想了解初识SpringBootWeb开发的新动态吗?本文将为您提供详细的信息,我们还将为您解答关于springboot网站开发的相关问题,此外,我们还将为您介绍关于1.初识Springboot、4.S
想了解初识SpringBoot Web开发的新动态吗?本文将为您提供详细的信息,我们还将为您解答关于springboot网站开发的相关问题,此外,我们还将为您介绍关于1.初识Springboot、4.Spring Boot web开发、java-study-springboot-基础学习-05-springboot web开发、spring boot框架学习5-spring boot的web开发(1)的新知识。
本文目录一览:- 初识SpringBoot Web开发(springboot网站开发)
- 1.初识Springboot
- 4.Spring Boot web开发
- java-study-springboot-基础学习-05-springboot web开发
- spring boot框架学习5-spring boot的web开发(1)

初识SpringBoot Web开发(springboot网站开发)
使用验证注解来实现表单验证
虽说前端的h5和js都可以完成表单的字段验证,但是这只能是防止一些小白、误操作而已。如果是一些别有用心的人,是很容易越过这些前端验证的,有句话就是说永远不要相信客户端传递过来的数据。所以前端验证之后,后端也需要再次进行表单字段的验证,以确保数据到后端后是正确的、符合规范的。本节就简单介绍一下,在SpringBoot的时候如何进行表单验证。
首先创建一个SpringBoot工程,其中pom.xml配置文件主要配置内容如下:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<!--和上面的 两者等价-->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>创建一个pojo类,在该类中需要验证的字段上加上验证注解。代码如下:
package org.zero01.domain;
import javax.validation.constraints.Min;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull;
public class Student {
@NotNull(message = "学生名字不能为空")
private String sname;
@Min(value = 18,message = "未成年禁止注册")
private int age;
@NotNull(message = "性别不能为空")
private String sex;
@NotNull(message = "联系地址不能为空")
private String address;
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"sname=''" + sname + ''\'''' +
", age=" + age +
", sex=''" + sex + ''\'''' +
", address=''" + address + ''\'''' +
''}'';
}
... getter setter 略 ...
}创建一个Controller类:
package org.zero01.controller;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.zero01.domain.Student;
import javax.validation.Valid;
@RestController
public class StudentController {
@PostMapping("register.do")
public Student register(@Valid Student student, BindingResult bindingResult){
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
// 打印错误信息
System.out.println(bindingResult.getFieldError().getDefaultMessage());
return null;
}
return student;
}
}启动运行类,代码如下:
package org.zero01;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SbWebApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SbWebApplication.class, args);
}
}使用postman进行测试,年龄不满18岁的情况:
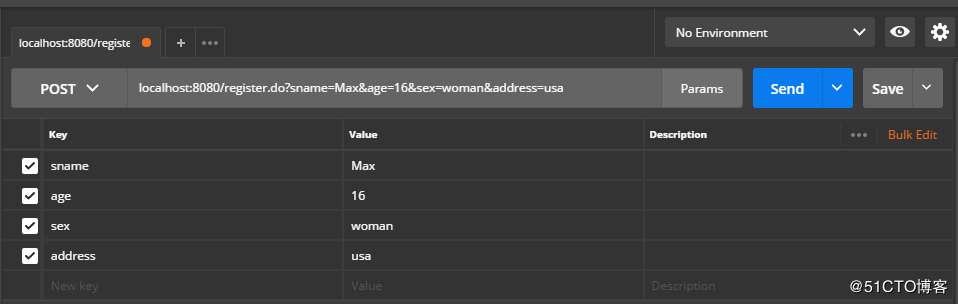
控制台打印结果:
未成年禁止注册非空字段为空的情况:
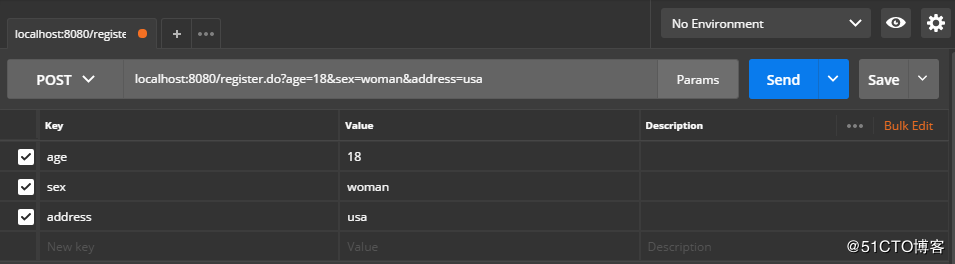
控制台打印结果:
学生名字不能为空使用AOP记录请求日志
我们都知道在Spring里的两大核心模块就是AOP和IOC,其中AOP为面向切面编程,这是一种编程思想或者说范式,它并不是某一种语言所特有的语法。
我们在开发业务代码的时候,经常有很多代码是通用且重复的,这些代码我们就可以作为一个切面提取出来,放在一个切面类中,进行一个统一的处理,这些处理就是指定在哪些切点织入哪些切面。
例如,像日志记录,检查用户是否登录,检查用户是否拥有管理员权限等十分通用且重复的功能代码,就可以被作为一个切面提取出来。而框架中的AOP模块,可以帮助我们很方便的去实现AOP的编程方式,让我们实现AOP更加简单。
本节将承接上一节,演示一下如何利用AOP实现简单的http请求日志的记录。首先创建一个切面类如下:
package org.zero01.aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@Aspect
@Component
public class HttpAspect {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HttpAspect.class);
@Pointcut("execution(public * org.zero01.controller.StudentController.*(..))")
public void log() {
}
@Before("log()")
public void beforeLog(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// 日志格式:url method clientIp classMethod param
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
logger.info("url = {}", request.getRequestURL());
logger.info("method = {}", request.getMethod());
logger.info("clientIp = {}", request.getRemoteHost());
logger.info("class_method = {}", joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName() + "." + joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
logger.info("param = {}", joinPoint.getArgs());
}
@AfterReturning(returning = "object", pointcut = "log()")
public void afterReturningLog(Object object) {
// 打印方法返回值内容
logger.info("response = {}", object);
}
}使用PostMan访问方式如下:
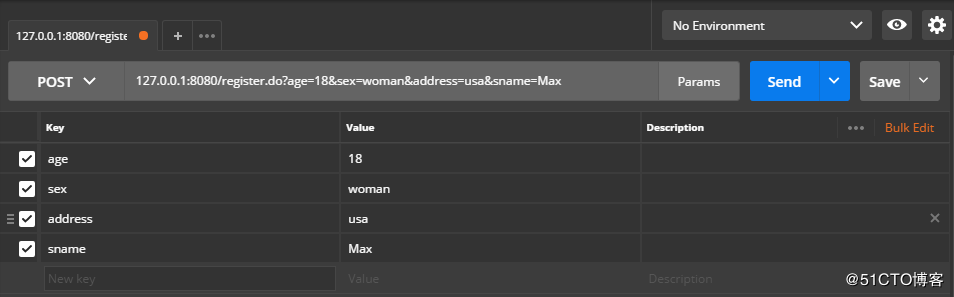
访问成功后,控制台输出日志如下:
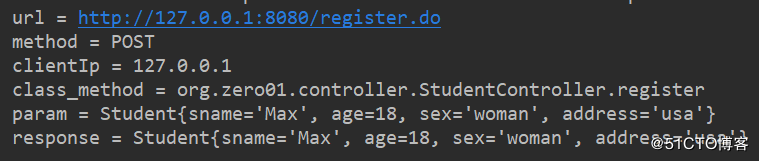
如此,我们就完成了http请求日志的记录。
封装统一的返回数据对象
我们在控制器类的方法中,总是需要返回各种不同类型的数据给客户端。例如,有时候需要返回集合对象、有时候返回字符串、有时候返回自定义对象等等。而且在一个方法里可能会因为处理的结果不同,而返回不同的对象。那么当一个方法中需要根据不同的处理结果返回不同的对象时,我们应该怎么办呢?可能有人会想到把方法的返回类型设定为Object不就可以了,的确是可以,但是这样返回的数据格式就不统一。前端接收到数据时,很不方便去展示,后端写接口文档的时候也不好写。所以我们应该统一返回数据的格式,而使用Object就无法做到这一点了。
所以我们需要将返回的数据统一封装在一个对象里,然后统一在控制器类的方法中,把这个对象设定为返回值类型即可,这样我们返回的数据格式就有了一个标准。那么我们就来开发一个这样的对象吧,首先新建一个枚举类,因为我们需要把一些通用的常量数据都封装在枚举类里,以后这些数据发生变动时,只需要修改枚举类即可。如果将这些常量数据硬编码写在代码里就得逐个去修改了,十分的难以维护。代码如下:
package org.zero01.enums;
public enum ResultEnum {
UNKONW_ERROR(-1, "未知错误"),
SUCCESS(0, "SUCCESS"),
ERROR(1, "ERROR"),
PRIMARY_SCHOOL(100, "小学生"),
MIDDLE_SCHOOL(101, "初中生");
private Integer code;
private String msg;
ResultEnum(Integer code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
}然后就是创建我们的返回数据封装对象了,在此之前,我们需要先定义好这个数据的一个标准格式。我这里定义的格式如下:
{
"code": 0,
"msg": "注册成功",
"data": {
"sname": "Max",
"age": 18,
"sex": "woman",
"address": "湖南"
}
}明确了数据的格式后,就可以开发我们的返回数据封装对象了。新建一个类,代码如下:
package org.zero01.domain;
import org.zero01.enums.ResultEnum;
/**
* @program: sb-web
* @description: 服务器统一的返回数据封装对象
* @author: 01
* @create: 2018-05-05 18:03
**/
public class Result<T> {
// 错误/正确码
private Integer code;
// 提示信息
private String msg;
// 返回的数据
private T data;
private Result(Integer code, String msg) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
}
private Result(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
private Result(Integer code, String msg, T data) {
this.code = code;
this.msg = msg;
this.data = data;
}
private Result() {
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
public static <T> Result<T> createBySucce***esultMessage(String msg) {
return new Result<T>(ResultEnum.SUCCESS.getCode(), msg);
}
public static <T> Result<T> createBySuccessCodeResult(Integer code, String msg) {
return new Result<T>(code, msg);
}
public static <T> Result<T> createBySucce***esult(String msg, T data) {
return new Result<T>(ResultEnum.SUCCESS.getCode(), msg, data);
}
public static <T> Result<T> createBySucce***esult() {
return new Result<T>(ResultEnum.SUCCESS.getCode());
}
public static <T> Result<T> createByErrorResult() {
return new Result<T>(ResultEnum.ERROR.getCode());
}
public static <T> Result<T> createByErrorResult(String msg, T data) {
return new Result<T>(ResultEnum.ERROR.getCode(), msg, data);
}
public static <T> Result<T> createByErrorCodeResult(Integer errorCode, String msg) {
return new Result<T>(errorCode, msg);
}
public static <T> Result<T> createByErrorResultMessage(String msg) {
return new Result<T>(ResultEnum.ERROR.getCode(), msg);
}
}接着修改我们之前的注册接口代码如下:
@PostMapping("register.do")
public Result<Student> register(@Valid Student student, BindingResult bindingResult) {
if (bindingResult.hasErrors()) {
return Result.createByErrorResultMessage(bindingResult.getFieldError().getDefaultMessage());
}
return Result.createBySucce***esult("注册成功", student);
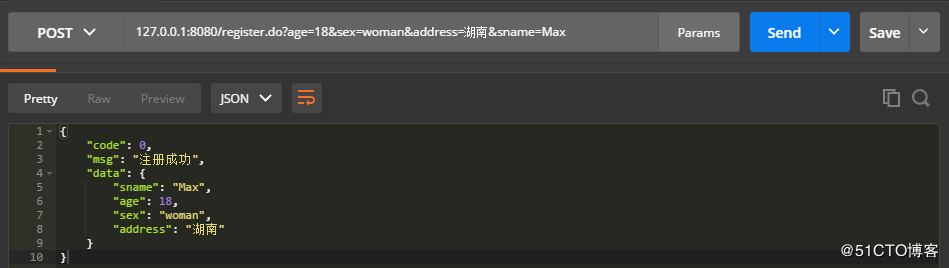
}使用PostMan进行测试,数据正常的情况:
学生姓名为空的情况:
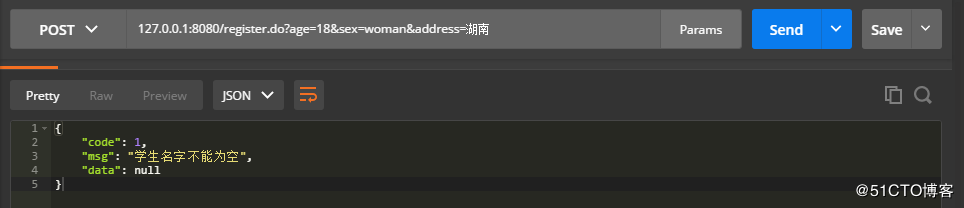
如上,可以看到,返回的数据格式都是一样的,code字段的值用于判断是一个success的结果还是一个error的结果,msg字段的值是提示信息,data字段则是存储具体的数据。有这样一个统一的格式后,前端也好解析这个json数据,我们后端在写接口文档的时候也好写了。
统一异常处理
一个系统或应用程序在运行的过程中,由于种种因素,肯定是会有抛异常的情况的。在系统出现异常时,由于服务的中断,数据可能会得不到返回,亦或者返回的是一个与我们定义的数据格式不相符的一个数据,这是我们不希望出现的问题。所以我们得进行一个全局统一的异常处理,拦截系统中会出现的异常,并进行处理。下面我们用一个小例子来做为演示。
例如,现在有一个业务需求如下:
- 获取某学生的年龄进行判断,小于10,抛出异常并返回“小学生”提示信息,大于10且小于16,抛出异常并返回“初中生”提示信息。
首先我们需要自定义一个异常,因为默认的异常构造器只接受一个字符串类型的数据,而我们返回的数据中有一个code,所以我们得自己定义个异常类。代码如下:
package org.zero01.exception;
/**
* @program: sb-web
* @description: 自定义异常
* @author: 01
* @create: 2018-05-05 19:01
**/
public class StudentException extends RuntimeException {
private Integer code;
public StudentException(Integer code, String msg) {
super(msg);
this.code = code;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
}新建一个 ErrorHandler 类,用于全局异常的拦截及处理。代码如下:
package org.zero01.handle;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.zero01.domain.Result;
import org.zero01.enums.ResultEnum;
import org.zero01.exception.StudentException;
/**
* @program: sb-web
* @description: 全局异常处理类
* @author: 01
* @create: 2018-05-05 18:48
**/
// 定义全局异常处理类
@ControllerAdvice
// Lombok的一个注解,用于日志打印
@Slf4j
public class ErrorHandler {
// 声明异常处理方法,传递哪一个异常对象的class,就代表该方法会拦截哪一个异常对象包括其子类
@ExceptionHandler(value = Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public Result exceptionHandle(Exception e) {
if (e instanceof StudentException) {
StudentException studentException = (StudentException) e;
// 返回统一的数据格式
return Result.createByErrorCodeResult(studentException.getCode(), studentException.getMessage());
}
// 打印异常日志
log.error("[系统异常]{}", e);
// 返回统一的数据格式
return Result.createByErrorCodeResult(ResultEnum.UNKONW_ERROR.getCode(), "服务器内部出现未知错误");
}
}注:我这里使用到了Lombok,如果对Lombok不熟悉的话,可以参考我之前写的一篇Lombok快速入门
在之前的控制类中,增加如下代码:
@Autowired
private IStudentService iStudentService;
@GetMapping("check_age.do")
public void checkAge(Integer age) throws Exception {
iStudentService.checkAge(age);
age.toString();
}我们都知道具体的逻辑都是写在service层的,所以新建一个service包,在该包中新建一个接口。代码如下:
package org.zero01.service;
public interface IStudentService {
void checkAge(Integer age) throws Exception;
}然后新建一个类,实现该接口。代码如下:
package org.zero01.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.zero01.enums.ResultEnum;
import org.zero01.exception.StudentException;
@Service("iStudentService")
public class StudentService implements IStudentService {
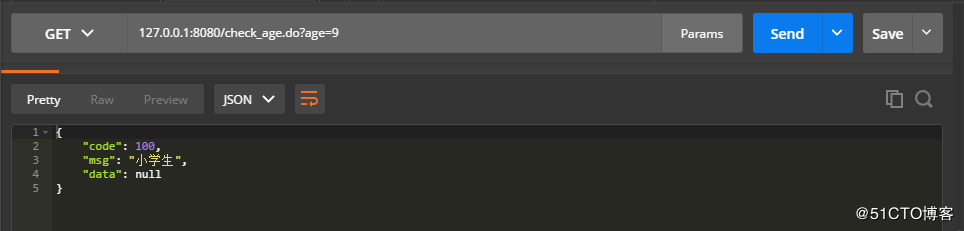
public void checkAge(Integer age) throws StudentException {
if (age < 10) {
throw new StudentException(ResultEnum.PRIMARY_SCHOOL.getCode(), ResultEnum.PRIMARY_SCHOOL.getMsg());
} else if (age > 10 && age < 16) {
throw new StudentException(ResultEnum.MIDDLE_SCHOOL.getCode(), ResultEnum.MIDDLE_SCHOOL.getMsg());
}
}
}完成以上的代码编写后,就可以开始进行测试了。age < 10 的情况:
age > 10 && age < 16 的情况:

age字段为空,出现系统异常的情况:
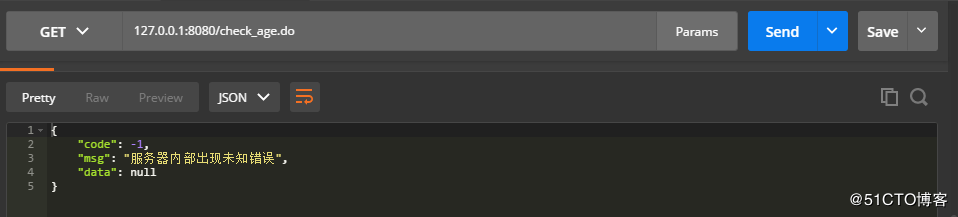
因为我们打印了日志,所以出现系统异常的时候也会输出日志信息,不至于我们无法定位到异常:
从以上的测试结果中可以看到,即便抛出了异常,我们返回的数据格式依旧是固定的,这样就不会由于系统出现异常而返回不一样的数据格式。
单元测试
我们一般会在开发完项目中的某一个功能的时候,就会进行一个单元测试。以确保交付项目时,我们的代码都是通过测试并且功能正常的,这是一个开发人员基本的素养。所以本节将简单介绍service层的测试与controller层的测试方式。
首先是service层的测试方式,service层的单元测试和我们平时写的测试没太大区别。在工程的test目录下,新建一个测试类,代码如下:
package org.zero01;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.zero01.domain.Result;
import org.zero01.domain.Student;
import org.zero01.service.IStudentService;
/**
* @program: sb-web
* @description: Student测试类
* @author: 01
* @create: 2018-05-05 21:46
**/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class StudentServiceTest {
@Autowired
private IStudentService iStudentService;
@Test
public void findOneTest() {
Result<Student> result = iStudentService.findOne(1);
Student student = result.getData();
Assert.assertEquals(18, student.getAge());
}
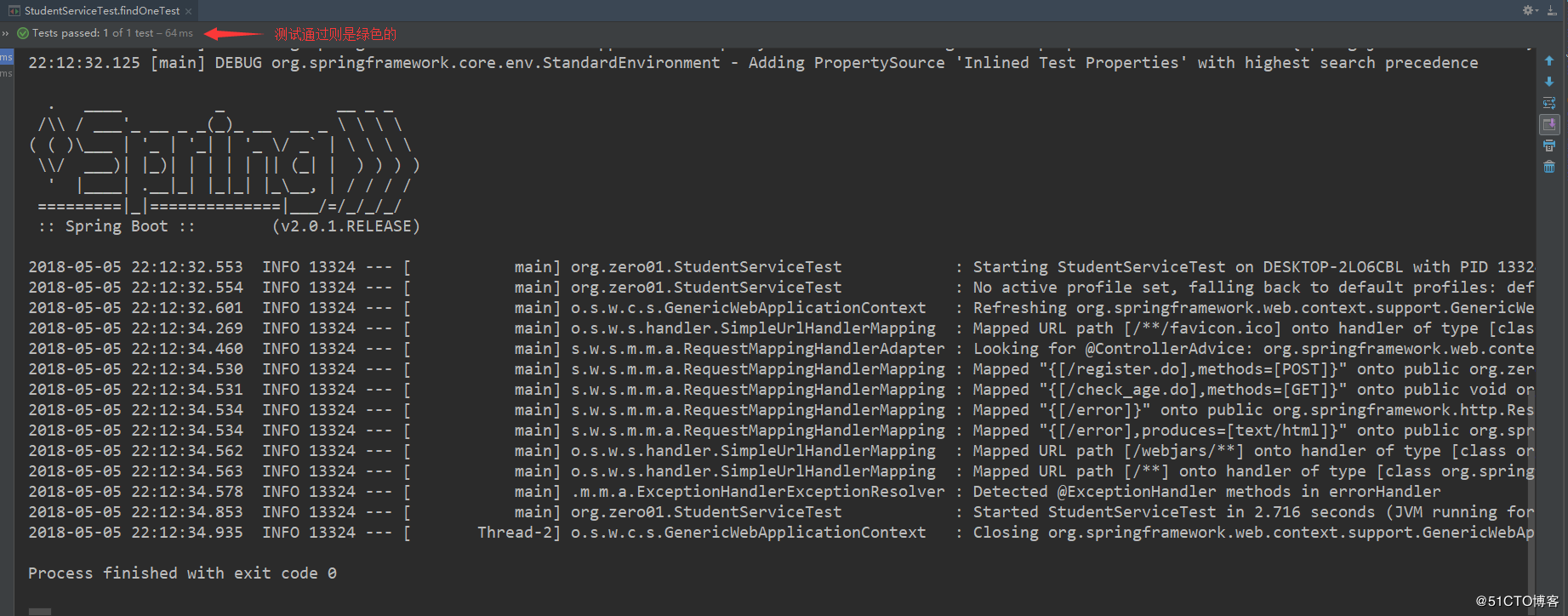
}执行该测试用例,运行结果如下:
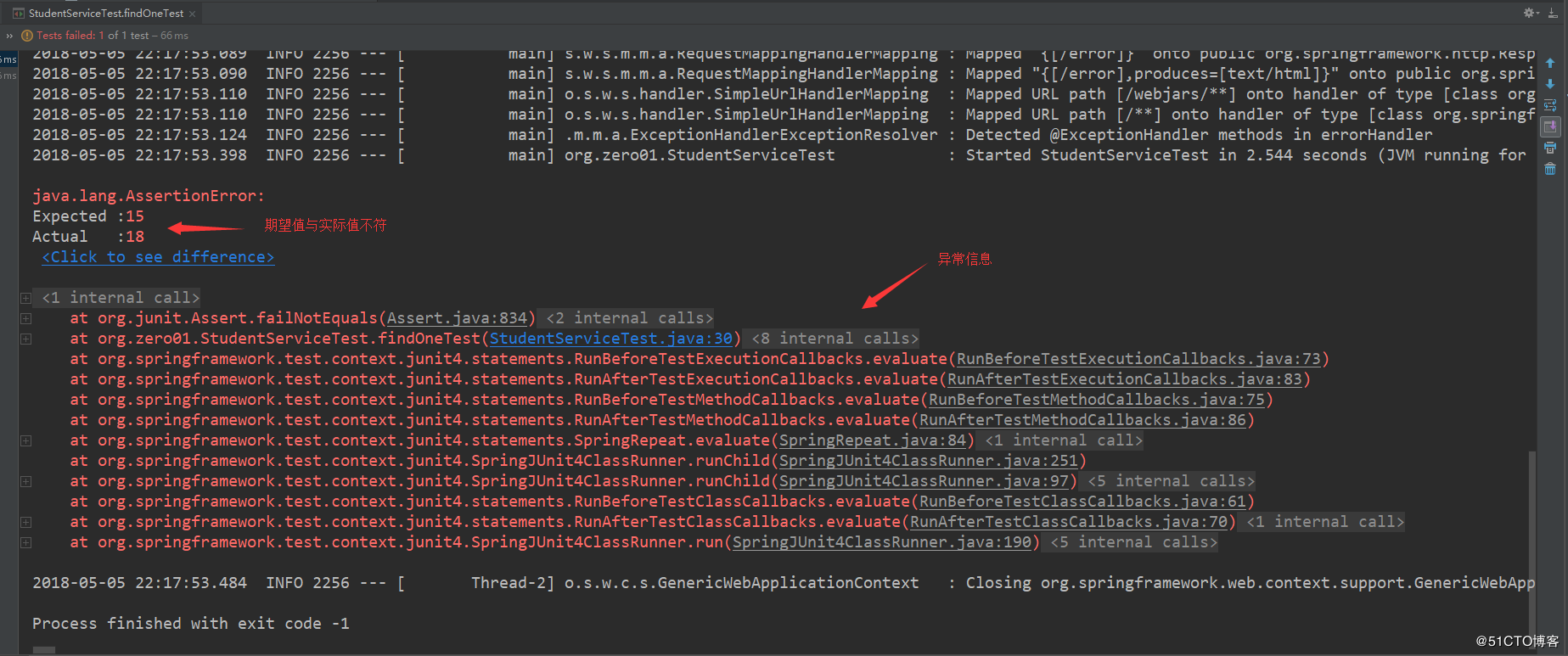
我们修改一下年龄为15,以此模拟一下测试不通过的情况:
service层的测试比较简单,就介绍到这。接下来我们看一下controller层的测试方式。IDEA中有一个比较方便的功能可以帮我们生成测试方法,到需要被测试的controller类中,按 Ctrl + Shift + t 就可以快速创建测试方法。如下,点击Create New Test:
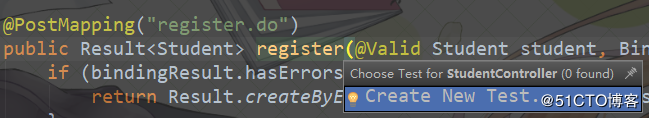
然后选择需要测试的方法:
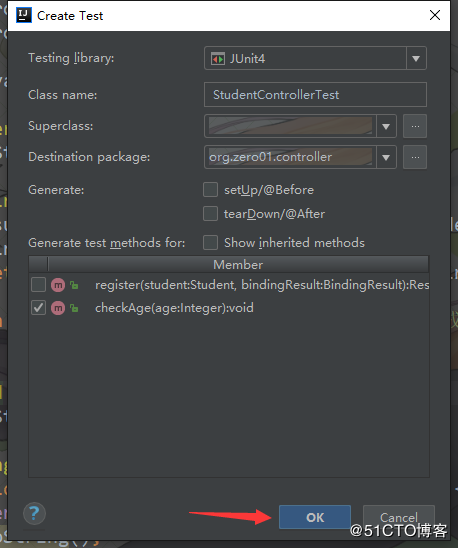
生成的测试用例代码如下:
package org.zero01.controller;
import org.junit.Test;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
public class StudentControllerTest {
@Test
public void checkAge() {
}
}接着我们来完成这个测试代码,controller层的测试和service层不太一样,因为需要访问url,而不是直接调用方法进行测试。测试代码如下:
package org.zero01.controller;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.AutoConfigureMockMvc;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class StudentControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
public void checkAge() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/check_age.do") // 使用get请求
.param("age","18")) // url参数
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk()); // 判断返回的状态是否正常
}
}运行该测试用例,因为我们之前实现了一个记录http访问日志的功能,所以可以直接通过控制台的输出日志来判断接口是否有被请求到:
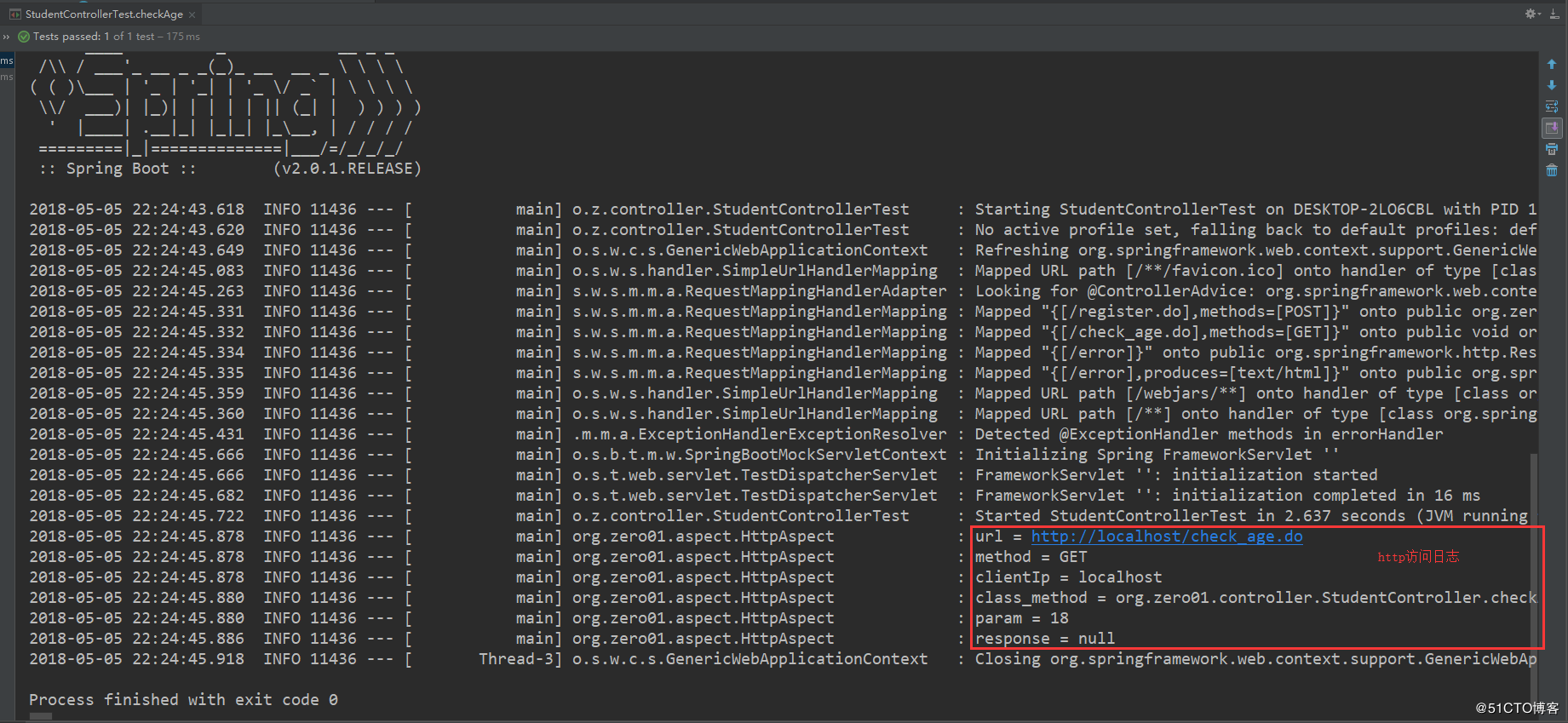
单元测试就介绍到这,毕竟一般我们不会在代码上测试controller层,而是使用postman或者restlet client等工具进行测试。

1.初识Springboot
Springboot开发条件
工具:Spring Tools Suite (STS) JDK:1.8
Springboot创建流程
1.
2.
测试案例
1.
2.

4.Spring Boot web开发
1.创建一个web模块
(1).创建SpringBoot应用,选中我们需要的模块;
(2).SpringBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行起来
(3).自己编写业务代码;
自动配置原理
xxxxAutoConfiguration:帮我们给容器中自动配置组件; xxxxProperties:配置类来封装配置文件的内容; |
2.SpringBoott对静态资源的映射规则
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false) public class ResourceProperties implements ResourceLoaderAware { //可以设置和静态资源有关的参数,缓存时间等 |
WebMvcAuotConfiguration: @Override public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) { logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled"); return; } Integer cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCachePeriod(); if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) { customizeResourceHandlerRegistration( registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**") .addResourceLocations( "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/") .setCachePeriod(cachePeriod)); } String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(); //静态资源文件夹映射 if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) { customizeResourceHandlerRegistration( registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern) .addResourceLocations( this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()) .setCachePeriod(cachePeriod)); } }
//配置index映射 @Bean public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping( ResourceProperties resourceProperties) { return new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(resourceProperties.getWelcomePage(), this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern()); }
//配置图标 @Configuration @ConditionalOnProperty(value = "spring.mvc.favicon.enabled", matchIfMissing = true) public static class FaviconConfiguration {
private final ResourceProperties resourceProperties;
public FaviconConfiguration(ResourceProperties resourceProperties) { this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties; }
@Bean public SimpleUrlHandlerMapping faviconHandlerMapping() { SimpleUrlHandlerMapping mapping = new SimpleUrlHandlerMapping(); mapping.setOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 1); //所有 **/favicon.ico mapping.setUrlMap(Collections.singletonMap("**/favicon.ico", faviconRequestHandler())); return mapping; }
@Bean public ResourceHttpRequestHandler faviconRequestHandler() { ResourceHttpRequestHandler requestHandler = new ResourceHttpRequestHandler(); requestHandler .setLocations(this.resourceProperties.getFaviconLocations()); return requestHandler; }
} |
(1). 所有/webjars/**,都去 classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/ 找资源;webjars:以jar包的方式引入静态资源
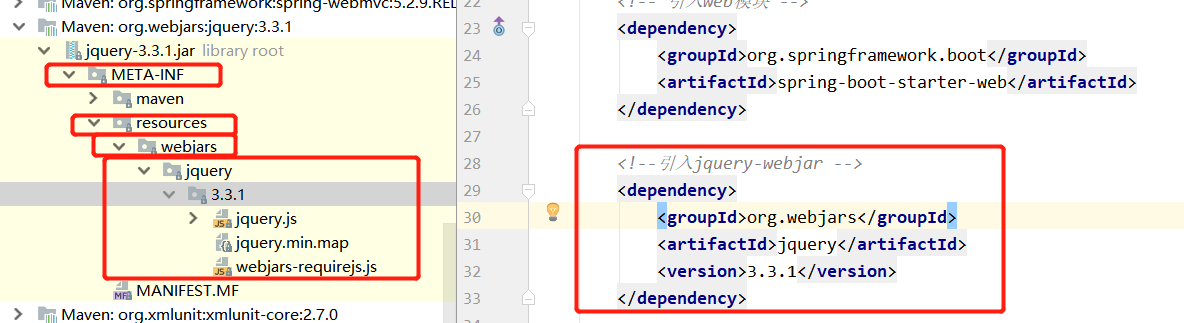
<!--引入jquery-webjar 在访问的时候只需要写webjars下面资源的名称即可 --> <dependency> <groupId>org.webjars</groupId> <artifactId>jquery</artifactId> <version>3.3.1</version> </dependency> |
访问:localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.3.1/jquery.js
(2)."/**" 访问当前项目的任何资源,到''静态资源文件夹''找映射
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" "/":当前项目的根路径 |
访问 > 
localhost:8080/abc ---> 去静态资源文件夹里面找abc
(3).index页; 静态资源文件夹下的所有index.html页面;被"/**"映射;
访问:localhost:8080/
(4). 图标**/favicon.ico都在静态资源文件下找
3.模板引擎
JSP、Velocity、Freemarker、Thymeleaf
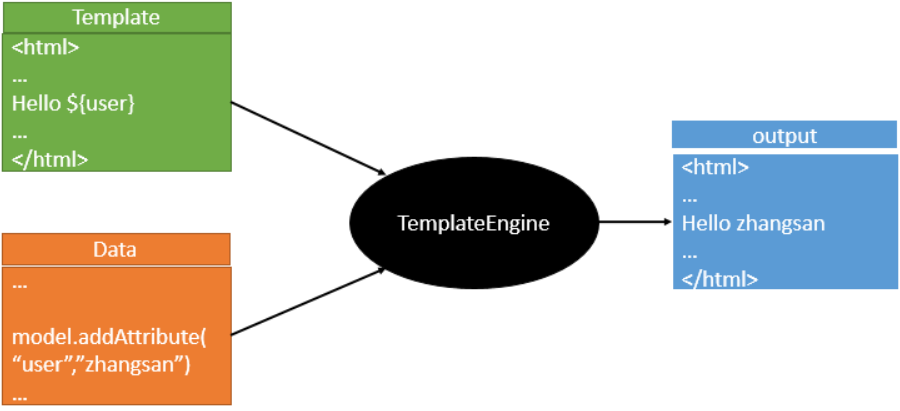
SpringBoot推荐使用的Thymeleaf,语法更简单,功能更强大.
(1).引入thymeleaf
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> <!--2.1.6--> </dependency> 切换thymeleaf版本 <properties> <thymeleaf.version>3.0.9.RELEASE</thymeleaf.version> <!-- 布局功能的支持程序 thymeleaf3主程序 layout2以上版本 --> <!-- thymeleaf2 layout1--> <thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version>2.2.2</thymeleaf-layout-dialect.version> </properties> |
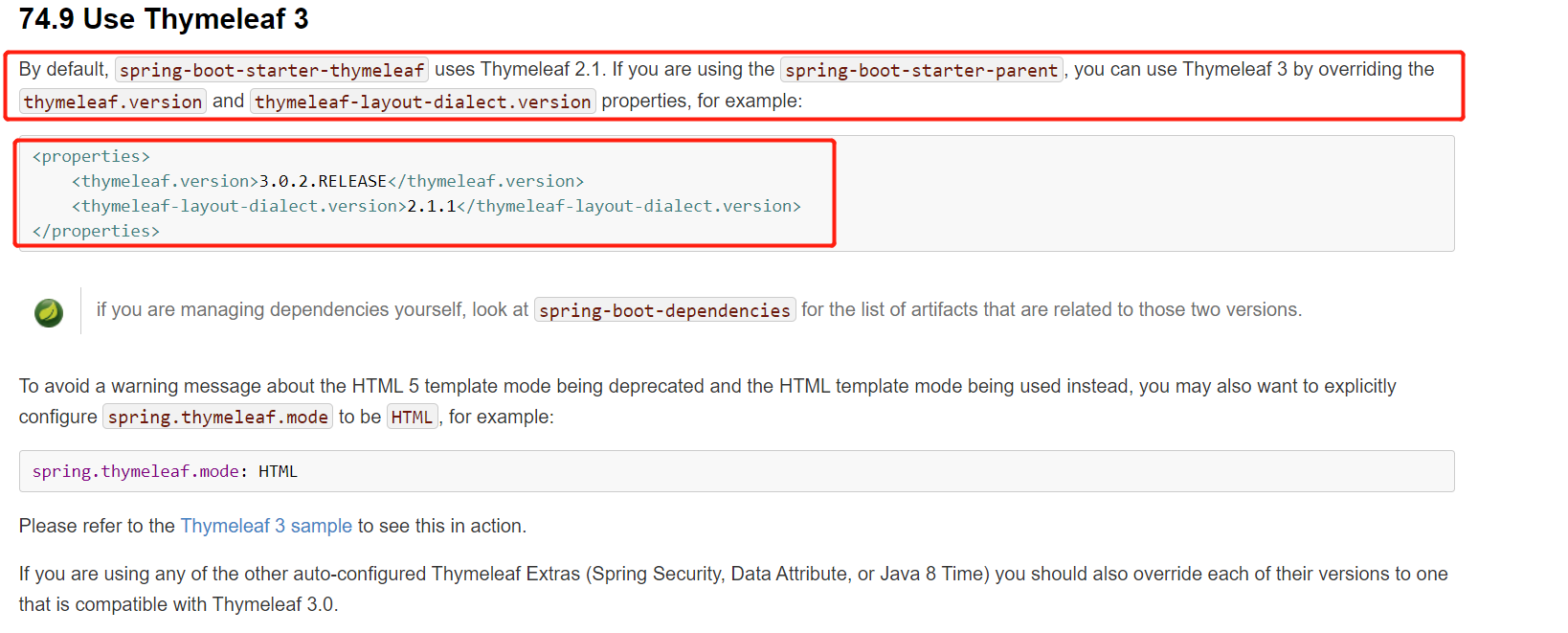
(2).使用thymeleaf
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.thymeleaf") public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
private static final MimeType DEFAULT_CONTENT_TYPE = MimeType.valueOf("text/html");
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html"; // |
把HTML页面放在classpath:/templates/,thymeleaf就能自动渲染;
开发文档
[1].添加名称空间
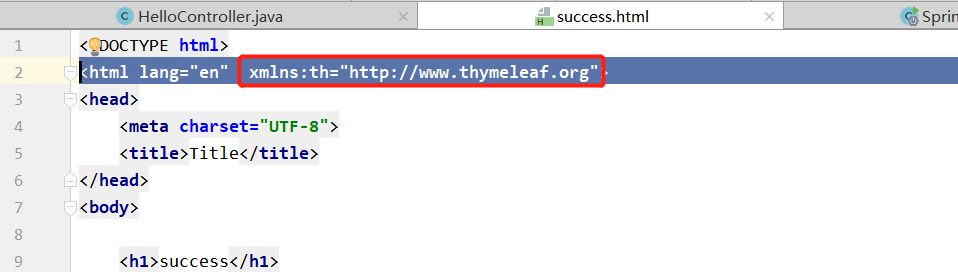
th="http://www.thymeleaf.org" |
[2].使用thymeleaf语法
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>成功!</h1> <!--th:text 将div里面的文本内容设置为 --> <div th:text="${hello}">这是显示欢迎信息</div> </body> </html> |
(3).thymeleaf语法
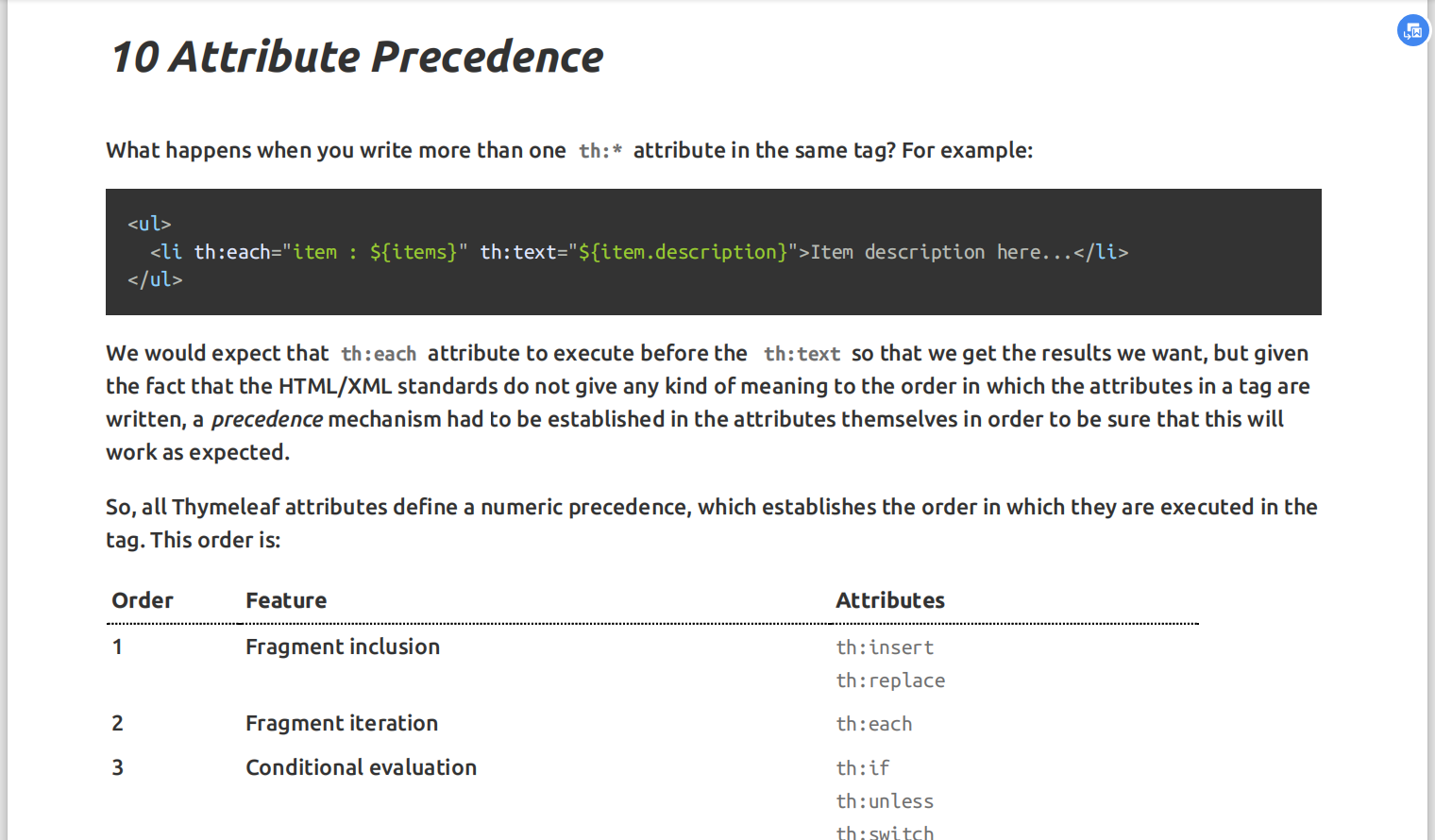
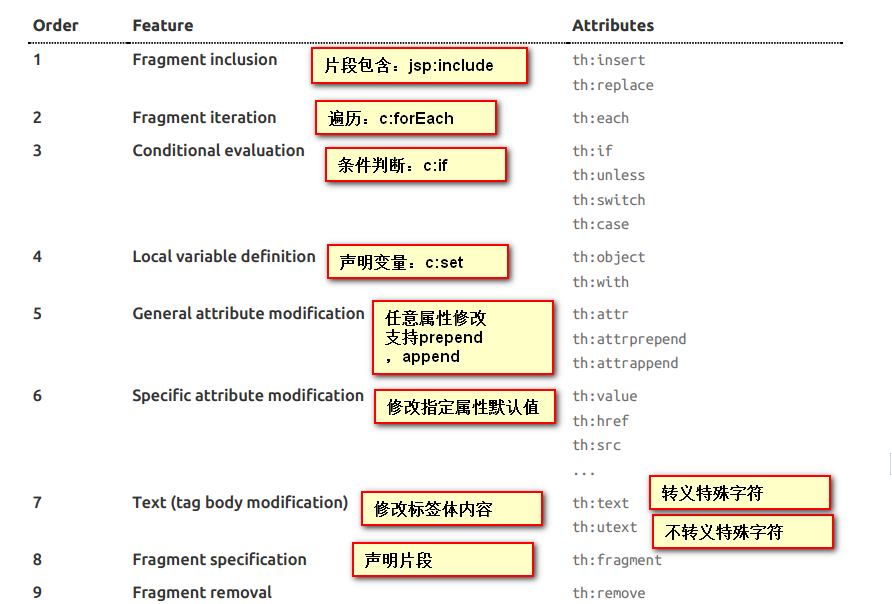
[1].th:text:改变当前元素里面的文本内容
th:任意html属性;来替换原生属性的值
[2].表达式
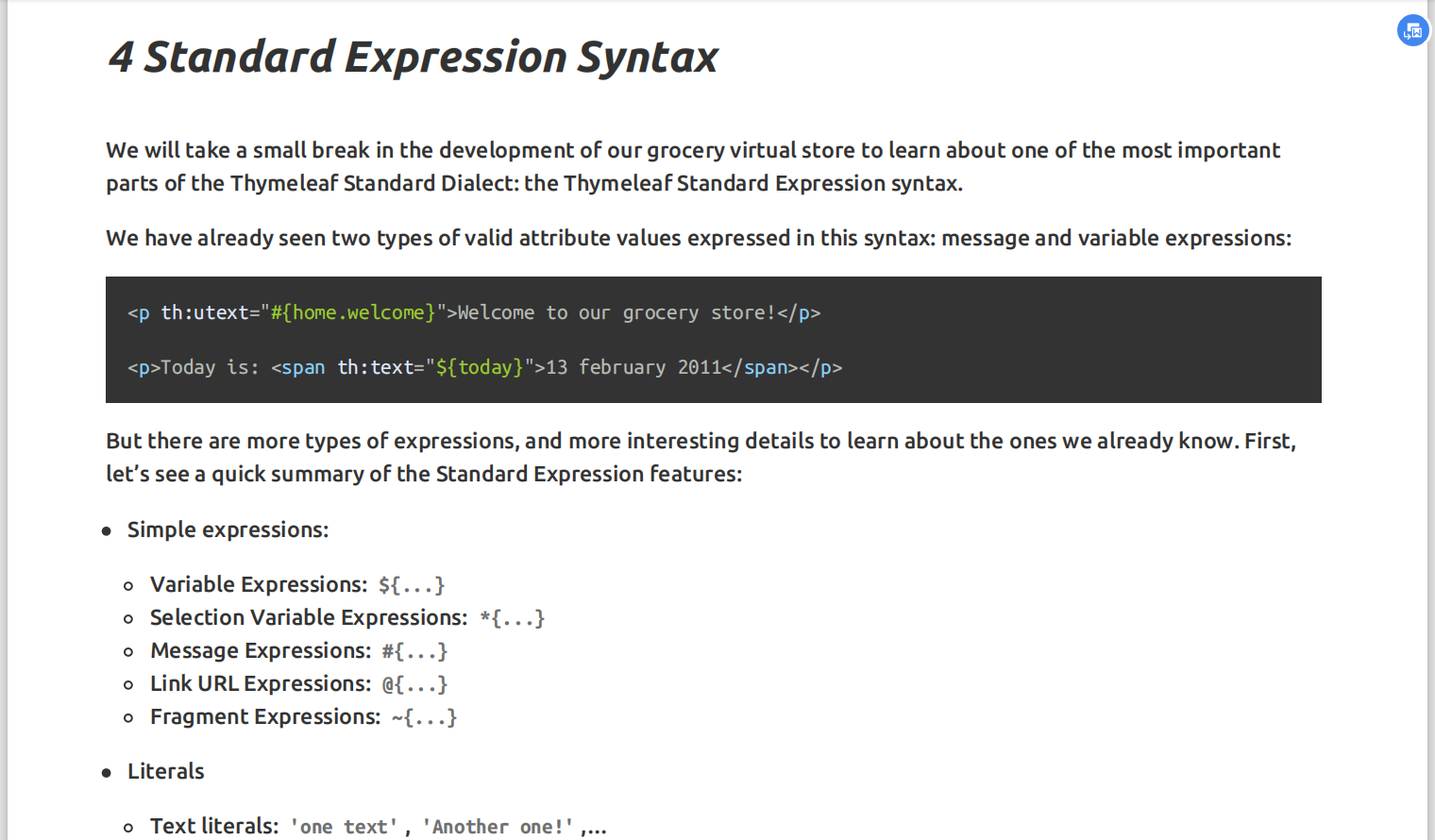
Simple expressions:(表达式语法) Variable Expressions: ${...}:获取变量值;OGNL; 1)、获取对象的属性、调用方法 2)、使用内置的基本对象: #ctx : the context object. #vars: the context variables. #locale : the context locale. #request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object. #response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object. #session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object. #servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object.
${session.foo} 3)、内置的一些工具对象: #execInfo : information about the template being processed. #messages : methods for obtaining externalized messages inside variables expressions, in the same way as they would be obtained using #{…} syntax. #uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs #conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any). #dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc. #calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects. #numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects. #strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc. #objects : methods for objects in general. #bools : methods for boolean evaluation. #arrays : methods for arrays. #lists : methods for lists. #sets : methods for sets. #maps : methods for maps. #aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections. #ids : methods for dealing with id attributes that might be repeated (for example, as a result of an iteration).
Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样; 补充:配合 th:object="${session.user}: <div th:object="${session.user}"> <p>Name: <span th:text="*{firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p> <p>Surname: <span th:text="*{lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p> <p>Nationality: <span th:text="*{nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p> </div>
Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容 Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL; @{/order/process(execId=${execId},execType=''FAST'')} Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式 <div th:insert="~{commons :: main}">...</div>
Literals(字面量) Text literals: ''one text'' , ''Another one!'' ,… Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,… Boolean literals: true , false Null literal: null Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,… Text operations:(文本操作) String concatenation: + Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}| Arithmetic operations:(数学运算) Binary operators: + , - , * , / , % Minus sign (unary operator): - Boolean operations:(布尔运算) Binary operators: and , or Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not Comparisons and equality:(比较运算) Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le ) Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne ) Conditional operators:条件运算(三元运算符) If-then: (if) ? (then) If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else) Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue) Special tokens: No-Operation: _ |
4.SpringMVC自动配置
官方文档
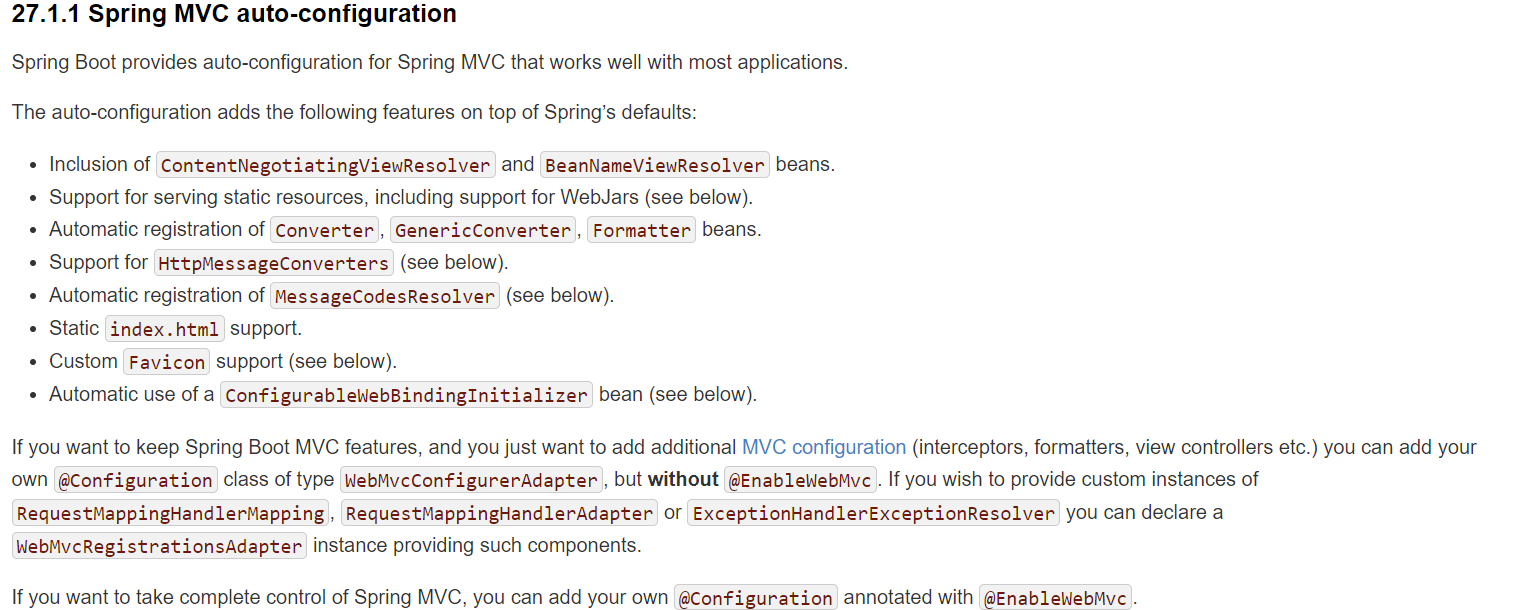
(1).Spring MVC auto-configuration
Spring Boot 自动配置SpringMVC
SpringBoot对SpringMVC的默认配置(WebMvcAutoConfiguration)
Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans.
自动配置了ViewResolver(视图解析器:根据方法的返回值得到视图对象(View),视图对象决定如何渲染(转发?重定向?))
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver:组合所有的视图解析器的
如何定制:我们可以自己给容器中添加一个视图解析器;自动的将其组合进来;
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (see below).
静态资源文件夹路径,webjars
Automatic registration of Converter, GenericConverter, Formatter beans.
Converter:转换器; public String hello(User user):类型转换使用Converter
Formatter格式化器; 2017.12.17===Date;
@Bean @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "date-format")//在文件中配置日期格式化的规则 public Formatter<Date> dateFormatter() { return new DateFormatter(this.mvcProperties.getDateFormat());//日期格式化组件 } |
自己添加的格式化器转换器,我们只需要放在容器中即可
Support for HttpMessageConverters (see below).
HttpMessageConverter:SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的;User--->Json;
`HttpMessageConverters` 是从容器中确定;获取所有的HttpMessageConverter;
自己给容器中添加HttpMessageConverter,只需要将自己的组件注册容器中(@Bean,@Component)
Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver (see below).
定义错误代码生成规则
Static index.html support.
静态首页访问
Custom Favicon support (see below).
自定义favicon.ico 图标
Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean (see below).
我们可以配置一个ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer来替换默认的;(添加到容器)
初始化WebDataBinder; 请求数据=====JavaBean; |
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web:web所有自动场景;
If you want to keep Spring Boot MVC features, and you just want to add additional MVC configuration (interceptors, formatters, view controllers etc.) you can add your own @Configuration class of type WebMvcConfigurerAdapter, but without @EnableWebMvc. If you wish to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping, RequestMappingHandlerAdapter or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver you can declare a WebMvcRegistrationsAdapter instance providing such components.
(2).扩展SpringMVC
<mvc:view-controller path="/hello" view-name="success"/> <mvc:interceptors> <mvc:interceptor> <mvc:mapping path="/hello"/> <bean></bean> </mvc:interceptor> </mvc:interceptors> |
编写配置类(@Configuration),是WebMvcConfigurerAdapter类型;不能标注@EnableWebMvc;
在保留所有的自动配置情况下,也能用我们扩展的配置
//使用 WebMvcConfigurer可以来扩展SpringMVC功能 //因为WebMvcConfigurerAdapter已经过时,所以我们使用接口WebMvcConfigurer替代 @Configuration public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { //super.addViewControllers(registry) //浏览器发送/pluto请求来到success registry.addViewController("/pluto").setViewName("success"); } } |
原理解析:
[1].WebMvcAutoConfiguration是SpringMVC自动配置类
[2].在做其他自动配置时会导入@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
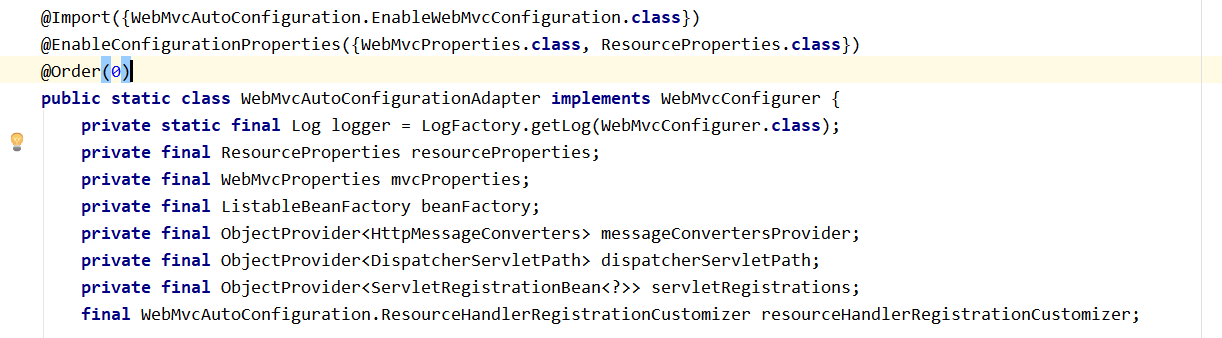
@Configuration public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration { private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();
//从容器中获取所有的WebMvcConfigurer @Autowired(required = false) public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) { if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) { this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers); //一个参考实现;将所有的WebMvcConfigurer相关配置都来一起调用; @Override // public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { // for (WebMvcConfigurer delegate : this.delegates) { // delegate.addViewControllers(registry); // } } } } |
[3].容器中所有的WebMvcConfigurer都会一起起作用
[4].手写的配置类也会被调用
结果:SpringMVC的自动配置和手写的扩展配置都起作用;
(3).全面接管SpringMVC
SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不需要;自己配置所有配置;所有的SpringMVC自动配置使其失效。
需要在配置类中添加@EnableWebMvc即可;
//使用 WebMvcConfigurer可以来扩展SpringMVC功能 //因为WebMvcConfigurerAdapter已经过时,所以我们使用接口WebMvcConfigurer替代 @EnableWebMvc @Configuration public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { //super.addViewControllers(registry) //浏览器发送/pluto请求来到success registry.addViewController("/pluto").setViewName("success"); } } |
原理解析:@EnableWebMvc自动配置失效
[1].@EnableWebMvc的核心
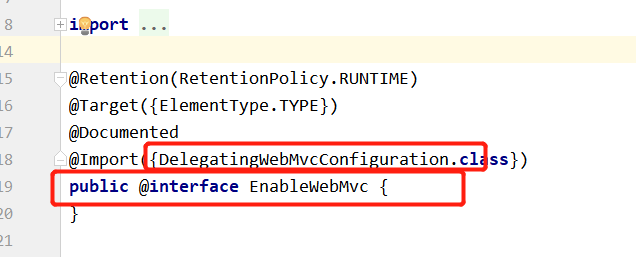
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) @Documented @Import({DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration.class}) public @interface EnableWebMvc { } |
[2].DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
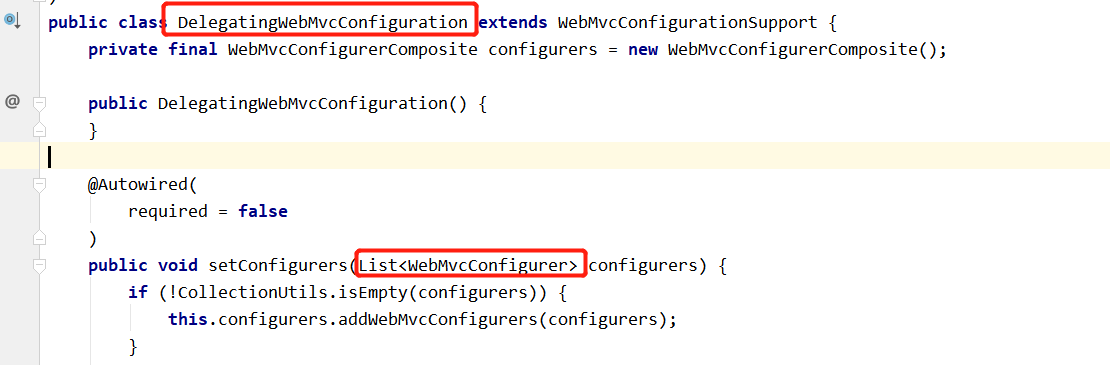
@Configuration( proxyBeanMethods = false ) public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport { |
[3].WebMvcAutoConfiguration
@Configuration( proxyBeanMethods = false ) @ConditionalOnWebApplication( type = Type.SERVLET ) @ConditionalOnClass({Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class}) //容器中没有这个组件的时候,这个自动配置类才生效 @ConditionalOnMissingBean({WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class}) @AutoConfigureOrder(-2147483638) @AutoConfigureAfter({DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class, ValidationAutoConfiguration.class}) public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration { |
[4].@EnableWebMvc将WebMvcConfigurationSupport组件导入进来
[5].导入的WebMvcConfigurationSupport只是SpringMVC最基本的功能
5.修改SpringBoot的默认配置
模式:
(1).SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(@Bean、@Component)如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有,才自动配置;如果有些组件可以有多个(ViewResolver)将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来;
(2).在SpringBoot中有非常多的xxxConfigurer帮助我们进行扩展配置
(3).在SpringBoot中v 有很多的xxxCustomizer帮助我们进行定制配置
6.RestfulCRUD
(1).访问首页(默认)
//使用 WebMvcConfigurer可以来扩展SpringMVC功能 //因为WebMvcConfigurerAdapter已经过时,所以我们使用接口WebMvcConfigurer替代 //@EnableWebMvc @Configuration public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { //super.addViewControllers(registry) //浏览器发送/pluto请求来到success registry.addViewController("/pluto").setViewName("success"); }
//所有的WebMvcConfigurer组件会一起起作用 //@Bean将组件注册在容器中 @Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){ WebMvcConfigurer dapter = new WebMvcConfigurer() { @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("login"); registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("login"); } }; return dapter; } } |
(2).国际化
[1].编写国际化配置文件
[2].使用ResourceBundleMessageSource管理国际化资源文件
[3].在页面使用fmt:message取出国际化内容
实现步骤:
[1].编写国际化配置文件
#login_zh_CN.properties login.btn=登录 login.password=密码 login.remember=记住我 login.tip=请登录 login.username=用户名
#login_en_US.properties login.btn=Sing In login.password=Password login.remember=remember me login.tip=Please sign in login.username=UserName
#login.properties login.btn=登录~ login.password=密码~ login.remember=记住我~ login.tip=请登录~ login.username=用户名~ |
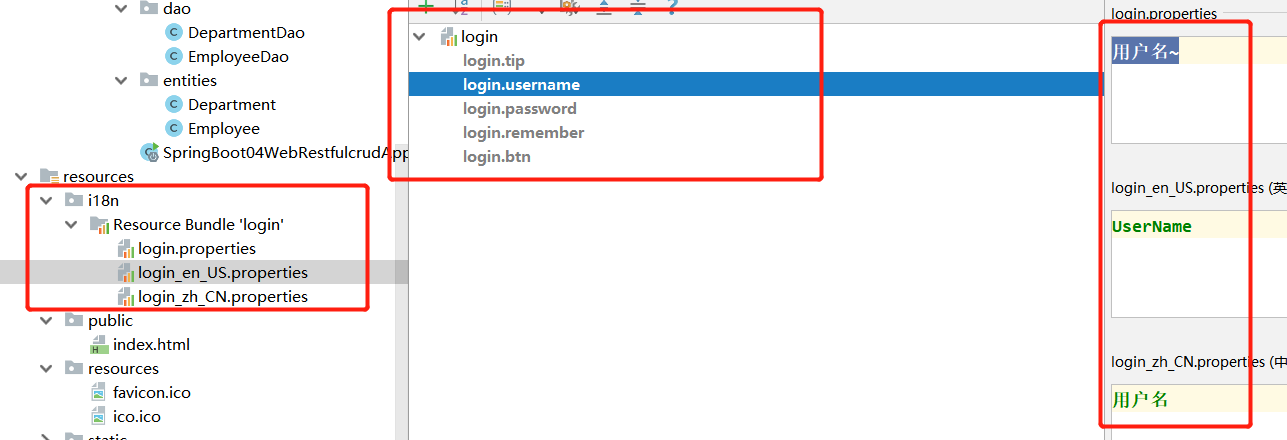
[2].SpringBoot自动配置好了管理国际化资源文件的组件
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.messages") public class MessageSourceAutoConfiguration {
/** * Comma-separated list of basenames (essentially a fully-qualified classpath * location), each following the ResourceBundle convention with relaxed support for * slash based locations. If it doesn''t contain a package qualifier (such as * "org.mypackage"), it will be resolved from the classpath root. */ private String basename = "messages"; //我们的配置文件可以直接放在类路径下叫messages.properties;
@Bean public MessageSource messageSource() { ResourceBundleMessageSource messageSource = new ResourceBundleMessageSource(); if (StringUtils.hasText(this.basename)) { //设置国际化资源文件的基础名(去掉语言国家代码的) messageSource.setBasenames(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray( StringUtils.trimAllWhitespace(this.basename))); } if (this.encoding != null) { messageSource.setDefaultEncoding(this.encoding.name()); } messageSource.setFallbackToSystemLocale(this.fallbackToSystemLocale); messageSource.setCacheSeconds(this.cacheSeconds); messageSource.setAlwaysUseMessageFormat(this.alwaysUseMessageFormat); return messageSource; } |
[3].取出国际化内容
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no"> <meta name="description" content=""> <meta name="author" content=""> <title>Signin Template for Bootstrap</title> <!-- Bootstrap core CSS --> <link href="asserts/css/bootstrap.min.css" th:href="@{/webjars/bootstrap/4.0.0/css/bootstrap.css}" rel="stylesheet"> <!-- Custom styles for this template --> <link href="asserts/css/signin.css" th:href="@{/asserts/css/signin.css}" rel="stylesheet"> </head>
<body class="text-center"> <form class="form-signin" action="dashboard.html"> <img class="mb-4" th:src="@{asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg}" src="asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg" alt="" width="72" height="72"> <h1 class="h3 mb-3 font-weight-normal" th:text="#{login.tip}">Please sign in</h1> <label class="sr-only" th:text="#{login.username}">Username</label> <input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="Username" th:placeholder="#{login.username}" required="" autofocus=""> <label class="sr-only" th:text="#{login.password}">Password</label> <input type="password" class="form-control" placeholder="Password" th:placeholder="#{login.password}" required=""> <div class="checkbox mb-3"> <label> <input type="checkbox" value="remember-me"> [[#{login.remember}]] </label> </div> <button class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-block" type="submit" th:text="#{login.btn}">Sign in</button> <p class="mt-5 mb-3 text-muted">© 2017-2018</p> <a class="btn btn-sm">中文</a> <a class="btn btn-sm">English</a> </form>
</body>
</html> |
如果出现乱码的现象,那么只需要重新改下编码就行。可以设置全局配置,也可以设置项目配置。以下是全局配置
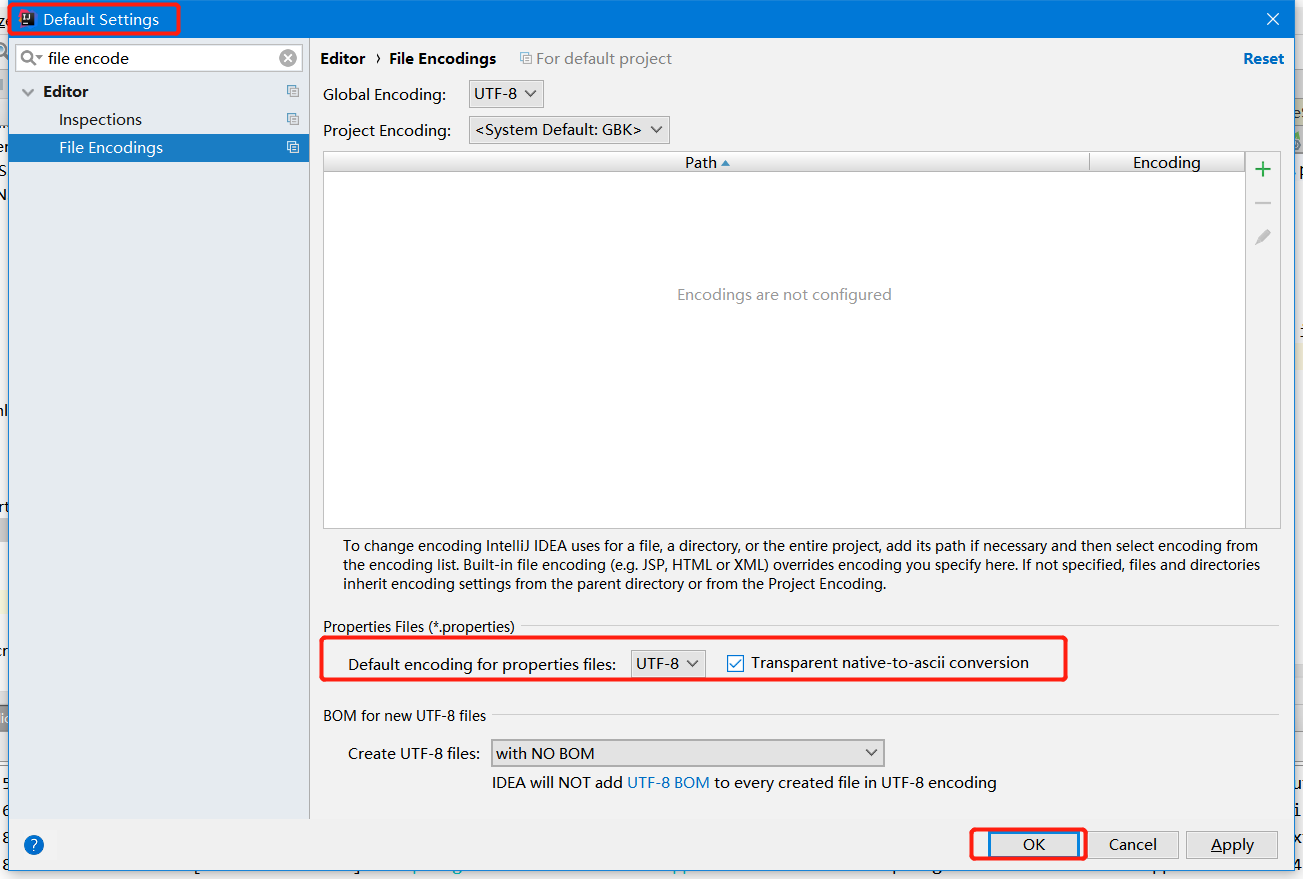
效果:根据浏览器语言设置的信息切换了国际化
原理解析:国际化Locale(区域信息对象);LocaleResolver(获取区域信息对象)
@Bean @ConditionalOnMissingBean @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "locale") public LocaleResolver localeResolver() { if (this.mvcProperties .getLocaleResolver() == WebMvcProperties.LocaleResolver.FIXED) { return new FixedLocaleResolver(this.mvcProperties.getLocale()); } AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver localeResolver = new AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver(); localeResolver.setDefaultLocale(this.mvcProperties.getLocale()); return localeResolver; } 默认的就是根据请求头带来的区域信息获取Locale进行国际化 |
[4].点击链接切换国际化
/** * 可以在连接上携带区域信息 */ public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver {
@Override public Locale resolveLocale(HttpServletRequest request) { String l = request.getParameter("l"); Locale locale = Locale.getDefault(); if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(l)){ String[] split = l.split("_"); locale = new Locale(split[0],split[1]); } return locale; }
@Override public void setLocale(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) {
} }
@Bean public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){ return new MyLocaleResolver(); } } |
(3).登录
开发期间模板引擎页面修改以后,如果想实时生效,需要执行以下两个步骤
[1].禁用模板引擎的缓存
# 禁用缓存 spring.thymeleaf.cache=false |
[2].重新编译
页面修改完成以后ctrl+f9 |
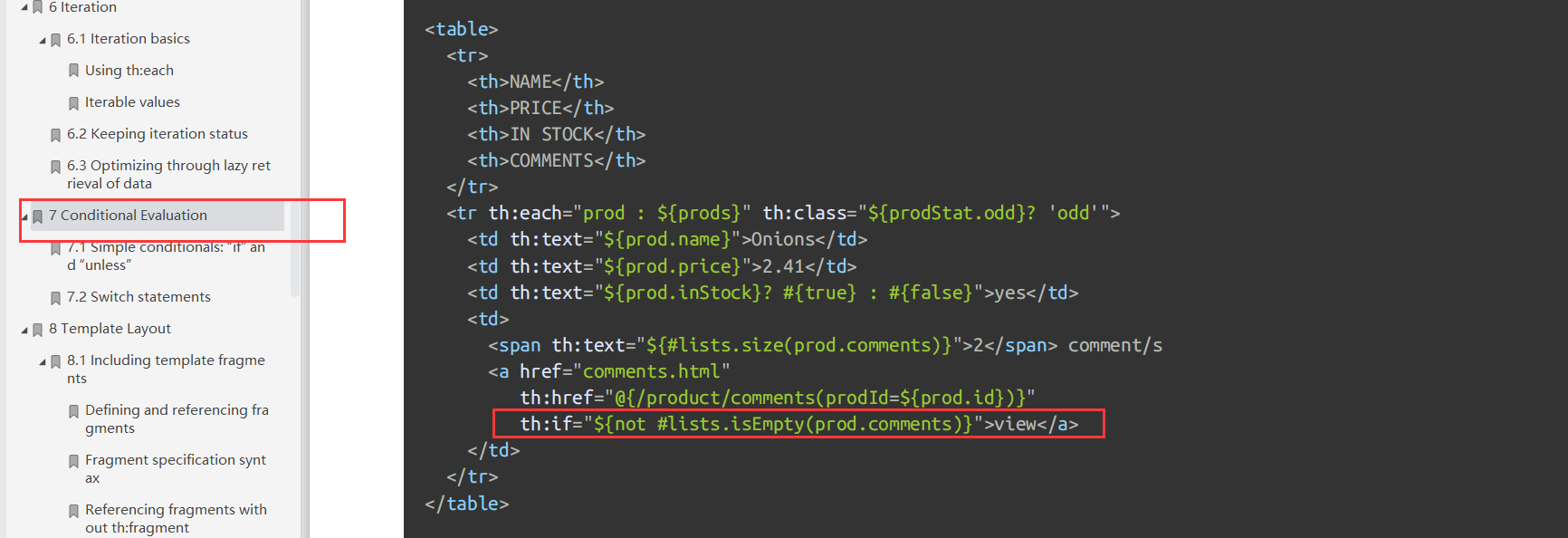
登陆错误消息的显示
<p th:text="${msg}" th:if="${not #strings.isEmpty(msg)}"></p> |
防止表单重复提交的办法:重定向
#LoginController.java if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(username)&& "123456".equals(password)){ //登录成功 防止表单重复提交,可以重定向到主页 return "redirect:/main.html"; |
#MyMvcConfig.java //所有的WebMvcConfigurer组件会一起起作用 //@Bean将组件注册在容器中 @Bean public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){ WebMvcConfigurer dapter = new WebMvcConfigurer() { @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("login"); registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("login"); registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard"); } }; return dapter; } |
(4).拦截器进行登陆检查
[1].拦截器
/** * 登录检查 */ public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor{ //目标方法执行之前 @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { Object user = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser"); if(user==null){ //未登录 返回登录页面 request.setAttribute("msg","没有权限请先登录"); request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request,response); return false; }else { //已登录 放行请求 return true; } } } |
[2].注册拦截器
//所有的WebMvcConfigurer组件会一起起作用 //@Bean将组件注册在容器中 @Bean public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){ WebMvcConfigurer dapter = new WebMvcConfigurer() { @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("login"); registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("login"); registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard"); }
//注册拦截器 @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { //super.addInterceptors(registry); //静态资源 *.css *.js //springboot已经做了静态资源映射 registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**") .excludePathPatterns("/index.html","/","/user/login"); }
};
return dapter; } |
(5).CRUD-员工列表
[1].需求分析
RestfulCRUD:CRUD满足Rest风格;
URI:/资源名称/资源标识 HTTP请求方式区分对资源CRUD操作
|
普通CRUD(uri来区分操作) |
RestfulCRUD |
查询 |
getEmp |
emp---GET |
添加 |
addEmp?xxx |
emp---POST |
修改 |
updateEmp?id=xxx&xxx=xx |
emp/{id}---PUT |
删除 |
deleteEmp?id=1 |
emp/{id}---DELETE |
[2].实验的请求架构
实验功能 |
请求URI |
请求方式 |
查询所有员工 |
emps |
GET |
查询某个员工(来到修改页面) |
emp/1 |
GET |
来到添加页面 |
emp |
GET |
添加员工 |
emp |
POST |
来到修改页面(查出员工进行信息回显) |
emp/1 |
GET |
修改员工 |
emp |
PUT |
删除员工 |
emp/1 |
DELETE |
[3].员工列表
thymeleaf公共页面元素抽取
1、抽取公共片段 <div th:fragment="copy"> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery </div>
2、引入公共片段 <div th:insert="~{footer :: copy}"></div> ~{templatename::selector}:模板名::选择器 ~{templatename::fragmentname}:模板名::片段名
3、默认效果: insert的公共片段在div标签中 如果使用th:insert等属性进行引入,可以不用写~{}: 行内写法可以加上:[[~{}]];[(~{})]; |
三种引入公共片段的th属性:
th:insert:将公共片段整个插入到声明引入的元素中
th:replace:将声明引入的元素替换为公共片段
th:include:将被引入的片段的内容包含进这个标签中
<footer th:fragment="copy"> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery </footer>
引入方式 <div th:insert="footer :: copy"></div> <div th:replace="footer :: copy"></div> <div th:include="footer :: copy"></div>
效果 <div> <footer> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery </footer> </div>
<footer> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery </footer>
<div> © 2011 The Good Thymes Virtual Grocery </div> |
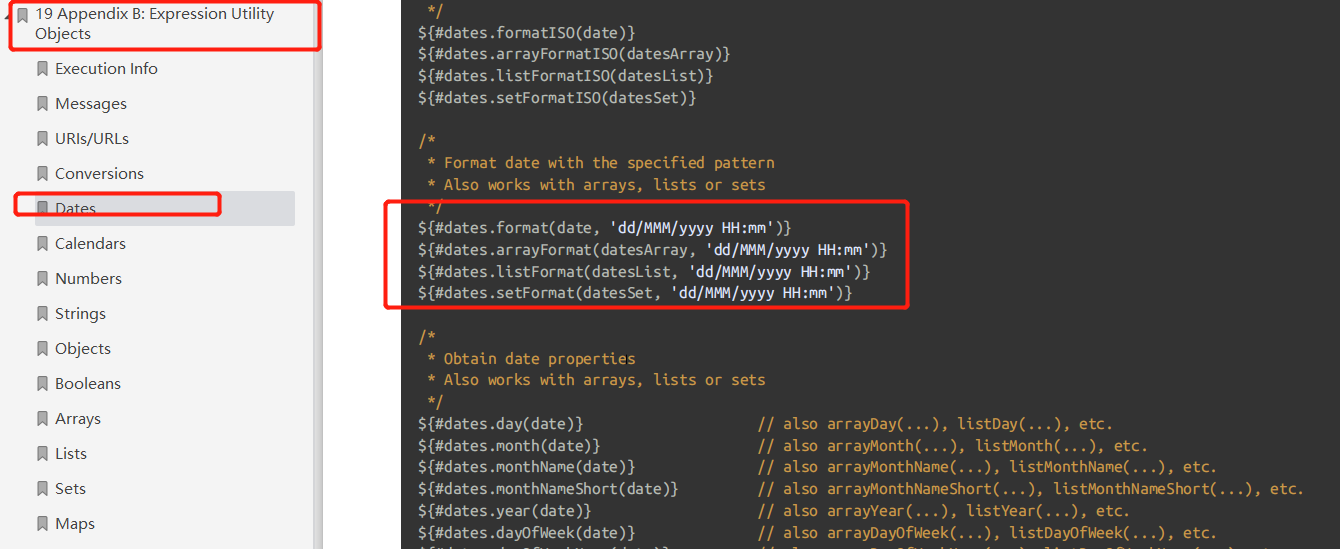
引入片段的时候传入参数
<nav id="sidebar"> <div > <ul > <li > <a th: href="#" th:href="@{/main.html}"> <svg <path d="M3 9l9-7 9 7v11a2 2 0 0 1-2 2H5a2 2 0 0 1-2-2z"></path> <polyline points="9 22 9 12 15 12 15 22"></polyline> &n......... |

java-study-springboot-基础学习-05-springboot web开发
SpringBoot 之web开发
1、自动配置类说明
Web开发的自动配置类: org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration
比如:
spring mvc的前后缀配置
在WebMvcAutoConfiguration中对应方法
对应配置文件
2、静态资源配置说明
如果进入SpringMVC的规则为/时,SpringBoot的默认静态资源的路径为:
spring.resources.static-locations=classpath:/META-INF/resources/,classpath:/resources/,classpath:/static/,classpath:/public/
如果某个静态文件不在上面的配置路径中,那么从浏览器中就访问不到了
3、自定义消息转化器
- 原有的spring mvc 配置
- springboot 配置
4、自定义拦截器
- 继承org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter
参考:https://github.com/chengbingh...

spring boot框架学习5-spring boot的web开发(1)
本章节主要内容:
通过前面的学习,我们了解并快速完成了spring boot第一个应用。spring boot企业级框架,那么spring boot怎么读取静态资源?如js文件夹,css文件以及png/jpg图片呢?怎么自定义消息转换器呢?怎么自定义spring mvc的配置呢?这些我们在公司都需要用的。这些怎么解决呢?在接下来的小节详细讲解这些。好了,现在开启spring boot的web开发第一节
本节主要:
1:spring boot 自动配置viewResolver
本文是《凯哥陪你学系列-框架学习之spring boot框架学习》中第五篇 spring boot框架学习5-spring boot的web开发(1)
声明:本文系凯哥Java(www.kaigejava.com)原创,未经允许,禁止转载!
一:spring boot自动配置viewResolver讲解
1.1:spring boot所有自动配置在哪个包下?
所有的配置都在spring-boot-autoconfigure这个包下。如下图:
1.2 spring bootviewResolver具体位置:

具体:org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.WebMvcAutoConfiguration
源码大致讲解:
1:@conditionalOnClass:条件选择注解
源码:
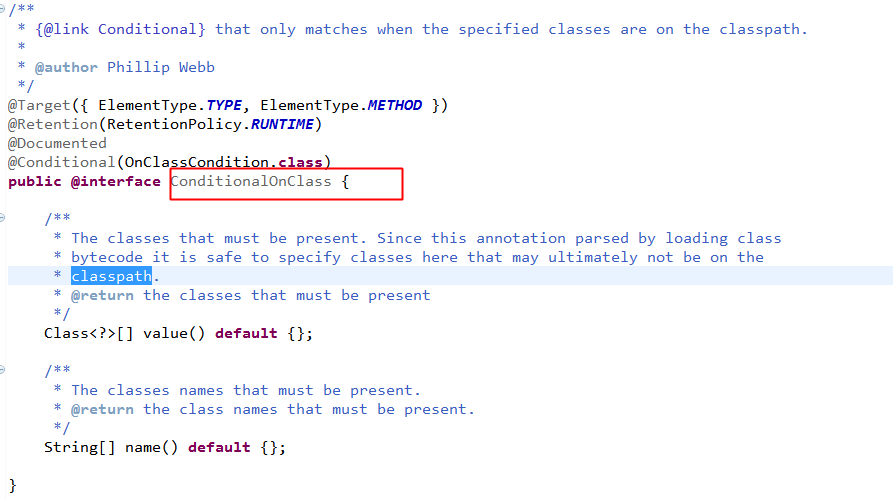
源码注释大致意思:只有value中配置的类在当前的classpath下才可以。
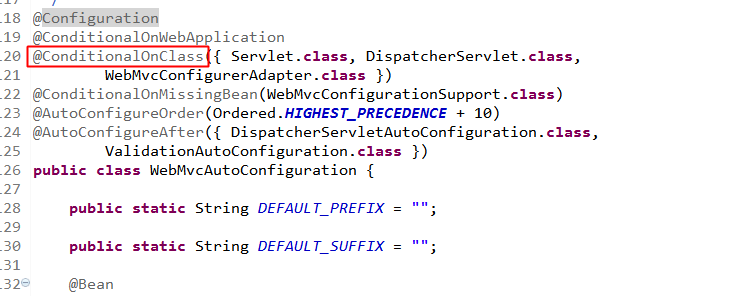
所以:
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class,
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter.class })含义:
当前项目必须含有Servlet、DispatcherServlet、WebMvcConfigurerAdapter三个条件同时存在,webMvcAutoConfiguration才起作用。
2:@ConditionalOnMissingBean:如果没有就创建一个。
源码注释:
如下图含义:
当没有request的过滤器时候创建一个。

请点击此处输入图片描述

3:查看WebMvcAutoConfiguration源码我们熟悉的其他
3.1:资源添加处理的handlers:

3.2校验validator相关的

3.3欢迎页面相关的:

源码讲解,相对来说是比较慢的,所以本节想讲解到这里。在接下来将讲解一个重点InternalResourceViewResolver以及读取静态资源文件。欢迎大家继续学习。
本系列其他文章:
spring boot框架学习学前掌握之重要注解(1)-spring的java配置方式
spring boot框架学习学前掌握之重要注解(2)-通过java的配置方式进行配置spring
spring boot框架学习学前掌握之重要注解(3)-通过注解方式读取外部资源配置文件
spring boot框架学习学前掌握之重要注解(4)-通过注解方式读取外部资源配置文件2
spring boot框架学习1-认识spring boot和快速入门
spring boot框架学习2-spring boot核心(1)
spring boot框架学习3-spring boot核心(2)
spring boot框架学习5-spring boot的web开发(1)
欢迎关注凯哥公众号:凯哥Java
欢迎访问凯哥个人网站:www.kaigejava.com
本文出处:http://www.kaigejava.com/article/detail/53
spring boot学习系列教程:http://kaigejava.com/article/list?cateid=3
今天的关于初识SpringBoot Web开发和springboot网站开发的分享已经结束,谢谢您的关注,如果想了解更多关于1.初识Springboot、4.Spring Boot web开发、java-study-springboot-基础学习-05-springboot web开发、spring boot框架学习5-spring boot的web开发(1)的相关知识,请在本站进行查询。
本文标签: