此处将为大家介绍关于QuestionAnsweringSystemv1.1发布,人机问答系统的详细内容,并且为您解答有关人机问题的相关问题,此外,我们还将为您介绍关于2021Top100C#/.NET
此处将为大家介绍关于QuestionAnsweringSystem v1.1 发布,人机问答系统的详细内容,并且为您解答有关人机问题的相关问题,此外,我们还将为您介绍关于2021 Top 100 C#/.NET Interview Questions And Answers、An Analysis of Visual Question Answering Algorithms翻译、Android SystemProperties和Settings.System介绍,不同应用间传递信息、c# – LINQ to Entities不能识别方法’System.String get_Item(System.String)’,的有用信息。
本文目录一览:- QuestionAnsweringSystem v1.1 发布,人机问答系统(人机问题)
- 2021 Top 100 C#/.NET Interview Questions And Answers
- An Analysis of Visual Question Answering Algorithms翻译
- Android SystemProperties和Settings.System介绍,不同应用间传递信息
- c# – LINQ to Entities不能识别方法’System.String get_Item(System.String)’,

QuestionAnsweringSystem v1.1 发布,人机问答系统(人机问题)
QuestionAnsweringSystem 是一个Java实现的人机问答系统,能够自动分析问题并给出候选答案。IBM人工智能计算机系统"沃森"(Watson)在2011年2月美国热门的电视 智力问答节目"危险边缘"(Jeopardy!)中战胜了两位人类冠军选手,QuestionAnsweringSystem就是IBM Watson的Java开源实现。
系统架构如下:
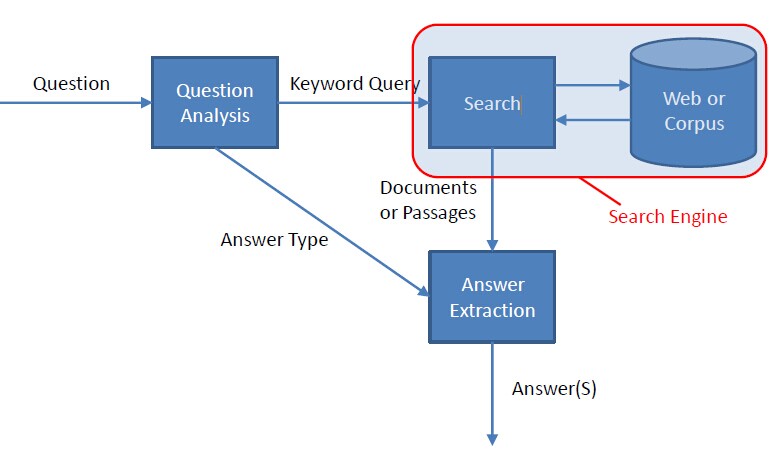
工作原理:
1、判断问题类型(答案类型),当前使用模式匹配的方法,将来支持更多的方法,如朴素贝叶斯分类器。
2、提取问题关键词。
3、利用问题关键词搜索多种数据源,当前的数据源主要是人工标注的语料库、谷歌、百度。
4、从搜索结果中根据问题类型(答案类型)提取候选答案。
5、结合问题以及搜索结果对候选答案进行打分。
6、返回得分最高的TopN项候选答案。目前支持5种问题类型(答案类型):
1、人名
如:
APDPlat的作者是谁?
APDPlat的发起人是谁?
谁死后布了七十二疑冢?
杨尚川最爱的女人是谁?
2、地名
如:
“海的女儿”是哪个城市的城徽?
世界上流经国家最多的河流是哪一条?
世界上最长的河流是什么?
汉城是哪个国家的首都?
3、机构团体名
如:
BMW是哪个汽车公司制造的?
长城信用卡是哪家银行发行的?
美国历史上第一所高等学府是哪个学校?
前身是红色中华通讯社的是什么?
4、数字
如:
全球表面积有多少平方公里?
撒哈拉有多少平方公里?
北京大学占地多少平方米?
撒哈拉有多少平方公里?
5、时间
如:
哪一年第一次提出“大跃进”的口号?
大庆油田是哪一年发现的?
澳门是在哪一年回归祖国怀抱的?
香港是在哪一年回归祖国怀抱的?API接口:
调用地址:
http://121.40.143.109/api/ask?n=1&q=APDPlat的作者是谁?
参数:
n表示需要返回的答案的个数
q表示问题
编码:
服务端和客户端均使用UTF-8编码
服务端需要修改tomcat配置文件conf/server.xml,在相应的Connector中加入配置URIEncoding="UTF-8"
返回json:
[
{
"answer": "杨尚川",
"score": 1
}
]使用说明:
1、初始化MySQL数据库:
在MySQL命令行中执行QuestionAnsweringSystem\src\main\resources\mysql\questionanswer.sql文件中的脚本
主机:127.0.0.1
端口:3306
数据库:questionanswer
用户名:root
密码:root2、构建war文件并部署到tomcat:
cd QuestionAnsweringSystem
mvn install
cp target\QuestionAnsweringSystem-1.0.war apache-tomcat-7.0.37/webapps/QuestionAnsweringSystem-1.0.war
启动tomcat3、打开浏览器访问:
http://localhost:8080/QuestionAnsweringSystem-1.0/
项目主页
可部署war包下载

2021 Top 100 C#/.NET Interview Questions And Answers
https://jackniu81.github.io/2021/04/22/2021-Top-100-C-NET-Interview-Questions-And-Answers/
1. What is the difference between “dispose” and “finalize” variables in C#?
- Dispose - This method uses interface – “IDisposable” interface and it will free up both managed and unmanaged codes like – database connection, files etc.
- Finalize - This method is called internally unlike Dispose method which is called explicitly. It is called by garbage collector and can’t be called from the code.
2. What does “Jagged Arrays” mean?
Answer: Jagged arrays refer to the array that has an element of type array. The dimensions and the sizes of the elements are different. An array of arrays is the other name of the jagged array.
3. What is a Class and an Object?
A ‘Class’ is an encapsulation of methods and properties that are used to represent an entity in real-time. Class brings all of the instances together in a single unit. An ‘Object’ is an instance of a Class, or a block of allocated memory that can be stored in the form of Variables, Array or a Collection.
4. Explain Code compilation in C
Code compilation has four steps which include:
- Compiling source code to Managed code by C# compiler
- Executing the assembly by CLR
- Combining the new code into assemblies
- Loading the Common Language Runtime (CLR)
5. What is the difference between Virtual method and Abstract method?
A Virtual method must always have a default implementation. An Abstract method does not have an implementation. An override keyword is not necessary here, though it can be used.
6. What is a Hashtable in C#?
A Hashtable is a collection that stores (Keys, Values) pairs. Here, the Keys are used to find the storage location and is immutable and cannot have duplicate entries in a Hashtable. The .Net Framework has provided a Hash Table class that contains all the functionality required to implement a hash table without any additional development. The hash table is a general-purpose dictionary collection. Each item within the collection is a DictionaryEntry object with two properties: a key object and a value object. These are known as Key/Value. When items are added to a hash table, a hash code is generated automatically. This code is hidden from the developer. Access to the table''s values is achieved using the key object for identification. As the items in the collection are sorted according to the hidden hash code, the items should be considered to be randomly ordered.
7. What is LINQ in C#?
LINQ stands for Language Integrated Query. LINQ is a data querying methodology that provides querying capabilities to .NET languages with a syntax similar to a SQL query.
LINQ has a great power of querying on any source of data. The data source could be collections of objects, database or XML files. We can easily retrieve data from any object that implements the IEnumerable<T> interface.
Advantages of LINQ
- LINQ offers an object-based, language-integrated way to query over data no matter where that data came from. So through LINQ, we can query a database and XML as well as collections.
- Compile-time syntax checking.
8. What are Indexers in C#?
C# introduces a new concept known as Indexers which are used for treating an object as an array. The indexers are usually known as smart arrays in C#. They are not an essential part of object-oriented programming.
Defining an indexer allows you to create classes that act as virtual arrays. Instances of that class can be accessed using the [] array access operator.
9. Difference between the Equality Operator (==) and Equals() Method in C
Both the == Operator and the Equals() method are used to compare two value type data items or reference type data items. The Equality Operator (==) is the comparison operator and the Equals() method compares the contents of a string. The == Operator compares the reference identity while the Equals() method compares only contents.
10. What''s the Difference between the Is and As operator in C
- "is" operator: In C# language, we use the "is" operator to check the object type. If two objects are of the same type, it returns true, else it returns false.
- "as" operator: The "as" operator behaves in a similar way as the "is" operator. The only difference is it returns the object if both are compatible with that type. Else it returns a null.
11. What are Different Ways a Method can be Overloaded?
Method overloading is a way to achieve compile-time polymorphism where we can use a method with the same name but different signatures. For example, the following code example has a method volume with three different signatures based on the number and type of parameters and return values.
12. What is Serialization?
Serialization converts a code to its binary format using a process. After it is converted to bytes, it can be easily stored and written to a disk. Serializations are useful so that the original form of the code isn’t lost and it can be retrieved later on.
13. What are the different types of Delegates?
The different types of Delegates are: Single Delegate, Multicast Delegate and Generic Delegate.
14. How to use extension methods?
An extension method is a static method of a static class, where the "this" modifier is applied to the first parameter. The type of the first parameter will be the type that is extended.
Extension methods are only in scope when you explicitly import the namespace into your source code with a using directive.
15. What is the difference between String and StringBuilder in C#?
StringBuilder and string are both used to string values, but both have many differences on the bases of instance creation and also in performance.
16. What are sealed classes in C#?
Sealed classes are used to restrict the inheritance feature of object-oriented programming. Once a class is defined as a sealed class, the class cannot be inherited.
In C#, the sealed modifier is used to define a class as sealed. In Visual Basic .NET the Not Inheritable keyword serves the purpose of the sealed class. If a class is derived from a sealed class then the compiler throws an error.
If you have ever noticed, structs are sealed. You cannot derive a class from a struct.
17. What is a Delegate? Explain.
A Delegate is a variable that holds the reference to a method. Hence it is a function pointer or reference type. All Delegates are derived from System.Delegate namespace. Both Delegate and the method that it refers to can have the same signature.
Declaring a delegate: public delegate void AddNumbers(int n);
After the declaration of a delegate, the object must be created by the delegate using the new keyword.
AddNumbers an1 = new AddNumbers(number);The delegate provides a kind of encapsulation to the reference method, which will internally get called when a delegate is called.
public delegate int myDel(int number);
public class Program
{
public int AddNumbers(int a)
{
int Sum = a + 10;
return Sum;
}
public void Start()
{
myDel DelgateExample = AddNumbers;
}
}In the above example, we have a delegate myDel which takes an integer value as a parameter. Class Program has a method of the same signature as the delegate, called AddNumbers().
If there is another method called Start() which creates an object of the delegate, then the object can be assigned to AddNumbers as it has the same signature as that of the delegate.
18. What are Events?
Events are user actions that generate notifications to the application to which it must respond. The user actions can be mouse movements, keypress and so on.
Programmatically, a class that raises an event is called a publisher and a class which responds/receives the event is called a subscriber. Event should have at least one subscriber else that event is never raised.
Delegates are used to declare Events.
Public delegate void PrintNumbers();
Event PrintNumbers myEvent;19. How to use Delegates with Events?
Delegates are used to raise events and handle them. Always a delegate needs to be declared first and then the Events are declared.
20. What do Multicast Delegates mean?
A Delegate that points to more than one method is called a Multicast Delegate. Multicasting is achieved by using + and += operator.
21. Explain Publishers and Subscribers in Events.
Publisher is a class responsible for publishing a message of different types of other classes. The message is nothing but Event as discussed in the above questions.
From the Example in Q #32, Class Patient is the Publisher class. It is generating an Event deathEvent, which is received by the other classes.
Subscribers capture the message of the type that it is interested in. Again, from the Example of Q#32, Class Insurance and Bank are Subscribers. They are interested in event deathEvent of type void.
22. What are Synchronous and Asynchronous operations?
Synchronization is a way to create a thread-safe code where only one thread can access the resource at any given time. The asynchronous call waits for the method to complete before continuing with the program flow.
Synchronous programming badly affects the UI operations when the user tries to perform time-consuming operations since only one thread will be used. In Asynchronous operation, the method call will immediately return so that the program can perform other operations while the called method completes its work in certain situations.
In C#, Async and Await keywords are used to achieve asynchronous programming. Look at Q #43 for more details on synchronous programming.
23. What is Reflection in C#?
Reflection is the ability of a code to access the metadata of the assembly during runtime. A program reflects upon itself and uses the metadata to inform the user or modify its behavior. Metadata refers to information about objects, methods.
The namespace System.Reflection contains methods and classes that manage the information of all the loaded types and methods. It is mainly used for windows applications, For Example, to view the properties of a button in a windows form.
The MemberInfo object of the class reflection is used to discover the attributes associated with a class.
Reflection is implemented in two steps, first, we get the type of the object, and then we use the type to identify members such as methods and properties.
To get type of a class, we can simply use,
Type mytype = myClass.GetType();Once we have a type of class, the other information about the class can be easily accessed.
System.Reflection.MemberInfo Info = mytype.GetMethod(“AddNumbers”);Above statement tries to find a method with name AddNumbers in the class myClass.
24. What is a Generic Class?
Generics or Generic class is used to create classes or objects which do not have any specific data type. The data type can be assigned during runtime, i.e when it is used in the program.
In case of other data type parameter comparisons, instead of creating many overloaded methods, we can create a generic class and pass a substitute data type, i.e T. So, T acts as a datatype until it is used specifically in the Main() method.
25. What is a Jagged Array?
A Jagged array is an array whose elements are arrays. It is also called as the array of arrays. It can be either single or multiple dimensions.
int[] jaggedArray = new int[4][];
) Name some properties of Array.
Properties of an Array include:
- Length: Gets the total number of elements in an array.
- IsFixedSize: Tells whether the array is fixed in size or not.
- IsReadOnly: Tells whether the array is read-only or not.
26. What is an Array Class?
An Array class is the base class for all arrays. It provides many properties and methods. It is present in the namespace system.
27. What is a String? What are the properties of a String Class?
A String is a collection of char objects. We can also declare string variables in c#.
string name = “C# Questions”;
A string class in C# represents a string. The properties of the string class are:
- Chars get the Char object in the current String.
- Length gets the number of objects in the current String.
28. Name some properties of Thread Class.
Few Properties of thread class are:
- IsAlive – contains value True when a thread is Active.
- Name – Can return the name of the thread. Also, can set a name for the thread.
- Priority – returns the prioritized value of the task set by the operating system.
- IsBackground – gets or sets a value which indicates whether a thread should be a background process or foreground.
- ThreadState– describes the thread state.
29. What are the different states of a Thread?
Different states of a thread are:
- Unstarted – Thread is created.
- Running – Thread starts execution.
- WaitSleepJoin – Thread calls sleep, calls wait on another object and calls join on another thread.
- Suspended – Thread has been suspended.
- Aborted – Thread is dead but not changed to state stopped.
- Stopped – Thread has stopped.
30. What are Async and Await?
Async and Await keywords are used to create asynchronous methods in C#.
Asynchronous programming means that the process runs independently of main or other processes.
31. Async Keyword
Async keyword is used for the method declaration.
32. What is a Deadlock?
A Deadlock is a situation where a process is not able to complete its execution because two or more processes are waiting for each other to finish. This usually occurs in multi-threading.
Here a shared resource is being held by a process and another process is waiting for the first process to release it and the thread holding the locked item is waiting for another process to complete.
33. Explain Lock, Monitors, and Mutex Object in Threading.
- Lock keyword ensures that only one thread can enter a particular section of the code at any given time.
lock(ObjA)means the lock is placed on ObjA until this process releases it, no other thread can access ObjA. - Mutex is also like a lock but it can work across multiple processes at a time. WaitOne() is used to lock and ReleaseMutex() is used to release the lock. But Mutex is slower than lock as it takes time to acquire and release it.
- Monitor.Enter and Monitor.Exit implements lock internally. a lock is a shortcut for Monitors.
lock(objA)internally calls.
Monitor.Enter(ObjA);
try
{
}
Finally {
Monitor.Exit(ObjA));
}34. What is a Race Condition?
Race condition occurs when two threads access the same resource and are trying to change it at the same time. The thread which will be able to access the resource first cannot be predicted.
If we have two threads, T1 and T2, and they are trying to access a shared resource called X. And if both the threads try to write a value to X, the last value written to X will be saved.
35. What is Thread Pooling?
Thread pool is a collection of threads. These threads can be used to perform tasks without disturbing the primary thread. Once the thread completes the task, the thread returns to the pool.
System.Threading.ThreadPool namespace has classes that manage the threads in the pool and its operations.
36. What is Serialization?
Serialization is a process of converting code to its binary format. Once it is converted to bytes, it can be easily stored and written to a disk or any such storage devices. Serializations are mainly useful when we do not want to lose the original form of the code and it can be retrieved anytime in the future.
Any class which is marked with the attribute [Serializable] will be converted to its binary form.
The reverse process of getting the C# code back from the binary form is called Deserialization.
To Serialize an object we need the object to be serialized, a stream that can contain the serialized object and namespace System.Runtime.Serialization can contain classes for serialization.
37. What are the types of Serialization?
The different types of Serialization are:
- XML serialization – It serializes all the public properties to the XML document. Since the data is in XML format, it can be easily read and manipulated in various formats. The classes reside in System.sml.Serialization.
- SOAP – Classes reside in System.Runtime.Serialization. Similar to XML but produces a complete SOAP compliant envelope that can be used by any system that understands SOAP.
- Binary Serialization – Allows any code to be converted to its binary form. Can serialize and restore public and non-public properties. It is faster and occupies less space.
38. What is an XSD file?
An XSD file stands for XML Schema Definition. It gives a structure for the XML file. It means it decides the elements that the XML should have and in what order and what properties should be present. Without an XSD file associated with XML, the XML can have any tags, any attributes, and any elements.
Xsd.exe tool converts the files to the XSD format. During Serialization of C# code, the classes are converted to XSD compliant format by xsd.exe.
39. What is an Object and a Class?
- Class is an encapsulation of properties and methods that are used to represent a real-time entity. It is a data structure that brings all the instances together in a single unit.
- Object is defined as an instance of a Class. Technically, it is just a block of memory allocated that can be stored in the form of variables, array or a collection.
40. What are the fundamental OOP concepts?
The four fundamental concepts of Object-Oriented Programming are:
- Encapsulation: Here, the internal representation of an object is hidden from the view outside the object’s definition. Only the required information can be accessed whereas the rest of the data implementation is hidden.
- Abstraction: It is a process of identifying the critical behavior and data of an object and eliminating the irrelevant details.
- Inheritance: It is the ability to create new classes from another class. It is done by accessing, modifying and extending the behavior of objects in the parent class.
- Polymorphism: The name means, one name, many forms. It is achieved by having multiple methods with the same name but different implementations.
41. What is Managed and Unmanaged code?
Managed code is a code that is executed by CLR (Common Language Runtime) i.e all application code is based on .Net platform. It is considered as managed because of the .Net framework which internally uses the garbage collector to clear up the unused memory.
Unmanaged code is any code that is executed by application runtime of any other framework apart from .Net. The application runtime will take care of memory, security and other performance operations.
42. What is an Interface?
Interface is a class with no implementation. The only thing that it contains is the declaration of methods, properties, and events.
43. Explain Get and Set Accessor properties?
Get and Set are called Accessors. These are made use by Properties. The property provides a mechanism to read, write the value of a private field. For accessing that private field, these accessors are used.
- Get Property is used to return the value of a property
- Set Property accessor is used to set the value.
44. What is a Thread? What is Multithreading?
A Thread is a set of instructions that can be executed, which will enable our program to perform concurrent processing. Concurrent processing helps us do more than one operation at a time. By default, C# has only one thread. But the other threads can be created to execute the code in parallel with the original thread.
Thread has a life cycle. It starts whenever a thread class is created and is terminated after the execution. System.Threading is the namespace which needs to be included to create threads and use its members.
Threads are created by extending the Thread Class. Start() method is used to begin thread execution.
//CallThread is the target method//
ThreadStart methodThread = new ThreadStart(CallThread);
Thread childThread = new Thread(methodThread);
childThread.Start();C# can execute more than one task at a time. This is done by handling different processes by different threads. This is called MultiThreading.
There are several thread methods that are used to handle multi-threaded operations: Start, Sleep, Abort, Suspend, Resume and Join.
45. What is “using” statement in C#?
“Using” keyword denotes that the particular namespace is being used by the program.
For Example, using System
Here, System is a namespace. The class Console is defined under System. So, we can use the console.writeline (“….”) or readline in our program.
46. Explain Abstraction.
Abstraction is one of the OOP concepts. It is used to display only the essential features of the class and hide unnecessary information.
Abstraction helps in knowing what is necessary and hiding the internal details from the outside world. Hiding of the internal information can be achieved by declaring such parameters as Private using the private keyword.
47. What are C# I/O classes? What are the commonly used I/O classes?
C# has System.IO namespace, consisting of classes that are used to perform various operations on files like creating, deleting, opening, closing, etc.
Some commonly used I/O classes are:
- File – Helps in manipulating a file.
- StreamWriter – Used for writing characters to a stream.
- StreamReader – Used for reading characters to a stream.
- StringWriter – Used for reading a string buffer.
- StringReader – Used for writing a string buffer.
- Path – Used for performing operations related to the path information.
48. What is StreamReader/StreamWriter class?
StreamReader and StreamWriter are classes of namespace System.IO. They are used when we want to read or write charact90, Reader-based data, respectively.
Some of the members of StreamReader are: Close(), Read(), Readline().
Members of StreamWriter are: Close(), Write(), Writeline().
Class Program1
{
using(StreamReader sr = new StreamReader(“C:\ReadMe.txt”)
{
//----------------code to read-------------------//
}
using(StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(“C:\ReadMe.txt”))
{
//-------------code to write-------------------//
}
}49. What is a Destructor in C#?
Destructor is used to clean up the memory and free the resources. But in C# this is done by the garbage collector on its own. System.GC.Collect() is called internally for cleaning up. But sometimes it may be necessary to implement destructors manually.
For Example:
~Car()
{
Console.writeline(“….”);
}50. What is an Abstract Class?
An Abstract class is a class which is denoted by abstract keyword and can be used only as a Base class. This class should always be inherited. An instance of the class itself cannot be created. If we do not want any program to create an object of a class, then such classes can be made abstract.
Any method in the abstract class does not have implementations in the same class. But they must be implemented in the child class.
For Example:
abstract class AB1
{
Public void Add();
}
Class childClass : AB1
{
childClass cs = new childClass ();
int Sum = cs.Add();
}All the methods in an abstract class are implicitly virtual methods. Hence, the virtual keyword should not be used with any methods in the abstract class.
51. How can one use nullable types in .Net?
Nullable types are defined as the types which can either take the normal value or the null value.
52. How to use nullable types in .Net?
Value types can take either their normal values or a null value. Such types are called nullable types.
Int? someID = null;
If(someID.HasVAlue)
{
}53. What is the difference between Continue and Break Statement?
Break statement breaks the loop. It makes the control of the program to exit the loop. Continue statement makes the control of the program to exit only the current iteration. It does not break the loop.
54. What is the difference between finally and finalize block?
finally block is called after the execution of try and catch block. It is used for exception handling. Regardless of whether an exception is caught or not, this block of code will be executed. Usually, this block will have a clean-up code.
finalize method is called just before garbage collection. It is used to perform clean up operations of Unmanaged code. It is automatically called when a given instance is not subsequently called.
55. What is an Array? Give the syntax for a single and multi-dimensional array?
An Array is used to store multiple variables of the same type. It is a collection of variables stored in a contiguous memory location.
For Example:
double numbers = new double[10];
int[] score = new int[4] {25,24,23,25};A single dimensional array is a linear array where the variables are stored in a single row. Above example is a single dimensional array.
Arrays can have more than one dimension. Multidimensional arrays are also called rectangular arrays.
For Example, int[,] numbers = new int[3,2] { {1,2} ,{2,3},{3,4} };
56. What are Boxing and Unboxing?
Converting a value type to reference type is called ‘Boxing’. Explicit conversion of the same reference type that is created by boxing back to value type is called ‘Unboxing’.
57. What is an Array used for?
An Array is used to store multiple variables of the same type and is a collection of variables stored in a contiguous memory location.
58. What is an Escape Sequence? Name the sequences in C
An Escape sequence is denoted by a backslash (). The backslash indicates that the character that follows it should be interpreted literally or that it is a special character. An escape sequence is considered as a single character.
59. What are the basic String Operations?
The basic String Operations are: Concatenate, Modify, Search, Compare.
60. What is an Escape Sequence? Name some String escape sequences in C#.
An Escape sequence is denoted by a backslash (). The backslash indicates that the character that follows it should be interpreted literally or it is a special character. An escape sequence is considered as a single character.
String escape sequences are as follows:
- \n – Newline character
- \b – Backspace
- \ – Backslash
- \’ – Single quote
\’’ – Double Quote
61. In C#.Net, what do indexers mean?
In C#, indexers are also known as smart arrays. They allow the instances of the class that are to be indexed in a similar as that of the array.
62. What are Regular expressions? Search a string using regular expressions?
Regular expression is a template to match a set of input. The pattern can consist of operators, constructs or character literals. Regex is used for string parsing and replacing the character string.
For Example:
- matches the preceding character zero or more times. So, a*b regex is equivalent to b, ab, aab, aaab and so on.
Searching a string using Regex:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string[] languages = { "C#", "Python", "Java" };
foreach(string s in languages)
{
if(System.Text.RegularExpressions.Regex.IsMatch(s,"Python"))
{
Console.WriteLine("Match found");
}
}
}The above example searches for “Python” against the set of inputs from the languages array. It uses Regex.IsMatch which returns true in case if the pattern is found in the input. The pattern can be any regular expression representing the input that we want to match.
63. State the difference between direct cast and ctype.
The difference between direct cast and ctype is that direct cast is used for the conversion of type of an object that requires the run time which is similar to the specified type in the direct cast. Whereas ctype is used for converting the conversion which is defined for the expression and the type.
64. How can one use the singleton design pattern in C#?
The singleton design pattern is used in C# when the class has one instance and the access is provided globally.
65. What are the basic String Operations? Explain.
Some of the basic string operations are:
- Concatenate: Two strings can be concatenated either by using a System.String.Concat or by using + operator.
- Modify: Replace(a,b) is used to replace a string with another string. Trim() is used to trim the string at the end or at the beginning.
- Compare: System.StringComparison() is used to compare two strings, either a case-sensitive comparison or not case sensitive. Mainly takes two parameters, original string, and string to be compared with.
- Search: StartWith, EndsWith methods are used to search a particular string.
66. What is Parsing? How to Parse a Date Time String?
Parsing converts a string into another data type.
For Example:
string text = “500”;
int num = int.Parse(text);500 is an integer. So, the Parse method converts the string 500 into its own base type, i.e int.
Follow the same method to convert a DateTime string.
string dateTime = “Jan 1, 2018”;
DateTime parsedValue = DateTime.Parse(dateTime);67. What are extension methods in C#?
Extension methods enable you to add methods to existing types without creating a new derived type, recompiling, or otherwise modifying the original type.
An extension method is a special kind of static method, but they are called as if they were instance methods on the extended type.
68. What is the difference between the Virtual method and the Abstract method?
The Virtual method must always have a default implementation. However, it can be overridden in the derived class, although it is not mandatory. It can be overridden using the override keyword.
An Abstract method does not have an implementation. It resides in the abstract class. It is mandatory that the derived class implements the abstract method. An override keyword is not necessary here though it can be used.
69. What are the types of errors in C#?
Answer: Following are the two types of error in C#:
- Compile-time error
- Run time error
70. What is the difference between method overriding and method overloading?
In method overriding, we change the method definition in the derived class that changes the method behavior.
Method overloading is creating a method with the same name within the same class having different signatures.
71. Why can''t you specify the accessibility modifier for methods inside the interface?
In an interface, we have virtual methods that do not have method definition. All the methods are there to be overridden in the derived class. That''s why they all are public.
72. What is an object pool in .NET?
An object pool is a container having objects ready to be used. It tracks the object that is currently in use, total number of objects in the pool. This reduces the overhead of creating and re-creating objects.
73. What is the difference between read-only and constant?
The difference between read-only and constant is that read-only is used during run time when the value has to be assigned. Constant variables are used during compilation time for declaration and initialization.
74. What are partial classes?
A partial class is only used to split the definition of a class in two or more classes in the same source code file or more than one source file. You can create a class definition in multiple files, but it will be compiled as one class at run time. Also, when you create an instance of this class, you can access all the methods from all source files with the same object.
Partial Classes can be created in the same namespace. It isn''t possible to create a partial class in a different namespace. So use the “partial” keyword with all the class names that you want to bind together with the same name of a class in the same namespace.
75. Can “this” be used in a static method?
No, “this” cannot be used in a static method as static methods are used for either static variables or static methods.
76. What is IEnumerable<> in C#?
IEnumerable is the parent interface for all non-generic collections in System.Collections namespace like ArrayList, HastTable etc. that can be enumerated. For the generic version of this interface as IEnumerable<T> which a parent interface of all generic collections class in System.Collections.Generic namespace like List<> and more.
In System.Collections.Generic.IEnumerable<T> have only a single method which is GetEnumerator() that returns an IEnumerator. IEnumerator provides the power to iterate through the collection by exposing a Current property and Move Next and Reset methods if we don’t have this interface as a parent so we can’t use iteration by foreach loop or can’t use that class object in our LINQ query.
77. What is the difference between late binding and early binding in C#?
Early Binding and Late Binding concepts belong to polymorphism in C#. Polymorphism is the feature of object-oriented programming that allows a language to use the same name in different forms. For example, a method named Add can add integers, doubles, and decimals.
78. What is the Constructor Chaining in C#?
Constructor chaining is a way to connect two or more classes in a relationship as Inheritance. In Constructor Chaining, every child class constructor is mapped to a parent class Constructor implicitly by base keyword, so when you create an instance of the child class, it will call the parent’s class Constructor. Without it, inheritance is not possible.
79. What’s the difference between the Array.CopyTo() and Array.Clone()?
The Array.Clone() method creates a shallow copy of an array. A shallow copy of an Array copies only the elements of the Array, whether they are reference types or value types, but it does not copy the objects that the references refer to. The references in the new Array point to the same objects that the references in the original Array point to.
The CopyTo() static method of the Array class copies a section of an array to another array. The CopyTo method copies all the elements of an array to another one-dimension array. The code listed in Listing 9 copies contents of an integer array to an array of object types.
80. Can Multiple Catch Blocks be executed in C#?
We can use multiple catch blocks with a try statement. Each catch block can catch a different exception. The following code example shows how to implement multiple catch statements with a single try statement.
81. What are Value types and Reference types in C#?
In C#, data types can be of two types, value types, and reference types. Value type variables contain their object (or data) directly. If we copy one value type variable to another then we are actually making a copy of the object for the second variable. Both of them will independently operate on their values, Value type data types are stored on a stack and reference data types are stored on a heap.
In C#, basic data types include int, char, bool, and long, which are value types. Classes and collections are reference types.
82. How do you use the “using” statement in C#?
There are two ways to use the using keyword in C#. One is as a directive and the other is as a statement. Let''s explain!
- using Directive
Generally, we use the using keyword to add namespaces in code-behind and class files. Then it makes available all the classes, interfaces and abstract classes and their methods and properties on the current page. Adding a namespace can be done in the following two ways: - Using Statement
This is another way to use the using keyword in C#. It plays a vital role in improving performance in Garbage Collection.
83. What are Anonymous Types in C#?
Anonymous types allow us to create new types without defining them. This is a way of defining read-only properties in a single object without having to define each type explicitly. Here, Type is generated by the compiler and is accessible only for the current block of code. The type of properties is also inferred by the compiler.
We can create anonymous types by using “new” keyword together with the object initializer.
84. Explain “static” keyword in C#?
“Static” keyword can be used for declaring a static member. If the class is made static then all the members of the class are also made static. If the variable is made static then it will have a single instance and the value change is updated in this instance.
85. What are the different types of classes in C#?
The different types of class in C# are
- Partial class – Allows its members to be divided or shared with multiple .cs files. It is denoted by the keyword ‘Partial’.
Sealed class – It is a class that cannot be inherited. To access the members of a sealed class, we need to create the object of the class. It is denoted by the keyword ‘Sealed’. - Abstract class – It is a class whose object cannot be instantiated. The class can only be inherited. It should contain at least one method. It is denoted by the keyword ‘abstract’.
- Static class – It is a class which does not allow inheritance. The members of the class are also static. It is denoted by the keyword ‘static’. This keyword tells the compiler to check for any accidental instances of the static class.
86. What is Managed and Unmanaged code?
Managed code is a code that is executed by CLR (Common Language Runtime). It is called ‘managed code’ because of the .Net framework which uses the garbage collector internally to clear up unused memory. ‘__Unmanaged code’ is any code that is executed by the application runtime of any other framework apart from .Net. The application runtime will take care of security, memory and other performance operations.
87. Explain Namespaces in C
Namespaces are used to organize large code projects. “System” is the most widely-used namespace in C#.
88. Explain Polymorphism
In programming, polymorphism means the same method but different implementations. It contains two types, Compile-time and Runtime. Compile time polymorphism is accomplished by operator overloading. Runtime polymorphism is accomplished by overriding. An example would be: a class has a method Void Add(), polymorphism is accomplished by Overloading the method, that is, void Add(int a, int b), void Add(int add) are all overloaded methods.
89. How is Exception Handling implemented in C#?
Exception handling is done using four keywords in C#:
- Try – contains a block of code that checks an exception.
- Catch – is a program that catches an exception with the help of exception handler.
- Finally – is a block of code written to execute even if an exception is not caught.
- Throw – Throws an exception when a problem occurs.

An Analysis of Visual Question Answering Algorithms翻译
Abstract
在视觉问答(VQA)中,算法必须回答关于图像的基于文本的问题。尽管自2014年末以来,VQA已经创建了多个数据集,但它们在内容和算法评估方式上都存在缺陷。结果,评估分数被夸大了,而且主要是通过回答更简单的问题来决定的,这使得比较不同的方法变得很困难。在本文中,我们使用一个名为任务驱动图像理解挑战(TDIUC)的新数据集来分析现有的VQA算法,该数据集有超过160万个问题,分为12个不同的类别。我们还引入了对给定图像没有意义的问题,以迫使VQA系统对图像内容进行推理。我们提出新的评估方案,以弥补过度代表的问题类型,并使其更容易研究算法的优势和弱点。我们分析了基线和最先进的VQA模型的性能,包括多模态紧致双线性池(MCB)、神经模块网络和循环回答单元。我们的实验建立了注意力如何比其他类别更有助于某些类别,确定哪些模型比其他模型更有效,并解释了简单的模型(例如MLP)如何通过简单地学习回答大的、简单的问题类别来超越更复杂的模型(MCB)。
1. Introduction
在开放式视觉问题解答(VQA)中,算法必须对有关图像的任意基于文本的问题产生答案[21,3]。 VQA是一个令人兴奋的计算机视觉问题,它要求系统能够执行许多任务。 真正解决VQA将是人工智能的一个里程碑,并将极大地促进人机交互。 但是,VQA数据集必须测试广泛的能力,才能充分衡量进度。
VQA的研究始于2014年底,当时DAQUAR数据集已经发布[21]。 包括DAQUAR在内,已经发布了六个主要的VQA数据集,并且算法得到了快速改进。 在最受欢迎的数据集“ VQA数据集” [3]上,最好的算法现在达到了70%的准确性[5](人类表现为83%)。 尽管这些结果令人鼓舞,但现有数据集在多种偏见方面存在严重问题。 此外,由于现有数据集无法将实例分为有意义的类别,因此比较各个算法的功能并不容易。 例如,与回答需要空间推理的问题相比,一种方法在颜色问题上可能更胜一筹。 由于颜色问题在数据集中更为常见,因此,由于使用了评估指标,因此在空间推理方面表现出色的算法将无法获得该功绩的适当奖励。
贡献:我们的论文有四个主要目的,旨在更好地分析和比较VQA算法:1)我们创建了一个新的VQA基准数据集,其中根据其解决的任务将问题分为12个不同的类别; 2)我们提出两个新的评估指标,以补偿数据集偏差的形式; 3)我们平衡是/否对象存在检测问题的数量,以评估均衡分布是否可以帮助算法更好地学习; 4)我们引入了荒谬的问题,这些问题迫使算法确定一个问题对于给定的图像是否有效。然后,我们使用新的数据集重新训练和评估基线和最新VQA算法。我们发现,我们提出的方法可以对VQA算法进行更细微的比较,并有助于我们更好地了解特定技术的优势。此外,它还使我们能够回答有关VQA算法的几个关键问题,例如,“算法的泛化能力是否受到数据集中偏差的阻碍?”,“使用空间注意力是否有助于回答特定的问题类型”,“ VQA算法在回答不太常见的问题上有多成功?”和“ VQA算法能否区分真实问题和荒谬问题?”

2. Background
2.1. Prior Natural Image VQA Datasets
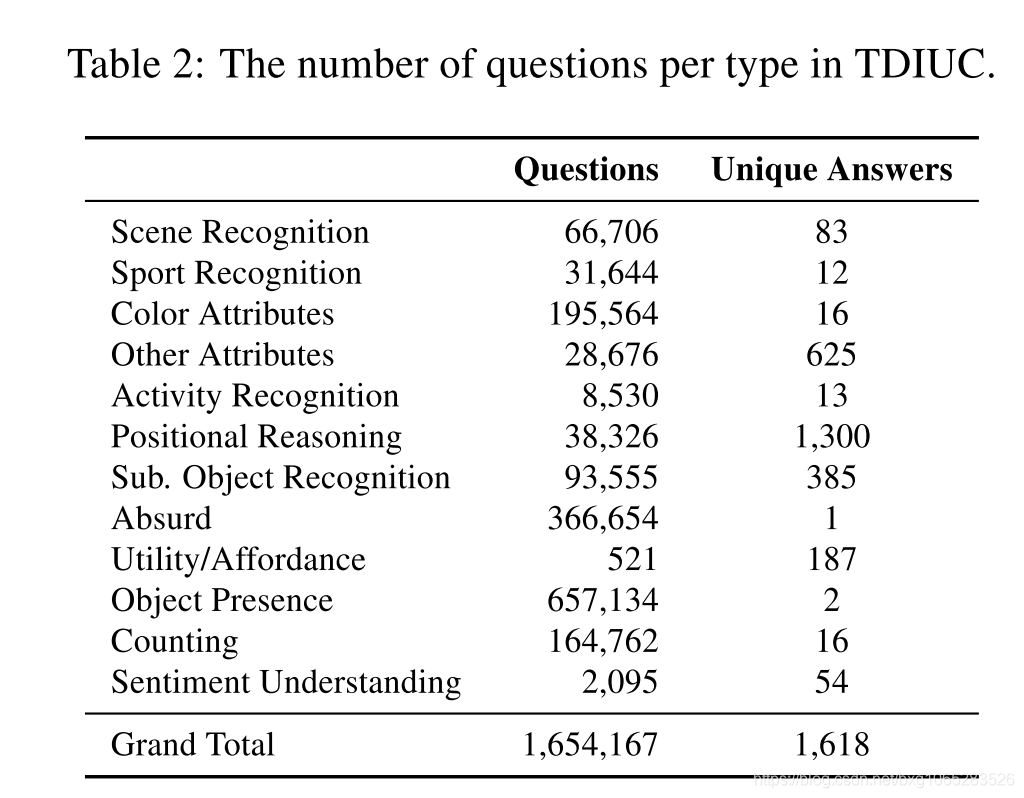
2014年至2016年间,已经发布了六个具有自然图像的VQA数据集:DAQUAR [21],COCO-QA [25],FM-IQA [6],VQA数据集[3],Visual7W [35]和Visual Genome [ 18]。 FM-IQA需要人为判断,尚未得到广泛使用,因此我们不再对其进行进一步讨论。 表1显示了其他数据集的统计信息。 在其他[13、34、29]之后,我们将包含自然图像的VQA数据集部分称为COCO-VQA。 详细的数据集评论可以在[14]和[28]中找到。
前面提到的所有VQA数据集都是有偏差的.DAQUAR和COCO-QA很小,并且问题类型的种类有限。 视觉基因组,Visual7W和COCO-VQA较大,但是它们存在一些偏差。 偏见的形式既有问的各种问题,也有人们为他们提供的答案。 对于COCO-VQA,仅使用问题特征进行训练的系统即可达到50%的准确性[13]。 这表明某些问题具有可预测的答案。 如果没有更细致的分析,确定哪种类型的问题更依赖于图像将是一项挑战。 对于使用Mechanical Turk制作的数据集,注释者通常会询问对象识别问题,例如“图像中有什么?”或“图像中是否有大象?”。 请注意,在后一个示例中,除非对象在图像中,否则注释者很少会问这种问题。 在COCO-VQA上,以“是否存在”开头的问题中有79%的答案是“是”。
2017年,引入了VQA 2.0 [7]数据集。在VQA 2.0中,对于两个不同的图像会询问相同的问题,并且指示注释者给出相反的答案,这有助于减少语言偏见。但是,除了语言偏见外,这些数据集在不同类型问题的分布以及每种问题类型内答案的分布方面也存在偏见。 VQA数据集使用的性能指标将每个测试实例的值均等(例如,简单准确性)。尽管有些人确实为基本问题类型计算了其他统计信息,但并未从这些子评分中计算出总体表现[3,25]。由于更容易产生偏见的问题类型也更加常见,这加剧了带有偏见的问题。与以“ Is”和“ Are”开头的问题相比,注释者很少问“为什么”和“哪里”开头的问题。例如,在COCO-VQA上,“是/不是”问题的准确性提高15%将使整体准确性提高5%以上,但是正确回答所有“为什么/在何处”问题的准确性将仅提高4.1%[14]。由于现有评估指标无法正确解决这些偏差,因此在这些数据集上训练的算法会学习利用这些偏差,从而导致在实际环境中部署时,系统运行不佳。
出于相关原因,过去十年中发布的主要基准测试不使用简单的准确性来评估图像识别和相关的计算机视觉任务,而是使用诸如每类平均值的准确性等指标来补偿不平衡的类别。 例如,在Caltech-101 [4]上,即使使用了平衡的训练数据,简单的准确性也无法解决这样一个事实,即某些类别比其他类别更容易分类(例如,面部和平面很容易且测试次数最多) 图片)。 每类平均准确性通过要求系统在每个类别上都做得很好来弥补这一点,即使类别中测试实例的数量相差很大。
现有基准测试不需要报告不同问题类型的准确性。 即使报告了问题,问题类型也可能过于粗糙而无用,例如,COCO-VQA中的“是/否”,“数字”和“其他”。 为了改善对VQA算法的分析,我们将问题分类为有意义的类型,计算子分数,并将其纳入我们的评估指标。
2.2. Synthetic Datasets that Fight Bias
先前的工作已经研究了VQA中的偏差并提出了对策。 在[33]中,创建了阴和阳数据集来研究对卡通图像具有相同数量的二进制(是/否)问题的影响。 他们发现,很难从平衡的数据集中回答问题。 这项工作意义重大,但仅限于是/否问题,其使用卡通图像的方法无法直接扩展到真实世界的图像。
本文的目标之一是确定算法可以轻松回答哪些类型的问题。在[1]中,提出了具有相似目标的SHAPES数据集。 SHAPES是一个小型数据集,由64个图像组成,这些图像是通过将彩色几何形状按不同的空间方向排列而组成的。每个图像具有相同的244个“是/否”问题,导致15,616个问题。尽管SHAPES是重要的辅助评估,但仅凭它不足以测试VQA算法。 SHAPES的主要局限性在于其所有图像均为2D形状,不能代表真实世界的图像。同样,合成语言和基本视觉推理(CLEVR)[12]也建议使用3D渲染几何对象来研究模型的推理能力。 CLEVR比SHAPES大,并使用3D渲染的几何对象。除了形状和颜色之外,它还为对象增加了材质属性。 CLEVR有五种类型的问题:属性查询,属性比较,整数比较,计数和存在。
SHAPES和CLEVR都是专门为组合语言方法量身定制的[1],并且低估了视觉推理的重要性。 例如,CLEVR问题“大球体上剩下的棕色金属物体所剩圆柱体的大小是多少?”需要苛刻的语言推理能力,但是解析简单的几何对象只需要有限的视觉理解。 与这三个综合数据集不同,我们的数据集包含自然图像和问题。 为了改进算法分析和比较,我们的数据集有更多(12)个明确定义的问题类型和新的评估指标。
3. TDIUC for Nuanced VQA Analysis
在过去两年中,多个公开发布的数据集刺激了VQA研究。 但是,由于评估指标存在偏差和问题,因此解释和比较VQA系统的性能可能是不透明的。 我们提出了一个新的基准数据集,该数据集明确地将问题分为12个不同的类别。 这样一来,您就可以衡量每个类别中的性能,并了解对于当今最佳系统而言,哪种问题是容易的还是很难的。 此外,我们使用评估指标来进一步补偿偏差。 我们将数据集称为“任务驱动图像理解挑战(TDIUC)”。 表1和图2分别显示了该数据集的总体统计数据和示例图像。
TDIUC有12种类型的问题被选择来代表经典计算机视觉任务和新颖的高级视觉任务,这些任务需要不同程度的图像理解和推理。 问题类型为:
- 1. Object Presence (e.g., ‘Is there a cat in the image?’)(是否有物体)
- 2. Subordinate Object Recognition (e.g., ‘What kind of furniture is in the picture?’)(对象种类识别)
- 3. Counting (e.g., ’How many horses are there?’) (数量)
- 4. Color Attributes (e.g., ‘What color is the man’s tie?’) (颜色)
- 5. Other Attributes (e.g., ‘What shape is the clock?’) (其他属性)
- 6. Activity Recognition (e.g., ‘What is the girl doing?’) (动作识别)
- 7. Sport Recognition (e.g.,‘What are they playing?’)(体育活动识别)
- 8. Positional Reasoning (e.g., ‘What is to the left of the man on the sofa?’)(位置推理)
- 9. Scene Classification (e.g., ‘What room is this?’)(场景分类)
- 10. Sentiment Understanding (e.g.,‘How is she feeling?’)(情绪理解)
- 11. Object Utilities and Affordances (e.g.,‘What object can be used to break glass?’)(用途)
- 12. Absurd (i.e., Nonsensical queries about the image)(错误)
表2给出了TDIUC中每个问题类型的数量。问题来自三个来源。 首先,我们从COCO-VQA和Visual Genome中导入了一部分问题。 其次,我们创建了从COCO的语义分段注释[19]和Visual Genome的对象和属性注释[18]生成问题的算法。 第三,我们使用人工注释器来确定某些问题类型。 在以下各节中,我们简要描述每种方法。
3.1. Importing Questions from Existing Datasets
我们从COCO-VQA和Visual Genome中导入了属于所有问题类型的问题,除了“对象实用程序和提供能力”。 我们通过使用大量的模板和正则表达式来做到这一点。 对于视觉基因组,我们导入了具有一个单词答案的问题。 对于COCO-VQA,我们导入了带有一两个单词答案的问题,并且其中五个或更多注释者同意。
对于颜色问题,如果其中包含单词“ color”且答案是常用颜色,则将导入该问题。 如果答案是九种常见运动之一或十五种常见活动之一,并且该问题包含描述动作或运动(例如玩耍,投掷等)的常见动词,则该问题被分类为活动或运动识别问题。 -答案必须以“有多少”开头,答案必须是一个小的可数整数(1-16)。 其他类别使用正则表达式确定。 例如,形式为“是否在感觉?”的问题被归类为情感理解,而形式“在它的右边/左边/后面是什么?”被归类为位置推理。
同样,“图像中的<OBJECT CATEGORY>是什么?”,类似的模板用于填充从属对象识别问题。 此方法也用于有关季节和天气的问题,例如,将“这是什么季节?”,“这是多雨/晴天/阴天?”或“什么样的天气?”导入场景分类。
3.2. Generating Questions using Image Annotations
COCO数据集和视觉基因组中的图像都有各自的区域,并附加了语义知识。 我们利用此信息使用问题模板生成新问题。 为了介绍多样性,我们为每种问题类型定义了多个模板,并使用注释来填充它们。 例如,为了计数,我们使用8个模板,例如“有多少<objects>?”,“照片中有多少<objects?”等。由于COCO和Visual Genome使用不同的注释格式,因此我们 分别讨论。
3.2.1 Questions Using COCO annotations
运动识别,计数,从属对象识别,对象存在,场景理解,位置推理和荒谬问题是从COCO创建的,类似于[15]中使用的方案。 为了进行计数,我们对图像注释中的对象实例数进行计数。 为了最大程度地减少歧义,只有在对象覆盖至少2,000像素的区域时才这样做。
为了识别从属对象,我们提出了一些问题,这些问题需要根据对象的较大语义类别来识别对象的从属对象分类。 为此,我们使用COCO超级类别,这是一个语义概念,涵盖同一主题下的多个对象,例如,“家具”超类别包含椅子,沙发等。如果图像仅包含一种类型的家具,则问题类似于 因为答案不是模棱两可,所以生成了“图片中的家具是什么?”。 使用类似的启发式方法,我们会提出有关识别食品,电子设备,厨房设备,动物和车辆的问题。
对于物体存在的问题,我们发现图像的物体面积大于2,000像素,并产生类似于“图片中是否存在<物体>?”的问题,这些问题的答案为“是”。 要创建否定问题,我们会提出有关图像中不存在的COCO对象的问题。 为了使这一点变得更困难,我们优先考虑问题的创建,这些问题是针对缺少对象的问题,这些对象属于图像中存在的对象的同一超类。 与包含沙发和电视相比,街道场景更可能包含卡车和小汽车。 因此,在街景场景中回答“卡车在吗?”比回答“沙发在吗?”要困难得多。
对于运动识别问题,我们会在注释中检测到特定运动设备的存在,并询问有关所进行运动类型的问题。 图片只能包含一项特定运动的运动器材。 使用类似的方法来创建场景理解问题。 例如,如果注释中有厕所和水槽,则该房间就是浴室,并且可以创建适当的场景识别问题。 此外,我们使用超级类别“室内”和“室外”来询问有关拍摄照片的位置的问题。
为了创建位置推理问题,我们使用边界框的相对位置来创建类似于“ <对象>的左边/右边是什么?”的问题,由于对象重叠,这可能是模棱两可的,因此我们采用以下试探法来消除 歧义:1)两个边界框之间的垂直距离应在较小的阈值之内; 2)物体的重叠长度不得超过对应物长度的一半; 3)物体在水平方向上的距离不应超过距离阈值,而距离阈值是通过主观判断最佳距离以减少歧义而确定的。 我们尝试生成上方/下方的问题,但结果不可靠。
荒谬的问题测试了算法根据图像内容判断问题何时无法回答的能力。 为此,我们列出给定图像中不存在的对象的列表,然后从TDIUC的其余部分中查找有关这些不存在的对象的问题,是/否和计数问题除外,其中包括导入的问题 来自COCO-VQA,自动生成的问题和手动创建的问题。 我们列出了每张图片都会“荒谬”的所有可能问题,并且我们统一为每张图片采样了三个问题。 实际上,我们将在整个数据集中多次重复相同的问题,在这个问题上它可以是真实问题,也可以是无意义的问题。 如果问题很荒谬,算法必须回答“不适用”。
3.2.2 Questions Using Visual Genome annotations
Visual Genome的注释包含区域描述,关系图和对象边界。 但是,注释既可以是非详尽的,也可以是重复的,这使得使用它们自动使质量检查对变得困难。 我们仅使用Visual Genome提出颜色和位置推理问题。 我们使用的方法与COCO所使用的方法相似,但是由于注释中的古怪之处,因此需要采取其他预防措施。 附录中提供了其他详细信息。
3.3. Manual Annotation
使用模板无法轻松创建情感理解和对象效用/负担问题,因此我们使用手动注释来创建这些模板。 培训了12位志愿者注释者来生成这些问题,他们使用了我们开发的基于Web的注释工具。 向他们显示了来自COCO和Visual Genome的随机图像,还可以上传图像。
3.4. Post Processing Post
对所有来源的问题都进行了后处理。 所有数字都转换为文本,例如2变成了2。 所有答案均转换为小写,并且删除了标点符号。 删除同一图像的重复问题。 所有问题的答案必须至少出现两次。 数据集被分为训练和测试分割,其中训练占70%,测试占30%。
4. Proposed Evaluation Metric
VQA研究的主要目标之一是构建能够执行许多任务的计算机视觉系统,而不是仅对一项特定任务具有专业知识(例如,对象识别)。 因此,有人认为VQA是一种视觉图灵测试[21]。 但是,如果使用简单的准确性来评估性能,则很难知道系统是否成功达到了此目标,因为某些问题类型比其他问题类型具有更多的问题。 在VQA中,预期问题类型的分布偏斜。 如果每个测试问题都得到同等对待,则很难评估在较罕见的问题类型上的表现并弥补偏差。 我们提出了多种措施来补偿偏差和偏斜分布。
为了补偿偏斜的问题类型分布,我们分别计算了12种问题类型的准确性。 但是,拥有最终的统一精度指标也很重要。 我们的总体指标是每个问题类型的所有准确性的算术和谐波均值,分别称为算术平均类型(Arithmetic MPT)准确性和谐波平均类型准确性(Harmonic MPT)。 与算术MPT不同,谐波MPT衡量系统在所有问题类型上均具有高分并偏向性能最低的类别的能力。
我们还使用归一化的指标,以每种问题类型内答案分布不平衡的形式补偿偏差,例如,重复次数最多的“两个”涵盖了所有计数类型问题的35%以上。 为此,我们分别计算问题类型中每个唯一答案的准确性,然后将它们平均化为问题类型。 为了计算总体性能,我们计算算术归一化平均类型(N-MPT)和谐波N-MPT分数。 未归一化的分数与归一化的分数之间的巨大差异表明,该算法无法推广到更稀有的答案。
5. Algorithms for VQA
尽管有其他公式(例如[6,10]),但大多数VQA系统将其公式化为分类问题,在该问题中,系统会给出图像和问题,并给出答案作为类别。 [3、25、5、27、9、16、11、20、24、26、29、31、32、34、10、22]。 几乎所有系统都使用CNN功能来表示图像,并使用递归神经网络(RNN)或用于问题的词袋模型。 我们简要回顾其中一些系统,重点关注我们在实验中比较的模型。 有关更全面的评论,请参见[14]和[28]。
两个简单的VQA基线是线性或多层感知器(MLP)分类器,它们将问题和图像嵌入彼此串联在一起作为输入[3、13、34],其中图像特征来自CNN的最后一个隐藏层。 这些简单的方法通常效果很好,并且可以与复杂的注意力模型竞争[13,34]。
在VQA模型中[5,27,32,30,31,20,9]对空间注意力进行了大量研究。 这些系统会根据与问题的相关性来权衡视觉特征,而不是使用全局特征(例如,从CNN的最后一个隐藏层开始)。 例如,回答“熊是什么颜色?”的目的是强调熊周围的视觉特征,而抑制其他特征。
MCB系统[5]赢得了CVPR-2016 VQA车间挑战赛。 除了使用空间注意力之外,它还隐式计算图像和问题特征之间的外部乘积,以确保它们的所有元素都相互作用。 显式地计算外部乘积将是缓慢的并且具有极高的尺寸,因此可以使用有效的近似来完成。 它使用一个长短期记忆(LSTM)网络来嵌入问题。
神经模块网络(NMN)是VQA的一种特别有趣的合成方法[1,2]。 主要思想是组成一系列离散模块(子网),这些模块可以一起执行以回答给定的问题。 为此,他们使用各种模块,例如,find(x)模块输出用于检测x的热图。 为了安排模块,首先将问题解析为简洁的表达式(称为S表达式),例如,“什么在汽车的右边?”被解析为(什么汽车);(什么正确);(什么 (和汽车右))。 使用这些表达式,模块被组合成一个序列来回答查询。
VQA的多步递归应答单元(RAU)模型是另一种最新方法[23]。 RAU中的每个推理步骤都包含一个完整的回答模块,该模块接受图像,问题和上一个LSTM步骤的输出。 这些中的每一个都是一个较大的LSTM网络的一部分,该网络逐渐地对该问题进行推理。
6. Experiments
我们在TDIUC上训练了多个基线模型以及最新的VQA方法。 我们使用的方法是:
- YES: Predicts ‘yes’ for all questions.
- REP: Predicts the most repeated answer in a question-type category using an oracle.
- QUES: A linear softmax classifier given only question features (image blind).
- IMG: A linear softmax classifier given only image fea- tures (question blind).
- Q+I: A linear classifier given the question and image..
- MLP: A 4-layer MLP fed question and image features.
- MCB: MCB [5] without spatial attention.
- MCB-A: MCB [5] with spatial attention.
- NMN: NMN from [1] with minor modifications.
- RAU: RAU [23] with minor modifications
对于图像功能,所有模型均使用具有448×448图像的ResNet-152 [8]。
QUES和IMG提供有关数据集中偏差的信息。 QUES,Q + I和MLP都使用4800维跳跃思想向量[17]来嵌入问题,就像在[13]中所做的那样。 对于图像功能,所有这些都使用标准化为单位长度的ResNet-152的“ pool5”层。 MLP是具有softmax输出层的4层网络。 3个ReLU隐藏层分别具有6000、4000和2000个单位。 在训练期间,对隐藏层使用了落差(0.3)。
对于MCB,MCB-A,NMN和RAU,我们使用了公开代码在TDIUC上进行训练。 除了将NMN和RAU的视觉表示升级为都使用ResNet-152之外,实验设置和超级参数与代码的默认选择保持不变。
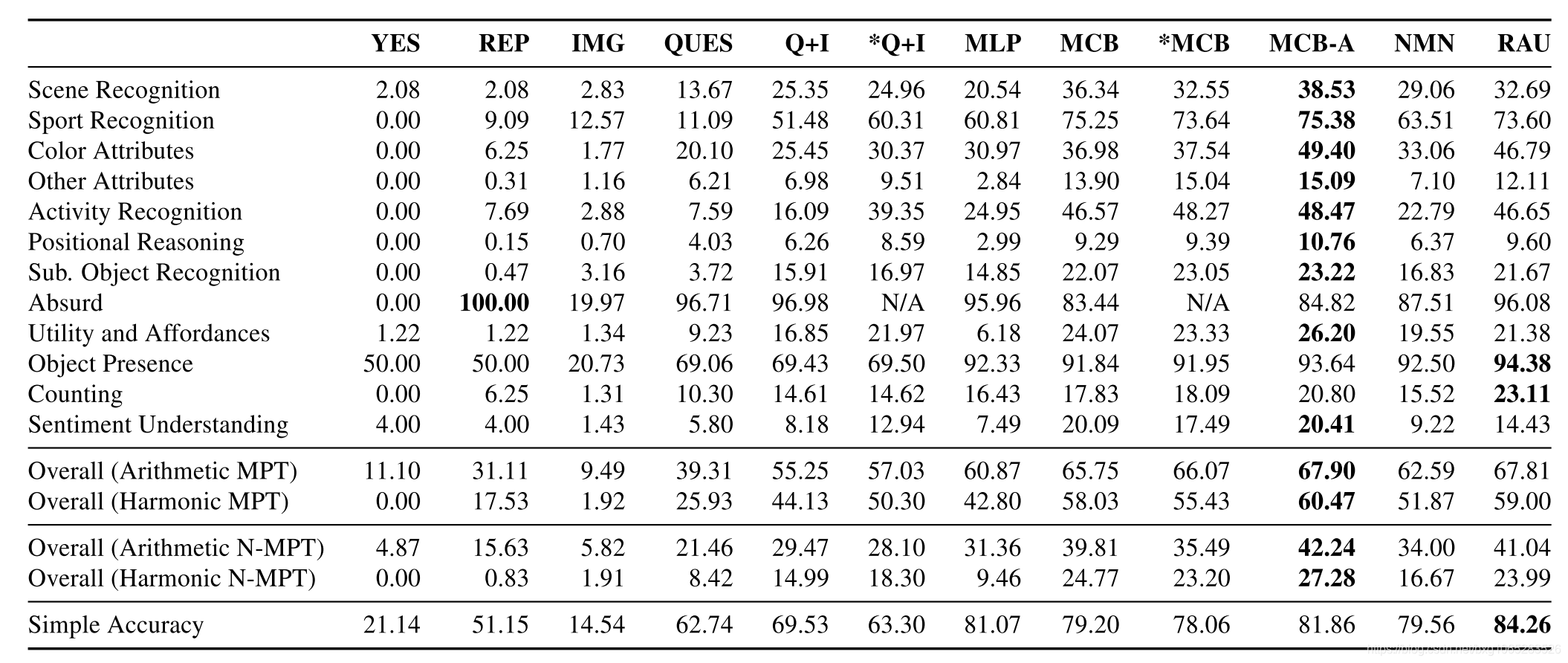
这些模型在TDIUC上的结果在表3中给出。表3中12种问题类型的每一种的准确率得分都在表3中给出,附录5在表5中给出了使用均值唯一答案进行归一化的得分。
7. Detailed Analysis of VQA Models
7.1. Easy Question-Types for Today’s Methods
通过查看表3,我们可以发现在MPT下某些问题类型相对容易(> 90%):场景识别,运动识别和物体存在。 荒谬的情况下也可以实现高精度,我们将在7.4节中进行更详细的讨论。 尽管有大量独特的答案,但从属对象的识别率仍较高(> 80%)。 尽管有大量训练数据,但所有方法的计数准确性均很低。 对于其余的问题类型,需要进行更多分析以查明性能较弱是由于训练数据量较少,偏倚还是模型限制所致。 接下来,我们将研究N-MPT可以弥补多少良好的性能是由于答案分布的偏差。

7.2. Effects of the Proposed Accuracy Metrics
我们的主要目标之一是通过简单地学习回答更多且更简单的问题类型来弥补算法可以取得高分这一事实。对于现有的数据集,早期的工作表明,使用简单的精度,简单的基线方法通常会比更复杂的方法[13,34,10]。在TDIUC上,MLP的简单准确性超过了MCB和NMN,但仔细检查后发现,MLP的得分高度取决于类别众多的类别(例如“荒谬”和“对象存在”)的性能。使用MPT,我们发现NMN和MCB均胜过MLP。检查每种问题类型的标准化分数(附录表5)显示出更加明显的差异,这也反映在表3所示的算术N-MPT分数中。这表明MLP容易过拟合。与RAU相比,MCB-A的效果要好于简单的精度,但RAU在所有旨在补偿偏斜的答案分布和偏见的指标上得分都较低。
比较未归一化和归一化度量可以帮助我们确定给定问题类型的VQA算法的归纳能力。这些分数之间的巨大差异表明,算法依赖于偏斜的答案分布来获得高分数。我们发现,对于MCB-A,从属对象识别的准确性从未归一化的85.54%降至归一化的23.22%,而对于场景识别,其准确率从93.06%(未归一)降至38.53%(归一)。这两个类别的答案分布都严重偏斜。从属对象识别中的前25个答案和场景识别中的前5个答案涵盖了各自问题类型中所有问题的80%以上。这表明看似简单的问题类型可能仅仅是由于算法学习了答案统计信息。真正简单的问题类型在未规范化和规范化指标方面的表现都相似。例如,尽管计数具有相同数量的唯一答案和更多的训练数据,但运动识别仅下降了17.39%,而计数下降了30.21%。通过比较规范化和未规范化指标之间性能的相对下降,我们还可以比较算法的泛化能力,例如,对于从属对象识别,RAU与MCB-A(85.54%)相比具有更高的非规范化分数(86.11%)。但是,对于归一化分数,MCB-A的性能(23.22%)明显高于RAU(21.67%)。这表明RAU可能更多地取决于答案分布。与MCB相比,可以对MLP进行类似的观察。
7.3. Can Algorithms Predict Rare Answers?
在上一节中,我们看到了VQA模型难以正确预测稀有答案。重复次数少的问题实际上难于回答,还是算法只是偏向更频繁的答案?为了对此进行研究,我们创建了TDIUC的子集,该子集仅包含答案重复少于1000次的问题。我们称此数据集为TDIUC-Tail,其中包含46,590个训练和22,065个测试问题。然后,我们在以下方面训练了MCB:1)完整的TDIUC数据集;和2)TDIUC尾巴。两种版本均在TDIUC-Tail的验证版上进行了评估。
我们发现,在所有问题类型上仅接受TDIUC-Tail训练的MCB胜过接受所有TDIUC训练的MCB(详细信息在附录表6和表7中)。这表明MCB能够学习正确预测稀有答案,但是它偏向于预测更常见的答案以最大化整体准确性。使用归一化的准确性会削弱VQA算法对答案统计信息的依赖,并且对于部署VQA系统,直接针对N-MPT优化可能会有用。
7.4. Effects of Including Absurd Questions
荒谬的问题迫使VQA系统查看图像以回答问题。 在TDIUC中,这些问题是从其余数据集中采样的,并且有很高的先验概率被回答为“不适用”。这在QUES模型中得到了证实,这在荒谬的情况下实现了很高的准确性; 但是,对于相同的问题,如果它们是图像的真品,则只能在这些问题上达到6.77%的准确性。 通过牺牲其他类别的性能可以实现良好的荒谬性能。 一个强大的VQA系统应该能够检测出荒谬的问题,而不会失败。 通过检查与荒谬问题相同的真实问题的准确性,我们可以量化算法将荒谬问题与真实问题区分开的能力。 我们发现,较复杂的模型(MCB:62.44%,MCB-A:68.83%),较简单的模型在这些问题上的准确性要低得多(QUES:6.77%,Q + I:34%)。
为了进一步研究这一点,我们训练了两种VQA系统,即Q + I和MCB,有无荒谬。结果列于表3。与没有完整问题的Q + I相比,对于经过培训的Q + I没有其他荒谬的问题,其他类别的准确度有了显着提高,尤其是对于用于抽样荒唐问题的问题类型,例如活动识别(使用荒谬的训练时为24%,没有训练时为48%)。在没有荒诞的情况下训练的Q + I模型的算术MPT准确性(57.03%)也比在荒谬的情况下训练的模型的MPT精度要高(除荒谬性以外,所有类别的MPT准确性均为51.45%)。这表明Q + I不能正确地区分荒谬和真实的问题,并且倾向于将真正的问题误认为是荒谬的。相比之下,功能更强大的模型MCB产生的荒谬结果更糟,但是在没有荒诞的情况下训练的版本与Q + I相比,差异要小得多,这表明MCB更具有识别荒谬问题的能力。
7.5. Effects of Balancing Object Presence
在7.3节中,我们看到偏斜的答案分布会影响泛化。即使对于简单的问题,此效果也很强,甚至影响最复杂的算法。当MCB-A在COCO-VQA和视觉基因组上接受培训时,请考虑一下MCB-A,即CVPR-2016 VQA Workshop Challenge的获胜者。当根据来自TDIUC的对象存在问题进行评估时,该问题包含50%的“是”和50%的“否”问题,它可以正确地以86.3%的准确度预测“是”的答案,而对于“否”的问题则仅为11.2%。回答。然而,在TDIUC上对其进行训练后,MCB-A能够通过“了解” COCO-VQA数据集的偏见获得95.02%的“是”和“ 92.26%”的“否”。数据集无偏时的性能良好。在[33]中也有关于平衡是/否问题的类似观察。数据集可以平衡简单的类别(例如对象存在),但是将相同的概念扩展到所有其他类别是一项艰巨的任务,并且破坏了现实世界的自然统计数据。采用平均平均值和归一化的准确性度量标准可以帮助弥补此问题。
7.6. Advantages of Attentive Models
通过将问题分解成各种类型,我们可以评估哪些类型最受关注。 我们通过比较有无注意的MCB模型(即MCB和MCB-A)来做到这一点。 如表3所示,注意力有助于改善几个问题类别的结果。 最明显的增加是颜色识别,属性识别,荒谬和计数。 所有这些问题类型均要求算法检测正确答案的指定对象(或缺少指定对象)。 MCB-A使用来自不同空间位置的局部特征而不是全局图像特征来计算注意力。 这有助于定位单个对象。 注意机制了解这些功能的相对重要性。 RAU还利用空间注意力并显示相似的增量。
7.7. Compositional and Modular Approaches
NMN和较小的RAU提出了VQA的组合方法。 对于COCO-VQA,使用简单的精度,NNN的性能比某些MLP模型差[13]。 对于希望逐步进行逻辑分析图像的问题(例如位置推理),我们希望它会比其他模型具有更好的性能。 但是,尽管使用MPT和N-MPT度量标准,NNN的表现要好于MLP,但在特定问题类型上我们没有看到任何实质性的好处。 这可能是因为NMN受“ S表达式”解析器质量的限制,该解析器在许多情况下会产生错误或误导性的解析。 例如,“最左边的那个人的外套是什么颜色?”被解析为(彩色外套);(彩色假);(彩色(和外套假))。 这种表达方式不仅无法解析“男人”(这是正确回答问题所必需的关键要素),而且还会错误地将“左”解释为休假的过去式。
RAU对多个跃点执行推理,并且由于每个跃点都包含完整的VQA系统,因此它可以学习在每个步骤中解决不同的任务。 由于它是端到端训练的,因此不需要依赖严格的问题解析。 它在检测荒谬问题上显示出非常好的性能,并且在其他类别上也表现出色。
8. Conclusion
我们介绍了TDIUC,这是一个VQA数据集,它由12种明确定义的问题类型(包括荒谬的问题)组成,并用它来对最新的VQA算法进行严格的分析。 我们提出了新的评估指标来补偿VQA数据集中的偏差。 结果表明,荒谬的问题和新的评估指标使人们对VQA算法的行为有了更深入的了解。

Android SystemProperties和Settings.System介绍,不同应用间传递信息
1 使用 SystemProperties.get
这中方法在framework里面 经常见到。
特别属性
如果属性名称以“ro.”开头,那么这个属性被视为只读属性。一旦设置,属性值不能改变。
如果属性名称以“persist.”开头,当设置这个属性时,其值也将写入/data/property。
在c++中就是对应JAVA的两个函数就是property_set, property_get,其实JAVA是通过JNI调用这两个函数的。
JAVAimport android.os.SystemProperties;
SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", zone.getID());
String lang= SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language");
C
#include <cutils/properties.h>
property_set("persist.sys.language", "zh");
property_get("persist.sys.language", propLang, "en");
在adb shell可以通过以下的命名读取和修改
#getprop persist.sys.language #setprop persist.sys.language zh
2 使用 Settings.System.putInt
这种方式会保存变量到Settings 数据库中,飞行模式等的开关就是用这种方式实现的。
在AndroidManifest.xml中包含权限:
<uses-permission android:name=”android.permission.WRITE_SETTINGS” />
在需要发送数据的java文件中,包含:
import android.provider.Settings; import android.content.ContentResolver; ContentResolver resolver = mContext.getContentResolver(); Settings.System.putInt(resolver,”inputFlag”,1);
同理,在接收数据端:
Settings.System.getInt(resolver,”inputFlag”,3);
mContext为所在应用的上下文。
文章出处:http://blog.csdn.net/offbye/article/details/6689322

c# – LINQ to Entities不能识别方法’System.String get_Item(System.String)’,
这是我的代码:
DateTime dtinicio = new DateTime();
DateTime dtFim = new DateTime();
Int32 codStatus = 0;
if(!string.IsNullOrEmpty(collection["txtDtinicial"]))
dtinicio = Convert.ToDateTime(collection["txtDtinicial"]);
if(!string.IsNullOrEmpty(collection["txtDtFinal"]))
dtFim = Convert.ToDateTime(collection["txtDtFinal"]);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(collection["StatusCliente"]))
Convert.ToInt32(collection["StatusCliente"]);
var listCLientResult = (from c in db.tbClientes
orderby c.id
where (c.effdt >= dtinicio || string.IsNullOrEmpty(collection["txtDtinicial"]) &&
(c.effdt <= dtFim || string.IsNullOrEmpty(collection["txtDtFinal"])) &&
(c.cod_status_viagem == codStatus || string.IsNullOrEmpty(collection["StatusCliente"])))
select c);
return View(listCLientResult);
我得到的错误是:
LINQ to Entities不能识别方法’System.String get_Item(System.String)’,它不能转换为存储库的表达式.
解决方法
这是我会做的:
DateTime dtinicio = DateTime.MinValue;
DateTime dtFim = DateTime.MaxValue;
Int32 codStatus = 0;
if(!string.IsNullOrEmpty(collection["txtDtinicial"]))
dtinicio = Convert.ToDateTime(collection["txtDtinicial"]);
if(!string.IsNullOrEmpty(collection["txtDtFinal"]))
dtFim = Convert.ToDateTime(collection["txtDtFinal"]);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(collection["StatusCliente"]))
codStatus = Convert.ToInt32(collection["StatusCliente"]);
var listCLientResult = (from c in db.tbClientes
orderby c.id
where (c.effdt >= dtinicio) &&
(c.effdt <= dtFim) &&
(c.cod_status_viagem == codStatus)
select c);
return View(listCLientResult);
通过将dtinicio和dtFim初始化为MinValue和MaxValue,您不需要检查它们是否在查询中定义.
我们今天的关于QuestionAnsweringSystem v1.1 发布,人机问答系统和人机问题的分享已经告一段落,感谢您的关注,如果您想了解更多关于2021 Top 100 C#/.NET Interview Questions And Answers、An Analysis of Visual Question Answering Algorithms翻译、Android SystemProperties和Settings.System介绍,不同应用间传递信息、c# – LINQ to Entities不能识别方法’System.String get_Item(System.String)’,的相关信息,请在本站查询。
本文标签:





