本文将介绍servlet解析演进的详细情况,特别是关于7-session的相关信息。我们将通过案例分析、数据研究等多种方式,帮助您更全面地了解这个主题,同时也将涉及一些关于HttpServletReq
本文将介绍servlet解析演进的详细情况,特别是关于7-session的相关信息。我们将通过案例分析、数据研究等多种方式,帮助您更全面地了解这个主题,同时也将涉及一些关于HttpServletRequest getSession()、HttpServletRequest.getSession特性和Session周期、java web(三):ServletContext、session、ServletConfig、request、response对象、javax.servlet.ServletException: Servlet.init() for servlet springServlet threw exception的知识。
本文目录一览:- servlet解析演进(7)-session(2)("/servlet/session")
- HttpServletRequest getSession()
- HttpServletRequest.getSession特性和Session周期
- java web(三):ServletContext、session、ServletConfig、request、response对象
- javax.servlet.ServletException: Servlet.init() for servlet springServlet threw exception

servlet解析演进(7)-session(2)("/servlet/session")
2、session管理器
session管理器类图如下。

下面简单解析下ManagerBase代码:
public abstract class ManagerBase implements Manager {
//缺省的加密算法MD5
protected static final String DEFAULT_ALGORITHM = "MD5";
//session随机位数
protected static final int SESSION_ID_BYTES = 16;
//创建session身份信息所使用的信息加密算法
protected String algorithm = DEFAULT_ALGORITHM;
//管理器关联的容器
protected Container container;
//该组件debug级别
protected int debug = 0;
//该管理器关联的缺省上下文
protected DefaultContext defaultContext = null;
//加密类实现
protected MessageDigest digest = null;
//是否是分布式session,如果为true,所有添加到管理器的session必须是可序列化的
protected boolean distributable;
//为增加随机数生成的熵所需的字符串
protected String entropy = null;
//类描述信息
private static final String info = "ManagerBase/1.0";
//检查session过期时间的最大时间间隔
protected int maxInactiveInterval = 60;
//类名描述
protected static String name = "ManagerBase";
//生成session信息所需的随机数
protected Random random = null;
//生成session所需的随机数生成类
protected String randomClass = "java.security.SecureRandom";
//被管理器回收的session信息集合
protected ArrayList recycled = new ArrayList();
//活跃的session信息集合
protected HashMap sessions = new HashMap();
//包描述信息
protected static StringManager sm =
StringManager.getManager(Constants.Package);
//属性变更监听器
protected PropertyChangeSupport support = new PropertyChangeSupport(this);
public String getAlgorithm() {
return (this.algorithm);
}
public void setAlgorithm(String algorithm) {
String oldAlgorithm = this.algorithm;
this.algorithm = algorithm;
support.firePropertyChange("algorithm", oldAlgorithm, this.algorithm);
}
public Container getContainer() {
return (this.container);
}
public void setContainer(Container container) {
Container oldContainer = this.container;
this.container = container;
support.firePropertyChange("container", oldContainer, this.container);
}
public DefaultContext getDefaultContext() {
return (this.defaultContext);
}
public void setDefaultContext(DefaultContext defaultContext) {
DefaultContext oldDefaultContext = this.defaultContext;
this.defaultContext = defaultContext;
support.firePropertyChange("defaultContext", oldDefaultContext, this.defaultContext);
}
public int getDebug() {
return (this.debug);
}
public void setDebug(int debug) {
this.debug = debug;
}
//返回计算session标识符的加密类对象,如果没有被创建,则在第一次调用的时候
//新创建一个加密类返回。
public synchronized MessageDigest getDigest() {
if (this.digest == null) {
if (debug >= 1)
log(sm.getString("managerBase.getting", algorithm));
try {
this.digest = MessageDigest.getInstance(algorithm);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
log(sm.getString("managerBase.digest", algorithm), e);
try {
this.digest = MessageDigest.getInstance(DEFAULT_ALGORITHM);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException f) {
log(sm.getString("managerBase.digest",
DEFAULT_ALGORITHM), e);
this.digest = null;
}
}
if (debug >= 1)
log(sm.getString("managerBase.gotten"));
}
return (this.digest);
}
public boolean getDistributable() {
return (this.distributable);
}
public void setDistributable(boolean distributable) {
boolean oldDistributable = this.distributable;
this.distributable = distributable;
support.firePropertyChange("distributable",
new Boolean(oldDistributable),
new Boolean(this.distributable));
}
//返回熵值,如果该字符没有设置,则计算一个"半有用"的值
public String getEntropy() {
// Calculate a semi-useful value if this has not been set
if (this.entropy == null)
setEntropy(this.toString());
return (this.entropy);
}
//设置熵值
public void setEntropy(String entropy) {
String oldEntropy = entropy;
this.entropy = entropy;
support.firePropertyChange("entropy", oldEntropy, this.entropy);
}
public String getInfo() {
return (this.info);
}
public int getMaxInactiveInterval() {
return (this.maxInactiveInterval);
}
public void setMaxInactiveInterval(int interval) {
int oldMaxInactiveInterval = this.maxInactiveInterval;
this.maxInactiveInterval = interval;
support.firePropertyChange("maxInactiveInterval",
new Integer(oldMaxInactiveInterval),
new Integer(this.maxInactiveInterval));
}
public String getName() {
return (name);
}
//返回随机数生成器实例
public synchronized Random getRandom() {
if (this.random == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (this.random == null) {
// Calculate the new random number generator seed
log(sm.getString("managerBase.seeding", randomClass));
long seed = System.currentTimeMillis();
//将entropy转成字符
char entropy[] = getEntropy().toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < entropy.length; i++) {
long update = ((byte) entropy[i]) << ((i % 8) * 8);
seed ^= update;
}
try {
// Construct and seed a new random number generator
Class clazz = Class.forName(randomClass);
this.random = (Random) clazz.newInstance();
this.random.setSeed(seed);
} catch (Exception e) {
// Fall back to the simple case
log(sm.getString("managerBase.random", randomClass),
e);
this.random = new java.util.Random();
this.random.setSeed(seed);
}
log(sm.getString("managerBase.complete", randomClass));
}
}
}
return (this.random);
}
public String getRandomClass() {
return (this.randomClass);
}
//设置随机类
public void setRandomClass(String randomClass) {
String oldRandomClass = this.randomClass;
this.randomClass = randomClass;
support.firePropertyChange("randomClass", oldRandomClass,
this.randomClass);
}
//添加session实例到sessions容器
public void add(Session session) {
synchronized (sessions) {
sessions.put(session.getId(), session);
}
}
public void addPropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener) {
support.addPropertyChangeListener(listener);
}
//创建session实例
public Session createSession() {
//如果回收站有session 则拿回收站的session,没有则重新生成一个
Session session = null;
synchronized (recycled) {
int size = recycled.size();
if (size > 0) {
//从回收站最后一位获取一个session实例
session = (Session) recycled.get(size - 1);
//删除回收站最后一个session实例
recycled.remove(size - 1);
}
}
//重新将session管理器设置进去。
if (session != null)
session.setManager(this);
else
//如果回收站没有session则重新创建一个session
session = new StandardSession(this);
//初始化新session属性,并返回
session.setNew(true);
session.setValid(true);
session.setCreationTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
session.setMaxInactiveInterval(this.maxInactiveInterval);
String sessionId = generateSessionId();
String jvmRoute = getJvmRoute();
// @todo Move appending of jvmRoute generateSessionId()???
//为sessionid添加jvmRout字段
if (jvmRoute != null) {
sessionId += ''.'' + jvmRoute;
session.setId(sessionId);
}
//设置session id
session.setId(sessionId);
return (session);
}
//获取该id的session信息
public Session findSession(String id) throws IOException {
if (id == null)
return (null);
synchronized (sessions) {
Session session = (Session) sessions.get(id);
return (session);
}
}
//将sessions转换为数组返回
public Session[] findSessions() {
Session results[] = null;
synchronized (sessions) {
results = new Session[sessions.size()];
results = (Session[]) sessions.values().toArray(results);
}
return (results);
}
public void remove(Session session) {
synchronized (sessions) {
sessions.remove(session.getId());
}
}
public void removePropertyChangeListener(PropertyChangeListener listener) {
support.removePropertyChangeListener(listener);
}
//产生sessionid
protected synchronized String generateSessionId() {
// Generate a byte array containing a session identifier
Random random = getRandom();
byte bytes[] = new byte[SESSION_ID_BYTES];
getRandom().nextBytes(bytes);
bytes = getDigest().digest(bytes);
// Render the result as a String of hexadecimal digits
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < bytes.length; i++) {
byte b1 = (byte) ((bytes[i] & 0xf0) >> 4);
byte b2 = (byte) (bytes[i] & 0x0f);
if (b1 < 10)
result.append((char) (''0'' + b1));
else
result.append((char) (''A'' + (b1 - 10)));
if (b2 < 10)
result.append((char) (''0'' + b2));
else
result.append((char) (''A'' + (b2 - 10)));
}
return (result.toString());
}
//获取到manger关联容器中Engin实例
public Engine getEngine() {
Engine e = null;
for (Container c = getContainer(); e == null && c != null ; c = c.getParent()) {
if (c != null && c instanceof Engine) {
e = (Engine)c;
}
}
return e;
}
public String getJvmRoute() {
//获取Engin的jvmRoute值
Engine e = getEngine();
return e == null ? null : e.getJvmRoute();
}
//获得容器中的日志实例打印日志
void log(String message) {
Logger logger = null;
if (container != null)
logger = container.getLogger();
if (logger != null)
logger.log(getName() + "[" + container.getName() + "]: "
+ message);
else {
String containerName = null;
if (container != null)
containerName = container.getName();
System.out.println(getName() + "[" + containerName
+ "]: " + message);
}
}
//获得日志的错误信息打印信息
void log(String message, Throwable throwable) {
Logger logger = null;
if (container != null)
logger = container.getLogger();
if (logger != null)
logger.log(getName() + "[" + container.getName() + "] "
+ message, throwable);
else {
String containerName = null;
if (container != null)
containerName = container.getName();
System.out.println(getName() + "[" + containerName
+ "]: " + message);
throwable.printStackTrace(System.out);
}
}
//添加已过期的session到recycled中
void recycle(Session session) {
synchronized (recycled) {
recycled.add(session);
}
}
} 未完待续
HttpServletRequest getSession()
1、打开文档 http://tomcat.apache.org/tomcat-5.5-doc/servletapi/
2、Packages javax.servlet.http
Interface HttpServletRequest
3、HttpSession getSession 方法
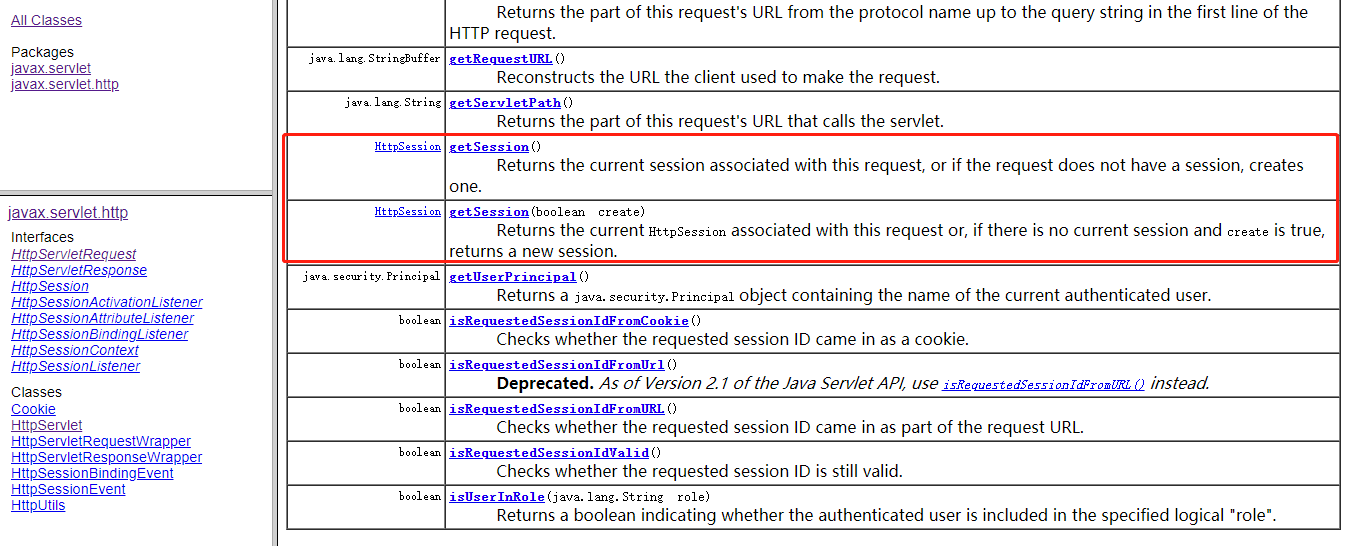
4、无入参方法: 当前请求有session时返回,没有则创建一个

5、有入参的方法:
true: 同不传入参,有则返回,无则创建新的session
false: 传false 且当前请求不存在session,则返回null

HttpServletRequest.getSession特性和Session周期
request.getSession()和HttpServletRequest.getSession(boolean)的区别Session的生命周期
HttpSession session=request.getSession();
1查询浏览器中是否有session对象,
2如果没有,就创建一个新的session对象
3如果有,就取出session对象
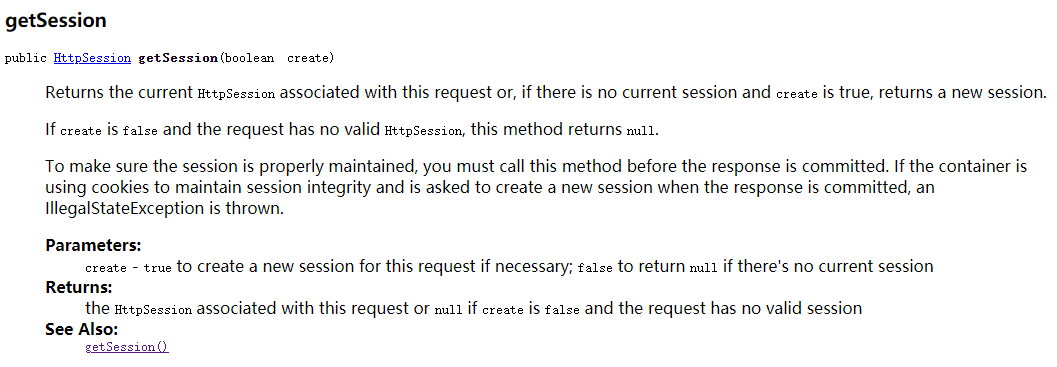
HttpSession session=HttpServletRequest.getSession(boolean);
当boolean为true时,和request.getSession()一样
当boolen为false时,只查询,没有查到,返回null
HttpSession 的生命周期:

java web(三):ServletContext、session、ServletConfig、request、response对象
上一篇讲了Servlet:
1)什么是Servlet【servlet本身就是一种Java类,这种Java类提供了web形式的方法,只要实现了servlet接口的类,都是一种servlet资源。】
2)三种方式创建Servlet(继承HTTPServlet使我们使用的)
3)Servlet的生命周期【通过三个成员方法体现】
一:ServletContext对象
ServletContext对象被称作应用/servlet上下文。
生命周期:
启动tomcat服务器被创建
关闭tomcat服务器被销毁【每个web项目有且只有一个ServletConfig对象】
获取方式:this.getServletContext(); this.getServletConfig.getServletContext();request.getServletContext();
作用范围:
在整个项目运行期间,有且只有一个ServletConfig对象,为所有用户共享。
使用:
1)web项目共享数据 setAttribute(String key,Object value); //已键值对存放数据,整个项目运行期间都存在
getAttribute(String key); //通过键获取数据
removeAttribute(String kye); //通过键移除数据
2)全局初始化参数
如果在web.xml中配置
<context-param>
<param-name>id</param-name>
<param-value>11</param-value>
<param-name>name</param-name>
<param-value>jack</param-value>
<param-name>age</param-name>
<param-value>18</param-value>
</context-param>
this.getServletContext().getInitParameter("id"); // 11
this.getServletContext().getInitParameter("name"); // jack
this.getServletContext().getInitParameter("age"); // 18
this.getServletConfig().getInitParameterNames(); //获得全局参数所有<param-name>值
3)获取web项目资源
this.getServletContext().getRealPath("WEB-INF/web.xml"); //获取web项目下指定文件的绝对路径【D:\apache_tomcat\apache-tomcat-7.0.62-windows-x64\apache-tomcat-7.0.62\webapps\StudyServlet\WEB-INF\web.xml】
InputStream getResourceAsStream(java.lang.String path); //获取web项目下指定资源的内容,返回的是字节输入流
浏览器请求一个Servlet,然后通过上面方法把一个html页面写过去。页面代码:
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext context = this.getServletContext();
//ips.html在webContent目录下
InputStream ips = context.getResourceAsStream("/ips.html");
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(ips));
String str = null;
while((str = reader.readLine()) != null)
response.getWriter().write(str);
}
浏览器效果:
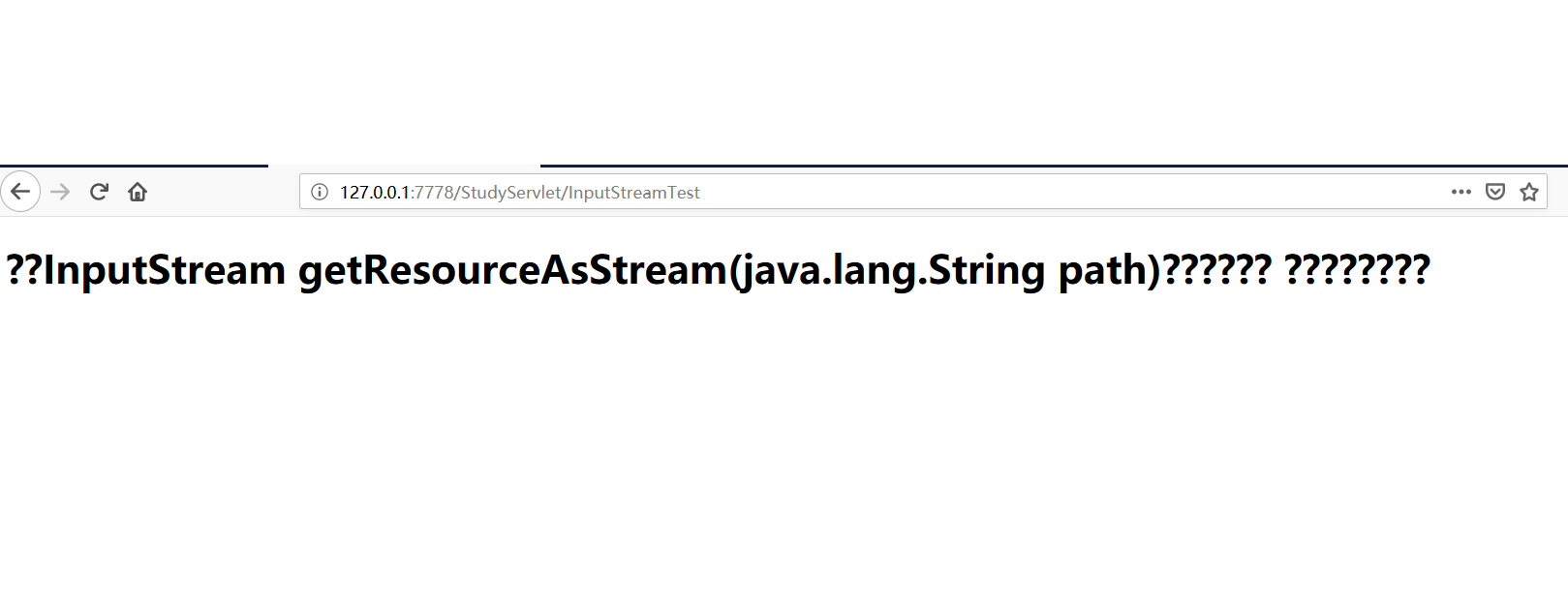
效果达到了,但出现???,这是中文乱码问题,后面会通过response解决。
二:HttpSession对象。
HpptSession对象和ServletContent对象类似,不过它的作用范围是一次会话期间,一次会话可以包括对此request请求。
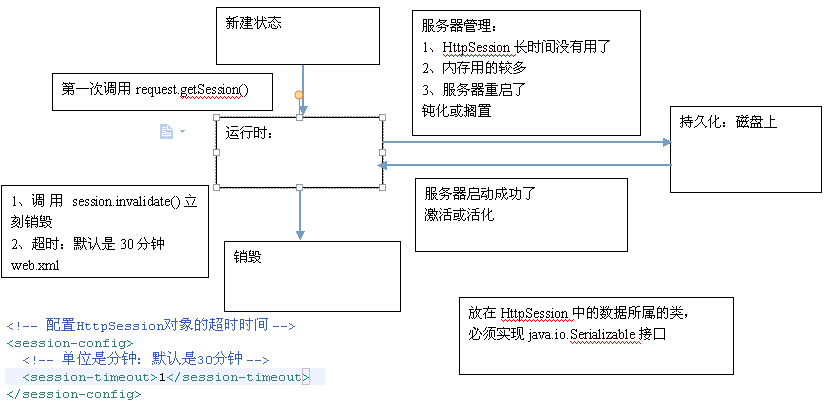
生命周期:第一次调用request.getSession(true);时被创建。【参数boolean类型,true是有session则返回,无则创建一个新的;false则返回一个null如果当前没有有效的session。无参的getSession是调用传入false的该方法】
调用session.invalidate()或自动超时则被销毁。默认超时时间30分钟,超时时间指:【客户端不与服务器进行交互的时间】。【代码设置:session.setMaxInactiveInterval(60*30);单位:秒;web.xml中设置:
<session-config>
<session-timeout>1</session-timeout>
</session-config>
该标签与servlet标签处于同一级别。单位:分钟,必须为整数
】
用途:一般用作一次会话期间保存数据,getAtrribute(),setAttribute(),removeAtrribute()用法和ServletContent对象用法一致。
注意:服务器异常关闭不会销毁session,丢失session。服务器正常关闭不会销毁session,也不会丢失。
三:ServletConfig对象
在Servlet 的配置文件中,可以用一个或多个<init-param>标签为servlet配置一些初始化参数。
当servlet配置了初始化参数之后,web容器在创建servlet实例对象时,会自动将这些初始化参数封装到ServletConfig对象中,并在调用servlet的init方法时,将ServletConfig对象传递给Servlet。进而,程序员通过Servlet对象得到当前servlet的初始化参数信息。
上一篇我们说过,一般会重写无参的init方法,所以通过this.getServletConfig()获得对象。
web.xml中:

servlet中:
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
ServletConfig config = this.getServletConfig();
config.getInitParameter("id"); //223
config.getInitParameter("age"); //jack
Enumeration<String> keys = config.getInitParameterNames();
while(keys.hasMoreElements())
System.out.println(keys.nextElement());
}
四:request对象、response对象
request对象的作用范围是一次http请求响应之内,request也可以存放数据,和ServletContent和session对象类似,不过作用范围比它们两个小。
request可以用过方法getParameter(String key):String;获取浏览器传递的参数【不管是在url后拼接参数的get提交方式或参数在请求体的post提交方式都是用该方法】,
getParameterNames():Enumeration<?>;可以获取所有的key值,没有参数则返回一个空的Enumeration。接收数据前可以调用setCharacterEncoding(charset);设置接收格式。
request还可以用于服务器内部跳转【还是一次http请求响应,所以request在N次内部跳转中是同一个】。request.getRequestDispatcher("HelloWorld").forword(request,reponse);
可以跳转到WebContent目录下的一个html页面或者跳转到另一个Servlet请求处理。
response对象作为响应向浏览器发送数据,可以通过setCharacterEncoding(charset)设置编码格式,setContentType("text/html;charset=utf-8")告诉浏览器已html文件解析。
getWriter()可以获得一个字符输入流,该流可以向浏览器写东西。
response还可以用作客户端重定向,sendRedirect(path)。例如:跳转到WebContent目录下的one.html,response.sendRedirect("one.html");
跳转到另一个Servlet,response.sendRedirect("HelloWorld")。【注意:不要加"/"】
"/"在服务器内部跳转和客户端重定向中怎么使用?代表这什么?
内部跳转加不加"/"不影响,客户端重定向不能加。"/"在服务器代表当前web项目【http://ip:port/项目名/】;
在客户端表示当前页面【http://ip:port/】。
注意: 在WebContent下有一个one.html和一个HTML目录,HTML目录下有一个two.html,两个html页面代码一样。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>测试</title>
</head>
<body>
<a href="HelloWorld">点击超链接进行跳转</a>
</body>
</html>
在浏览器分别访问http://127.0.0.1:7778/StudyServlet/one.html和http://127.0.0.1:7778/StudyServlet/HTML/two.html,然后点击超链接进行跳转。
在two.html中点击超链接发生错误,错误提示【HTTP Status 404 - /StudyServlet/HTML/HelloWorld】,404---没有该资源。为啥呐?因为在客户端页面发送请求是相对于
当前路径的,这可能不方便。可以通过base标签设置。<base href="http://127.0.0.1:7778/StudyServlet/"></base>,这样在一个页面访问另一个资源时就可以相对于base标签设置的了。
等后面学了jsp可以不必限定死协议、ip、port、项目名。
request.getScheme();//获取协议 http
request.getServerName(); //获取ip,127.0.0.1
request.getServerPort(); //获取端口,7778
request.getContextPath(); //获取项目名,StudyServlet
response,response还有很多方法,具体可以查API。request和resonse的具体用法下一篇讲。
总结:
1.SevletContext对象。获取途径,生命周期,作用范围,以及一些该对象的一些用法【存取数据,获取全局配置参数,获取web项目资源】
2.HTTPSession对象。session对象和上面类似,只是作用范围变成了一次会话期间。
3.ServletConfig对象一般用作来获取web.xml中servlet配置中<init-param>...</init-param>里的参数。如果servlet配置了<load-on-startup>正整数</load-on-startup>,
init方法就可以随服务器启动而被调用,继而可以在init中利用该对象做一些初始化配置。
4.request和response对象。一般用来服务器内部跳转和客户端重定向。
当然还有其他用法。下一篇通过一个小项目讲解request和response一些具体用法:比如文件的上传和下载...

javax.servlet.ServletException: Servlet.init() for servlet springServlet threw exception
javax.servlet.ServletException: Servlet.init() for servlet springServlet threw exceptionat org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapper.initServlet(StandardWrapper.java:1309)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapper.loadServlet(StandardWrapper.java:1197)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapper.allocate(StandardWrapper.java:864)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve.invoke(StandardWrapperValve.java:134)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextValve.invoke(StandardContextValve.java:122)
at org.apache.catalina.authenticator.AuthenticatorBase.invoke(AuthenticatorBase.java:505)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardHostValve.invoke(StandardHostValve.java:170)
at org.apache.catalina.valves.ErrorReportValve.invoke(ErrorReportValve.java:103)
at org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve.invoke(AccessLogValve.java:956)
at org.apache.catalina.core.StandardEngineValve.invoke(StandardEngineValve.java:116)
at org.apache.catalina.connector.CoyoteAdapter.service(CoyoteAdapter.java:423)
at org.apache.coyote.http11.AbstractHttp11Processor.process(AbstractHttp11Processor.java:1079)
at org.apache.coyote.AbstractProtocol$AbstractConnectionHandler.process(AbstractProtocol.java:625)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.net.JIoEndpoint$SocketProcessor.run(JIoEndpoint.java:316)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1145)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:615)
at org.apache.tomcat.util.threads.TaskThread$WrappingRunnable.run(TaskThread.java:61)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:745)
Caused by: java.lang.NoClassDefFoundError: List
at java.lang.Class.getDeclaredMethods0(Native Method)
at java.lang.Class.privateGetDeclaredMethods(Class.java:2615)
at java.lang.Class.getDeclaredMethods(Class.java:1860)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.buildLifecycleMetadata(InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:199)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.findLifecycleMetadata(InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:181)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:124)
at org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:282)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:909)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:512)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:475)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory$1.getObject(AbstractBeanFactory.java:302)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton(DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java:228)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:298)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:193)
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:706)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(AbstractApplicationContext.java:762)
at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:482)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(FrameworkServlet.java:658)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.createWebApplicationContext(FrameworkServlet.java:624)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.createWebApplicationContext(FrameworkServlet.java:672)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.initWebApplicationContext(FrameworkServlet.java:543)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet.initServletBean(FrameworkServlet.java:484)
at org.springframework.web.servlet.HttpServletBean.init(HttpServletBean.java:136)
at javax.servlet.GenericServlet.init(GenericServlet.java:158)
关于servlet解析演进和7-session的介绍现已完结,谢谢您的耐心阅读,如果想了解更多关于HttpServletRequest getSession()、HttpServletRequest.getSession特性和Session周期、java web(三):ServletContext、session、ServletConfig、request、response对象、javax.servlet.ServletException: Servlet.init() for servlet springServlet threw exception的相关知识,请在本站寻找。
本文标签:





