本文将为您提供关于在Springboot中创建自定义JasyptPropertySource的详细介绍,我们还将为您解释springboot自定义validator的相关知识,同时,我们还将为您提供关
本文将为您提供关于在Springboot中创建自定义Jasypt PropertySource的详细介绍,我们还将为您解释springboot自定义validator的相关知识,同时,我们还将为您提供关于3springboot:springboot配置文件(配置文件、YAML、属性文件值注入<@Value、@ConfigurationProperties、@PropertySource,@...、java – Spring boot无法找到PropertySource:找不到标签、javascript – 创建自定义PropTypes,扩展react中的默认PropTypes、org.springframework.boot.bind.PropertySourcesPropertyValues的实例源码的实用信息。
本文目录一览:- 在Springboot中创建自定义Jasypt PropertySource(springboot自定义validator)
- 3springboot:springboot配置文件(配置文件、YAML、属性文件值注入<@Value、@ConfigurationProperties、@PropertySource,@...
- java – Spring boot无法找到PropertySource:找不到标签
- javascript – 创建自定义PropTypes,扩展react中的默认PropTypes
- org.springframework.boot.bind.PropertySourcesPropertyValues的实例源码
在Springboot中创建自定义Jasypt PropertySource(springboot自定义validator)
我正在使用Spring
Boot创建一个访问数据库的简单Web应用程序。我通过在中设置spring.datasource.*属性来利用DataSource的自动配置功能application.properties。一切都很棒,而且非常快-
伟大的工作人员@ Spring!
我公司的政策是不应使用明文密码。因此,我需要进行sping.datasource.password加密。经过一番挖掘之后,我决定创建一个org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader实现,该实现将创建一个jasyptorg.jasypt.spring31.properties.EncryptablePropertiesPropertySource,如下所示:
public class EncryptedPropertySourceLoader implements PropertySourceLoader{ private final StandardPBEStringEncryptor encryptor = new StandardPBEStringEncryptor(); public EncryptedPropertySourceLoader() { //TODO: this could be taken from an environment variable this.encryptor.setPassword("password"); } @Override public String[] getFileExtensions() { return new String[]{"properties"}; } @Override public PropertySource<?> load(final String name, final Resource resource, final String profile) throws IOException { if (profile == null) { final Properties props = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); if (!props.isEmpty()) { return new EncryptablePropertiesPropertySource(name, props, this.encryptor); } } return null; }}然后,我将其包装在它自己的jar中,并带有一个META-INF/spring.factories文件,如下所示:
org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader=com.mycompany.spring.boot.env.EncryptedPropertySourceLoader当从Maven使用运行时,此方法非常有效mvn spring-boot:run。当我使用进行独立战争时会发生问题java -jar my-app.war。该应用程序仍然加载,但是当我尝试连接数据库时失败,因为密码值仍然被加密。添加日志记录将显示EncryptedPropertySourceLoader从未加载。
对我来说,这听起来像是类路径问题。在maven下运行时,jar的加载顺序很严格,但是一旦进入了tomcat的tomcat,就无话可说,我的自定义jar应该在Spring
Boot之前加载。
我尝试将以下内容添加到我的pom.xml中,以确保保留classpth,但它似乎没有任何效果。
<build> <pluginManagement> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId> <artifactId>maven-war-plugin</artifactId> <configuration> <failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml> <archive> <manifest> <mainClass>${start-class}</mainClass> <addClasspath>true</addClasspath> </manifest> </archive> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </pluginManagement> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins></build>有人有什么想法吗?提前致谢。
更新:
向前迈进了一步:我已经设法通过使EncryptedPropertySourceLoader类实现org.springframework.core.PriorityOrdered接口并HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE从中返回来解决此问题getOrder()。现在,这已解决了不使用PropertySourceLoader的问题。但是,现在尝试解密属性时会引发以下错误:
org.jasypt.exceptions.EncryptionInitializationException: java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException: PBEWithMD5AndDES SecretKeyFactory not available at org.jasypt.encryption.pbe.StandardPBEByteEncryptor.initialize(StandardPBEByteEncryptor.java:716) at org.jasypt.encryption.pbe.StandardPBEStringEncryptor.initialize(StandardPBEStringEncryptor.java:553) at org.jasypt.encryption.pbe.StandardPBEStringEncryptor.decrypt(StandardPBEStringEncryptor.java:705) at org.jasypt.properties.PropertyValueEncryptionUtils.decrypt(PropertyValueEncryptionUtils.java:72) at org.jasypt.properties.EncryptableProperties.decode(EncryptableProperties.java:230) at org.jasypt.properties.EncryptableProperties.get(EncryptableProperties.java:209) at org.springframework.core.env.MapPropertySource.getProperty(MapPropertySource.java:36) at org.springframework.boot.env.EnumerableCompositePropertySource.getProperty(EnumerableCompositePropertySource.java:49) at org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener$ConfigurationPropertySources.getProperty(ConfigFileApplicationListener.java:490)同样,从运行时不会发生这种情况,mvn spring-boot:run但是从可执行war文件运行时会发生这种情况。两种方案都使用相同的JVM(jdk1.6.0_35)。Google /
Stackoverflow上的结果表明这是Java安全策略的一个问题,但是从maven运行时它确实可以工作,我想我可以对此予以保留。可能是包装问题…
答案1
小编典典这里有两个问题。
1)EncryptedPropertySourceLoader的加载需要高于标准PropertiesPropertySourceLoader的加载。这可以通过实现PriorityOrder接口来实现,如下所示:
public class EncryptedPropertySourceLoader implements PropertySourceLoader, PriorityOrdered{ private final StandardPBEStringEncryptor encryptor = new StandardPBEStringEncryptor(); public EncryptedPropertySourceLoader() { this.encryptor.setPassword("password"); //TODO: this could be taken from an environment variable } @Override public String[] getFileExtensions() { return new String[]{"properties"}; } @Override public PropertySource<?> load(final String name, final Resource resource, final String profile) throws IOException { if (profile == null) { //load the properties final Properties props = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); if (!props.isEmpty()) { //create the encryptable properties property source return new EncryptablePropertiesPropertySource(name, props, this.encryptor); } } return null; } @Override public int getOrder() { return HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE; }}使用将从订单中org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader加载结果的类。意味着应首先返回此类,并将负责为*
.proerpties文件提供PropertySourceLoader实现。org.springframework.boot.env.PropertySourceLoader``META-INF/spring.factories``org.springframework.core.OrderComparator
2)第二个问题是可执行JAR / WAR的类加载问题,这似乎是由Windows上的Spring
Boot版本1.1.2.RELEASE中的错误引起的。降至版本1.1.1.RELEASE或版本1.1.3RELEASE解决了在maven外部运行时类和属性文件未加载的各种问题。
3springboot:springboot配置文件(配置文件、YAML、属性文件值注入<@Value、@ConfigurationProperties、@PropertySource,@...
1.配置文件:
配置文件有两种(开头均是application,主要是文件的后缀):
作用:修改springboot自动配置的默认值
位置:
配置文件放在src/main/resourcr目录或者 类路径/config 下
2.YAML:
YAML(YAML Ain''t Markup Language)
YAML A Markup Language:是一个标记语言
YAML isn''t Markup Language:不是一个标记语言;
标记语言:
以前的配置文件;大多都使用的是 xxxx.xml文件;
YAML:以数据为中心,比json、xml等更适合做配置文件;
参考:http://yaml.org/
该语法风格:
server:
port: 8088
使用语法:
k:(空格)v:表示一对键值对(空格必须有);
以空格的缩进来控制层级关系;只要是左对齐的一列数据,都是同一个层级的
值的写法:
字面量:普通的值(数字,字符串,布尔)
k: v:字面直接来写;
字符串默认不用加上单引号或者双引号;
" ":双引号;不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符;特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思
name: "zhangsan \n lisi":输出;zhangsan 换行 lisi
'' '':单引号;会转义特殊字符,特殊字符最终只是一个普通的字符串数据
name: ‘zhangsan \n
1.对象、Map(属性和值)(键值对):
注意空格
Person:
name:xxxx
age:12行内写法:
Person: {name:xxx,age=12}2.数组(List、Set):
用-(空格) 值表示数组中的一个元素行内写法
gender: [gril,boy]
导入配置文件处理器,配置文件进行绑定就会有提示
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
3.代码测试

//将配置文件中的每一个属性的值映射到这个组件中
//告诉springboot将本类中的所有属性和配置文件中的相关配置进行绑定
//(prefix = "person")将配置文件中以person下的所有属性进行绑定
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private boolean boss;//布尔值
private Date bir;//时间
private Map<String,Object> map;//Map
private List<String> lists;//List
private Dog dog;//对象
}public class Dog {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
在yml配置文件中
person:
name: Mr
age: 14
boss: true
bir: 2018/12/21
map: {m1: v1,m2: v2}
lists:
- mc
- mt
dog:
name: dogdog
age: 10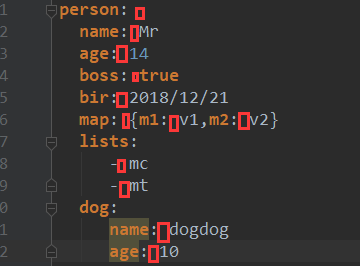
测试:
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class Springboot01ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
Person person;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}Person{name=''Mr'', age=14, boss=true, bir=Fri Dec 21 00:00:00 CST 2018, map={m1=v1, m2=v2},
lists=[mc, mt], dog=Dog{name=''dogdog'', age=10}}
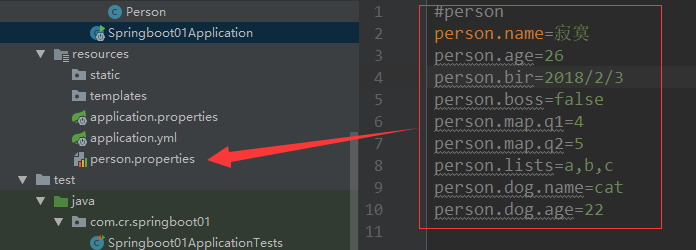
使用properties后缀的:
person.name=mr
person.age=22
person.bir=2018/12/11
person.boss=true
person.map.q1=1
person.map.q2=2
person.lists=a,b,c
person.dog.name=cat
person.dog.age=22 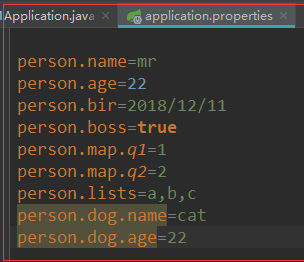
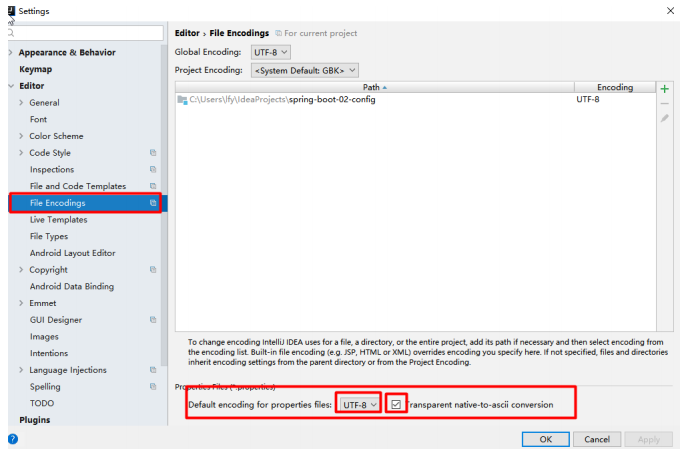
关于乱码的问题:
properties配置文件在idea中默认utf-8可能会乱码
4.配置文件值注入@Value
@Value:1.字面量 2.#{spel} 3.${key}从环境变量配置文件中取值
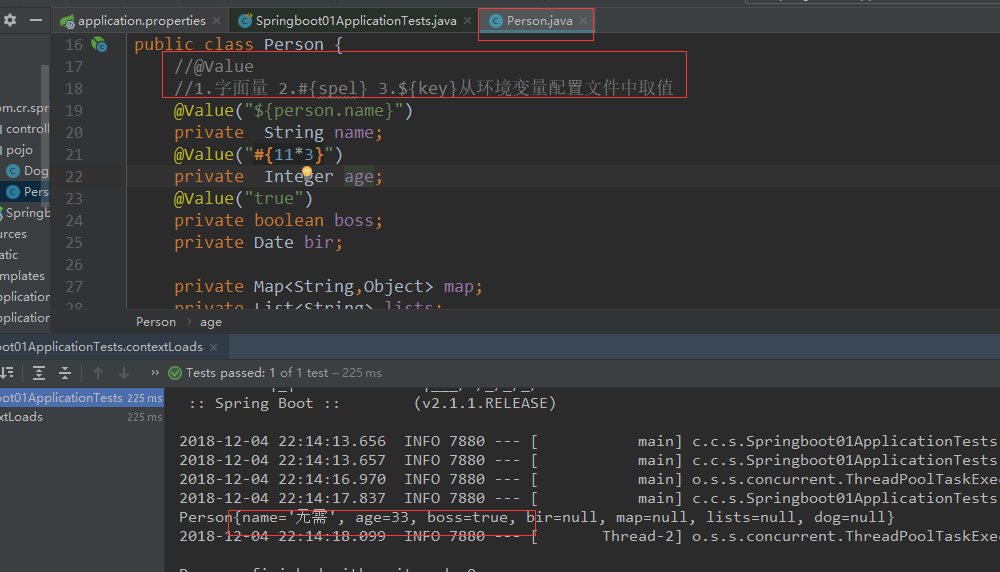
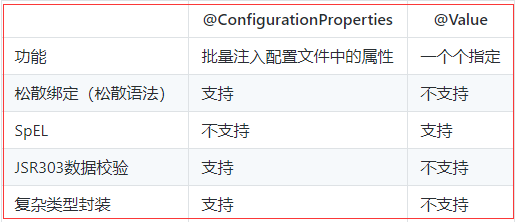
@Value获取值和@ConfigurationProperties获取值比较
松散语法绑定:last_name = last-name = lastName 他们取的值都是相同的
配置文件yml还是properties他们都能获取到值;
如果说,我们只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用@Value;
如果说,我们专门编写了一个javaBean来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用@ConfigurationProperties;
数据校验:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
@Validated
public class Person {
@Email
private String name;
...
}
获取配置文件中的某个值:
@ResponseBody
@Controller
public class Helloword {
@Value("${person.name}")
private String name;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "Hello tow!" + name;
}
}
5@PropertySource,@ImportResource
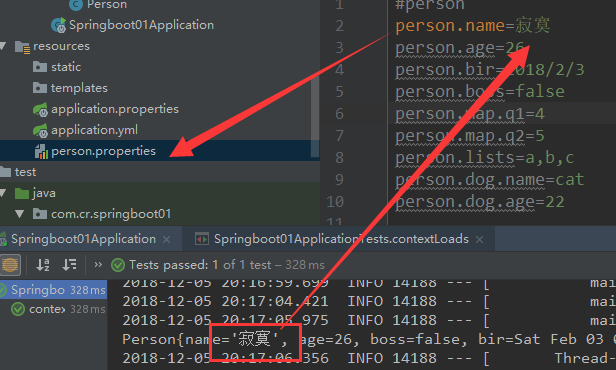
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:/person.properties"})
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private boolean boss;
private Date bir;
...
}
@ImportResource
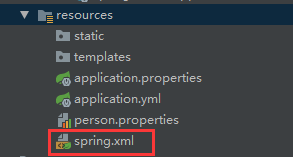
@ImportResource:导入Spring的配置文件,让配置文件里面的内容生效;
Spring Boot里面没有Spring的配置文件,我们自己编写的配置文件,也不能自动识别;
想让Spring的配置文件生效,加载进来;@ImportResource标注在一个配置类上
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:spring.xml"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot01Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot01Application.class, args);
}
}public class helloword {
public void hello(){
System.out.println("hello");
}
} 
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="hello" class="com.cr.springboot01.ImportSoource.helloword"></bean>
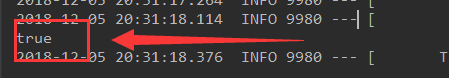
</beans>@Autowired
ApplicationContext app;
@Test
public void testImportSourcr(){
boolean h = app.containsBean("hello");
System.out.println(h);
} 
@Bean
全注解方式:
新建一个配置类
//配置类,指明当前类使配置类,代替xml配置文件
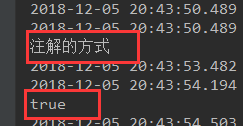
@Configuration
public class MyConfig {
//将方法的返回值添加到容器中,容器中这个组件默认的id就是方法名
@Bean
public Helloword hello(){
System.out.println("注解的方式");
return new Helloword();
}
}@Autowired
ApplicationContext app;
@Test
public void testImportSourcr(){
boolean h = app.containsBean("hello");
System.out.println(h);
} 
java – Spring boot无法找到PropertySource:找不到标签
我正在尝试设置Spring Cloud Config Server,但是服务配置服务器,它运行在端口8888上是正确的,另一个服务应该在端口18060上运行,但是因为我启动的原因,它为我分配端口8080和返回警告“无法找到PropertySource:标签未找到”,我该怎么办?谢谢 !!!
首先在您的应用程序中启用调试模式.(在您的属性文件中:logging.level.= DEBUG.这只是为了确保问题与我的相同或者您可能有任何线索可能出错.)
然后启动应用程序并查看日志.日志显示配置的服务器URI以及获取所有属性资源的URL.
比较两个URL – 日志中的URL和配置服务器URI.
问题是错误地定义了属性文件的URL最后可能有空格. (当你从某个地方复制过去时会发生这种情况)示例:
spring.cloud.config.uri = http:localhost:<的值端口><另外的空白空间>
如果是这种情况,客户端的日志显示localhost:/ 20%/<应用名称> /<个人资料>
只需删除帖子空白空间.那它应该工作!
javascript – 创建自定义PropTypes,扩展react中的默认PropTypes
我正在尝试创建一个自定义PropType,用于检查数组是否具有数值并且长度为2(并且对数字的排序有一些约束).
显然我可以为前两个约束做Array.PropType.arrayOf(Array.PropType.number).
我想在我的自定义PropType中重用它(而不是推出我自己的数字和数组检查).
我怎么做?
您的函数将传递三个参数:props,propName,componentName
从文档中查看React.PropTypes中显示的倒数第二个示例.
所以应该满足你的约束的函数是:
function isTwoelementArrayOfNumbers( props,componentName ){
var _array = props[ propName ];
if( _array && _array.constructor === Array && _array.length === 2 ){
if( !_array.every(
function isNumber( element ){
return typeof element === 'number';
})
){
return new Error('elements must be numbers!');
}
}
else{
return new Error('2 element array of numbers not provided!');
}
}
...in your react element
propTypes:{
numArray: isTwoelementArrayOfNumbers
},
org.springframework.boot.bind.PropertySourcesPropertyValues的实例源码
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,AnnotatedTypeMetadata Metadata) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) context
.getEnvironment();
ResourceProperties properties = new ResourceProperties();
RelaxedDataBinder binder = new RelaxedDataBinder(properties,"spring.resources");
binder.bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(environment.getPropertySources()));
Boolean match = properties.getChain().getEnabled();
if (match == null) {
boolean webJarsLocatorPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBJAR_ASSERT_LOCATOR,getClass().getClassLoader());
return new ConditionOutcome(webJarsLocatorPresent,"Webjars locator (" + WEBJAR_ASSERT_LOCATOR + ") is "
+ (webJarsLocatorPresent ? "present" : "absent"));
}
return new ConditionOutcome(match,"Resource chain is " + (match ? "enabled" : "disabled"));
}
@Override public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,"Resource chain is " + (match ? "enabled" : "disabled")); }
private List<String> getExcludeAutoConfigurationsproperty() {
if (getEnvironment() instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
Excludes excludes = new Excludes();
RelaxedDataBinder binder = new RelaxedDataBinder(excludes,"spring.autoconfigure.");
binder.bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(
((ConfigurableEnvironment) getEnvironment()).getPropertySources()));
return excludes.getExclude();
}
RelaxedPropertyResolver resolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(getEnvironment(),"spring.autoconfigure.");
String[] exclude = resolver.getProperty("exclude",String[].class);
return (Arrays.asList(exclude == null ? new String[0] : exclude));
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
this.target = new HashMap<String,Object>();
new RelaxedDataBinder(this.target).bind(
new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(this.environment.getPropertySources()));
this.propertyResolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(environment);
}
private List<String> getExcludeAutoConfigurationsproperty() {
if (getEnvironment() instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
Excludes excludes = new Excludes();
RelaxedDataBinder binder = new RelaxedDataBinder(excludes,String[].class);
return (Arrays.asList(exclude == null ? new String[0] : exclude));
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
this.target = new HashMap<String,Object>();
new RelaxedDataBinder(this.target).bind(
new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(this.environment.getPropertySources()));
this.propertyResolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(environment);
}
@Override
public ConditionOutcome getMatchOutcome(ConditionContext context,"spring.resources");
binder.bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(environment.getPropertySources()));
Boolean match = properties.getChain().getEnabled();
return new ConditionOutcome(match,"Resource chain is " + (match ? "enabled" : "disabled"));
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
this.target = new HashMap<String,Object>();
new RelaxedDataBinder(this.target).bind(
new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(this.environment.getPropertySources()));
this.propertyResolver = new RelaxedPropertyResolver(environment);
}
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
if (!isHasCloudConfigLocator(this.propertySourceLocators)) {
logger.info("未启用Config Server管理配置");
return;
}
logger.info("检查Config Service配置资源");
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
logger.info("加载PropertySources源:" + propertySources.size() + "个");
CloudConfigSupportProperties configSupportProperties = new CloudConfigSupportProperties();
new RelaxedDataBinder(configSupportProperties,CloudConfigSupportProperties.CONfig_PREFIX)
.bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(propertySources));
if (!configSupportProperties.isEnable()) {
logger.warn("未启用配置备份功能,可使用{}.enable打开",CloudConfigSupportProperties.CONfig_PREFIX);
return;
}
if (isCloudConfigLoaded(propertySources)) {
PropertySource cloudConfigSource = getLoadedCloudPropertySource(propertySources);
logger.info("成功获取ConfigService配置资源");
//备份
Map<String,Object> backupPropertyMap = makeBackupPropertyMap(cloudConfigSource);
dobackup(backupPropertyMap,configSupportProperties.getFile());
} else {
logger.error("获取ConfigService配置资源失败");
Properties backupProperty = loadBackupProperty(configSupportProperties.getFile());
if (backupProperty != null) {
HashMap backupsourceMap = new HashMap<>(backupProperty);
PropertySource backupsource = new MapPropertySource("backupsource",backupsourceMap);
propertySources.addFirst(backupsource);
logger.warn("使用备份的配置启动:{}",configSupportProperties.getFile());
}
}
}
public Restifyapiclient client(RestifyableType type) {
Restifyapiclient restifyapiclient = new Restifyapiclient();
RelaxedDataBinder dataBinder = new RelaxedDataBinder(restifyapiclient,"restify." + type.name());
ConfigurableEnvironment configurableEnvironment = (ConfigurableEnvironment) environment;
dataBinder.bind(new PropertySourcesPropertyValues(configurableEnvironment.getPropertySources()));
return restifyapiclient;
}
今天的关于在Springboot中创建自定义Jasypt PropertySource和springboot自定义validator的分享已经结束,谢谢您的关注,如果想了解更多关于3springboot:springboot配置文件(配置文件、YAML、属性文件值注入<@Value、@ConfigurationProperties、@PropertySource,@...、java – Spring boot无法找到PropertySource:找不到标签、javascript – 创建自定义PropTypes,扩展react中的默认PropTypes、org.springframework.boot.bind.PropertySourcesPropertyValues的实例源码的相关知识,请在本站进行查询。
本文标签:





