行效果如上图所示。,更多android面试题..
Android中并没有提供直接做3D翻转的动画,所以关于3D翻转的动画效果需要我们自己实现,那么我们首先来分析一下Animation 和 Transformation。
Animation动画的主要接口,其中主要定义了动画的一些属性比如开始时间,持续时间,是否重复播放等等。而Transformation中则包含一个矩阵和alpha值,矩阵是用来做平移,旋转和缩放动画的,而alpha值是用来做alpha动画的,要实现3D旋转动画我们需要继承自Animation类来实现,我们需要重载getTransformation和applyTransformation,在getTransformation中Animation会根据动画的属性来产生一系列的差值点,然后将这些差值点传给applyTransformation,这个函数将根据这些点来生成不同的Transformation。下面是具体实现:
package com.example.textviewtest;
import android.graphics.Camera;
import android.graphics.Matrix;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.Transformation;
public class Rotate3dAnimation extends Animation {
// 开始角度
private final float mFromDegrees;
// 结束角度
private final float mToDegrees;
// 中心点
private final float mCenterX;
private final float mCenterY;
private final float mDepthZ;
// 是否需要扭曲
private final boolean mReverse;
// 摄像头
private Camera mCamera;
public Rotate3dAnimation(float fromDegrees, float toDegrees, float centerX,
float centerY, float depthZ, boolean reverse) {
mFromDegrees = fromDegrees;
mToDegrees = toDegrees;
mCenterX = centerX;
mCenterY = centerY;
mDepthZ = depthZ;
mReverse = reverse;
}
@Override
public void initialize(int width, int height, int parentWidth,
int parentHeight) {
super.initialize(width, height, parentWidth, parentHeight);
mCamera = new Camera();
}
// 生成Transformation
@Override
protected void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime, Transformation t) {
final float fromDegrees = mFromDegrees;
// 生成中间角度
float degrees = fromDegrees
+ ((mToDegrees - fromDegrees) * interpolatedTime);
final float centerX = mCenterX;
final float centerY = mCenterY;
final Camera camera = mCamera;
final Matrix matrix = t.getMatrix();
camera.save();
if (mReverse) {
camera.translate(0.0f, 0.0f, mDepthZ * interpolatedTime);
} else {
camera.translate(0.0f, 0.0f, mDepthZ * (1.0f - interpolatedTime));
}
camera.rotateY(degrees);
// 取得变换后的矩阵
camera.getMatrix(matrix);
camera.restore();
matrix.preTranslate(-centerX, -centerY);
matrix.postTranslate(centerX, centerY);
}
}其中包括了旋转的开始和结束角度,中心点、是否扭曲、和一个Camera,这里我们主要分析applyTransformation函数,其中第一个参数就是通过getTransformation函数传递的差指点,然后我们根据这个差值通过线性差值算法计算出一个中间角度degrees,Camera类是用来实现绕Y轴旋转后透视投影的,因此我们首先通过t.getMatrix()取得当前的矩阵,然后通过camera.translate来对矩阵进行平移变换操作,camera.rotateY进行旋转。这样我们就可以很轻松的实现3D旋转效果了。
下面是布局文件main.xml:
MainActivity的代码如下:
package com.example.textviewtest;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.animation.AccelerateInterpolator;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.DecelerateInterpolator;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private TextView tv;
private Button btn;
private int count = 1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
tv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv);
tv.setText(String.valueOf(count));
btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.next_btn);
applyRotation(0, 90);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
applyRotation(0, 90);
}
});
}
private void applyRotation(float start, float end) {
// 计算中心点
final float centerX = tv.getWidth() / 2.0f;
final float centerY = tv.getHeight() / 2.0f;
final Rotate3dAnimation rotation = new Rotate3dAnimation(start, end,
centerX, centerY, 310.0f, true);
rotation.setDuration(500);
rotation.setFillAfter(true);
rotation.setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator());
// 设置监听
rotation.setAnimationListener(new DisplayNextView());
tv.startAnimation(rotation);
}
private final class DisplayNextView implements Animation.AnimationListener {
public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) {
}
// 动画结束
public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) {
tv.post(new SwapViews());
}
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) {
}
}
private final class SwapViews implements Runnable {
public void run() {
final float centerX = tv.getWidth() / 2.0f;
final float centerY = tv.getHeight() / 2.0f;
Rotate3dAnimation rotation = null;
tv.requestFocus();
rotation = new Rotate3dAnimation(90, 0, centerX, centerY, 310.0f,
false);
rotation.setDuration(500);
rotation.setFillAfter(true);
rotation.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());
// 开始动画
tv.startAnimation(rotation);
tv.setText(String.valueOf(count++));
}
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.activity_main, menu);
return true;
}
}
Android 3D 图片滚动效果怎么适应不同安卓版本
自己写了一个3D图片的滚动效果,可是在不同的安卓版本上效果有着明显的差异,有的版本已经变形的不能看,求大牛帮忙看看。下面附上两幅图。第一幅是4.0的也是需要的效果图,第二张是4.1的,开始变形了,其他的变得更厉害。



Android 3D 旋转动画效果
主要介绍一下如何实现 View 的 3D 旋转效果,实现的主要原理就是围绕 Y 轴旋转,同时在 Z 轴方面上有一个深入的缩放。
演示的 demo 主要有以下几个重点:
1,自定义旋转动画
2,动画做完后,重置 ImageView
1,自定义动画类
@Override
protected void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime, Transformation t)
{
final float fromDegrees = mFromDegrees;
float degrees = fromDegrees + ((mToDegrees - fromDegrees) * interpolatedTime);
final float centerX = mCenterX;
final float centerY = mCenterY;
final Camera camera = mCamera;
final Matrix matrix = t.getMatrix();
camera.save();
if (mReverse) {
camera.translate(0.0f, 0.0f, mDepthZ * interpolatedTime);
} else {
camera.translate(0.0f, 0.0f, mDepthZ * (1.0f - interpolatedTime));
}
camera.rotateY(degrees);
camera.getMatrix(matrix);
camera.restore();
matrix.preTranslate(-centerX, -centerY);
matrix.postTranslate(centerX, centerY);
}
2,如何使用这个动画类
在 Activity 中,我们有两个大小一样的 ImageView,它们都放在 FrameLayout 中,这样他们位置是重叠的,对最上面的 ImageView 做动画(旋转角度从 0 到 90),当动画做完后,再对后面的 ImageView 做动画(旋转角度从 90 到 180),在这里,要控制相应的 ImageView 隐藏或显示。
private final class DisplayNextView implements Animation.AnimationListener {
public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) {
}
public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) {
mContainer.post(new SwapViews());
}
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) {
}
}
private final class SwapViews implements Runnable
{
@Override
public void run()
{
mImageView1.setVisibility(View.GONE);
mImageView2.setVisibility(View.GONE);
mIndex++;
if (0 == mIndex % 2)
{
mStartAnimView = mImageView1;
}
else
{
mStartAnimView = mImageView2;
}
mStartAnimView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mStartAnimView.requestFocus();
Rotate3dAnimation rotation = new Rotate3dAnimation(
-90,
0,
mCenterX,
mCenterY, mDepthZ, false);
rotation.setDuration(mDuration);
rotation.setFillAfter(true);
rotation.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());
mStartAnimView.startAnimation(rotation);
}
}
3,完整代码如下
Rotate3dAnimActivity.java
public class Rotate3dAnimActivity extends Activity
{
ImageView mImageView1 = null;
ImageView mImageView2 = null;
ImageView mStartAnimView = null;
View mContainer = null;
int mDuration = 500;
float mCenterX = 0.0f;
float mCenterY = 0.0f;
float mDepthZ = 0.0f;
int mIndex = 0;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.rotate_anim);
mImageView1 = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.imageView1);
mImageView2 = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.imageView2);
mContainer = findViewById(R.id.container);
mStartAnimView = mImageView1;
findViewById(R.id.button1).setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener()
{
@Override
public void onClick(View v)
{
mCenterX = mContainer.getWidth() / 2;
mCenterY = mContainer.getHeight() / 2;
getDepthZ();
applyRotation(mStartAnimView, 0, 90);
}
});
InputMethodManager imm = (InputMethodManager)getSystemService(INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE);
imm.hideSoftInputFromWindow(getWindow().getDecorView().getWindowToken(), InputMethodManager.HIDE_NOT_ALWAYS);
}
private void getDepthZ()
{
EditText editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edit_depthz);
String string = editText.getText().toString();
try
{
mDepthZ = (float)Integer.parseInt(string);
//mDepthZ = Math.min(mDepthZ, 300.0f);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void applyRotation(View animView, float startAngle, float toAngle)
{
float centerX = mCenterX;
float centerY = mCenterY;
Rotate3dAnimation rotation = new Rotate3dAnimation(
startAngle, toAngle, centerX, centerY, mDepthZ, true);
rotation.setDuration(mDuration);
rotation.setFillAfter(true);
rotation.setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator());
rotation.setAnimationListener(new DisplayNextView());
animView.startAnimation(rotation);
}
/**
* This class listens for the end of the first half of the animation.
* It then posts a new action that effectively swaps the views when the container
* is rotated 90 degrees and thus invisible.
*/
private final class DisplayNextView implements Animation.AnimationListener {
public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) {
}
public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) {
mContainer.post(new SwapViews());
}
public void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) {
}
}
private final class SwapViews implements Runnable
{
@Override
public void run()
{
mImageView1.setVisibility(View.GONE);
mImageView2.setVisibility(View.GONE);
mIndex++;
if (0 == mIndex % 2)
{
mStartAnimView = mImageView1;
}
else
{
mStartAnimView = mImageView2;
}
mStartAnimView.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mStartAnimView.requestFocus();
Rotate3dAnimation rotation = new Rotate3dAnimation(
-90,
0,
mCenterX,
mCenterY, mDepthZ, false);
rotation.setDuration(mDuration);
rotation.setFillAfter(true);
rotation.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());
mStartAnimView.startAnimation(rotation);
}
}
}
rotate_anim.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:text="Do 3d animation" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft="20px"
android:text="Input Depth on Z axis. [0, 300]"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edit_depthz"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:text="0"/>
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/container"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView1"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:src="@drawable/f" />
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView2"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_margin="20dp"
android:src="@drawable/s"
android:visibility="gone"/>
</FrameLayout>
</LinearLayout>
Rotate3dAnimation.java
package com.nj1s.lib.anim;
import android.graphics.Camera;
import android.graphics.Matrix;
import android.view.animation.Animation;
import android.view.animation.Transformation;
/**
* An animation that rotates the view on the Y axis between two specified angles.
* This animation also adds a translation on the Z axis (depth) to improve the effect.
*/
public class Rotate3dAnimation extends Animation {
private final float mFromDegrees;
private final float mToDegrees;
private final float mCenterX;
private final float mCenterY;
private final float mDepthZ;
private final boolean mReverse;
private Camera mCamera;
/**
* Creates a new 3D rotation on the Y axis. The rotation is defined by its
* start angle and its end angle. Both angles are in degrees. The rotation
* is performed around a center point on the 2D space, definied by a pair
* of X and Y coordinates, called centerX and centerY. When the animation
* starts, a translation on the Z axis (depth) is performed. The length
* of the translation can be specified, as well as whether the translation
* should be reversed in time.
*
* @param fromDegrees the start angle of the 3D rotation
* @param toDegrees the end angle of the 3D rotation
* @param centerX the X center of the 3D rotation
* @param centerY the Y center of the 3D rotation
* @param reverse true if the translation should be reversed, false otherwise
*/
public Rotate3dAnimation(float fromDegrees, float toDegrees,
float centerX, float centerY, float depthZ, boolean reverse) {
mFromDegrees = fromDegrees;
mToDegrees = toDegrees;
mCenterX = centerX;
mCenterY = centerY;
mDepthZ = depthZ;
mReverse = reverse;
}
@Override
public void initialize(int width, int height, int parentWidth, int parentHeight) {
super.initialize(width, height, parentWidth, parentHeight);
mCamera = new Camera();
}
@Override
protected void applyTransformation(float interpolatedTime, Transformation t) {
final float fromDegrees = mFromDegrees;
float degrees = fromDegrees + ((mToDegrees - fromDegrees) * interpolatedTime);
final float centerX = mCenterX;
final float centerY = mCenterY;
final Camera camera = mCamera;
final Matrix matrix = t.getMatrix();
camera.save();
if (mReverse) {
camera.translate(0.0f, 0.0f, mDepthZ * interpolatedTime);
} else {
camera.translate(0.0f, 0.0f, mDepthZ * (1.0f - interpolatedTime));
}
camera.rotateY(degrees);
camera.getMatrix(matrix);
camera.restore();
matrix.preTranslate(-centerX, -centerY);
matrix.postTranslate(centerX, centerY);
}
}

Android GPS定位测试(附效果图和示例)
今天因为工作需要,把以前编写的一个gps测试程序拿出来重新修改了一下。这个程序说起来有些历史了,是我11年编写的,那时候学了android开发没多久,算是一个实验性的作品。现在工作需要,重新拿出来修整。同时发现我对android的gps服务了解并不深,所以今天特意阅读了有关gps服务的一些资料,把相关知识点记录下来。
本人做了GPS相关的嵌入式软件已经几年了,所以说起要做个测试GPS定位模块的程序,第一反应就是串口读取GPS模块的数据,然后解析GPS的NMEA格式数据。NMEA是一种标准化数据格式,不仅仅GPS上应用了,其他一些工业通信也是使用这种标准化数据格式。解析相关数据然后显示出来,就完成了一个基本的GPS定位测试功能。
查了一下才发现Android上做GPS相关定位服务,不需要读取NMEA数据分析,Android已经封装好了相关服务,你要做的就是调用API。这个不知道应该觉得爽还是觉得纠结。(Android也提供了读取NMEA接口,下面会说到)
1、Android 定位服务
下面我们先来看看Android有关定位服务提供的支持:
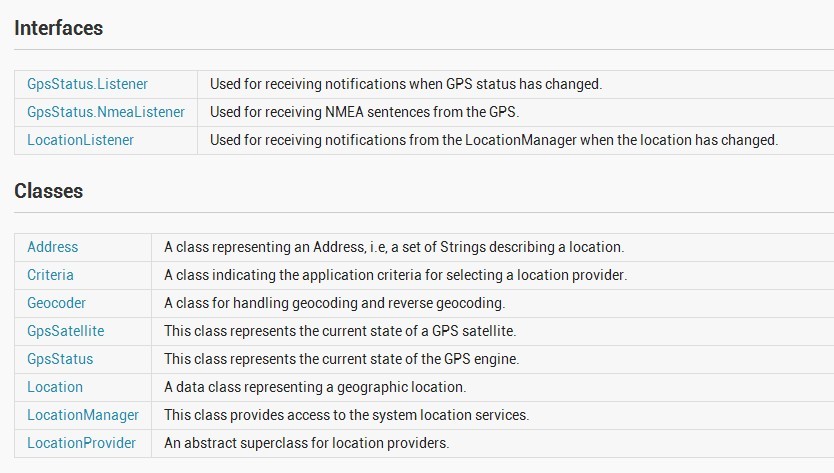
Android定位服务都是位于location下,上面都有相关说明,这里就不详细解析。有一点有需要说说的
是:GpsStatus.NmeaListener 官方的说法是可以读取NMEA数据,但是我这里测试发现,并没有读取到NMEA的数据。查阅过一些资料,说是google在底层并没有实现数据反馈的功能。有时间,需要查看一下源码。
2、LocationManager定位
//获取定位服务
LocationManager locationManager = (LocationManager) this.getSystemService(Context.LOCATION_SERVICE);
//判断是否已经打开GPS模块
if (locationManager.isProviderEnabled(android.location.LocationManager.GPS_PROVIDER))
{
//GPS模块打开,可以定位操作
}// 通过GPS定位 String LocateType= locationManager.GPS_PROVIDER; Location location = locationManager.getLastKnownLocation(LocateType); // 设置监听器,设置自动更新间隔这里设置1000ms,移动距离:0米。 locationManager.requestLocationUpdates(provider, 1000, 0, locationListener); // 设置状态监听回调函数。statusListener是监听的回调函数。 locationManager.addGpsStatusListener(statusListener); //另外给出 通过network定位设置 String LocateType= locationManager.NETWORK_PROVIDER; Location location = locationManager.getLastKnownLocation(LocateType);
3、GpsStatus监听器
上面给出了定位服务的初始化设置步骤,但我们都知道GPS卫星是定期广播数据的,也就是说会定期收到卫星的GPS数据。我们并不能跟卫星主动申请数据,只能被动接收数据。(中国的北斗2倒是可以发送卫星报文给卫星)因此我们需要注册一个监听器来处理卫星返回的数据。
private final GpsStatus.Listener statusListener = new GpsStatus.Listener()
{
public void onGpsStatusChanged(int event)
{
// GPS状态变化时的回调,获取当前状态
GpsStatus status = locationManager.getGpsStatus(null);
//自己编写的方法,获取卫星状态相关数据
GetGPSStatus(event, status);
}
};4、获取搜索到的卫星
private void GetGPSStatus(int event, GpsStatus status)
{
Log.d(TAG, "enter the updateGpsStatus()");
if (status == null)
{
}
else if (event == GpsStatus.GPS_EVENT_SATELLITE_STATUS)
{
//获取最大的卫星数(这个只是一个预设值)
int maxSatellites = status.getMaxSatellites();
Iterator<GpsSatellite> it = status.getSatellites().iterator();
numSatelliteList.clear();
//记录实际的卫星数目
int count = 0;
while (it.hasNext() && count <= maxSatellites)
{
//保存卫星的数据到一个队列,用于刷新界面
GpsSatellite s = it.next();
numSatelliteList.add(s);
count++;
Log.d(TAG, "updateGpsStatus----count="+count);
}
mSatelliteNum = numSatelliteList.size();
}
else if(event==GpsStatus.GPS_EVENT_STARTED)
{
//定位启动
}
else if(event==GpsStatus.GPS_EVENT_STOPPED)
{
//定位结束
}
}上面就是从状态值里面获取搜索到的卫星数目,主要是通过status.getSatellites()实现。获取到的GpsSatellite对象,
保存到一个队列里面,用于后面刷新界面。上面是获取GPS状态监听器,除了GPS状态外,我们还需要监听一个服务,
就是:LocationListener,定位监听器,监听位置的变化。这个对做定位服务的应用来说,十分重要。
5、LocationListener监听器
private final LocationListener locationListener = new LocationListener()
{
public void onLocationChanged(Location location)
{
//当坐标改变时触发此函数,如果Provider传进相同的坐标,它就不会被触发
updateToNewLocation(location);
Log.d(TAG, "LocationListener onLocationChanged");
}
public void onProviderDisabled(String provider)
{
//Provider被disable时触发此函数,比如GPS被关闭
Log.d(TAG, "LocationListener onProviderDisabled");
}
public void onProviderEnabled(String provider)
{
// Provider被enable时触发此函数,比如GPS被打开
Log.d(TAG, "LocationListener onProviderEnabled");
}
public void onStatusChanged(String provider, int status, Bundle extras)
{
Log.d(TAG, "LocationListener onStatusChanged");
// Provider的转态在可用、暂时不可用和无服务三个状态直接切换时触发此函数
if (status == LocationProvider.OUT_OF_SERVICE || status == LocationProvider.TEMPORARILY_UNAVAILABLE) {
}
}
};位置监听回调是用来处理GPS位置发生变化的时候,自动回调的方法,我们可以从这里获取到当前的GPS数据。另外我们可以通过回调函数提供的location参数,获取GPS的地理位置信息,包括经纬度、速度、海拔等信息。
6、获取地理位置信息(经纬度、卫星数目、海拔、定位状态)
//location对象是从上面定位服务回调函数的参数获取。 mLatitude = location.getLatitude(); // 经度 mLongitude = location.getLongitude(); // 纬度 mAltitude = location.getAltitude(); //海拔 mSpeed = location.getSpeed(); //速度 mBearing = location.getBearing(); //方向
7、获取指定卫星信息(方向角、高度角、信噪比)
//temgGpsSatellite就是我们上面保存的搜索到的卫星 //方向角 float azimuth = temgGpsSatellite.getAzimuth(); //高度角 float elevation = temgGpsSatellite.getElevation(); //信噪比 float snr = temgGpsSatellite.getSnr();
利用方向角、高度角我们可以绘画出一个二维图形,表示卫星在地球哪个方位,信噪比作用更大。一般的卫星定位测试软件,都提供了信噪比的状态图,这是表示GPS模块搜星能力的代表。
8、绘画二维卫星位置图
下面是我做的GPS测试的效果图:
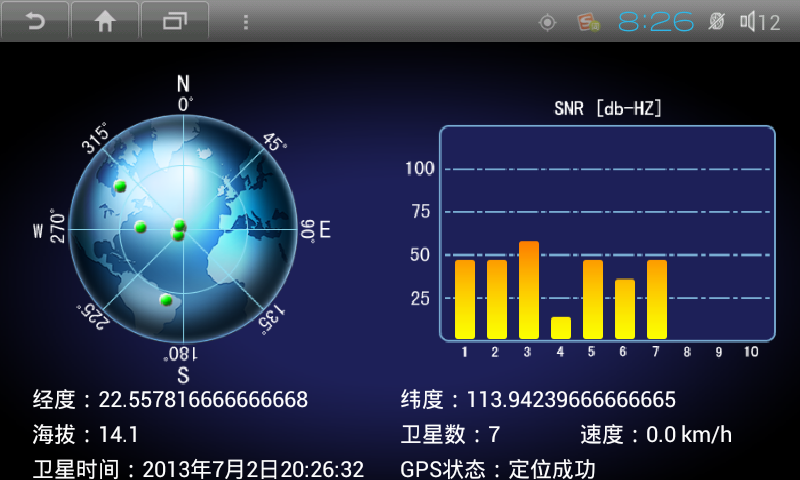
下面给出一个根据方向角和高度角,计算卫星二维图里面位置的方法,上面效果图左边的绿色圆点就代表卫星位置。
右边的信噪比柱状图,代表卫星的接收信号能力。
//根据方向角和高度角计算出,卫星显示的位置 Point point = new Point(); int x = mEarthHeartX; //左边地球圆形的圆心位置X坐标 int y = mEarthHeartY; //左边地球圆形的圆心位置Y坐标 int r = mEarthR; x+=(int)((r*elevation*Math.sin(Math.PI*azimuth/180)/90)); y-=(int)((r*elevation*Math.cos(Math.PI*azimuth/180)/90)); point.x = x; point.y = y; //point就是你需要绘画卫星图的起始坐标
信噪比的绘画,就是一个单位换算,这里就不给代码了。
9、总结:
Android为我们提供了很方便的位置服务,主要通过GpsStatus、LocationManager、GpsSatellite这几个类实现相关服务和监听。
不过个人觉得如果能直接读取NMEA的数据也是很方便,起码对于某些应用来说,可以获取更多信息。
更多Android GPS定位测试(附效果图和示例)相关文章请关注PHP中文网!
今天关于Android 3D效果图片库和android3d效果实现的讲解已经结束,谢谢您的阅读,如果想了解更多关于3D翻转效果介绍,Android动画分析、Android 3D 图片滚动效果怎么适应不同安卓版本、Android 3D 旋转动画效果、Android GPS定位测试(附效果图和示例)的相关知识,请在本站搜索。
本文标签:





