本文将为您提供关于h:inputText绑定到String属性正在提交空字符串而不是null的详细介绍,我们还将为您解释input数据绑定的相关知识,同时,我们还将为您提供关于AndroidMater
本文将为您提供关于h:inputText绑定到String属性正在提交空字符串而不是null的详细介绍,我们还将为您解释input数据绑定的相关知识,同时,我们还将为您提供关于Android Material Design控件使用(2)——FloatButton TextInputEditText TextInputLayout 按钮和输入框、android – 什么更快?一个intent.putExtras(捆绑带字符串)或许多intent.putExtra(字符串)?、Angular 4“无法绑定到’ngModel’,因为它不是’input’的已知属性.”、asp.net-mvc – 如何设置TextBox的空字符串而不是null的默认值的实用信息。
本文目录一览:- h:inputText绑定到String属性正在提交空字符串而不是null(input数据绑定)
- Android Material Design控件使用(2)——FloatButton TextInputEditText TextInputLayout 按钮和输入框
- android – 什么更快?一个intent.putExtras(捆绑带字符串)或许多intent.putExtra(字符串)?
- Angular 4“无法绑定到’ngModel’,因为它不是’input’的已知属性.”
- asp.net-mvc – 如何设置TextBox的空字符串而不是null的默认值

h:inputText绑定到String属性正在提交空字符串而不是null(input数据绑定)
我在Tomcat上有一个JSF 2.0应用程序,其中有许多<h:inputText>字段可以在数据库中输入数据。某些字段不是必需的。
<h:inputText value="#{registerBean.user.phoneNumber}" id="phoneNumber"> <f:validateLength maximum="20" /></h:inputText>当用户将该字段留空时,JSF会设置空字符串""而不是null。
我如何在不检查每个字符串的情况下解决此问题
if (string.equals("")) { string = null; }答案1
小编典典您可以配置JSF 2.x的解释由以下空提交的数据为空context-param的web.xml(其中有一个很长的名字,这也将是为什么我不记得它;)):
<context-param> <param-name>javax.faces.INTERPRET_EMPTY_STRING_SUBMITTED_VALUES_AS_NULL</param-name> <param-value>true</param-value></context-param>作为参考和感兴趣的人,在JSF 1.2(因此不是1.1或更旧的版本,因为在设计上不可能有Converterforjava.lang.String),可以通过以下方法解决Converter:
public class EmptyToNullStringConverter implements Converter { public Object getAsObject(FacesContext facesContext, UIComponent component, String submittedValue) { if (submittedValue == null || submittedValue.isEmpty()) { if (component instanceof EditableValueHolder) { ((EditableValueHolder) component).setSubmittedValue(null); } return null; } return submittedValue; } public String getAsString(FacesContext facesContext, UIComponent component, Object modelValue) { return (modelValue == null) ? "" : modelValue.toString(); }}…需要在faces-config.xml以下位置进行注册:
<converter> <converter-for-class>java.lang.String</converter-for-class> <converter-class>com.example.EmptyToNullStringConverter</converter-class></converter>如果您尚未使用Java 6,请替换submittedValue.empty()为submittedValue.length() == 0。
也可以看看
- balusc.omnifaces

Android Material Design控件使用(2)——FloatButton TextInputEditText TextInputLayout 按钮和输入框
FloatingActionButton
1. 使用FloatingActionButton的情形
FAB代表一个App或一个页面中最主要的操作,如果一个App的每个页面都有FAB,则通常表示该App最主要的功能是通过该FAB操作的。
为了突出FAB的重要性,一个页面最好只有一个FAB 使用的时候需要导入desgin包,Android Studio 新版本都已经自动导入了,这里就不多说
compile ''com.android.support:design:25.1.0''
2. FloatingActionButton的大小一般有两种大小(官方)
- 56 * 56dp :默认的大小,最常用的尺寸。
- 40 * 40 dp :Mini版。 当然也是可以改变大小,不过一般使用
按钮中间图标大小官方推荐为 24*24dp
3.FloatingActionButton的属性
FloatingActionButton是继承ImageView,包含了ImageView的所有属性,除此之外,还有几个新增加的特殊属性,需要使用命名空间来使用。
引入命名空间:xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
| 属性名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| elevation | 阴影的高度 |
| fabSize | FAB的大小,为normal时,大小为:56 * 56dp ,为mini时,大小为: 40 * 40 dp |
| backgroundTint | FAB的背景颜色 |
| rippleColor | 点击FAB时,形成的波纹颜色 |
TextInputEditText
介绍
TextInputEditText是EditText的子类,相当于完善了有些EditText的缺点
当我们的界面处于全屏时,点击一个
EditText,默认情况下不是在它下面弹出键盘,而是进入到输入法的一个全屏的输入界面(通过配置android:imeOptions=”flagNoExtractUi”可以设为直接在当前界面显示)
如果我们给
EditText套上了一个TextInputLayout时,TextInputLayout会拿到EditText的hint显示出来并把EditText本身的hint设为空.这样我们在全屏的输入界面上,就显示不出来我们设置hint,因此TextInputEditText重写了EditText
TextInputLayout
介绍
这个布局其实是与EditText连用,可以实现密码框的显示与隐藏,和点击输入的时候,会将提示文字浮现在上方
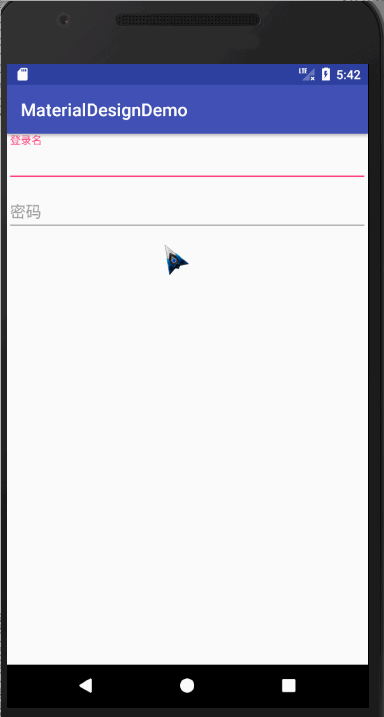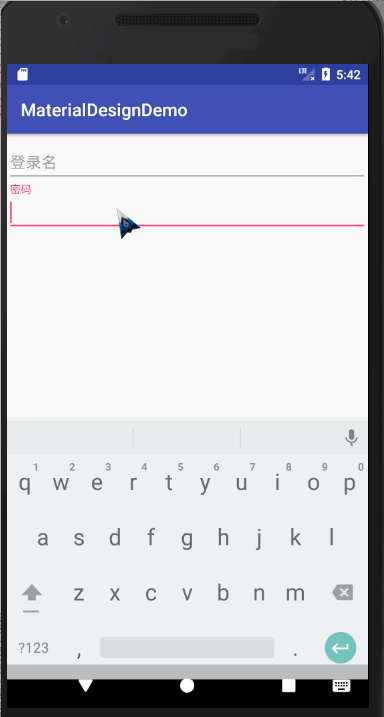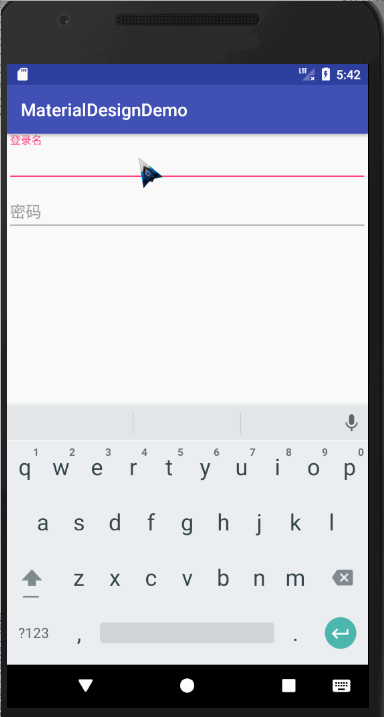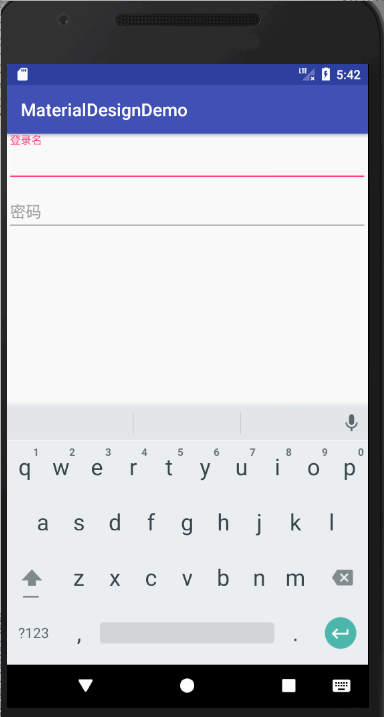
代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.wan.homework.activity.Homework1Activity">
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputEditText
android:id="@+id/username"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="用户名"/>
</android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout>
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<EditText
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:id="@+id/password"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="密码"/>
</android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout>
</LinearLayout>
错误提示
TextInputLayout其实内置了一个用来显示错误提示的方法,方法名为setError,效果如下

我们可以按钮的点击事件中,对用户的输入进行判断,从而显示错误信息
val userName = input_login_name.editText?.text.toString()
//验证用户输入
if (userName.isBlank()) {
input_login_name.error = "用户名还未输入哦!"
}
PS:如果想要清空错误信息,将错误信息设置为""即可
input_login_name.error = ""
密码的显示与隐藏

如果想要实现此效果,只需要在将TextInputLayout的EditText的inputType属性设置为textpassword,将TextInputLayout的自定义属性passwordToggleEnabled设置为true即可
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout
android:id="@+id/input_password"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:passwordToggleEnabled="true">
<android.support.design.widget.TextInputEditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="密码"
android:inputType="textPassword"/>
</android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout>
属性
| 属性名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| app:Theme | 设置下划线或其他的颜色属性 |
| android.support.design:counterEnabled | 是否显示计数器 |
| android.support.design:counterMaxLength | 设置计数器的最大值,与counterEnabled同时使用 |
| android.support.design:counterTextAppearance | 计数器的字体样式 |
| android.support.design:counterOverflowTextAppearance | 输入字符大于我们限定个数字符时的字体样式 |
| android.support.design:errorEnabled | 是否显示错误信息 |
| android.support.design:errorTextAppearance | 错误信息的字体样式 |
| android.support.design:hintAnimationEnabled | 是否显示hint的动画,默认true |
| android.support.design:hintEnabled | 是否使用hint属性,默认true |
| android.support.design:hintTextAppearance | 设置hint的文字样式(指运行动画效果之后的样式) |
| android.support.design:passwordToggleDrawable | 设置密码开关Drawable图片,于passwordToggleEnabled同时使用 |
| android.support.design:passwordToggleEnabled | 是否显示密码开关图片,需要EditText设置inputType |
| android.support.design:passwordToggleTint | 设置密码开关图片颜色 |
| android.support.design:passwordToggleTintMode | 设置密码开关图片(混合颜色模式),与passwordToggleTint同时使用 |
原文出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/stars-one/p/10348492.html

android – 什么更快?一个intent.putExtras(捆绑带字符串)或许多intent.putExtra(字符串)?
什么更快?将一堆字符串值添加到一个包中,然后将其添加到一个意图?或者只是使用intent.putExtra()将值添加到intent中?或者它没有太大区别?
谷歌搜索给了我教程,但没有太多答案.只是出于好奇,想知道是否会影响使用其中一个的性能. This接近了,但没有回答我想知道的事情.
根据source code,Intent.putExtra(String,String)方法如下所示:
public Intent putExtra(String name,String value) {
if (mExtras == null) {
mExtras = new Bundle();
}
mExtras.putString(name,value);
return this;
}
因此,它将始终检查是否已创建Bundle mExtras.这就是为什么对于大量的String添加可能会慢一点. Intent.putExtras(Bundle)看起来像这样:
public Intent putExtras(Bundle extras) {
if (mExtras == null) {
mExtras = new Bundle();
}
mExtras.putAll(extras);
return this;
}
因此,它将仅检查(mExtras == null)一次,然后使用Bundle.putAll()将所有值添加到内部Bundle mExtras:
public void putAll(Bundle map) {
unparcel();
map.unparcel();
mMap.putAll(map.mMap);
// fd state is Now kNown if and only if both bundles already knew
mHasFds |= map.mHasFds;
mFdsKNown = mFdsKNown && map.mFdsKNown;
}
Bundle由Map(确切地说是HashMap)备份,因此将所有字符串一次添加到此映射也应该比逐个添加字符串更快.

Angular 4“无法绑定到’ngModel’,因为它不是’input’的已知属性.”
这似乎是一个流行的问题,但解决方案都建议导入FormsModule,而这正在完成.
错误是:
无法绑定到’ngModel’,因为它不是’input’的已知属性. (”
<label for="city">City</label> <input type="text" id="city" [ERROR ->][(ngModel)]="chosenCity"> <input type="button" value="Get Weather" (click)="getWeather(chosenCity)" "):
模板和组件代码如下:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { Http } from '@angular/http';
@Component({
selector: 'weather',templateUrl: './weather.component.html'
})
export class WeatherComponent {
public weather: Weather;
constructor( private http: Http) {
}
public getWeather(chosenCity: string): void {
this.http.get('/api/weather/city/' + chosenCity).subscribe(result => {
this.weather = result.json();
});
}
}
interface Weather {
temp: string;
summary: string;
city: string;
}
<h1>Weather check</h1>
<label for="city">City</label>
<input type="text" id="city" [(ngModel)]="chosenCity">
<input type="button" value="Get Weather" (click)="getWeather(chosenCity)" />
<div *ngIf="weather">
<h3>Weather for {{weather.city}}</h3>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Temp</th>
<th>Summary</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>{{weather.temp}}</td>
<td>{{weather.summary}}</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
app.module.shared.ts如下:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { AppComponent } from './components/app/app.component'
import { NavMenuComponent } from './components/navmenu/navmenu.component';
import { HomeComponent } from './components/home/home.component';
import { FetchDataComponent } from './components/fetchdata/fetchdata.component';
import { CounterComponent } from './components/counter/counter.component';
import { HelloWorldComponent } from './components/helloworld/helloworld.component';
import { WeatherComponent } from './components/weather/weather.component';
export const sharedConfig: NgModule = {
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ],declarations: [
AppComponent,NavMenuComponent,CounterComponent,FetchDataComponent,HomeComponent,HelloWorldComponent,WeatherComponent
],imports: [
RouterModule.forRoot([
{ path: '',redirectTo: 'home',pathMatch: 'full' },{ path: 'home',component: HomeComponent },{ path: 'counter',component: CounterComponent },{ path: 'fetch-data',component: FetchDataComponent },{ path: 'hello',component: HelloWorldComponent },{ path: 'weather',component: WeatherComponent },{ path: '**',redirectTo: 'home' }
])
]
};
app.module.client.ts文件如下:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { browserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { FormsModule,ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { HttpModule } from '@angular/http';
import { sharedConfig } from './app.module.shared';
@NgModule({
bootstrap: sharedConfig.bootstrap,declarations: sharedConfig.declarations,imports: [
browserModule,HttpModule,FormsModule,ReactiveFormsModule,...sharedConfig.imports
],providers: [
{ provide: 'ORIGIN_URL',useValue: location.origin }
]
})
export class AppModule {
}
如果有人可以向我指出我做错了什么,我将非常感激,但我找到的每篇文章都表明可以通过导入FormsModule解决问题.
解决方法
你的app.module.shared.ts应该是这样的.
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule } from '@angular/router';
import { FormsModule,ReactiveFormsModule } from '@angular/forms';
import { AppComponent } from './components/app/app.component'
import { NavMenuComponent } from './components/navmenu/navmenu.component';
import { HomeComponent } from './components/home/home.component';
import { FetchDataComponent } from './components/fetchdata/fetchdata.component';
import { CounterComponent } from './components/counter/counter.component';
import { HelloWorldComponent } from './components/helloworld/helloworld.component';
import { WeatherComponent } from './components/weather/weather.component';
export const sharedConfig: NgModule = {
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ],imports: [
FormsModule,ReactiveFormsModule
RouterModule.forRoot([
{ path: '',redirectTo: 'home' }
])
]
};

asp.net-mvc – 如何设置TextBox的空字符串而不是null的默认值
但是,我发现,对于用户输入要保存的对象的属性的强类型视图,如果未输入某些字段,则将其分配为空。
然后当您尝试保存更改时,验证失败。
所以不是将每个属性设置为一个空字符串,如何自动将窗体上的每个TextBox设置为默认值为空字符串而不是空值?
解决方法
[displayFormat(ConvertEmptyStringToNull=false)]
所以每当有人发表一个空文本字段的表单,这些将是一个空字符串,而不是null …
关于h:inputText绑定到String属性正在提交空字符串而不是null和input数据绑定的问题我们已经讲解完毕,感谢您的阅读,如果还想了解更多关于Android Material Design控件使用(2)——FloatButton TextInputEditText TextInputLayout 按钮和输入框、android – 什么更快?一个intent.putExtras(捆绑带字符串)或许多intent.putExtra(字符串)?、Angular 4“无法绑定到’ngModel’,因为它不是’input’的已知属性.”、asp.net-mvc – 如何设置TextBox的空字符串而不是null的默认值等相关内容,可以在本站寻找。
本文标签:





